Severe Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 6 Associated Disease in Two African Elephants Under Human Care in Austria
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Case 1 (E1)
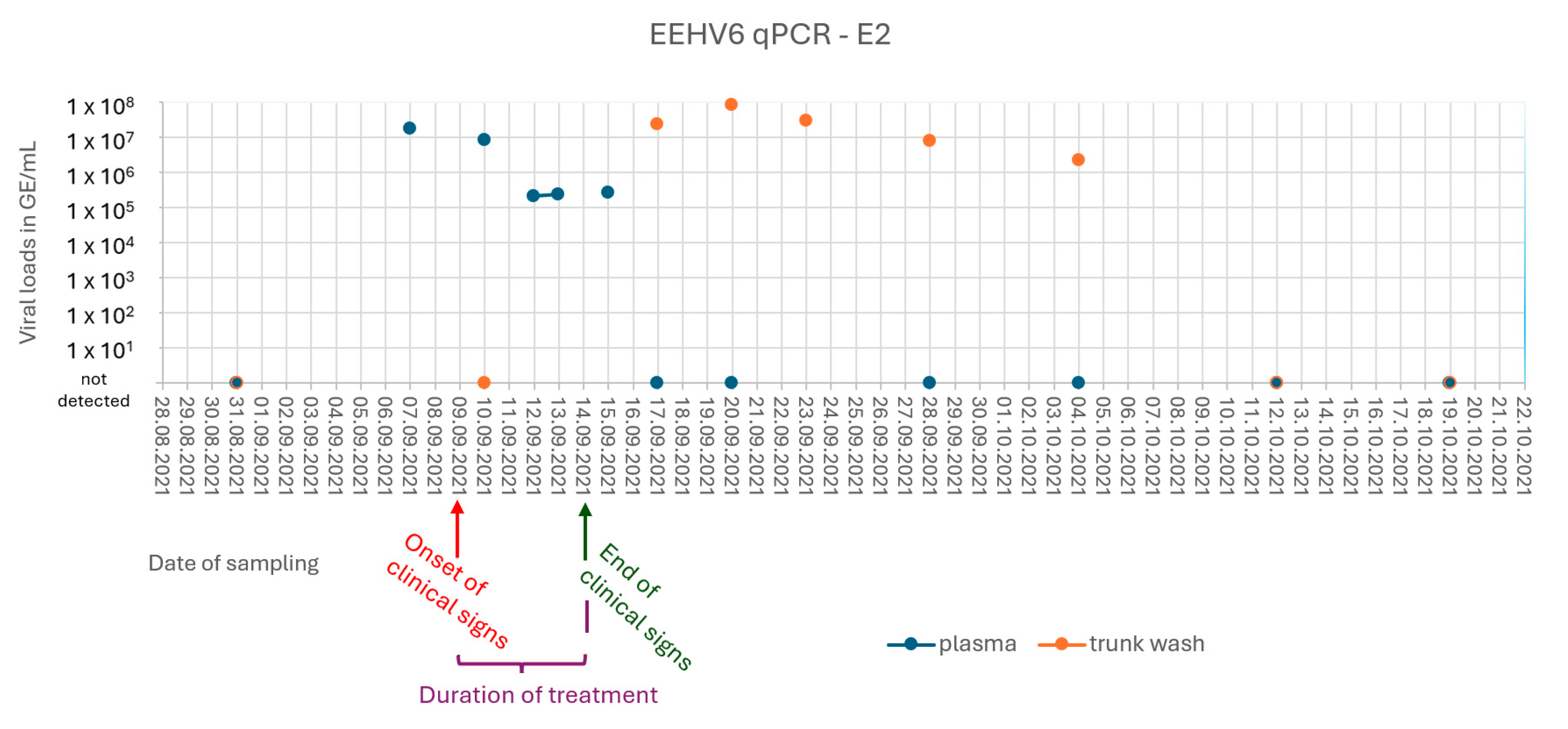
2.3. Case 2 (E2)
2.4. EEHV-Specific Antibody Status of the Vienna Zoo Elephant Herd
2.5. Further Herd Monitoring and EEHV3 Detection
3. Results
3.1. Case 1—Pathological and Virological Findings
3.2. Case 2 (E2) and Subclinical Shedding in Animal E3
3.3. EEHV-Specific Antibody Status of the Vienna Zoo Elephant Herd
3.4. Further Herd Monitoring and EEHV3 Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EEHV | Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| BID | Lat.: bis in die (twice a day) |
| Ct | Cycle threshold |
| INIBs | Intranuclear inclusion bodies |
References
- Richman, L.K.; Montali, R.J.; Garber, R.L.; Kennedy, M.A.; Lehnhardt, J.; Hildebrandt, T.; Schmitt, D.; Hardy, D.; Alcendor, D.J.; Hayward, G.S. Novel Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses Fatal for Asian and African Elephants. Science 1999, 283, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fickel, J.; Richman, L.K.; Montali, R.; Schaftenaar, W.; Göritz, F.; Hildebrandt, T.B.; Pitra, C. A Variant of the Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus in Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus) in European Zoos. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 82, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, M.M.; Helmick, K.; Ochsenreiter, J.; Richman, L.K.; Latimer, E.; Wise, A.G.; Maes, R.K.; Kiupel, M.; Nordhausen, R.W.; Zong, J.C.; et al. Clinico-Pathologic Features of Fatal Disease Attributed to New Variants of Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses in Two Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus). Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, E.; Zong, J.-C.; Heaggans, S.Y.; Richman, L.K.; Hayward, G.S. Detection and Evaluation of Novel Herpesviruses in Routine and Pathological Samples from Asian and African Elephants: Identification of Two New Probosciviruses (EEHV5 and EEHV6) and Two New Gammaherpesviruses (EGHV3B and EGHV5). Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 104, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, G.S. Editorial: Conservation: Clarifying the Risk from Herpesvirus to Captive Asian Elephants. Vet. Rec. 2012, 170, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.Y.; Latimer, E.M.; Hayward, G.S. Review of Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses and Acute Hemorrhagic Disease. ILAR J. 2016, 56, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongmakee, P.; Suttiyaporn, S.; Changpetch, W.; Kongkham, W.; Mongkolphan, C.; Tonchiangsai, K.; Lertwatcharasarakul, P.; Sripiboon, S.; Siriaroonrat, B.; Banlunara, W. Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpes Virus Type 6 Infection in a Captive African Elephant (Loxodonta africana) in Thailand. In Proceedings of the EEHV Workshop, Houston, TX, USA, 17–18 February 2015; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Bronson, E.; McClure, M.; Sohl, J.; Wiedner, E.; Cox, S.; Latimer, E.M.; Pearson, V.R.; Hayward, G.S.; Fuery, A.; Ling, P.D. Epidemiologic evaluation of elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus 3B infection in an african elephant (Loxodonta africana). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2017, 48, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayette, M.A.; Brenner, E.E.; Garner, M.M.; Bowman, M.R.; Latimer, E.; Proudfoot, J.S. Acute Hemorrhagic Disease Due to Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 3a Infection in Five African Elephants (Loxodonta Africana) at One North American Zoological Institution. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2021, 52, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.-C.; Latimer, E.M.; Long, S.Y.; Richman, L.K.; Heaggans, S.Y.; Hayward, G.S. Comparative Genome Analysis of Four Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses, EEHV3, EEHV4, EEHV5, and EEHV6, from Cases of Hemorrhagic Disease or Viremia. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13547–13569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.-C.; Heaggans, S.Y.; Long, S.Y.; Latimer, E.M.; Nofs, S.A.; Bronson, E.; Casares, M.; Fouraker, M.D.; Pearson, V.R.; Richman, L.K.; et al. Detection of Quiescent Infections with Multiple Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses (EEHVs), Including EEHV2, EEHV3, EEHV6, and EEHV7, within Lymphoid Lung Nodules or Lung and Spleen Tissue Samples from Five Asymptomatic Adult African Elephants. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3028–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, G.S.; Davison, A.J.; Watson, M.; Kerr, K.; Sanderson, S.; Bouts, T.; Steinbach, F.; Dastjerdi, A. Complete Genome Sequences of Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses 1A and 1B Determined Directly from Fatal Cases. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6700–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, L.K.; Zong, J.-C.; Latimer, E.M.; Lock, J.; Fleischer, R.C.; Heaggans, S.Y.; Hayward, G.S. Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses EEHV1A, EEHV1B, and EEHV2 from Cases of Hemorrhagic Disease Are Highly Diverged from Other Mammalian Herpesviruses and May Form a New Subfamily. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13523–13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, J.J.; Zong, J.C.; Latimer, E.; Tan, J.; Herron, A.; Hayward, G.S.; Ling, P.D. Detection of Pathogenic Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus in Routine Trunk Washes from Healthy Adult Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus) by Use of a Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2010, 71, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, J.J.; Cray, C.; Rodriguez, M.; Arheart, K.L.; Ling, P.D.; Herron, A. Acute Phase Protein Expression during Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus-1 Viremia in Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2013, 44, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, L.; Zong, J.C.; Tan, J.; Mejia, A.; Heaggans, S.Y.; Nofs, S.A.; Stanton, J.J.; Flanagan, J.P.; Howard, L.; Latimer, E.; et al. Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 5, a Newly Recognized Elephant Herpesvirus Associated with Clinical and Subclinical Infections in Captive Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2013, 44, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, A.; Evans, T.S.; Molter, C.; Howard, L.L.; Ling, P.; Goldstein, T.; Gilardi, K. Noninvasive sampling for detection of elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus and genomic DNA in Asian (Elephas maximus) and African (Loxodonta africana) elephants. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2020, 51, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, J.J.; Zong, J.C.; Eng, C.; Howard, L.; Flanagan, J.; Stevens, M.; Schmitt, D.; Wiedner, E.; Graham, D.; Junge, R.E.; et al. Kinetics of Viral Loads and Genotypic Analysis of Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus-1 Infection in Captive Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2013, 44, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, E.; Ling, P.; Pursell, T.; Hayward, G.; Proudfoot, J.; Fayette, M.; Bowman, M. EEHV7 in Two Juvenile African Elephants. In Proceedings of the AZA TAG Omaha, Baltimore, MD, USA, 27 August–1 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vandevanter, D.R.; Warrener, P.; Bennett, L.; Schultz, E.R.; CoulteEEHVr, S.; Garber, R.L.; Rose, T.M. Detection and Analysis of Diverse Herpesviral Species by Consensus Primer PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Underwood, D.; Driver, L.; Kistler, C.; Diallo, I.; Kirkland, P.D. Evaluation of a Duplex Reverse-Transcription Real-Time PCR Assay for the Detection of Encephalomyocarditis Virus. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornweg, T.E.; Schaftenaar, W.; Maurer, G.; van den Doel, P.B.; Molenaar, F.M.; Chamouard-Galante, A.; Vercammen, F.; Rutten, V.P.M.G.; de Haan, C.A.M. Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus Is Omnipresent in Elephants in European Zoos and an Asian Elephant Range Country. Viruses 2021, 13, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornweg, T.E.; Schaftenaar, W.; Rutten, V.P.M.G.; de Haan, C.A.M. Low GH/GL (Sub)Species-Specific Antibody Levels Indicate Elephants at Risk of Fatal Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus Hemorrhagic Disease. Viruses 2024, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, J.J.; Nofs, S.A.; Peng, R.; Hayward, G.S.; Ling, P.D. Development and Validation of Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Assays to Detect Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses-2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 186, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, K.L.; Kristensen, A.T.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Denk, D. Retrospective Review of 27 European Cases of Fatal Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus-Haemorrhagic Disease Reveals Evidence of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, L.K.; Montali, R.J.; Cambre, R.C.; Schmitt, D.; Hardy, D.; Hildbrandt, T.; Bengis, R.G.; Hamzeh, F.M.; Shahkolahi, A.; Hayward, G.S. Clinical and pathological findings of a newly recognized disease of elephants caused by endotheliotropic herpesviruses. J. Wildl. Dis. 2000, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, G.S.; Davison, A.J.; Kerr, K.; Stidworthy, M.F.; Redrobe, S.; Steinbach, F.; Dastjerdi, A.; Denk, D. First Fatality Associated with Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 5 in an Asian Elephant: Pathological Findings and Complete Viral Genome Sequence. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, L.K.; Montali, R.J.; Hayward, G.S. Review of a Newly Recognized Disease of Elephants Caused by Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses. Zoo Biol. 2000, 19, 383–392. Available online: https://repository.si.edu/bitstream/handle/10088/4235/Richman2000.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Reid, C.E.; Hildebrandt, T.B.; Marx, N.; Hunt, M.; Thy, N.; Reynes, J.M.; Schaftenaar, W.; Fickel, J. Endotheliotropic Elephant Herpes Virus (EEHV) Infection. The First PCR-Confirmed Fatal Case in Asia. Vet. Q. 2006, 28, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornweg, T.E.; Perera, V.P.; Karunarathne, R.N.S.; Schaftenaar, W.; Mahakapuge, T.A.N.; Kalupahana, A.W.; Rutten, V.P.M.G.; de Haan, C.A.M. Young Elephants in a Large Herd Maintain High Levels of Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus-Specific Antibodies and Do Not Succumb to Fatal Haemorrhagic Disease. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e3379–e3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, H.; Raines, J.; Burgdorf-Moisuk, A.; Connolly, M.; Wilson, S.; Ripple, L.; Rivera, S.; McCain, S.; Latimer, E. Selected instances of elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus shedding in trunk secretions by african elephants (Loxodonta africana) in comparison to shedding by asian elephants (Elephas maximus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2024, 55, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, S.; Howard, L. Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) in Asia Recommendations from the 1st Asian EEHV Strategy Meeting Guidelines for ManaGeMent; Wildlife Reserves Singapore Group: Singapore, 2016; Available online: https://eehvinfo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Asia-EEHV-Brochure_FinalLoRes_DEC2016.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).


| Virus/PCR | Primer Sequences (All Targeting POL Gene) | Reference | PCR Kit |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEHV (pan-PCR, semi-nested) | Pan-EEHV-1F/1nF (A1): 5′-ACAAACACGCTGTCRGTRTCYCCRTA-3′Pan-EEHV-1R (B1): 5′-GTATTTGATTTYGCNAGYYTGTAYCC-3′Pan-EEHV-nR (B2): 5′-TGYAAYGCCGTNTAYGGATTYACCGG-3′ | [4] | a |
| EEHV-6 (nested PCR) | EEHV6_aF: 5′-GTGCCGAGTATAGCTTATCCG-3′EEHV6_aR: 5′-GCAGAATATTCGCGTGCATGC-3′EEHV6_nF: 5′-CATGGTCTATCTTACAGTCTACTAGC-3′EEHV6_nR: 5′-CTAGCATTATACAGGCATACAACCTG-3’ | this study | |
| EEHV-6 (qPCR) | qEEHV-6-FW2: 5-GCATACAACCTGTGTTATTGTAC-3′qEEHV-6-RV: 5′-CGCTCTGCTAACCATGATGT-3′qEEHV-6-Probe: FAM-5′-ACCGATGACAATTTAACGTCACTTAGA-3‘-BHQ1 | * | b |
| Date of Sampling | Genome Equivalents Per Milliliter |
|---|---|
| 31.08.2021 | 9.28 × 105 |
| 20.09.2021 | 6.95 × 104 |
| 02.11.2021 | 1.99 × 105 |
| 20.07.2022 | 1.05 × 105 |
| 17.10.2022 | 1.06 × 106 |
| 19.10.2022 | 1.18 × 106 |
| 19.12.2022 | 5.66 × 104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knüppel, S.; Balfanz, F.; Riedel, C.; Strauss, V.; Hoornweg, T.E.; Dimmel, K.; Walk, K.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Posautz, A.; Voracek, T.; et al. Severe Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 6 Associated Disease in Two African Elephants Under Human Care in Austria. Animals 2025, 15, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101482
Knüppel S, Balfanz F, Riedel C, Strauss V, Hoornweg TE, Dimmel K, Walk K, Kübber-Heiss A, Posautz A, Voracek T, et al. Severe Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 6 Associated Disease in Two African Elephants Under Human Care in Austria. Animals. 2025; 15(10):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101482
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnüppel, Stella, Folko Balfanz, Christiane Riedel, Verena Strauss, Tabitha E. Hoornweg, Katharina Dimmel, Karin Walk, Anna Kübber-Heiss, Annika Posautz, Thomas Voracek, and et al. 2025. "Severe Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 6 Associated Disease in Two African Elephants Under Human Care in Austria" Animals 15, no. 10: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101482
APA StyleKnüppel, S., Balfanz, F., Riedel, C., Strauss, V., Hoornweg, T. E., Dimmel, K., Walk, K., Kübber-Heiss, A., Posautz, A., Voracek, T., Abdelgawad, A., Trimpert, J., Hering-Hagenbeck, S., Rümenapf, T., & Auer, A. (2025). Severe Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus 6 Associated Disease in Two African Elephants Under Human Care in Austria. Animals, 15(10), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101482






