Miniaturizing Nanotoxicity Assays in Daphnids
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culturing of Daphnids and Toxicity Exposures
2.2. Sample Homogenization and Biochemical Assays
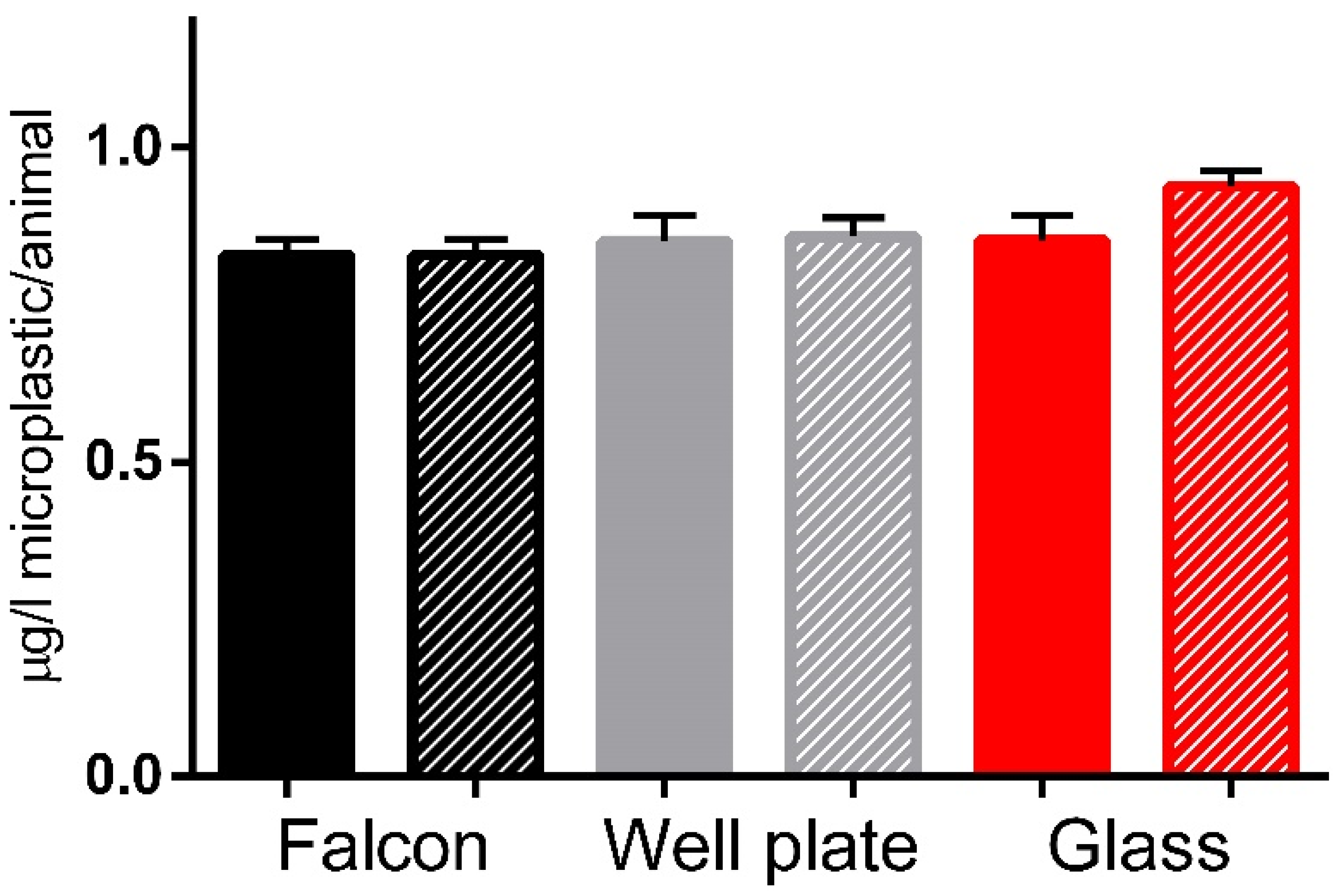
2.3. Feeding and Imaging of Daphnids
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Exposure to Silver Nano Ink in Different Vessels and Volumes Impacts Mortality
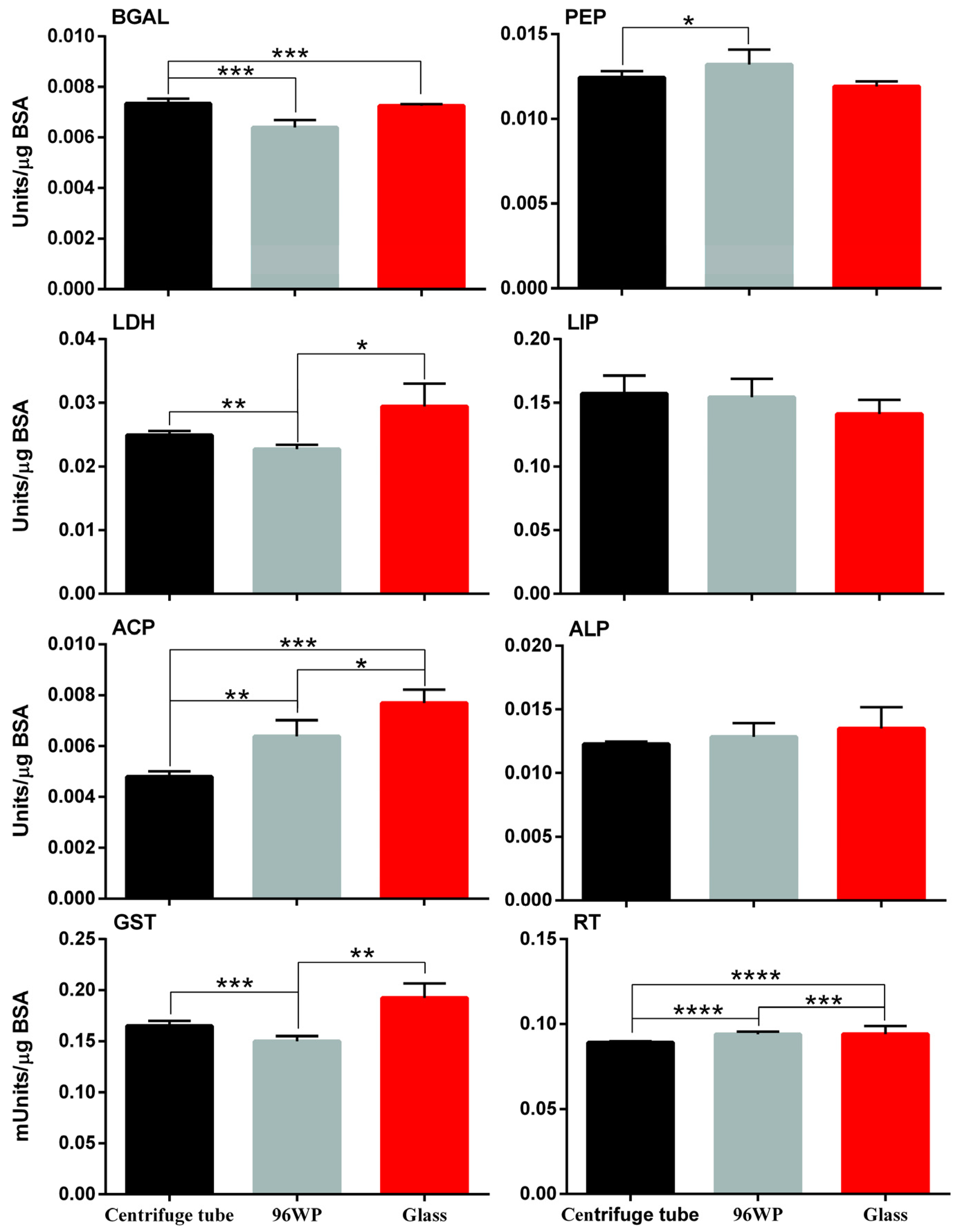
3.2. Physiology Responses following Exposure to the Silver Nano Ink
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharifi, S.; Behzadi, S.; Laurent, S.; Forrest, M.L.; Stroeve, P.; Mahmoudi, M. Toxicity of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2323–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundschuh, M.; Filser, J.; Luderwald, S.; McKee, M.S.; Metreveli, G.; Schaumann, G.E.; Schulz, R.; Wagner, S. Nanoparticles in the environment: Where do we come from, where do we go to? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altammar, K.A. A review on nanoparticles: Characteristics, synthesis, applications, and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1155622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, C.D.; Grintzalis, K.; Zervoudakis, G.; Papapostolou, I. Mechanism of Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 binding to proteins: A hydrophobic assay for nanogram quantities of proteins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.S.; Lin, C.C.; Chang, G.G. Metal-catalyzed oxidation and cleavage of octopus glutathione transferase by the Cu(II)-ascorbate system. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 21, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.S. The state of the art of nanomaterials and its applications in energy saving. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2023, 47, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, A.L.; Vejerano, E.P.; Zhou, X.Z.; Marr, L.C. Nanomaterial disposal by incineration. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1652–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanpradit, P.; Peerakietkhajorn, S. Disturbances in growth, oxidative stress, energy reserves and the expressions of related genes in Daphnia magna after exposure to ZnO under thermal stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhanova, A.; Bozrova, S.; Sokolov, P.; Berestovoy, M.; Karaulov, A.; Nabiev, I. Dependence of Nanoparticle Toxicity on Their Physical and Chemical Properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.; Shineh, G.; Mobaraki, M.; Doughty, S.; Tayebi, L. Structural parameters of nanoparticles affecting their toxicity for biomedical applications: A review. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2023, 25, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.W.; An, J.; Chua, C.K.; Tran, T. Metallic Nanoparticle Inks for 3D Printing of Electronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, S.; Johari, S.A.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jeon, Y.B.; Choi, H.J.; Moon, M.C.; Yu, I.J. Toxicity of various silver nanoparticles compared to silver ions in Daphnia magna. J. Nanobiotechnology 2012, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.W.; Cambre, M.; Lee, H.J. The Toxicity of Nanoparticles Depends on Multiple Molecular and Physicochemical Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levard, C.; Hotze, E.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Brown, G.E. Environmental Transformations of Silver Nanoparticles: Impact on Stability and Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol 2012, 46, 6900–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.Y.; Liu, N.; Xie, Q.T.; Zhu, L.Z.; Ge, F. Polystyrene microplastics facilitate the biotoxicity and biomagnification of ZnO nanoparticles in the food chain from algae to daphnia. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noss, C.; Dabrunz, A.; Rosenfeldt, R.R.; Lorke, A.; Schulz, R. Three-Dimensional Analysis of the Swimming Behavior of Daphnia magna Exposed to Nanosized Titanium Dioxide. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrunz, A.; Duester, L.; Prasse, C.; Seitz, F.; Rosenfeldt, R.; Schilde, C.; Schaumann, G.E.; Schulz, R. Biological Surface Coating and Molting Inhibition as Mechanisms of TiO2 Nanoparticle Toxicity in Daphnia magna. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conine, A.L.; Frost, P.C. Variable toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Daphnia magna: Effects of algal particles and animal nutrition. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Beasley, A.; Mozhayeva, D.; Engelhard, C.; Witte, K. Defective defence in Daphnia daughters: Silver nanoparticles inhibit anti-predator defence in offspring but not in maternal Daphnia magna. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoheisel, S.M.; Diamond, S.; Mount, D. Comparison of nanosilver and ionic silver toxicity in Daphnia magna and Pimephales promelas. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2557–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, J.; Sakka, Y.; Bertrand, C.; Koser, J.; Filser, J. Adaptation of the Daphnia sp. acute toxicity test: Miniaturization and prolongation for the testing of nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakavas, D.; Panagiotidis, K.; Rochfort, K.D.; Grintzalis, K. Surface-to-Volume Ratio Affects the Toxicity of Nanoinks in Daphnids. Stresses 2023, 3, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grintzalis, K.; Dai, W.; Panagiotidis, K.; Belavgeni, A.; Viant, M.R. Miniaturising acute toxicity and feeding rate measurements in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelpsiene, E.; Ekvall, M.T.; Lundqvist, M.; Torstensson, O.; Hua, J.; Cedervall, T. Review of ecotoxicological studies of widely used polystyrene nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, A.M.; Bebenek, I.; Bonzo, J.A.; Bourcier, T.; Davis Bruno, K.L.; Carlson, D.B.; Dubinion, J.; Elayan, I.; Harrouk, W.; Lee, S.L.; et al. An FDA/CDER perspective on nonclinical testing strategies: Classical toxicology approaches and new approach methodologies (NAMs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2020, 114, 104662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westmoreland, C.; Bender, H.J.; Doe, J.E.; Jacobs, M.N.; Kass, G.E.N.; Madia, F.; Mahony, C.; Manou, I.; Maxwell, G.; Prieto, P.; et al. Use of New Approach Methodologies (NAMs) in regulatory decisions for chemical safety: Report from an EPAA Deep Dive Workshop. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2022, 135, 105261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, L.M.; Paparella, M.; Burden, N.; Constantine, L.; Margiotta-Casaluci, L.; Miller, T.H.; Moe, S.J.; Owen, S.F.; Schaffert, A.; Sikanen, T. Big Question to Developing Solutions: A Decade of Progress in the Development of Aquatic New Approach Methodologies from 2012 to 2022. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 43, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, K.; Ellis, L.J.A.; Davoudi, H.H.; Supian, S.; Maia, M.T.; Silva, G.H.; Guo, Z.L.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Lynch, I. Daphnia as a model organism to probe biological responses to nanomaterials-from individual to population effects via adverse outcome pathways. Front. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 1178482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, K.A.; Brill, J.L.; Norberg-King, T.; Barron, M.G.; Carr, G.; Belanger, S.E. Daphnia magna and Ceriodaphnia dubia Have Similar Sensitivity in Standard Acute and Chronic Toxicity Tests. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrazin, J.; Sperfeld, E. Food quality mediates responses of Daphnia magna life history traits and heat tolerance to elevated temperature. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.Y.K.; Ryu, C.S.; Lee, S.A.; Adeli, Z.; Meupea, B.T.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.J. Endocrine-disrupting potential and toxicological effect of para-phenylphenol on Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 113965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotidis, K.; Engelmann, B.; Krauss, M.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.E.; Altenburger, R.; Rochfort, K.D.; Grintzalis, K. The impact of amine and carboxyl functionalised microplastics on the physiology of daphnids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 132023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelpsiene, E.; Chang, T.; Khort, A.; Bernfur, K.; Odnevall, I.; Cedervall, T.; Hua, J. The effect of natural biomolecules on yttrium oxide nanoparticles from a Daphnia magna survival rate perspective. Nanotoxicology 2023, 17, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalaki, A.; McGivern, A.R.; Poschet, G.; Buttner, M.; Altenburger, R.; Grintzalis, K. The Effects of Single and Combined Stressors on Daphnids-Enzyme Markers of Physiology and Metabolomics Validate the Impact of Pollution. Toxics 2022, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, M.; Li, X.; Abdallah, M.A.-E.; Stubbings, W.; Yan, N.; Barnard, M.; Guo, L.-H.; Colbourne, J.K.; Orsini, L. Daphnia as a Sentinel Species for Environmental Health Protection: A Perspective on Biomonitoring and Bioremediation of Chemical Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14237–14248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, K.; Virgiliou, C.; Theodoridis, G.; Gika, H.; Grintzalis, K. The impact of pharmaceutical pollutants on daphnids—A metabolomic approach. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 100, 104157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremias, G.; Jesus, F.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Goncalves, F.J.M.; Asselman, J.; Pereira, J.L. New insights on the effects of ionic liquid structural changes at the gene expression level: Molecular mechanisms of toxicity in Daphnia magna. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Cheng, Y.H.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Dong, Z.M.; Fan, W.H. Nano-TiO2 modifies heavy metal bioaccumulation in Daphnia magna: A model study. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.H.; Li, X.; Song, J.X. Transcriptomic Analysis of Diethylstilbestrol in Daphnia Magna: Energy Metabolism and Growth Inhibition. Toxics 2023, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakrashi, S.; Tan, C.; Wang, W.X. Bioaccumulation-based silver nanoparticle toxicity in Daphnia magna and maternal impacts. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 3359–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyogi, S.; Wood, C.M. Biotic ligand model, a flexible tool for developing site-specific water quality guidelines for metals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6177–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.J.; Li, S.G.; Wang, X.K. Toxic Effects and Molecular Mechanism of Different Types of Silver Nanoparticles to the Aquatic Crustacean Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12868–12878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grintzalis, K.; Papapostolou, I.; Georgiou, C.D. Assays for the Quantification of Antioxidant Enzymes in Fungi. In Laboratory Protocols in Fungal Biology: Current Methods in Fungal Biology; Gupta, V.K., Tuohy, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grintzalis, K.; Georgiou, C.D.; Schneider, Y.J. An accurate and sensitive Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250-based assay for protein determination. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 480, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Acker, S.A.B.E.; van Balen, G.P.; van den Berg, D.J.; Bast, A.; van der Vijgh, W.J.F. Influence of iron chelation on the antioxidant activity of flavonoids. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 56, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.T.; Mira, M.L.; Florencio, M.H.; Jennings, K.R. Iron and copper chelation by flavonoids: An electrospray mass spectrometry study. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2002, 92, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grintzalis, K.; Papapostolou, I.; Zisimopoulos, D.; Stamatiou, I.; Georgiou, C.D. Multiparametric protocol for the determination of thiol redox state in living matter. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 74, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannouli, M.; Panagiotidis, K.; Rochfort, K.D.; Grintzalis, K. Development and application of a sensitive feeding assay for daphnids based on the ingestion of fluorescent microparticles. Environ. Sci.-Adv. 2023, 2, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulm, L.; Krivohlavek, A.; Jurasin, D.; Ljubojevic, M.; Sinko, G.; Crnkovic, T.; Zuntar, I.; Sikic, S.; Vrcek, I.V. Response of biochemical biomarkers in the aquatic crustacean Daphnia magna exposed to silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19990–19999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, H.Q. Genotoxic Effects on Fed with Aquatic Green Algae Exposed to Silver Nanoclusters. Water 2023, 15, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.B.; Freches, A.R.; Rodrigues, M.; Nunes, B.; Antunes, S.C. Transgenerational Effects of Toxicants: An Extension of the Daphnia 21-day Chronic Assay? Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 74, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekamge, S.; Miranda, A.F.; Ball, A.S.; Shukla, R.; Nugegoda, D. The toxicity of coated silver nanoparticles to Daphnia carinata and trophic transfer from alga Raphidocelis subcapitata. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobashy, M.M.; Abd Elkodous, M.; Shabaka, S.H.; Younis, S.A.; Alshangiti, D.M.; Madani, M.; Al-Gahtany, S.A.; Elkhatib, W.F.; Noreddin, A.M.; Nady, N.; et al. An overview of methods for production and detection of silver nanoparticles, with emphasis on their fate and toxicological effects on human, soil, and aquatic environment. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 954–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polowczyk, I.; Kozlecki, T.; Bastrzyk, A. Adsorption of Silver Nanoparticles on Glass Beads Surface. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, Y.; Koeser, J.; Filser, J. How test vessel properties affect the fate of silver nitrate and sterically stabilized silver nanoparticles in two different test designs used for acute tests with. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 2495–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozefczak, M.; Remans, T.; Vangronsveld, J.; Cuypers, A. Glutathione Is a Key Player in Metal-Induced Oxidative Stress Defenses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3145–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; Hansen, J.M. Oxidative Stress, Thiols, and Redox Profiles. In Developmental Toxicology: Methods and Protocols; Harris, C., Hansen, J.M., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
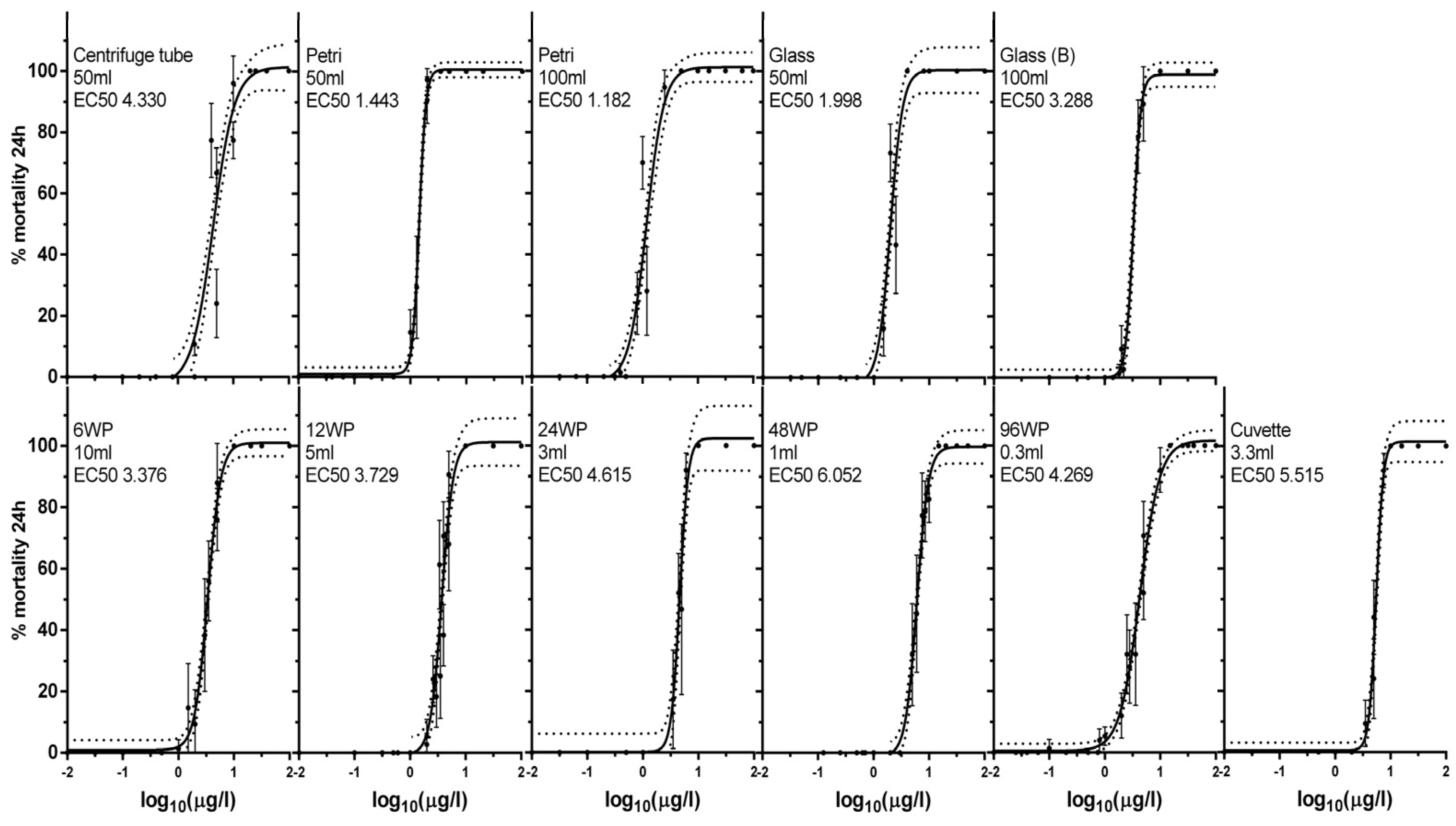
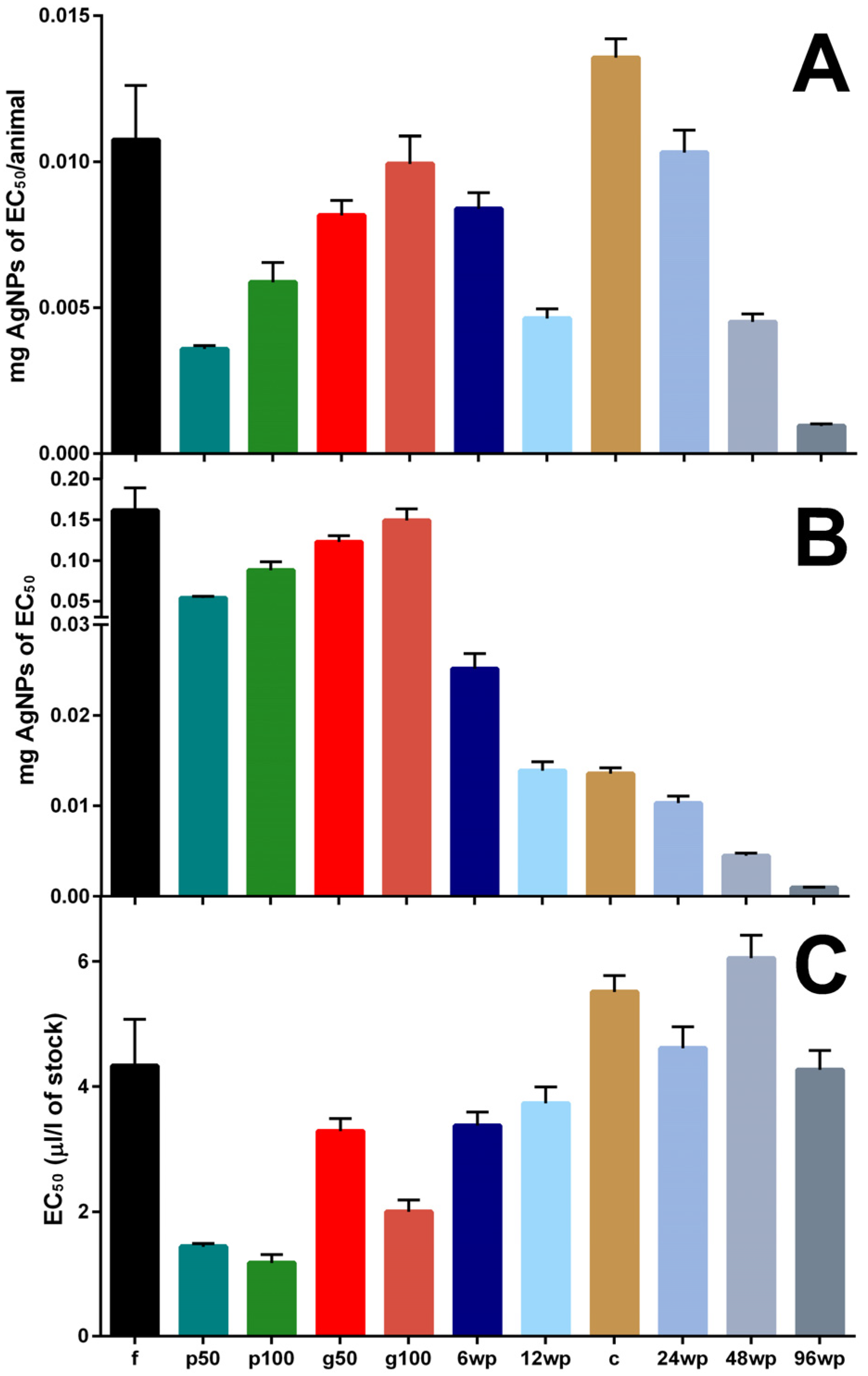
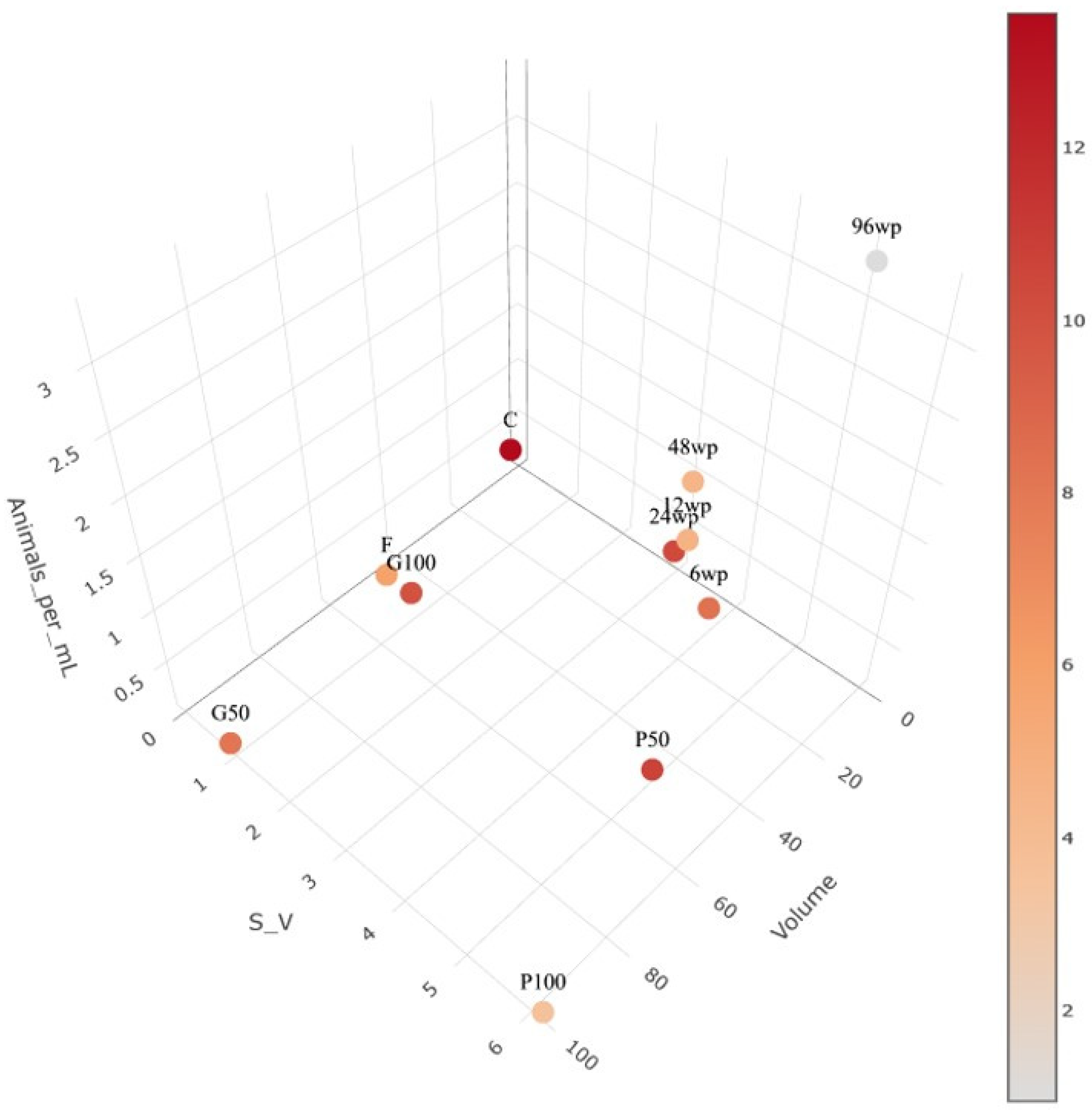
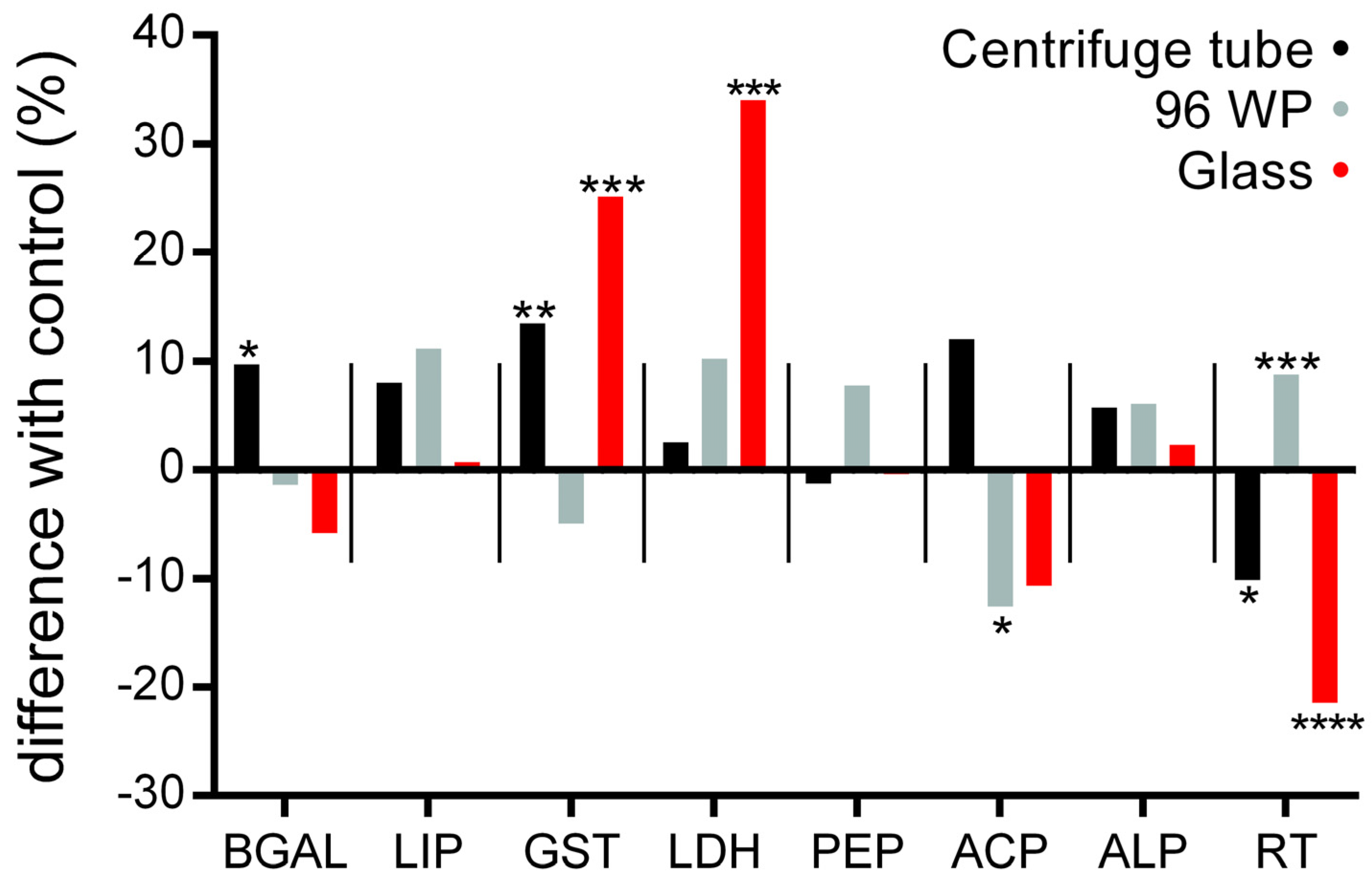
| Vessel | 6-Well Plate | 12-Well Plate | 24-Well Plate | 48-Well Plate | 96-Well Plate | Cuvette | Petri Dish (50 mL) | Petri Dish (100 mL) | Centrifuge Tube | Glass Vessel (100 mL) | Glass Vessel (50 mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation | 6wp | 12wp | 24wp | 48wp | 96wp | C | P50 | P100 | f | G100 | G50 |
| Volume (mL) | 10 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0.3 | 3.3 | 50 | 100 | 50 | 100 | 50 |
| Animals | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Animals/mL | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.33 | 1 | 3.33 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.3 |
| S:V | 3.98 | 3.32 | 3.03 | 3.14 | 5.13 | 0.03 | 5.09 | 6.16 | 0.49 | 0.92 | 0.96 |
| EC1 | 0.974 | 1.264 | 2.060 | 2.042 | 0.629 | 2.807 | 0.77 | 0.221 | 0.561 | 0.615 | 1.605 |
| EC50 | 3.376 | 3.729 | 4.615 | 6.052 | 4.269 | 5.515 | 1.443 | 1.182 | 4.330 | 1.998 | 3.288 |
| (min–max) | (3.17–3.60) | (3.43–4.00) | (4.3–4.96) | (5.71–6.42) | (3.98–4.58) | (5.27–5.78) | (1.36–1.49) | (1.06–1.32) | (3.69–5.08) | (1.82–2.19) | (3.1–3.49) |
| Hill slope | 3.697 | 4.246 | 5.696 | 4.230 | 2.400 | 6.804 | 7.321 | 2.744 | 2.248 | 3.898 | 6.407 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kakavas, D.; Panagiotidis, K.; Rochfort, K.D.; Grintzalis, K. Miniaturizing Nanotoxicity Assays in Daphnids. Animals 2024, 14, 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142046
Kakavas D, Panagiotidis K, Rochfort KD, Grintzalis K. Miniaturizing Nanotoxicity Assays in Daphnids. Animals. 2024; 14(14):2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142046
Chicago/Turabian StyleKakavas, Dimitrios, Konstantinos Panagiotidis, Keith D. Rochfort, and Konstantinos Grintzalis. 2024. "Miniaturizing Nanotoxicity Assays in Daphnids" Animals 14, no. 14: 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142046
APA StyleKakavas, D., Panagiotidis, K., Rochfort, K. D., & Grintzalis, K. (2024). Miniaturizing Nanotoxicity Assays in Daphnids. Animals, 14(14), 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142046









