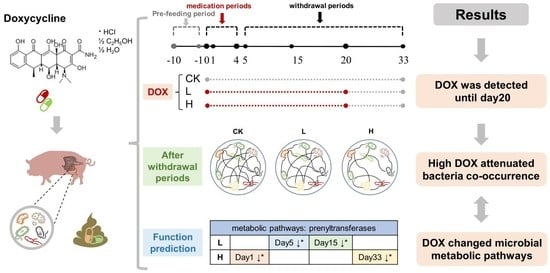
Doxycycline Attenuates Pig Intestinal Microbial Interactions and Changes Microbial Metabolic Pathways
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Determination of Doxycycline Concentration
2.3. Total DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Trends in the Residual Concentration of Doxycycline
3.2. Diversity of the Bacterial Community
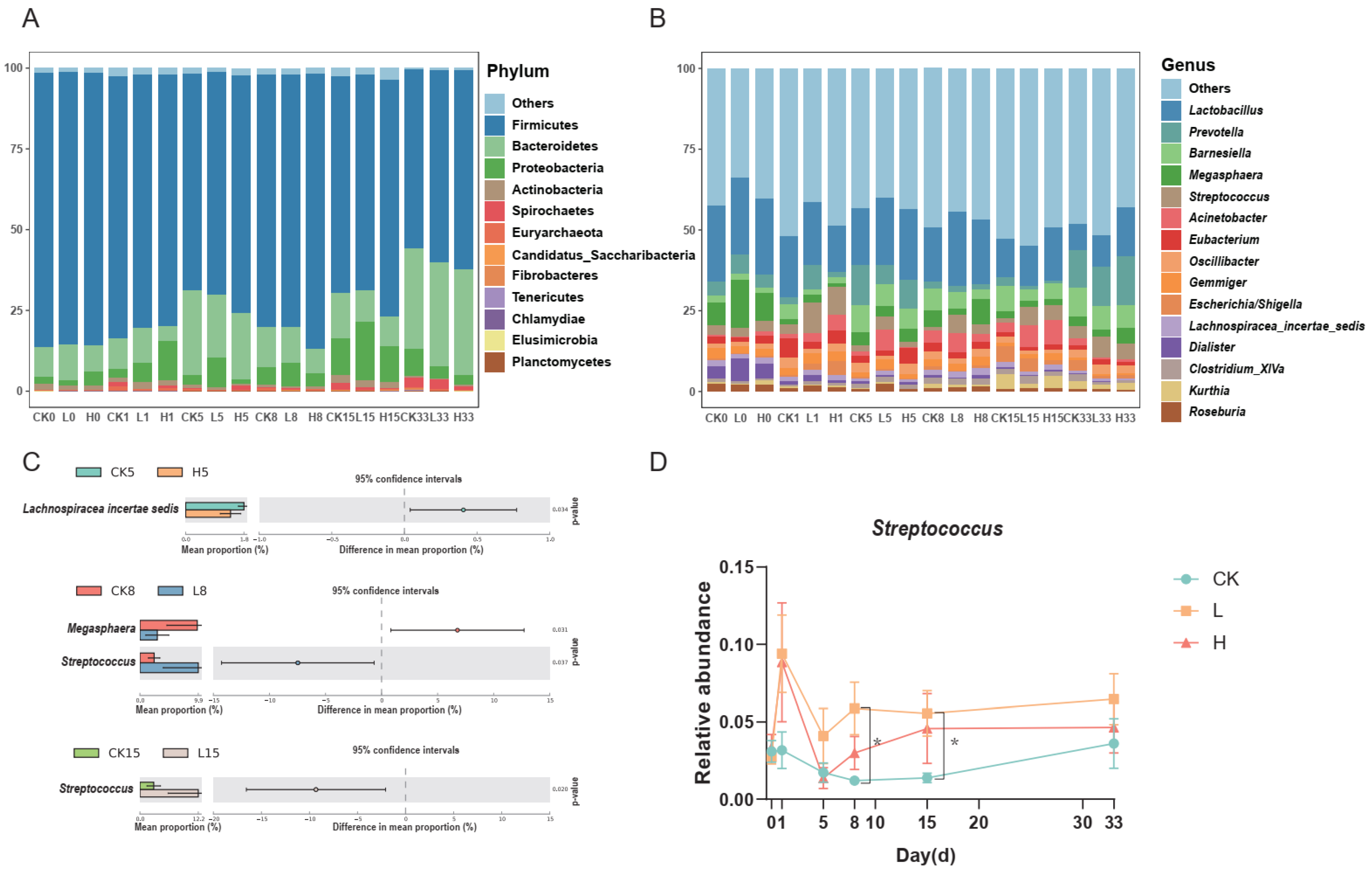
3.3. Bacterial Community Structure at the Phylum and Genus Levels
3.4. Correlation between Doxycycline Concentration and Relative Abundance of Microorganisms
3.5. Cooccurrence Networks among the Bacterial Genera
3.6. PICRUSt2 Function Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiseo, K.; Huber, L.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Jaiswal, S.; Sodhi, K.K.; Shree, P.; Singh, D.K.; Agrawal, P.K.; Shukla, P. Antibiotics bioremediation: Perspectives on its ecotoxicity and resistance. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henehan, M.; Montuno, M.; De Benedetto, A. Doxycycline as an anti-inflammatory agent: Updates in dermatology. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, B.A.; Domenico, P.; Cunha, C.B. Pharmacodynamics of doxycycline. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2000, 6, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwudi, C.U. rRNA Binding Sites and the Molecular Mechanism of Action of the Tetracyclines. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 4433–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G.; Pan, C.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L. Comprehensive Evaluation of Antibiotics Emission and Fate in the River Basins of China: Source Analysis, Multimedia Modeling, and Linkage to Bacterial Resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Zou, Y.D.; Liao, X.D.; Liang, J.B.; Wu, Y.B. The excretion and environmental effects of amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, and doxycycline residues in layer chicken manure. Poultry. Sci. 2016, 95, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoetendal, E.G.; Cheng, B.; Koike, S.; Mackie, R.I. Molecular microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract: From phylogeny to function. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2004, 5, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Boynton, F.D.D.; Ericsson, A.C.; Uchihashi, M.; Dunbar, M.L.; Wilkinson, J.E. Doxycycline induces dysbiosis in female C57BL/6NCrl mice. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matto, J.; Maukonen, J.; Alakomi, H.L.; Suihko, M.L.; Saarela, M. Influence of oral doxycycline therapy on the diversity and antibiotic susceptibility of human intestinal bifidobacterial population. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looft, T.; Allen, H.K.; Cantarel, B.L.; Levine, U.Y.; Bayles, D.O.; Alt, D.P.; Henrissat, B.; Stanton, T.B. Bacteria, phages and pigs: The effects of in-feed antibiotics on the microbiome at different gut locations. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthisinghe, T.P.; Wang, F.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Xi, L.; Dong, W.; Fang, M. Long-term exposure to TET increases body weight of juvenile zebrafish as indicated in host metabolism and gut microbiome. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wen, X.; Mi, J.; Wu, Y. Adding a complex microbial agent twice to the composting of laying-hen manure promoted doxycycline degradation with a low risk on spreading tetracycline resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funabashi, M.; Grove, T.L.; Wang, M.; Varma, Y.; McFadden, M.E.; Brown, L.C.; Guo, C.; Higginbottom, S.; Almo, S.C.; Fischbach, M.A. A metabolic pathway for bile acid dehydroxylation by the gut microbiome. Nature 2020, 582, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, B.; Ruiz, N. Function and Biogenesis of Lipopolysaccharides. EcoSal. Plus 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Kakarla, D.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M.; Yoon, Y.E.; Lee, Y.B. Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) contamination as a global agro-ecological issue: A critical view. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B.A. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Dong, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Shang, B. Additional function of pasteurisation pretreatment in combination with anaerobic digestion on antibiotic removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmari, I.; Barcza, T.; Kormoczy, P.S.; Laczay, P. Ecotoxicological assessment of doxycycline in soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2012, 47, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbylik-Sikorska, M.; Gajda, A.; Nowacka-Kozak, E.; Posyniak, A. Doxycycline transfer from substrate to white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) and assessment of the potential consumer exposure. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewska, M.; Blazejewska, A.; Czapko, A.; Popowska, M. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Animal Manure—Consequences of Its Application in Agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 610656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Hu, H.W.; Gou, M.; Wang, J.T.; Chen, D.; He, J.Z. Temporal succession of soil antibiotic resistance genes following application of swine, cattle and poultry manures spiked with or without antibiotics. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Zhu, D.; Giles, M.; Yang, X.R.; Daniell, T.; Neilson, R.; Zhu, Y.G. Phyllosphere of staple crops under pig manure fertilization, a reservoir of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Xu, J.; Xiang, G.; Cao, Z.; Yan, Q.; Mi, J.; Ma, B.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liao, X.; et al. Multiple driving factors contribute to the variations of typical antibiotic resistance genes in different parts of soil-lettuce system. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.R.; Collins, J.J.; Relman, D.A. Antibiotics and the gut microbiota. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 4212–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.Y.; Yoon, S.S. Disruption of the Gut Ecosystem by Antibiotics. Yonsei Med. J. 2018, 59, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, A.; Crook, N.; Dantas, G. The effects of antibiotics on the microbiome throughout development and alternative approaches for therapeutic modulation. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; El khader, I.; Casellas, F.; Lopez Vivancos, J.; Garcia Cors, M.; Santiago, A.; Cuenca, S.; Guarner, F.; Manichanh, C. Short-term effect of antibiotics on human gut microbiota. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marker, L.M.; Hammer, A.S.; Andresen, L.; Isaack, P.; Clausen, T.; Byskov, K.; Honore, O.L.; Jensen, S.K.; Bahl, M.I. Short-term effect of oral amoxicillin treatment on the gut microbial community composition in farm mink (Neovison vison). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Ma, C.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.; Su, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Feed-additive probiotics accelerate yet antibiotics delay intestinal microbiota maturation in broiler chicken. Microbiome 2017, 5, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Feng, J.; Xue, R.; Ma, J.; Lou, L.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Deng, O.; Xie, L. The insufficient extraction of DNA from swine manures may underestimate the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes as well as ignore their potential hosts. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Ma, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X. Compost-bulking agents reduce the reservoir of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in manures by modifying bacterial microbiota. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Qin, W.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Hu, J. How Streptococcus suis serotype 2 attempts to avoid attack by host immune defenses. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.G.; Trampuz, A.; Di Luca, M. Synergistic antibiotic activity against planktonic and biofilm-embedded Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus oralis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 3085–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Yan, B.; Shutes, B.; Xu, Y.; Fu, B.; Wen, H. Isolation and characterization of a salt-tolerant denitrifying bacterium Alishewanella sp. F2 from seawall muddy water. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, R.; Hu, J.; Xing, S.; Huang, C.; Mi, J.; Liao, X. Dominant denitrifying bacteria are important hosts of antibiotic resistance genes in pig farm anoxic-oxic wastewater treatment processes. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, C.J. Antibiotics as food for bacteria. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 752–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.D.; Lawson, P.A.; Collins, M.D.; Falsen, E.; Tanner, R.S. Cloacibacterium normanense gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacterium in the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from municipal wastewater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martin, C.; Perez-Gonzalez, C.J.; Gonzalez-Toril, E.; Exposito, F.J.; Aguilera, A.; Diaz, J.P. Airborne Bacterial Community Composition According to Their Origin in Tenerife, Canary Islands. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 732961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, I.; Tyagi, K.; Bhutiani, R.; Chandra, K.; Kumar, V. Bacterial diversity assessment of world’s largest sewage-fed fish farms with special reference to water quality: A Ramsar site. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 42372–42386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racero, L.; Barberis, C.; Traglia, G.; Loza, M.S.; Vay, C.; Almuzara, M. Infections due to Vagococcus spp. Microbiological and clinical aspects and literature review. Enferm. Infec. Microbiol. Clin. 2021, 39, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Jiao, D.; Zhao, W.; Li, A.; Li, R.; Du, X.D. Emergence of a Novel tet(L) Variant in Campylobacter spp. of Chicken Origin in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65, e01622-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, J. Antimicrobial Resistance in Campylobacter spp. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, ARBA-0013-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.C.; Han, J.; Ferreira, R.B.; Lolic, P.; Borchers, C.H.; Finlay, B.B. Effect of antibiotic treatment on the intestinal metabolome. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Malwal, S.R.; Baig, N.; Schurig-Briccio, L.A.; Gao, Z.; Vaidya, G.S.; Yang, K.; Abutaleb, N.S.; Seleem, M.N.; Gennis, R.B.; et al. Discovery of Prenyltransferase Inhibitors with In Vitro and In Vivo Antibacterial Activity. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 2979–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.Y.; Cheng, T.H.; Wang, A.H. Structure, catalysis, and inhibition mechanism of prenyltransferase. IUBMB Life 2021, 73, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, A.; Kaysiewicz, J.; Markowska, J.; Huczynski, A. Doxycycline, salinomycin, monensin and ivermectin repositioned as cancer drugs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.R.; Haileselassie, Y.; Nguyen, L.P.; Tropini, C.; Wang, M.; Becker, L.S.; Sim, D.; Jarr, K.; Spear, E.T.; Singh, G.; et al. Dysbiosis-Induced Secondary Bile Acid Deficiency Promotes Intestinal Inflammation. Cell. Host. Microbe 2020, 27, 659–670.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Han, M.; Heinrich, B.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Sandhu, M.; Agdashian, D.; Terabe, M.; Berzofsky, J.A.; Fako, V.; et al. Gut microbiome-mediated bile acid metabolism regulates liver cancer via NKT cells. Science 2018, 360, eaan5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Liang, J.; Chen, W.; Wen, X.; Zhang, N.; Ma, B.; Zou, Y.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y.; Liao, X.; et al. Doxycycline Attenuates Pig Intestinal Microbial Interactions and Changes Microbial Metabolic Pathways. Animals 2023, 13, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081293
Xu J, Liang J, Chen W, Wen X, Zhang N, Ma B, Zou Y, Mi J, Wang Y, Liao X, et al. Doxycycline Attenuates Pig Intestinal Microbial Interactions and Changes Microbial Metabolic Pathways. Animals. 2023; 13(8):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081293
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiaojiao, Jiadi Liang, Wenjun Chen, Xin Wen, Na Zhang, Baohua Ma, Yongde Zou, Jiandui Mi, Yan Wang, Xindi Liao, and et al. 2023. "Doxycycline Attenuates Pig Intestinal Microbial Interactions and Changes Microbial Metabolic Pathways" Animals 13, no. 8: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081293
APA StyleXu, J., Liang, J., Chen, W., Wen, X., Zhang, N., Ma, B., Zou, Y., Mi, J., Wang, Y., Liao, X., & Wu, Y. (2023). Doxycycline Attenuates Pig Intestinal Microbial Interactions and Changes Microbial Metabolic Pathways. Animals, 13(8), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081293