Identification of Metabolites in Muscles of Lueyang Black-Bone Chickens: A Comparative Analysis of Caged and Cage-Free Rearing Modes Using Untargeted Metabolomic Techniques
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval Statement
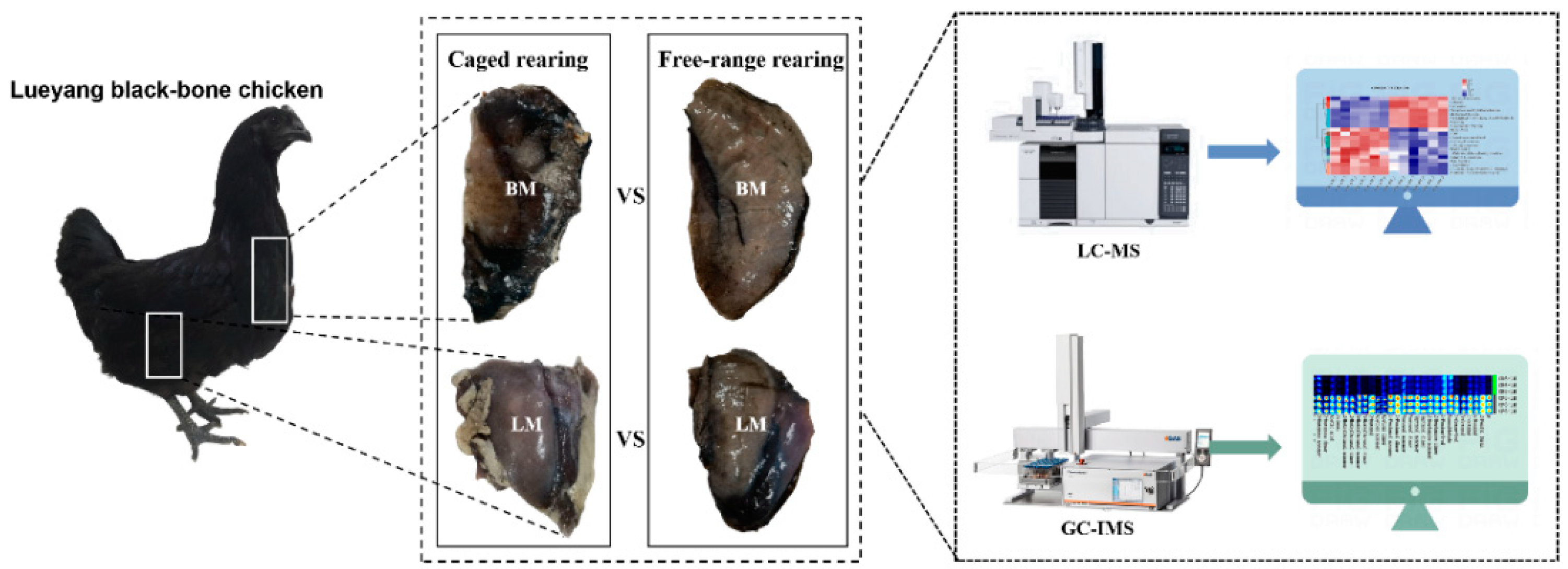
2.2. Animal Resources and Rearing Systems
2.3. Carcass Yield and Meat Quality Assessment
2.4. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis
2.5. Comparative Analysis of the Volatile Organic Compounds
2.6. Correlation Analysis of Metabolites and Volatile Organic Compounds
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chicken Carcass Yield and Meat Quality under Different Rearing Systems
3.2. Untargeted Metabolomics and Differential Metabolite Analysis
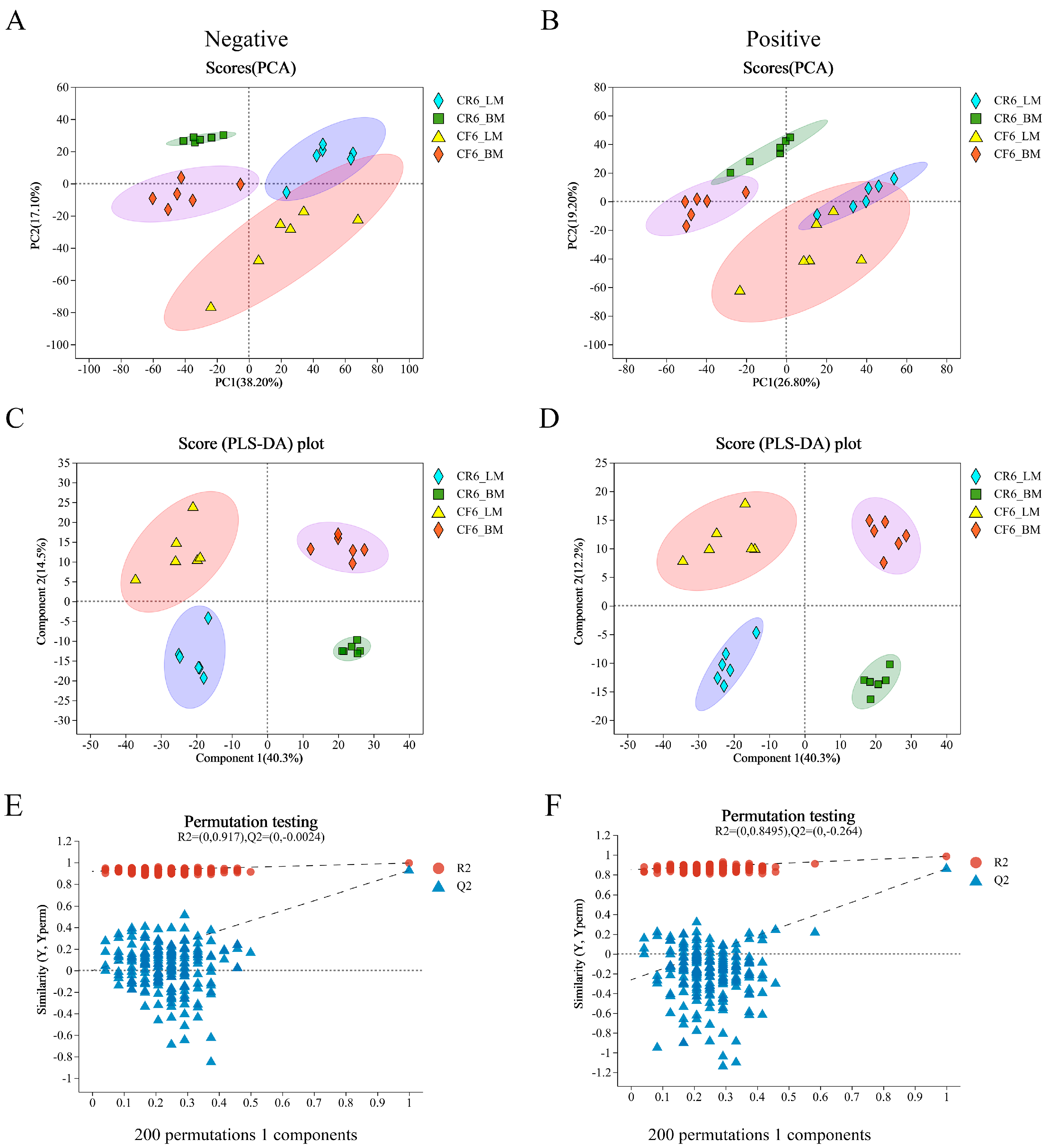
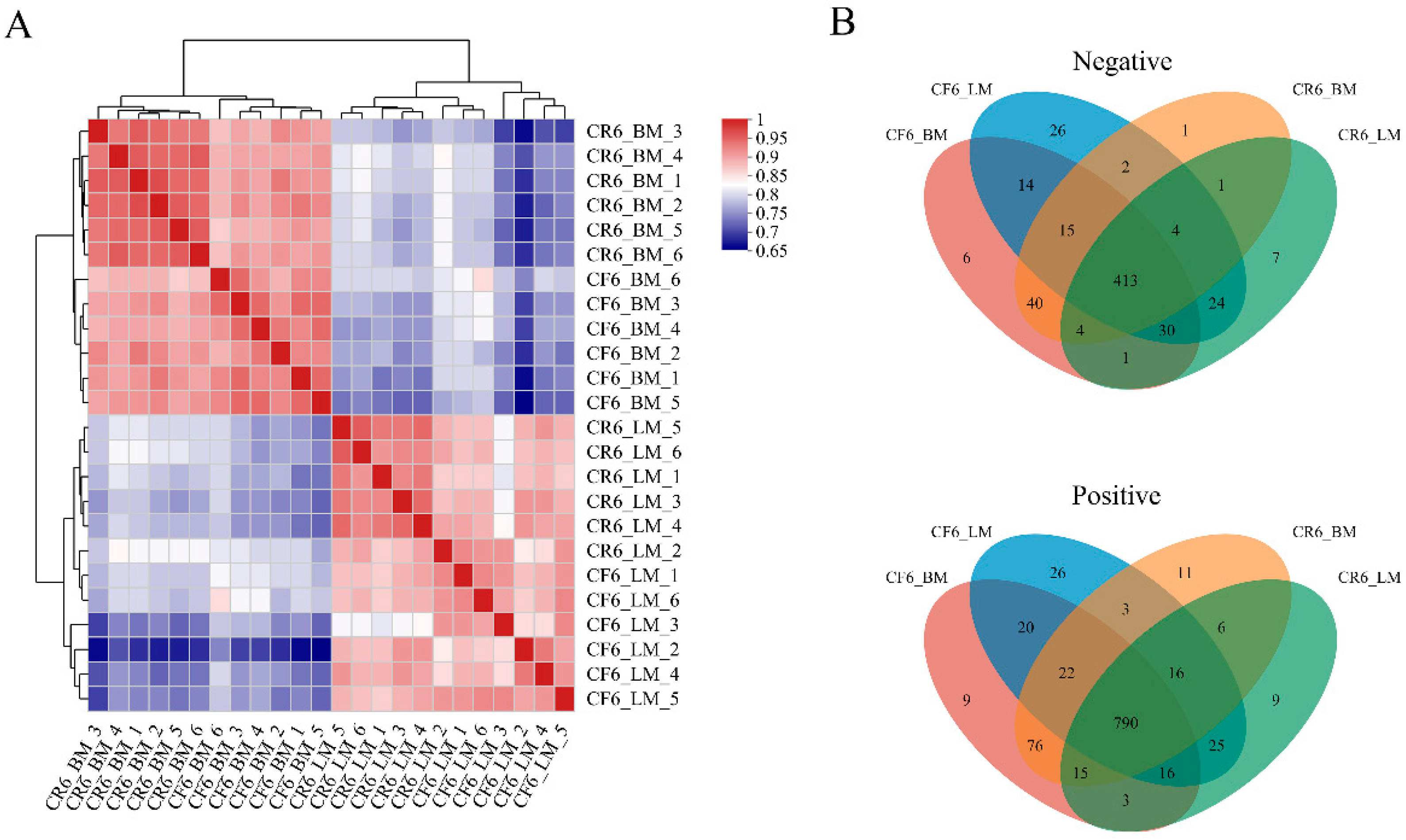
3.2.1. Quality Control of the Metabolomes of Muscle Samples
3.2.2. Analysis of All Metabolites
3.2.3. Screening and Correlation Analysis of Differential Metabolites
3.2.4. Analysis of Differential Metabolite Clusters
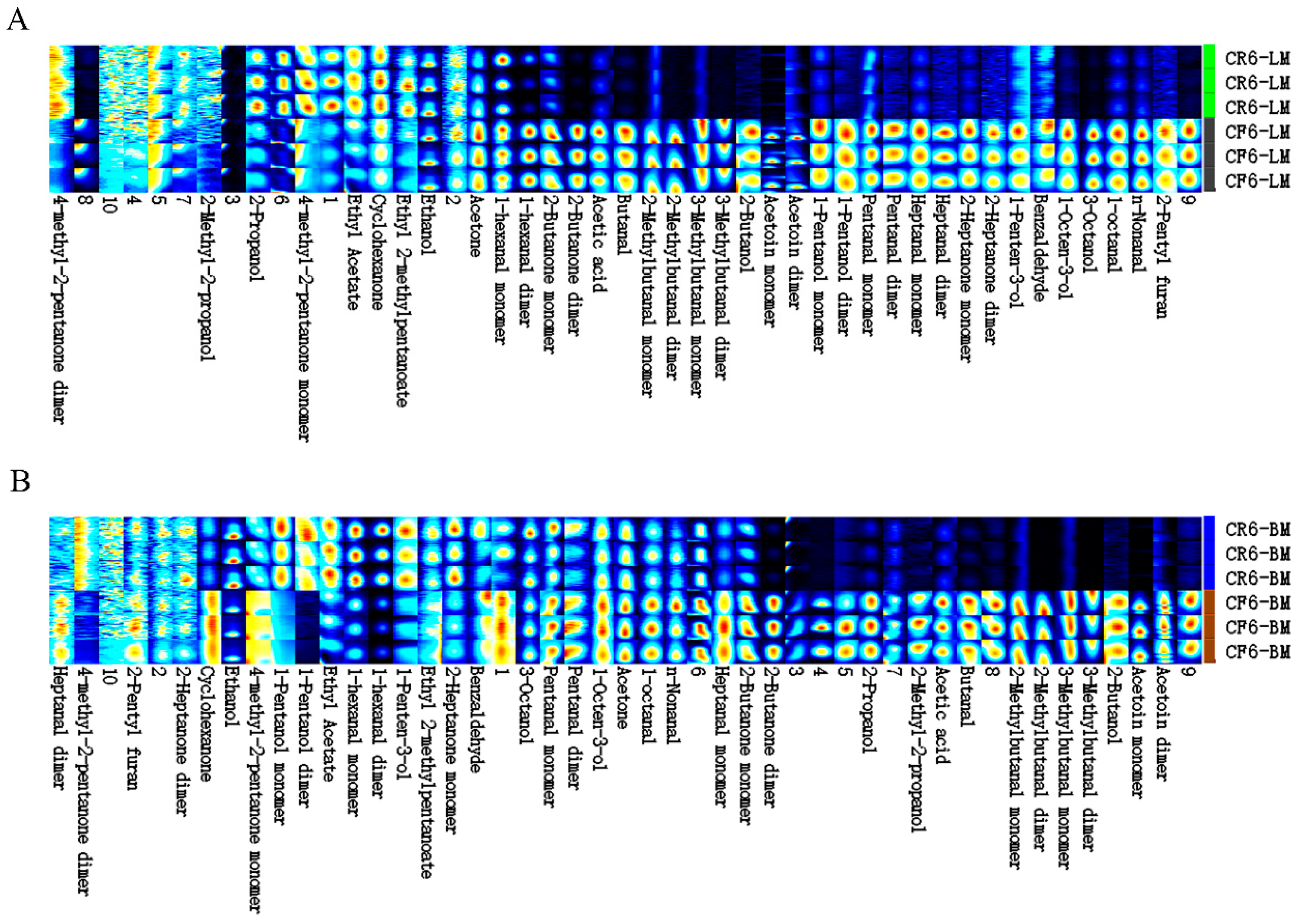
3.3. Analysis of the Volatile Organic Compounds in Chicken Meat
3.4. Correlations between Differential Metabolites and Volatile Organic Compounds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, W.Q.; Li, H.F.; Wang, J.Y.; Shu, J.T.; Zhu, C.H.; Song, W.T.; Song, C.; Ji, G.G.; Liu, H.X. Molecular genetic diversity and maternal origin of Chinese black-bone chicken breeds. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 3275–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Shi, X.; Hu, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, K.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, G. Comparative Metabolomics Analysis Reveals the Unique Nutritional Characteristics of Breed and Feed on Muscles in Chinese Taihe Black-Bone Silky Fowl. Metabolites 2022, 12, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Wei, Y.; Feng, Z.; Fang, L.; Li, M.; Ren, J.; Liu, W.; Gan, J. In vitro immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects of oligopeptides and four characteristic peptides in black-bone silky fowl (Gallus gallus domesticus Brisson). J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nganvongpanit, K.; Kaewkumpai, P.; Kochagul, V.; Pringproa, K.; Punyapornwithaya, V.; Mekchay, S. Distribution of Melanin Pigmentation in 33 Organs of Thai Black-Bone Chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus). Animals 2020, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.; Zu, P.; Rao, Y.; Li, W.; Mou, T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, F. Comparative analysis of melanin deposition between Chishui silky fowl and Taihe silky fowl. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2021, 49, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Nie, S.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M. Purification and identification of novel antioxidative peptide released from Black-bone silky fowl (Gallus gallus domesticus Brisson). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 237, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant Activity of Proteins and Peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komiyama, T.; Xiong, G.; Chen, W.; Jiang, K.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Liao, X. Integrated transcriptome and proteome analysis reveals the unique molecular features and nutritional components on the muscles in Chinese Taihe black-bone silky fowl chicken. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanetti, V.; Mancinelli, A.C.; Pascucci, L.; Menchetti, L.; Castellini, C.; Mugnai, C.; Fiorilla, E.; Miniscalco, B.; Chiattelli, D.; Franciosini, M.P.; et al. Effect of rearing systems on immune status, stress parameters, intestinal morphology, and mortality in conventional and local chicken breeds. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo Ghanima, M.M.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Othman, S.I.; Taha, A.E.; Allam, A.A.; Eid Abdel-Moneim, A.-M. Impact of different rearing systems on growth, carcass traits, oxidative stress biomarkers, and humoral immunity of broilers exposed to heat stress. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3070–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Fan, X.; Yang, L.; He, T.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Geng, Z. Effects of rearing systems on growth performance, carcass yield, meat quality, lymphoid organ indices, and serum biochemistry of Wannan Yellow chickens. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semwogerere, F.; Neethling, J.; Muchenje, V.; Hoffman, L.C. Effects of production systems on the carcass and meat quality characteristics of spent laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1990–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buijs, S.; Keeling, L.; Rettenbacher, S.; Van Poucke, E.; Tuyttens, F.A.M. Stocking density effects on broiler welfare: Identifying sensitive ranges for different indicators. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellini, C.; Berri, C.; Le Bihan-Duval, E.; Martino, G. Qualitative attributes and consumer perception of organic and free-range poultry meat. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2008, 64, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.H. Fat metabolism in exercise--with special reference to training and growth hormone administration. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2004, 14, 74–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.C.B.; Bacurau, A.V.; Bueno, C.R.; Cunha, T.C.; Tanaka, L.Y.; Jardim, M.A.; Ramires, P.R.; Brum, P.C. Aerobic exercise training improves Ca2+ handling and redox status of skeletal muscle in mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 235, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Jo, C.; Tariq, M.R. Meat flavor precursors and factors influencing flavor precursors—A systematic review. Meat Sci. 2015, 110, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, F.; Rong, L.; Cai, J.; Yang, S.; Jia, Z.; Li, S. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profile Analysis of Muscles Reveals Pathways and Biomarkers Involved in Flavor Differences between Caged and Cage-Free Chickens. Foods 2022, 11, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Yin, T.; Liu, L.; Kong, M.; Li, H.; et al. Rearing system causes changes of behavior, microbiome, and gene expression of chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3365–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.S.; Mahmud, A.; Mehmood, S.; Pasha, T.N.; Hussain, J.; Khan, M.T. Blood biochemistry and immune response in Aseel chicken under free range, semi-intensive, and confinement rearing systems. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, C.E.; Rothrock, M.J.; Mishra, A. Mapping foodborne pathogen contamination throughout the conventional and alternative poultry supply chains. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.K.; Yin, Y.J.; Lu, H.Z.; Wang, L. The complete mitochondrial genome and molecular phylogeny of Lueyang black-bone chicken. Br. Poult. Sci. 2018, 59, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, R.; Zhang, T.; Ma, H.; Lu, H.; Yuan, G. Transcriptomic analysis of thigh muscle of Lueyang black-bone chicken in free-range and caged feeding. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 34, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Cao, C.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Bao, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of Different Rearing Systems on Lueyang Black-Bone Chickens: Meat Quality, Amino Acid Composition, and Breast Muscle Transcriptome. Genes 2022, 13, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Yan, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, R.; Chen, M.; Yin, J.; Zhang, X. Insights into the mechanism of L-malic acid on drip loss of chicken meat under commercial conditions. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Zhang, D.; Xu, G.; Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Jia, Y.; Qu, L. Effects of different rearing systems on meat production traits and meat fiber microstructure of Beijing-you chicken. Anim. Sci. J. 2014, 86, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, R.; Wang, T.; Ding, W. Characterization of the Volatile Compounds of Zhenba Bacon at Different Process Stages Using GC–MS and GC–IMS. Foods 2021, 10, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.T.; Ramesh, T.; Toh, X.R.; Nguyen, L.N. Emerging roles of lysophospholipids in health and disease. Prog. Lipid Res. 2020, 80, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traina, G. The neurobiology of acetyl-L-carnitine. Front. Biosci. 2016, 1, 1314–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldyrev, A.A.; Aldini, G.; Derave, W. Physiology and Pathophysiology of Carnosine. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1803–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Qi, Z.; Luo, D.; Hu, J.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, M.; Hou, S. Effects of Pantothenic Acid Supplementation on Growth Performance, Carcass Traits, Plasma Parameters of Starter White Pekin Ducks Fed a Corn–Soybean Meal Diet. Animals 2021, 11, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.B.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Zou, J.M.; Chang, L.L.; Fu, S.Y. Effect of free-range days on a local chicken breed: Growth performance, carcass yield, meat quality, and lymphoid organ index. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, N.A.; Rafiq, A.; Kumar, F.; Singh, V.; Shukla, V. Determinants of broiler chicken meat quality and factors affecting them: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2997–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagace, T.A.; Ridgway, N.D. The role of phospholipids in the biological activity and structure of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 2499–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Wang, D.; Li, C. Changes of intramuscular phospholipids and free fatty acids during the processing of Nanjing dry-cured duck. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. A Comprehensive Review on Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; Decker, E.A. The Role of Oxygen in Lipid Oxidation Reactions: A Review. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Bazer, F.W.; Burghardt, R.C.; Johnson, G.A.; Kim, S.W.; Knabe, D.A.; Li, P.; Li, X.; McKnight, J.R.; Satterfield, M.C.; et al. Proline and hydroxyproline metabolism: Implications for animal and human nutrition. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, G. Roles of dietary glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in collagen synthesis and animal growth. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Dai, Z.; Hu, C.A.; Wu, G. Metabolism, Nutrition, and Redox Signaling of Hydroxyproline. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.J.; Jiang, Q.Y.; Zhang, T.; Yin, Y.L.; Li, F.N.; Deng, J.P.; Wu, G.Y.; Kong, X.F. Dietary supplementation with arginine and glutamic acid modifies growth performance, carcass traits, and meat quality in growing-finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 2680–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Furukawa, K.; Toyomizu, M.; Nochi, T.; Bailey, C.A.; Wu, G. Interorgan Metabolism, Nutritional Impacts, and Safety of Dietary L-Glutamate and L-Glutamine in Poultry. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1332, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poompramun, C.; Molee, W.; Thumanu, K.; Molee, A. The significant influence of residual feed intake on flavor precursors and biomolecules in slow-growing Korat chicken meat. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasena, D.D.; Ahn, D.U.; Nam, K.C.; Jo, C. Flavour chemistry of chicken meat: A review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashdorj, D.; Amna, T.; Hwang, I. Influence of specific taste-active components on meat flavor as affected by intrinsic and extrinsic factors: An overview. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Yin, M.; Yang, L. Specific expression pattern of IMP metabolism related-genes in chicken muscle between cage and free range conditions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Ya-Ting, J.; Jin-Xuan, C.; Yin-Ji, C.; Yang-Ying, S.; Xiao-Qun, Z.; Dao-Dong, P.; Chang-Rong, O.; Ning, G. Study on lipolysis-oxidation and volatile flavour compounds of dry-cured goose with different curing salt content during production. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Luan, H.; Bu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Ji, G. Flavor characteristics of shrimp sauces with different fermentation and storage time. Lwt 2019, 110, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, M.; Ruiz, J.; del Pulgar, J.S.; Pérez-Palacios, T.; Antequera, T. Volatile compound profile of sous-vide cooked lamb loins at different temperature–time combinations. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Liu, L.; Yuan, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wen, J.; Cui, H. A Comparison of Different Tissues Identifies the Main Precursors of Volatile Substances in Chicken Meat. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 927618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Hu, J.; Chen, W. Analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and flavour development in dry-cured grass carp by high-throughput sequencing, volatile flavour analysis and metabolomics. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Cui, W.; Gao, Y.; Li, P.; Pu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B. Analysis of the volatile compounds in Fuliji roast chicken during processing and storage based on GC-IMS. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Treatments | Traits (n = 10) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| pH (24 h) | Shear Force (N) | Drip Loss (%) | |
| CR6_LM | 5.58 ± 0.27 a | 24.15 ± 1.93 b | 2.30% ± 0.43% a |
| CR6_BM | 5.60 ± 0.21 a | 27.79 ± 1.9 ab | 2.77% ± 0.41% a |
| CF6_LM | 5.80 ± 0.28 a | 27.98 ± 2.43 a | 2.24% ± 0.41% a |
| CF6_BM | 5.91 ± 0.14 a | 31.39 ± 2.08 a | 2.30% ± 0.43% a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Gao, J.; Li, G.; Cheng, J.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, W.; Lu, H. Identification of Metabolites in Muscles of Lueyang Black-Bone Chickens: A Comparative Analysis of Caged and Cage-Free Rearing Modes Using Untargeted Metabolomic Techniques. Animals 2024, 14, 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142041
Wang L, Gao J, Li G, Cheng J, Yuan G, Zhang T, Zeng W, Lu H. Identification of Metabolites in Muscles of Lueyang Black-Bone Chickens: A Comparative Analysis of Caged and Cage-Free Rearing Modes Using Untargeted Metabolomic Techniques. Animals. 2024; 14(14):2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142041
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ling, Jie Gao, Guojin Li, Jia Cheng, Guoqiang Yuan, Tao Zhang, Wenxian Zeng, and Hongzhao Lu. 2024. "Identification of Metabolites in Muscles of Lueyang Black-Bone Chickens: A Comparative Analysis of Caged and Cage-Free Rearing Modes Using Untargeted Metabolomic Techniques" Animals 14, no. 14: 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142041
APA StyleWang, L., Gao, J., Li, G., Cheng, J., Yuan, G., Zhang, T., Zeng, W., & Lu, H. (2024). Identification of Metabolites in Muscles of Lueyang Black-Bone Chickens: A Comparative Analysis of Caged and Cage-Free Rearing Modes Using Untargeted Metabolomic Techniques. Animals, 14(14), 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142041




