The Effects of Temperature and Humidity Index on Growth Performance, Colon Microbiota, and Serum Metabolome of Ira Rabbits
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
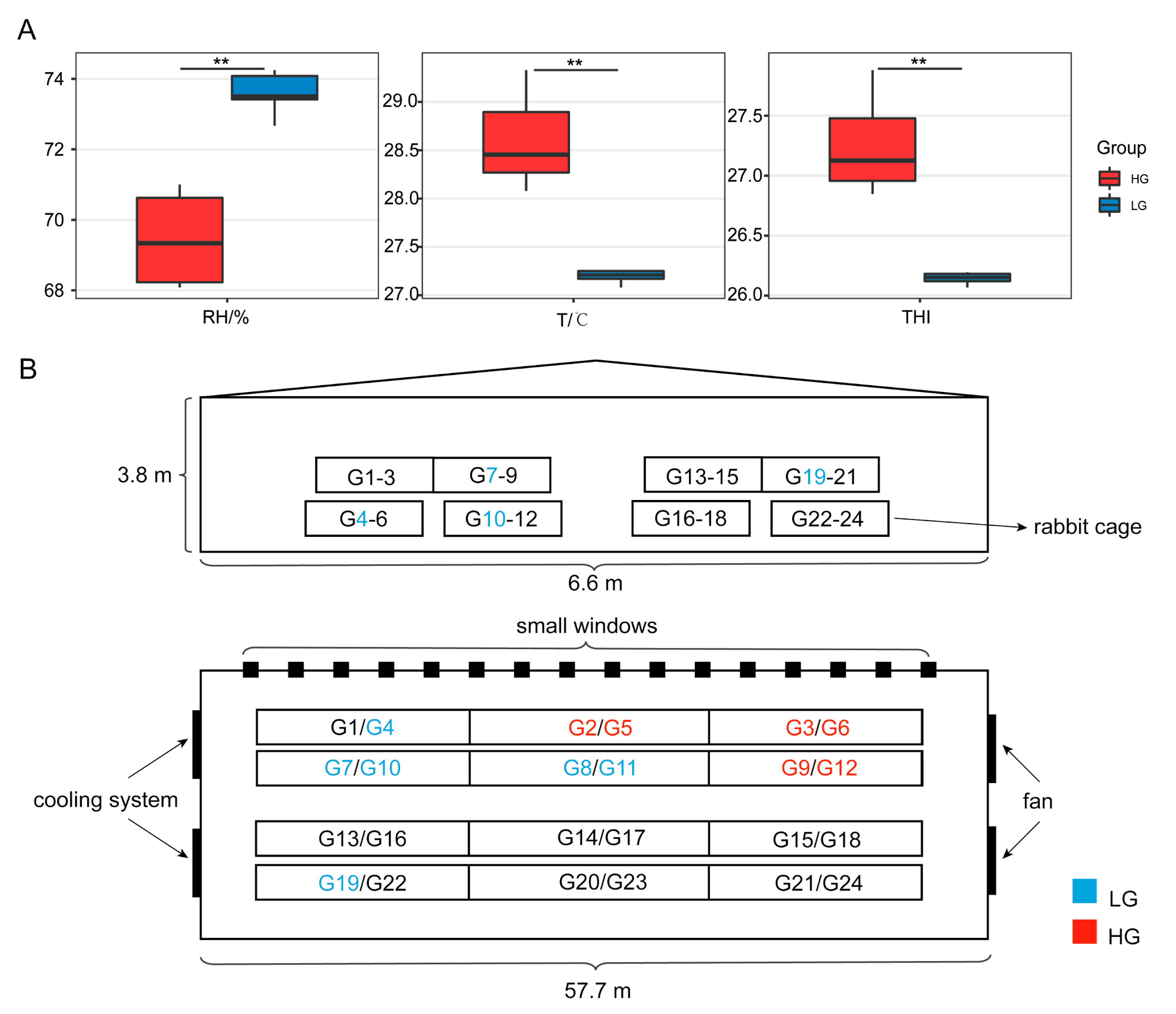
2.1. Animals Feeding
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Colon Microbiome Analysis
2.5. Colon Transcriptome Analysis
2.6. Serum Metabolomics Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. Group Performance
3.2. Environmental Factors Data Statistics
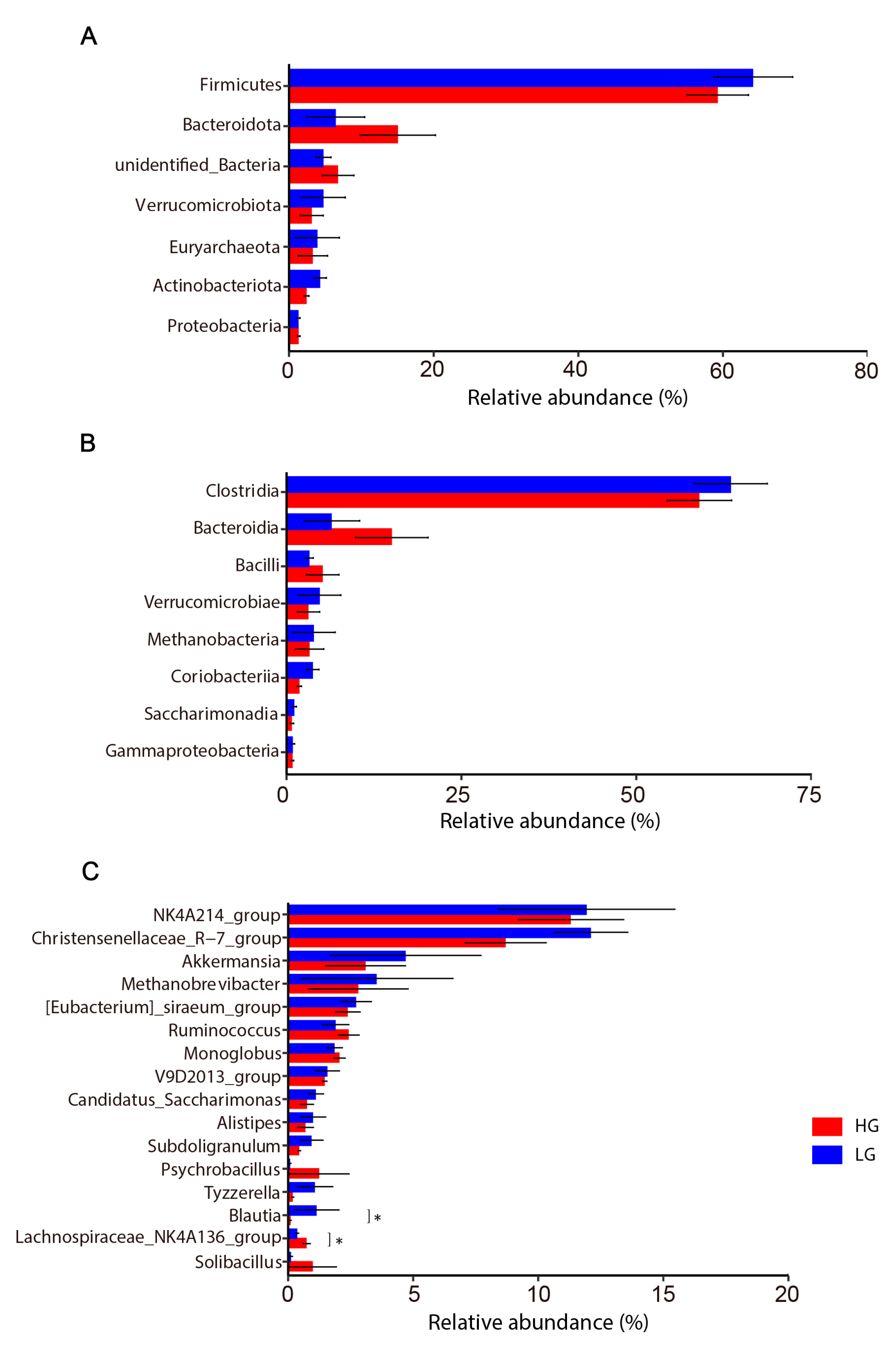
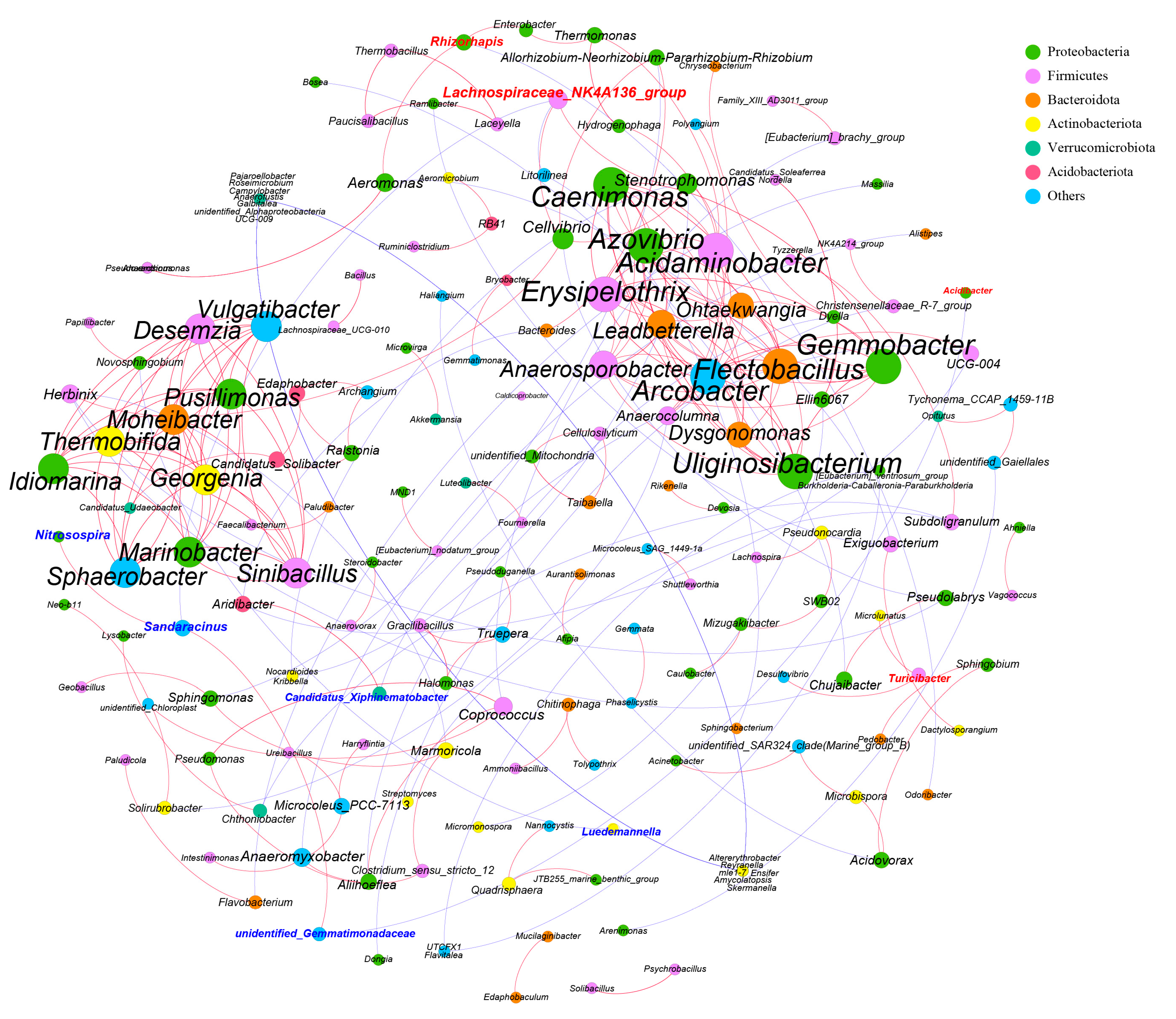
3.3. Colon Microbiota Changes
3.4. Colon Transcriptome Analysis
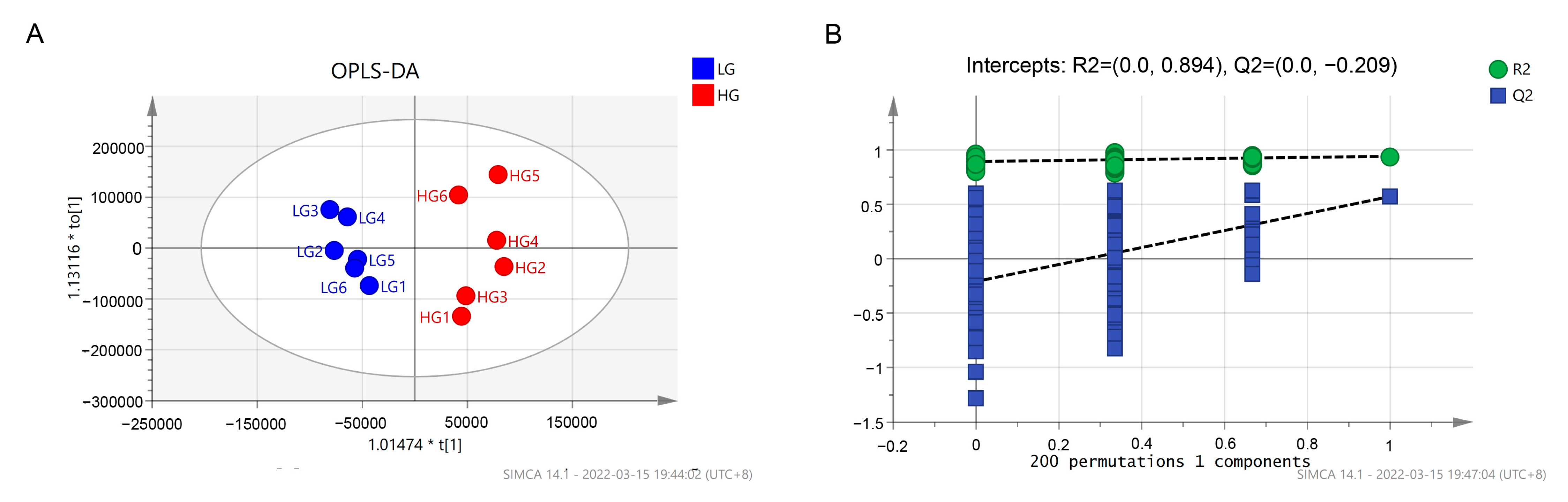
3.5. Serum Metabolome Analysis
3.6. Correlation between the Intestinal Microbiota, DEGs and DMs
4. Discussion
4.1. Group Performance
4.2. Colon Microbiota Changes
4.3. Colon Transcriptome Analysis
4.4. Serum Metabolome Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. The Statistics Division of the FAO. 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Ayyat, M.S.; Al-Sagheer, A.A.; El-Latif, K.M.A.; Khalil, B.A. Organic Selenium, Probiotics, and Prebiotics Effects on Growth, Blood Biochemistry, and Carcass Traits of Growing Rabbits During Summer and Winter Seasons. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladimeji, A.M.; Johnson, T.G.; Metwally, K.; Farghly, M.; Mahrose, K.M. Environmental heat stress in rabbits: Implications and ameliorations. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2021, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmund, G.; Ågerstrand, M.; Antonelli, A.; Backhaus, T.; Brodin, T.; Diamond, M.L.; Erdelen, W.R.; Evers, D.C.; Hoffmann, T.; Hueffer, T.; et al. Addressing chemical pollution in biodiversity research. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 3240–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asseng, S.; Spankuch, D.; Hernandez-Ochoa, I.M.; Laporta, J. The upper temperature thresholds of life. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e378–e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marai, I.F.M.; Haeeb, A.A.M. Buffalo’s biological functions as affected by heat stress—A review. Livest. Sci. 2010, 127, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marai, I.; Habeeb, A.; Gad, A. Rabbits’ productive, reproductive and physiological performance traits as affected by heat stress: A review. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2002, 78, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamidi, W.A.; Osunade, J.A. Temperature-Humidity Index (THI) in rabbits’ pens at different building orientations and openings: A measure of animal comfortability in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Malawi J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 14, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.; Ferraz, P.F.P.; Santos, L.M.D.; Ferraz, G.; Rossi, G.; Barbari, M. Effect of the Spatial Distribution of the Temperature and Humidity Index in a New Zealand White Rabbit House on Respiratory Frequency and Ear Surface Temperature. Animals 2021, 11, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutwedu, V.B.; Nyongesa, A.W.; Oduma, J.A.; Kitaa, J.M.; Mbaria, J.M. Thermal stress causes oxidative stress and physiological changes in female rabbits. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 95, 102780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasoob, T.B.; Yu, D.; Khalid, A.R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Saad, H.M.; Hang, S. Oral administration of Moringa oleifera leaf powder relieves oxidative stress, modulates mucosal immune response and cecal microbiota after exposure to heat stress in New Zealand White rabbits. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Chen, X.; Pan, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Xiao, T.; Gan, Q.F. Dynamic distribution of gut microbiota in meat rabbits at different growth stages and relationship with average daily gain (ADG). BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, B.; Wu, W.; Fang, W.; Wen, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H. Heat stress-induced mucosal barrier dysfunction is potentially associated with gut microbiota dysbiosis in pigs. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 8, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, A.K.; Kar, I. Heat stress on microbiota composition, barrier integrity, and nutrient transport in gut, production performance, and its amelioration in farm animals. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 211–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaén-Téllez, J.A.; Sánchez-Guerrero, M.J.; Valera, M.; González-Redondo, P. Influence of Stress Assessed through Infrared Thermography and Environmental Parameters on the Performance of Fattening Rabbits. Animals 2021, 11, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marai, I.; Ayyat, M.; El-Monem, U.A. Growth performance and reproductive traits at first parity of New Zealand white female rabbits as affected by heat stress and its alleviation under Egyptian conditions. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2001, 33, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekow, C.A. Basic Experimental Methods in the Rabbit; Veterans Affairs Puget Sound Health Care System: Seattle, WA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebas, F.; Coudert, P.; Rouvier, R.; De Rochambeau, H. The Rabbit-Husbandry, Health and Production; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.M.; Zimmerman, K.; Smith, S.A. Hematological assessment in pet rabbits: Blood sample collection and blood cell identification. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2015, 18, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Yuan, X.; Yang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y. Rabbit microbiota across the whole body revealed by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Gevers, D.; Earl, A.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Ward, D.V.; Giannoukos, G.; Ciulla, D.; Tabbaa, D.; Highlander, S.K.; Sodergren, E.; et al. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warton, D.I.; Wright, S.T.; Wang, Y. Distance-based multivariate analyses confound location and dispersion effects. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siren, J.; Valimaki, N.; Makinen, V. Indexing Graphs for Path Queries with Applications in Genome Research. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2014, 11, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.; Luo, H.; Huo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; et al. KOBAS-i: Intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W317–W325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, T.; Major, H.; Plumb, R.; Wilson, A.J.; Wilson, I.D. A pragmatic and readily implemented quality control strategy for HPLC-MS and GC-MS-based metabonomic analysis. Analyst 2006, 131, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; Wilson, I.D.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling procedures for urine using UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballini, A.; Scacco, S.; Boccellino, M.; Santacroce, L.; Arrigoni, R. Microbiota and Obesity: Where Are We Now? Biology 2020, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartuche, L.; Pascual, M.; Gómez, E.A.; Blasco, A. Economic weights in rabbit meat production. World Rabbit. Sci. 2014, 22, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimen, I.B.; Najar, T.; Ghram, A.; Abdrrabba, M. Heat stress effects on livestock: Molecular, cellular and metabolic aspects, a review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paci, G.; Preziuso, G.; D’Agata, M.; Russo, C.; Zotte, A.D. Effect of stocking density and group size on growth performance, carcass traits and meat quality of outdoor-reared rabbits. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Teng, J.L.L.; Chiu, T.H.; Chan, E.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Panagiotou, G.; Zhai, S.L.; Woo, P.C.Y. Differential Microbial Communities of Omnivorous and Herbivorous Cattle in Southern China. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zong, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, M. Heat Stress Alters the Intestinal Microbiota and Metabolomic Profiles in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 706772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Temperature and humidity index (THI)-induced rumen bacterial community changes in goats. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3193–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Zhou, L.; Xue, S.; Gan, Q. Effects of Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) on Finishing Weight of Meat Rabbits. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Deng, F.; Jia, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.W.; Lai, S.J. Gut microbiota profiling with differential tolerance against the reduced dietary fibre level in rabbit. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avershina, E.; Lundgard, K.; Sekelja, M.; Dotterud, C.; Storro, O.; Oien, T.; Johnsen, R.; Rudi, K. Transition from infant- to adult-like gut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Feng, J.H.; Zhang, M.H.; Li, X.M.; Ma, D.D.; Chang, S.S. Effects of high ambient temperature on the community structure and composition of ileal microbiome of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2153–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Patil, Y.; Gong, D.; Yu, T.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Yu, Z.; Ma, X.; Yong, Y.; et al. Heat Stress-Induced Dysbiosis of Porcine Colon Microbiota Plays a Role in Intestinal Damage: A Fecal Microbiota Profile. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 686902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mao, B.; Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Cui, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Blautia-a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1875796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Yan, X.; Su, L. Anti-inflammation effects of fucosylated chondroitin sulphate from Acaudina molpadioides by altering gut microbiota in obese mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, K.E.B.; Lærke, H.N.; Hedemann, M.S.; Nielsen, T.S.; Ingerslev, A.K.; Nielsen, D.S.G.; Theil, P.K.; Purup, S.; Hald, S.; Schioldan, A.G.; et al. Impact of Diet-Modulated Butyrate Production on Intestinal Barrier Function and Inflammation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, P.J.; Centelles-Lodeiro, J.; Ellis, D.; Cook, D.P.; Sassi, G.; Verlinden, L.; Verstuyf, A.; Raes, J.; Mathieu, C.; Gysemans, C. High Serum Vitamin D Concentrations, Induced via Diet, Trigger Immune and Intestinal Microbiota Alterations Leading to Type 1 Diabetes Protection in NOD Mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 902678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, F. Effects of heat stress on growth performance, carcass traits, serum metabolism, and intestinal microflora of meat rabbits. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 998095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, B.; Conceição, L.L.D.; Mendes, T.A.O.; Ferreira, C.; Gonçalves, R.V.; Peluzio, M. Use of the synbiotic VSL#3 and yacon-based concentrate attenuates intestinal damage and reduces the abundance of Candidatus Saccharimonas in a colitis-associated carcinogenesis model. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.A.; Gu, W.; Lee, I.A.; Joh, E.H.; Kim, D.H. High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Li, D.; Ke, W.; Liang, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Resveratrol-induced gut microbiota reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, A.D.; Knox, N.; Kabakchiev, B.; Milgrom, R.; Kirsch, R.; Cohen, Z.; McLeod, R.S.; Guttman, D.S.; Krause, D.O.; Silverberg, M.S. Characterization of the gut-associated microbiome in inflammatory pouch complications following ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ye, T.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Jamil, A.M.; Zhou, Y.; Hua, G.; Liang, A.; Deng, T.; Yang, L. Identifying Hub Genes for Heat Tolerance in Water Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Using Transcriptome Data. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbecki, J.; Kupnicka, P.; Chlubek, M.; Goracy, J.; Gutowska, I.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. CXCR2 Receptor: Regulation of Expression, Signal Transduction, and Involvement in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrin, N.P.; Plata-Salamán, C.R. Cytokine-cytokine interactions and the brain. Brain Res. Bull. 2000, 51, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Xu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Su, L. NF-kappaB signaling is essential for resistance to heat stress-induced early stage apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, M.K.; Kumar, V.G.; Sejian, V.; Bagath, M.; Krishnan, G.; Bhatta, R. Toll-like receptors: Significance, ligands, signaling pathways, and functions in mammals. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 37, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, R.J.; Collier, J.L.; Rhoads, R.P.; Baumgard, L.H. Invited review: Genes involved in the bovine heat stress response. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; McGoldrick, L.L.; Demirkhanyan, L.; Leslie, M.; Zakharian, E.; Sobolevsky, A.I. Structural basis of temperature sensation by the TRP channel TRPV3. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, W.M.; Hunter, D.J. Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Inhibitors and Related Agents for Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: A Comprehensive Review. BioDrugs 2021, 35, 611–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, A.; Cross, P.J.; Dobson, R.C.J.; Adams, L.E.; Savka, M.A.; Hudson, A.O. A Three-Ring Circus: Metabolism of the Three Proteogenic Aromatic Amino Acids and Their Role in the Health of Plants and Animals. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.-H.; Nejad, J.G.; Peng, D.-Q.; Kim, H.-R.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, H.-G. Characterization of Short-Term Heat Stress in Holstein Dairy Cows Using Altered Indicators of Metabolomics, Blood Parameters, Milk MicroRNA-216 and Characteristics. Animals 2021, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjwani, U.; Kumar, B.; Kizhekkedath, J.; Kolpe, R.; Suresh, A.; Ravi, D.; Thakur, L.; Anand, J.P.; Kumar, S.; Ray, K.; et al. Tyrosine Supplementation A Nutraceutical Approach to Counter Heat Stress Induced Cognitive Decline. Def. Life Sci. J. 2021, 6, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, H.; Zhou, P.; Song, F.; Dong, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Dong, X. Effect of Heat Stress on Bovine Mammary Cellular Metabolites and Gene Transcription Related to Amino Acid Metabolism, Amino Acid Transportation and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Signaling. Animals 2021, 11, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Elzo, M.A.; Shao, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, S.; Fan, H.; Jia, X.; Lai, S. Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Intestinal Pathogenesis and Self-Repair in Rabbits Fed an Antibiotic-Free Diet. Animals 2021, 11, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, N.S.; Swinton, P.; de Oliveira, L.F.; da Silva, R.P.; da Eira Silva, V.; Nemezio, K.; Yamaguchi, G.; Artioli, G.G.; Gualano, B.; Saunders, B.; et al. The Muscle Carnosine Response to Beta-Alanine Supplementation: A Systematic Review with Bayesian Individual and Aggregate Data E-Max Model and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.E.; Stout, J.R.; Kendall, K.L.; Fukuda, D.H.; Cramer, J.T. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: The effects of beta-alanine supplementation in women. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xiang, Q.; Mao, B.; Tang, X.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Protective Effects of Microbiome-Derived Inosine on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Liver Damage and Inflammation in Mice via Mediating the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7619–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romling, U.; Galperin, M.Y.; Gomelsky, M. Cyclic di-GMP: The first 25 years of a universal bacterial second messenger. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhu, G.; Tong, Q. Effect of uracil on pullulan production by Aureobasidium pullulans CGMCC1234. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Xiong, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J. Toxic effects of ammonia and thermal stress on the intestinal microbiota and transcriptomic and metabolomic responses of Litopenaeus vannamei. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Sang, Y.; Qin, R.; Su, Y.; Cui, Z.; Mang, Z.; Li, H.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, S.; et al. Metabolic intermediate acetyl phosphate modulates bacterial virulence via acetylation. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whicher, A.; Camprubi, E.; Pinna, S.; Herschy, B.; Lane, N. Acetyl Phosphate as a Primordial Energy Currency at the Origin of Life. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2018, 48, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, S.; Chong, K. Comparative metabolomic analysis reveals a reactive oxygen species-dominated dynamic model underlying chilling environment adaptation and tolerance in rice. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 1295–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Su, C.; Qian, C.; Pan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, A. Metabolomics Reveals Metabolic Alterations in Membranous Nephropathy and IgA nephropathy. Res. Sq. 2022; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Vendrov, K.C.; Simmons, B.P.; Schuck, R.N.; Stouffer, G.A.; Lee, C.R. Urinary 11-dehydro-thromboxane B2 levels are associated with vascular inflammation and prognosis in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018, 134, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.A.; Vasudevan, A.; Sathyamoorthy, M.; Schussler, J.M.; Velasco, C.E.; Lopez, L.R.; Swift, C.; Peterson, M.; Bennett-Firmin, J.; Schiffmann, R.; et al. Urinary 11-Dehydro-Thromboxane B2 and Mortality in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 119, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Abdelsattar, M.M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Chai, J. In Vitro Modulation of Rumen Fermentation by Microbiota from the Recombination of Rumen Fluid and Solid Phases. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0338722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.Y.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, X.J.; Sun, H.Z.; Liu, J.X. Integrated meta-omics reveals new ruminal microbial features associated with feed efficiency in dairy cattle. Microbiome 2022, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Items | Groups | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LG | HG | ||
| Weanling weight (kg) | 0.73 ± 0.01 | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 0.14 |
| Final weight (kg) | 2.33 ± 0.10 | 2.05 ± 0.08 | 0.09 |
| ADG (g) | 46.99 ± 3.10 | 39.52 ± 2.25 | 0.01 |
| ADFI (g) | 183.34 ± 4.01 | 151.48 ± 8.37 | <0.01 |
| FCR | 3.94 ± 0.32 | 3.87 ± 0.37 | 0.82 |
| Metabolites | HG-Mean | LG-Mean | VIP | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-palmitoylglycerophosphocholine | 5,156,691,973.42 | 3,276,134,737.27 | 7.2196 | 0.0053 |
| N-Alpha-acetyllysine | 2,000,058,212.65 | 1,457,960,754.95 | 3.9255 | 0.0494 |
| Acetylphosphate | 244,067,959.73 | 56,877,793.81 | 1.8856 | 0.0086 |
| 16-Hydroxy hexadecanoic acid | 101,453,823.92 | 70,654,908.76 | 1.0470 | 0.0103 |
| 11-Dehydro-thromboxane B2 | 47,712,514.02 | 15,821,077.55 | 1.0134 | 0.0115 |
| Uracil | 170,915,960.33 | 239,164,164.80 | 1.3382 | 0.0171 |
| Kynurenic acid | 73,581,930.85 | 195,575,186.82 | 1.2896 | 0.0121 |
| Inosine | 38,334,884.30 | 91,956,808.77 | 1.0915 | 0.0049 |
| GMP | 464,681,530.15 | 709,621,428.81 | 1.6793 | 0.0000 |
| beta-Alanine | 644,361,176.34 | 727,140,676.69 | 1.6930 | 0.0053 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Abdelsattar, M.M.; Gu, M.; Zhao, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, P.; Huang, C.; Fang, S.; Gan, Q. The Effects of Temperature and Humidity Index on Growth Performance, Colon Microbiota, and Serum Metabolome of Ira Rabbits. Animals 2023, 13, 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13121971
Li K, Abdelsattar MM, Gu M, Zhao W, Liu H, Li Y, Guo P, Huang C, Fang S, Gan Q. The Effects of Temperature and Humidity Index on Growth Performance, Colon Microbiota, and Serum Metabolome of Ira Rabbits. Animals. 2023; 13(12):1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13121971
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Keyao, Mahmoud M. Abdelsattar, Mingming Gu, Wei Zhao, Haoyu Liu, Yafei Li, Pingting Guo, Caiyun Huang, Shaoming Fang, and Qianfu Gan. 2023. "The Effects of Temperature and Humidity Index on Growth Performance, Colon Microbiota, and Serum Metabolome of Ira Rabbits" Animals 13, no. 12: 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13121971
APA StyleLi, K., Abdelsattar, M. M., Gu, M., Zhao, W., Liu, H., Li, Y., Guo, P., Huang, C., Fang, S., & Gan, Q. (2023). The Effects of Temperature and Humidity Index on Growth Performance, Colon Microbiota, and Serum Metabolome of Ira Rabbits. Animals, 13(12), 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13121971







