Temporal Microbial Dynamics in Feces Discriminate by Nutrition, Fecal Color, Consistency and Sample Type in Suckling and Newly Weaned Piglets
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Housing and Feeding
2.2. Body Weight Measurements and Collection of Fecal Samples
2.3. DNA Extraction, Quantitative PCR and 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatical Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Litters and Estimated Creep Feed Intake
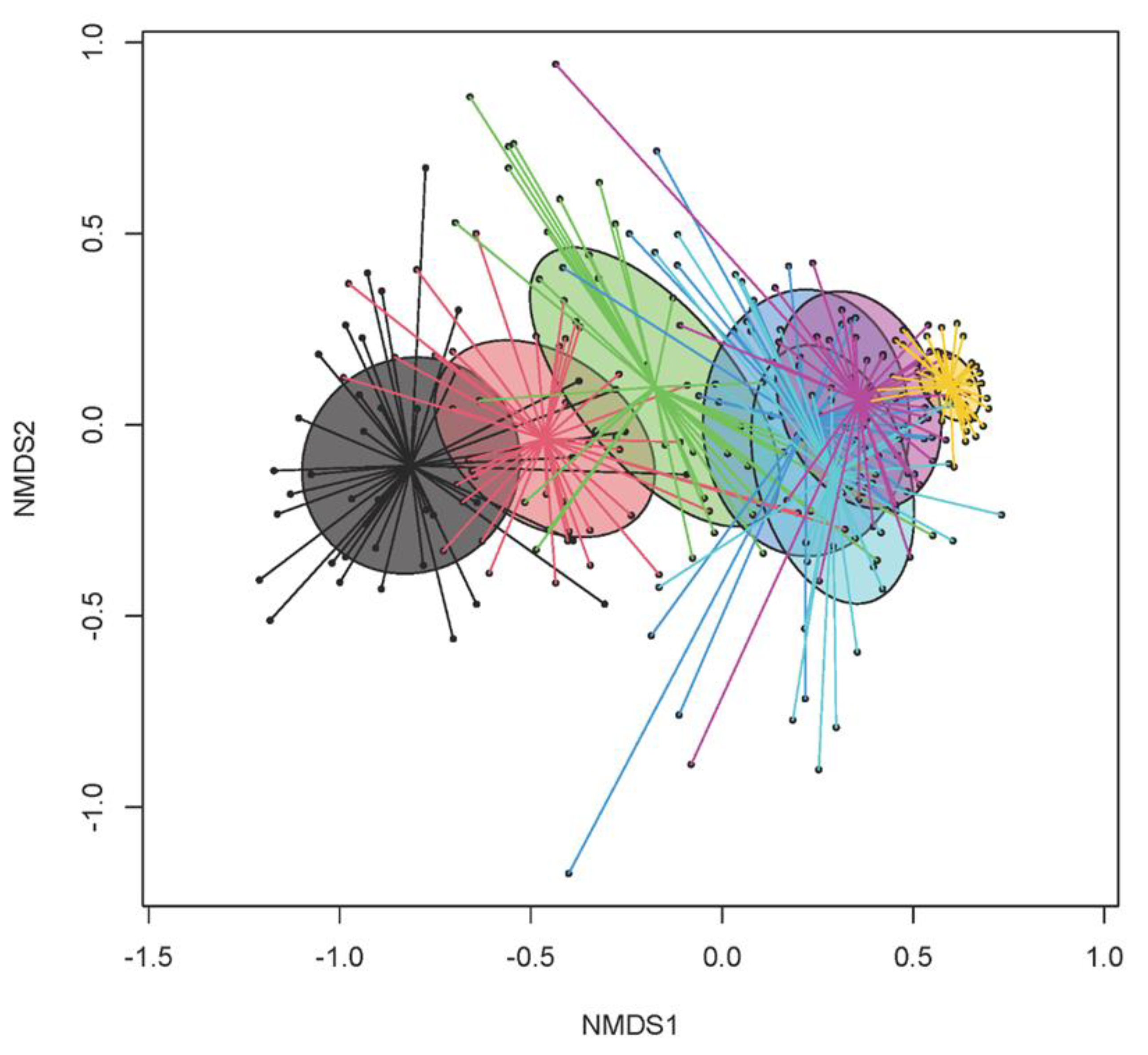
3.2. Temporal Dynamics in Bacterial Microbiome
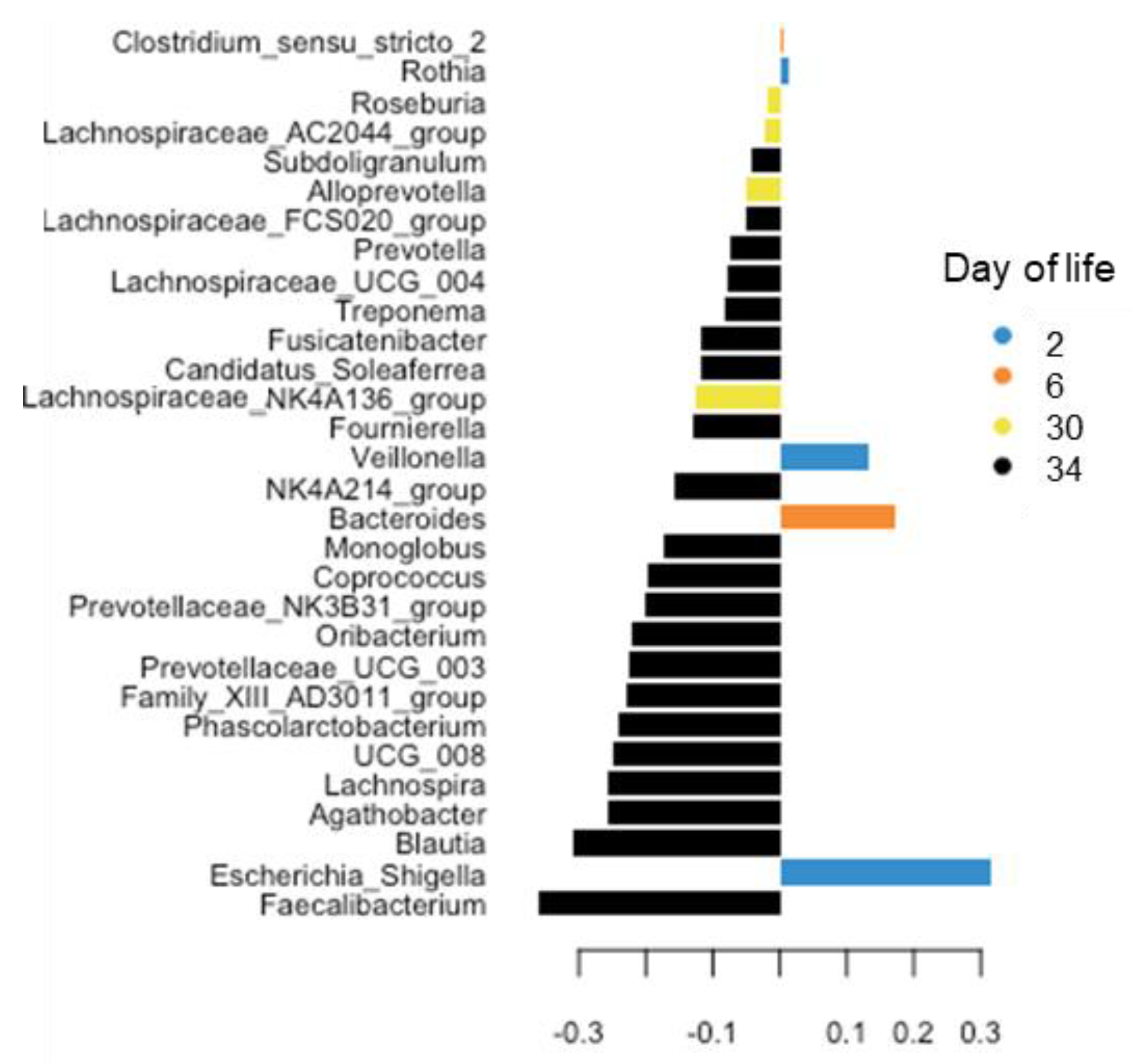
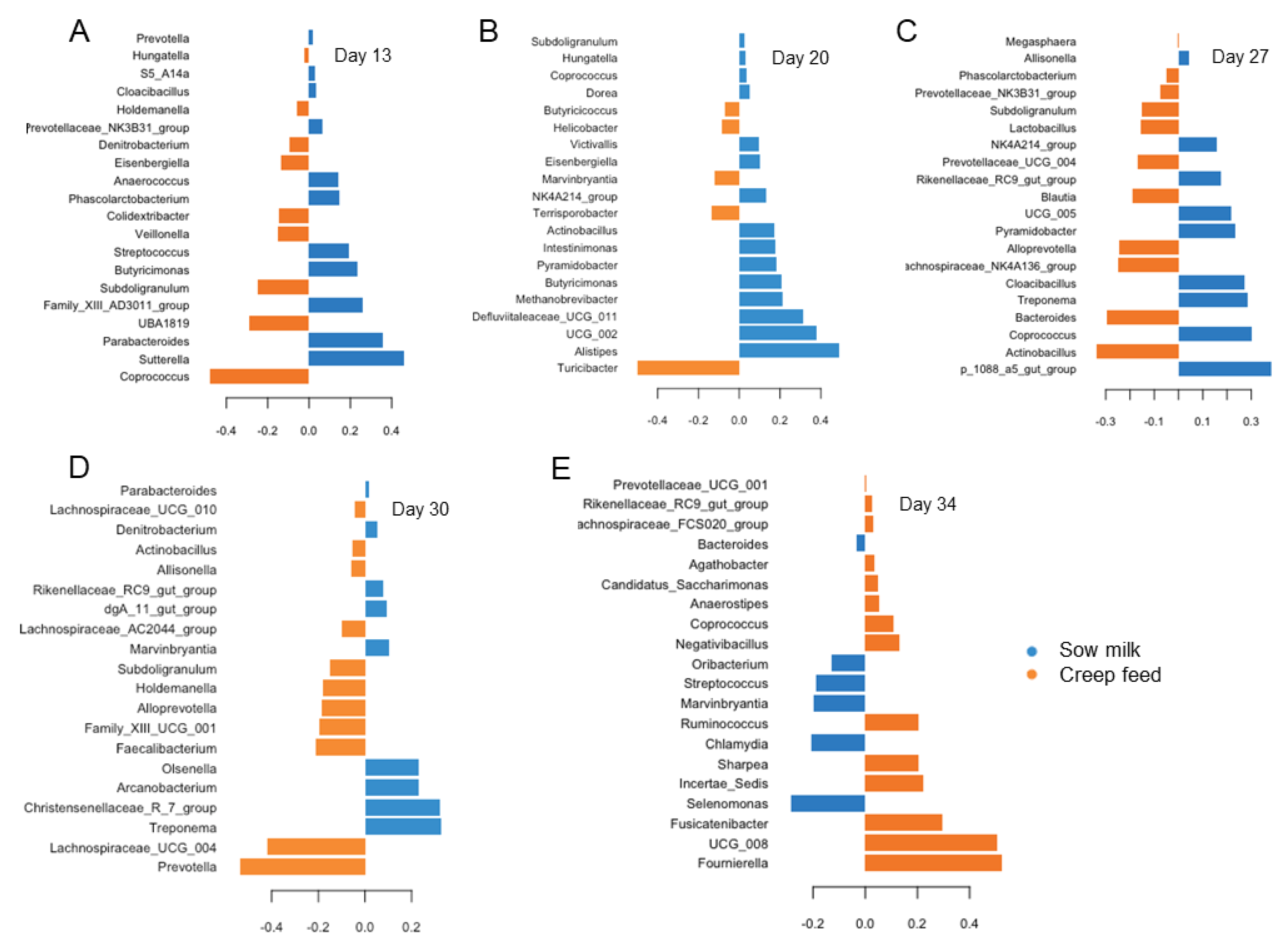
3.3. Differences in Age-Related Bacterial Development Due to Creep Feeding
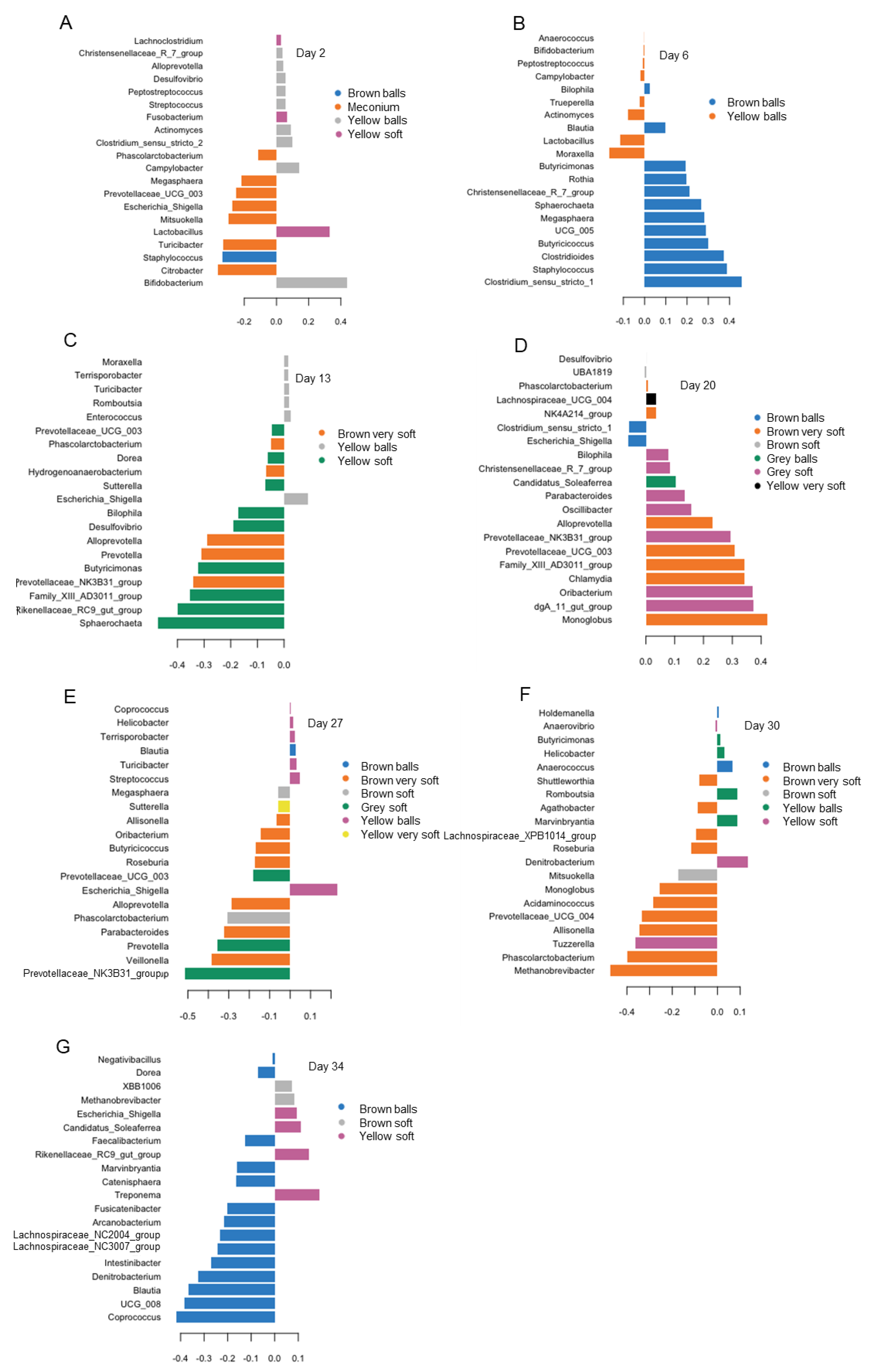
3.4. Differences in Bacterial Abundances between Feces of Varying Color and Consistency
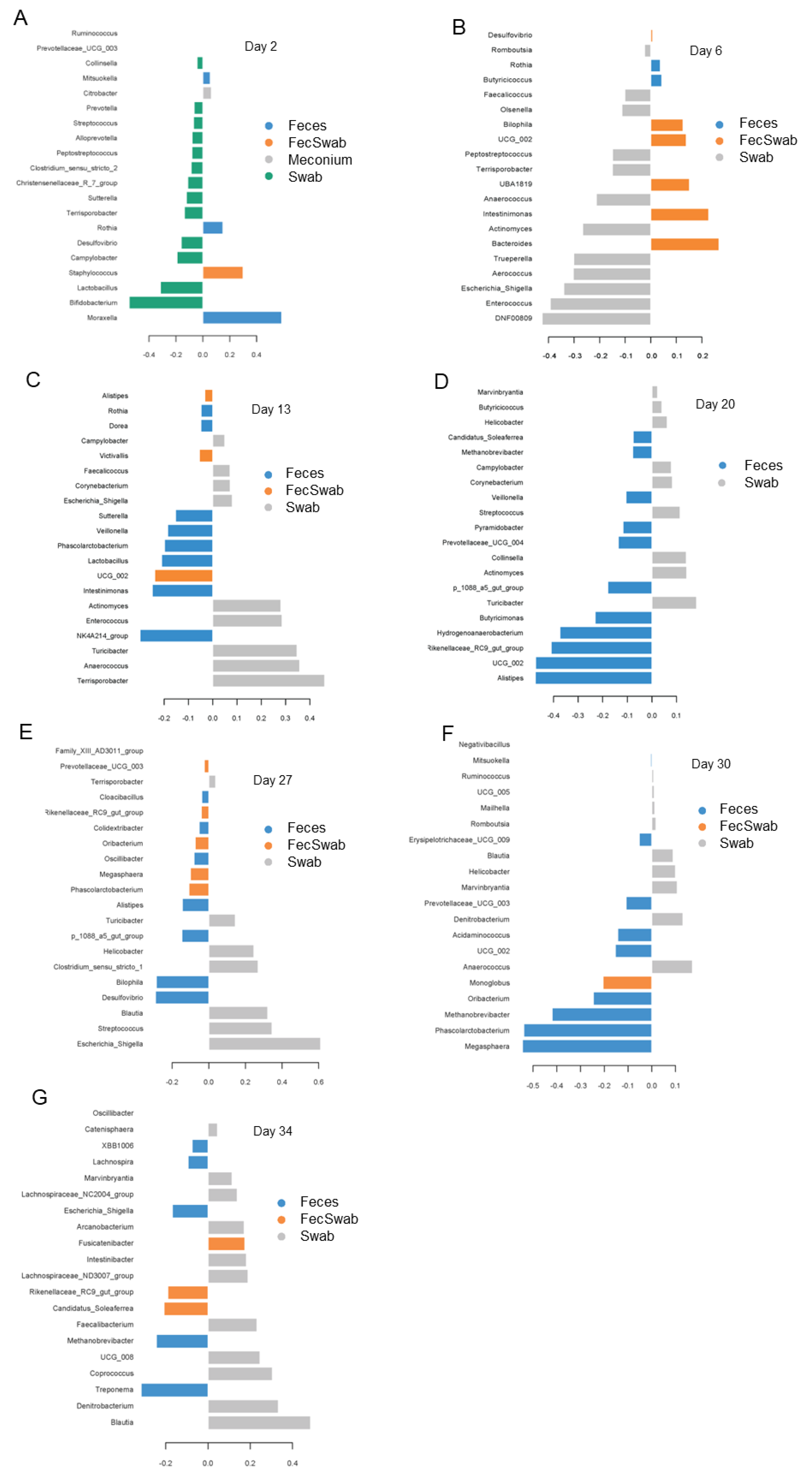
3.5. Differences in Bacterial Abundances between Feces and Swab Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Seok, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, B.N.; Johnson, T.J.; Isaacson, R.E.; Kim, H.B. Piglet gut microbial shifts early in life: Causes and effects. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, U.M.; Curião, T.; Wilkinson, T.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Reyer, H.; Ryan, T.; Calderon-Diaz, J.A.; Crispie, F.; Cotter, P.D.; Creevey, C.J.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation in gestating sows and neonatal offspring alters lifetime intestinal microbiota and growth in offspring. mSystems 2018, 3, e00134-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruczizka, U.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.; Unterweger, C.; Mann, E.; Schwarz, L.; Knecht, C.; Hennig-Pauka, I. Early parenteral administration of ceftiofur has gender-specific short- and long-term Effects on the fecal microbiota and growth in pigs from the suckling to growing phase. Animals 2019, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schokker, D.; Zhang, J.; Vastenhouw, S.A.; Heilig, H.G.; Smidt, H.; Rebel, J.M.; Smits, M.A. Long-lasting effects of early-life antibiotic treatment and routine animal handling on gut microbiota composition and immune system in pigs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, I.E.; Schmidt, B.; Stokes, C.R.; Lewis, M.; Bailey, M.; Aminov, R.I.; Prosser, J.I.; Gill, B.P.; Pluske, J.R.; Mayer, C.D.; et al. Environmentally-acquired bacteria influence microbial diversity and natural innate immune responses at gut surfaces. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladrigas-García, M.; Durán, M.; D’Angelo, M.; Coma, J.; Pérez, J.F.; Martín-Orúe, S.M. An insight into the commercial piglet’s microbial gut colonization: From birth towards weaning. Anim. Microbiome 2022, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schokker, D.; Fledderus, J.; Jansen, R.; Vastenhouw, S.A.; de Bree, F.M.; Smits, M.A.; Jansman, A.A.J.M. Supplementation of fructooligosaccharides to suckling piglets affects intestinal microbiota colonization and immune development. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 2139–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U. Porcine gut microbiota and host interactions during the transition from the suckling to post-weaning phase. In Gut Microbiota, Immunity, and Health in Production Animals; Kogut, M.H., Zhang, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, F.; Vötterl, J.C.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Sassu, E.L.; Schwarz, L.; Renzhammer, R.; Bünger, M.; Sharma, S.; Koger, S.; Sener-Aydemir, A.; et al. Exposure to plant-oriented microbiome altered jejunal and colonic innate immune response and barrier function more strongly in suckling than in weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrgesen, N.; Madsen, J.G.; Larsen, C.; Kjeldsen, N.J.; Cilieborg, M.S.; Amdi, C. The effect of feeding liquid or dry creep feed on growth performance, feed disappearance, enzyme activity and number of eaters in suckling piglets. Animals 2021, 11, 3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, R.; Middelkoop, A.; Bolhuis, J.E.; Kleerebezem, M. Legitimate and reliable determination of the age-related intestinal microbiome in young piglets; rectal swabs and fecal samples provide comparable insights. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Sener-Aydemir, A.; Sharma, S.; Lerch, F. Postnatal development of gut microbial activity and their importance for jejunal motility in piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, A.P.; Rome, V.; Richard, M.; Formal, M.; David-Le Gall, S.; Boudry, G. Post-natal co-development of the microbiota and gut barrier function follows different paths in the small and large intestine in piglets. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1430–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhai, Z.; He, C.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, W.; et al. The dynamic distribution of porcine microbiota across different ages and gastrointestinal tract segments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Klinsoda, J.; Vötterl, J.C.; Verhovsek, D. Maturational changes alter effects of dietary phytase xupplementation on the fecal microbiome in fattening pigs. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, A.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Karembe, H.; Sperling, D.; Koger, S.; Joachim, A. Shifts in the fecal microbial community of Cystoisospora suis infected piglets in response to toltrazuril. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frese, S.A.; Parker, K.; Calvert, C.C.; Mills, D.A. Diet shapes the gut microbiome of pigs during nursing and weaning. Microbiome 2015, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, L.; Li, X.; Zhong, H.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ge, L. Identification of the core bacteria in rectums of diarrheic and non-diarrheic piglets. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Lerch, F.; Yosi, F.; Vötterl, J.C.; Koger, S.; Aigensberger, M.; Rennhofer, P.M.; Berthiller, F.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E. Creep feeding and weaning influence the postnatal evolution of the plasma metabolome in neonatal piglets. Metabolites 2023, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (NRC). Nutrient Requirements of Swine, 10th ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Lawlor, P.G.; Magowan, E.; Zebeli, Q. Effect of freezing conditions on fecal bacterial composition in pigs. Animals 2016, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.; McMurdie, P.; Rosen, M.; Han, A.; Johnson, A.; Holmes, S. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Meth. 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package R Package Version 2.6–4. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Lê Cao, K.A. MixOmics: A R package for ‘omics feature selection and multiple data integration. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, S.; Miragoli, F.; Pisacane, V.; Rebecchi, A.; Morelli, L.; Callegari, M.L. Archaeal microbiota population in piglet feces shifts in response to weaning: Methanobrevibacter smithii is replaced with Methanobrevibacter boviskoreani. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Rao, Y.; Tu, X.; Wang, Z.; Gong, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, X. Gut archaea associated with bacteria colonization and succession during piglet weaning transitions. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, J.; Frese, S.A.; Mills, D.A.; Barile, D. Characterization of porcine milk oligosaccharides during early lactation and their relation to the fecal microbiome. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7733–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, U.Y.; Looft, T.; Allen, H.K.; Stanton, T.B. Butyrate-producing bacteria, including mucin degraders, from the swine intestinal tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3879–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.; Guo, P.; Liu, L.; Ma, N.; Levesque, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Dietary fiber increases butyrate-producing bacteria and improves the growth performance of weaned piglets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7995–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, E.M.; Kilcoyne, M.; Walsh, D.; Joshi, L.; Hickey, R.M. A whey fraction rich in immunoglobulin G combined with Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis ATCC 15697 exhibits synergistic effects against Campylobacter jejuni. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.; Lane, J.A.; Mariño, K.; Al Busadah, K.A.; Carrington, S.D.; Hickey, R.M.; Rudd, P.M. A comparative study of free oligosaccharides in the milk of domestic animals. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1313–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, F.J.; Fukuma, N.M.; Mikkelsen, D.; Flanagan, B.M.; Williams, B.A.; Lisle, A.T.; Cuív, P.Ó.; Morrison, M.; Gidley, M.J. Food starch structure impacts gut microbiome composition. mSphere 2018. 3, e00086-18. [CrossRef]
- Alessi, A.M.; Gray, V.; Farquharson, F.M.; Flores-López, A.; Shaw, S.; Stead, D.; Wegmann, U.; Shearman, C.; Gasson, M.; Collie-Duguid, E.S.R.; et al. β-Glucan is a major growth substrate for human gut bacteria related to Coprococcus eutactus. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 2150–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wexler, H.M. Bacteroides: The good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 593–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diether, N.E.; Willing, B.P. Microbial fermentation of dietary protein: An important factor in diet-microbe-host Interaction. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, S.; Gadonna-Widehem, P.; Rome, V.; Hamoudi, D.; Rhazi, L.; Lakhal, L.; Larcher, T.; Bahi-Jaber, N.; Pinon-Quintana, A.; Guyonvarch, A.; et al. Characterisation of early-life fecal microbiota in susceptible and healthy pigs to post-weaning diarrhoea. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, A.; Gardiner, J.; Ho, C.; Rees, P.; Chadda, K.; Baker, A.; Sutcliffe, A.G. Population-based screening methods in biliary atresia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2023, 108, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H. Bacteroides and Prevotella. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeckhaut, V.; Van Immerseel, F.; Teirlynck, E.; Pasmans, F.; Fievez, V.; Snauwaert, C.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Louis, P.; Vandamme, P. Butyricicoccus pullicaecorum gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic, butyrate-producing bacterium isolated from the caecal content of a broiler chicken. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 2799–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Diversity, metabolism and microbial ecology of butyrate-producing bacteria from the human large intestine. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 294, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Oshima, K.; Toh, H.; Khasnobish, A.; Fujii, Y.; Arakawa, K.; Morita, H. Draft genome sequence of Butyricimonas faecihominis 30A1, isolated from feces of a Japanese Alzheimer’s disease patient. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00462-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja, S.; Stoll, C.; Krammer, U.; Hippe, B.; Duszka, K.; Debebe, T.; Höfinger, I.; König, J.; Pointner, A.; Haslberger, A. Five days periodic fasting elevates levels of longevity related Christensenella and sirtuin expression in humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; De Waal, E.C.; Uitterlinden, A.G. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvester, J.T.; Karnati SK, R.; Yu, Z.; Morrison, M.; Firkins, J.L. Development of an assay to quantify rumen ciliate protozoal biomass in cows using real-time PCR. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3378–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urubschurov, V.; Büsing, K.; Janczyk, P.; Souffrant, W.B.; Zeyner, A. Development and evaluation of qPCR assay for quantitation of Kazachstania slooffiae and total yeasts occurring in the porcine gut. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Hernandez-Sanabria, E.; Guan, L.L. Assessment of the microbial ecology of ruminal methanogens in cattle with different feed efficiencies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6524–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Day of Life (DoL) | 2 | 6 | 13 | 20 | 27 | 30 | 34 | p-Value | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feeding (Feed) | Sow Milk | Sow Milk | Sow Milk | Creep Feed | Sow Milk | Creep Feed | Sow Milk | Creep Feed | Sow Milk | Creep Feed | Sow Milk | Creep Feed | Pooled SEM | DoL | Feed | DoL × Feed |
| Total bacteria | 8.5 | 8.6 | 8.4 | 8.6 | 8.8 | 8.3 | 8.1 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 8.7 | 8.8 | 0.17 | 0.673 | 0.785 | 0.022 |
| Total archaea | 3.6 | 3.9 | 4.9 | 5.1 | 5.9 | 4.8 | 4.6 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 5.1 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 0.22 | <0.001 | 0.313 | 0.001 |
| Fungi and yeasts | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 4.2 | 4.6 | 0.17 | <0.001 | 0.182 | 0.855 |
| Total protozoa | ND | ND | 3.6 | ND | 4.5 | ND | ND | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.2 | 5.8 | 5.5 | 0.44 | <0.001 | 0.978 | 0.918 |
| Chao1 | 133 | 189 | 227 | 200 | 309 | 294 | 308 | 304 | 448 | 450 | 539 | 588 | 26.61 | <0.001 | 0.898 | 0.897 |
| Shannon | 2.62 | 3.33 | 3.48 | 3.38 | 4.20 | 3.87 | 4.13 | 4.15 | 4.71 | 4.62 | 4.98 | 5.24 | 0.14 | <0.001 | 0.332 | 0.258 |
| Simpson | 0.80 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.02 | <0.001 | 0.220 | 0.501 |
| Day of Life (DoL) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Color | Brown | Brown | Yellow | Yellow | Yellow | Brown | Yellow | Yellow | Brown | Brown | Yellow | Yellow | Brown | Brown | Brown | Grey | Grey | Yellow | Yellow | Yellow |
| Consistency | Balls | Meconium | Balls | Very Soft | Soft | Balls | Balls | Soft | Balls | Very Soft | Balls | Soft | Balls | Very Soft | Soft | Balls | Soft | Balls | Very Soft | Soft |
| Total bacteria | 8.3 | 8.1 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 8.6 | 8.7 | 8.6 | 8.4 | 8.2 | 8.8 | 8.6 | 9.0 | 8.7 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 9.2 | 9.0 | 8.4 | 8.7 | 8.9 |
| Total archaea | 2.6 | 3.5 | 3.8 | 4.3 | 2.6 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 4.0 | 4.6 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 5.2 | 3.9 | 5.9 |
| Fungi and yeasts | 3.3 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4.6 | 3.9 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.1 | 3.7 | 4.3 |
| Total protozoa | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Chao1 | 112 | 101 | 143 | 147 | 151 | 189 | 189 | 176 | 216 | 185 | 212 | 250 | 274 | 540 | 233 | 471 | 437 | 292 | 226 | 346 |
| Shannon | 2.48 | 2.10 | 2.75 | 2.60 | 3.07 | 3.39 | 3.31 | 3.60 | 3.51 | 3.70 | 3.36 | 4.14 | 3.84 | 5.02 | 4.18 | 4.71 | 4.83 | 3.96 | 3.90 | 4.34 |
| Simpson | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| Day | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | |||
| Color | Brown | Brown | Brown | Grey | Yellow | Yellow | Yellow | Brown | Brown | Brown | Yellow | Yellow | Brown | Brown | Brown | Yellow | Yellow | |||
| Consistency | Balls | Very Soft | Soft | Soft | Balls | Very Soft | Soft | Balls | Very Soft | Soft | Balls | Soft | Balls | Very Soft | Soft | Balls | Soft | Pooled SEM | ||
| Total bacteria | 7.4 | 8.7 | 8.9 | 9.0 | 8.8 | 7.4 | 8.6 | 8.2 | 8.4 | 9.2 | 8.7 | 9.5 | 9.1 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 9.3 | 8.4 | 0.42 | ||
| Total archaea | 3.8 | 4.7 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 5.4 | 3.0 | 5.4 | 5.0 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 5.4 | 6.0 | 5.9 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 5.2 | 6.1 | 0.52 | ||
| Fungi and yeasts | 4.2 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 2.3 | 3.6 | 4.7 | 4.5 | 3.7 | 4.4 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 3.7 | 5.0 | 5.7 | 3.1 | 0.38 | ||
| Total protozoa | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 3.8 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 4.4 | ND | 5.8 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 4.9 | 6.8 | 0.71 | ||
| Chao1 | 274 | 518 | 317 | 389 | 290 | 327 | 242 | 479 | 448 | 493 | 378 | 694 | 596 | 523 | 597 | 583 | 268 | 65.91 | ||
| Shannon | 4.05 | 4.78 | 4.54 | 4.50 | 4.04 | 4.24 | 3.85 | 4.80 | 4.63 | 5.20 | 4.32 | 5.37 | 5.34 | 4.90 | 5.17 | 4.26 | 4.63 | 0.36 | ||
| Simpson | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 1.01 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.04 | ||
| p-Value | ||||||||||||||||||||
| DoL | Color | DoL × Color | Consistency | DoL × Consistency | Color × Consistency | DoL × Color × Consistency | ||||||||||||||
| Total bacteria | 0.857 | 0.764 | 0.908 | 0.324 | 0.638 | 0.332 | 0.037 | |||||||||||||
| Fungi and yeasts | 0.042 | 0.236 | 0.718 | 0.077 | <0.001 | 0.056 | 0.041 | |||||||||||||
| Total protozoa | 0.034 | 0.428 | 0.339 | 0.214 | 0.244 | 0.348 | 0.421 | |||||||||||||
| Total archaea | <0.001 | 0.474 | 0.558 | 0.163 | 0.055 | 0.029 | 0.138 | |||||||||||||
| Chao1 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.646 | 0.928 | 0.004 | 0.026 | 0.038 | |||||||||||||
| Shannon | <0.001 | 0.043 | 0.756 | 0.342 | 0.554 | 0.499 | 0.462 | |||||||||||||
| Simpson | 0.005 | 0.684 | 1.000 | 0.027 | 0.979 | 0.993 | 0.951 | |||||||||||||
| Day of Life (DoL) | 2 | 6 | 13 | 20 | 27 | 30 | 34 | p-Value | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Type | F + S | F | M | S | F + S | F | S | F + S | F | S | F + S | F | S | F + S | F | S | F + S | F | S | F + S | F | S | Pooled SEM | DoL | Type | DoL× Type |
| Total bacteria | 8.4 | 8.2 | 8.1 | 8.8 | 8.8 | 8.6 | 8.4 | 8.8 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 8.6 | 8.9 | 8.0 | 8.8 | 8.1 | 8.8 | 8.7 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 8.7 | 8.4 | 9.1 | 0.25 | 0.887 | 0.115 | <0.001 |
| Total archaea | 2.6 | 4.3 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 5.1 | 4.6 | 5.1 | 5.7 | 5.7 | 4.8 | 5.1 | 4.5 | 5.4 | 5.4 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 5.8 | 0.36 | <0.001 | 0.775 | 0.012 |
| Fungi and yeasts | 3.1 | 4.9 | 3.3 | 4.1 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 4.3 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 4.2 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 4.3 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 3.9 | 4.7 | 5.3 | 4.0 | 4.7 | 0.24 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.016 |
| Total protozoa | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 4.8 | 5.2 | 3.9 | 4.5 | 5.8 | 5.8 | 0.44 | 0.053 | 0.119 | 0.049 |
| Chao1 | 101 | 181 | 93 | 155 | 167 | 171 | 210 | 197 | 218 | 217 | 259 | 300 | 317 | 337 | 327 | 268 | 478 | 371 | 479 | 623 | 525 | 595 | 40.64 | <0.001 | 0.466 | 0.303 |
| Shannon | 2.64 | 3.18 | 2.08 | 2.75 | 3.40 | 3.37 | 3.28 | 3.76 | 3.64 | 3.12 | 3.97 | 4.20 | 3.85 | 4.39 | 4.27 | 3.88 | 4.90 | 4.39 | 4.74 | 5.45 | 4.97 | 5.20 | 0.22 | <0.001 | 0.031 | 0.148 |
| Simpson | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.72 | 0.80 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.03 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.681 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Lerch, F.; Yosi, F.; Vötterl, J.; Ehmig, J.; Koger, S.; Verhovsek, D. Temporal Microbial Dynamics in Feces Discriminate by Nutrition, Fecal Color, Consistency and Sample Type in Suckling and Newly Weaned Piglets. Animals 2023, 13, 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13142251
Metzler-Zebeli BU, Lerch F, Yosi F, Vötterl J, Ehmig J, Koger S, Verhovsek D. Temporal Microbial Dynamics in Feces Discriminate by Nutrition, Fecal Color, Consistency and Sample Type in Suckling and Newly Weaned Piglets. Animals. 2023; 13(14):2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13142251
Chicago/Turabian StyleMetzler-Zebeli, Barbara U., Frederike Lerch, Fitra Yosi, Julia Vötterl, Juliane Ehmig, Simone Koger, and Doris Verhovsek. 2023. "Temporal Microbial Dynamics in Feces Discriminate by Nutrition, Fecal Color, Consistency and Sample Type in Suckling and Newly Weaned Piglets" Animals 13, no. 14: 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13142251
APA StyleMetzler-Zebeli, B. U., Lerch, F., Yosi, F., Vötterl, J., Ehmig, J., Koger, S., & Verhovsek, D. (2023). Temporal Microbial Dynamics in Feces Discriminate by Nutrition, Fecal Color, Consistency and Sample Type in Suckling and Newly Weaned Piglets. Animals, 13(14), 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13142251






