Evolutionary Patterns of Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy and Implantation in Eutherian Mammals
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preimplantation Development
3. Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy
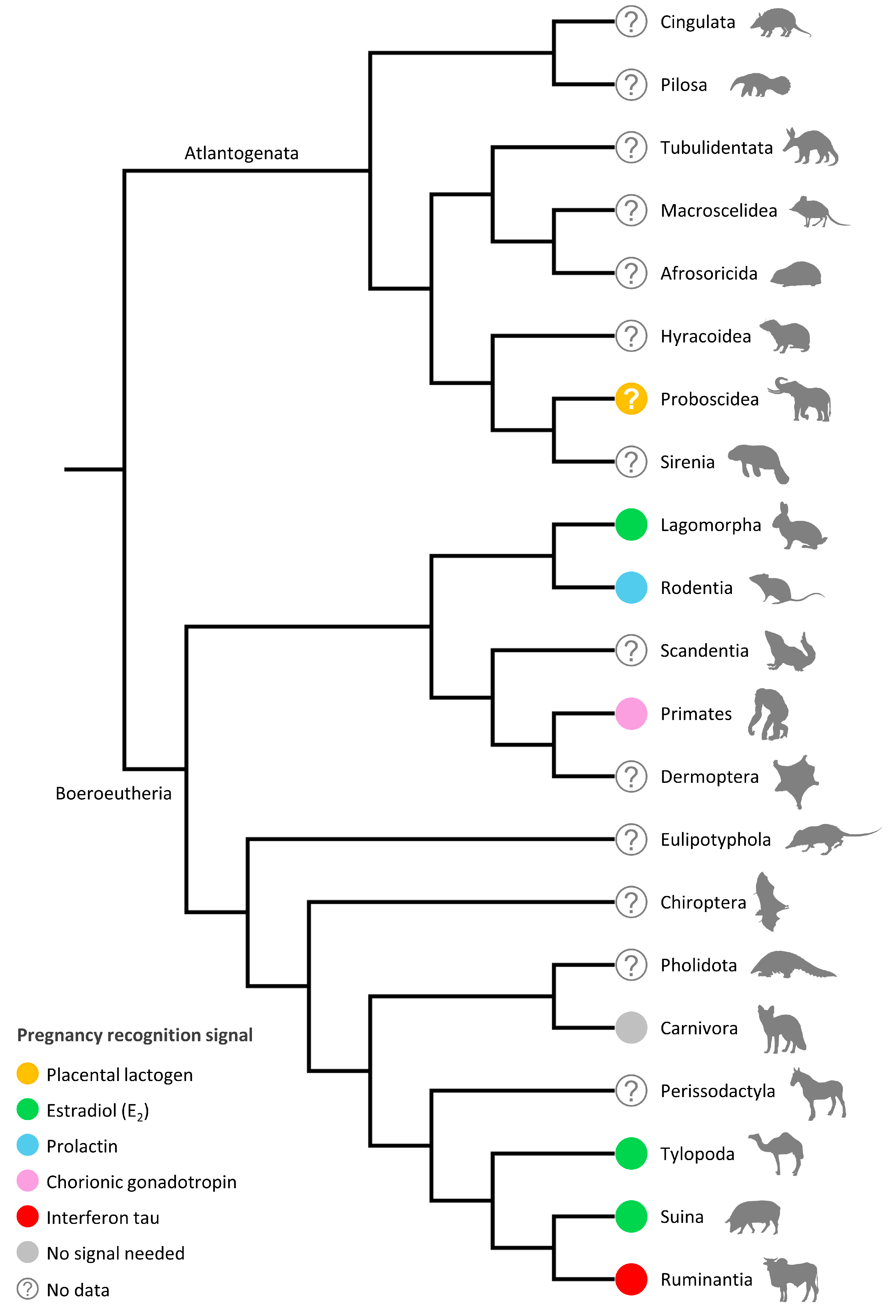
4. Implantation
4.1. Mechanisms and Modes of Implantation
4.2. Patterns of Evolutionary Change in Implantation Modes

5. Concluding Remarks and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blackburn, D.G. Evolution of Vertebrate Viviparity and Specializations for Fetal Nutrition: A Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis. J. Morphol. 2015, 276, 961–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.F.; Thompson, M.B. A Review of the Evolution of Viviparity in Squamate Reptiles: The Past, Present and Future Role of Molecular Biology and Genomics. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2011, 181, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazer, F.W.; Spencer, T.E.; Johnson, G.A.; Burghardt, R.C.; Wu, G. Comparative Aspects of Implantation. Reproduction 2009, 138, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazer, F.W. History of Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy. In Regulation of Implantation and Establishment of Pregnancy in Mammals: Tribute to 45 Year Anniversary of Roger V. Short’s “Maternal Recognition Of pregnancy"; Geisert, R.D., Fuller, F.W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 5–25. [Google Scholar]
- Psychoyos, A. Endocrine Control of Egg Implantation. In Handbook of Physiology; Greep, R.O., Astwood, E.G., Geiger, S.R., Eds.; American Physiological Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1973; pp. 187–215. [Google Scholar]
- Bazer, F.W.; Simmen, R.C.M.; Simmen, F.A. Comparative Aspects of Conceptus Signals for Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 622, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, P.W.; Diaz, D.; Alarcón, V.; Ordoñez, C. Effect of the Reproductive State of Female Alpacas on Embryonic Mortality Rate. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2010, 71, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, K.J.; Schust, D.J. Genetic Considerations in Recurrent Pregnancy Loss. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a023119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardong, K.V. Vertebrates: Comparative Anatomy, Function, Evolution, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Seshagiri, P.B.; Sen Roy, S.; Sireesha, G.; Rao, R.P. Cellular and Molecular Regulation of Mammalian Blastocyst Hatching. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2009, 83, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senger, P.L. Pathways to Pregnancy and Parturition, 2nd Revised ed.; Current Conceptions, Inc.: Pullman, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Paulson, E.E.; Comizzoli, P. Endometrial Receptivity and Embryo Implantation in Carnivores—Commonalities and Differences with Other Mammalian Species. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 104, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piliszek, A.; Madeja, Z.E. Pre-Implantation Development of Domestic Animals. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology: Cell Fate in Mammalian Development; Plusa, B., Hadjantonakis, A.-K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; Volume 128, pp. 267–294. [Google Scholar]
- Wimsatt, W.A. Some Comparative Aspects of Implantation. Biol. Reprod. 1975, 12, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renfree, M.B.; Fenelon, J.C. The Enigma of Embryonic Diapause. Development 2017, 144, 3199–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renfree, M.B.; Shaw, G. Diapause. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000, 62, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowen, M.R.; Erez, O.; Romero, R.; Wildman, D.E. The Evolution of Embryo Implantation. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 58, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenelon, J.C.; Banerjee, A.; Murphy, B.D. Embryonic Diapause: Development on Hold. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 58, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; DeMayo, F.J. Animal Models of Implantation. Reproduction 2004, 128, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norwitz, E.R.; Schust, D.J.; Fisher, S.J. Implantation and the Survival of Early Pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.A.; Geisert, R.D.; Johnson, G.A.; Spencer, T.E. Implantation and Placentation in Ruminants. In Placentation in Mammals: Tribute to E. C. Amoroso’s Lifetime Contributions to Viviparity; Geisert, R.D., Spencer, T.E., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 129–154. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, G.A.; Bazer, F.W.; Seo, H. The Early Stages of Implantation and Placentation in the Pig. In Placentation in Mammals: Tribute to E. C. Amoroso’s Lifetime Contributions to Viviparity; Geisert, R.D., Spencer, T.E., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 234, pp. 61–89. [Google Scholar]
- Antczak, D.F.; Allen, W.R. Placentation in Equids. In Placentation in Mammals: Tribute to E. C. Amoroso’s Lifetime Contributions to Viviparity; Geisert, R.D., Spencer, T.E., Eds.; Springer Nature: Gewerbestrasse, Austria, 2021; pp. 91–128. [Google Scholar]
- Abdoon, A.S.; Giraud-Delville, C.; Kandil, O.M.; Kerboeuf-Giraud, A.; Eozénou, C.; Carvalho, A.V.; Julian, S.; Sandra, O. Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy and Implantation Are Not Associated with an Interferon Response of the Endometrium to the Presence of the Conceptus in Dromedary Camel. Theriogenology 2017, 90, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis Neto, A.; Pereira, F.; Santos, T.; Ambrosio, C.; Leiser, R.; Miglino, M. Morpho-Physical Recording of Bovine Conceptus (Bos indicus) and Placenta from Days 20 to 70 of Pregnancy. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2010, 45, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddox-Hyttel, P.; Alexopoulos, N.; Vajta, G.; Lewis, I.; Rogers, P.; Cann, L.; Callesen, H.; Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Trounson, A. Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Characterization of the Initial Post-Hatching Development of Bovine Embryos. Reproduction 2003, 125, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazer, F.W.; Thatcher, W.W. Theory of Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy in Swine Based on Estrogen Controlled Endocrine versus Exocrine Secretion of Prostaglandin F2α by the Uterine Endometrium. Prostaglandins 1977, 14, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazer, F.W.; Johnson, G.A. Pig Blastocyst–Uterine Interactions. Differentiation 2014, 87, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazer, F.W. Pregnancy Recognition Signaling Mechanisms in Ruminants and Pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor, P.; Guimarães, D.A.; López-Béjar, M. Progesterone and Estradiol-17β as a Potential Method for Pregnancy Diagnosis in the Collared Peccary (Pecari tajacu). Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.A.; Smith, B.B.; Timm, K.I.; Menino, A.R. Estradiol Production by Preimplantation Blastocysts and Increased Serum Progesterone following Estradiol Treatment in Llamas. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2007, 102, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.P.; Gallelli, M.F.; Herrera, J.M.; Benavente, M.A.; Rossetto, L.; Aba, M.A. Current Knowledge about the Processes of Luteolysis and Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy in Camelids. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2023, 58, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, A.P.F.; Hearn, J.P.; Michael, A.E. The Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy in Mammals. J. Zool. 1990, 221, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazer, F.W.; Spencer, T.E. Hormones and Pregnancy in Eutherian Mammals. In Hormones and Reproduction of Vertebrates, Volume 5—Mammals; Norris, D.O., Lopez, K.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Taya, K.; Watanabe, G.; Stansfield, F.J.; Allen, W.R. Placentation in the African Elephant (Loxodonta africana). V. The Trophoblast Secretes Placental Lactogen. Placenta 2011, 32, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lueders, I.; Niemuller, C.; Rich, P.; Gray, C.; Hermes, R.; Goeritz, F.; Hildebrandt, T.B. Gestating for 22 Months: Luteal Development and Pregnancy Maintenance in Elephants. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 3687–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, G.T. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin and Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy. In Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy—Ciba Foundation Symposium 64; Heap, R.B., Ed.; Excerpta Medica: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ticconi, C.; Zicari, A.; Belmonte, A.; Realacci, M.; Rao, C.V.; Piccione, E. Pregnancy-Promoting Actions of HCG in Human Myometrium and Fetal Membranes. Placenta 2007, 28, S137–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, J.P.; Webley, G.E.; Gidley-Baird, A.A. Chorionic Gonadotrophin and Embryo-Maternal Recognition during the Peri-Implantation Period in Primates. Reproduction 1991, 92, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, W.W.; Binelli, M.; Burke, J.; Staples, C.R.; Ambrose, J.D.; Coelho, S. Antiluteolytic Signals between the Conceptus and Endometrium. Theriogenology 1997, 47, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swegen, A. Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy in the Mare: Does It Exist and Why Do We Care? Reproduction 2021, 161, R139–R155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalewski, M.P.; Gram, A.; Kautz, E.; Graubner, F.R. The Dog: Nonconformist, Not Only in Maternal Recognition Signaling. In Regulation of Implantation and Establishment of Pregnancy in Mammals: Tribute to 45 Year Anniversary of Roger V. Short’s “Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy”; Geisert, R.D., Bazer, F.W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 215–237. [Google Scholar]
- Tyndale-Biscoe, C.H.; Renfree, M. Reproductive Physiology of Marsupials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Renfree, M.B. Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy in Marsupials. Rev. Reprod. 2000, 5, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renfree, M.B. Marsupials: Placental Mammals with a Difference. Placenta 2010, 31, S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, Y.P.; Selwood, L. Histological Differences between Gravid and Non-Gravid Uteri in the Dasyurid Marsupial, Sminthopsis macroura (Spencer). Reproduction 1997, 111, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, O.W.; Chavan, A.R.; Pavlicev, M.; Protopapas, S.; Callahan, R.; Maziarz, J.; Wagner, G.P. Endometrial Recognition of Pregnancy Occurs in the Grey Short-Tailed Opossum (Monodelphis domestica). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20190691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freyer, C.; Zeller, U.; Renfree, M.B. The Marsupial Placenta: A Phylogenetic Analysis. J. Exp. Zool. A Comp. Exp. Biol. 2003, 299A, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, A.M. Evolution of Placental Hormones: Implications for Animal Models. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 891927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maston, G.A.; Ruvolo, M. Chorionic Gonadotropin Has a Recent Origin within Primates and an Evolutionary History of Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.M.; Ezashi, T.; Rosenfeld, C.S.; Ealy, A.D.; Kubisch, H.M. Evolution of the Interferon Tau Genes and Their Promoters, and Maternal-Trophoblast Interactions in Control of Their Expression. Reproduction. Suppl. 2003, 61, 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Magadum, S.; Banerjee, U.; Murugan, P.; Gangapur, D.; Ravikesavan, R. Gene Duplication as a Major Force in Evolution. J. Genet. 2013, 92, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachos, F.E. Mammalian Phylogenetics: A Short Overview of Recent Advances. In Handbook of the Mammals of Europe; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mossman, H.W. Vertebrate Fetal Membranes: Comparative Ontogeny and Morphology, Evolution, Phylogenetic Significance, Basic Functions, Research Opportunities; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, T.E.; Johnson, G.A.; Burghardt, R.C.; Bazer, F.W. Progesterone Regulation of Periimplantation Conceptus Development and Implantation: Genes and Conundrums. Havemeyer Found. Monogr. Ser. 2008, 21, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Badwaik, N.K.; Rasweiler, J.J. Pregnancy. In Reproductive Biology of Bats; Crichton, E.G., Krutzsch, P.H., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2000; pp. 221–293. [Google Scholar]
- Luckett, W.P. Superordinal and Intraordinal Affinities of Rodents: Developmental Evidence from the Dentition and Placentation. In Evolutionary Relationships among Rodents; Luckett, W.P., Hartenberger, J.L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 227–276. [Google Scholar]
- Mossman, H.W. Comparative Morphogenesis of the Fetal Membranes and Accessory Uterine Structures. Contrib. Embryol. Carnegie Inst. Wash. 1937, 26, 129–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, A.M.; Enders, A.C. Placentation in Mammals Once Grouped as Insectivores. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2010, 54, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enders, A.C.; Blankenship, T.N.; Goodman, S.M.; Soarimalala, V.; Carter, A.M. Placental Diversity in Malagasy Tenrecs: Placentation in Shrew Tenrecs (Microgale Spp.), the Mole-like Rice Tenrec (Oryzorictes hova) and the Web-Footed Tenrec (Limnogale mergulus). Placenta 2007, 28, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuser, C.H.; Wislocki, G.B. Early Development of the Sloth (Bradypus griseus) and Its Similarity to That of Man. Contrib. Embryol. Carnegie Inst. Wash. 1935, 25, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, M.L. The Development of the Baboon (Papio Sp.) Placenta during the Fetal Period of Gestation. Am. J. Anat. 1969, 126, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade-Smith, J.; Richmond, M.E. Induced Ovulation, Development of the Corpus Luteum, and Tubal Transport in the Striped Skunk (Mephitis mephitis). Am. J. Anat. 1978, 153, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoroso, E.C.; Hancock, N.A.; Kellas, L. The Foetal Membranes and Placenta of the Hippopotamus (Hippopotamus Amphibious (Linnaeues)). Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1958, 130, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Uchida, T.A. Ultrastructural Observations of Delayed Implantation in the Japanese Long-Fingered Bat, Miniopterus schreibersii fuliginosus. Reproduction 1983, 69, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heideman, P.D. Delayed Development in Fischer’s Pygmy Fruit Bat, Haplonycteris fischeri, in the Philippines. Reproduction 1989, 85, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferner, K.; Siniza, S.; Zeller, U. The Placentation of Eulipotyphla—Reconstructing a Morphotype of the Mammalian Placenta. J. Morphol. 2014, 275, 1122–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, C.A. Fetal Membranes of the Canadian Porcupine, Erethizon dorsatum. Am. J. Anat. 1959, 104, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mess, A.; Carter, A.M. Evolutionary Transformations of Fetal Membrane Characters in Eutheria with Special Reference to Afrotheria. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2006, 306B, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Horst, C.J. The Placentation of Elephantulus. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 1949, 32, 435–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduor-Okelo, D.; Katema, R.M.; Carter, A.M. Placenta and Fetal Membranes of the Four-Toed Elephant Shrew, Petrodromus tetradactylus. Placenta 2004, 25, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oduor-Okelo, D. Histology of the Chorioallantoic Placenta of the Golden-Rumped Elephant Shrew (Rhynchocyon Chrysopygus Gunther, 1881). Anat. Anz. 1984, 157, 395–407. [Google Scholar]
- Makori, N.; Oduor-Okelo, D.; Otianga-Owiti, G. Morphogenesis of the Foetal Membranes and Placenta of the Root-rat (Tachyoryctes splendens (Rüppel)). Afr. J. Ecol. 1991, 29, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlett, G.W.D. Notes on the Embryology of a Phyllostomid Bat. Am. J. Anat. 1935, 56, 327–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckett, W.P.; Mossman, H.W. Development and Phylogenetic Significance of the Fetal Membranes and Placenta of the African Hystricognathous Rodents Bathyergus and Hystrix. Am. J. Anat. 1981, 162, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.B.; Araújo Júnior, H.N.; Moura, C.E.B.; Favaron, P.O.; Pereira, A.F.; Oliveira, M.F. Placental Development in the Early Stages of Red-Rumped Agouti Pregnancy (Dasyprocta leporina Linnaeus, 1758). J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 24, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckett, W.P. Monophyletic or Diphyletic Origins of Anthropoidea and Hystricognathi. In Evolutionary Biology of the New World Monkeys and Continental Drift; Ciochon, R.L., Chiarelli, A.B., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 347–368. [Google Scholar]
- Oduor-Okelo, D.; Gombe, S. Development of the Foetal Membranes in the Cane Rat (Thryonomys swinderianus): A Re-interpretation. Afr. J. Ecol. 1991, 29, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.M.; Mess, A. Evolution of the Placenta and Associated Reproductive Characters in Bats. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2008, 310B, 428–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckett, W.P. Ontogeny of the Fetal Membranes and Placenta: Their Bearing on Primate Phylogeny. In Phylogeny of the Primates: A multidisciplinary Approach; Luckett, W.P., Szalay, F.S., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 157–182. [Google Scholar]
- Mess, A. Evolutionary Transformations of Chorioallantoic Placental Characters in Rodentia with Special Reference to Hystricognath Species. J. Exp. Zool. A Comp. Exp. Biol. 2003, 299A, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérard, P. Études Sur l’ovogenèse et l’ontogenèse Chez Les Lemuriens Du Genre Galago. Arch. Biol. 1932, 43, 93–151. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, J.P. On the Placentation of Tupaia. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1965, 146, 278–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, H. The Giant Cell Trophoblast of the Senegal Galago (Galago senegalensis senegalensis) and Its Bearing on the Evolution of the Primate Placenta. J. Zool. 1967, 152, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimsatt, W.A.; Enders, A.C. Structure and Morphogenesis of the Uterus, Placenta, and Paraplacental Organs of the Neotropical Disc-winged Bat Thyroptera Tricolor Spix (Microchiroptera: Thyropteridae). Am. J. Anat. 1980, 159, 209–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossman, H.W.; Hisaw, F.L. The Fetal Membranes of the Pocket Gopher, Illustrating an Intermediate Type of Rodent Membrane Formation. I. From the Unfertilized Tubal Egg to the Beginning of the Allantois. Am. J. Anat. 1940, 66, 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, C.E. Phyletic Relationships among Some Rodents with Special Consideration of Sigmodon Based on Embryological Data. Trans. Ky. Acad. Sci. 1953, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Lu, Q.; Zhao, H. A Molecular Phylogeny for All 21 Families within Chiroptera (Bats). Integr. Zool. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.C.; Amador, L.I.; Giannini, N.P. Explosive Radiation at the Origin of Old World Fruit Bats (Chiroptera, Pteropodidae). Org. Divers. Evol. 2021, 21, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, M.A.; Cadar, D.; Horváth, B.; Merino-Viteri, A.; Murienne, J. Revised Phylogeny from Complete Mitochondrial Genomes of Phyllostomid Bats Resolves Subfamilial Classification. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2022, 196, 1591–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elía, G.; Fabre, P.-H.; Lessa, E.P. Rodent Systematics in an Age of Discovery: Recent Advances and Prospects. J. Mammal. 2019, 100, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanga-Kanfi, S.; Miranda, H.; Penn, O.; Pupko, T.; DeBry, R.W.; Huchon, D. Rodent Phylogeny Revised: Analysis of Six Nuclear Genes from All Major Rodent Clades. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammal Diversity Database. Mammal Diversity Database (Version 1.12.1). 2024. Available online: https://www.mammaldiversity.org (accessed on 15 May 2024).
| Implantation Type | Order | Family |
|---|---|---|
| Superficial | Afrosoricida | Chrysochloridae [54,58,59], Potamogalidae [59], Tenrecidae [54,58,59,60] |
| Hyracoidea | Procaviidae [54] | |
| Proboscidea | Elephantidae [54] | |
| Tubulidentata | Orycteropodidae [54] | |
| Cingulata | Chlamyphoridae [54], Dasypodidae [54] | |
| Pilosa | Bradypodidae [61], Choloepodidae [54] | |
| Dermoptera | Cynocephalidae [54,58] | |
| Lagomorpha | Leporidae [54,58], Ochotonidae [54] | |
| *Primates | Atelidae [58], Cebidae [54,58], Cercopithecidae [58,62], Cheirogaleidae [54], Galagidae [58], Lorisidae [54,58], Tarsiidae [54] | |
| *Rodentia | Anomaluridae [54], Aplodontiidae [54], Castoridae [54], Ctenodactylidae [54], Pedetidae [54], Sciuridae [54] | |
| Scandentia | Tupaiidae [58] | |
| Carnivora | Canidae [54], Felidae [54], Mephitidae [17,63], Mustelidae [54], Otariidae [54], Procyonidae [54], Ursidae [54] | |
| Artiodactyla | Balaenopteridae [54], Bovidae [54], Camelidae [32], Cervidae [58], Hippopotamidae [64], Suidae [54], Tayassuidae [54], Tragulidae [58] | |
| *Chiroptera | Emballonuridae [54,56], Miniopteridae [56,65], Molossidae [56], Natalidae [54], Hipposideridae [56], Megadermatidae [56], *Phillostomidae (Macrotus [56]), *Pteropodidae (Haplonycteris [66], Rousettus [54]), Rhinolophidae [56], Rhinopomatidae, Vespertilionidae [56] | |
| *Eulipotyphla | *Soricidae (Soricinae [54,59,67]), Talpidae [54,59] | |
| Perissodactyla | Equidae [54] | |
| Pholidota | Manidae [54] | |
| Partially interstitial | *Chiroptera | *Pteropodidae (Pteropus [56]), Noctilionidae [54] |
| *Rodentia | Dipodidae, Erethizontidae [54,68], Zapodidae [54] | |
| Secondary interstitial | Macroscelidea | Macroscelididae [69,70,71,72] |
| *Chiroptera | *Phyllostomidae (Carollia [56], Glossophaga [56]) | |
| *Eulipotyphla | Erinaceidae [59], *Soricidae (Crocidurinae [59]) | |
| *Rodentia | Cricetidae [57], Muridae [57], Spalacidae [73] | |
| Primary interstitial | *Chiroptera | *Phyllostomidae (Anoura [74], Artibeus, Desmodus [54,56], Uroderma [54]) |
| *Primates | Hominidae [54], Hylobatidae [54], Pongidae [54] | |
| *Rodentia | Bathyergidae [75], Caviidae [54], Chinchillidae [54], Dasyproctidae [76], Echimyidae, Hystricidae [75,77], Octodontidae, Thryonomyidae [78] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braz, H.B.; Barreto, R.d.S.N.; Silva-Júnior, L.N.d.; Horvath-Pereira, B.d.O.; Silva, T.S.d.; Silva, M.D.d.; Acuña, F.; Miglino, M.A. Evolutionary Patterns of Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy and Implantation in Eutherian Mammals. Animals 2024, 14, 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142077
Braz HB, Barreto RdSN, Silva-Júnior LNd, Horvath-Pereira BdO, Silva TSd, Silva MDd, Acuña F, Miglino MA. Evolutionary Patterns of Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy and Implantation in Eutherian Mammals. Animals. 2024; 14(14):2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142077
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraz, Henrique Bartolomeu, Rodrigo da Silva Nunes Barreto, Leandro Norberto da Silva-Júnior, Bianca de Oliveira Horvath-Pereira, Thamires Santos da Silva, Mônica Duarte da Silva, Francisco Acuña, and Maria Angelica Miglino. 2024. "Evolutionary Patterns of Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy and Implantation in Eutherian Mammals" Animals 14, no. 14: 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142077
APA StyleBraz, H. B., Barreto, R. d. S. N., Silva-Júnior, L. N. d., Horvath-Pereira, B. d. O., Silva, T. S. d., Silva, M. D. d., Acuña, F., & Miglino, M. A. (2024). Evolutionary Patterns of Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy and Implantation in Eutherian Mammals. Animals, 14(14), 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142077






