The Bioaccumulation, Fractionation and Health Risk of Rare Earth Elements in Wild Fish of Guangzhou City, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area and Fish Collection
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Assessment Method
2.3.1. The Parameters of Rare Earth Elements
2.3.2. The Evaluation of Health Risk in Fish
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Bioaccumulation of REEs in Fish
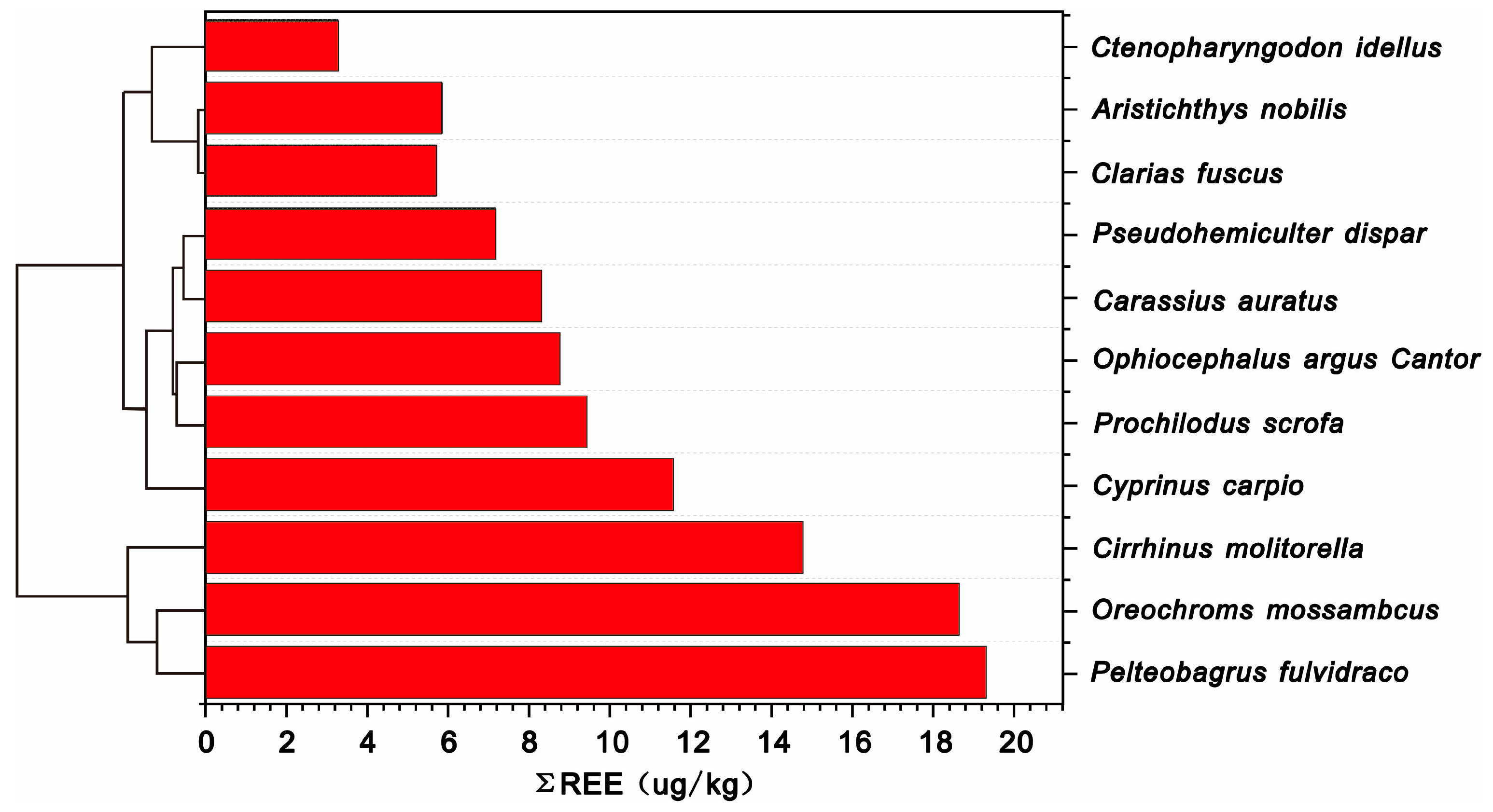
3.2. The Bioaccumulation of REEs in Different Fish Species
3.3. The Impacts of Feeding Behaviors on REEs Bioaccumulation
3.4. The Impacts of Living Habitats on REEs Bioaccumulation
3.5. The Impacts of Fish Size on Their REEs Bioaccumulation
3.6. The Assessment of Health Risk Associated with REEs Bioaccumulation in Fish
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhong, Q.; Han, G. Discrimination of brewing technologies and assessment of health risks based on rare earth elements: Evidence of fingerprint in Chinese famous vinegars. Food Chem. 2025, 464 Pt 1, 141539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, N.; Chaudhary, M.Z.; Anjum, M.; Abid, J. Pollution level assessment, source apportionment, and health hazards of heavy metals and rare earth elements in the sediment core from the coast of Karachi, Pakistan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209 Pt A, 117078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Nie, Y. Geochemical characteristics of sediments in the southern Mid-Atlantic Ridge indicate hydrothermal activity: Evidence from rare earth elements. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 168, 107041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Shi, X.; Huang, M.; Shen, F.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, F.; Liu, J. Enhanced deep-water circulation facilitated rare earth elements enrichment in pelagic sediments from the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Glob. Planet. Change 2024, 242, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Mangori, L.; Danha, C.; Chaukura, N.; Dunjana, N.; Sanganyado, E. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, H.; Yang, H.; Tan, T.; Ren, G.; You, M.; Wu, L.; Yang, M.; Bai, Y.; Xia, S.; Song, S.; et al. Navigating the rare earth elements landscape: Challenges, innovations, and sustainability. Miner. Eng. 2024, 216, 108889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, G.; Si, W.; Xie, Z. Rare earth elements in the upstream of Yangtze River Delta: Spatio-temporal distributions, sources and speciations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209 Pt A, 117103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Han, G. Rare earth elements reveal the human health and environmental concerns in the largest tributary of the Mekong river, Northeastern Thailand. Environ. Res. 2024, 252 Pt 3, 118968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-G.; Wang, Y.-S.; Jordan, R.W.; Su, H.; Jiang, S.-J. Probabilistic ecotoxicological risk assessment of heavy metal and rare earth element mixtures in aquatic biota using the DGT technique in coastal sediments. Chemosphere 2023, 329, 138592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancel, S.; Cachot, J.; Bon, C.; Rochard, É.; Geffard, O. A critical review of pollution active biomonitoring using sentinel fish: Challenges and opportunities. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 360, 124661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Cai, J.; Song, Z.; Liao, X.; Chen, X.; Miao, X. Bioaccumulation, contamination and health risks of trace elements in wild fish in Chongqing City, China: A consumer guidance regarding fish size. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, R.; Elabed, S.; Masarani, A.; Almulla, A.; Almheiri, S.; Koniyath, R.; Semerjian, L.; Abass, K. Human biomonitoring of environmental contaminants in Gulf Countries—Current status and future directions. Environ. Res. 2023, 236 Pt 1, 116650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Zheng, Y.; Sanghamitra, S.S.; Liu, M.; Elizabeth, L.L.-M.; Kenneth, M.A.; Parsons, P.J.; Kannan, K.; Rej, R.; Wang, W.; et al. Biomonitoring of exposure to Great Lakes contaminants among licensed anglers and Burmese refugees in Western New York: Toxic metals and persistent organic pollutants, 2010–2015. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 240, 113918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.U.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Jin, X.; Yang, S.; Ding, L.; Feng, L.; Wang, B.; Li, P. Human biomonitoring of heavy metals exposure in different age- and gender-groups based on fish consumption patterns in typical coastal cities of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, H. The Size Screening Could Greatly Degrade the Health Risk of Fish Consuming Associated to Metals Pollution—An Investigation of Angling Fish in Guangzhou, China. Toxics 2023, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recabarren-Villalón, T.; Ronda, A.C.; Oliva, A.L.; Cazorla, A.L.; Marcovecchio, J.E.; Arias, A.H. Seasonal distribution pattern and bioaccumulation of Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in four bioindicator coastal fishes of Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Gutang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Microplastic and associated emerging contaminants in marine fish from the South China Sea: Exposure and human risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, S.; Jain, A.; Yadav, S.; Dubey, A.; Trivedi, S.P. A review on heavy metal-induced toxicity in fishes: Bioaccumulation, antioxidant defense system, histopathological manifestations, and transcriptional profiling of genes. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 83, 127377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Miao, X.; Song, M.; Zhang, H. The Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Metals among Two Most Consumed Species of Angling Fish (Cyprinus carpio and Pseudohemiculter dispar) in Liuzhou (China): Winter Should Be Treated as a Suitable Season for Fish Angling. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Tang, X.; Xie, Z.; Liu, L.; Luo, S.; Huang, Q.; Zou, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, J. Analysis and health risk assessment of toxic and essential elements of the wild fish caught by anglers in Liuzhou as a large industrial city of China. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhou, C. Health Risk Assessment of Metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, As, Hg, Se) in Angling Fish with Different Lengths Collected from Liuzhou, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zhou, L.; Lu, S.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. Occurrence and spatiotemporal distribution of natural and synthetic steroid hormones in soil, water, and sediment systems in suburban agricultural area of Guangzhou City, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Rong, H.; Chu, Z.; Luo, H.; Zhao, M.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C. Screening and quantification of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in municipal wastewater treatment facilities in Guangzhou, China. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 226, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, D.; Cai, D.-j.; Chen, S.-j.; Dong, H.; Lin, G.-z.; Wang, B.-g.; Yang, J. Health risk assessment of exposure to multiple pollutants in Guangzhou. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 5418–5426. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Wang, W.-X. Dissolved rare earth elements in the Pearl River Delta: Using Gd as a tracer of anthropogenic activity from river towards the sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856 Pt 2, 159241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Dang, D.H.; Wang, W.; Evans, R.D.; Wang, W.-X. Rare earth elements in the Pearl River Delta of China: Potential impacts of the REE industry on water, suspended particles and oysters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, C.; Cao, X. Heavy metals content and distribution in the surface sediments of the Guangzhou section of the Pearl River, Southern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, X.; Lin, C.; Chen, X. Arsenic content and fractionation in the surface sediments of the Guangzhou section of the Pearl River in Southern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, L.; Xiaojuan, H.; Jiangluan, J.; Junyi, Z.; Zhihui, W.; Yufeng, Y. Comparison of the water quality of the surface microlayer and subsurface water in the Guangzhou segment of the Pearl River, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 475–491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, R.; Cui, J.; Gan, S.; Pan, J.; Guo, P. Improvement of water quality in the Pearl River Estuary, China: A long-term (2008–2017) case study of temporal-spatial variation, source identification and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface water of Guangzhou. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21084–21097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Sharing Platform for Reference Materials. Available online: https://www.ncrm.org.cn/Web/OrderingEn/MaterialDetail?autoID=8116 (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Wang, X.-N.; Gu, Y.-G.; Wang, Z.-H. Rare earth elements in different trophic level marine wild fish species. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292 Pt A, 118346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/iris/basic-information-about-integrated-risk-information-system#guidance (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Ren, L.; Nie, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y. Concentration, correlation, and health risk assessment of rare earth elements in different edible parts of the swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) in Shandong Province, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Liu, Y.; Teng, E.; Rui, K. Background value characteristics of rare earth elements in Chinese soil. Environ. Sci. 1991, 5, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, B.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in freshwater fish of Dongting Lake, China: Effects of feeding habits, habitat preferences and body size. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 112, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garneroa, P.L.; Monferran, M.V.; González, G.A.; Griboff, J.; de los Ángeles, B.M. Assessment of exposure to metals, As and Se in water and sediment of a freshwater reservoir and their bioaccumulation in fish species of different feeding and habitat preferences. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, J.E.; Boyd, R.S.; Rajakaruna, N. Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. The seasonal variation in heavy metal accumulation in the food web in the coastal waters of Jiangsu based on carbon and nitrogen isotope technology. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 297, 118649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Song, M.; Xu, G.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, H. The Accumulation and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Liujiang River Basin in Southern China and Their Threatening on Water Security. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Chen, L.; Hao, Y.; An, J.; Xu, T.; Bao, W.; Chen, X.; Liao, X.; Xie, Y. The variations of heavy metals sources varied their aggregated concentration and health risk in sediments of karst rivers—A case study in Liujiang River Basin, Southwest China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116171. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, Z.; Miao, D.; He, X. Effects of heavy metals speciations in sediments on their bioaccumulation in wild fish in rivers in Liuzhou—A typical karst catchment in southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sysolyatina, M.A.; Olkova, A.S. Sources of rare earth elements in the environment and their impact on living organisms. Environ. Rev. 2023, 31, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras-Rivera, G.; Górski, K.; Colin, N. Behavioral biomarkers in fishes: A non-lethal approach to assess the effects of chemical pollution on freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahjahan, M.; Taslima, K.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Emran, M.; Alam, S.I.; Faggio, C. Effects of heavy metals on fish physiology—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.K.M.M.; Hamed, M.; Hasan, J.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Niyogi, S.; Chivers, D.P. A review of the neurobehavioural, physiological, and reproductive toxicity of microplastics in fishes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 282, 116712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croizier, G.L.; Schaal, G.; Gallon, R.; Fall, M.; Grand, F.L.; Munaron, J.-M.; Rouget, M.-L.; Machu, E.; Loc’h, F.L.; Laë, R.; et al. Trophic ecology influence on metal bioaccumulation in marine fish: Inference from stable isotope and fatty acid analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Qu, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, M.; Xin, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y. Urbanization reduces fish taxonomic and functional diversity while increases phylogenetic diversity in subtropical rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcagni, M.; Juncos, R.; Rizzo, A.; Pavlin, M.; Fajon, V.; Arribére, M.A.; Horvat, M.; Ribeiro, S.G. Species- and habitat-specific bioaccumulation of total mercury and methylmercury in the food web of a deep oligotrophic lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 612, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.M.; Gomes, J.M.; Reis, G.C.L.; Hoyos, D.C.M.; Custódio, F.B.; Gloria, M.B.A. Biogenic amines in amazonian fish and their health effects are affected by species and season of capture. Food Control 2021, 123, 107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, R.S.; Luxwolda, M.F.; Offringa, P.J.; Boersma, E.R.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J.; Muskieta, F.A.J. Gestational age dependent changes of the fetal brain, liver and adipose tissue fatty acid compositions in a population with high fish intakes. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2012, 86, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species | Num | Length | Weight | Living Habitats | Feeding Behaviors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | g | ||||
| Prochilodus scrofa | 8 | 23–27 | 176.6–287.9 | Demersal | Omnivore |
| Ctenopharyngodon idellus | 3 | 18.2–22.5 | 90.1–127.1 | Demersal | Herbivore |
| Ophiocephalus argus Cantor | 8 | 26.5–34.5 | 163.5–434.3 | Demersal | Carnivore |
| Pelteobagrus fulvidraco | 3 | 12.1–15.2 | 24.7–31.6 | Demersal | Omnivore |
| Carassius auratus | 11 | 11.5–23 | 223.8 | Demersal | Omnivore |
| Pseudohemiculter dispar | 10 | 13–20 | 19–60.4 | Pelagic | Omnivore |
| Cyprinus carpio | 30 | 13–26.5 | 30.1–606.1 | Demersal | Omnivore |
| Cirrhinus molitorella | 18 | 16.5–46 | 56.7–1087.6 | Demersal | Omnivore |
| Oreochroms mossambcus | 35 | 11.3–26 | 31.3–334.3 | Demersal | Omnivore |
| Clarias fuscus | 5 | 22–30 | 102.6–265.8 | Demersal | Carnivore |
| Aristichthys nobilis | 6 | 21.5–44 | 110.7–786.5 | Pelagic | Omnivore |
| ICP-MS | |
|---|---|
| RF power | 1550 W |
| Plasma, carrier and makeup gas flow | 14, 1.0025 and 0.8 L min−1, respectively |
| Spray chamber temperature | 2 °C |
| Cones | Pt |
| Integration time | 0.1 s |
| Peak pattern | 1 point per mass |
| Replicates per analysis | 10 |
| Parameters | Children | Adults | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| GW (g/d) | 59.69 | 59.69 | [20,34] |
| EF (days/year) | 365 | 365 | |
| ED (year) | 6 | 70 | |
| BW (kg) | 30 | 60 | |
| AT (day/year) | 6 × 365 | 70 × 365 |
| REEs | LRs/HRs | ΔEu | ΔCe | LREEs | HREEs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All fish | 13.14 ± 11.43 | 4.99 ± 2.06 | 1.85 ± 0.94 | 1.02 ± 0.18 | 10.64 ± 9.29 | 2.50 ± 2.28 |
| Chinese Soil [35] | 176.75 | 3.78 | 0.65 | 0.96 | 139.79 | 36.96 |
| Prochilodus scrofa | 9.42 ± 6.05 | 4.62 ± 1.1 | 1.26 | 1.04 ± 0.13 | 7.65 ± 4.91 | 1.76 ± 1.17 |
| Ctenopharyngodon idellus | 3.26 | 6.75 | — | 0.74 | 2.84 | 0.42 |
| Ophiocephalus argus Cantor | 8.72 ± 6.95 | 7.01 ± 1.36 | — | 0.93 ± 0.19 | 7.73 ± 6.35 | 0.99 ± 0.6 |
| Pelteobagrus fulvidraco | 19.29 | 4.25 | 1.26 | 1.05 | 15.62 | 3.67 |
| Carassius auratus | 8.30 ± 4.69 | 5.94 ± 2.24 | 2.32 ± 0.77 | 1.00 ± 0.18 | 6.89 ± 3.81 | 1.41 ± 0.9 |
| Pseudohemiculter dispar | 7.16 ± 3.15 | 4.43 ± 0.57 | — | 1.24 | 5.76 ± 2.42 | 1.40 ± 0.73 |
| Cyprinus carpio | 11.55 ± 5.82 | 5.63 ± 2.41 | 2.22 ± 0.89 | 1.01 ± 1.04 | 9.70 ± 5.08 | 1.86 ± 0.96 |
| Cirrhinus molitorella | 14.75 ± 15.66 | 5.51 ± 1.45 | 1.68 ± 1.00 | 1.07 ± 0.29 | 12.37 ± 13.11 | 2.38 ± 2.59 |
| Oreochroms mossambcus | 18.62 ± 13.53 | 3.45 ± 1.23 | 1.63 ± 0.87 | 1.03 ± 0.1 | 14.28 ± 10.9 | 4.34 ± 2.92 |
| Clarias fuscus | 5.71 ± 2.76 | 7.21 ± 2.79 | — | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 4.79 ± 2.12 | 0.91 ± 0.65 |
| Aristichthys nobilis | 5.84 ± 2.85 | 5.33 ± 1.04 | 2.64 ± 0.45 | 0.98 ± 0.19 | 4.90 ± 2.43 | 0.94 ± 0.44 |
| ΣREEs | LRs/HRs | ΔEu | ΔCe | LREEs | HREEs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omnivore | 11.86 | 4.90 | 1.86 | 1.05 | 9.65 | 2.22 |
| Carnivore | 7.22 | 7.11 | — | 0.89 | 6.26 | 0.95 |
| Herbivore | 3.26 | 6.75 | — | 0.74 | 2.84 | 0.42 |
| Pelagic | 6.50 | 4.88 | 2.64 | 1.11 | 5.33 | 1.17 |
| Demersal | 11.07 | 5.60 | 1.73 | 0.97 | 9.10 | 1.97 |
| Chinese Soil | 176.75 | 3.78 | 0.65 | 0.96 | 139.79 | 36.96 |
| Weight | ΣREEs | LRs/HRs | ΔEu | ΔCe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | 0.920 * | −0.500 * | 0.418 * | −0.470 * | 0.019 |
| Weight | - | −0.392 * | 0.290 * | −0.441 * | −0.043 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, X.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Hao, Y.; Bao, W. The Bioaccumulation, Fractionation and Health Risk of Rare Earth Elements in Wild Fish of Guangzhou City, China. Animals 2024, 14, 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243567
Miao X, Wei X, Zhao X, Hao Y, Bao W. The Bioaccumulation, Fractionation and Health Risk of Rare Earth Elements in Wild Fish of Guangzhou City, China. Animals. 2024; 14(24):3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243567
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Xiongyi, Xueqin Wei, Xiqian Zhao, Yupei Hao, and Wei Bao. 2024. "The Bioaccumulation, Fractionation and Health Risk of Rare Earth Elements in Wild Fish of Guangzhou City, China" Animals 14, no. 24: 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243567
APA StyleMiao, X., Wei, X., Zhao, X., Hao, Y., & Bao, W. (2024). The Bioaccumulation, Fractionation and Health Risk of Rare Earth Elements in Wild Fish of Guangzhou City, China. Animals, 14(24), 3567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14243567





