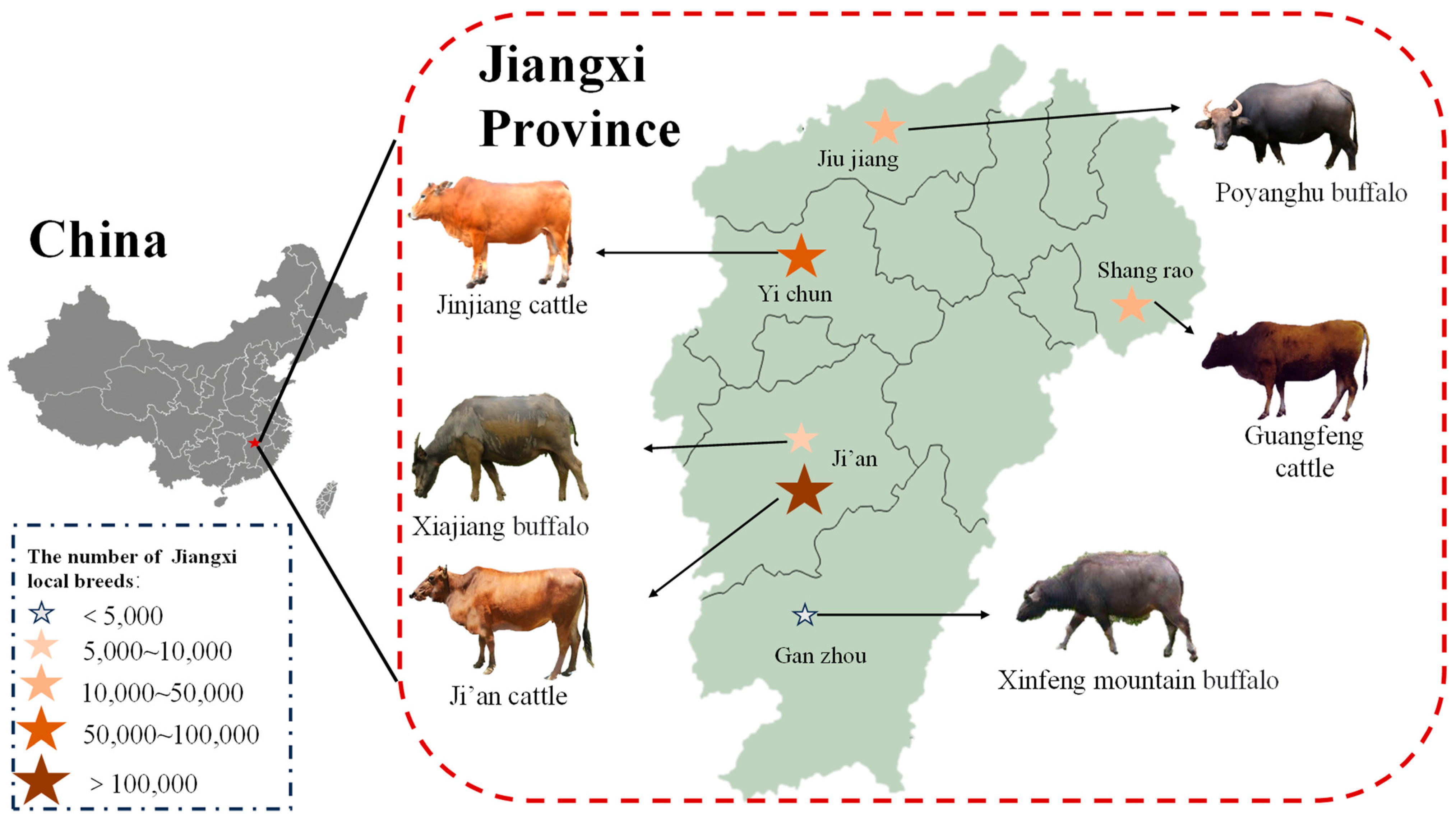
Study on the Carcass Traits, Meat Quality, and Nutritional Attributes of Six Kinds of Jiangxi Local Breeds Cattle
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Determination of pH Value
2.2. Determination of Meat Color
2.3. Determination of Water Retention and Shear Force
2.4. Determination of Nutrients in LD Muscle
2.5. Determination of Fatty Acids
2.6. Determination of Amino Acids
2.7. Determination of Inosine Acid and Guanylate Content
2.8. Histological Analyses
2.9. Determination of Muscle Fiber Type
2.10. Statistical Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Slaughter Performance
3.2. Comparison of Meat Quality
3.3. Comparison of the Nutritional Ingredients
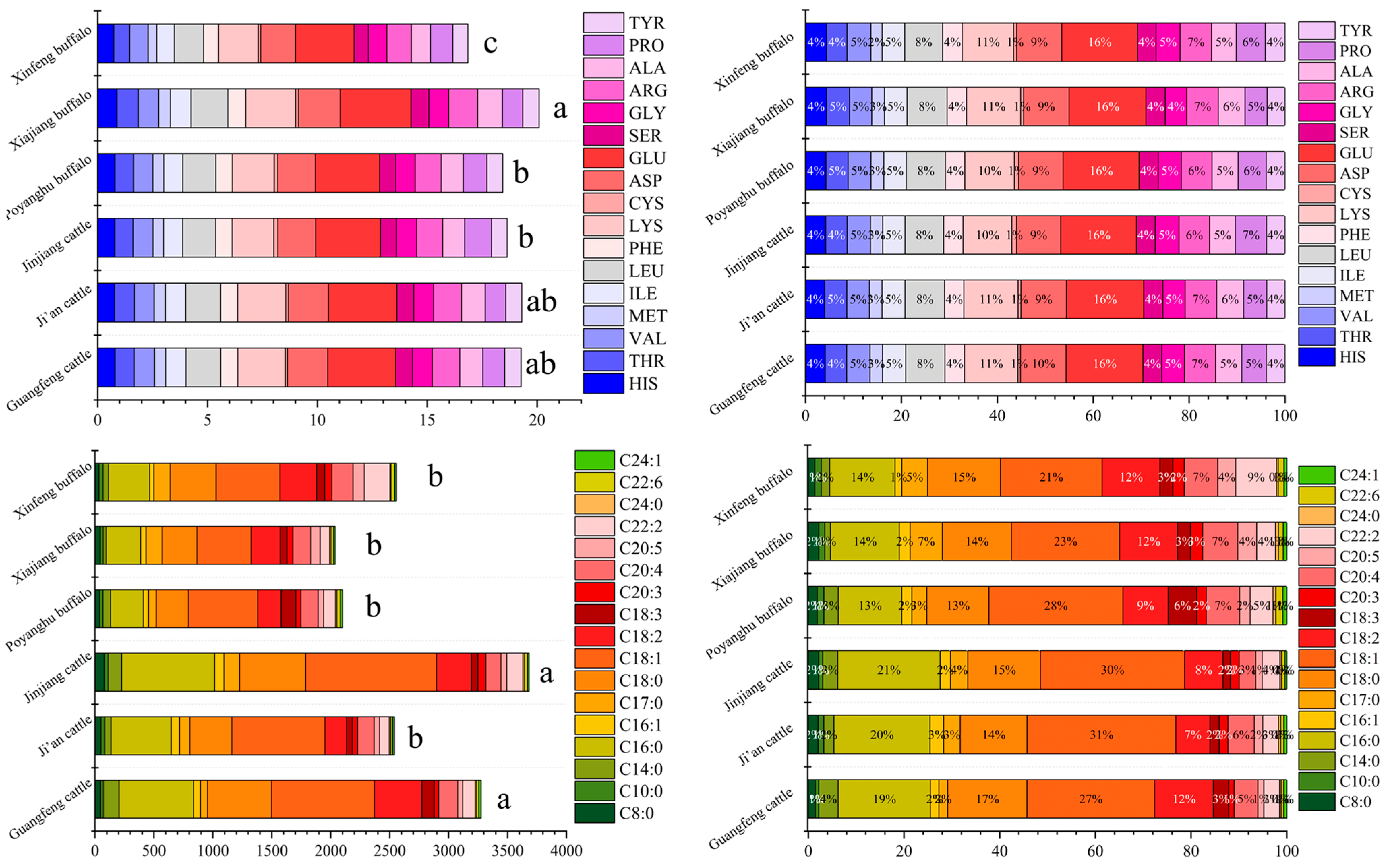
3.4. Amino Acid Composition of Different Breeds
3.5. Comparison of Fatty Acid Composition
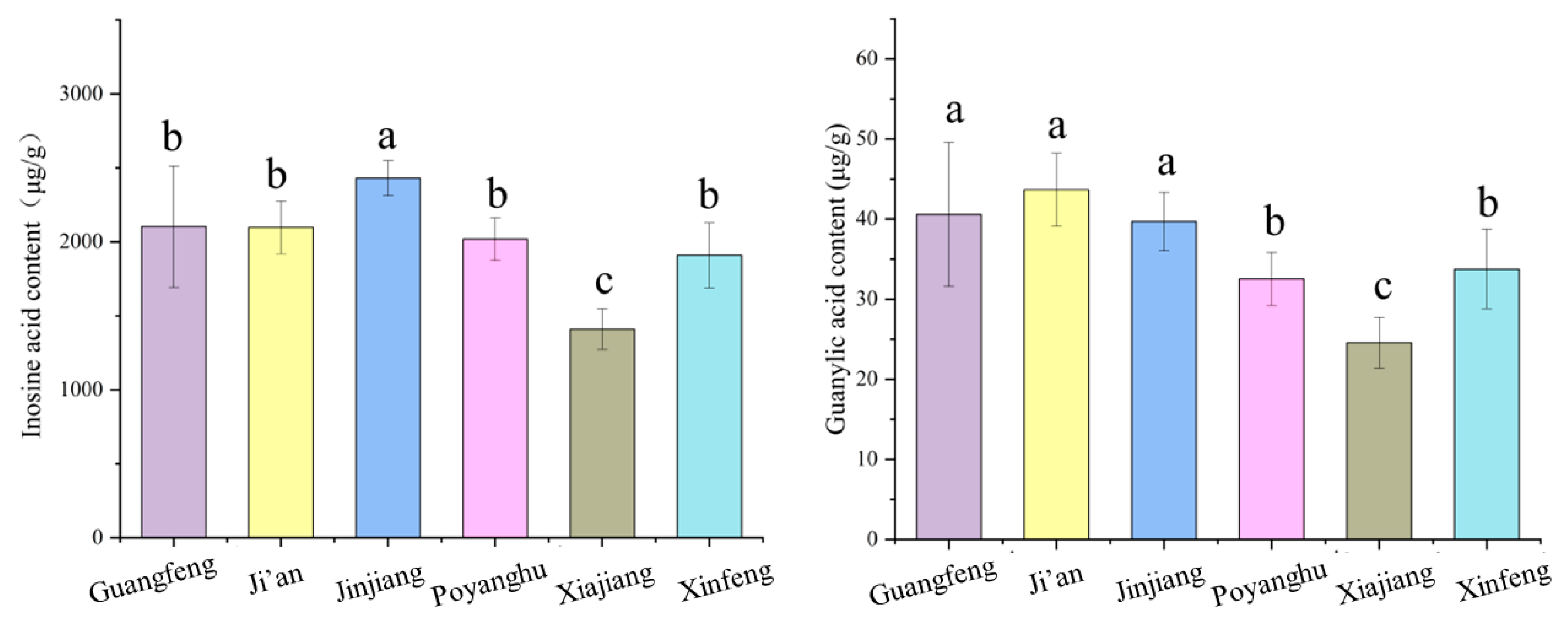
3.6. Comparison of Flavor Nucleotides
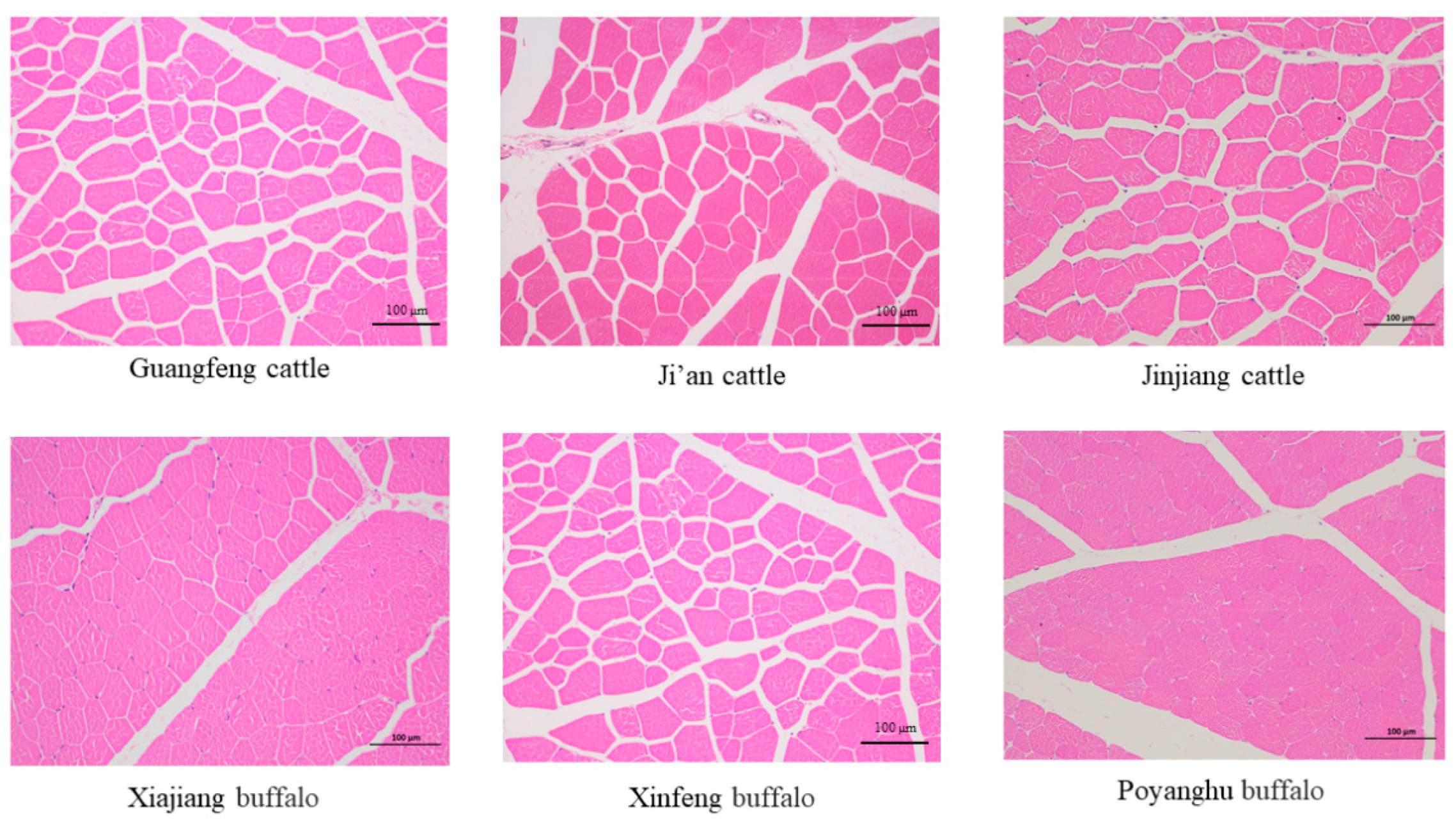
3.7. Comparison of Muscle Fiber Morphology and Muscle Bundle Properties
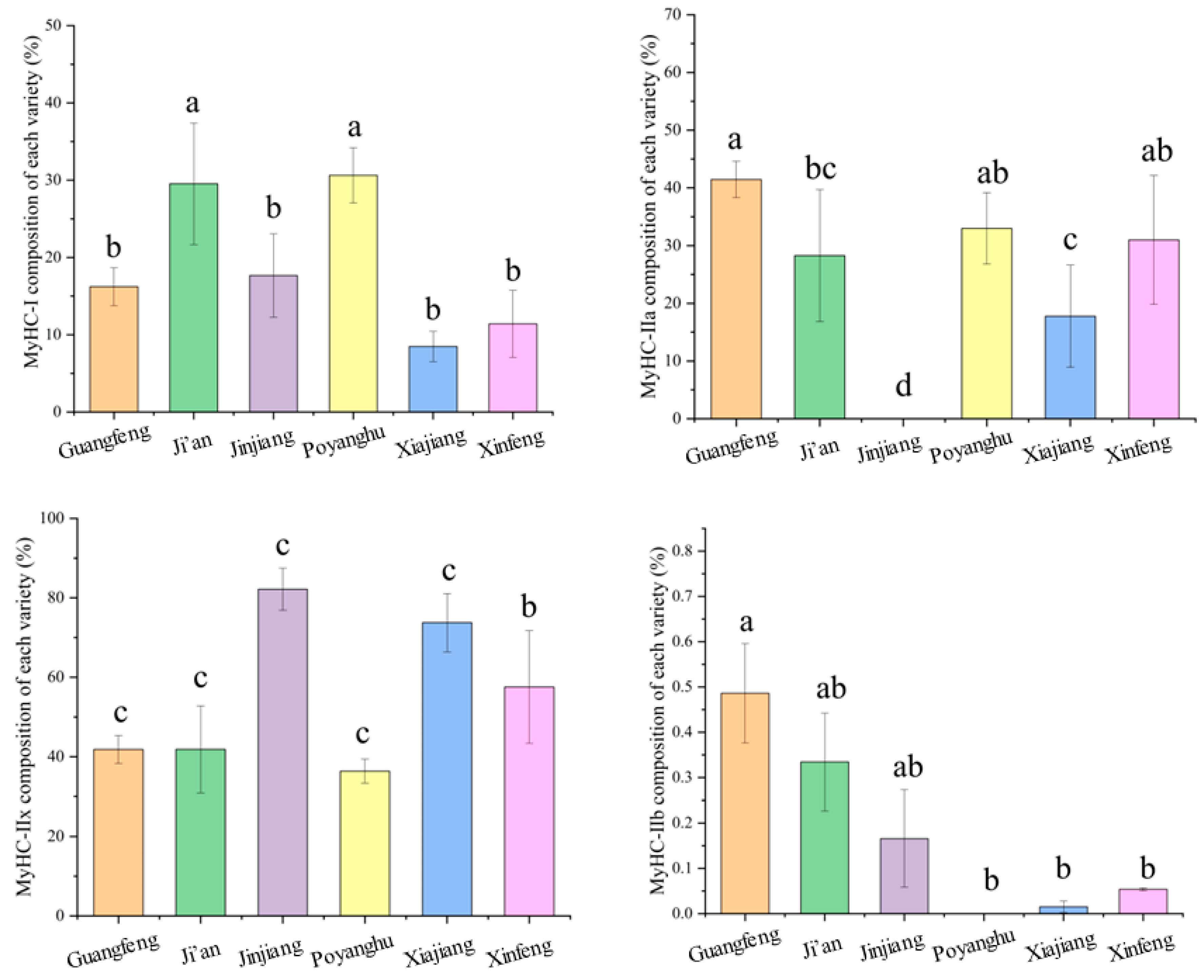
3.8. Comparison of Muscle Fiber
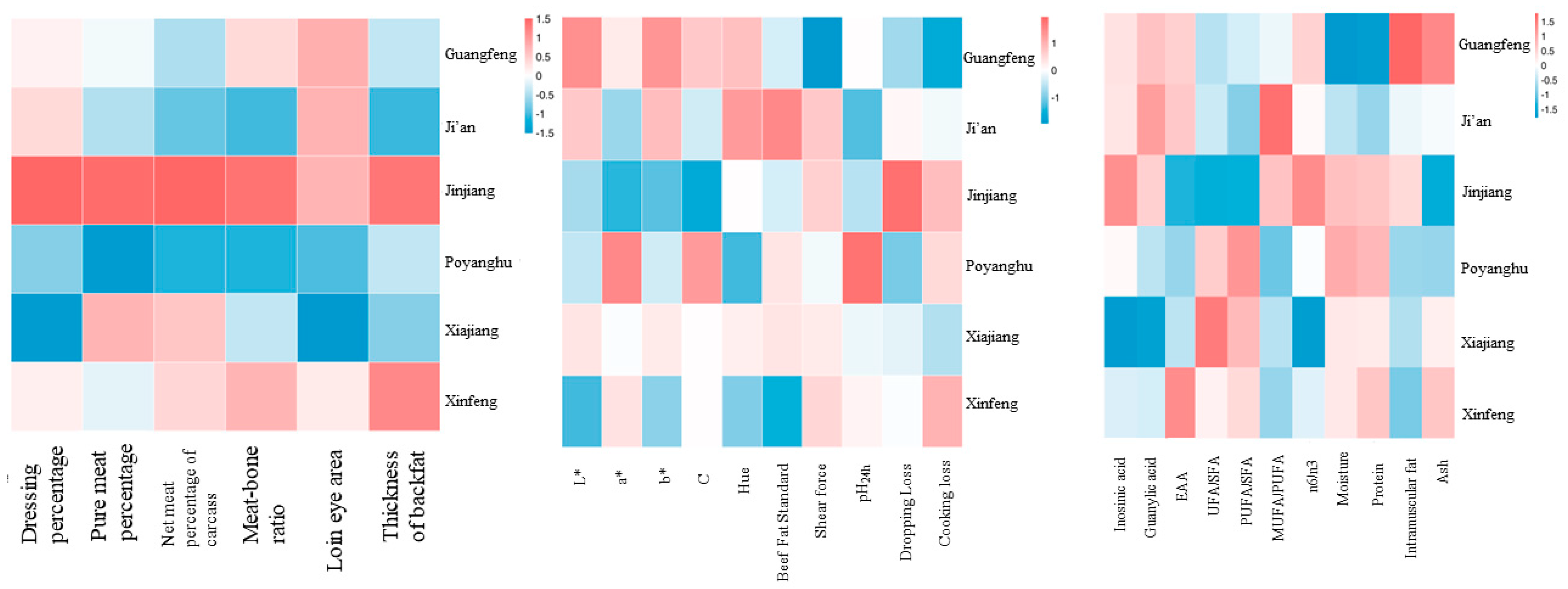
3.9. Correlation Analysis between Varieties and Characters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, G.H.; Liu, L.; Xiu, X.L.; Jian, H.M.; Wang, L.Z.; Sun, B.Z.; Tong, B.S. Productivity and carcass characteristics of pure and crossbred Chinese Yellow Cattle. Meat Sci. 2001, 58, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, H.O.; Upadhyay, D. Chapter Three—Global livestock production systems: Classification, status, and future trends. In Emerging Issues in Climate Smart Livestock Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 47–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, D.L.; Hong, S.J.; Wang, H.H.; Wu, L. Emerging markets for imported beef in China: Results from a consumer choice experiment in Beijing. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Porto-Neto, L.R.; Sonstegard, T.S.; Liu, G.E.; Bickhart, D.M.; Da Silva, M.V.; Machado, M.A.; Utsunomiya, Y.T.; Garcia, J.F.; Gondro, C.; Van Tassell, C.P. Genomic divergence of zebu and taurine cattle identified through high-density SNP genotyping. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickhart, D.M.; Xu, L.; Hutchison, J.L.; Cole, J.B.; Null, D.J.; Schroeder, S.G.; Song, J.; Garcia, J.F.; Sonstegard, T.S.; Van Tassell, C.P.; et al. Diversity and population-genetic properties of copy number variations and multicopy genes in cattle. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherf, B.D.; Pilling, D. The Second Report on the State of the World’s Animal Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Shaping the future of livestock. In Proceedings of the 10th Global Forum for Food and Agriculture (GFFA), Berlin, Germany,, 18–20 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Gao, H.; Liu, G.E.; et al. Genome-wide scan reveals genetic divergence and diverse adaptive selection in Chinese local cattle. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Ding, Y. The importance of work animals in rural China. World Anim. Rev. 1996, 86, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhan, J.; Shen, J.; Qu, K.; Hanif, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, N.; Chen, H.; Huang, B.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing reveals diversity, global and local ancestry proportions in Yunling cattle. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2020, 137, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, G.; Brscic, M.; Gottardo, F. Main critical factors affecting the welfare of beef cattle and veal calves raised under intensive rearing systems in Italy: A review. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancy, J.T.; Nelson, H.L. Effects of breed type and supplementation during grazing on carcass traits and meat quality of bulls fattened on improved savannah. Livest. Sci. 2009, 121, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, M.L. Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Profile of Hulunbuir Lambs under Different Grazing Intensities and Supplementary Feeding Levels. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2024, 32, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R. Research on influence factors of inosine acid content in livestock and poultry muscle. J. Shaanxi Univ. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2021, 37, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.L.; Zan, L.S.; Wang, H.C. Chinese beef cattle improvement should pay attention to several technical links. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 48, 61–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zou, Y.; Wang, P.; Qu, M.R.; Zheng, W.B.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.Q.; Zhu, X.Q. Prevalence and multilocus genotyping of Cryptosporidium spp. in cattle in Jiangxi Province, southeastern China. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.Q. Prevalence and genotypes/subtypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Blastocystis sp. in different breeds of cattle in Jiangxi Province, southeastern China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 98, 105216. [Google Scholar]
- NY 467-2001; Hygienic Quarantine Rules for Slaughtering Livestock and Poultry. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2001.
- Serra, X.; Gil, M.; Gispert, M.; Guerrero, L.; Oliver, M.A.; Sañudo, C.; Campo, M.M.; Panea, B.; Olleta, J.L.; Quintanilla, R.; et al. Characterisation of young bulls of the Bruna dels Pirineus cattle breed (selected from old Brown Swiss) in relation to carcass, meat quality and biochemical traits. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 425–436. [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo, J.A.; Bai, Y.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Cai, W.; Bickhart, D.M.; Liu, G.; Barao, S.M.; Sonstegard, T.; Song, J. Growth curve, blood parameters and carcass traits of grass-fed Angus steers. Animal 2021, 15, 100381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oattes, J.L.; Shao, T.; Henley, P.A.; Shike, D.W. Fetal programming effects of early weaning on subsequent parity calf performance. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2021, 5, txab049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyanzad, M.R. Comparison of carcass composition of Iranian fat-tailed sheep. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 18, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, H.E.; Scollan, N.D.; Enser, M.; Hughes, S.I.; Richardson, R.I.; Wood, J.D. Effects of breed and a concentrate or grass silage diet on beef quality in cattle of 3 ages. I. Animal performance, carcass quality and muscle fatty acid composition. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jin, Y.; Yan, Z. Study on slaughtering performance and meat quality of yaks around lake. Food Ind. J. 2016, 7, 172–174. [Google Scholar]
- Swatland, H.J. The cellular basis of postnatal muscle growth. In Structure and Development of Meat Animals and Poultry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 365–424. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.X.; Meng, Q.X.; Ren, L.P.; Shi, F.H.; Zhou, B. Effect of cattle breed on finishing performance, carcass characteristics and economic benefits under typical beef production system in China. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 11, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngapo, T.M.; Dransfield, E. British consumers preferred fatness levels in beef: Surveys from 1955, 1982 and 2002. Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Thu, N. Meat quality: Understanding of meat tenderness and influence of fat content on meat flavor. J. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2006, 12, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Uğurlu, M.; Ekiz, B.; Teke, B. Meat quality traits of male Herik lambs raised under an intensive fattening system. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2017, 41, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, C.E.; Cornforth, D.P.; Whittier, D. Consumer preferences for beef color and packaging did not affect eating satisfaction. Meat Sci. 2001, 57, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.T.; Kim, G.D.; Hwang, Y.H.; Ryu, Y.C. Control of fresh meat quality through manipulation of muscle fiber characteristics. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 828–836. [Google Scholar]
- Renerre, M. Factors involved in the discoloration of beef meat. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1982, 25, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Hur, S.J.; Yang, H.S.; Moon, S.H.; Hwang, Y.H.; Park, G.B.; Joo, S.T. Discoloration characteristics of 3 major muscles from cattle during cold storage. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, C1–C5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, J.A.; Pegg, R. Meat Color, Montana State University and Saskatchewan Food Product Innovation, Program University of Saskatchewan. 2010. Available online: https://docobook.com/meat-color-safe-spectrum.html (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- Toldrá, F. Meat: Chemistry and biochemistry. In Handbook of Food Science, Technology and Engineering; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Vergara, H.; Molin, A.; Gallego, L. Influence of sex and slaughter weight on carcass and meat quality in light and medium weight lambs produced in intensive systems. Meat Sci. 1999, 52, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultgren, J.; Segerkvist, K.A.; Berg, C. Preslaughter stress and beef quality in relation to slaughter transport of cattle. Livest. Sci. 2022, 264, 105073. [Google Scholar]
- Warriss, P.D. Meat Science: An Introductory Text; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Abebe, G.; Kannan, G.; Goetsch, A.L. Effects of small ruminant species and origin (highland and lowland) and length of rest and feeding period on harvest measurements in Ethiopia. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 834–847. [Google Scholar]
- Losada-Espinosa, N.; Estévez-Moreno, L.X.; Bautista-Fernández, M. Cattle welfare assessment at the slaughterhouse level: Integrated risk profiles based on the animal’s origin, pre-slaughter logistics, and iceberg indicators. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 197, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.C.; Gray, G.D.; Hale, D.S. National Beef Quality Audit–2011: In-plant survey of targeted carcass characteristics related to quality, quantity, value, and marketing of fed steers and heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 5143–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geletu, U.S.; Usmael, M.A.; Mummed, Y.Y. Quality of cattle meat and its compositional constituents. Vet. Med. Int. 2021, 2021, 7340495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchello, J.A.; Dryden, F.D. While Ideas differ Meat Quality Is defined. Progress. Agric. Ariz. 1968, 20, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, K.L.; Miller, M.F.; Hoover, L.C.; Wu, C.K.; Brittin, H.C.; Ramsey, C.B. Effect of beef tenderness on consumer satisfaction with steaks consumed in the home and restaurant. J. Anim. Sci. 1996, 74, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, A.; Daly, C.C.; Devine, C.E. The effects of the ultimate pH of meat on tenderness changes during ageing. Meat Sci. 1996, 42, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.X.; Luo, W.J.; Lei, L. Nutritional composition analysis and quality evaluation of cattle in different regions of Guizhou Province (China). Czech J. Food Sci. 2023, 41, 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Essen-Gustavsson, B.; Karlsson, A.; Lundström, K. Intramuscular fat and muscle fibre lipid contents in halothane-gene-free pigs fed high or low protein diets and its relation to meat quality. Meat Sci. 1994, 38, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Jiang, H. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Intramuscular Fat Development and Growth in Cattle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, F.W.; Charmley, E.; Gardiner, C.P. Diet and genetics influence beef cattle performance and meat quality characteristics. Foods 2019, 8, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillin, K.W.; Hoffman, L.C. Improving the quality of meat from ratites. In Improving the Sensory and Nutritional Quality of Fresh Meat; Kerry, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 418–446. [Google Scholar]
- Bouton, P.E.; Ford, A.L.; Harris, P.V.; Ratcliff, D. Objective assessment of meat juiciness. J. Food Sci. 1975, 40, 884–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimenova, A. Biochemical and Sensory Profile of Meat from Dairy and Beef Cattle. Master’s Thesis, Itä-Suomen yliopisto, Kuopio, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Purslow, P.P.; Oiseth, S.; Hughes, J. The structural basis of cooking loss in beef: Variations with temperature and ageing. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornberg, E.V.A. Effects of heat on meat proteins–Implications on structure and quality of meat products. Meat Sci. 2005, 70, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.M.; Kim, B.C. Muscle fiber characteristics, myofibrillar protein isoforms, and meat quality. Livest. Sci. 2009, 122, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichhardt, C.C.; Feuz, R.; Brady, T.J.; Motsinger, L.A.; Briggs, R.K.; Bowman, B.R.; Garcia, M.D.; Larsen, R.; Thornton, K.J. Interactions between cattle breed type and anabolic implant strategy impact circulating serum metabolites, feedlot performance, feeding behavior, carcass characteristics, and economic return in beef steers. Domest. Anim. Endocrin 2021, 77, 106633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.J.; Mente, A.; Maroleanu, A. Intake of saturated and trans unsaturated fatty acids and risk of all cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.D.; Richardson, R.I.; Nute, G.R. Effects of fatty acids on meat quality: A review. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.; Magistrali, A.; Butler, G. Nutritional benefits from fatty acids in organic and grass-fed beef. Foods 2022, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Diet, Nutrition and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases; World Health Organ Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Volume 916, pp. 1–149. [Google Scholar]
- Scollan, N.; Hocquette, J.F.; Nuernberg, K. Innovations in beef production systems that enhance the nutritional and health value of beef lipids and their relationship with meat quality. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, T.T.; Blanton, J.R., Jr.; Riley, D.G.; Chase, C.C., Jr.; Coleman, S.W.; Phillips, W.A.; Brooks, J.C.; Miller, M.F.; Thompson, L.D. Intramuscular fat and fatty acid composition of longissimus muscle from divergent pure breeds of cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Jo, C.; Tariq, M.R. Meat flavor precursors and factors influencing flavor precursors—A systematic review. Meat Sci. 2015, 110, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturdivant, C.A.; Lunt, D.K.; Smith, G.C. Fatty acid composition of subcutaneous and intramuscular adipose tissues and M. longissimus dorsi of Wagyu cattle. Meat Sci. 1992, 32, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint WHO/FAO/UNU Expert Consultation. Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in Human Nutrition: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Holló, G.; Csapó, J.; Szűcs, E.; Tőzsér, J.; Repa, I.; Holló, I. Influence of Breed, Slaughter Weight and Gender on Chemical Composition of Beef. Part 1. Amino Acid Profile and Biological Value of Proteins. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 14, 1555–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopálenský Josef Suchý, P.; Straková, E.; Šimek, F.; Macháček, M.; Herzig, I. Amino acid levels in muscle tissue of eight meat cattle breeds. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 62, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, C.R.; Hodgen, J.M. A fresh look at meat flavor. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustan, A.C.; Drevon, C.A. Fatty acids: Structures and properties. eLS 2005, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Corbin, C.H.; O’Quinn, T.G.; Garmyn, A.J.; Legako, J.F.; Hunt, M.R.; Dinh, T.T.N.; Rathmann, R.J.; Brooks, J.C.; Miller, M.F. Sensory evaluation of tender beef strip loin steaks of varying marbling levels and quality treatments. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, S.L.; Black, J.M.; Davis, G.W. Flavor and selected chemical components of ground beef from steers backgrounded on pasture and fed corn up to 140 days. J. Food Sci. 1982, 47, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, C.; Abbott, A.; Doyle, P.; Nader, G.; Larson, S. A review of fatty acid profiles and antioxidant content in grass-fed and grain-fed beef. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Kim, Y.H.B.; Cooper, B. Metabolomics profiling to determine the effect of postmortem aging on color and lipid oxidative stabilities of different bovine muscles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6708–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyquist, K.M.; O’Quinn, T.G.; Drey, L.N.; Lucherk, L.W.; Brooks, J.C.; Miller, M.F.; Legako, J.F. Palatability of beef chuck, loin, and round muscles from three USDA quality grades. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 4276–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yancey, E.J.; Grobbel, J.P.; Dikeman, M.E. Effects of total iron, myoglobin, hemoglobin, and lipid oxidation of uncooked muscles on livery flavor development and volatiles of cooked beef steaks. Meat Sci. 2006, 73, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.K.; Luckemeyer, T.J.; Kerth, C.R. Descriptive beef flavor and texture attributes relationships with consumer acceptance of US light beef eaters. Meat Sci. 2023, 204, 109252. [Google Scholar]
| Gene | Primers | Product Size (bp) | Accession NO. |
|---|---|---|---|
| MyHC-I | Forward: 5′-AACCTGTCCAAGTTCCGCAAG-3′ Reverse: 3′-AGATGTGGCACGGCTACTCCT-3′ | 148 | NM_174727 |
| MyHC-IIa | Forward: 5′-TGGAGCGGATGAAGAAGAACA-3′ Reverse: 3′-GCTTCTGCTCACTCTCTACCTCTC-3′ | 159 | NM_001166227 |
| MyHC-IIb | Forward: 5′-AGTGCTATCCCAGAGGGTCAGT-3′ Reverse: 3′-AGCTTTTCATCTCGCATCTCCT-3′ | 161 | AY227972 |
| MyHC-IIx | Forward: 5′-AGTGCTATCCCAGAGGGTCAGT-3′ Reverse: 3′-AGCTTTTCATCTCGCATCTCCT-3′ | 226 | NM_174117 |
| GAPDH | Forward: 5′-AGGGCTGCTTTTAATTCTGGC-3′ Reverse: 5′-TGACTGTGCCGTTGAACTTGC-3′ | 124 | NM_001034034 |
| Species | Guangfeng Cattle | Ji’an Cattle | Jinjiang Cattle | Poyanghu Buffalo | Xiajiang Buffalo | Xinfeng Mountain Buffalo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | |||||||
| Dressing percentage (%) | 49.69 ± 1.41 b | 50.49 ± 1.85 b | 53.82 ± 1.63 a | 47.2 ± 1.62 c | 44.88 ± 1.96 d | 49.78 ± 1.55 b | |
| Net meat percentage (%) | 37.49 ± 1.22 b | 36.36 ± 1.91 b | 41.98 ± 1.51 a | 33.36 ± 1.36 c | 33.97 ± 1.62 c | 37.27 ± 1.68 b | |
| Meat–bone ratio | 3.96 ± 0.43 bc | 3.24 ± 0.69 d | 4.49 ± 0.47 a | 3.20 ± 0.32 d | 3.58 ± 0.26 cd | 4.16 ± 0.51 b | |
| Loin eye muscle area (cm2) | 62.40 ± 7.27 a | 62.2 ± 9.85 a | 61.8 ± 12.73 a | 42.1 ± 4.87 b | 36.3 ± 8.05 b | 55.50 ± 8.57 a | |
| Thickness of backfat (mm) | 0.20 ± 0.11 bc | 0.16 ± 0.08 c | 0.30 ± 0.10 a | 0.20 ± 0.07 bc | 0.18 ± 0.05 c | 0.29 ± 0.15 ab | |
| Species | Guangfeng Cattle | Ji’an Cattle | Jinjiang Cattle | Poyanghu Buffalo | Xiajiang Buffalo | Xinfeng Mountain Buffalo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | |||||||
| L* | 31.10 ± 1.88 a | 30.35 ± 1.71 ab | 28.97 ± 1.94 cd | 29.16 ± 1.68 bcd | 29.99 ± 1.51 abc | 28.33 ± 1.45 d | |
| a* | 10.98 ± 1.46 b | 10.07 ± 1.69 bc | 9.53 ± 1.66 c | 12.08 ± 1.71 a | 10.71 ± 1.33 b | 11.07 ± 1.17 b | |
| b* | 7.22 ± 1.19 a | 6.92 ± 1.31 ab | 5.76 ± 1.48 d | 6.24 ± 1.22 bcd | 6.60 ± 1.03 bcd | 5.95 ± 0.84 cd | |
| C* | 13.16 ± 1.75 ab | 12.25 ± 1.97 b | 11.18 ± 1.96 c | 13.63 ± 1.88 a | 12.60 ± 1.52 ab | 12.60 ± 1.16 ab | |
| H° | 33.25 ± 3.05 a | 34.52 ± 4.19 ab | 31.05 ± 5.51 bc | 27.34 ± 3.87 d | 31.65 ± 3.31 ab | 28.31 ± 4.01 cd | |
| Beef fat standard | 3.30 ± 0.90 bc | 4.10 ± 0.54 a | 3.30 ± 0.64 bc | 3.60 ± 0.66 ab | 3.60 ± 0.49 ab | 2.80 ± 0.40 c | |
| Shear force (kg/cm2) | 7.50 ± 1.43 b | 10.30 ± 1.79 a | 10.22 ± 1.31 a | 9.49 ± 1.46 a | 9.87 ± 2.39 a | 10.13 ± 1.53 a | |
| pH45min | 6.91 ± 0.57 a | 6.71 ± 0.14 b | 6.61 ± 0.28 b | 6.65 ± 0.21 b | 6.53 ± 0.19 b | 6.64 ± 0.10 b | |
| pH24h | 5.76 ± 0.30 b | 5.57 ± 0.07 c | 5.67 ± 0.17 bc | 5.98 ± 0.08 a | 5.74 ± 0.16 bc | 5.78 ± 0.27 b | |
| Dripping loss (%) | 1.41 ± 0.29 b | 1.69 ± 0.56 b | 2.26 ± 0.64 a | 1.32 ± 0.29 b | 1.58 ± 0.28 b | 1.65 ± 0.27 b | |
| Cooking loss (%) | 19.29 ± 4.16 c | 23.13 ± 3.37 ab | 25.56 ± 2.83 a | 24.63 ± 2.06 ab | 21.81 ± 2.36 b | 25.97 ± 3.87 a | |
| Species | Guangfeng Cattle | Ji’an Cattle | Jinjiang Cattle | Poyanghu Buffalo | Xiajiang Buffalo | Xinfeng Mountain Buffalo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | |||||||
| Moisture (%) | 73.63 ± 2.29 b | 75.07 ± 2.46 ab | 76.41 ± 0.98 a | 76.69 ± 0.85 a | 75.88 ± 1.16 ab | 75.89 ± 4.92 ab | |
| Protein (%) | 18.46 ± 1.70 b | 19.89 ± 2.33 ab | 21.96 ± 1.03 a | 22.23 ± 1.12 a | 21.30 ± 2.55 a | 21.95 ± 4.73 a | |
| Intramuscular fat (%) | 1.87 ± 0.46 a | 0.91 ± 0.41 bc | 1.20 ± 0.65 b | 0.62 ± 0.29 c | 0.69 ± 0.25 c | 0.51 ± 0.21 c | |
| Ash (%) | 1.06 ± 0.11 a | 1.00 ± 0.08 a | 0.94 ± 0.04 a | 0.97 ± 0.08 a | 1.01 ± 0.07 a | 1.03 ± 0.22 a | |
| Species | Guangfeng Cattle | Ji’an Cattle | Jinjiang Cattle | Poyanghu Buffalo | Xiajiang Buffalo | Xinfeng Mountain Buffalo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/100 g | |||||||
| Aspartate | 1.84 ± 0.12 ab | 1.83 ± 0.17 ab | 1.72 ± 0.11 b | 1.58 ± 0.08 c | 1.71 ± 0.09 b | 1.91 ± 0.16 a | |
| Glutamate | 3.09 ± 0.21 ab | 3.11 ± 0.27 ab | 2.94 ± 0.20 b | 2.66 ± 0.15 c | 2.93 ± 0.11 b | 3.22 ± 0.25 a | |
| Serine | 0.76 ± 0.05 b | 0.78 ± 0.07 ab | 0.73 ± 0.04 b | 0.65 ± 0.04 c | 0.74 ± 0.02 c | 0.82 ± 0.06 a | |
| Glycine | 0.91 ± 0.08 a | 0.89 ± 0.08 a | 0.92 ± 0.08 a | 0.85 ± 0.06 a | 0.89 ± 0.06 a | 0.90 ± 0.08 a | |
| Histidine | 0.79 ± 0.06 b | 0.77 ± 0.06 b | 0.78 ± 0.06 b | 0.74 ± 0.04 b | 0.79 ± 0.03 b | 0.88 ± 0.06 a | |
| Arginine | 1.25 ± 0.09 ab | 1.27 ± 0.12 ab | 1.19 ± 0.08 bc | 1.10 ± 0.06 c | 1.18 ± 0.06 bc | 1.32 ± 0.12 a | |
| Threonine | 0.86 ± 0.06 b | 0.90 ± 0.07 b | 0.83 ± 0.05 b | 0.72 ± 0.05 c | 0.85 ± 0.03 b | 0.97 ± 0.08 a | |
| Alanine | 1.05 ± 0.07 ab | 1.09 ± 0.09 a | 1.00 ± 0.06 b | 0.87 ± 0.07 c | 1.01 ± 0.05 b | 1.12 ± 0.12 a | |
| Proline | 0.99 ± 0.11 bc | 0.93 ± 0.06 c | 1.22 ± 0.07 a | 1.02 ± 0.21 bc | 1.08 ± 0.10 b | 0.93 ± 0.04 c | |
| Tyrosine | 0.75 ± 0.05 a | 0.74 ± 0.06 ab | 0.72 ± 0.04 ab | 0.69 ± 0.05 b | 0.72 ± 0.02 cb | 0.75 ± 0.04 a | |
| Valine | 0.94 ± 0.06 a | 0.91 ± 0.06 a | 0.90 ± 0.05 ab | 0.84 ± 0.06 b | 0.88 ± 0.04 cb | 0.93 ± 0.07 a | |
| Methionine | 0.50 ± 0.03 ab | 0.51 ± 0.04 ab | 0.48 ± 0.03 ab | 0.39 ± 0.05 c | 0.49 ± 0.03 cb | 0.53 ± 0.05 a | |
| Isoleucine | 0.93 ± 0.06 a | 0.93 ± 0.07 a | 0.87 ± 0.05 b | 0.79 ± 0.04 c | 0.86 ± 0.03 b | 0.95 ± 0.09 a | |
| Leucine | 1.58 ± 0.10 ab | 1.59 ± 0.12 ab | 1.50 ± 0.09 b | 1.33 ± 0.07 c | 1.51 ± 0.05 b | 1.67 ± 0.15 a | |
| Cysteine | 0.10 ± 0.03 c | 0.11 ± 0.02 c | 0.19 ± 0.03 ab | 0.11 ± 0.05 c | 0.16 ± 0.05 ab | 0.12 ± 0.04 bc | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.78 ± 0.05 ab | 0.78 ± 0.06 ab | 0.76 ± 0.04 b | 0.69 ± 0.04 c | 0.75 ± 0.02 b | 0.81 ± 0.06 a | |
| Lysine | 2.15 ± 0.16 a | 2.19 ± 0.21 a | 1.89 ± 0.15 b | 1.81 ± 0.09 b | 1.91 ± 0.11 b | 2.27 ± 0.24 a | |
| Umami AA | 4.92 ± 0.33 ab | 4.94 ± 0.43 ab | 4.66 ± 0.31 b | 4.25 ± 0.23 c | 4.63 ± 0.18 b | 5.13 ± 0.43 a | |
| Sweet AA | 4.57 ± 0.33 a | 4.58 ± 0.34 a | 4.70 ± 0.27 a | 4.11 ± 0.35 b | 4.56 ± 0.19 a | 4.73 ± 0.33 a | |
| Bitter AA | 7.52 ± 0.47 ab | 7.48 ± 0.58 ab | 7.19 ± 0.41 b | 6.58 ± 0.36 c | 7.18 ± 0.25 b | 7.84 ± 0.64 a | |
| EAA (%) | 44.29 ± 0.38 b | 44.34 ± 0.27 b | 43.01 ± 0.34 d | 43.39 ± 0.42 cd | 43.57 ± 0.34 c | 43.31 ± 0.62 a | |
| NEAA (%) | 55.17 ± 0.33 c | 55.07 ± 0.32 c | 55.99 ± 0.36 a | 55.95 ± 0.25 a | 55.56 ± 0.30 b | 54.55 ± 0.65 d | |
| EAA/NEAA | 0.80 ± 0.01 b | 0.81 ± 0.02 b | 0.77 ± 0.01 d | 0.78 ± 0.01 cd | 0.78 ± 0.01 c | 0.82 ± 0.02 a | |
| Species | Guangfeng Cattle | Ji’an Cattle | Jinjiang Cattle | Poyanghu Buffalo | Xiajiang Buffalo | Xinfeng Mountain Buffalo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 g/kg | |||||||
| C8:0 | 47.10 ± 14.01 b | 52.25 ± 25.67 b | 79.92 ± 26.62 a | 34.67 ± 16.61 b | 38.76 ± 13.02 b | 44.66 ± 15.20 b | |
| C10:0 | 23.59 ± 6.17 b | 29.98 ± 9.53 ab | 30.96 ± 9.94 ab | 34.37 ± 15.47 a | 29.53 ± 4.67 ab | 25.56 ± 7.45 ab | |
| C14:0 | 133.81 ± 142.78 a | 53.67 ± 22.81 bc | 115.06 ± 36.83 ab | 44.46 ± 18.16 c | 63.39 ± 26.68 bc | 24.01 ± 9.65 c | |
| C16:0 | 631.09 ± 236.12 ab | 510.27 ± 208.59 bc | 788.90 ± 315.35 a | 349.89 ± 92.57 cd | 278.09 ± 65.37 d | 293.12 ± 37.71 d | |
| C16:1 | 58.42 ± 25.90 abc | 71.67 ± 40.69 ab | 79.68 ± 35.72 a | 36.12 ± 7.68 c | 44.46 ± 9.00 bc | 46.18 ± 35.68 bc | |
| C17:0 | 59.80 ± 28.57 c | 88.48 ± 29.06 b | 132.66 ± 26.83 a | 138.06 ± 41.84 a | 65.63 ± 6.58 bc | 137.54 ± 27.44 a | |
| C18:0 | 543.37 ± 160.51 a | 355.03 ± 136.21 b | 559.49 ± 196.47 a | 389.76 ± 124.24 b | 272.73 ± 69.81 b | 294.02 ± 114.83 b | |
| C18:1n9c | 873.61 ± 437.44 ab | 789.80 ± 358.35 abc | 1110.85 ± 548.96 a | 543.05 ± 319.91 bc | 588.26 ± 203.17 bc | 460.55 ± 119.41 c | |
| C18:2n6c | 402.57 ± 114.11 a | 181.24 ± 78.40 c | 294.31 ± 79.08 b | 309.03 ± 36.40 b | 198.70 ± 31.28 c | 246.53 ± 65.11 bc | |
| C18:3n3 | 104.32 ± 25.62 b | 50.01 ± 18.32 c | 57.43 ± 23.28 c | 68.82 ± 12.22 c | 125.51 ± 14.22 a | 55.96 ± 18.04 c | |
| C20:3n6 | 37.99 ± 15.61 c | 45.69 ± 23.90 bc | 67.90 ± 30.47 a | 61.46 ± 16.37 ab | 41.72 ± 16.27 bc | 51.55 ± 22.74 abc | |
| C20:4n6 | 161.87 ± 38.56 ab | 139.77 ± 55.81 ab | 127.73 ± 37.98 b | 179.28 ± 53.76 a | 146.54 ± 19.83 ab | 149.59 ± 50.14 ab | |
| C20:5n3 | 41.22 ± 14.63 b | 44.53 ± 20.78 b | 49.02 ± 16.06 b | 95.63 ± 15.99 a | 46.14 ± 21.47 b | 80.78 ± 21.16 a | |
| C22:2n6 | 108.42 ± 49.65 b | 84.03 ± 48.60 b | 136.86 ± 68.07 b | 218.08 ± 89.49 a | 100.43 ± 19.15 b | 79.79 ± 29.66 b | |
| C22:6n3 | 18.25 ± 11.27 b | 16.91 ± 10.57 b | 26.04 ± 11.62 ab | 31.23 ± 11.19 a | 30.74 ± 13.60 a | 20.27 ± 11.41 ab | |
| C24:0 | 10.36 ± 3.46 a | 11.45 ± 5.92 a | 12.55 ± 3.83 a | 8.93 ± 3.69 a | 12.29 ± 5.72 a | 12.77 ± 4.63 a | |
| C24:1n9 | 19.94 ± 13.31 a | 15.19 ± 6.12 a | 13.67 ± 11.93 a | 14.32 ± 6.79 a | 17.10 ± 9.15 a | 14.84 ± 8.66 a | |
| SFA | 1449.12 ± 481.38 a | 1101.13 ± 311.66 b | 1719.54 ± 522.87 a | 1000.14 ± 196.94 b | 760.42 ± 125.95 b | 831.68 ± 131.33 b | |
| UFA | 1826.61 ± 373.31 ab | 1438.64 ± 221.49 cd | 1963.49 ± 580.01 a | 1557.02 ± 219.46 bc | 1339.60 ± 224.76 cd | 1206.04 ± 90.63 d | |
| MUFA | 951.97 ± 454.21 ab | 876.66 ± 383.62 abc | 1204.20 ± 581.54 a | 593.49 ± 321.57 bc | 649.82 ± 201.54 bc | 521.57 ± 131.99 c | |
| PUFA | 874.64 ± 123.47 ab | 562.18 ± 195.21 d | 759.29 ± 105.93 bc | 963.53 ± 150.57 a | 689.78 ± 65.40 cd | 684.47 ± 127.40 cd | |
| UFA/SFA | 1.34 ± 0.26 c | 1.37 ± 0.25 c | 1.15 ± 0.09 d | 1.57 ± 0.12 b | 1.77 ± 0.13 a | 1.48 ± 0.23 bc | |
| PUFA/SFA | 0.70 ± 0.32 bc | 0.59 ± 0.32 c | 0.48 ± 0.15 c | 1.01 ± 0.27 a | 0.92 ± 0.11 ab | 0.85 ± 0.21 ab | |
| MUFA/PUFA | 1.17 ± 0.70 b | 2.16 ± 1.85 a | 1.63 ± 0.91 ab | 0.68 ± 0.51 b | 0.94 ± 0.28 b | 0.82 ± 0.33 b | |
| PUFA n = 3 | 163.79 ± 22.55 b | 111.45 ± 31.80 d | 132.49 ± 28.52 cd | 195.68 ± 23.29 a | 202.39 ± 30.72 a | 157.01 ± 35.50 bc | |
| PUFA n = 6 | 710.85 ± 111.64 ab | 450.73 ± 167.37 d | 626.80 ± 115.02 bc | 767.85 ± 135.31 a | 487.39 ± 55.39 d | 527.46 ± 132.38 cd | |
| n6:n3 ratio | 4.38 ± 0.70 a | 3.99 ± 0.59 a | 5.11 ± 0.89 a | 3.93 ± 0.85 a | 2.46 ± 0.92 b | 3.72 ± 0.85 a | |
| Species | Guangfeng Cattle | Ji’an Cattle | Jinjiang Yellow Cattle | Poyanghu Buffalo | Xiajiang Buffalo | Xinfeng Mountain Buffalo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | |||||||
| Fiber diameter (μm) | 47.42 ± 5.73 a | 49.55 ± 5.52 a | 50.02 ± 2.92 a | 43.17 ± 5.73 ab | 35.47 ± 5.24 c | 38.42 ± 3.48 bc | |
| Fiber cross-sectional area (μm2) | 2333.53 ± 605.48 a | 2546.02 ± 553.01 a | 2537.49 ± 328.52 a | 1897.01 ± 503.11 ab | 1302.31 ± 397.58 b | 1594.60 ± 358.18 b | |
| Fiber density (N/mm2) | 324.09 ± 22.10 bc | 412.32 ± 79.30 bc | 354.83 ± 50.01 c | 535.74 ± 112.57 a | 533.29 ± 102.10 a | 488.50 ± 84.34 ab | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lu, G.; Yang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Fu, C.; Tian, F.; Qiu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Study on the Carcass Traits, Meat Quality, and Nutritional Attributes of Six Kinds of Jiangxi Local Breeds Cattle. Animals 2024, 14, 3053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213053
Zhang Y, Wei Y, Lu G, Yang Y, Pan Y, Fu C, Tian F, Qiu Q, Zhao X, Li Y, et al. Study on the Carcass Traits, Meat Quality, and Nutritional Attributes of Six Kinds of Jiangxi Local Breeds Cattle. Animals. 2024; 14(21):3053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213053
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yang, Yuting Wei, Guwei Lu, Youxiang Yang, Yuting Pan, Chuanpei Fu, Fazhan Tian, Qinghua Qiu, Xianghui Zhao, Yanjiao Li, and et al. 2024. "Study on the Carcass Traits, Meat Quality, and Nutritional Attributes of Six Kinds of Jiangxi Local Breeds Cattle" Animals 14, no. 21: 3053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213053
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wei, Y., Lu, G., Yang, Y., Pan, Y., Fu, C., Tian, F., Qiu, Q., Zhao, X., Li, Y., Chen, L., Wang, W., & Ouyang, K. (2024). Study on the Carcass Traits, Meat Quality, and Nutritional Attributes of Six Kinds of Jiangxi Local Breeds Cattle. Animals, 14(21), 3053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14213053






