Molecular Detection and Genotyping of Chlamydia psittaci in Birds in Buenos Aires City, Argentina
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Samples
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Molecular Diagnosis
2.5. Sequencing of ompA Gene
2.6. Sequence Comparison and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis and Geographic Information System (GIS)
3. Results
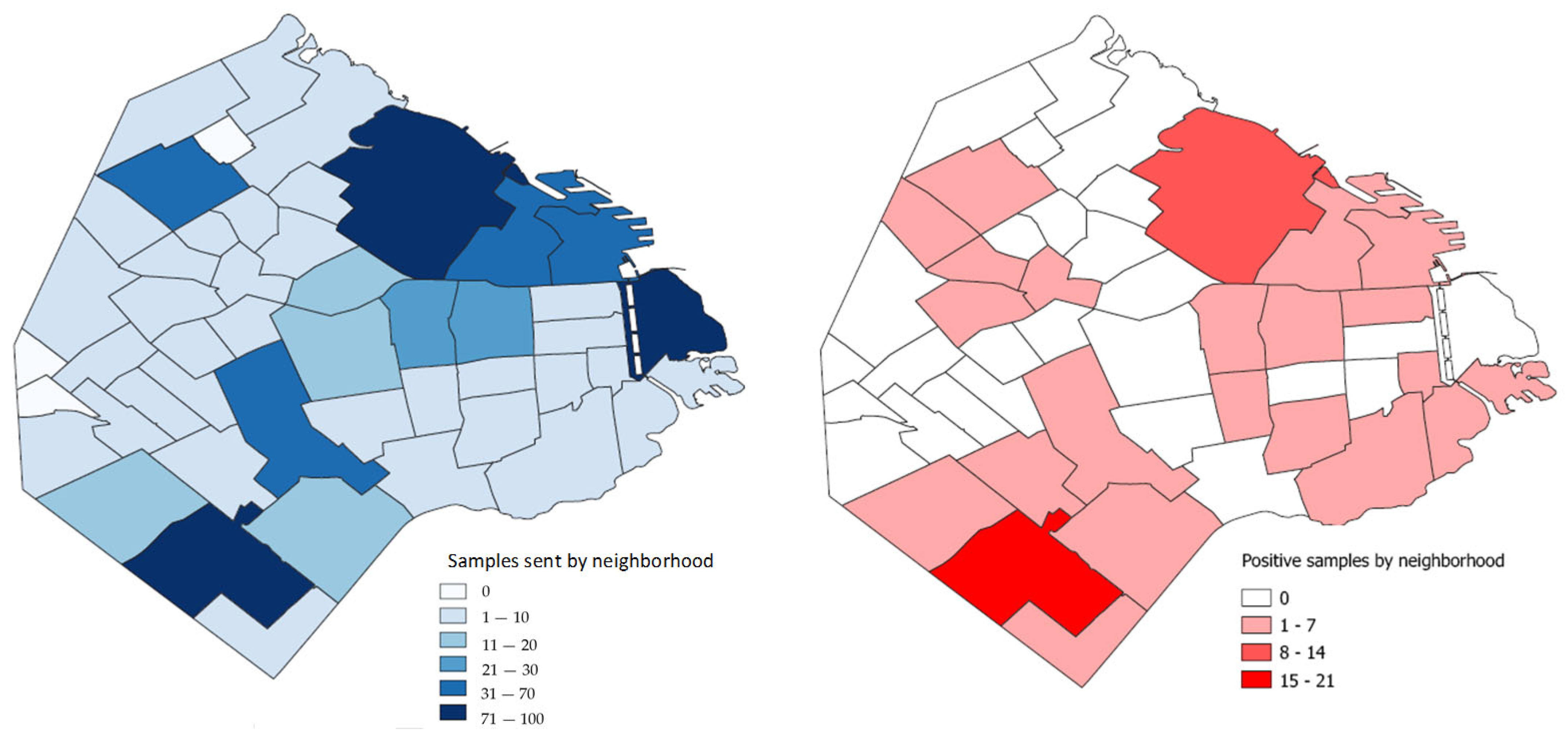
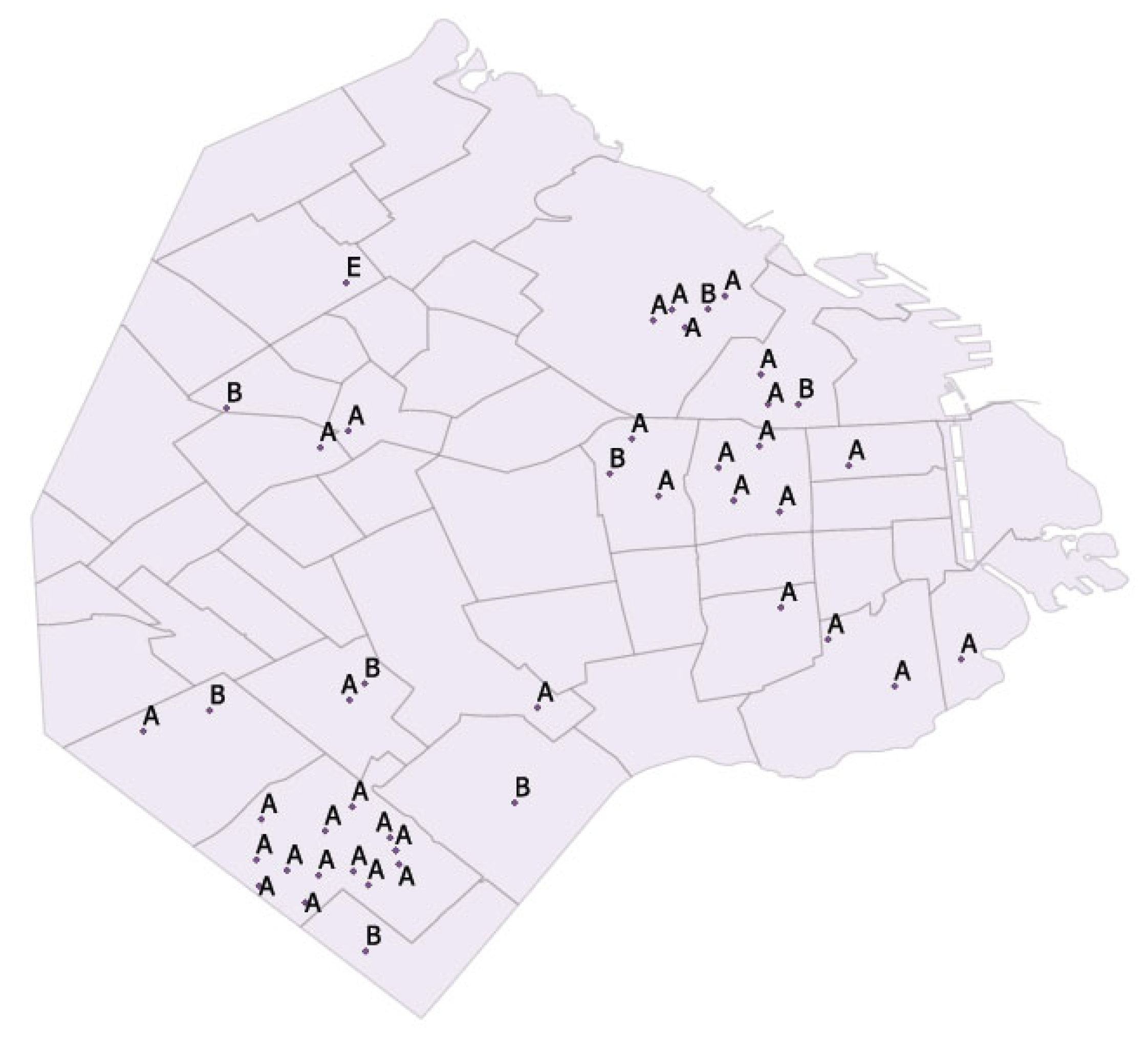
3.1. Species of Birds and Sample Location
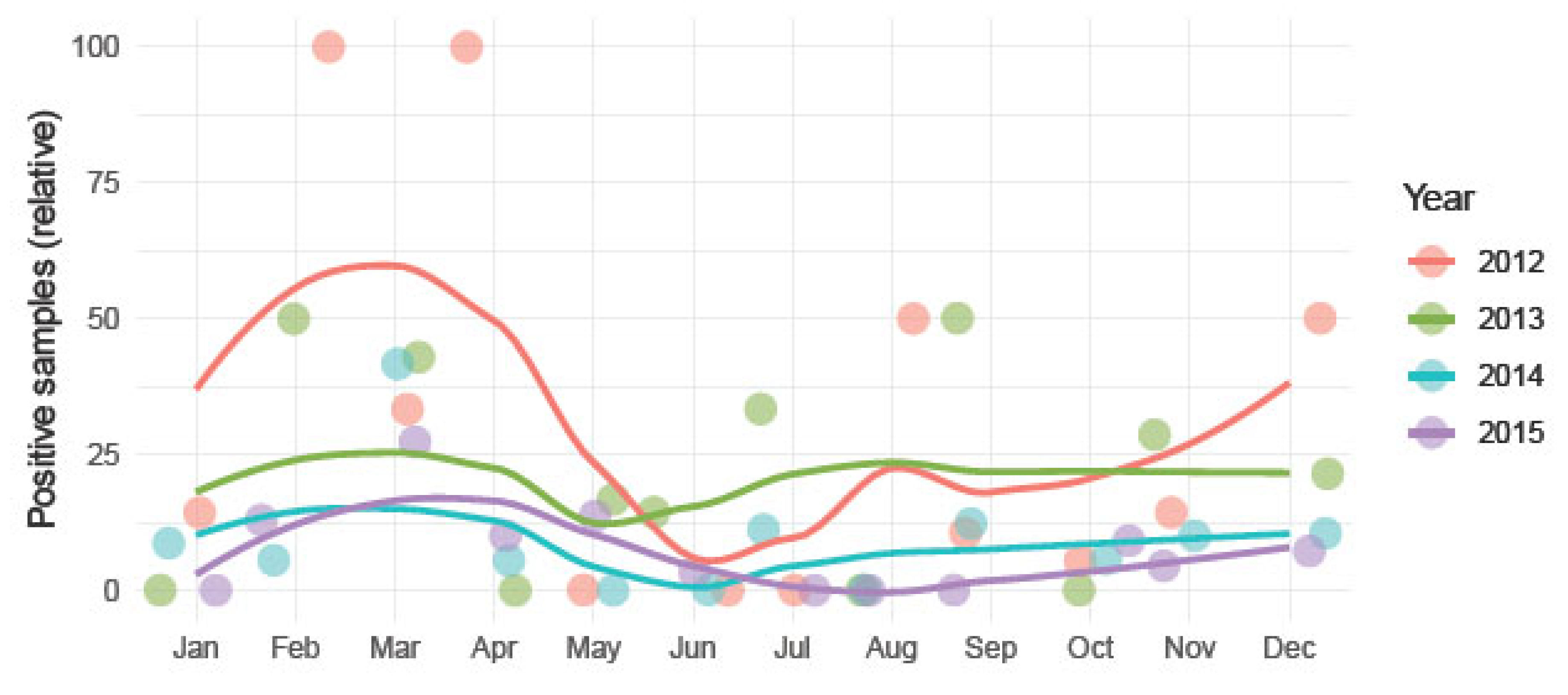
3.2. Chlamydia Psittaci Frequency
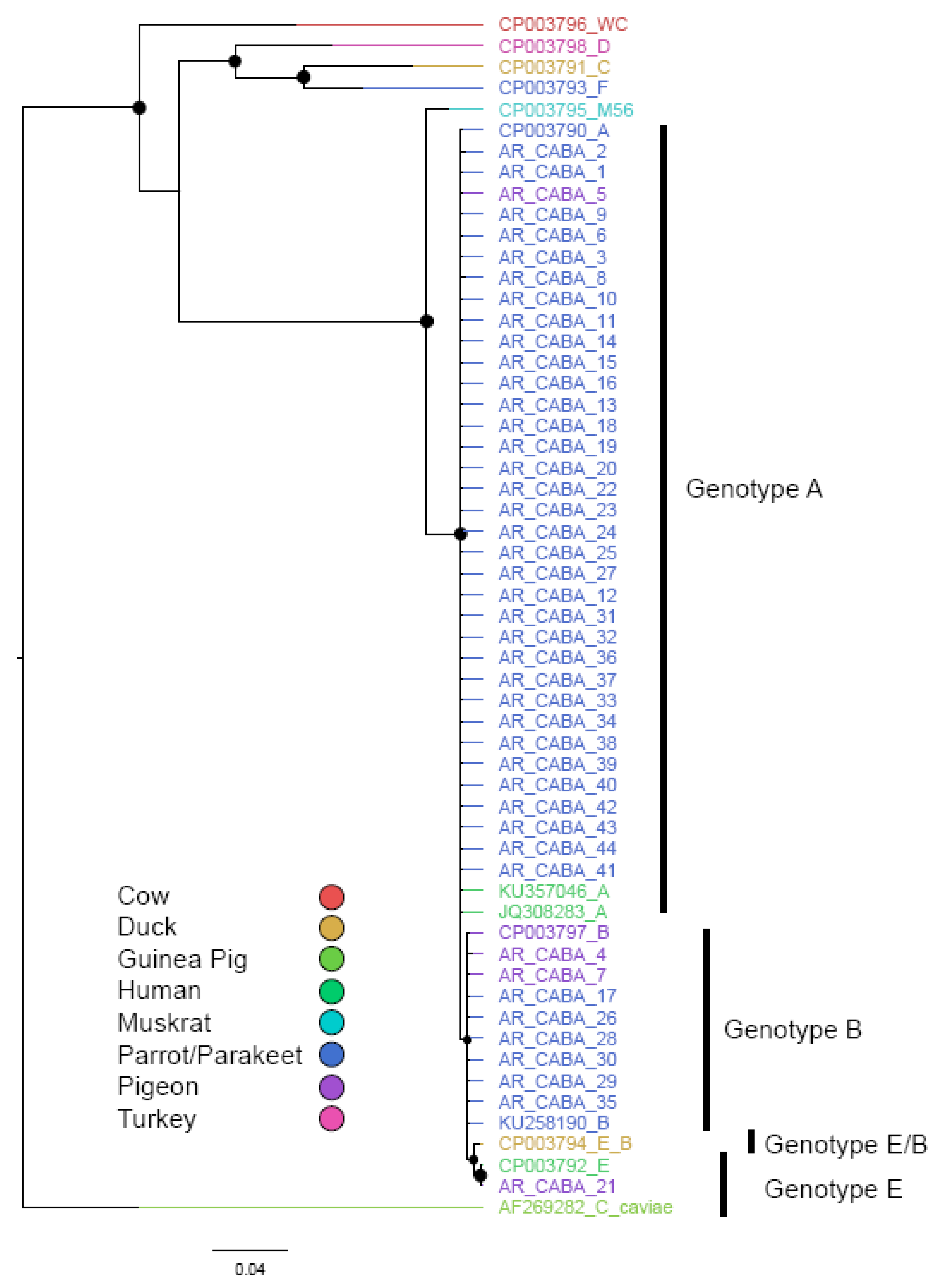
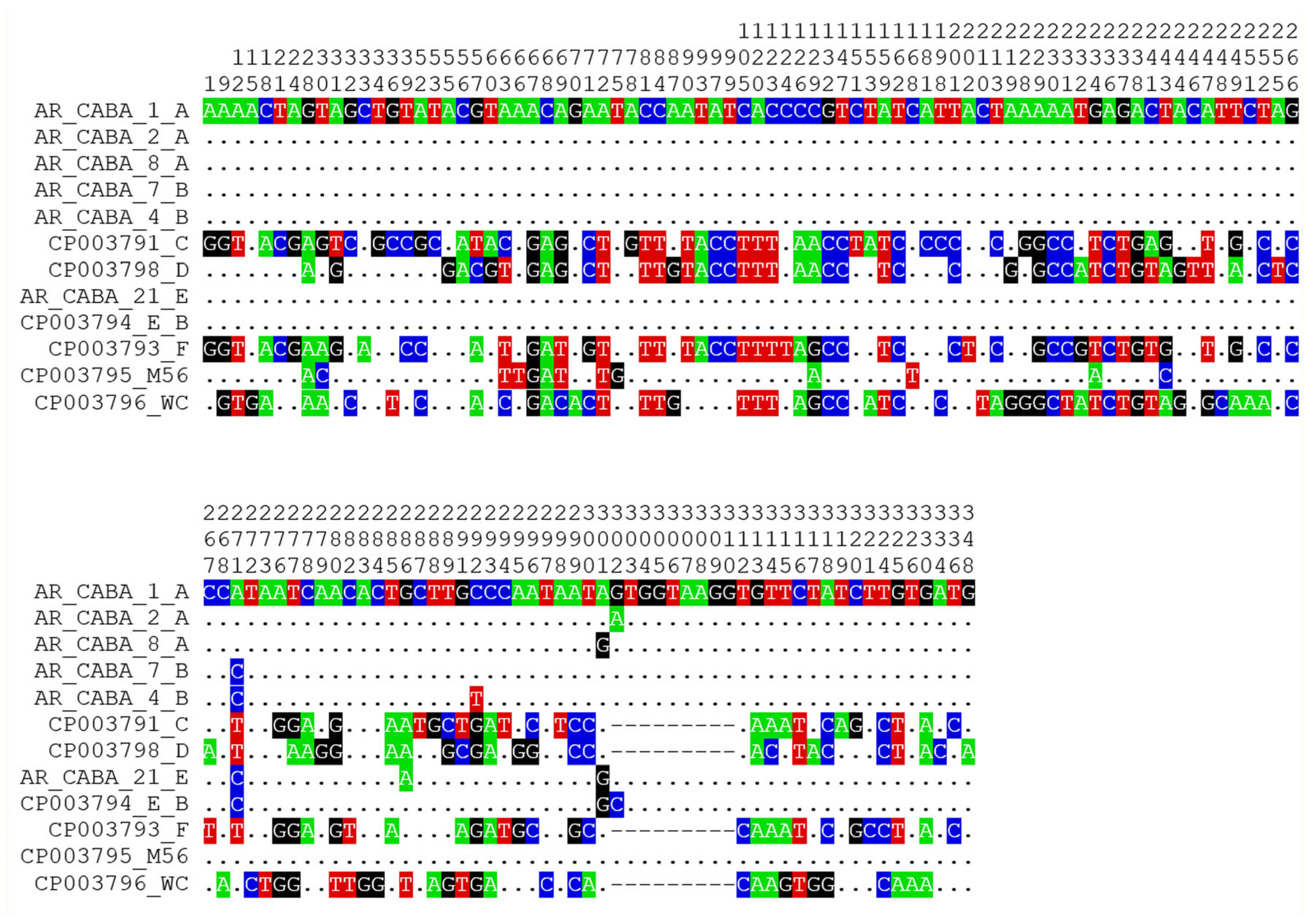
3.3. Genotyping by ompA Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanrompay, D.; Harkinezhad, T.; van de Walle, M.; Beeckman, D.; van Droogenbroeck, C.; Verminnen, K.; Leten, R.; Martel, A.; Cauwerts, K. Chlamydophila psittaci transmission from pet birds to humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, A.A.; Vanrompay, D. Avian chlamydiosis. In Diseases of Poultry; Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 971–986. ISBN 978-0-8138-0718-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kaleta, E.F.; Taday, E.M. Avian host range of Chlamydophila spp. based on isolation, antigen detection and serology. Avian Pathol. 2003, 32, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, H.S.; Berg, M.L.; Bennett, A.T.D. A Review of Chlamydial Infections in Wild Birds. Pathogens 2021, 10, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, C.; Jelocnik, M.; Micallef, M.L.; Galea, F.; Taylor-Brown, A.; Bogema, D.R.; Liu, M.; O’Rourke, B.; Chicken, C.; Carrick, J.; et al. An epizootic of Chlamydia psittaci equine reproductive loss associated with suspected spillover from native Australian parrots. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkinezhad, T.; Geens, T.; Vanrompay, D. Chlamydophila psittaci infections in birds: A review with emphasis on zoonotic consequences. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 135, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanrompay, D. Avian chlamydiosis. In Disease of Paultry, 14th ed.; Swayne, D.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1086–1107. ISBN 978-1-1193-7116-8. [Google Scholar]
- Beeckman, D.S.; Vanrompay, D.C. Zoonotic Chlamydophila psittaci infections from a clinical perspective. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knittler, M.R.; Sachse, K. Chlamydia psittaci: Update on an underestimated zoonotic agent. Pathog. Dis. 2015, 73, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geens, T.; Desplanques, A.; Van Loock, M.; Bönner, B.M.; Kaleta, E.F.; Magnino, S.; Andersen, A.A.; Everett, K.D.; Vanrompay, D. Sequencing of the Chlamydophila psittaci ompA gene reveals a new genotype, E/B, and the need for a rapid discriminatory genotyping method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2456–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachse, K.; Laroucau, K.; Hotzel, H.; Schubert, E.; Ehricht, R.; Slickers, P. Genotyping of Chlamydophila psittaci using a new DNA microarray assay based on sequence analysis of ompA genes. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, S.A.; Peighambari, S.M. PCR-based diagnosis, molecular characterization and detection of atypical strains of avian Chlamydia psittaci in companion and wild birds. Avian Pathol. 2013, 42, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, T.D.; Joseph, S.J.; Didelot, X.; Liang, B.; Patel, L.; Dean, D. Comparative analysis of Chlamydia psittaci genomes reveals the recent emergence of a pathogenic lineage with a broad host range. mBio 2013, 4, e00604-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorimore, F.; Aaziz, R.; de Barbeyrac, B.; Peuchant, O.; Szymańska-Czerwińska, M.; Herrmann, B.; Schnee, C.; Laroucau, K. A New SNP-Based Genotyping Method for C. psittaci: Application to Field Samples for Quick Identification. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frutos, M.C.; Monetti, M.S.; Vaulet, L.G.; Cadario, M.E.; Fermepin, M.R.; Ré, V.E.; Cuffini, C.G. Genetic diversity of Chlamydia among captive birds from central Argentina. Avian Pathol. 2015, 44, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadario, M.E.; Frutos, M.C.; Arias, M.B.; Origlia, J.A.; Zelaya, V.; Madariaga, M.J.; Lara, C.S.; Ré, V.; Cuffini, C.G. Epidemiological and molecular characteristics of Chlamydia psittaci from 8 human cases of psittacosis and 4 related birds in Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2017, 49, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origlia, J.A.; Cadario, M.E.; Frutos, M.C.; Lopez, N.F.; Corva, S.; Unzaga, M.F.; Piscopo, M.V.; Cuffini, C.; Petruccelli, M.A. Detection and molecular characterization of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia abortus in psittacine pet birds in Buenos Aires province, Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coordenadas Geográficas de Buenos Aires. Available online: https://www.geodatos.net/coordenadas/argentina/buenos-aires (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Resultados del Censo 2022. Available online: https://censo.gob.ar/index.php/datos_definitivos_caba/ (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Messmer, T.O.; Skelton, S.K.; Moroney, J.F.; Daugharty, H.; Fields, B.S. Application of a nested, multiplex PCR to psittacosis outbreaks. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2043–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, K.; Hotzel, H. Detection and differentiation of Chlamydiae by nested PCR. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Sachse, K., Ed.; Humana Press Inc.: Clifton, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 123–136. ISBN 978-1-5882-9049-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for making accurate alignments of many protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, J. Mr Modeltest 2.2; Program distributed by the author; Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.4.2. 2014. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villesen, P. FaBox: An online toolbox for fasta sequences. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rienzo, J.A.; Casanoves, F.; Balzarini, M.G.; Gonzalez, L.; Tablada, M.; Robledo, C.W. InfoStat Versión 2020. Centro de Transferencia InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. Available online: http://www.infostat.com.ar (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- QGIS Development Team. Quantum GIS Geographic Information System (QGIS 3.8 Zanzibar). Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. 2019. Available online: http://qgis.org/es/site (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Van Lent, S.; Piet, J.R.; Beeckman, D.; van der Ende, A.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Bavoil, P.; Myers, G.; Vanrompay, D.; Pannekoek, Y. Full genome sequences of all nine Chlamydia psittaci genotype reference strains. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 6930–6931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadario, M.E.; Madariaga, M.J.; Seleiman, M.; Ruggieri, D.; Arias, M.; Zintgraff, J.; Gury Dohmen, F.; Lara, C.; Rivollier, G.; Fonseca, L.; et al. Brote de Psitacosis en San Antonio Oeste (Río Negro). Diciembre 2012–Febrero 2013. Rev. Argent. Zoonosis Enfermedades Infecc. Emerg. 2015, X, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Piasecki, T.; Chrząstek, K.; Wieliczko, A. Detection and identification of Chlamydophila psittaci in asymptomatic parrots in Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheleby-Elías, J.; Solórzano-Morales, A.; Romero-Zuñiga, J.J.; Dolz, G. Molecular Detection and Genotyping of Chlamydia psittaci in Captive Psittacines from Costa Rica. Vet. Med. Int. 2013, 2013, 142962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.L.; Dias, R.A.; Raso, T.F. Screening of Feral Pigeons (Columba livia) for Pathogens of Veterinary and Medical Importance. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2016, 18, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Li, K.P.; Hsieh, M.K.; Chang, P.C.; Shien, J.H.; Ou, S.C. Prevalence and Genotyping of Chlamydia psittaci from Domestic Waterfowl, Companion Birds, and Wild Birds in Taiwan. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahzounieh, M.; Moloudizargari, M.; Ghasemi Shams Abadi, M.; Baninameh, Z.; Heidari Khoei, H. Prevalence Rate and Phylogenetic Analysis of Chlamydia psittaci in Pigeon and House Sparrow Specimens and the Potential Human Infection Risk in Chahrmahal-va-Bakhtiari, Iran. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 15, e67565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantchev, A.; Sting, R.; Bauerfeind, R.; Tyczka, J.; Sachse, K. New real-time PCR tests for species-specific detection of Chlamydophila psittaci and Chlamydophila abortus from tissue samples. Vet. J. 2009, 181, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, M.; Christerson, L.; Waldenström, J.; Lindberg, P.; Helander, B.; Gunnarsson, G.; Herrmann, B.; Olsen, B. Chlamydia psittaci in birds of prey, Sweden. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2012, 2, 8435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Plaza, P.I.; Blanco, G.; Madariaga, M.J.; Boeri, E.; Teijeiro, M.L.; Bianco, G.; Lambertucci, S.A. Scavenger birds exploiting rubbish dumps: Pathogens at the gates. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouffroy, S.J.; Schlueter, A.H.; Bildfell, R.J.; Rockey, D.D. Rhabdochlamydia spp. in an Oregon raptor. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2016, 28, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; An, I.; Oem, J.K.; Wang, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Shin, J.H.; Woo, C.; Kim, Y.; Jo, S.D.; Son, K.; et al. Molecular prevalence and genotyping of Chlamydia spp. in wild birds from South Korea. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amery-Gale, J.; Legione, A.R.; Marenda, M.S.; Owens, J.; Eden, P.A.; Konsak-Ilievski, B.M.; Whiteley, P.L.; Dobson, E.C.; Browne, E.A.; Slocombe, R.F.; et al. Surveillance for Chlamydia spp. with Multilocus Sequence Typing Analysis in wild and captive birds in Victoria, Australia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaziz, R.; Gourlay, P.; Vorimore, F.; Sachse, K.; Siarkou, V.I.; Laroucau, K. Chlamydiaceae in North Atlantic Seabirds Admitted to a Wildlife Rescue Center in Western France. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4581–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeya, H.; Sato, S.; Maruyama, S. Prevalence and characterization of Chlamydia DNA in zoo animals in Japan. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 59, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachse, K.; Laroucau, K.; Vanrompay, D. Avian Chlamydiosis. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 2, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, K.; Kuehlewind, S.; Ruettger, A.; Schubert, E.; Rohde, G. More than classical Chlamydia psittaci in urban pigeons. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattmann, P.; Marti, H.; Borel, N.; Jelocnik, M.; Albini, S.; Vogler, B.R. Chlamydiaceae in wild, feral and domestic pigeons in Switzerland and insight into population dynamics by Chlamydia psittaci multilocus sequence typing. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannekoek, Y.; Dickx, V.; Beeckman, D.S.; Jolley, K.A.; Keijzers, W.C.; Vretou, E.; Maiden, M.C.; Vanrompay, D.; van der Ende, A. Multi locus sequence typing of Chlamydia reveals an association between Chlamydia psittaci genotypes and host species. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, A.; Fatemeh, A.; Jamshid, R. Detection of Chlamydia psittaci Genotypes Among Birds in Northeast Iran. J. Avian Med. Surg. 2019, 33, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briceño, C.; Sandoval-Rodríguez, A.; Yévenes, K.; Larraechea, M.; Morgado, A.; Chappuzeau, C.; Muñoz, V.; Dufflocq, P.; Olivares, F. Interactions between Invasive Monk Parakeets (Myiopsitta monachus) and Other Bird Species during Nesting Seasons in Santiago, Chile. Animals 2019, 9, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Brito, D.; Carrete, M.; Blanco, G.; Romero-Vidal, P.; Senar, J.C.; Mori, E.; White, T.H., Jr.; Luna, Á.; Tella, J.L. The Role of Monk Parakeets as Nest-Site Facilitators in Their Native and Invaded Areas. Biology 2021, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Santo, M.; Battisti, C.; Bologna, M.A. Interspecific interactions in nesting and feeding urban sites among introduced Monk Parakeet (Myiopsitta monachus) and syntopic bird species. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 29, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, J.L.; Brewer, G.L. Use of Monk Parakeet (Myiopsitta monachus) nests by Speckled Teal (Anas flavirostris) in eastern Argentina. Ornitol. Neotrop. 2004, 15, 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Nores, M. Use of Active Monk Parakeet Nests by Common Pigeons and Response by the Host. Wilson J. Ornithol. 2009, 121, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martella, M.B.; Navarro, J.L.; Bucher, E.H. Vertebrados asociados a los nidos de la cotorra argentina Myiopsitta monachus en Córdoba y La Rioja. Physis 1985, 43, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- De Lucca, E.R. Nidificación del Halconcito Colorado (Falco sparverius) en nidos de Cotorra (Myiopsitta monachus). Hornero Rev. Ornitol. Neotrop. 1992, 13, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Order | Family | Genus | Species (n = 983) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accipitriformes | Accipitridae | Buteogallus | Buteogallus coronatus (n = 5) |
| Geranoaetus | Geranoaetus melanoleucus (n = 1) | ||
| Parabuteo | Parabuteo unicinctus (n = 13) | ||
| Rupornis | Rupornis magnirostris (n = 9) | ||
| Anseriformes | Anatidae | Anas | Anas platyrhynchos domesticus (n = 32) |
| Anas versicolor (n = 1) | |||
| Anser | Anser anser (n = 68) | ||
| Cathartiformes | Cathartidae | Vultur | Vultur gryphus (n = 40) |
| Charadriiformes | Laridae | Chroicocephalus | Chroicocephalus maculipennis (n = 1) |
| Larus | Larus dominicanus (n = 6) | ||
| Columbiformes | Columbidae | Columba | Columba livia (n = 61) |
| Streptopelia | Streptopelia decaocto (n = 1) | ||
| Zenaida | Zenaida auriculata (n = 52) | ||
| Falconiformes | Falconidae | Caracara | Caracara plancus (n = 15) |
| Falco | Falco sparverius (n = 2) | ||
| Milvago | Milvago chimango (n = 10) | ||
| Galliformes | Phasianidae | Chrysolophus | Chrysolophus pictus (n = 2) |
| Gallus | Gallus gallus domesticus (n = 30) | ||
| Lophura | Lophura nycthemera (n = 2) | ||
| Phasianus | Phasianus colchicus (n = 1) | ||
| Gruiformes | Aramidae | Aramus | Aramus guarauna (n = 2) |
| Rallidae | Aramides | Aramides cajaneus (n = 1) | |
| Gallinula | Gallinula chloropus (n = 1) | ||
| Pardirallus | Pardirallus maculatus (n = 2) | ||
| Passeriformes | Cardinalidae | Cyanoloxia | Cyanoloxia brissonii (n = 1) |
| Fringillidae | Spinus | Spinus atratus (n = 1) | |
| Sporagra | Sporagra crassirostris (n = 2) | ||
| Furnariidae | Lepidocolaptes | Lepidocolaptes angustirostris (n = 1) | |
| Icteridae | Agelaioides | Agelaioides badius (n = 1) | |
| Molothrus | Molothrus bonariensis (n = 1) | ||
| Mimidae | Mimus | Mimus saturninus (n = 1) | |
| Parulidae | Geothlypis | Geothlypis aequinoctialis (n = 2) | |
| Passerellidae | Zonotrichia | Zonotrichia capensis (n = 5) | |
| Sturnidae | Sturnus | Sturnus vulgaris (n = 1) | |
| Thraupidae | Pipraeidea | Pipraeidea bonariensis (n = 2) | |
| Poospiza | Poospiza nigrorufa (n = 5) | ||
| Saltator | Saltator aurantiirostris (n = 1) | ||
| Sicalis | Sicalis flaveola pelzelni (n = 12) | ||
| Sporophila | Sporophila caerulescens (n = 1) | ||
| Turdidae | Turdus | Turdus rufiventris (n = 5) | |
| Tyrannidae | Pitangus | Pitangus sulphuratus (n = 1) | |
| Elaenia | Elaenia parvirostris (n = 1) | ||
| Pelecaniformes | Ardeidae | Syrigma | Syrigma sibilatrix (n = 1) |
| Psittaciformes | Cacatuidae | Nymphicus | Nymphicus hollandicus (n = 2) |
| Psittacidae | Agapornis | Agapornis roseicollis (n = 11) | |
| Amazona | Amazona aestiva (n = 274) | ||
| Ara | Ara chloropterus (n = 44) | ||
| Cyanoliseus | Cyanoliseus patagonus (n = 15) | ||
| Myiopsitta | Myiopsitta monachus (n = 175) | ||
| Psittaculidae | Melopsittacus | Melopsittacus undulatus (n = 29) | |
| Strigiformes | Strigidae | Asio | Asio clamator (n = 5) |
| Athene | Athene cunicularia (n = 7) | ||
| Glaucidium | Glaucidium brasilianum (n = 1) | ||
| Tytonidae | Tyto | Tyto alba (n = 7) | |
| Struthioniformes | Dromaiidae | Dromaius | Dromaius novaehollandiae (n = 5) |
| Suliformes | Phalacrocoracidae | Phalacrocorax | Phalacrocorax brasilianus (n = 5) |
| Birds | N° Examined | Family | Species | N° Positive for C. psittaci |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psittacines | 550 | Psittacidae Psittaculidae | Amazona aestiva | 30 |
| Ara chloropterus | 2 | |||
| Myiopsitta monachus | 34 | |||
| Melopsittacus undulatus | 3 | |||
| Non-psittacines | 283 | Accipitridae | Buteogallus coronatus | 1 |
| Anatidae | Anser caerulescens | 3 | ||
| Cathartidae | Vultur gryphus | 1 | ||
| Columbidae | Columba livia | 7 | ||
| Zenaida auriculata | 2 | |||
| 150 | Other orders | 0 | ||
| Total | 983 | 83 |
| ID Number | Species | Genotype | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR_CABA_1 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227480 |
| AR_CABA_2 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227481 |
| AR_CABA_3 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227482 |
| AR_CABA_4 | Columba livia | B | OR227483 |
| AR_CABA_5 | Columba livia | A | OR227484 |
| AR_CABA_6 | Amazona aestiva | A | OR227485 |
| AR_CABA_7 | Columba livia | B | OR227486 |
| AR_CABA_8 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227487 |
| AR_CABA_9 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227488 |
| AR_CABA_10 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227489 |
| AR_CABA_11 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227490 |
| AR_CABA_12 | Amazona aestiva | A | OR227491 |
| AR_CABA_13 | Amazona aestiva | A | OR227492 |
| AR_CABA_14 | Amazona aestiva | A | OR227493 |
| AR_CABA_15 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227494 |
| AR_CABA_16 | Amazona aestiva | A | OR227495 |
| AR_CABA_17 | Myiopsitta monachus | B | OR227496 |
| AR_CABA_18 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227497 |
| AR_CABA_19 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227498 |
| AR_CABA_20 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227499 |
| AR_CABA_21 | Columba livia | E | OR227500 |
| AR_CABA_22 | Melopsittacus undulatus | A | OR227501 |
| AR_CABA_23 | Melopsittacus undulatus | A | OR227502 |
| AR_CABA_24 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227503 |
| AR_CABA_25 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227504 |
| AR_CABA_26 | Ara chloropterus | B | OR227505 |
| AR_CABA_27 | Ara chloropterus | A | OR227506 |
| AR_CABA_28 | Amazona aestiva | B | OR227507 |
| AR_CABA_29 | Amazona aestiva | B | OR227508 |
| AR_CABA_30 | Amazona aestiva | B | OR227509 |
| AR_CABA_31 | Amazona aestiva | A | OR227510 |
| AR_CABA_32 | Amazona aestiva | A | OR227511 |
| AR_CABA_33 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227512 |
| AR_CABA_34 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227513 |
| AR_CABA_35 | Amazona aestiva | B | OR227514 |
| AR_CABA_36 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227515 |
| AR_CABA_37 | Amazona aestiva | A | OR227516 |
| AR_CABA_38 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227517 |
| AR_CABA_39 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227518 |
| AR_CABA_40 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227519 |
| AR_CABA_41 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227520 |
| AR_CABA_42 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227521 |
| AR_CABA_43 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227522 |
| AR_CABA_44 | Myiopsitta monachus | A | OR227523 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madariaga, M.J.; Caraballo, D.A.; Teijeiro, M.L.; Boeri, E.J.; Cadario, M.E. Molecular Detection and Genotyping of Chlamydia psittaci in Birds in Buenos Aires City, Argentina. Animals 2024, 14, 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14223286
Madariaga MJ, Caraballo DA, Teijeiro ML, Boeri EJ, Cadario ME. Molecular Detection and Genotyping of Chlamydia psittaci in Birds in Buenos Aires City, Argentina. Animals. 2024; 14(22):3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14223286
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadariaga, María Julia, Diego Alfredo Caraballo, María Luisa Teijeiro, Eduardo Jorge Boeri, and María Estela Cadario. 2024. "Molecular Detection and Genotyping of Chlamydia psittaci in Birds in Buenos Aires City, Argentina" Animals 14, no. 22: 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14223286
APA StyleMadariaga, M. J., Caraballo, D. A., Teijeiro, M. L., Boeri, E. J., & Cadario, M. E. (2024). Molecular Detection and Genotyping of Chlamydia psittaci in Birds in Buenos Aires City, Argentina. Animals, 14(22), 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14223286







