The Relationship Between Soil and Gut Microbiota Influences the Adaptive Strategies of Goitered Gazelles in the Qaidam Basin
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
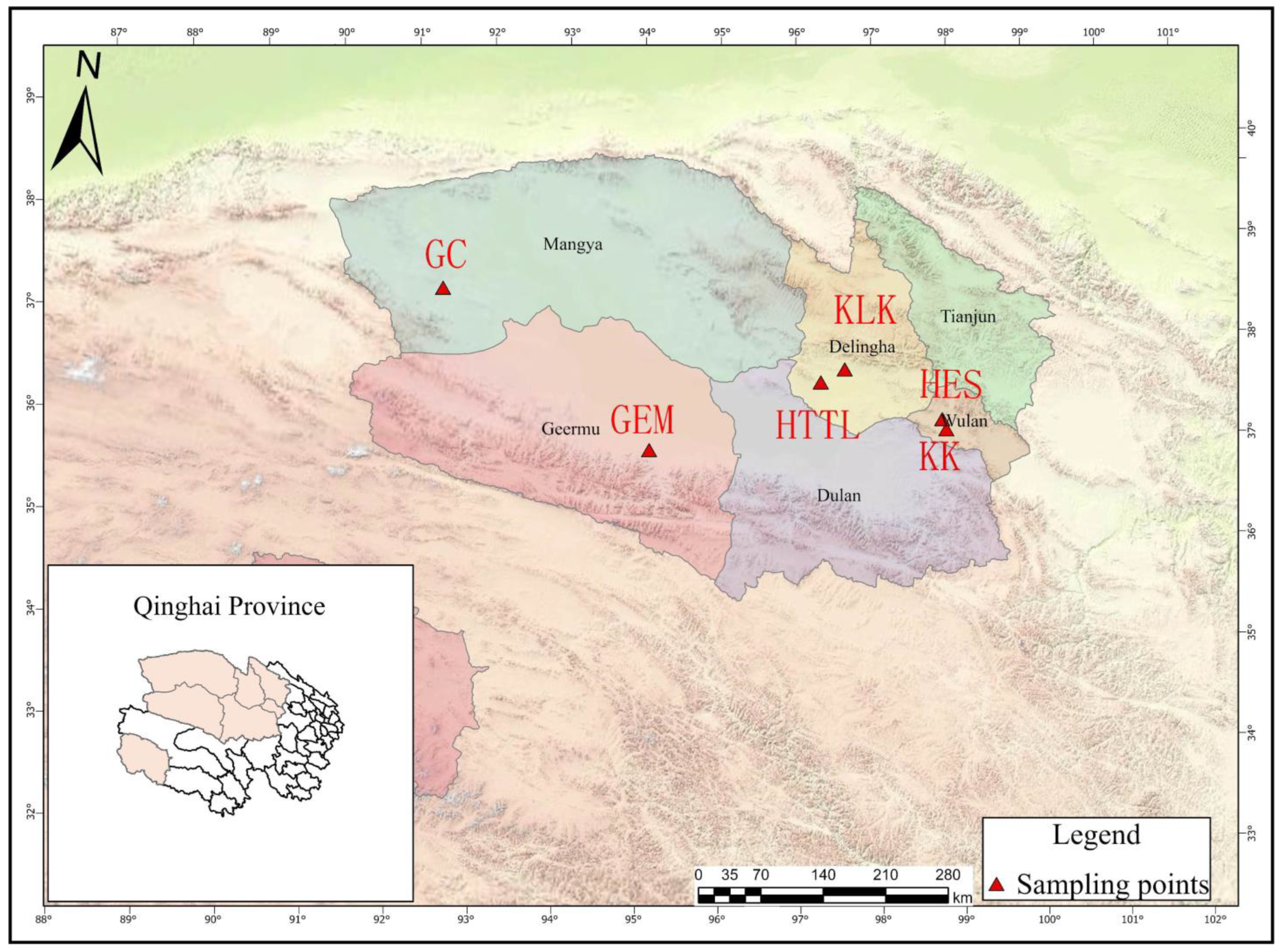
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Methods
2.4. Source Tracing Analysis
2.5. Ecological Assembly Process of Soil and Gut Microbiota
3. Results
3.1. Raw Data
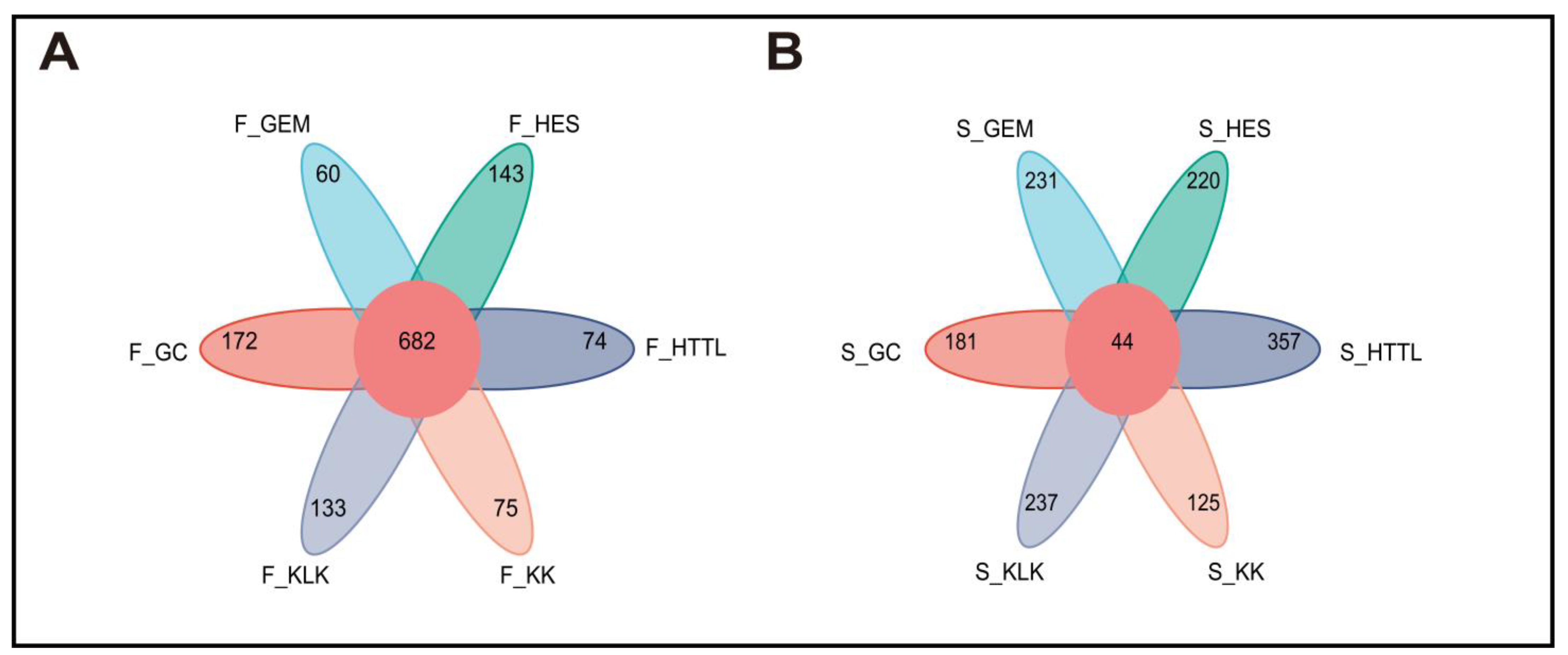
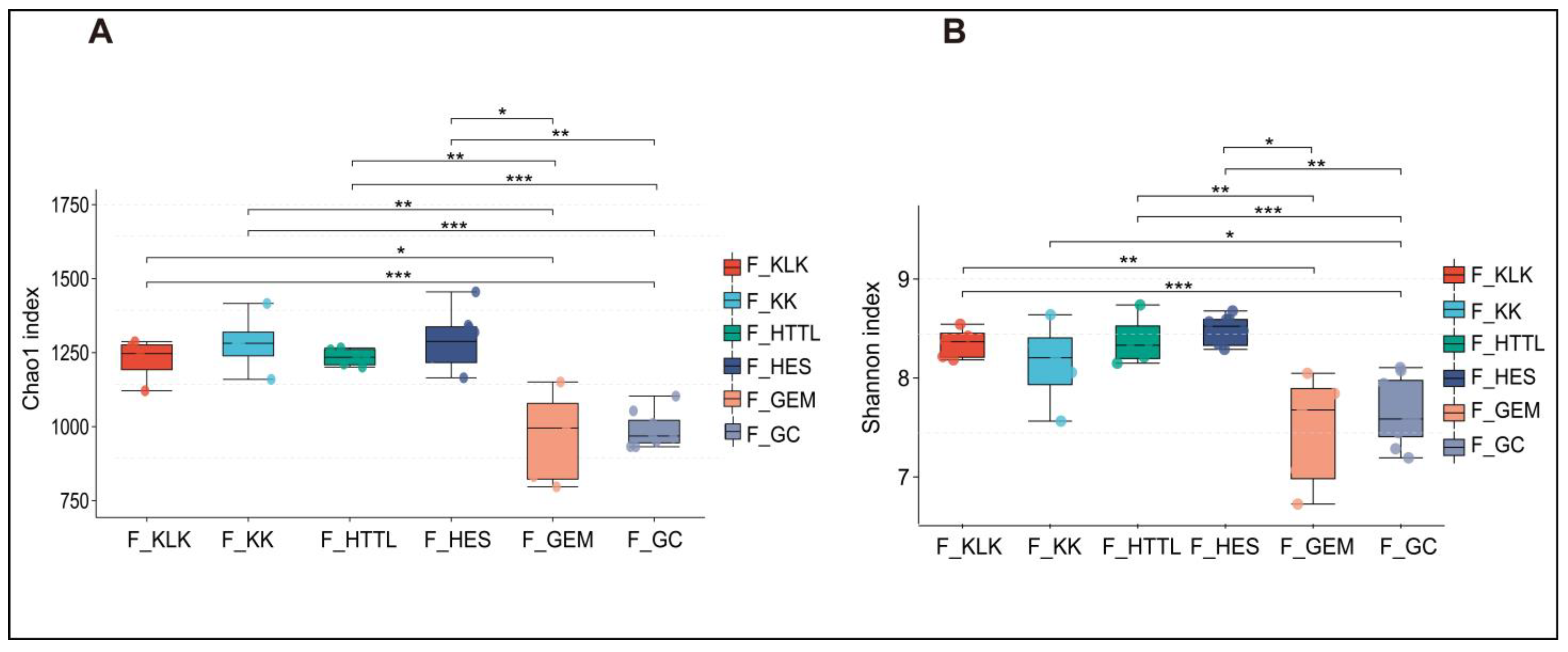
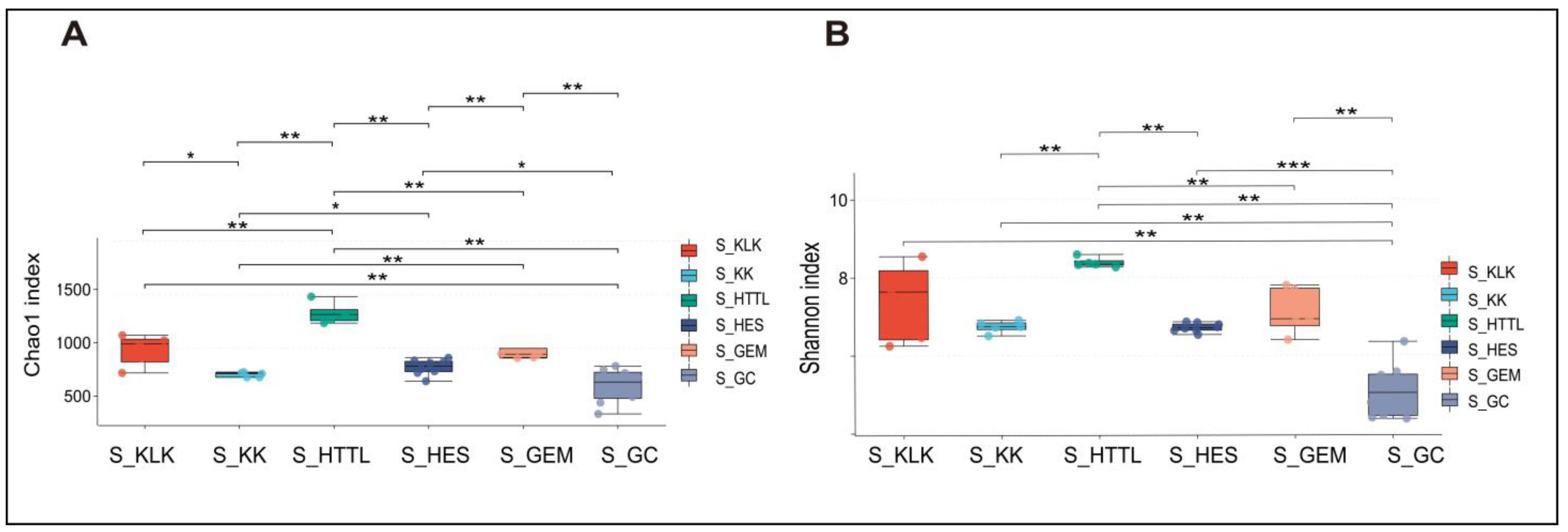
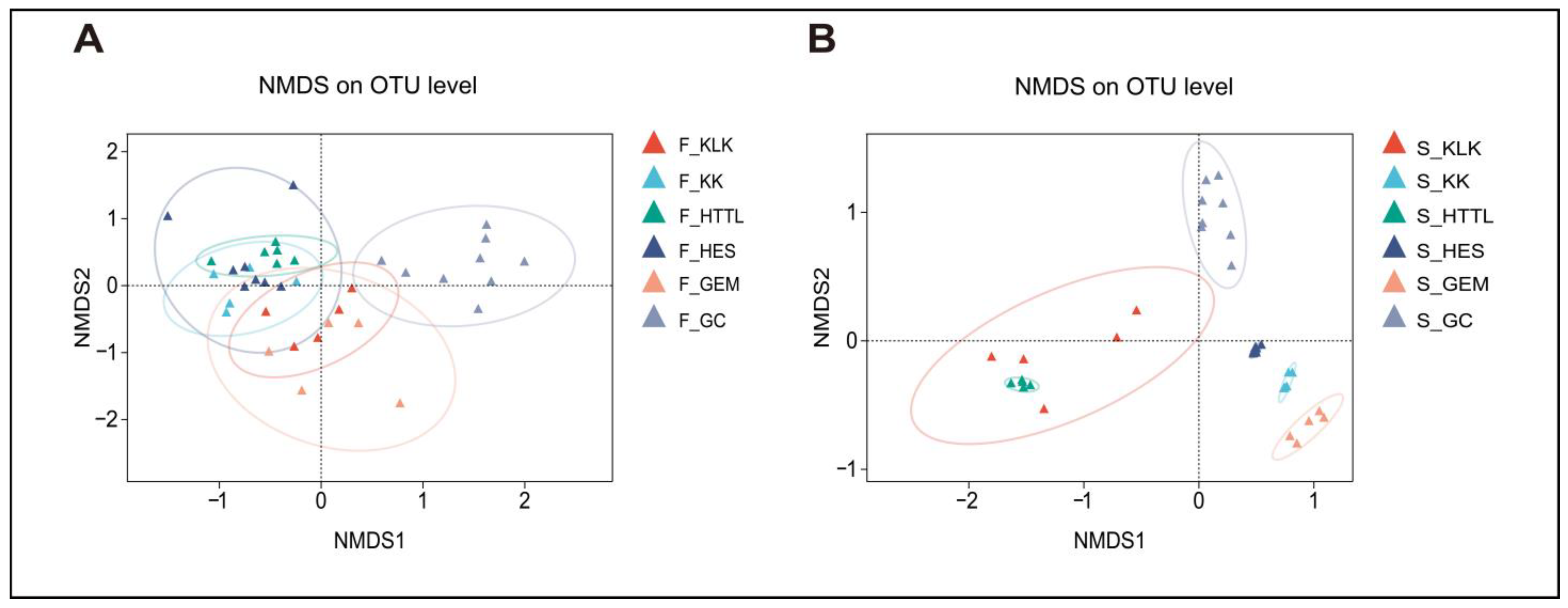
3.2. Composition and Diversity of Soil and Gut Microbiota
3.3. Gut Microbial Source Tracking from Soil Microbiota
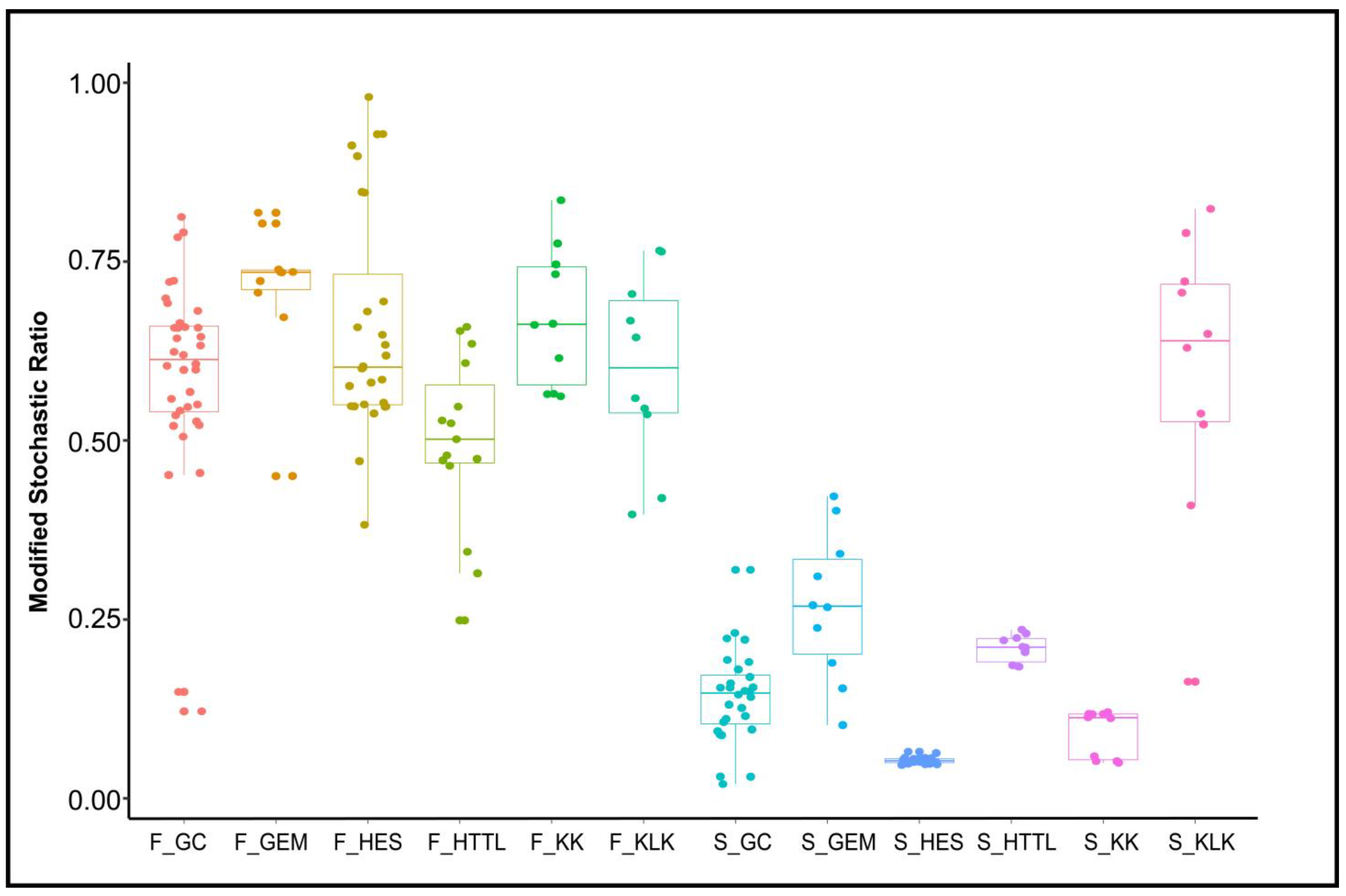
3.4. Dominant Ecological Processes in Gut and Soil Microbiota
4. Discussion
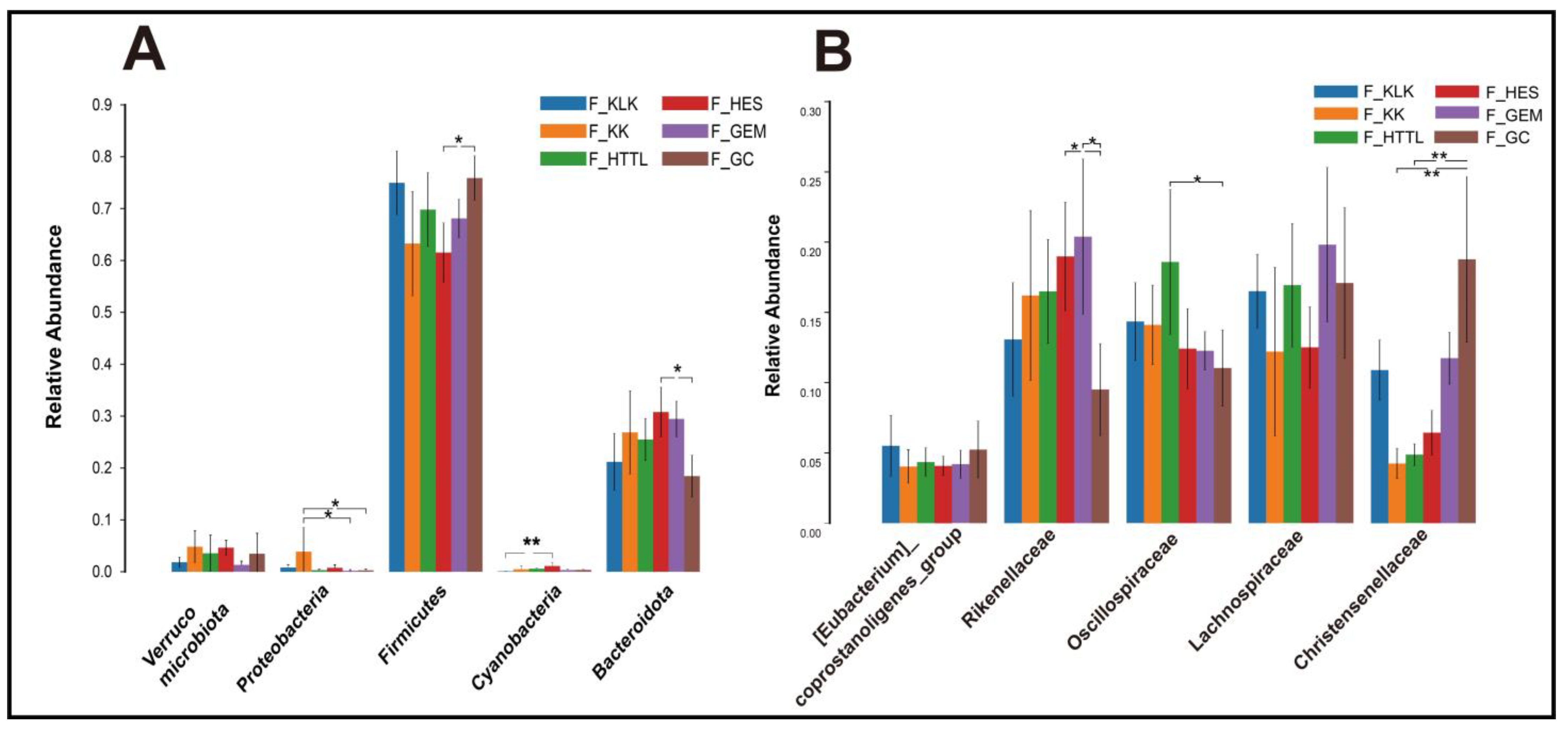
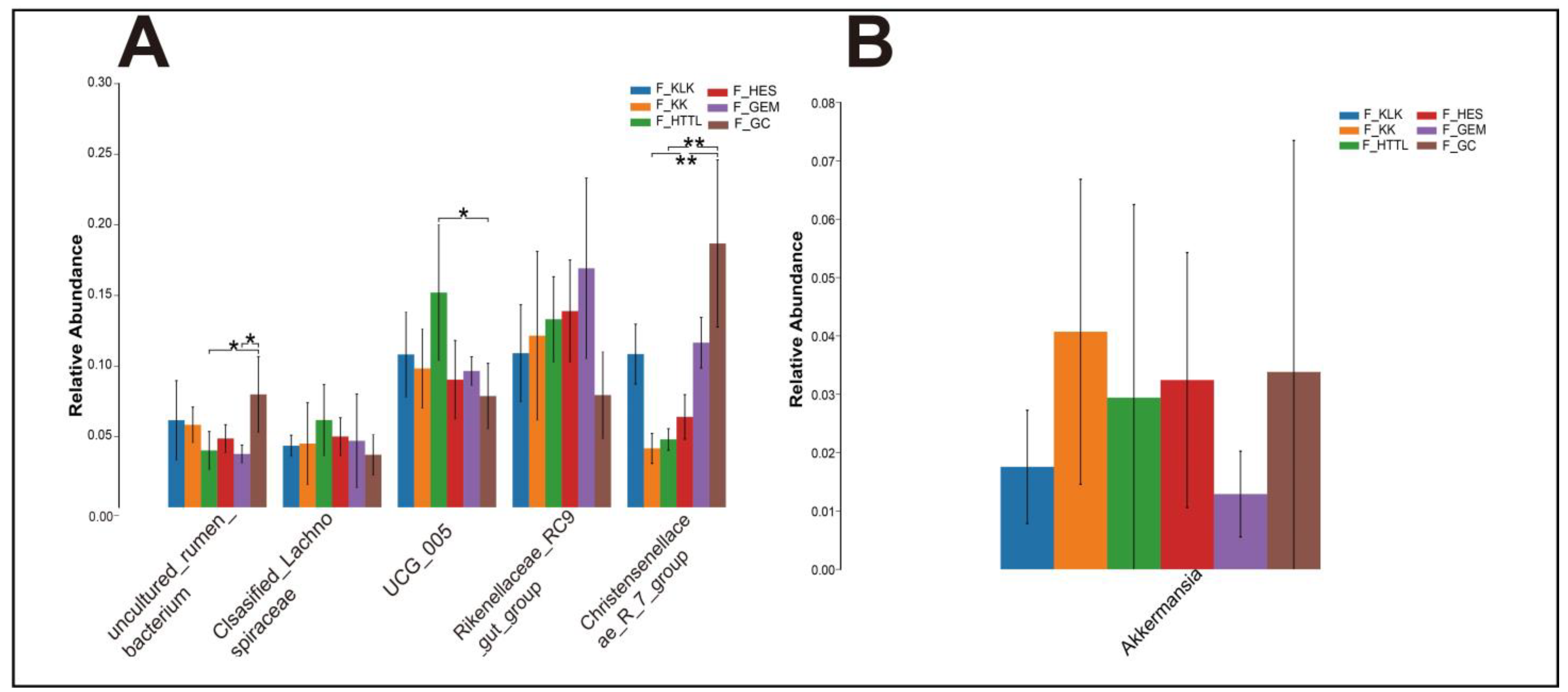
4.1. Differences in Soil and Gut Microbial Diversity Across Six Regions
4.2. Variations in Source Tracking Results Linked to Host Needs
4.3. Differences in Ecological Processes of Soil and Gut Microbiota
4.4. Diverse Adaptation Strategies of Goitered Gazelles via Soil Microbial Utilization Across Regions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Gao, H.; Jiang, F.; Liu, D.; Hou, Y.; Chi, X.; Qin, W.; Song, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, T. Comparative analysis of gut microbial composition and functions in Przewalski’s gazelle (Procapra przewalskii) from various habitats. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 913358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yang, X.; Dou, H.; Lyu, T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.; Shang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H. Comparative analysis of the gut microbiota of mongolian gazelle (Procapra gutturosa) under fragmented habitats. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 830321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, C.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Xia, T.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y. Comparative analyses of fecal microbiota in European mouflon (Ovis orientalis musimon) and blue sheep (Pseudois nayaur) living at low or high altitudes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUCN SSC; Antelope Specialist Group IUCN. Gazella subgutterosa, Goitered gazelle. In The IUCN Red LIST of Threatened Species; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ismayil, Z.; Muhtar, S.; Ababaikeri, B.; Satar, A.; Eli, S.; Halik, M. Influence of environmental factors on genetic diversity of Gazella subgotturosa in Xinjiang, China. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2019, 39, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Feng, G.; Ma, Y. Study on the Type of Saline-alkaline Land and Saltion Correlation of Qaidam Basin. Sci. Technol. Qinghai Agric. For. 2016, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.Q.; Hou, D.J.; Qu, X.Y.; Guo, K. A plot-based dataset of plant communities on the Qaidam Basin, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 48, 534–540. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.-Y.; Xue-Yu, H. Vegetation of China with reference to its geographical distribution. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1983, 70, 509–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Qiao, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, W. Food habits of goitered gazelles (Gazella subgutturosa sairensis) in northern Xinjiang. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2008, 28, 280. [Google Scholar]
- Tancheng, D.; Hongjun, C.; Yong, C.; Hongpan, W.; Lei, H.; Yan, G. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic status of Gazella subgutturosa at the Mountain Kalamaili Ungulate Nature Reserve, Xinjiang. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2016, 36, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Qiao, J.; Xia, C.; Yang, W.; Li, Y. Seasonal variations of bedding site characteristics of Gazella subgutturosa in Kalamaili Mountain Nature Reserve. Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 687–692. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.-J.; Qiao, J.-F.; Yang, W.-K.; Xu, W.-X.; Liu, W.; Li, Y. Diurnal behaviors time budgets and activity rhythms of Gazella subgutturosa in winter. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 283. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Xu, W.; Qiao, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, W. Diurnal behavioral time budgets of the Goitered gazelle across seasons in the Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve, Xinjiang. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2010, 30, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Xu, W.; Yang, W.; David, B.; Qiao, J.; Liu, W. Vigilance in Goitred gazelle (Gazella subgutturosa): Effect of seasons, sexes and group size. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2011, 31, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, W.; Song, P.; Lin, G.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, T. Gut microbiota plasticity influences the adaptability of wild and domestic animals in co-inhabited areas. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Song, P.; Zhang, S. Seasonal and Soil Microbiota Effects on the Adaptive Strategies of Wild Goitered Gazelles Based on the Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 918090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Weng, F.C.-H.; Shaw, G.T.-W.; Wang, D. Habitat and indigenous gut microbes contribute to the plasticity of gut microbiome in oriental river prawn during rapid environmental change. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.; Boutin, S.; Humphries, M.; Dantzer, B.; Gorrell, J.; Coltman, D.; McAdam, A.; Wu, M. Seasonal, spatial, and maternal effects on gut microbiome in wild red squirrels. Microbiome 2017, 5, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, K.P.; Gratz, S.W.; Sheridan, P.O.; Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H. The influence of diet on the gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Gao, H.; Wu, G.; Qin, W.; Song, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, T. Comparison of gut microbiota diversity between wild and captive bharals (Pseudois nayaur). BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Gao, H.; Song, P.; Liang, C.; Jiang, F.; Xu, B.; Liu, D.; Zhang, T. Captivity shifts gut microbiota communities in white-lipped deer (Cervus albirostris). Animals 2022, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, D.; Brahmaprakash, G. Soil microbes are shaped by soil physico-chemical properties: A brief review of existing literature. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2021, 33, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, M. Distribution pattern of soil microbial population in salt-affected soils. In Towards the Rational Use of High Salinity Tolerant Plants: Deliberations about High Salinity Tolerant Plants and Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 1, pp. 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Bai, Z.; Cheng, F.; Jiang, H.; Mao, C.; Sun, X.; Lu, Z. Soil is a key factor influencing gut microbiota and its effect is comparable to that exerted by diet for mice. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottman, N.; Ruokolainen, L.; Suomalainen, A.; Sinkko, H.; Karisola, P.; Lehtimäki, J.; Lehto, M.; Hanski, I.; Alenius, H.; Fyhrquist, N. Soil exposure modifies the gut microbiota and supports immune tolerance in a mouse model. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1198–1206.e1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, N.; Tsai, T.C.; Maxwell, C.; Carbonero, F. Early exposure to agricultural soil accelerates the maturation of the early-life pig gut microbiota. Anaerobe 2017, 45, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreychev, A.; Zhalilov, A.; Kuznetsov, V. The state of local steepe woodchuck (Marmota bobak) populations in the Republic of Mordovia. Zool. Zhurnal 2015, 94, 723–730. [Google Scholar]
- Barão, I.; Queirós, J.; Vale-Gonçalves, H.; Paupério, J.; Pita, R. Landscape characteristics affecting small Mammal occurrence in heterogeneous Olive Grove Agro-ecosystems. Conservation 2022, 2, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yan, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, F.; Song, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, T. Microbial biogeography along the gastrointestinal tract segments of sympatric subterranean rodents (Eospalax baileyi and Eospalax cansus). Animals 2021, 11, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Jiang, F.; Liu, D.; Cai, Z.; Gao, H.; Gu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Xu, B.; Zhang, T. Gut microbiota non-convergence and adaptations in sympatric Tibetan and Przewalski’s gazelles. Iscience 2024, 27, 109117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, K.H.; Roux, K.H. High and low annealing temperatures increase both specificity and yield in touchdown and stepdown PCR. Biotechniques 1996, 20, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innis, M.A.; Gelfand, D.H.; Sninsky, J.J.; White, T.J. PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ardui, S.; Ameur, A.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Hestand, M.S. Single molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing comes of age: Applications and utilities for medical diagnostics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robeson, M.S.; O’Rourke, D.R.; Kaehler, B.D.; Ziemski, M.; Dillon, M.R.; Foster, J.T.; Bokulich, N.A. RESCRIPt: Reproducible sequence taxonomy reference database management. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenhav, L.; Thompson, M.; Joseph, T.A.; Briscoe, L.; Furman, O.; Bogumil, D.; Mizrahi, I.; Pe’er, I.; Halperin, E. FEAST: Fast expectation-maximization for microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The R Development Core Team. In R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013.
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’hara, R.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Ordination Methods, Diversity Analysis and Other Functions for Community and Vegetation Ecologists. 2016. Available online: http://cran.rproject.org/package=vegan (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Somerfield, P.J.; Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) for 2-way layouts using a generalised ANOSIM statistic, with comparative notes on Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). Austral Ecol. 2021, 46, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Rubio, V. ggplot2-elegant graphics for data analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 77, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Deng, Y.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhou, J. A general framework for quantitatively assessing ecological stochasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16892–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xue, K.; Liang, Y.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; Stahl, D.A.; et al. Stochasticity, succession, and environmental perturbations in a fluidic ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, E836–E845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Lu, R.; Zhao, J.; Ma, L. Assessment of soil quality in typical wind erosion area of Qaidam Basin. J. Desert Res. 2023, 3, 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, P. Investigation on the vegetations in Tsaidam Basin. J. aridland Resour. 2019, 33, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.-W.; Chong, W.; Rui, X.; Wang, L.-j. Effects of salinity on the soil microbial community and soil fertility. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemunik, G.; Turner, B.L.; Lambers, H.; Laliberté, E. Increasing plant species diversity and extreme species turnover accompany declining soil fertility along a long-term chronosequence in a biodiversity hotspot. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemergut, D.R.; Schmidt, S.K.; Fukami, T.; O’Neill, S.P.; Bilinski, T.M.; Stanish, L.F.; Knelman, J.E.; Darcy, J.L.; Lynch, R.C.; Wickey, P. Patterns and processes of microbial community assembly. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002–e00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, P.; Leach, J.E.; Tringe, S.G.; Sa, T.; Singh, B.K. Plant–microbiome interactions: From community assembly to plant health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, N.M.; Gore, J. Stochastic assembly produces heterogeneous communities in the Caenorhabditis elegans intestine. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2000633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota—Masters of host development and physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, A.R.; Stephens, W.Z.; Stagaman, K.; Wong, S.; Rawls, J.F.; Guillemin, K.; Bohannan, B.J. Contribution of neutral processes to the assembly of gut microbial communities in the zebrafish over host development. ISME J. 2016, 10, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Nair, G.B. Homeostasis and dysbiosis of the gut microbiome in health and disease. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.-z. Global assembly of microbial communities. Msystems 2023, 8, e01289-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Kou, Y.; Yao, M.; He, Z.; Li, X. Distinct mechanisms shape soil bacterial and fungal co-occurrence networks in a mountain ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yao, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Wu, J.; Wen, A.; Xie, M.; Ni, Q.; Zhang, M.; Peng, G. Characterization of the gut microbiota in six geographical populations of Chinese rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta), implying an adaptation to high-altitude environment. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomp, J.E.; Murphy, M.T.; Smith, S.B.; McKay, J.E.; Ferrera, I.; Reysenbach, A.L. Cloacal microbial communities of female spotted towhees Pipilo maculatus: Microgeographic variation and individual sources of variability. J. Avian Biol. 2008, 39, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.C.; Cary, S.C.; Hogg, I.D. The phylogeography of Adelie penguin faecal flora. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N. Microbial biogeography: Patterns in microbial diversity across space and time. In Accessing Uncultivated Microorganisms: From the Environment to Organisms and Genomes and Back; ASM: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 95–115. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, E.; Cotter, P.; Healy, S.; Marques, T.M.; O’sullivan, O.; Fouhy, F.; Clarke, S.; O’toole, P.; Quigley, E.M.; Stanton, C. Composition and energy harvesting capacity of the gut microbiota: Relationship to diet, obesity and time in mouse models. Gut 2010, 59, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, L.; Jia, S.; Tang, X.; Fu, H.; Li, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Seasonal variations in the composition and functional profiles of gut microbiota reflect dietary changes in plateau pikas. Integr. Zool. 2022, 17, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.-N.; Guo, W.-H.; Hu, H.; Zhou, A.-R.; Liu, Q.-P.; Zheng, B.-D.; Zeng, S.-X. Effect of a polyphenol-rich Canarium album extract on the composition of the gut microbiota of mice fed a high-fat diet. Molecules 2018, 23, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | Soil Contribution Range/% | Soil Contribution Average/% |
|---|---|---|
| GC | 6.26–12.20 | 8.94 (±2.97) |
| GEM | 1.29–2.92 | 2.08 (±0.82) |
| HES | 1.17–3.49 | 2.47 (±1.16) |
| HTTL | 0.54–3.11 | 1.80 (±1.29) |
| KK | 2.60–8.96 | 5.43 (±3.18) |
| KLK | 1.33–5.42 | 2.88 (±2.05) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, B.; Qin, W. The Relationship Between Soil and Gut Microbiota Influences the Adaptive Strategies of Goitered Gazelles in the Qaidam Basin. Animals 2024, 14, 3621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243621
Wang Y, Li B, Xu B, Qin W. The Relationship Between Soil and Gut Microbiota Influences the Adaptive Strategies of Goitered Gazelles in the Qaidam Basin. Animals. 2024; 14(24):3621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243621
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yiran, Bin Li, Bo Xu, and Wen Qin. 2024. "The Relationship Between Soil and Gut Microbiota Influences the Adaptive Strategies of Goitered Gazelles in the Qaidam Basin" Animals 14, no. 24: 3621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243621
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, B., Xu, B., & Qin, W. (2024). The Relationship Between Soil and Gut Microbiota Influences the Adaptive Strategies of Goitered Gazelles in the Qaidam Basin. Animals, 14(24), 3621. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243621





