Impact of Nutritional Tea Polyphenols on Growth, Feed Efficiency, Biochemical Traits, Antioxidant Capacity, Haematological Parameters and Immunity in Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feed Ingredients and Test Diets
2.2. Experimental Conditions
2.3. Growth Performance
2.4. Sampling Procedures
2.5. Proximate Composition Analysis
2.6. Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.7. Measurement of Antioxidant Status
2.8. Hematological Parameters
2.9. Immunological Parameters
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth, Feeding Performances, and Survival
3.2. Proximate Composition
3.3. Biochemical Blood Parameters
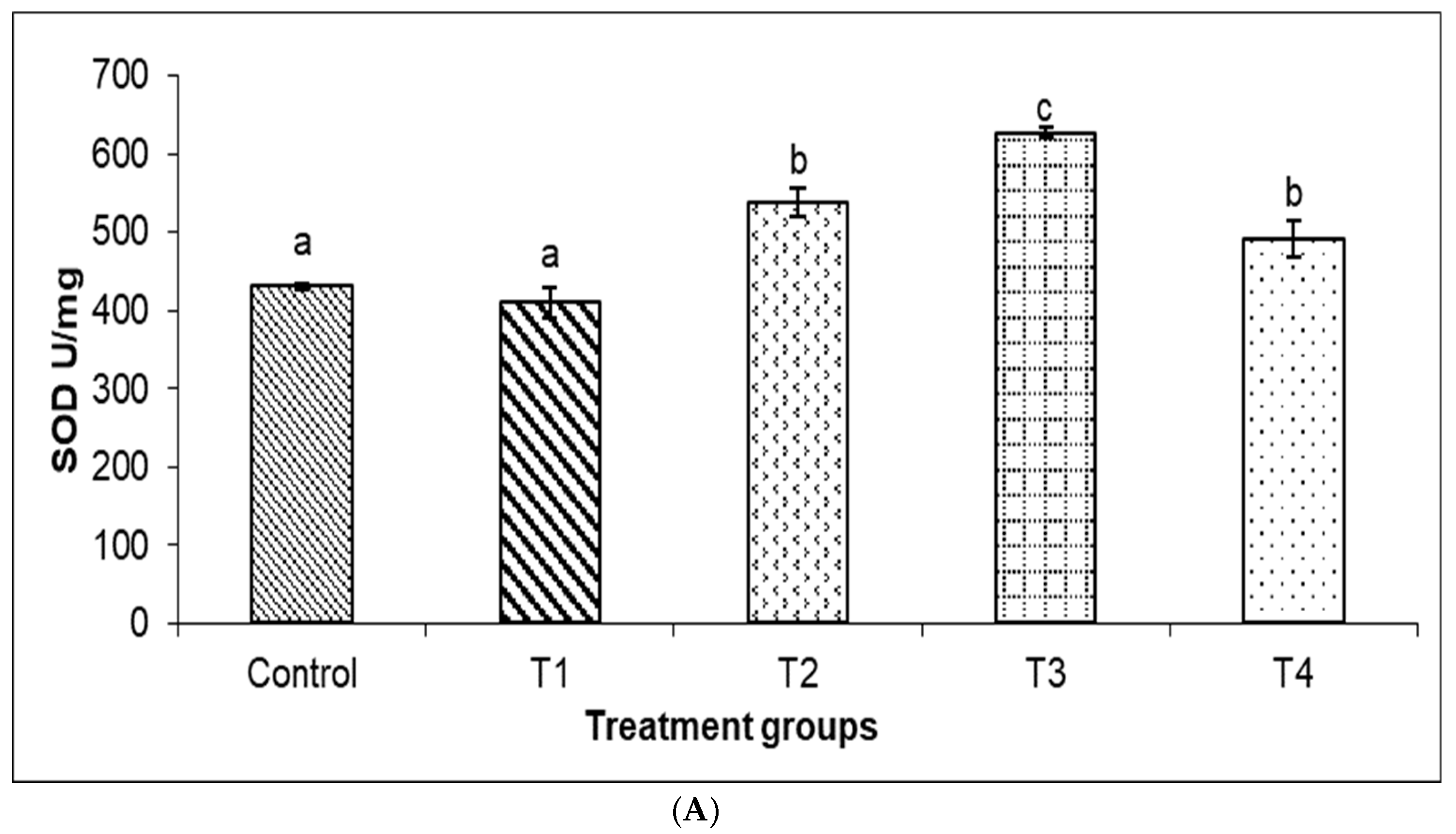
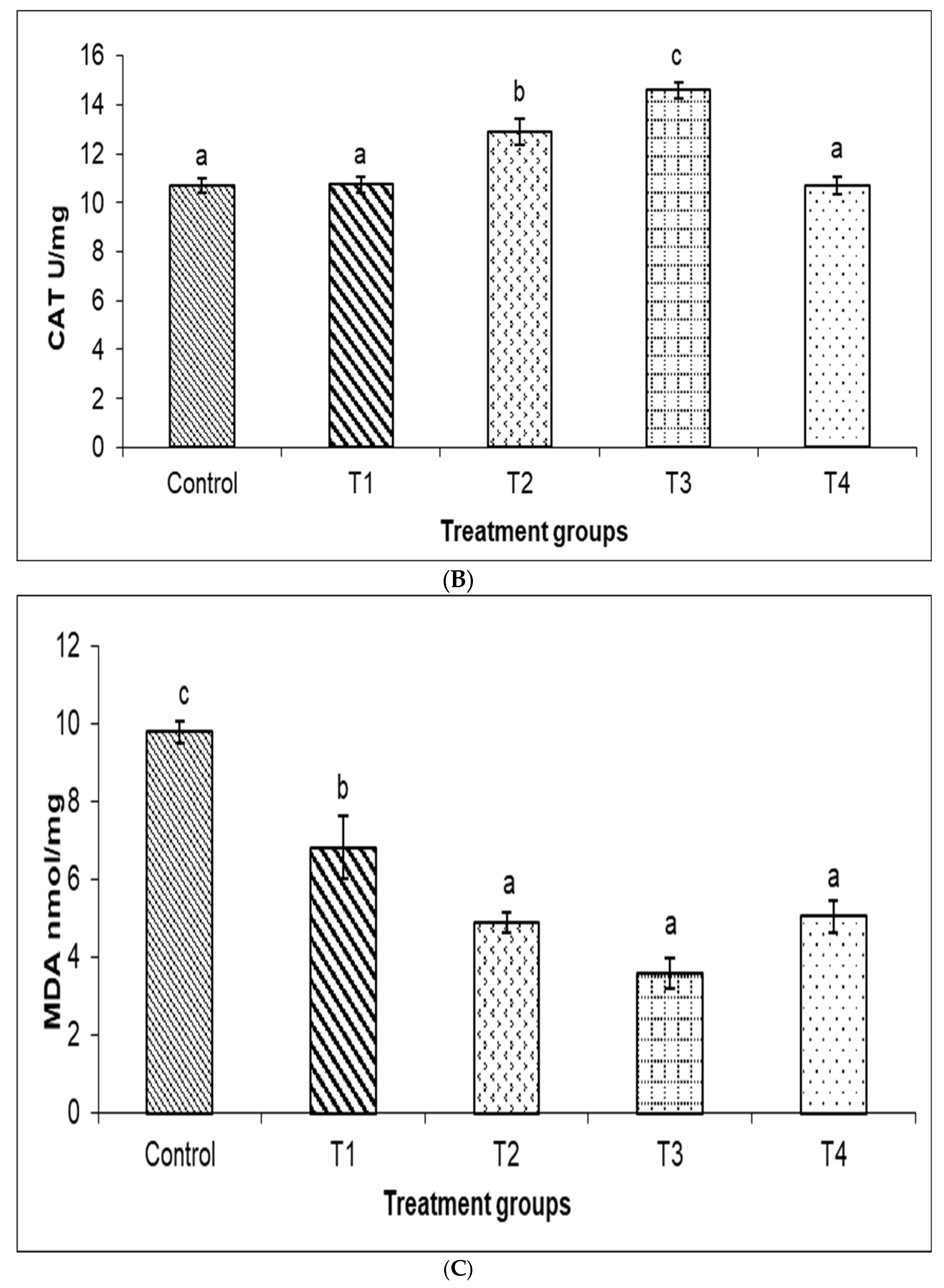
3.4. Antioxidant Enzyme Parameters
3.5. Hematological Parameters
3.6. Immunological Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuraini, A.; Somchit, M.N.; Solihah, M.H.; Goh, Y.M.; Arifah, A.K.; Zakaria, M.S.; Mat-Jais, A.M. Fatty acid and amino acid composition of three local Malaysian Channa spp. fish. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.; Oliveira, M.C.; Attia, Y.A.; Kamal, M.; Almohmadi, H.A.; Youssef, I.M.; Khalifa, N.E.; Moustafa, M.; Al-Shehri, M.; Taha, A.E. The efficacy of polyphenols as an antioxidant agent: An updated review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouarab-Chibane, L.; Forquet, V.; Lantéri, P.; Clément, Y.; Léonard-Akkari, L.; Oulahal, N.; Degraeve, P.; Bordes, C. Antibacterial Properties of Polyphenols: Characterization and QSAR (Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship) Models. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, R. Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H. Biological potential and mechanisms of Tea’s bioactive compounds: An Updated review. J. Adv. Res. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.B.; Wan, X.C.; Shang, Y.Y.; Hu, J.W.; Shao, L.; Chen, W.; Li, D.X. Polyphenol content of plasma and litter after the oral administration of green tea and tea polyphenols in chickens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.M.; Wan, X.C.; Zhan, J.F.; Ho, C.T. Focusing on the recent progress of tea polyphenol chemistry and perspectives. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 11, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, D.O.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, L. A Review on the Weight-Loss Effects of Oxidized Tea Polyphenols. Molecules 2018, 23, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.; Noh, S. Green tea as inhibitor of the intestinal absorption of lipids: Potential mechanism for its lipid-lowering effect. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Ahmad, M.H.; Seden, M.E.A. Use of green tea, Camellia sinensis L., in Practical diet for growth and protection of nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.), against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2010, 41, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ngada, R.S.; Abdel-Wahab, A.M.; El-Bahr, S.M. Effect of Dietary supplementation of Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) on Growth, Body Composition and Serum Biochemistry of the Asian Seabass, Lates calcarifer Fingerlings. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2017, 8, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meguro, S.; Hasumura, T.; Hase, T. Body fat accumulation in zebrafish is induced by a diet rich in fat and reduced by supplementation with green tea extract. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yue, H.; Ruan, R.; Ye, H.; Li, Z.; Li, C. Dietary Epiallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) improves non-specific immune response of Chinese rice field eel (Monopterus albus). Aquac. Nutr. 2023, 2023, 6512136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, T.L.; Wan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Overturf, K.; Barrows, K.; Liu, K. Effect of dietary green tea supplementation on growth, fat content, and muscle fatty acid profile of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1073–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, J.L. Pacific Fishes of Canada. Bull. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1973, 180, 1–740, reprinted in Bull. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1975, 1980, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture-Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.R.; Guo, M.J.; Yu, L.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Wang, Q.H.; Li, F.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.Y.; Hou, J.Y. Effects of Dietary Riboflavin Supplementation on the Growth Performance, Body Composition and Anti-Oxidative Capacity of Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) Post-Smolts. Animals 2022, 12, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Hu, Y.J.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.L.; Tian, Y.N.; Chen, J.S.; Ai, Q.H.; Xiao, T.Y. Effects of dietary tea polyphenols on growth, immunity and lipid metabolism of juvenile black carp Mylopharyngodon piceus. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Bagher, D.; Hoseinifer, S.H.; Morshedi, V.; Paolucci, M. Benefical role of polyphenols as feed additives on growth performances, immune response and antioxidant status of Lates calcarifer (Bloch, 1790) juveniles. Aquaculture 2022, 552, 737955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yu, H.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, S.; Fan, X.; Fan, Y.; Shan, L. Dietary vitamin A requires of coho salmon Oncorhynchus kisutch (Walbaum, 1792) post smolts. Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H. Effect of Dietary Manganese on the Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism, and Antioxidant Capacity in the Post-Larval Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Animals 2023, 13, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natt, M.P.; Herrick, C.A. A new blood diluent for counting the erythrocytes and leucocytes of the chicken. Poult. Sci. 1952, 31, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, A.; Ahmad, S.Z. Hematological and serum biochemical parameters of five freshwater snow trout fish species from river Jhelum of Kashmir Himalaya, India. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 28, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukmechi, A.; Andani, R.; Manaffar, H.R.; Sheikhzadeh, R. Dietary administration of Beta-mercapto-ethanol treated Saccharomyces cerevisiae enhanced the growth, innate immune response and disease resistance of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamil, L.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Immunomodulatory effects of nisin in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2003, 14, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasiack, A.S.; Bauman, C.P. Neutrophil activity as a potent indicator for concomitant analysis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1996, 37, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, D.G.; Haminiuk, C.W.I.; Pedro, A.C.; Fernandes, I.A.A.; Maciel, G.M. Processing, chemical signature and food industry applications of Camellia sinensis teas: An overview. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kai, L.; Wei, F.; Dan, X.; Kangsen, M.; Qinghui, A. Effects of tea polyphenols on growth, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism related gene expression of turbot (Scopthalmus maximus). J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 2405–2412. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, N.; Araki, T.; Tamaru, Y.; Inoue, M. Influence of green tea polyphenols on feed performance, growth performance, and fish body component in yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata). Jpn. J. Food Chem. 2002, 9, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.; Lee, S.; Rha, S.; Yoon, H.; Park, H.; Han, K.; Kim, S. Dietary green tea extract improves growth performance, body composition, and stress recovery in the juvenile black rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli. Aquac. Int. 2013, 21, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q. Effects of dietary tea polyphenols on growth, biochemical and antioxidant responses, fatty acid composition and expression of lipid metabolism related genes of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.C.; Wang, X.; Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Limbu, S.M.; Li, R.X.; Zhou, W.H.; Qiao, F.; Zhang, F.M.; Du, Z.Y. Different effects of two dietary levels of tea polyphenols on the lipid deposition, immunity and antioxidant capacity of juvenile GIFT tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed a high-fat diet. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, P.; Sean, L.; Tibbetts, N. Nutrition, Feeding, and Behavior of Fish. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2009, 12, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E. Effects of green tea extracts on freshwater angelfish, Pterophyllum scalare growth performance. Mar. Sci. Technol. Bull. 2017, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Lee, S.M.; Park, B.H.; Ji, S.C.; Lee, J.; Bae, J.; Oh, S.Y. Effect of dietary inclusion of various sources of green tea on growth, body composition and blood chemistry of the juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 33, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, Y.; Ji, H.; Yu, H. The effect of green tea waste on growth and health of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 16, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thawonsuwan, J.; Kiron, V.; Satoh, S.; Panigrahi, A.; Verlhac, V. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) affects the antioxidant and immune defense of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 36, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cory, H.; Passarelli, S.; Szeto, J.; Tamez, M.; Mattei, J. The role of polyphenols in human health and food systems: A mini-review. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocher, D.R. Fatty acid requirements in ontogeny of marine and freshwater fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Grajales, S.; Muriel, P. Antioxidants in liver health. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 6, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Lambert, J.D.; Sang, S. Antioxidative and anti-carcinogenic activities of tea polyphenols. Arch. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Xu, M.M.; Kang, K.K.; Tang, S.G.; Guo, S.C. The effects and combinational effects of Bacillus subtilis and montmorillonite on the intestional health status in laying hens. Poultry Sci. 2020, 99, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nootash, S.; Sheikhzadeh, N.; Baradaran, B.; Oushani, A.K.; Moghadam, M.R.M.; Nofouzi, K.; Monfaredan, A.; Aghebati, L.; Zare, F.; Shabanzadeh, F. Green tea (Camellia sinensis) administration induces expression of immune relevant genes and biochemical parameters in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Lin, W.; Hou, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Li, D. The protective roles of dietary selenium yeast and tea polyphenols growth performance and ammonia tolerance of juvenile Wucheng Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witeska, M.; Kondera, E.; Ługowska, K.; Bojarski, B. Hematological methods in fish–Not only for beginners. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, D.M.; Zaccone, G.; Alesci, A.; Kuciel, M.; Hussein, M.T.; Sayed, R.K.A. Main Components of Fish Immunity: An Overview of the Fish Immune System. Fishes 2023, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A. Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against viruses and bacteria. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, R.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Imanpour, M.R.; Mazandarani, M.; Sanchouli, H.; Paolucci, M. Effects of dietary polyphenols on mucosal and humoral immune responses, antioxidant defense and growth gene expression in beluga sturgeon (Huso huso). Aquaculture 2020, 52H8, 735494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Jahazi, M.A.; Nikdehghan, N.; Doan, H.V.; Volpe, M.G.; Paolucci, P. Effects of dietary polyphenols from agricultural by-products on mucosal and humoral immune and antioxidant responses of convict cichlid (Amatitlania nigrofasciata). Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, S.; Salati, A.P.; Falahatkar, B.; Azarm, A.M. Effect of green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) on growth, blood and immune parameters in sturgeon hybrid (Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus) fed oxidized fish oil. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 17, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, E.M.; Rahmani, A.H.; Aly, S.M. Immunostimulants and fish culture: An overview. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2015, 5, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory role of polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, C.M.; Sandrasaigaran, P.; Tong, C.K.; Adam, A.; Ramasamy, R. Immunomodulatory activity of polyphenols derived from Cassia auriculata flowers in aged rats. Cell. Immunol. 2011, 271, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meydani, M.; Hasan, S.T. Dietary polyphenols and obesity. Nutrients 2010, 2, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Jiang, H.; Fang, J. Regulation of immune function by polyphenols. J. Immmunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1264074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikhzadeh, N.; Nofouzi, K.; Delazar, A.; Oushani, A. Immunomodulatory effects of decaffeinated green tea (Camellia sinensis) on the immune system of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 1268–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, R.; Balasundaram, C.; Heo, M.S. Influence of diet enriched with green tea on innate humoral and cellular immune response of kelp grouper (Epinephelus bruneus) to Vibrio carchariae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Control | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IW (g) | 180.43 ± 0.23 | 180.6 ± 0.20 | 180.33 ± 0.131 | 180.53 ± 0.17 | 180.7 ± 0.05 |
| FW (g) | 461.56 ± 2.23 a | 494.01 ± 10.6 b | 531 ± 4.06 c | 567.55 ± 9.14 d | 531.59 ± 3.17 c |
| FL (cm) | 32.33 ± 0.67 a | 35.33 ± 0.17 bc | 37.6 ± 0.55 d | 33.3 ± 0.75 ab | 36 ± 0.89 cd |
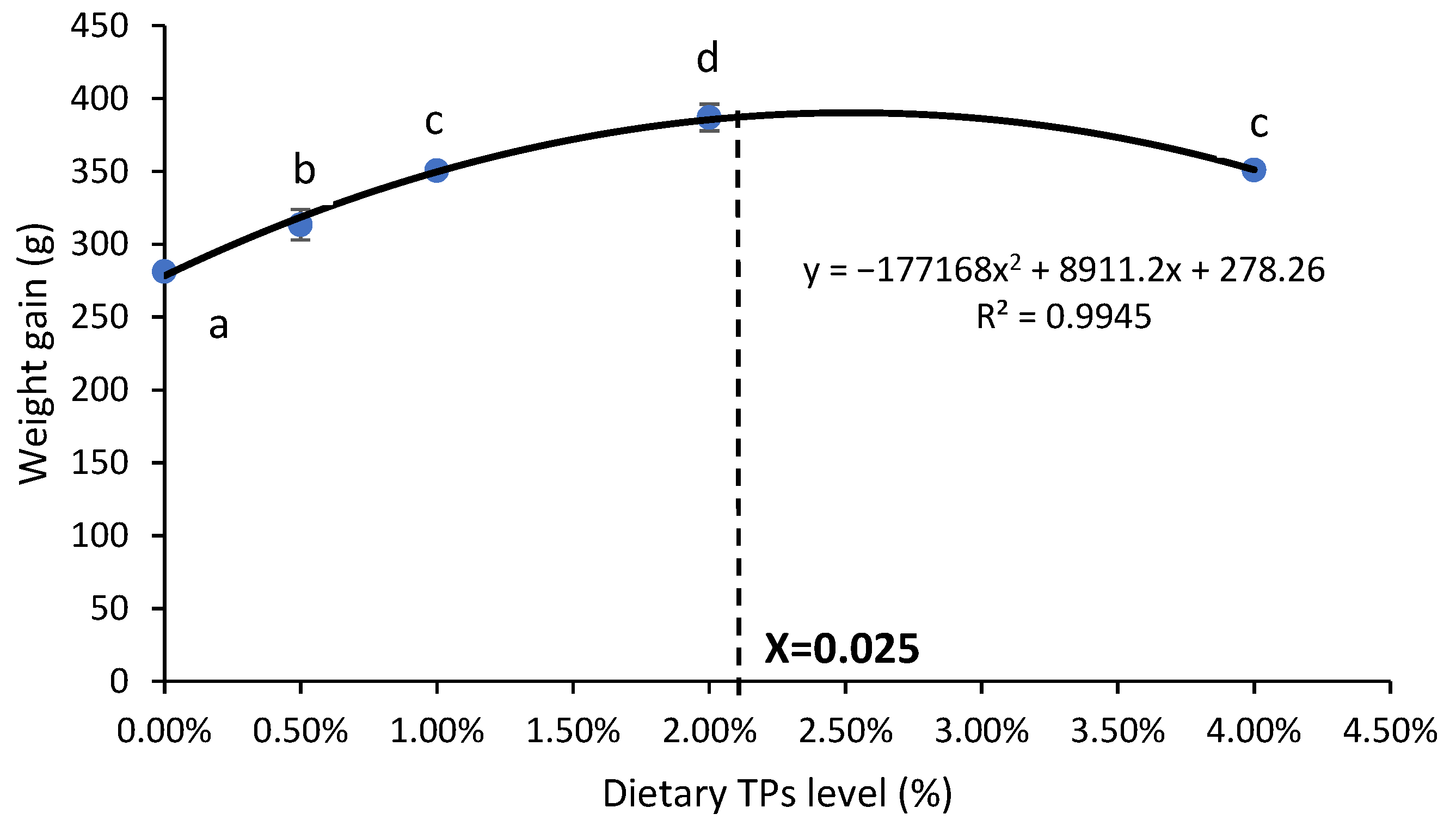
| WG (g) | 281.13 ± 2.46 a | 313.41 ± 10.52 b | 350.66 ± 3.94 c | 387.02 ± 9.10 d | 350.89 ± 3.21 c |
| RGR (%) | 155.81 ± 1.56 a | 173.53 ± 5.64 b | 194.45 ± 2.05 c | 214.37 ± 4.99 d | 194.18 ± 1.82 c |
| DGR (g/day) | 4.01 ± 0.03 a | 4.47 ± 0.15 b | 5.00 ± 0.05 c | 5.52 ± 0.13 d | 5.01 ± 0.04 c |
| SGR (%/day) | 1.34 ± 0.08 a | 1.43 ± 0.02 b | 1.54 ± 0.09 c | 1.63 ± 0.02 d | 1.54 ± 0.08 c |
| FCR | 1.79 ± 0.18 d | 1.61 ± 0.05 c | 1.44 ± 0.01 b | 1.30 ± 0.02 a | 1.44 ± 0.013 b |
| FE (%) | 55.65 ± 0.55 a | 61.97 ± 2.03 b | 69.44 ± 0.73 c | 76.56 ± 1.78 d | 69.35 ± 0.65 c |
| CF (%) | 1.37 ± 0.09 | 1.11 ± 0.018 | 1.00 ± 0.04 | 1.54 ± 0.12 | 1.14 ± 0.08 |
| HSI (%) | 1.21 ± 0.04 | 1.53 ± 0.088 | 1.47 ± 0.07 | 1.21 ± 0.22 | 1.43 ± 0.27 |
| VSI (%) | 7.12 ± 0.31 ab | 8.63 ± 0.58 b | 7.36 ± 0.50 ab | 5.84 ± 0.72 a | 7.24 ± 0.49 ab |
| SR (%) | 93.3 ± 6.67 | 96.6 ± 3.33 | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 |
| Parameters | Control | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude lipid (%) | 9.70 ± 0.007 b | 9.62 ± 0.03 ab | 9.23 ± 0.01 a | 9.74 ± 0.01 b | 9.67 ± 0.08 ab |
| Crude protein (%) | 14.15 ± 0.05 b | 14.21 ± 0.07 b | 13.61 ± 0.10 a | 14.28 ± 0.23 b | 13.93 ± 0.03 ab |
| Ash (%) | 2.71 ± 0.09 | 2.34 ± 0.04 | 2.35 ± 0.02 | 2.26 ± 0.05 | 2.30 ± 0.84 |
| Moisture (%) | 77.15 ± 0.09 | 77.00 ± 0.11 | 77.99 ± 0.16 | 76.94 ± 0.36 | 77.48 ± 0.06 |
| Parameters | Control | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT (U/mL) | 6.82 ± 0.11 d | 5.02 ± 0.50 c | 1.89 ± 0.30 a | 0.90 ± 0.05 a | 3.04 ± 0.39 b |
| GOT (U/mL) | 15.30 ± 1.62 | 16.01 ± 1.60 | 14.78 ± 1.56 | 16.99 ± 1.00 | 11.89 ± 4.9 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 1.60 ± 0.08 ab | 4.38 ± 0.40 d | 3.14 ± 0.56 c | 0.97 ± 0.10 a | 2.42 ± 0.122 bc |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 1.75 ± 0.16 | 1.43 ± 0.10 | 1.24 ± 0.11 | 1.03 ± 0.17 | 1.47 ± 0.40 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 1.76 ± 0.13 ab | 1.53 ± 0.09 abc | 1.21 ± 0.12 a | 1.39 ± 0.19 ab | 1.95 ± 0.15 c |
| TC (mg/dL) | 16.46 ± 1.78 | 12.57 ± 0.33 | 10.8 ± 1.20 | 10.06 ± 0.42 | 10.46 ± 4.10 |
| ALP (U/mL) | 3.41 ± 0.40 | 4.03 ± 0.25 | 3.67 ± 0.31 | 4.03 ± 0.24 | 3.28 ± 0.55 |
| CAT (U/mL) | 6.88 ± 0.40 a | 7.13 ± 1.39 a | 15.96 ± 0.66 b | 18.54 ± 0.16 b | 9.41 ± 3.62 a |
| Treatment | Control | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (106/mm3) | 1.56 ± 0.60 b | 1.91 ± 0.01 ab | 2.14 ± 0.01 a | 2.24 ± 0.005 b | 2.11 ± 0.018 ab |
| WBC (103/mm3) | 12.53 ± 0.11 b | 13.34 ± 0.09 b | 1.85 ± 0.04 a | 14.20 ± 0.03 b | 12.87 ± 0.24 ab |
| Hb (g/dL) | 8.86 ± 0.17 a | 9.27 ± 0.03 b | 10.33 ± 0.09 c | 11.19 ± 0.08 e | 10.75 ± 0.06 d |
| Hct (%) | 28.57 ± 0.03 b | 25.88 ± 0.32 a | 28.14 ± 0.40 b | 30.74 ± 0.40 c | 28.48 ± 0.02 b |
| MCV (fl) | 182.93 ± 7.17 b | 135.15 ± 1.17 a | 131.34 ± 1.02 a | 137.04 ± 1.79 a | 134.64 ± 1.13 a |
| MCH (pg) | 56.79 ± 3.10 | 48.45 ± 0.23 | 48.23 ± 0.38 | 49.74 ± 0.38 | 50.84 ± 0.69 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 31.02 ± 0.64 a | 35.85 ± 0.45 a | 36.72 ± 0.37 b | 36.30 ± 0.21 a | 37.75 ± 0.26 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Sattanathan, G.; Yu, L.; Li, L.; Xiao, Y. Impact of Nutritional Tea Polyphenols on Growth, Feed Efficiency, Biochemical Traits, Antioxidant Capacity, Haematological Parameters and Immunity in Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Animals 2024, 14, 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142104
Yu H, Sattanathan G, Yu L, Li L, Xiao Y. Impact of Nutritional Tea Polyphenols on Growth, Feed Efficiency, Biochemical Traits, Antioxidant Capacity, Haematological Parameters and Immunity in Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Animals. 2024; 14(14):2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142104
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hairui, Govindharajan Sattanathan, Leyong Yu, Lingyao Li, and Yufang Xiao. 2024. "Impact of Nutritional Tea Polyphenols on Growth, Feed Efficiency, Biochemical Traits, Antioxidant Capacity, Haematological Parameters and Immunity in Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch)" Animals 14, no. 14: 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142104
APA StyleYu, H., Sattanathan, G., Yu, L., Li, L., & Xiao, Y. (2024). Impact of Nutritional Tea Polyphenols on Growth, Feed Efficiency, Biochemical Traits, Antioxidant Capacity, Haematological Parameters and Immunity in Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Animals, 14(14), 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142104







