Simple Summary
The intracellular zoonotic protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii affects humans and animals worldwide. Consuming T. gondii infected undercooked meat, raw milk, or their byproducts poses a significant risk to humans. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain monitoring of the prevalence of T. gondii in food animals. Little is known about T. gondii prevalence in cattle in Egypt. This study was conducted in Qena, southern Egypt, and specific antibodies to T. gondii were identified in 9.1% (33/362) of serum samples using commercial ELISA. The only identified risk factor for increased seroprevalence was the animals’ increasing age. This survey revealed a prevalent T. gondii infection in cattle herds in the Qena governorate and updated information on T. gondii in cattle in Egypt. Additionally, 154 milk samples were taken from the sampled dairy cows and tested for T. gondii antibodies. There was a strong association between the serum and milk samples, with a prevalence of 12.3% (19/154) in serum samples and 9.7% (15/154) in milk samples, respectively. This suggests that the non-invasive and simple-to-obtain milk samples could be a suitable replacement for blood samples in the detection of T. gondii antibodies in dairy animals.
Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii is an intracellular protozoan parasite of veterinary and public health importance. Infection may lead to abortion in susceptible pregnant animals and women, and potentially fatal health complications in immunocompromised individuals. In this study, we aimed to provide an update on the seroprevalence of, and risk factors for, T. gondii antibodies in cattle from Qena, southern Egypt. Additionally, we investigated if raw milk and serum samples from the same animals reacted similarly in a commercial ELISA, thus potentially reducing the invasiveness of future serosurveillance studies. Cattle serum samples (n = 362) from three locations in the Qena governorate (Qena, Qus, and Al Waqf cities), of both sexes and different ages were collected. From most dairy cows, a corresponding milk sample (n = 154) was additionally obtained. We found that the overall seroprevalence in serum samples was 9.1% (33/362). Increasing age was the sole risk factor identified in our study among all tested parameters (location, age, sex, lactating yes or no). Thus, older cattle (more than 3 years old) exhibited significantly higher rates of T. gondii antibodies (11.7%; p = 0.033, odd ratio = 4.3) in comparison to animals younger than 1 year (2.9%). In the corresponding serum and milk samples, the prevalence was 12.3% (19/154) in serum samples, and 9.7% (15/154) in milk samples, respectively. A high correlation was observed between the two sample types with a concordance of 97.4%, a kappa value of 0.87, and a Pearson r correlation coefficient of 0.85. When the serum ELISA was taken as the gold standard, the milk ELISA had the following characteristics: sensitivity (78.9%), specificity (100%), positive predictive value (100%), negative predictive value (97.1%), and area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (0.6, p = 0.0011). In this study, we confirmed the frequent occurrence of T. gondii antibodies in cattle in southern Egypt and demonstrated that non-invasive milk samples may be used instead of serum samples for seroprevalence studies in dairy cows.
1. Introduction
Toxoplasma gondii is a widespread protozoan parasite that can infect many hosts, including humans, animals, and marine mammals [1,2,3]. The definitive hosts of the parasite are cats, which shed oocysts that are resistant to environmental conditions. Other animals, including cattle, become infected with T. gondii after ingesting the sporulated oocysts shed by cats [3,4]. Toxoplasma gondii infections in livestock can pose a potential risk to public health through ingestion of tissue cysts in raw or undercooked meat of infected animals [5]. The consumption of raw milk and milk byproducts was significantly correlated with the risk of human toxoplasmosis, particularly caprine products [5,6,7].
Globally, approximately one-third of human beings are infected with T. gondii, although this varies greatly among populations [3,8]. In immunocompetent individuals, the majority of infections appear to be asymptomatic. Contrastingly, in immunocompromised individuals and fetuses, the parasite can cause significant illness [9]. Abortions have been reported as the most important clinical manifestation in farm animals, especially in sheep, and can lead to economic losses. However, reports on clinical toxoplasmosis in naturally infected cattle are rare [10,11,12]. There is little evidence of the existence of viable T. gondii infections, even though a number of investigations employing PCR methods revealed up to 10 or 20% of T. gondii-positive cattle tissues [10,11]. The parasite DNA was detected in cow’s milk samples from Brazil (2.8%) [13], Iran (3.5%) [14], and Poland (15.9%) [15]. Furthermore, it was revealed that consuming raw cow’s milk byproduct was linked to T. gondii human infection [16]. Additionally, tachyzoites survived in the pH conditions of cow’s milk, which may suggest that unpasteurized cow’s milk might transmit infection [17].
Many reports have investigated T. gondii infections in humans and animals in Egypt but the current situation of toxoplasmosis in Egypt is unclear [18]. Physicians commonly believe that toxoplasmosis is the cause of abortions and pregnancy-related complications, but the published literature lacks a clear diagnosis and is poorly structured. Considerable studies in Egypt have investigated the role of T. gondii in congenital toxoplasmosis in humans, but they lacked a precise diagnosis, and the majority of them rely on serological findings. There have also been reports of ocular toxoplasmosis with symptoms of uveitis and chorioretinitis based on positive serology and the lesion [18]. In Egypt, toxoplasmosis-related animal abortions were only documented in sheep and goats. Toxoplasma gondii infection was detected by serological testing in aborted ewes and does, and T. gondii DNA was found in the tissues of the aborted fetuses [19]. Furthermore, Toxoplasma antibodies were detected in pregnant ewes and does from a flock with a history of abortion [20,21].
Several studies on the seroprevalence of T. gondii-specific antibodies in cattle have been published during the past few decades, with an estimated global seroprevalence of 16.94% [22]. There is a lack of studies investigating cattle, especially in southern Egyptian regions [18]. The cattle population in Egypt is estimated at approximately 5.1 million heads [23]. Two studies tested cattle from northern Egypt for antibodies to T. gondii and found seroprevalences of 10.75% and 5.3%, respectively [24]. Only one study investigated cattle in southern Egypt and found a seroprevalence of 23.6% using the latex agglutination test and TgGRA7-based ELISA [25]. The aim of this study was to (1) update the prevalence and assess the risk factors associated with T. gondii antibodies in cattle in Qena governorate, southern Egypt, and (2) to assess whether non-invasive milk samples can be used instead of serum samples for such surveys in dairy cows.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
This study was carried out in compliance with the guidelines set forth by the South Valley University, Qena, Egypt, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Research Board. It was approved by South Valley University’s Research Code of Ethics under code number 36 (RCOE-36).
2.2. Description of Animal and Region of the Study
A total of 362 randomly collected serum samples from apparently healthy cattle were obtained from different locations in the Qena governorate, southern Egypt (Qena, Qus, and Al Waqf cities; Figure 1). The samples represented cattle of different sexes (male and female) and various age groups. To determine the risk factors for toxoplasmosis infection in the investigated animals, we assessed the location, sex, age, and lactation. From 154 dairy cows, a milk sample was obtained in addition to the serum sample (Table 1). The availability of samples and owner cooperation determined the numbers and groups of tested animals in this study.
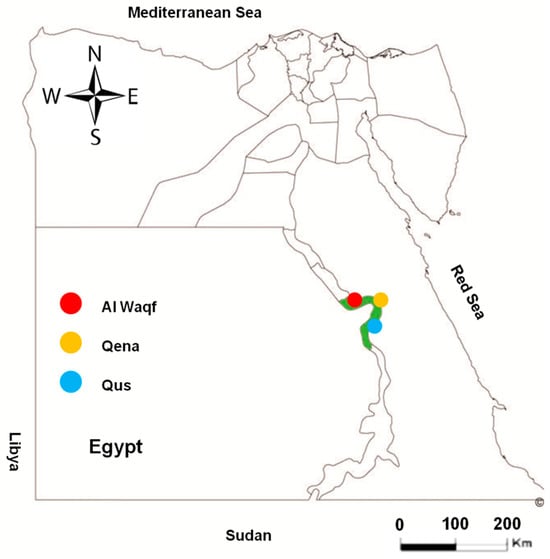
Figure 1.
Map of Egypt showing the place of sample collection. Area with green color in the map refers to the investigated Qena governorate. Colored circles show the different cities of Qena that were investigated in this study.

Table 1.
Details of collected samples.
2.3. Sample Collection and Preparation
The blood samples were obtained using the jugular vein puncture procedure from the studied cattle and placed into glass tubes devoid of anticoagulant. After centrifuging the blood at 2200× g for 15 min at room temperature, the serum was collected and stored at −20 °C until analysis.
Milk samples were centrifuged at 1000× g for 10 min and lactoserum was extracted from the layer beneath the cream. The lactoserum was then kept at −20 °C until use.
2.4. ELISA for Antibody Detection
Anti-T. gondii antibodies were detected using the indirect multi-species ELISA assay for Toxoplasma gondii detection (ID.vet, Grabels, France) following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Briefly, both test serum samples and controls were subjected to a 1:10 dilution. Lactoserum samples were used undiluted, as outlined earlier [26,27]. The proportion of sample (S) to positive (P) ratio (S/P%) for each tested sample was calculated using the optical density (OD) values and the following formula: S/P (%) = (OD sample − OD negative control)/(OD positive control − OD negative control) × 100. A sample was regarded as negative if the S/P% was less than 40%, doubtful if S/P% was between 40% and 50%, and the test was deemed positive if the S/P% was greater than 50%. All ELISA results were measured at 450 nm using an Infinite® F50/Robotic ELISA reader (Tecan Group Ltd., Männedorf, Switzerland) to determine the optical densities (ODs).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The differences in the seroprevalence rates and associated risk factors were assessed with the Fisher exact probability test (two-tailed), along with 95% confidence intervals (including continuity correction), and odds ratios. This analysis was conducted using the online statistical platform www.vassarstats.net (accession on 26 September 2024). GraphPad Prism version 5 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) was used to estimate p-values. The Bonferroni post hoc test was used after one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to determine the significance between various ELISA groups. A p-value < 0.05 indicated that the difference was significant [28,29].
3. Results
3.1. Seroprevalence and Risk Factor Analysis of Toxoplasma gondii Seropositivity in Cattle in Qena
Out of 362 cattle examined, 33 serum samples tested positive for T. gondii antibodies (9.1%; 95% CI: 6.4–12.7) using a commercial iELISA. Among the 362 examined cattle, 154 cows had both raw milk and serum samples available for testing. Out of these, 19 serum samples and 15 milk samples tested positive for specific antibodies against T. gondii, resulting in seropositive rates of 12.3% (95% CI: 7.8–18.8) and 9.7% (95% CI: 5.7–15.8), respectively. It was observed that four cows had positive serum samples but negative milk samples (Table 2).

Table 2.
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in cattle of Qena, southern Egypt.
The prevalence of T. gondii antibodies in tested cattle from Qena, southern Egypt, was evaluated in relation to the following available variables: location, sex, and age. Only age had a significant impact on the seropositive rate among these variables. Cattle over the age of three years had a significantly higher prevalence of T. gondii antibodies (11.7%; odds ratio = 4.3; p = 0.033) than the reference group of animals younger than one year (2.9%) (Table 3). According to the lactation status of adult dairy cows ≥2.5 years old (n = 168), T. gondii antibodies were detected only in 10 (6.5%) samples collected from lactating cows.

Table 3.
Risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in cattle of Qena, southern Egypt.
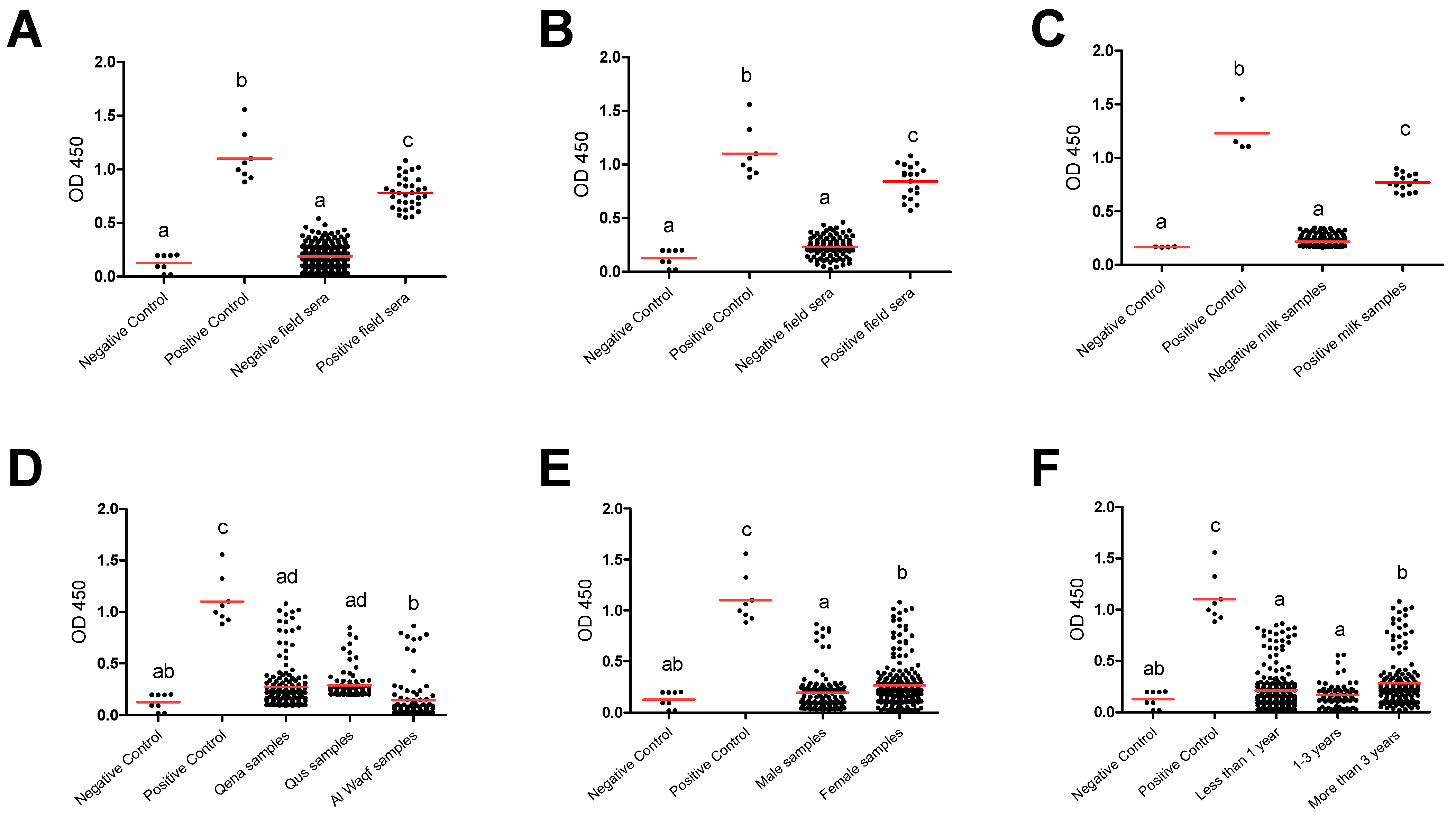
Furthermore, group comparisons of ELISA optical densities (OD) from negative and positive controls, as well as from different groups, were conducted to evaluate the seroreactivity against T. gondii. In all tested groups, the OD values for the antibody levels from the positive controls were considerably greater than those from the negative samples and negative controls. Furthermore, compared to negative field samples and negative controls, positive field sera were substantially higher. This outcome demonstrates the efficacy and validity of the iELISA kits employed in our investigation to effectively separate the tested samples’ seroreactivity levels. The substantial difference between the positive and negative samples as well as the similar outcomes between the positive samples and the positive controls suggested this impact. This effect was indicated in the significant difference between positive and negative samples and the comparable results between positive samples and positive controls in totally used serum samples (n = 362) (Figure 2A). A similar effect was also observed when a comparison was conducted for the serum samples (Figure 2B) and milk samples (Figure 2C) collected from lactating cows (n = 154). Also, a comparison was conducted among negative and positive controls, as well as different factors such as location (Qena vs. Qus vs. Al Waqf cities), sex (males vs. females), and age groups (<1 year old vs. ≥1–<3 years old vs. ≥3 years old). The OD values of samples from Qena and Qus cities were markedly higher than those from Al Waqf city (p < 0.05) (Figure 2D). The OD values from female samples were higher than those from male samples (Figure 2E). Notably, samples belonging to older aged cattle (≥3 years old) exhibited higher OD values compared to those from both young (<1 year old) and mid-aged cattle (≥1–<3 years old) (p < 0.05) (Figure 2F).
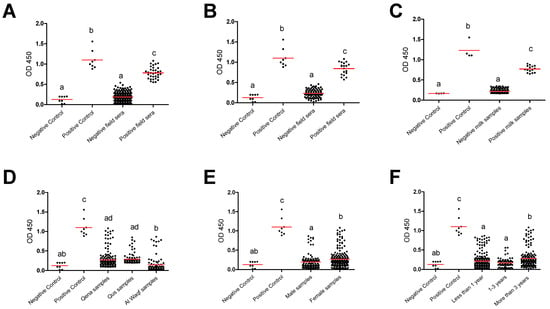
Figure 2.
Reactivity of anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in tested cattle groups. All samples (dots) were tested against control negative and positive samples provided by the commercial ELISA kit for detection of specific antibodies against T. gondii and classified as positive or negative according to the manufacturer’s instructions. (A) OD values of serum samples from all tested cattle (n = 362), (B) serum samples from dairy cows (n = 154), and (C) corresponding milk samples from dairy cows (n = 154). OD values of serum samples in relation to the different locations (D), sexes (E), and ages (F). Each red line represents the mean of each group. The different letters above the groups in the graphs indicate statistically significant differences in other groups (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc analysis, p < 0.05).
3.2. Analysis of the Correlation Between Milk and Serum Samples Using the Same Commercial ELISA
According to Vassarstats.net, online software analysis, the estimated prevalence was 12.3% (CI 95%; 7.7–18.8). This value is consistent with the data we manually computed from the serum antibody level (Table 2). In comparison to serum antibody ELISA for cow’s milk, the results showed that the milk antibody ELISA had the following characteristics: sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, false positive, negative predictive value, and false negative value of 78.9%, 100%, 100%, 0%, 97.1%, and 2.9%, respectively. Moreover, when comparing milk and serum tests from the same animal and using the same ELISA assay, our testing approach showed a high concordance (97.4%) and a significant kappa value (0.87) (Table 4).

Table 4.
Diagnostic parameters of serum compared to raw milk samples in tested cows using ELISA.
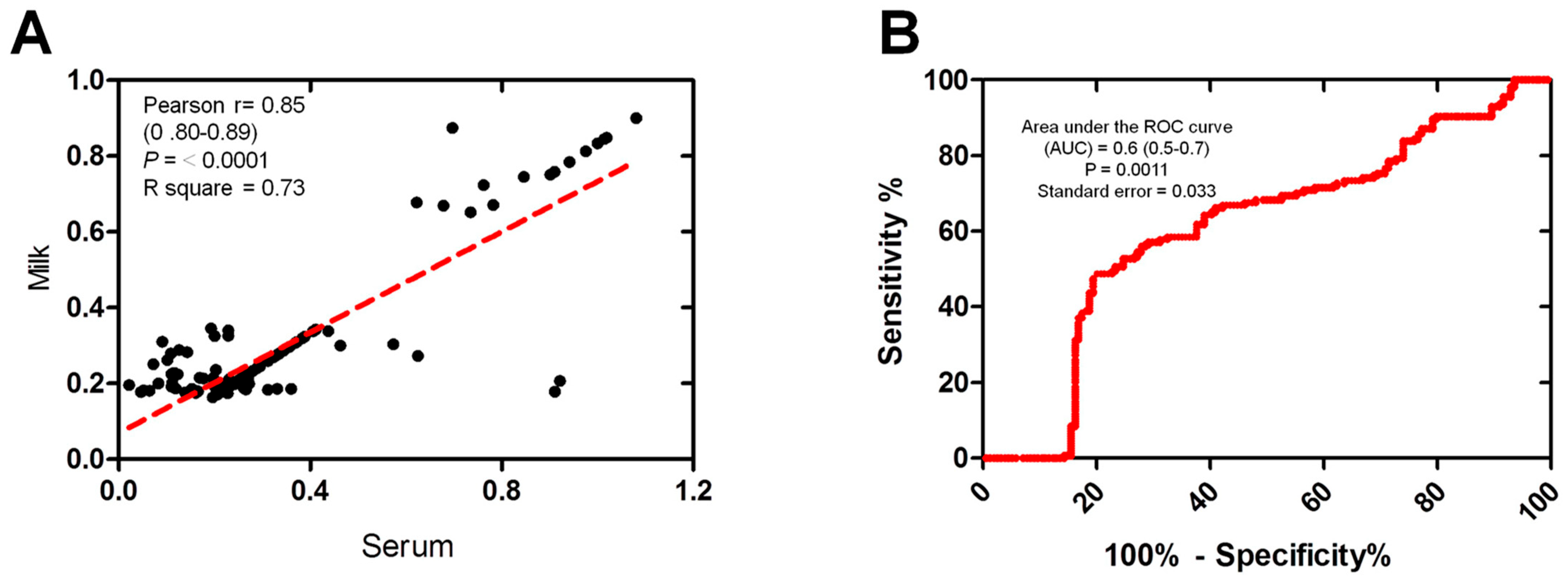
The correlation between the serum and milk antibodies OD readings, which were both measured using the same ELISA test, was also examined. Scatter plots illustrate the correlation between the OD values obtained from milk and serum samples within the tested group (n = 154). A strong correlation was observed between the milk and serum samples using ELISA OD (Pearson’s r = 0.85, p ≤ 0.0001, R square = 0.73) (Figure 3A). The accuracy of the immunoassays for ELISA was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC). The estimated AUC was 0.6 (CI 95%: 0.5–0.7), indicating the moderately high performance of the milk samples in comparison to the serum samples (Figure 3B).
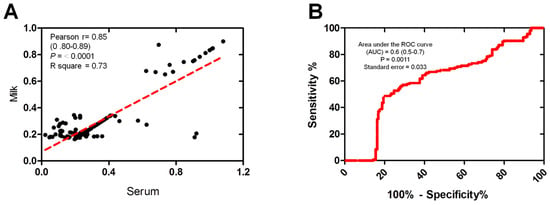
Figure 3.
The correlation between milk and serum samples reactivity. (A) Correlation between milk and the corresponding serum samples using the same ELISA. Scatter graphs show the correlation between OD values recorded for milk and serum samples (n = 154 each) from the same animals. The equation represents the approximation formula. The break line represents the calculated line of best fit. Correlation coefficients were calculated using Pearson’s correlation coefficient: |r| = 0.70, strong correlation; |r| > 0.5–<0.7, moderately strong correlation; and |r| = 0.3–0.5 weak-to-moderate correlation. (B) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve values were calculated using the area under the curve (AUC) as a diagnostic accuracy test to validate the milk against serum samples of the same animals (n = 154) using the same ELISA kit. The ROC curve for the milk samples against serum samples shows an area under the curve of 0.6 (95% CI: 0.5–0.7).
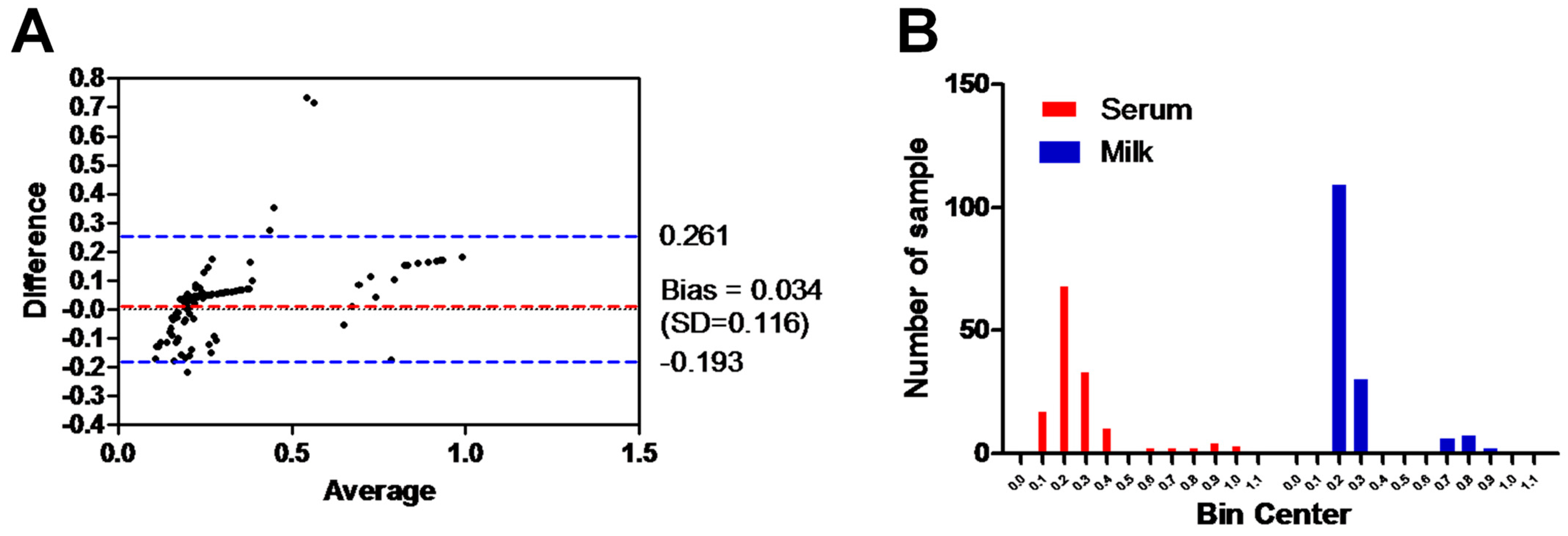
The Bland–Altman plot of ELISA testing between the milk and serum samples of the same animals and using the same ELISA test was performed. The range of the dotted blue lines is 0.261 to −0.193 of the standard deviation (SD), which is 0.034 from the mean (dotted red line). The majority of data points indicate good agreement between the two samples, falling within the range of ±0.116 SDs (Figure 4A). Additionally, the histogram of the milk and serum samples tested with the same ELISA assay demonstrated a strong correlation in the frequency distribution of the obtained data (milk samples, 0.27 ± 0.17 SD; serum samples, 0.31 ± 0.22 SD) for the total number of values (n = 154). Majority of samples laid between OD value 0.2 and 0.3 for milk (90.3%; 139/154) and serum samples (66.9%; 103/154) (Figure 4B).
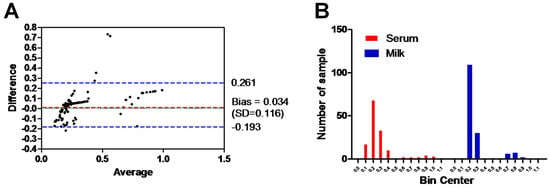
Figure 4.
Analysis of the results between milk and serum samples. (A) Bland–Altman plot of ELISA testing between the milk and serum samples (shown as black dots). Dotted bluish lines between 0.2 and −0.193 of the standard deviation of 0.116 from mean (dotted red line). (B) Histogram of the tested milk samples against serum samples using the same ELISA shows the frequency distribution of obtained data. The x axis represents the OD values and the y axis indicates the number of samples represented in each bar. The frequency distribution of obtained data using serum milk samples was 0.27 ± 0.17 SD and using serum samples was 0.31 ± 0.22 SD.
4. Discussion
In this study, we conducted a cross-sectional study to update the prevalence and the risk factors associated with T. gondii antibodies in cattle in Qena governorate, southern Egypt, and to analyze the correlation between the antibody reactivity in milk and serum samples. There are various serological tests available to detect T. gondii infection, of which the ELISA has been the most commonly used method [9,30,31]. When testing samples, using milk instead of serum offers a range of benefits. Not only is collecting milk samples simpler and more cost-effective, but it also reduces the risk of unintentional needle-transmitted diseases and minimizes the productivity losses associated with stress [32]. Even if parasites cannot be directly detected, seroprevalence can indicate the risk of human infection from raw milk consumption if there is a correlation between the presence of viable parasites and the detection of antibodies to T. gondii.
Herein, the total seroprevalence of T. gondii using serum samples from all tested cattle (n = 362) was 9.1%. This seropositive rate was lower than that reported in our previous study conducted using cattle (24.4%) from Qena and (21.1%) from Sohag, Egypt [25]. This discrepancy might be related to using a different ELISA approach based on T. gondii dense granule protein 7 (TgGRA7) antigen in the previous study, added to the difference in time, place, and animals of sample collection. However, our seropositive rate was similar to that reported in cattle (10.75%) from Sharkia, northern Egypt, using T. gondii surface antigen 2 (TgSAG2)-based ELISA [24] and higher than that detected in cattle (5.3%) from Beheira, northern Egypt, using the same commercial ELISA kit [33]. Recent meta-analysis studies on a worldwide scale predicted pooled prevalences that were similar to the seroprevalence found in the cattle under investigation. For cattle globally, a pooled seroprevalence of 16.94% was calculated [22]. The prevalence of T. gondii infection in 3366 cattle studied in Africa varied from 3.6% to 32%, with an overall estimated frequency of 12% [34]. The total pooled T. gondii seroprevalence in cattle in China was 10.1% (4217/39,274), which is comparable to our prevalence [35]. Although country-specific seroprevalence varies greatly, a higher overall pooled prevalence of T. gondii in cattle was found at 31% when compared to the neighboring country, Sudan [36].
In the 154 cows for which raw milk samples and serum samples were available, 19 serum samples and 15 milk samples tested positive, resulting in seropositive rates of 12.3% and 9.7%, respectively. Therefore, four cows had milk samples testing negative despite having positive serum samples. The stage of lactation can affect the antibody levels in both serum and milk samples [37]. However, the natural levels of immunoglobulins in cow’s milk during lactation may cause varying prevalence in serum and milk samples, requiring further investigation. Our detected rate (9.7%) was higher than that detected by our previous report conducted using cattle (2.4%) from the Sohag governorate and using the same ELISA [12]. This latter was a pioneering study that provided valuable and novel data on serological and molecular detection of T. gondii in individual and bulk samples of raw milk of different ruminant animals from different Egyptian regions. However, the unavailability of corresponding serum samples was considered a limitation that we attempted to avoid in the present study. Thus, the data of the current study could be regarded as a confirmatory record regarding the usefulness of commercial ELISA and protocols in the detection of anti-T. gondii antibodies in bovine milk.
A risk factor assessment was conducted based on serum testing of the total cattle population. In the current study, we analyzed location, age, sex, and lactation as risk factors for T. gondii seropositivity. However, only age was identified as a risk factor for infection because the older aged cattle had a significantly higher seroprevalence than young cattle. The effect of location and sex was similar to that reported previously in cattle from Qena and Sohag by our group [25], but it conflicted with the effect of age because no difference was detected according to age. Globally, age was considered as an important risk factor for T. gondii seropositivity when cattle were investigated in Switzerland [38], and in Portugal [39]. Furthermore, Klun et al. (2006) [40] detected the location but not the sex or age as a risk factor for T. gondii infection in cattle from Serbia. Age but not sex also influenced the seropositivity of T. gondii in cattle from China [41].
In addition to our previous data [27], the findings of the current study corroborated the suitability of milk samples from cattle in monitoring T. gondii antibodies. This was supported by the good agreement between the results of the milk samples when tested against serum samples of the corresponding cows and using the same ELISA kit. These results were analyzed using quantitative (number of positive vs. negative samples) and qualitative (OD values of positive vs. negative samples) approaches. Several statistical analysis tests were used, indicating the utility of milk samples for the detection of T. gondii antibody using our employed commercial ELISA. Online software analysis (Vassarstats.net) demonstrated high sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV. Also, the Pearson r correlation coefficient, the area under the ROC curve, the Bland–Altman plot, and the histogram of ELISA revealed a high correlation between analyzed milk and bovine serum. These parameters are commonly used in analyzing different diagnostic approaches either for methods or samples and great adequacy has been reported [42,43,44,45]. However, further studies testing combined milk and serum samples from cattle and other animal species are required to further validate such results.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we present an update on the seroprevalence of T. gondii antibodies in cattle from Qena, southern Egypt. Increasing age of the animals was identified as the sole risk factor for higher seroprevalence in our study. Corresponding serum and milk samples of dairy cows were highly correlated, indicating that non-invasive and easy-to-obtain milk samples might be a valid substitute for serum samples in future studies on T. gondii seroprevalence in dairy animals. Our findings might be used as a platform for efficient diagnosis of T. gondii in Egypt and consequently assist in the development of more potent control strategies for such infection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and design, R.M.F. and C.F.F.; experiments, R.M.F. and E.-S.E.-A.; formal analysis and investigation, R.M.F. and C.F.F.; resources and shared materials, R.M.F., A.S.A., M.Z.A., A.M.A., M.A.O., O.M.K. and C.F.F. writing—original draft, R.M.F., E.-S.E.-A., A.S.A. and C.F.F.; writing—review and editing, R.M.F., A.S.A., M.Z.A., A.M.A., M.A.O., O.M.K. and C.F.F. Project administration and funding acquisition, R.M.F. and C.F.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This study was carried out in compliance with the guidelines set forth by the South Valley University, Qena, Egypt, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Research Board. It was approved by South Valley University’s Research Code of Ethics under code number 36 (RCOE-36).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article. Raw data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank all veterinarians who helped in collecting blood samples from the tested animals and the animal owners for their cooperation in providing animals and the required data and information of each animal. We appreciate the great help of our colleagues at the Department of Animal Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, South Valley University, Qena, for their cooperation and technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.E.; Chirukandoth, S.; Dubey, J.P. Biology and epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii in man and animals. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2005, 6, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, S.A.; Jones, J.L.; Conrad, P.A.; Patton, S.; Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Epidemiology, feline clinical aspects, and prevention. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeria, S.; Dubey, J.P. Foodborne transmission of Toxoplasma gondii infection in the last decade. An overview. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughattas, S. Toxoplasma infection and milk consumption: Meta-analysis of assumptions and evidences. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2924–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-García, P.J.; Planas, N.; Llobat, L. Toxoplasma gondii in foods: Prevalence, control, and safety. Foods 2022, 11, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G. Laboratory diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185 (Suppl. S1), S73–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, S.; Basso, W.; Silván, J.B.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Maksimov, P.; Gethmann, J.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: Risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Yang, Y.R. Public health significance of Toxoplasma gondii infections in cattle: 2009–2020. J. Parasitol. 2020, 106, 772–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeri, T.; Sarvi, S.; Moosazadeh, M.; Daryani, A. Global prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in the aborted fetuses and ruminants that had an abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 290, 109370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Fonseca, F.M.; Sato, A.P.; Becker, A.P.B.B.; Pinto, G.O.D.P.A.; de Souza, G.S.; Perotta, J.H.; de Barros Filho, I.R.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Locatelli-Dittrich, R. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in milk of dairy cows from southern Brazil. Parasitol. Int. 2023, 95, 102750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehkordi, F.S.; Haghighi Borujeni, M.R.; Rahimi, E.; Abdizadeh, R. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in raw caprine, ovine, buffalo, bovine, and camel milk using cell cultivation, cat bioassay, capture ELISA, and PCR methods in Iran. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisak, E.; Zając, V.; Sroka, J.; Sawczyn, A.; Kloc, A.; Dutkiewicz, J.; Wójcik-Fatla, A. Presence of pathogenic Rickettsiae and protozoan in samples of raw milk from cows, goats, and sheep. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, M.A.; Pinto-Ferreira, F.; de Almeida, R.P.A.; Martins, F.D.C.; Pires, A.L.; Mareze, M.; Mitsuka-Breganó, R.; Freire, R.L.; da Rocha Moreira, R.V.; Borges, J.M.; et al. Artisan fresh cheese from raw cow’s milk as a possible route of transmission in a toxoplasmosis outbreak, in Brazil. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koethe, M.; Schade, C.; Fehlhaber, K.; Ludewig, M. Survival of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites in simulated gastric fluid and cow’s milk. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 233, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.E.; Villena, I.; Dubey, J.P. A review on toxoplasmosis in humans and animals from Egypt. Parasitology 2020, 147, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.F.; Sokkar, S.M.; Desouky, H.M.; Soror, A.H. Abortion due to toxoplasmosis in small ruminants. Glob. Vet. 2008, 2, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Ghany, A.M.; Amin, M.A.M. Epidemiology and molecular detection of zoonotic Toxoplasma gondii in cat feces and seroprevalence of anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in pregnant women and sheep. J. Life Sci. 2012, 9, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Khater, H.; Khalifa, N.; Barakat, A. Serological and molecular studies of ovine and human toxoplasmosis with a trial of treatment of infected ewe. Sci. J. Vet. Adv. 2013, 2, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Shariatzadeh, S.A.; Sarvi, S.; Hosseini, S.A.; Sharif, M.; Gholami, S.; Pagheh, A.S.; Montazeri, F.; Nayeri, T.; Nakhaei, M.; Galeh, T.M.; et al. The global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in bovines: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1417–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food Agriculture Organization (FAO). The Long-Term Future of Livestock and Fishery in Egypt—Production Targets in the Face of Uncertainty; Food Agriculture Organization (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Huang, P.; Salem, T.A.; Talaat, R.M.; Nasr, M.I.; Xuan, X.; Nishikawa, Y. Prevalence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in Northern Egypt. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fereig, R.M.; Mahmoud, H.Y.; Mohamed, S.G.; AbouLaila, M.R.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Osman, S.A.; Zidan, S.A.; El-Khodary, S.A.; Mohamed, A.E.A.; Nishikawa, Y. Seroprevalence and epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii in farm animals in different regions of Egypt. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2016, 3–4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Zanzani, S.A.; Stradiotto, K.; Olivieri, E.; Villa, L.; Manfredi, M.T. Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in bulk tank milk samples of caprine dairy herds. J. Parasitol. 2018, 104, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereig, R.M.; Abdelbaky, H.H.; Mazeed, A.M.; El-Alfy, E.S.; Saleh, S.; Omar, M.A.; Alsayeqh, A.F.; Frey, C.F. Prevalence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii antibodies and DNA in raw milk of various ruminants in Egypt. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereig, R.M.; Abdelbaky, H.H.; El-Alfy, E.S.; El-Diasty, M.; Elsayed, A.; Mahmoud, H.Y.A.H.; Ali, A.O.; Ahmed, A.; Mossaad, E.; Alsayeqh, A.F.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in camels recently imported to Egypt from Sudan and a global systematic review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1042279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereig, R.M.; Wareth, G.; Abdelbaky, H.H.; Mazeed, A.M.; El-Diasty, M.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Mahmoud, H.Y.A.H.; Ali, A.O.; El-Tayeb, A.; Alsayeqh, A.F.; et al. Seroprevalence of Specific Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, and Brucella spp. in Sheep and Goats in Egypt. Animals 2022, 12, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Karanis, P.; Fallahi, S. Advances in serological, imaging techniques and molecular diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection. Infection 2018, 46, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, R.A.M.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Marciano, M.A.M.; Mazuz, M.L.; Pereira-Chioccola, V.L.; Fux, B. Toxoplasmosis in human and animals around the world. Diagnosis and perspectives in the one health approach. Acta Trop. 2022, 231, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schares, G.; Bärwald, A.; Staubach, C.; Wurm, R.; Rauser, M.; Conraths, F.J.; Schroeder, C. Adaptation of a commercial ELISA for the detection of antibodies against Neospora caninum in bovine milk. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 120, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, S.; Hamada, R.; Sobhy, K.; Frey, C.F.; Fereig, R.M. Seroprevalence and risk factors analysis of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii in cattle of Beheira, Egypt. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1122092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonouhewa, A.B.N.; Akpo, Y.; Sessou, P.; Adoligbe, C.; Yessinou, E.; Hounmanou, Y.G.; Assogba, M.N.; Youssao, I.; Farougou, S. Toxoplasma gondii infection in meat animals from Africa: Systematic review and meta-analysis of sero-epidemiological studies. Vet. World 2017, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Q.L.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Tian, T.; Leng, X.; Li, J.M.; Shi, K.; Zhang, N.Z.; Du, R.; Zhao, Q. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in cattle in China from 2010 to 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop. 2020, 211, 105439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, A.A.; Ahmed, M.; Bello, I.I.; Tawor, A.; Ahmed, A.O.; Khider, M.; Elduma, A.H. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in domestic animals in Sudan: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Vet. Eurasia 2022, 48, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Zanzani, S.A.; Villa, L.; Manfredi, M.T. Toxoplasma gondii in naturally infected goats: Monitoring of specific IgG levels in serum and milk during lactation and parasitic DNA detection in milk. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 170, 104738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger-Schoch, A.E.; Bernet, D.; Doherr, M.G.; Gottstein, B.; Frey, C.F. Toxoplasma gondii in Switzerland: A serosurvey based on meat juice analysis of slaughtered pigs, wild boar, sheep and cattle. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.P.; Dubey, J.P.; Neto, F.; Rodrigues, A.; Martins, T.; Rodrigues, M.; Cardoso, L. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in cattle, sheep, goats and pigs from the north of Portugal for human consumption. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 193, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klun, I.; Djurkovic-Djakovoc, O.; Katic-Radivojevic, S.; Nikolic, A. Cross-sectional survey on Toxoplasma gondii infection in cattle, sheep and pigs in Serbia: Seroprevalence and risk factors. Vet. Parasitol 2006, 135, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.H.; Wang, C.R.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, Z.H.; Chang, Q.C.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, S.M.; Zou, F.C.; Zhu, X.Q. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in beef cattle and dairy cattle in northeast China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrem, T.M.; Bartlett, P.C.; Donohue, H.; Voisinet, B.D.; Houseman, J.T. Performance of a commercial serum ELISA for the detection of antibodies to Neospora caninum in whole and skim milk samples. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raez-Bravo, A.; Granados, J.E.; Serrano, E.; Dellamaria, D.; Casais, R.; Rossi, L.; Puigdemont, A.; Cano-Manuel, F.J.; Fandos, P.; Pérez, J.M.; et al. Evaluation of three enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for sarcoptic mange diagnosis and assessment in the Iberian ibex, Capra pyrenaica. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogan, J.E., Jr. Analytical and clinical evaluation of two methods for measuring erythrocyte sedimentation rate in eastern Indigo Snakes (Drymarchon couperi). Animals 2023, 13, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fereig, R.M.; Altwaim, S.A.; Frey, C.F. Evaluation of a commercial serum competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Neospora caninum-specific antibodies in raw milk of ruminants. Parasitologia 2024, 4, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).