Pen Surface Temperature as a Predictor of Daily Water Intake and Tympanic Temperature in Steers Finished in Feedlots
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Micrometeorological and Water Intake Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Daily Water Intake Model Development
3.2. Tympanic Temperature Model Development
3.3. Daily Water Intake Models’ Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arias, R.A. Environmental Factors Affecting Daily Water Intake on Cattle Finished in Feedlots; University of Nebraska-Lincoln: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Meador, H.N. Evaluating and Developing Water Intake Equations for Growing and Finishing Feedlot Steers; University of Tennessee: Knoxville, KN, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, M.P.; Self, H.L. Factors affecting water consumption by feedlot cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 1972, 35, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hicks, R.B.; Owens, F.N.; Gill, D.R.; Martin, J.J.; Strasia, C.A. Water Intake by Feedlot Steers; Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 1988; pp. 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, R.A.; Mader, T.L. Environmental factors affecting daily water intake on cattle finished in feedlots. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brew, M.N.; Myer, R.O.; Hersom, M.J.; Carter, J.N.; Elzo, M.A.; Hansen, G.R.; Riley, D.G. Water intake and factors affecting water intake of growing beef cattle. Livest. Sci. 2011, 140, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlberg, C.M.; Allwardt, K.; Broocks, A.; Bruno, K.; McPhillips, L.; Taylor, A.; Krehbiel, C.R.; Calvo-Lorenzo, M.S.; Richards, C.J.; Place, S.E.; et al. Environmental effects on water intake and water intake prediction in growing beef cattle1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 4368–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, V.A. Heat as a stress factor in herbivores under tropical conditions. In Herbivore Nutrition in the Subtropics and Tropics; Gilchrist, F.M.C., Mackie, R.I., Eds.; The Science Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 89–105. [Google Scholar]
- Silanikove, N. Effect of heat stress on the welfare of extensively managed domestic ruminants. Livest Prod. Sci. 2000, 67, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadzere, C.T.; Murphy, M.R.; Silanikove, N.; Maltz, E. Heat stress in lactating dairy cows: A review. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2002, 77, 59–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.G. Weather and Climate and Animal Production. In Guide to Agricultural Meteorological Practices (GAMP) WMO-No.134; Stigter, K., Ed.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; p. 21. Available online: https://library.wmo.int/doc_num.php?explnum_id=3996 (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- NRC. Effect of Environment on Nutrient Requirements of Domestic Animals; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1981; p. 152. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S. Management Strategies to Reduce Heat Stress in Feedlot Cattle Dissertation; University of Nebraska-Lincoln: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.; Mader, T.L. Adjustments for Wind Speed and Solar Radiation to the Temperature Humidity Index. Neb. Beef Cattle Rep. 2003, 49–51, MP 80-A. University of Nebraska. Available online: https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/animalscinbcr/224 (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Mader, T.L.; Davis, M.S.; Gaughan, J.B. Effect of sprinkling on feedlot microclimate and cattle behavior. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2007, 51, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monin, A.S.; Obukhov, A.M. The basic laws of turbulent mixing in the surface layer of the atmosphere. Akad Nauk USSR Acad. Sci. 1954, 24, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Mader, T.L.; Dahlquist, J.M.; Gaughan, J.B. Wind protection effects and airflow patterns in outside feedlots. J. Anim. Sci. 1997, 75, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoso, E.; Stull, R. Wind and temperature profiles in the radix layer: The bottom fifth of the convective boundary layer. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1998, 37, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, V.A. Body temperature in beef cattle: Its control and relevance to production in the tropics. J. Anim. Sci. 1986, 62, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.S.; Shrode, R.R.; Leighton, R.E.; Rupel, I.W. A study of the influence of solar radiation on physiological responses of dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 1960, 43, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Young, B.A.; Purwanto, B.P.; Nakamasu, F.; Matsumoto, T. Effect of solar radiation on the heat load of dairy heifers. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1994, 45, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.B.; Rogers, A.R.; Schütz, K.E. Effect of solar radiation on dairy cattle behaviour, use of shade and body temperature in a pasture-based system. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 109, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, N.A.; Mason, A.M.; Todd, R.W.; Rhoades, M.; Parker, D.B. Chemical Composition of Pen Surface Layers of Beef Cattle Feedyards1. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2009, 25, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeter, M. Drinking Water Intake by Finishing Yearling Beef Steers; West Texas A&M University: Canyon, TX, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sexson, J.L.; Wagner, J.J.; Engle, T.E.; Eickhoff, J. Predicting water intake by yearling feedlot steers. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, R.B.; Owens, F.N.; Gill, D.R.; Oltjen, J.W.; Lake, R.P. Daily dry matter intake by feedlot cattle: Influence of breed and gender. J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 68, 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, W.T.; Branine, M.E.; Bryant, T.C.; Archibeque, S.L.; Wagner, J.J. PSI-9 Effect of Pen-Surface Temperature and Trace Mineral Source on Infrared Hide Temperature in Cattle Raised in Confinement Under a Natural-Feeding Protocol in Summer. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitlohner, F.M.; Galyean, M.L.; McGlone, J.J. Shade effects on performance, carcass traits, physiology, and behavior of heat-stressed feedlot heifers. J. Anim Sci. 2002, 80, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown-Brandl, T.M.; Chitko-McKown, C.G.; Eigenberg, R.A.; Mayer, J.J.; Welsh, T.H.; Davis, J.D.; Purswell, J.L. Physiological responses of feedlot heifers provided access to different levels of shade. Animal 2017, 11, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.V.; Latack, B.C.; Zinn, R.A. PSXIV-3 Effect of pen mud Accumulation on the Growth Performance Growing-Finishing Calf-fed Holstein Steers in the Feedlot During Summer in Southern California. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, 354–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, M.R.; Devereux, J.; Phillips, F.; Lewis, R.; Naylor, T.; Kearton, T.; Hill, C.J.; Weidemann, S. Field measurement of beef pen manure methane and nitrous oxide reveals a surprise for inventory calculations. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.; Mader, T.L. Effect of Altered Feeding and Sprinkling on Performance and Body Temperature of Steers Finished in the Summer; University of Nebraska-Lincoln: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2002; pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Marcillac-Embertson, N.M.; Robinson, P.H.; Fadel, J.G.; Mitloehner, F.M. Effects of shade and sprinklers on performance, behavior, physiology, and the environment of heifers. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 11th ed.; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 740. [Google Scholar]
- Harpstead, M.I.; Sauer, T.J.; Benett, W.F. Soil Science Simplified, 4th ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, G.; Kumar, A. Surface energy fluxes and crop water stress index in groundnut under irrigated ecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 146, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchester, C.F.; Morris, M.J. Water intake rates of cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 1956, 15, 722–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, D.; Prados, L.F.; Menezes, A.C.B.; Silva, B.C.; Pacheco, M.V.C.; Silva, F.A.S.; Costa e Silva, L.F.; Detmann, E.; Engle, T.E.; Valadares Filho, S.C. Prediction of water intake to Bos indicus beef cattle raised under tropical conditions1. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, R.A.; Mader, T.L. Effects on Environmental Factors on Body Temperature of Feedlot Cattle; University of Nebraska: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2009; pp. 102–104. [Google Scholar]
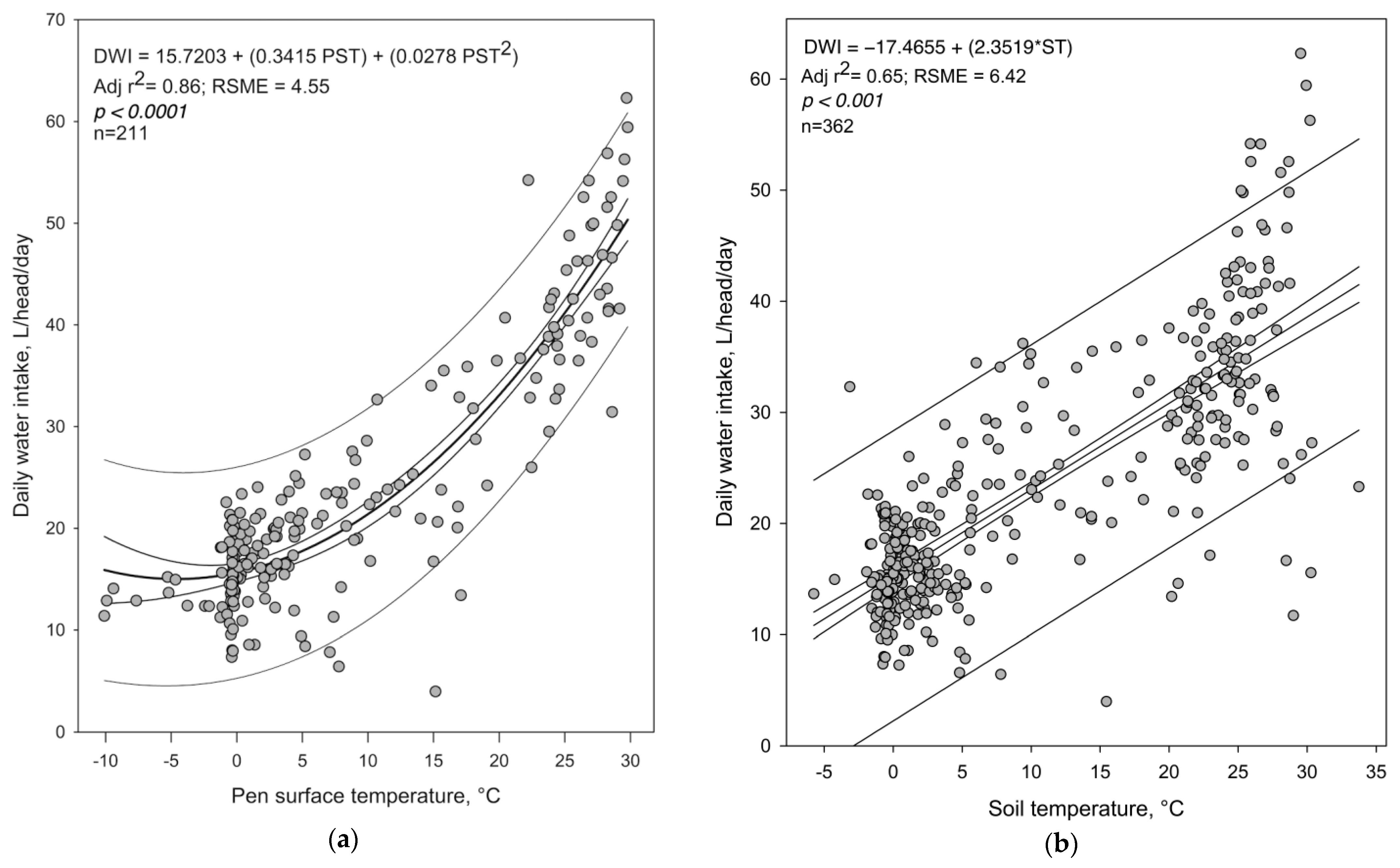
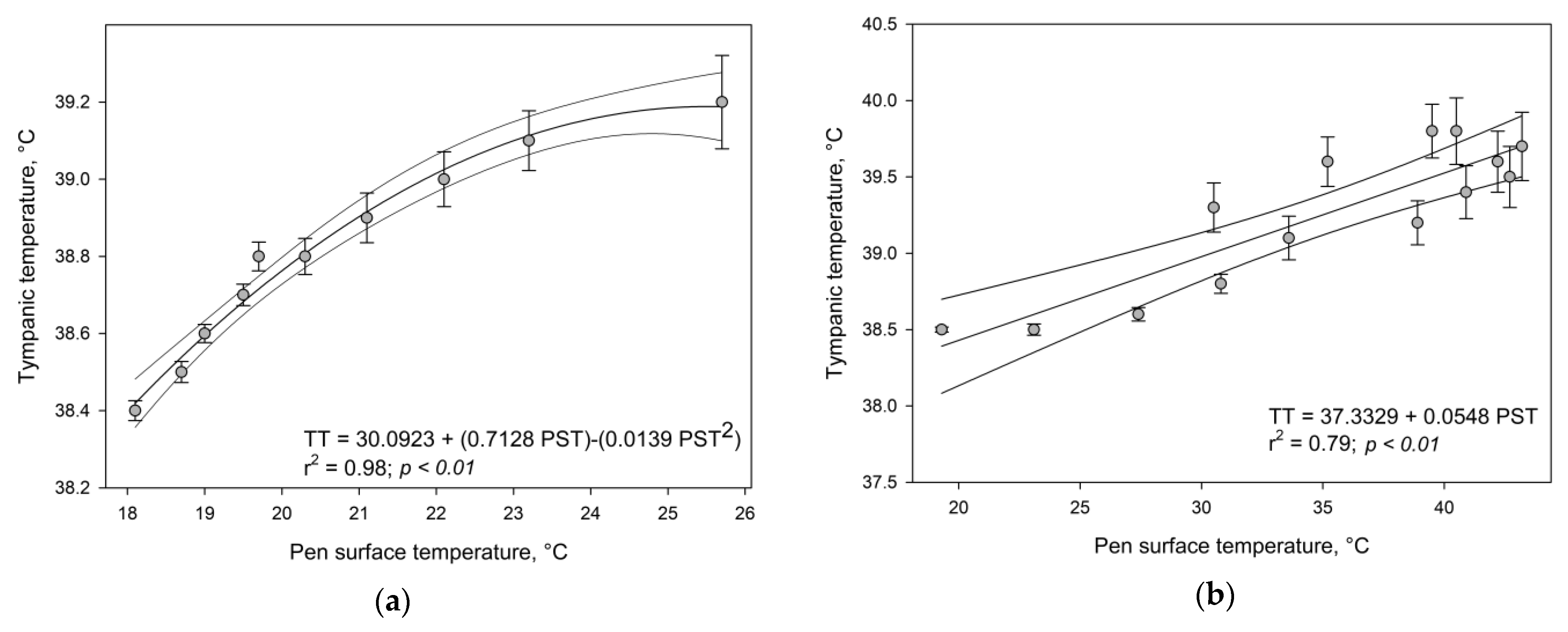
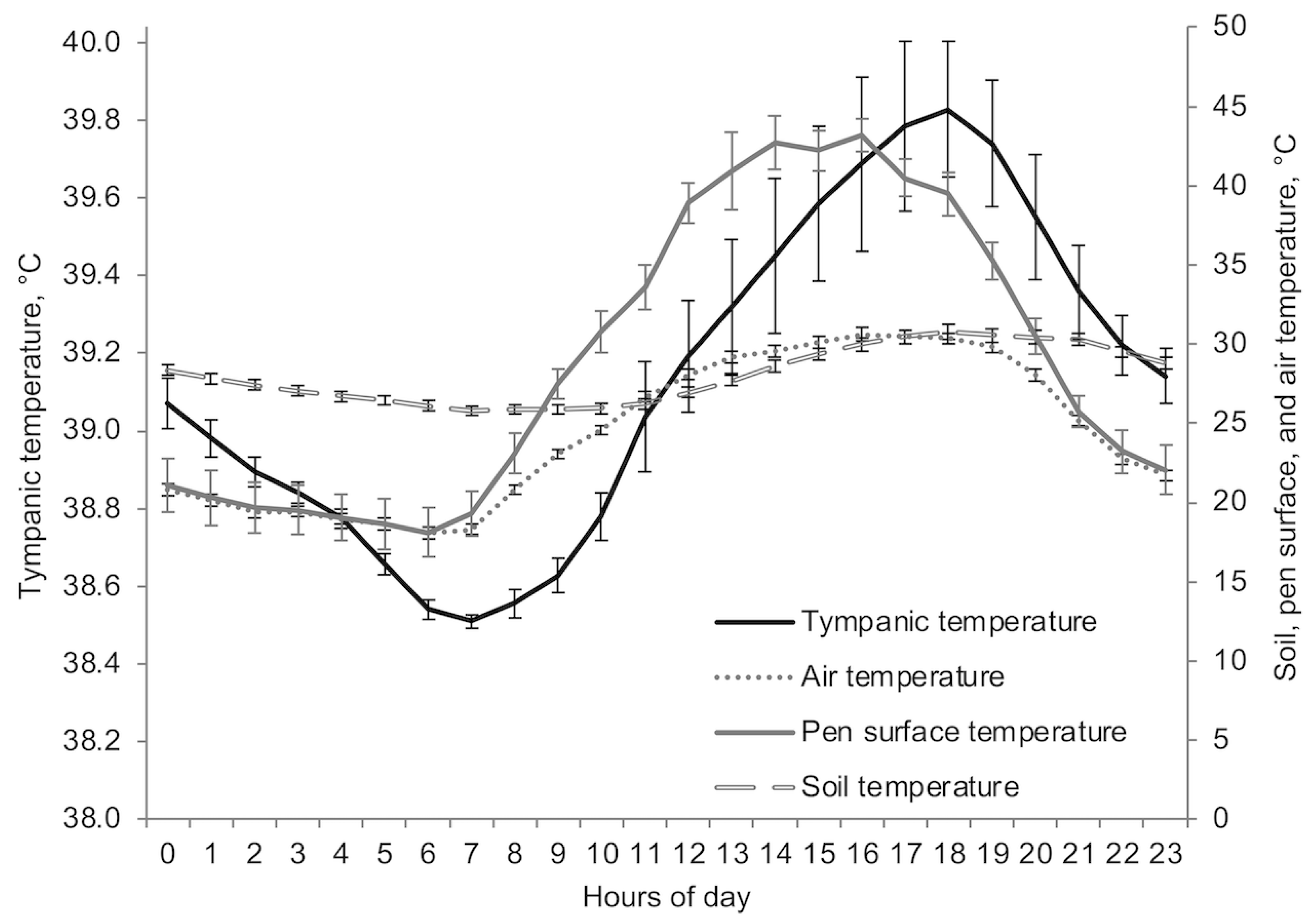
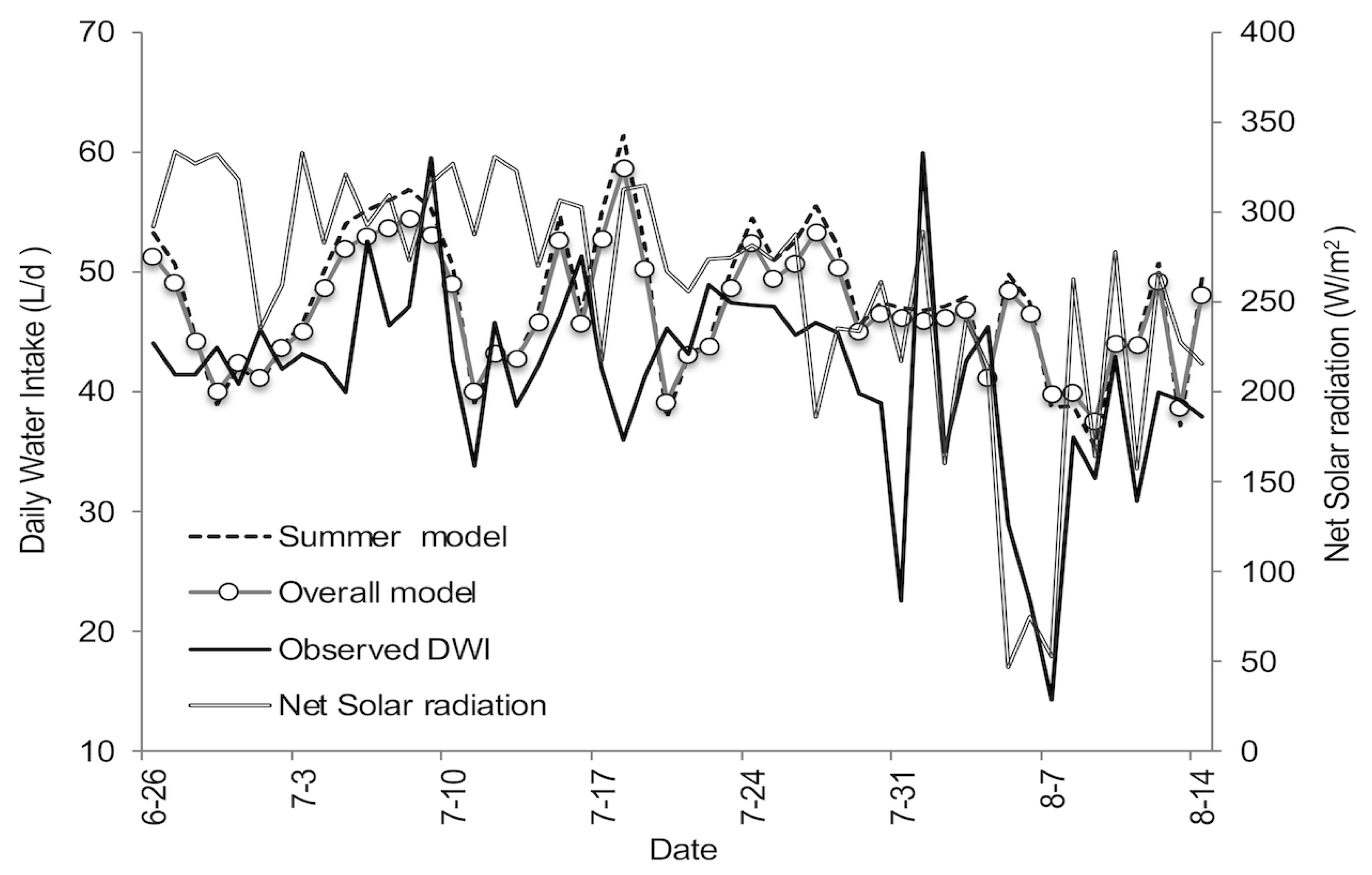
| Predictor Variable and Models | Linear | Quadratic | Cubic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil temperature | Overall n = 362 | 0.65 (<0.01) | 0.65 (0.02) | 0.65 (0.28) |
| Summer n = 143 | 0.08 (<0.01) | 0.11 (0.08) | 0.10 (0.64) | |
| Pen surface temperature | Overall n = 211 | 0.82 (<0.01) | 0.86 (<0.01) | 0.87 (<0.01) |
| Summer n = 55 | 0.69 (<0.01) | 0.68 (0.85) | 0.72 (<0.01) | |
| ST, °C | AT, °C | PST, °C | SR, W/m2 | WS, m/s | THI | TT, °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 27.98 | 24.22 | 24.41 | 197.50 | 2.31 | 71.43 | 39.24 |
| SEM | 0.38 | 0.91 | 1.50 | 43.50 | 0.21 | 1.16 | 0.08 |
| Min | 23.31 | 11.50 | 7.74 | −80.83 | 0.61 | 52.96 | 38.52 |
| Max | 32.15 | 34.46 | 40.82 | 683.32 | 6.00 | 83.25 | 40.44 |
| Item | Observed Daily Water Intake | Predicted Daily Water Intake | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summer Model | Overall Model | ||
| Mean | 41.5 | 47.6 | 46.7 |
| SEM | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.7 |
| Maximum | 59.9 | 61.4 | 58.7 |
| Minimum | 14.3 | 35.4 | 37.5 |
| Range | 45.6 | 26.0 | 21.2 |
| Model and Correlation | Overall Period | July (31 Days) | August (15 Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 0.42 | ns | 0.56 |
| Quadratic | 0.47 | ns | 0.55 |
| Cubic | 0.48 | ns | 0.54 |
| Correlation | 0.66 | 0.02 | 0.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arias, R.A.; Mader, T.L. Pen Surface Temperature as a Predictor of Daily Water Intake and Tympanic Temperature in Steers Finished in Feedlots. Animals 2023, 13, 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13071150
Arias RA, Mader TL. Pen Surface Temperature as a Predictor of Daily Water Intake and Tympanic Temperature in Steers Finished in Feedlots. Animals. 2023; 13(7):1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13071150
Chicago/Turabian StyleArias, Rodrigo A., and Terry L. Mader. 2023. "Pen Surface Temperature as a Predictor of Daily Water Intake and Tympanic Temperature in Steers Finished in Feedlots" Animals 13, no. 7: 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13071150
APA StyleArias, R. A., & Mader, T. L. (2023). Pen Surface Temperature as a Predictor of Daily Water Intake and Tympanic Temperature in Steers Finished in Feedlots. Animals, 13(7), 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13071150





