Physiological Impairment and Biochemical Modifications Induced by Triclosan in Mediterranean Mussels
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Specimens’ Collection and Exposure Preparation
2.2. Physiological Parameters Determination
2.3. Biomarker’s Determination
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
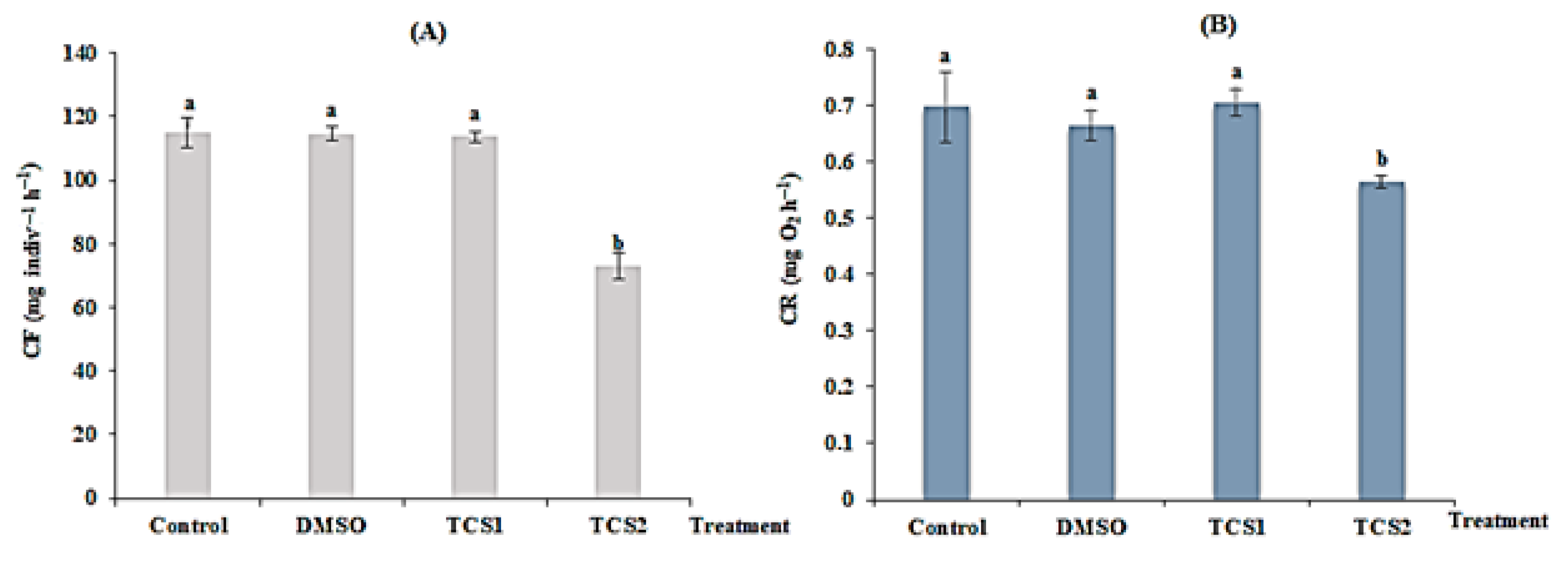
3.1. Triclosan Impact on Mussel’s Physiology
3.2. Effects of Triclosan on Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
3.3. Effects of Triclosan on MDA Levels and AChE Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franzellitti, S.; Buratti, S.; Du, B.; Haddad, S.P.; Chambliss, C.K.; Brooks, B.W.; Fabbri, E. A multibiomarker approach to explore interactive effects of propranolol and fluoxetine in marine mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 205, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, B.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Zimmermann, J.; Nicholls, R.J. Future coastal population growth and exposure to sea-level rise and coastal flooding—A global assessment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taştan, B.E.; Tekinay, T.; Celik, H.S.; Özdemir, C.; Cakir, D.N. Toxicity assessment of pesticide triclosan by aquatic organisms and degradation studies. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2017, 91, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daughton, C.G.; Ternes, T. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: Agents of subtle change? Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 907–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perron, M.M.; Ho, K.T.; Cantwell, M.G.; Burgess, R.M.; Pelletier, M.C. Effects of triclosan on marine benthic and epibenthic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1861–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orvos, D.R.; Versteeg, D.J.; Inauen, J.; Capdevielle, M.; Rothenstein, A.; Cunningham, V. Aquatic toxicity of triclosan. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2002, 21, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Contaminants of Emerging Concern Including Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products. 2015. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/wqc/contaminants-emerging-concern-including-pharmaceuticals-and-personal-care-products (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Zhao, J.-L.; Ying, G.-G.; Liu, Y.-S.; Chen, F.; Yang, J.-F.; Wang, L. Occurrence and risks of triclosan and triclocarban in the Pearl River system, South China: From source to the receiving environment. J. Hazard. Mat. 2010, 179, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintado-Herrera, M.G.; Gonz_alez-Mazo, E.; Lara-Martín, P.A. Determining the distribution of triclosan and methyl triclosan in estuarine settings. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaseri, H.; Forbes, P.B. A review of monitoring methods for triclosan and its occurrence in aquatic environments. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhoen, N.; Skirrow, R.C.; Osachoff, H.; Wigmore, H.; Clapson, D.J.; Gunderson, M.P.; Helbing, C.C. The bactericidal agent triclosan modulates thyroid hormone-associated gene expression and disrupts postembryonic anuran development. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalew, T.E.; Halden, R.U. Environmental exposure of aquatic and terrestrial biota to triclosan and triclocarban. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Ass. 2009, 45, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, B.; Feijão, E.; Cruz de Carvalho, R.; Matos, A.R.; Cabrita, M.T.; Novais, S.C.; Moutinho, A.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Marques, J.C.; Caçador, I.; et al. Effect Biomarkers of the Widespread Antimicrobial Triclosan in a Marine Model Diatom. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobre, C.R.; Moreno, B.B.; Alves, A.V.; de Lima Rosa, J.; Fontes, M.K.; de Campos, B.G.; Pereira, C.D.S. Combined effects of polyethylene spiked with the antimicrobial triclosan on the swamp ghost crab (Ucides cordatus; Linnaeus, 1763). Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.C.; Pena, A.; Fernandes, J.O. Mussels as bioindicators of diclofenac contamination in coastal environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduč, T.; Medaković, D.; Hamer, B. Mytilus galloprovincialis as a bioindicator of environmental conditions: The case of the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2011, 47, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Diaz, M.L.; Franzellitti, S.; Buratti, S.; Valbonesi, P.; Capuzzo, A.; Fabbri, E. Effects of environmental concentrations of the antiepilectic drug carbamazepine on biomarkers and cAMP-mediated cell signaling in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 94, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilin, J.; Pestana, J.L.T.; Ferreira, N.G.; Loureiro, S.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; Soares, A.M. Physiological responses of the European cockle Cerastoderma edule (Bivalvia: Cardidae) as indicators of coastal lagoon pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 435, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Xu, L.; Guo, Z.; Xu, H.; Xie, H.Q.; Zhao, B. Acetylcholinesterase is a potential biomarker for a broad spectrum of organic environmental pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8065–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.N.; Eom, H.J.; Nam, S.E.; Shin, Y.K.; Rhee, J.S. Chlorothalonil induces oxidative stress and reduces enzymatic activities of Na+/K+-ATPase and acetylcholinesterase in gill tissues of marine bivalves. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Fang, J.; Gao, Y.; Du, M.; Fang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Lin, F.; Jiang, Z. Biomarkers responses in Manila clam, Ruditapes philippinarum after single and combined exposure to mercury and benzo[a]pyrene. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. 2019, 220, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, J. The estimation of filtering rate from the clearance of suspensions. Mar. Biol. 1969, 2, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basti, L.; Nagai, S.; Watanabe, S.; Oda, T.; Tanaka, Y. Neuroenzymatic activity and physiological energetics in Manila clam, Ruditapes philippinarum, during short-term sublethal exposure to harmful alga, Heterocapsa circularisquama. Aquat. Toxicol 2016, 176, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, S.P. Ferrous ion oxidation in presence of ferric ion indicator xylenol orange for measurement of hydroperoxides. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 233, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Marklund, S.; Marklund, G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase. In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Bergmeyer, H.U., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1974; pp. 671–684. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, W.; Trelease, R.N.; Eising, R. Two temporally synthesized charge subunits interact to form the five isoformes of cottonseed (Gossypium hirsutum) catalase. Biochemistry 1990, 269, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S-transferases.The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 25, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, H.; Grudniewska, J. Evaluation of oxidative stress markers in the heart and liver of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss walbaum) exposed to the formalin. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 1819–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analyt. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, Â.; Silva, M.G.; Soares, A.M.; Freitas, R. Concentrations levels and effects of 17alpha-Ethinylestradiol in freshwater and marine waters and bivalves: A review. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkin, P.; Widdows, J.; Evans, S.V.; Staþ, F.J.; Yan, T. Effect of Neurotoxic Pesticides on the Feeding Rate of Marine Mussels (Mytilus edulis). Pestic. Sci. 1997, 49, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidani, W.; Sellami, B.; Khazri, A.; Mezni, A.; Dellali, M.; Joubert, O.; Sheehane, D.; Beyrem, H. Metal accumulation, biochemical and behavioral responses on the Mediterranean clams Ruditapes decussatus exposed to two photocatalyst nanocomposites (TiO2 NPs and AuTiO2NPs). Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 208, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Vieira, L.R.; Branco, V.; Carvalho, C.; Guilhermino, L. Microplastics increase mercury bioconcentration in gills and bioaccumulation in the liver, and cause oxidative stress and damage in Dicentrarchus labrax juveniles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesne, S.; Liess, M.; Bird, D.J. Sub-lethal effects of metal exposure: Physiological and behavioural responses of the estuarine bivalve Macoma balthica. Mar. Environ. Res. 2004, 58, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, S.; Gaw, S.; Marsden, I.D.; McRae, N.K. Biomarker responses in New Zealand green-lipped mussels Perna canaliculus exposed to microplastics and triclosan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolton, A.; Champeau, O.; Barrick, A.; Boundy, M.; Tremblay, L.A.; Vignier, J. Characterization of the effects of triclosan on sperm and embryos of Mytilus and Perna mussel species. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 245, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.; Almeida, Â.; Calisto, V.; Esteves, V.I.; Schneider, R.J.; Wrona, F.J.; Soares, A.M.; Figueira, E.; Freitas, R. Physiological and biochemical alterations induced in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis after short and long-term exposure to carbamazepine. Water Res. 2017, 117, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, E. Bivalve Molluscs: Biology, Ecology and Culture; Fishing News Books: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y.; Bang, K.S. The effects of enteral feeding improvement massage on premature infants: A randomised controlled trial. J. Clin. Nurs. 2018, 27, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatov, A.A.; Gostyukhina, O.L.; Golovina, I.V. Antioxidant enzyme complex of tissues of the bivalve Mytilus galloprovincialis Lam. under normal and oxidative-stress conditions: A review. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2007, 43, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.R.; Wu, J.C.; Xue, Y.Q. Effects of chronic exposure of 2,4-dichlorophenol on the antioxidant system in liver of freshwater fish Carassius auratus. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.; Coppola, F.; Costa, S.; Pretti, C.; Intorre, L.; Meucci, V.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Solé, M. The influence of temperature on the effects induced by Triclosan and Diclofenac in mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parenti, C.C.; Ghilardi, A.; Della Torre, C.; Mandelli, M.; Magni, S.; Del Giacco, L.; Binelli, A. Environmental concentrations of triclosan activate cellular defense mechanism and generate cytotoxicity on zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranho, L.A.; Baena-Nogueras, R.M.; Lara-Martín, P.A.; Del Valls, T.A.; Martín-Díaz, M.L. Bioavailability, oxidative stress, neurotoxicity and genotoxicity of pharmaceuticals bound to marine sediments. The use of the polychaete Hediste diversicolor as bioindicator species. Environ. Res. 2014, 134, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, M.K.; Gusso-Choueri, P.K.; Maranho, L.A.; de Souza Abessa, D.M.; Mazur, W.A.; de Campos, B.G.; Guimarães, L.L.; de Toledo, A.; Lebre, M.S.; Marques, J.R.; et al. A tiered approach to assess effects of diclofenac on the brown mussel Perna perna: A contribution to characterize the hazard. Water Res. 2018, 132, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Ciacci, C.; Lorusso, L.C.; Betti, M.; Gallo, G.; Pojana, G.; Marcomini, A. Effects of Triclosan on Mytilus galloprovincialis hemocyte function and digestive gland enzyme activities: Possible modes of action on non-target organisms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 145, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tu, Y.; Song, C.; Li, T.; Lin, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, C. Interactions between the antimicrobial agent triclosan and the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 172, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rey, M.; Bebianno, M.J. Effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) diclofenac exposure in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 148, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świacka, K.; Maculewicz, J.; Świeżak, J.; Caban, M.; Smolarz, K. A multi-biomarker approach to assess toxicity of diclofenac and 4-OH diclofenac in Mytilus trossulus mussels-First evidence of diclofenac metabolite impact on molluscs. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Nie, X.P.; Liao, W.; Yang, Y.F.; Ying, G.G. Toxic effects of triclosan on the detoxification system and breeding of Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ai, W.; Sun, L.; Fang, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, H. Triclosan-induced liver injury in zebrafish (Danio rerio) via regulating MAPK/p53 signaling pathway. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 222, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Gilabert, A.; Porte, C. Precision cut tissue slices to investigate the effects of triclosan exposure in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicol. In Vitro 2022, 85, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storey, K.B. Oxidative stress: Animal adaptations in nature. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1996, 29, 1715–1733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.; Domingues, I.; Koppe Grisolia, C.; Soares, A.M. Effects of triclosan on zebrafish early-life stages and adults. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouzidi, I.; Mougin, K.; Beyrem, H.; Alghonaim, M.I.; Alsalamah, S.A.; Qurtam, A.A.; Mahmoudi, E.; Boufahja, F.; Sellami, B. Physiological Impairment and Biochemical Modifications Induced by Triclosan in Mediterranean Mussels. Animals 2023, 13, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040583
Bouzidi I, Mougin K, Beyrem H, Alghonaim MI, Alsalamah SA, Qurtam AA, Mahmoudi E, Boufahja F, Sellami B. Physiological Impairment and Biochemical Modifications Induced by Triclosan in Mediterranean Mussels. Animals. 2023; 13(4):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040583
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouzidi, Imen, Karine Mougin, Hamouda Beyrem, Mohammed I. Alghonaim, Sulaiman A. Alsalamah, Ashraf A. Qurtam, Ezzeddine Mahmoudi, Fehmi Boufahja, and Badreddine Sellami. 2023. "Physiological Impairment and Biochemical Modifications Induced by Triclosan in Mediterranean Mussels" Animals 13, no. 4: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040583
APA StyleBouzidi, I., Mougin, K., Beyrem, H., Alghonaim, M. I., Alsalamah, S. A., Qurtam, A. A., Mahmoudi, E., Boufahja, F., & Sellami, B. (2023). Physiological Impairment and Biochemical Modifications Induced by Triclosan in Mediterranean Mussels. Animals, 13(4), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040583




