Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies Functional Genes for Environmental Adaptability in Chinese Geese
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Sequencing and Variant Calling
2.4. Acquisition and Analysis of Environmental Data
2.5. Genetic Diversity Analysis
2.6. Population Structure and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Detection of SNPs Associated with Environmental Adaptations
2.8. Functional SNPs Detection Approach
2.9. Gene Annotation and KEGG Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Mapping Quality and Variant Discovery
3.2. Population Genetic Diversity of Chinese Geese
3.3. Population Genomic Divergence
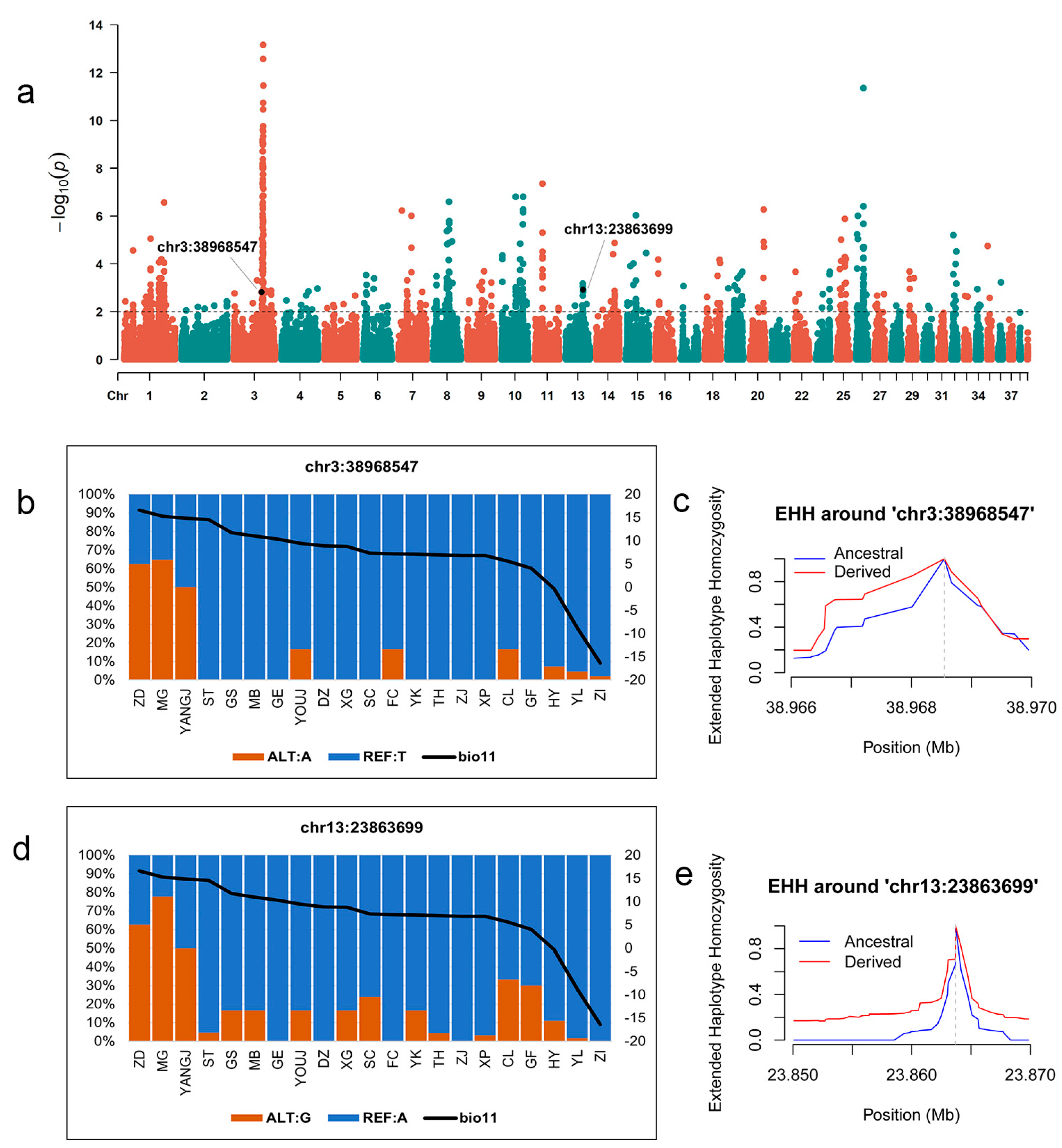
3.4. Identification of Genomic Variants Associated with Local Climate Adaptability
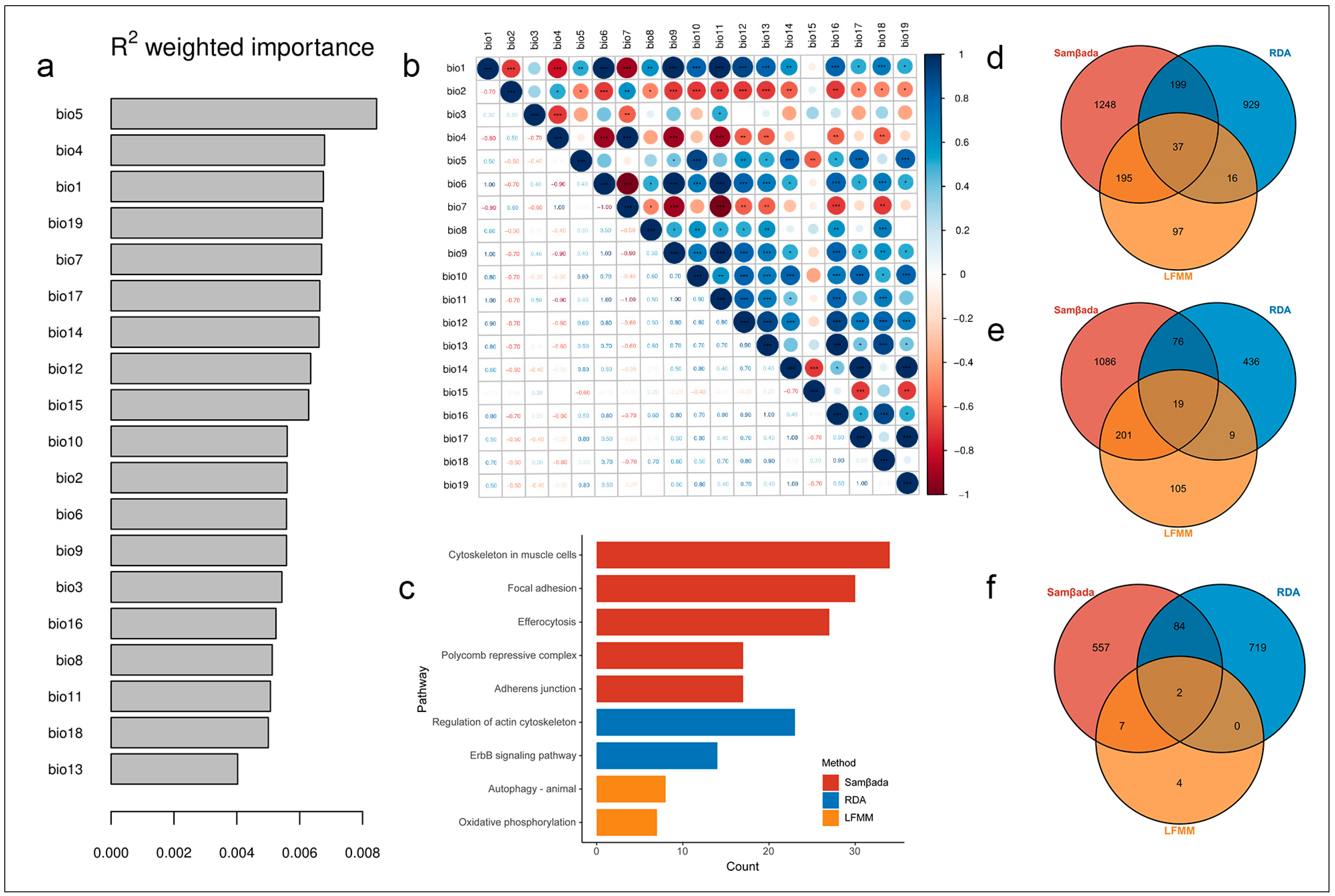
3.5. SNPs Associated with Environmental Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FAF1 | Fas-Associated Factor 1 |
| RSF1 | Remodeling and Spacing Factor 1 |
| SLC6A14 | Solute Carrier Family 6 Member 14 |
| SLC4A11 | Solute Carrier Family 4 Member 11 |
| SLC38A7 | Solute Carrier Family 38 Member 7 |
| SLC38A1 | Solute Carrier Family 38 Member 1 |
| SLC36A4 | Solute Carrier Family 36 Member 4 |
| SLC34A2 | Solute Carrier Family 34 Member 2 |
| SLC22A15 | Solute Carrier Family 22 Member 15 |
| SLC16A1 | Solute Carrier Family 16 Member 1 |
| NDUFS5 | Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Subunit S5 |
| NDUFB5 | Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Subunit B5 |
| NDUFB2 | Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Subunit B2 |
| EXOC4 | Exocyst Complex Component 4 |
| GEA | Genetic–environment association |
| CL | Changle goose |
| DZ | Daozhou goose |
| FC | Fengcheng White goose |
| GE | Gang goose |
| GFW | Guangfeng White goose |
| GS | Gushi goose |
| MB | Minbei White goose |
| MG | Manggang goose |
| ST | Shitou goose |
| TH | Taihu goose |
| XG | Xingguo Grey goose |
| YangJ | Yangjiang goose |
| YK | Yongkang goose |
| YouJ | Youjiang goose |
| ZD | Zhedong White goose |
| ZJ | Zhijin goose |
| YL | Yili goose |
| HY | Huoyan goose |
| XP | Xupu goose |
| ZI | Zi goose |
| SC | Sichuan White goose |
| SNPs | Single-nucleotide polymorphisms |
| EHH | Extend haplotype homozygosity |
| CDS | Coding sequencing |
References
- Price, E.O. Behavioral development in animals undergoing domestication. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1999, 65, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.-C.; Zhang, J. Evolutionary adaptations to new environments generally reverse plastic phenotypic changes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, J.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, Z.; Ning, Z.; Qu, L. Origins, timing and introgression of domestic geese revealed by whole genome data. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, M.; Itahashi, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Sun, G.; Hsu, K.H.; Gakuhari, T.; Yoneda, M.; Jiang, L.; Yang, G.; Nakamura, S. Multiple lines of evidence of early goose domestication in a 7,000-y-old rice cultivation village in the lower Yangtze River, China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2117064119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yang, N. Animal Genetic Resources of Poultry in China; Zhang, B., Zhang, W., Gu, J., Wu, C., Eds.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, Q.; Pu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, L. Whole-genome sequencing identifies functional genes for environmental adaptation in Chinese sheep. J. Genet. Genom. 2024, 51, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, J.; Tuersuntuoheti, M.; Zhou, W.; Han, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S. Landscape genomics reveals adaptive divergence of indigenous sheep in different ecological environments of Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Shao, D.; Yang, L.; Liang, Q.; Han, W.; Xue, Q.; Qu, L.; Leng, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. Whole genome analyses reveal novel genes associated with chicken adaptation to tropical and frigid environments. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 47, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjelloun, B.; Leempoel, K.; Boyer, F.; Stucki, S.; Streeter, I.; Orozco-terWengel, P.; Alberto, F.J.; Servin, B.; Biscarini, F.; Alberti, A.; et al. Multiple genomic solutions for local adaptation in two closely related species (sheep and goats) facing the same climatic constraints. Mol. Ecol. 2024, 33, e17257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Han, X.M.; Huang, C.P.; Zhong, L.; Adeola, A.C.; Irwin, D.M.; Xie, H.B.; Zhang, Y.P. Population Genomics Analysis Revealed Origin and High-altitude Adaptation of Tibetan Pigs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.D.; Yang, C.P.; Wang, M.S.; Dong, K.Z.; Yan, D.W.; Hao, Z.Q.; Fan, S.Q.; Chu, S.Z.; Shen, Q.S.; Jiang, L.P.; et al. Convergent genomic signatures of high-altitude adaptation among domestic mammals. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Gu, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Genomic Analysis Reveals Candidate Genes Underlying Sex-Linked Eyelid Coloboma, Feather Color Traits, and Climatic Adaptation in Huoyan Geese. Animals 2023, 13, 3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhang, H.; Ni, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Wang, Q. Insights into genetic diversity and phenotypic variations in domestic geese through comprehensive population and pan-genome analysis. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, B.G.; Frischauf, A.-M. [15] Isolation of genomic DNA. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 152, pp. 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gao, G.; Lin, Y.; Hu, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, G. Pacific Biosciences assembly with Hi-C mapping generates an improved, chromosome-level goose genome. Gigascience 2020, 9, giaa114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, B.S.; Cockerham, C.C. Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 1984, 38, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuillan, R.; Leutenegger, A.L.; Abdel-Rahman, R.; Franklin, C.S.; Pericic, M.; Barac-Lauc, L.; Smolej-Narancic, N.; Janicijevic, B.; Polasek, O.; Tenesa, A.; et al. Runs of homozygosity in European populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Kim, C.; Paterson, A.H. SNPhylo: A pipeline to construct a phylogenetic tree from huge SNP data. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frichot, E.; Schoville, S.D.; Bouchard, G.; François, O. Testing for associations between loci and environmental gradients using latent factor mixed models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1687–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucki, S.; Orozco-terWengel, P.; Forester, B.R.; Duruz, S.; Colli, L.; Masembe, C.; Negrini, R.; Landguth, E.; Jones, M.R.; Consortium, N. High performance computation of landscape genomic models including local indicators of spatial association. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 1072–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capblancq, T.; Forester, B. Redundancy Analysis (RDA): A Swiss Army knife for landscape genomics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 2298–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, N.; Smith, S.J.; Pitcher, C.R. Gradient forests: Calculating importance gradients on physical predictors. Ecology 2012, 93, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, P.C.; Reich, D.E.; Higgins, J.M.; Levine, H.Z.; Richter, D.J.; Schaffner, S.F.; Gabriel, S.B.; Platko, J.V.; Patterson, N.J.; McDonald, G.J.; et al. Detecting recent positive selection in the human genome from haplotype structure. Nature 2002, 419, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. Eggnog-mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang da, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Yee, S.W.; Kim, R.B.; Giacomini, K.M. SLC transporters as therapeutic targets: Emerging opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.; Wang, H.; Hou, X.; Li, H.; Cheng, G.; Wang, N.; Zhu, X.; Yu, J.; Luan, W.; Liu, F.; et al. Microarray analysis of gene expression profiles of rat small intestine in response to heat stress. J. Biomol. Screen. 2011, 16, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.Q.; Liao, T.T.; Yang, W.R.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.Y.; Wang, X.Z. Heat stress-induced autophagy promotes lactate secretion in cultured immature boar Sertoli cells by inhibiting apoptosis and driving SLC2A3, LDHA, and SLC16A1 expression. Theriogenology 2017, 87, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Pandey, A.; Kumar, L.; Devi, A.; Kushwaha, B.; Vishvkarma, R.; Maikhuri, J.P.; Rajender, S.; Gupta, G. The thermo-sensitive gene expression signatures of spermatogenesis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigoulet, M.; Bouchez, C.L.; Paumard, P.; Ransac, S.; Cuvellier, S.; Duvezin-Caubet, S.; Mazat, J.P.; Devin, A. Cell energy metabolism: An update. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2020, 1861, 148276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.; Segaran, A.; Lord, S. Targeting OXPHOS and the electron transport chain in cancer; Molecular and therapeutic implications. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86 Pt 2, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Iino, M. Sec8 regulates cytokeratin8 phosphorylation and cell migration by controlling the ERK and p38 MAPK signalling pathways. Cell Signal 2015, 27, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindstaff, K.K.; Yeaman, C.; Anandasabapathy, N.; Hsu, S.C.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E.; Scheller, R.H.; Nelson, W.J. Sec6/8 complex is recruited to cell-cell contacts and specifies transport vesicle delivery to the basal-lateral membrane in epithelial cells. Cell 1998, 93, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Long, Z.; Dan, X.; Feng, J.; Shi, T.; Jia, C.; Zhang, X.; Lai, Q.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Genomic insights into local adaptation and future climate-induced vulnerability of a keystone forest tree in East Asia. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Qu, C.; Wen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, T.; Nie, C.; Li, X.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal genetic adaptation to cold conditions in the chickens. Genomics 2022, 114, 110485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malnic, B.; Godfrey, P.A.; Buck, L.B. The human olfactory receptor gene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2584–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.W.; Tzeng, C.R. The novel serine proteases, prtn3 and prss23, in murine blastocyst development and hatching. Fertil. Steril. 2007, 88, S312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, M.E.; Brosnan, J.T. Histidine Metabolism and Function. J. Nutr. 2020, 150 (Suppl. S1), 2570s–2575s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; O’Reilly, P.F.; Aschard, H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Richards, J.B.; Dupuis, J.; Ingelsson, E.; Karasik, D.; Pilz, S.; Berry, D.; et al. Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Yu, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Qu, C.; Qu, L. Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies Functional Genes for Environmental Adaptability in Chinese Geese. Animals 2025, 15, 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101395
Ren X, Yu J, Zhao X, Zhang X, Wang G, Jiang X, Li X, Qu C, Qu L. Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies Functional Genes for Environmental Adaptability in Chinese Geese. Animals. 2025; 15(10):1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101395
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xufang, Jincheng Yu, Xiurong Zhao, Xinye Zhang, Gang Wang, Xiaoyu Jiang, Xianyao Li, Changqing Qu, and Lujiang Qu. 2025. "Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies Functional Genes for Environmental Adaptability in Chinese Geese" Animals 15, no. 10: 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101395
APA StyleRen, X., Yu, J., Zhao, X., Zhang, X., Wang, G., Jiang, X., Li, X., Qu, C., & Qu, L. (2025). Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies Functional Genes for Environmental Adaptability in Chinese Geese. Animals, 15(10), 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101395






