Simple Summary
Dentex maroccanus otolith morphometrics and growth from the South Aegean Sea were studied using image analysis techniques. A circular or square shape can be assumed for the otoliths of the species in the Mediterranean, with small individuals presenting more circular-shaped otoliths than the larger ones. Differences between sexes were identified for some of the otolith parameters, while the growth parameters did not differ between them. Eviscerated, instead of total, weight is proposed to be used for the estimation of the weight–length relationship. The results of this study provide new information on the biological characteristics of this species in the Mediterranean Sea.
Abstract
Otoliths are important structures for balance and hearing of fish and constitute a useful tool in fisheries science. This study provides, for the first time in the Mediterranean, information on the otolith morphometrics of Dentex maroccanus, collected from the South Aegean Sea, and enriches the existing information on its age and growth by sex. The otolith shape variables examined showed a more circular to square otolith shape, related to the body size. Significant differences between sexes were detected for the otolith Area, Diameter, Perimeter, and Radius. Exponential regressions were used to examine the relationship of the otolith variables with total body length, from which five showed a strong correlation (Diameter, Width, Radius, Area, and Perimeter). The eviscerated weight–length relationship exhibited an isometric growth for both sexes, whereas when total weight was applied, a positive allometric growth was found for females. Sagittal otolith readings revealed four age groups for females and five for males. A Bhattacharya method was used for age validation. Von Bertalanffy growth parameters were as follows: L∞ = 23.08, k = 0.27, t0 = −1.93 for females and L∞ = 24.07, k = 0.24, t0 = −2.26 for males. This research offers valuable biological information for Dentex maroccanus useful in fisheries science.
1. Introduction
Otoliths are calcified structures in the inner ear of fish that are used in various fields of biological, fisheries, and palaeontological studies, such as stock identification, age determination, taxonomy, ontogeny, phylogenetics, palaeoichthyology, determination of predator–prey interactions, and dietary studies (e.g., [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]). Otoliths continue to be a valuable tool currently since they offer a cost-effective and straightforward way to differentiate species and populations [13] as well as to study fish age and growth [14]. The study of the annual age and growth of fish is fundamental for the knowledge of growth rate in life history studies and stock assessment [14], information important in fisheries studies. The examination of otolith morphometrics can give information for paleodiversity, species separation, stock identification and discrimination, determination of population structure, as well as environmental and habitat variability [15,16,17,18,19]. Differences in otolith shape seem to be the result of the cooperative influence of genetics and environment [20,21,22,23], moderated through growth rate [6]. The shape indices represent the pattern of otolith growth in a two-dimensional surface [24]; in many species, otolith morphology varies from a round, circular shape in larval to an irregular, more elongated shape in adult fish [6,24]. Therefore, studying otolith morphology can inform about the evolutionary adaptations of species to their respective habitats and help in comprehending fish evolution and diversification [25], contributing in species identification [2], distinguishing stocks [26] and indicating how a fish adapts to environmental changes [27]. Lastly, the study and findings of sexual dimorphism in otolith shape of a species can offer information about possible different growth rates, distinct habitat usage, and sex-specific hormone levels between the two sexes [28,29,30,31,32].
The Morocco dentex, Dentex maroccanus Valenciennes, 1830, is a sparid demersal species. It is distributed in the Eastern Atlantic from the Bay of Biscay (occasionally further north) to the Gulf of Guinea, as well as in the southern, eastern, and central areas of the Mediterranean Sea [33,34,35]. The species occurs at depths ranging from 20 to 500 m, on various types of substrates, such as sand, gravel, or conglomerates [33,36]. It is a by-catch species of low economic value, which is mainly fished by trawl and artisanal fisheries [37]. Previous studies, conducted in the Aegean Sea, verified a relationship between this species distribution and environmental factors showing that salinity, temperature, and depth are the main drivers of its abundance [38,39].
Although there are some studies regarding the distribution, reproduction, population parameters, diet composition, and body morphometrics of D. maroccanus in the Mediterranean Sea [36,37,40,41,42,43,44,45], there is no information on the otolith morphometrics of this species. Age and growth by sex of the Morocco dentex in the Mediterranean Sea have been estimated in Tunisian and Algerian waters based on scales [46,47]. Moreover, two studies have been conducted in the North Aegean Sea based on otolith readings but for both sexes combined [48,49].
The objectives of the present work were as follows: (a) to investigate D. maroccanus otolith morphometrics for the first time in the Mediterranean and to examine possible differences in sagitta otolith shape between sexes, and (b) to improve our knowledge on the age and growth of this species and compare these biological characteristics with those from other areas. This information will be useful for biological and fisheries studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
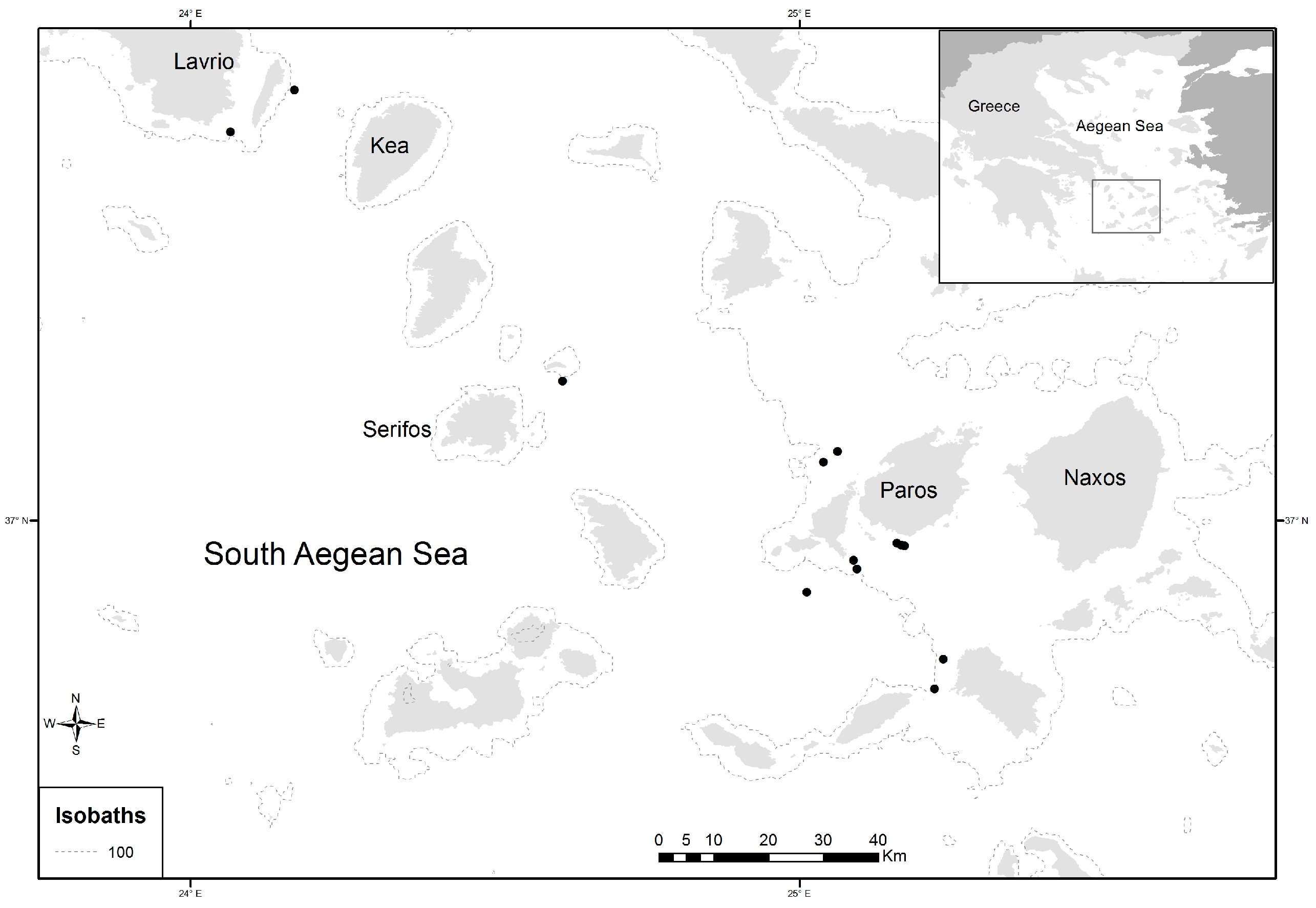
In total, 405 individuals of D. maroccanus were collected during two experimental fishing surveys in September–October of 2014 and May–June of 2015. Sampling was performed at 13 stations (depths between 70 and 185 m) located in the South Aegean Sea (Figure 1), using bottom trawl nets. Individual total body length (TL, cm) and sex, identified by macroscopic examination of the gonads, were reported for each specimen. Their sizes ranged from 9.2 to 19.2 cm total length (TL). Left and right sagittal otoliths from each fish were extracted, rinsed with fresh water, and stored dry. Calibrated digital images of the right otolith were obtained under reflected light using a binocular stereoscope connected to the digital Image-Pro Plus software system (Version 4.5.0.29), which was also used to measure the otolith morphometric variables.
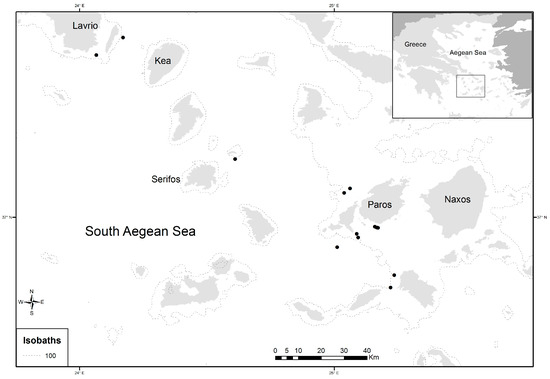
Figure 1.
Map of study area and location of sampling sites (dots in black) of Dentex maroccanus in the South Aegean Sea.
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Length Frequency Distribution
The length (TL) frequency distribution of the D. maroccanus samples was calculated based on classes of 0.5 cm intervals for the study area.
2.2.2. Otolith Morphometrics
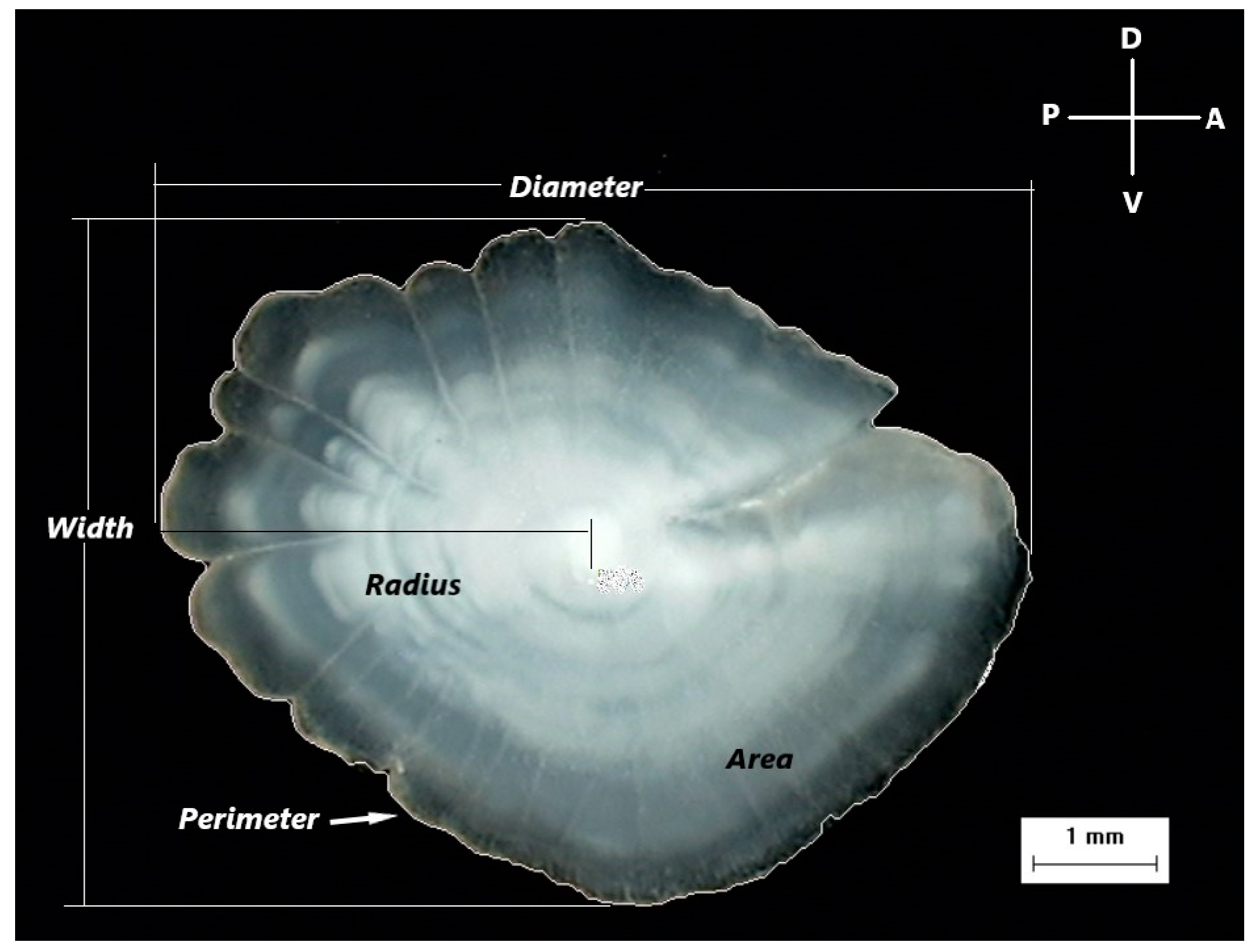
Due to the statistically significant difference (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, p < 0.01) in the total body length frequency distribution between the two sexes, an approximately similar size range was used for the examined individuals to eliminate the effect of size on otolith variables. In total, 141 females and 143 males were used in the morphometric analysis, with length classes ranging between 92 and 181 mm and 96 and 186 mm, respectively. The new selected female and male samples did not show any statistically significant difference (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, p = 0.051). Otolith morphometric measurements were carried out on the digital images of otoliths, excluding incomplete or damaged otoliths. The following otolith morphometric variables were examined: Radius (R, mm)—the longest distance from the otolith nucleus to the postrostrum; Diameter (D, mm)—the maximum distance between the rostrum and the postrostrum passing through the nucleus of the otolith; Width (W, mm)—the maximum distance between ventral and dorsal edges, a line perpendicular to Diameter; Area (A, mm2)—calculated for the largest surface area of the otolith; Perimeter (P, mm)—the length of the outline of the otolith using a polygonal outline; and Roundness (Rn)—the ratio between the actual area and the area of a circle of the same length (Figure 2).
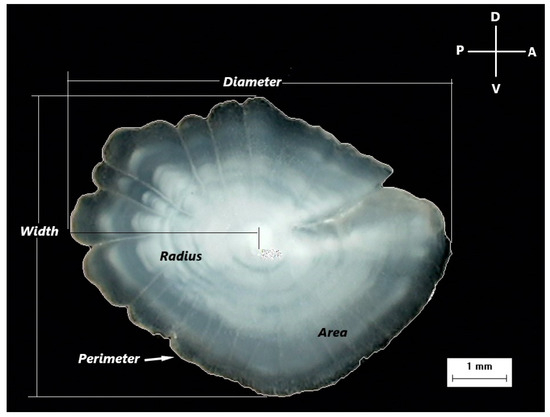
Figure 2.
A digital image of the otolith of Dentex maroccanus from the South Aegean Sea, with the measured morphometric variables (Diameter, Width, Radius, Area, Perimeter), the orientation of the otolith (D: Dorsal, V: Ventral, P: Posterior, A: Anterior), and the scale of the image.
Similarly, four additional shape indices (C: Circularity, Rc: Rectangularity, FF: Form Factor, and E: Ellipticity) were calculated using the following formulae [2,50]:
C = (Perimeter2/Area): Circularity compares otolith shape to a perfect circle showing values equal to 4π;
Rc = [Area/(Diameter × Width)]: Rectangularity describes the variations in the otolith length and width with respect to the area, with 1.0 indicating a perfect square;
FF = [(4π × Area)/Perimeter2]: Form Factor is a means to estimate the surface area irregularity, with a perfect circle taking values of 1.0;
E = [(Diameter − Width)/(Diameter + Width)]: Ellipticity indicates whether the changes in the axes are proportional.
The relationship of each morphometric variable with TL was examined for females and males separately applying the exponential regression (Y = a*TLb, where Y is the otolith variable in mm, TL is the Total Length in mm, a is the intercept, and b is the slope of the regression). For the shape variables of which negative relationship with TL was detected, a comparison between small and large individuals (of the two sexes combined) was performed with a one-way analysis of variance. The threshold between small and large samples was defined at the length of 130 mm.
Descriptive statistics (Mean ± Standard Error) for each morphometric variable of the D. maroccanus otoliths were applied. A multivariate GLM (General Linear Model) was assigned to test the effect of sex on otolith variables and identify the importance of each one of them to this effect. To ensure unbiased comparisons between sexes, the size-effect had to be removed from the variables with statistically significant relationship with TL, converting them to standardized values. For the standardization of the variables related with TL, the following procedures were performed: (i) analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to identify if the slope b of the regression Y = a*TLb was consistent between the two sexes, (ii) otolith variables which did not present consistent b between the two sexes were excluded from the analysis [51], and (iii) for the otolith variables with consistent b, the formula of Elliott et al. [52] was used to calculate the standardized values of the otolith variables: Ms = Mo(TLs/TLo)b, where Ms = standardized otolith variable, Mo = measured otolith variable, TLs = overall (arithmetic) mean total length for all fish from all samples in each analysis, and TLo = total length of specimen, based on a common within-sex b for each measured otolith variable, estimated by a common exponential regression for both sexes. In the present study, the otolith variable Width was excluded from the GLM analysis because of a not-consistent b between the two sexes, which did not permit us to calculate the standardized values of this variable. Therefore, for the GLM analysis, the nine otolith variables (except Width) were used as dependent variables, while sex was used as independent. Because of the detection of non-normality, log, square root, and 1/x transformation were used when needed.
2.2.3. Growth and Age
The weight–length relationship (WLR) was estimated for data from 185 females and 220 males. The power function W = a*TLb was used to estimate the relationship between TL (in cm) and Total Weight (TW) or Eviscerated Weight (EW) (in gr), where a is the intercept, and b is the slope of the regression. Both forms of weight were used to test the effect on the growth type (isometry/allometry). For each sex, the null hypothesis for isometric growth (Ho: b = 3) was tested by using Student’s t-test. Comparison of the weight–length regressions for the two sexes was performed using analysis of covariance. Differences were considered at the significant level of a = 0.05.
For age estimation, 185 females and 220 males were used. Hyaline growth rings, which are formed once a year and represent the time of reduced growth, were counted and measured from the nucleus to the post-rostrum of the right otolith’s distal surface. Age estimation was conducted by two readers. Age length keys were produced for females and males. Growth parameters of the Von Bertalanffy growth equation were estimated by sex, based on this Equation: Lt = L∞ (1 − e−K(t−t0)), where Lt is the predicted length at age t in cm, L∞ is the asymptotic length expressing the mean length that the fish would reach if it would grow indefinitely in cm, k is the growth coefficient which determines the rate at which the fish approaches L∞ in year−1, and t0 is the hypothetical age at length zero in years. Growth parameters between sexes were tested using Student’s t-test. The growth performance index Φ′ = Log (K) + 2Log (L∞) [53] was estimated for males and females, separately.
Age validation was based on the Bhattacharya method (1967) [54], as applied by FiSAT II (version 1.2.2 computer program) [55]. The method was used to discriminate normal distributions that correspond to age groups.
3. Results
3.1. Length Distribution
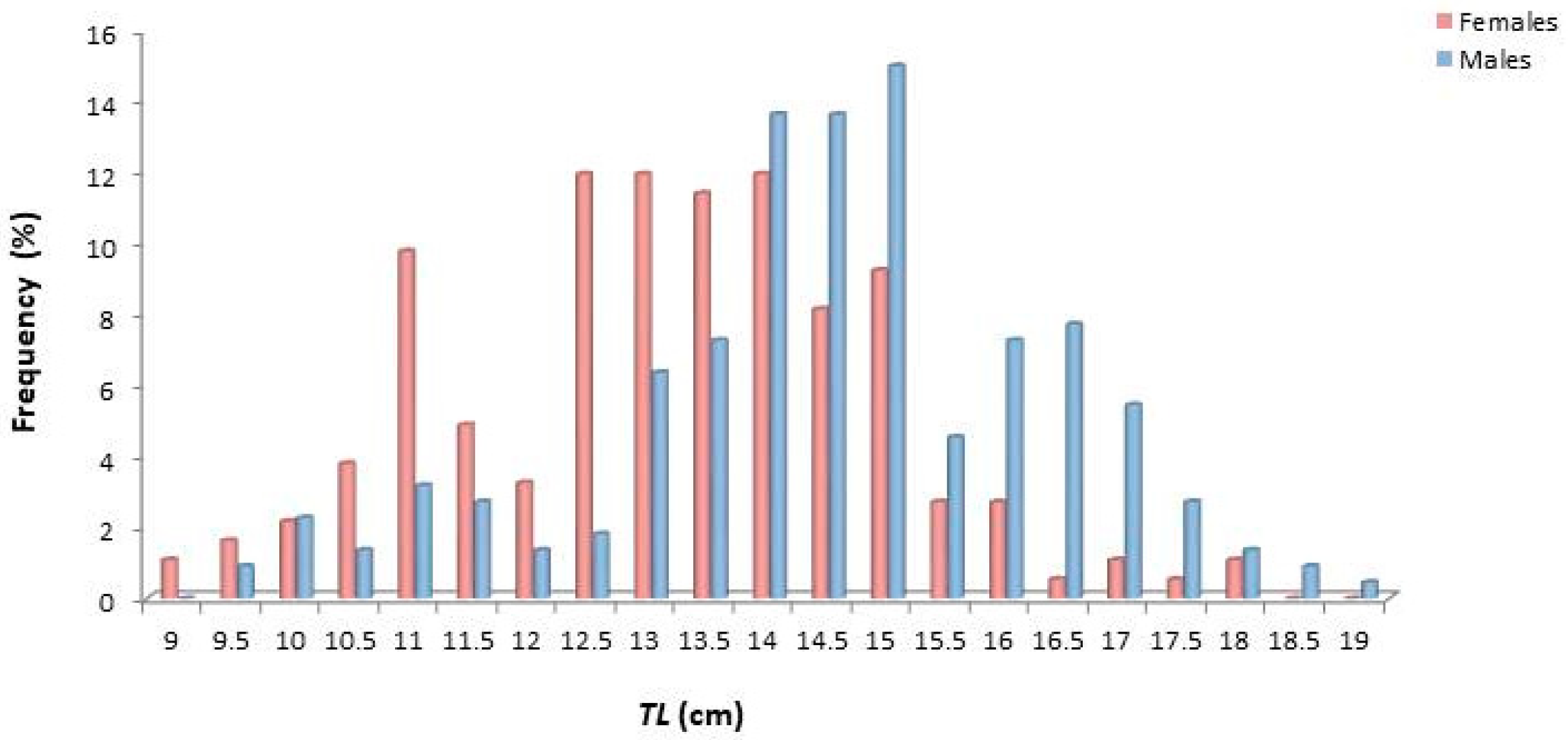
The size of females varied from 9.2 to 18.1 cm TL, while that of males from 9.6 to 19.2 cm (Figure 3). Males showed dominance towards greater sizes, while females were generally smaller in size.
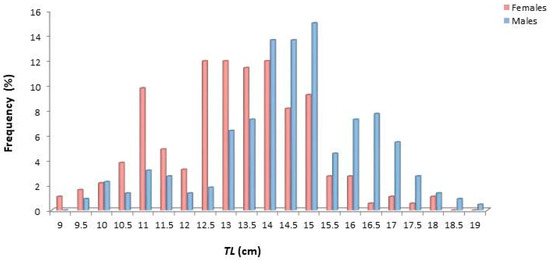
Figure 3.
Length frequency distribution (TL, cm) of female and male Dentex maroccanus in the South Aegean Sea.
3.2. Otolith Morphometrics
The results of the exponential relationship between each otolith variable and TL for females and males separately are shown in Table 1. These relationships were statistically significant, except for Rectangularity (Rc) (in both sexes) and Ellipticity (E) (in females) (p-value > 0.05). The Diameter (D), Width (W), Radius (R), Area (A), and Perimeter (P) of the otolith showed a strong positive relationship with TL. The values of the shape indices Roundness (Rn), Circularity (C), and Form Factor (FF) showed a statistically significant but weak correlation with TL. Comparison of regression lines for each otolith variable between females and males showed differences for the variable of Width (W) (p-value = 0.02), while for the other examined variables, no differences were detected (p-value > 0.05). Further examination of the negative relationship found for Roundness (Rn) and Circularity (C) with TL, using ANOVA, showed a statistically significant difference between small and larger individuals (p-value < 0.05), with mean values being higher in smaller individuals than the larger ones.

Table 1.
Exponential regression between various otolith morphometric variables and fish total length (TL) of Dentex maroccanus for females and males: intercept value (a), regression slope (b), coefficient of determination (R2), correlation coefficient (r), and *: significant relation (p-value < 0.05); D: Diameter, W: Width, R: Radius, A: Area, P: Perimeter, Rn: Roundness, C: Circularity, Rc: Rectangularity, FF: Form Factor, E: Ellipticity. The p-value of the regressions and the p-value of the comparison of the slope b of the regression lines between sexes (ANCOVA) are also given.
The descriptive statistics of the otolith morphometric variables by sex are given in Table 2. Females presented higher standardized values of the otolith variables than males. For both sexes, Circularity (C) presented mean value > 4π, those for the Form Factor (FF) were close to 1, while that for Rectangularity (Rc) was less than 1, and that for Ellipticity (E) was quite lower than 1 (Table 2).

Table 2.
Mean ± Standard Error (SE) of the otolith morphometric variables for females and males of Dentex maroccanus in the South Aegean Sea. The standardized values are also given (italics). D: Diameter, W: Width, R: Radius, A: Area, P: Perimeter, Rn: Roundness, C: Circularity, Rc: Rectangularity, FF: Form factor, E: Ellipticity. The common b value used for the estimation of their standardized values is also presented for the parameters significantly correlated with total length (TL).
The multivariate GLM, which has taken into consideration all the variables (except Width as explained in M&M), showed statistically significant relationships between four otolith variables (A, D, P, R) and sex, with, more importantly, the otolith Area, followed by the otolith Diameter (Table 3).

Table 3.
Results of multivariate GLM analysis showing the effect of sex on each otolith variable of Dentex maroccanus. SS: Sum of Squares; df: degrees of freedom; MS: Mean Square; D: Diameter, LOG R: logarithm of Radius, LOG A: logarithm of Area, LOG P: logarithm of Perimeter, Rn: Roundness, C: Circularity, Rc: Rectangularity, SQRT FF: Square root of Form factor, E: Ellipticity.
3.3. Growth and Age
The weight–length relationship parameters for females and males are given in Table 4. In case of TW (Table 4a), the value of b for males did not differ significantly from 3, which indicates isometric growth (t-test = 1.33; p-value = 0.18). For females, b differed significantly from 3, which means that females exhibited allometric growth (t-test = 3.51; p-value = 0.0005). However, when EW (Table 4b) was used for the estimation of the relationship between weight and length, the value of b did not differ significantly from 3 for both sexes (females t-test = 1.84, p-value = 0.067; males t-test = 1.66, p-value = 0.098), which indicates isometric growth. The comparison of the slope between sexes did not show a statistically significant difference in both cases (TW: p-value = 0.0895; EW: p-value = 0.7056).

Table 4.
(a: top, b: bottom) Weight–Length relationship parameters of Dentex maroccanus in the South Aegean Sea by sex; total length (TL) in cm, total weight (TW) in gr, eviscerated weight (EW) in gr, regression intercept (a), regression slope (b), correlation coefficient (r), coefficient of determination (R2). p-value at significance level α = 0.05.
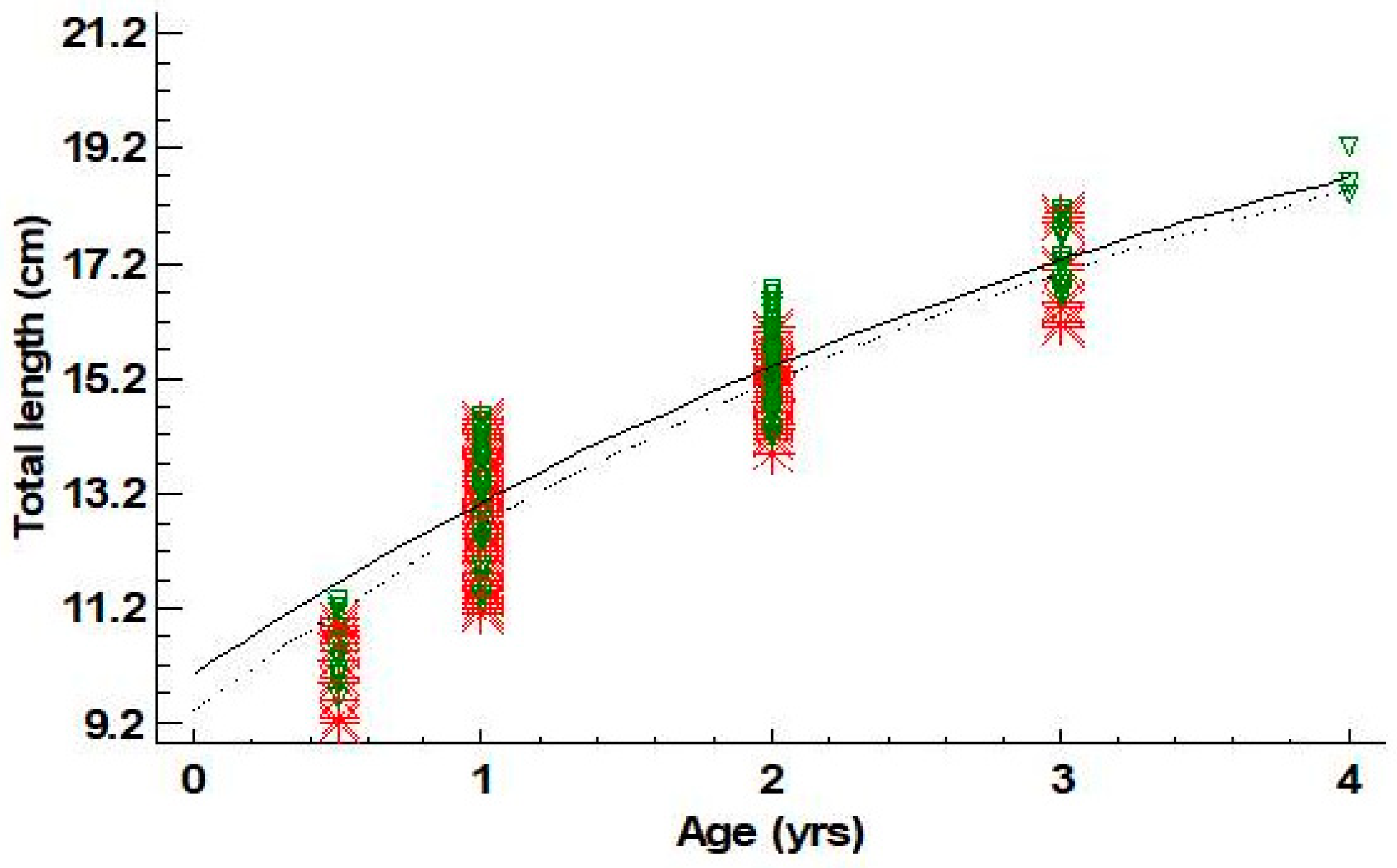
Estimated ages for males ranged between 0+ and 4 years old; those of females ranged between 0+ and 3. For males, the age group 2 was dominant (43.6%), while for females, the age group 1 was the one prevailing (58.4%) (Table 5). Four and five groups (cohorts) could be defined using the Bhattacharya method from length frequency data for females and males, respectively (Table 6). The mean lengths of these cohorts were quite similar to the mean lengths derived from the age–length key for the age groups I–III for females and I–IV for males (Table 6). Von Bertalanffy growth curves are shown in Figure 4. Growth parameters and growth performance index Φ′ for females and males are presented in Table 7. Statistically significant differences were not found for L∞ and k between sexes (L∞: p-value = 0.85; k: p-value = 0.82).

Table 5.
Age–length key of Dentex maroccanus in South Aegean Sea by sex (N: Sample size, %: Percentage of sample, MTL: Mean Total Length in cm, SE: Standard Error).

Table 6.
Computed mean length-at-age (cm) separated by Bhattacharya method (FiSAT program) for female and male Dentex maroccanus in South Aegean Sea (S.D.: Standard Deviation; S.I.: Separation Index).
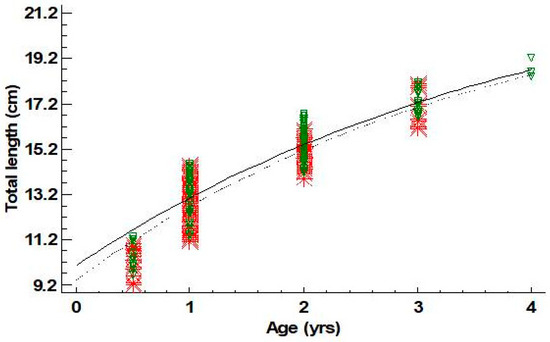
Figure 4.
Von Bertalanffy growth curves fitted for females (- -*- -) and males (─∇─) of Dentex maroccanus in the South Aegean Sea (red asterisks: female observations—green triangles: male observations).

Table 7.
Von Bertalanffy growth parameters and growth performance index of Dentex maroccanus from different areas of the Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea [L∞: asymptotic length (cm), k: growth coefficient (yrs−1), t0: hypothetical age at length zero (yrs), Φ′: growth performance index].
4. Discussion
In the current study, the age and growth of D. maroccanus were studied for the first time in the South Aegean Sea, contributing updated information to the biology of the species in the Mediterranean. Furthermore, for the first time in the Mediterranean, the morphological features of sagittal otoliths of D. maroccanus were analyzed in order to examine the otolith shape and their relationship with body size, offering information that might be used in the future in other comparative studies of the species from different areas. Finally, differences in the otolith morphology between sexes were examined for the first time in the Mediterranean.
Shape indices studied indicated that the otoliths of the Morocco dentex have a more circular-to-square shape because of the quite high estimated values of Roundness, Form factor, and Rectangularity. A more pentagonal shape for the otoliths of the species from the central-eastern Atlantic was assumed by Tuset et al. [15]. Regarding Circularity, the mean value by sex estimated in the present study was within the range of values reported by the above-mentioned researchers. However, this was not the case for Rectangularity, indicating that the otolith shape of the species in the Mediterranean is squarer than that of the Atlantic. Otolith shape is known to be influenced by ontogenetic [9], as well as environmental abiotic factors, such as water temperature [23,58]. Therefore, the differences identified between the current study and the one of Tuset et al. [15] might be due to the different fish size range of the examined samples (larger specimens in the Atlantic Ocean: 14.9–28.5 cm, than the specimens of the current study: 9.2–19.2 cm) or to the different environmental conditions between the two study areas.
In the present study, higher values of the standardized morphometric variables Diameter, Radius, Area, and Perimeter were found for females than males, with more pronounced differences for A and D. However, no significant sex differences were detected regarding the otolith shape. Different otolith growth patterns between sexes have been described for various species (e.g., Prionotus nudigula—[59], Porichthys notatus—[60]). No sex-specific differences regarding the otolith shape were also reported for other species such as Gadus morhua [21] and Xiphias gladius [61]. Variability in otolith morphometrics between the sexes has been associated with differences in environmental factors, distinct habitat usage, growth rate, sex-specific hormone levels, and reproductive behavior [1,10,28,29,30,31,32]. The shape and size of the sagittal may affect hearing capacities [62], and it is believed that large sagittae increase hearing sensitivity [63], which seems to be a more important attribute in benthic than pelagic species [22]. However, Kever et al. [62] found no direct link between otolith size and hearing capacities of the two ophidiiform species studied. Interestingly, Popper et al. [64] suggested that it is more likely that the selective pressures on otolith size and ear function are more related to the response to the rapid motions of the animals rather than to hearing. Lastly, diet composition has been related to otolith shape [65]. The differences identified in the present study between the otoliths of male and female D. maroccanus may be related to the hearing and/or swimming abilities and/or diet preferences of the two sexes. In fact, in eastern Algeria, differences in the feeding habits of the species were reported between the two sexes [42]. No literature was found regarding the hearing and swimming abilities of the species.
The exponential regression model was found to be more appropriate than the linear to describe the relationship between fish length and otolith variables, as also found in other relevant studies [66,67]. The negative relationship of Roundness and Circularity with total length indicated that the otoliths of D. maroccanus become less circular with increased body size. This better explains the otolith pentagonal shape mentioned by Tuset et al. [15], who examined larger individuals than those of this study. The equations between the otolith variables and total length are particularly useful for further otolith-size predictions (e.g., dietary studies), paleontological studies related to back-calculations of fish size and growth patterns, and ontogenetic studies related to otolith shape [68].
The examination of the weight–length relationship based on the eviscerated weight showed an isometric growth for female D. maroccanus, while the use of total weight revealed positive allometry. Taking into consideration that the spawning period of D. maroccanus in the Mediterranean has been recorded in summer and autumn [43,47,48] and that the sampling of the present study took place within this period, the two different types of growth found in females could be attributed to the weight of mature gonads affecting their total weight and finally the total weight–length relationship. Therefore, the use of eviscerated weight is recommended for the WLR study. López-Pérez et al. [69] suggest the use of eviscerated dry weight, since it more accurately reflects muscular growth, irrespective of trophic behavior (full or empty guts) or gonadal weight (important at maturation). Weight–length relationship studies for D. maroccanus from other Mediterranean areas showed variability expressed as positive or negative allometry and isometry [46,47,48,49,70]. Such differences in the parameter b of the WLR could be attributed to factors such as the sampling area, the sampling season, the life-history stage of the species, or the nutritional state of each individual [70,71], but they could also be related to the use of total or eviscerated weight, as proved in our study.
In the present study, the growth parameters of D. maroccanus did not differ between females and males, which implies that the two sexes approach their asymptotic length at a similar rate. The asymptotic maximum length for both sexes combined (23.14 cm TL) was the lowest among those reported by other studies conducted in the Mediterranean Sea (Table 7). In general, it seems that the L∞ values from the Atlantic and the southwestern Mediterranean were higher than those from the eastern Mediterranean. This could be attributed to the lower nutrient contents in the latter area compared to the western Mediterranean Sea. Similarly, the growth performance index Φ′ of D. maroccanus revealed the lowest values in the eastern basin of the Mediterranean Sea, while the highest value (2.45) has been reported from Algeria [47]. It could also be noticed that the Φ′ values reported in the studies from various areas of the Aegean Sea, including those of the present work (Table 7), are quite similar, which may indicate a connectivity among the populations of the species in this region.
The present work provided important information concerning otolith morphometrics and age and growth of D. maroccanus, as well as existing differences between males and females. Further studies should reveal the potential effect of environment on these features and the link between the physiological and behavioral characteristics in them.
5. Conclusions
The results of the present study showed differences in the otolith morphometry of D. maroccanus between the two sexes and differences in the species growth pattern between eastern and western Mediterranean. Otolith morphometry, as well as age and growth, can be used to answer a variety of ecological and physiological questions. However, the complexity concerning otoliths and its implications for biological processes do not allow for a single-factor explanation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L., I.L., C.M. and A.A.; methodology, A.L., I.L., C.M. and A.A.; formal analysis, A.L., I.L., C.M. and A.A.; investigation, A.L., I.L., C.M. and A.A.; data curation, A.L. and I.L.; writing—original draft preparation, A.L.; writing—review and editing, A.L., I.L., C.M. and A.A.; visualization, A.L. and I.L.; supervision, C.M. and A.A.; project administration, C.M. and A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The present research involved no animal experimentation or harm. Samples were collected dead from experimental survey and permits for animal collections were not required.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Samples for this study were obtained from the Epilexis Project of the HCMR (O.P.F. 2007-2013, Code 185365). We especially thank Kaminas, A., Pappou, G., Rekleiti, A. and Stromplou, D. for taking the biological parameters of the fish and for providing the otoliths used in this work and Dokos, J. for the map design.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Campana, S.E.; Casselman, J.M. Stock discrimination using otolith shape analysis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 1062–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuset, V.M.; Lombarte, A.; González, J.A.; Pertusa, J.F.; Lorente, M.J. Comparative morphology of the sagittal otolith in Serranus spp. J. Fish. Biol. 2003, 63, 1491–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, M.; McCormick, M.I. Feeding history influences otolith shape in tropical fish. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2004, 278, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Nin, B.; Tores, G.; Lombarte, A.; Recasens, L. Otolith growth and age estimation in the European hake. J. Fish. Biol. 2005, 53, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimori, A.; Jawad, L.A.J.; Al-Kharusi, L.H.; Al-Mamry, J.M.; Reichenbacher, B. Late Pleistocene to Holocene diversification and historical zoogeography of the Arabian killifish (Aphanius dispar) inferred from otolith morphology. Sci. Mar. 2012, 76, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignon, M. Ontogenetic trajectories of otolith shape during shift in habitat use: Interaction between otolith growth and environment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 420–421, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, J.; Manjabacas, A.; Tuset, V.M.; Lombarte, A. Relationships between otolith and fish size from Mediterranean and north-eastern Atlantic species to be used in predator–prey studies. J. Fish. Biol. 2016, 89, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombarte, A.; Miletić, M.; Kovačić, M.; Otero-Ferrer, J.L.; Tuset, V.M. Identifying sagittal otoliths of Mediterranean Sea gobies: Variability among phylogenetic lineages. J. Fish. Biol. 2018, 92, 1768–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolé, F.G.; Callicó Fortunato, R.; Thompson, G.A.; Volpedo, A.V. Application of otolith morphometry for the study of ontogenetic variations of Odontesthes argentinensis. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2019, 102, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, B.; Volpedo, A.; Fávaro, L. Ontogenetic and sexual variation in the sagitta otolith of Menticirrhus americanus (Teleostei; Sciaenidae) (Linnaeus, 1758) in a subtropical environment. Pap. Avulsos. Zool. 2020, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahé, K.; MacKenzie, K.; Ider, D.; Massaro, A.; Hamed, O.; Jurado-Ruzafa, A.; Gonçalves, P.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Jadaud, A.; Mytilineou, C.; et al. Directional Bilateral Asymmetry in Fish Otolith: A Potential Tool to Evaluate Stock Boundaries? Symmetry 2021, 13, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, B.M.; Oliveira-Freitas, M.; Lapuch, I.; Volpedo, A.V.; Vitule, J.R. Age, growth, and ontogenetic variation in the sagitta otolith of Opsanus beta (Goode & Bean, 1880), a non-native species in a wetland of international importance. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2022, 50, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, C.J.C.; Barnuevo, K.D.E.; Delloro, E.S., Jr.; Cabebe-Barnuevo, R.A.; Calizo, J.K.S.; Lumayno, S.D.P.; Babaran, R.P. Otolith Morphometric and Shape Distinction of Three Redfin Species under the Genus Decapterus (Teleostei: Carangidae) from Sulu Sea, Philippines. Fishes 2023, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S.E. Otolith science entering the 21st century. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2005, 56, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuset, V.M.; Lombarte, A.; Assis, C.A. Otolith atlas for the western Mediterranean, north and central eastern Atlantic. Sci. Mar. 2008, 72, 7–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemaa, S.; Bacha, M.; Khalaf, G.; Dessailly, D.; Rabhi, K.; Amara, R. What can otolith shape analysis tell us about population structure of the European sardine, Sardina pilchardus, from Atlantic and Mediterranean waters? J. Sea Res. 2015, 96, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echreshavi, S.; Esmaeili, H.R.; Teimori, A.; Safaie, M. Otolith morphology: A hidden tool in the taxonomic study of goatfishes (Teleostei: Perciformes: Mullidae). Zool. Stud. 2021, 60, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, J. Otoliths and Their Applications in Fishery Science. Fishes 2023, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforidou, V.; Mytilineou, C.; Alexandropoulos, A.; Anastasopoulou, A. Age, Growth, and Otolith Morphometrics of Trachinus draco (L., 1758) and Trachinus radiatus (Cuvier, 1829) in the Eastern Mediterranean. Fishes 2024, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpedo, A.; Echeverría, D.D. Ecomorphological patterns of the sagitta in fish on the continental shelf off Argentine. Fish. Res. 2003, 60, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, M.; Doering-Arjes, P.; Kastowsky, M.; Mosegaard, H. Effects of sex, stock, and environment on the shape of known-age Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) otoliths. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombarte, A.; Palmer, M.; Matallanas, J.; Gómez-Zurita, J.; Morales-Nin, B. Ecomorphological trends and phylogenetic inertia of otolith sagittae in Nototheniidae. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2010, 89, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignon, M.; Morat, F. Environmental and genetic determinant of otolith shape revealed by a non-indigenous tropical fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 411, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Chen, C.; Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, R.; Gao, T. The use of otolith shape to identify stocks of redlip mullet, Liza haematocheilus. Pak. J. Zool. 2020, 52, 2265–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hu, L.; Song, Y.; Xie, H.; Yang, L.; Serekbol, G.; Huo, B.; Chen, S. The Evolution of Three Schizothoracinae Species from Two Major River Systems in Northwest China Based on Otolith Morphology and Skeletal Structure. Biology 2024, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolles, K.L.; Begg, G.A. Distinctions between Silver Hake (Merluccius bilinearis) Stocks in U.S. Waters of the Northwest Atlantic Based on Whole Otolith Morphometric. Fish. Bull. 2000, 98, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Mahe, K.; Gourtay, C.; Defruit, G.B.; Chantre, C.; de Pontual, H.; Amara, R.; Claireaux, G.; Audet, C.; Zarnbonino-Infante, J.L.; Ernande, B. Do environmental conditions (temperature and food composition) affect otolith shape during fish early juvenile phase? An experimental approach applied to European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2019, 521, 151239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuset, V.M.; Imondi, R.; Aguado, G.; Otero-Ferrer, J.L.; Santschi, L.; Lombarte, A.; Love, M. Otolith patterns of rockfishes from the northeastern Pacific. J. Morphol. 2015, 276, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuset, V.M.; Otero-Ferrer, J.L.; Stransky, C.; Imondi, R.; Orlov, A.; Zhenjiang, Y.; Venerus, L.; Santschi, L.; Afanasiev, P.; Zhuang, L.O.; et al. Otolith shape lends support to the sensory drive hypothesis in rockfishes. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 2083–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, E.; Boistel, R.; Bahri, M.A.; Plenevaux, A.; Schwarzhans, W. Sexual dimorphism in the sonic system and otolith morphology of Neobythites gilli (Ophidiiformes). J. Zool. 2018, 305, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaux, F.; Rasmuson, L.K.; Kautzi, L.A.; Rankin, P.S.; Blume, M.T.O.; Lawrence, K.A.; Bohn, S.; O’Malley, K.G. Sex matters: Otolith shape and genomic variation in deacon rockfish (Sebastes diaconus). Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 13153–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başusta, N.; Dürrani, Ö. Sexual dimorphism in the otolith shape of shi drum, Umbrina cirrosa (L.), in the eastern Mediterranean Sea: Fish size–otolith size relationships. J. Fish. Biol. 2021, 99, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauchot, M.L.; Hureau, J.C. Sparidae. In Fishes of the North-Eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean (FNAM); Whitehead, P.J.P., Bauchot, M.L., Hureau, J.C., Nielsen, J., Tortonese, E., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1986; Volumr II, pp. 883–907. [Google Scholar]
- Golani, D.; Öztürk, B.; Başusta, N. Fishes of the Eastern Mediterranean; Publication no. 24; Turkish Marine Research Foundation: Istanbul, Turkey, 2006; 259p. [Google Scholar]
- Grech, D.; Asciutto, E.; Bakiu, R.; Battaglia, P.; Ben-Grira, C.; Öznur, Y.Ç.; Cappuccinelli, R.; Carmona, L.; Chebaane, S.; Crocetta, F.; et al. New records of rarely reported species in the Mediterranean Sea (July 2023). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2023, 24, 392–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemida, F.; Ghazli, R. Contribution à l’ecologie de Dentex maroccanus (Valenciennes, 1830) des cotes Algeriennes: Repartition geographique, bathymetrique et en fonction du substrat. Rapp. Comm. Int. L’exploration Mer Mediterr. (CIESM) Marseille Fr. 1998, 35, 448–449. [Google Scholar]
- Mina, A.; Mytilineou, C.; Kaminas, A.; Rekleiti, A.; Siapatis, A.; Anastasopoulou, A. Feeding Habits of Dentex maroccanus and the Effect of Body Size. Animals 2023, 13, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maravelias, C.D.; Tsitsika, E.V.; Papaconstantinou, C. Evidence of Morocco dentex (Dentex maroccanus) distribution in the NE Mediterranean and relationships with environmental factors determined by Generalized Additive Modelling. Fish. Oceanogr. 2007, 16, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakopoulos, C.; Mytilineou, C. Distribution pattern of Dentex maroccanus in relation to environmental factors in the Aegean Sea. In Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Applied Ichthyology, Oceanography & Aquatic Environment, Virtual, 4–6 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chemmam-Abdelkader, B.; Kraiem, M.M.; El Abed, A. Période de ponte, sex-ratio et maturité sexuelle de Dentex maroccanus (Teleostei, Sparidae) des côtes tunisiennes. Bull. Inst. Natn. Scien. Tech. Mer. Salammbô 2002, 29, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bayhan, B.; Sever, T.M.; Heral, O. Diet composition of the Morocco dentex: Dentex maroccanus Valenciennes, 1830 (Teleostei: Sparidae) in the central Turkish Aegean Sea. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2017, 46, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohdeb, R.; Derbal, F.; Kara, M.H. Diet composition and variations of Morocco dentex Dentex maroccanus (Sparidae) from eastern Algeria. Cybium 2017, 41, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Taylan, B.; Bayhan, B.; Heral, O. Fecundity of Morocco Dentex Dentex maroccanus Valenciennes, 1830 distributed in Izmir Bay (Central Aegean Sea of Turkey). TURJAF 2018, 6, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromplou, D.; Mina, A.; Pappou, G.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Mytilineou, C. Morphometric characteristics of Dentex maroccanus in the Aegean Sea. In Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Applied Ichthyology, Oceanography & Aquatic Environment, Virtual, 4–6 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kontaş Yalçınkaya, S. Some Population Parameters of Morocco dentex, Dentex maroccanus Valenciennes, 1830 in the Northeastern Mediterranean Sea. Cumhur. Sci. J. 2023, 44, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemmam-Abdelkader, B.; Kraiem, M.M.; El Abed, A. Etude de l’age et de la croissance de deux especes de dentes (Dentex dentex et Dentex maroccanus) des cotes Tunisiennes. Bull. Inst. Natn. Scien. Tech. Mer Salammbô 2004, 31, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mohdeb, R.; Kara, M.H. Age, growth and reproduction of Morocco dentex Dentex maroccanus (Valenciennes, 1830) in Eastern coasts of Algeria. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 2014, 95, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, G.; İşmen, A.; Arslan, M. Age, Growth, and Reproduction of Dentex maroccanus (Actinopterygii: Perciformes: Sparidae) in the Saros Bay (North Aegean Sea). Acta Ichthyo. Piscat. 2014, 44, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heral, O.; Bayhan, B. Age and Growth of Morocco Dentex Dentex maroccanus Valenciennes, 1830 (Actinopterygii: Sparidae) in Izmir Bay, Central Aegean Sea, Turkey. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2020, 72, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ponton, D. Is geometric morphometrics efficient for comparing otolith shape of different fish species? J. Morphol. 2006, 267, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguera, A.; Brophy, D. Use of saggital otolith shape analysis to discriminate Northeast Atlantic and Western Mediterranean stocks of Atlantic saury, Scomberesox saurus saurus (Walbaum). Fish. Res. 2011, 110, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, N.G.; Haskard, K.; Koslow, J.A. Morphometric analysis of orange roughy (Hoplostethus atlanticus) off the continental slope of southern Australia. J. Fish. Biol. 1995, 46, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Munro, J.L. Once More on the Comparison of Growth in Fish and Invertebrates. ICLARM Fishbyte 1984, 2, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, C.G. A simple method of resolution of a distribution into Gaussian components. Biometrics 1967, 23, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayanilo, F.; Sparre, P.; Pauly, D. FAO-ICLARM Stock Assessment Tool II (FiSAT II) Revised version—User’s Guide. FAO Comput. Inf. Ser. 2005, 8, 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Loc, N.X.; Wojciechowski, J. Comparative biology of fish from genus Dentex (Sparidae) of north-west African coast. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 1972, 2, 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lamrini, A.; Bouymajjane, A. Biologie de Dentex maroccanus (Valenciennes, 1830) dans la region de Safi. Actes L’institut Agron. Vet. Hassan II Rabat (Maroc) 2002, 22, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hussy, K. Otolith shape in juvenile cod (Gadus morhua): Ontogenetic and environmental effects. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 364, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpedo, A.; Thompson, G. Diferencias en el crecimiento de las sagittae de Prionotus nudigula Ginsburg, 1950 (Piscis: Triglidae) en relación al sexo. Boletín Inst. Espańol Oceanogr. 1996, 12, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, A.P.H.; Adragna, J.B.; Balshine, S. Otolith morphology varies between populations, sexes and male alternative reproductive tactics in a vocal toadfish Porichthys notatus. J. Fish. Biol. 2017, 90, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahé, K.; Evano, H.; Mille, T.; Muths, D.; Bourjea, J. Otolith shape as a valuable tool to evaluate the stock structure of swordfish Xiphias gladius in the Indian Ocean. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 38, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kéver, L.; Colleye, O.; Herrel, A.; Romans, P.; Parmentier, E. Hearing capacities and otolith size in two ophidiiform species (Ophidion rochei and Carapus acus). J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar]
- Lombarte, A.; Cruz, A. Otolith size trends in marine fish communities from different depth strata. J. Fish. Biol. 2007, 71, 53–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, A.N.; Ramcharitar, J.; Campana, S.E. Why otoliths? Insights from inner ear physiology and fisheries biology. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2005, 56, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mille, T.; Mahé, K.; Cachera, M.; Villanueva, M.C.; De Pontual, H.; Ernande, B. Diet is correlated with otolith shape in marine fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 555, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, M.; Saygin, S.; Polat, N. Relationships between otolith size and total length of bluefish, Pomatomus saltatrix (Linnaeus, 1766) in Black Sea (Turkey). North-West J. Zool. 2017, 13, 169–171. [Google Scholar]
- Yedier, S. Otolith shape analysis and relationships between total length and otolith dimensions of European barracuda, Sphyraena sphyraena in the Mediterranean Sea. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2021, 20, 1080–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuset, V.M.; Otero-Ferrer, J.L.; Siliprandi, C.; Manjabacas, A.; Marti-Puig, P.; Lombarte, A. Paradox of otolith shape indices: Routine but overestimated use. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 78, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, C.; Olivar, M.P.; Hulley, P.A.; Tuset, V.M. Length–weight relationships of mesopelagic fishes from the equatorial and tropical Atlantic waters: Influence of environment and body shape. J. Fish. Biol. 2020, 96, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evagelopoulos, A.; Batjakas, I.; Koutsoubas, D. Length–weight relationships of 9 commercial fish species from the North Aegean Sea. Acta Adriat. 2017, 58, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese. Cube law, condition factor and weight–length relationships: History, metaanalysis and recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).