Simple Summary
The supplementation of diets for broiler chickens has increased due to the increasing demand of consumers for antibiotic-free broiler products. Nevertheless, the benefits of probiotics for intestinal barrier and immune functions, as well as on growth performance in chickens, are still controversially discussed. In performing a meta-analysis, we found that dietary supplementation with probiotics of various genera/species can enforce intestinal barrier function. Moreover, our meta-regressions indicated that in pathogen-challenged birds, probiotics might effectively help reduce gut inflammation by suppressing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Probiotics further sustained the intestinal histomorphology and hence digestive and absorptive processes in challenged and non-challenged chickens.
Abstract
Data published in the literature about the favorable effects of dietary probiotics on gut health in broiler chickens are inconsistent. To obtain a more comprehensive understanding, we conducted a meta-analysis to assess the effects of probiotics on the gut barrier and immune-related gene expression, histomorphology, and growth in chickens that were either challenged or non-challenged with pathogens. From the 54 articles published between 2012 and 2022, subsets of data, separately for non-challenged and challenged conditions, for response variables were created. The mean dietary probiotic concentrations ranged from 4.7 to 6.2 and 4.7 to 7.2 log10 colony-forming unit/kg under non-challenged and challenged conditions, respectively. Probiotics increased the expression of genes for mucins and tight junction proteins in the jejunum and ileum at weeks 3 and 6. The stimulatory effect of probiotics on tight junction protein expression was partly stronger in challenged than in non-challenged birds. Meta-regressions also showed an anti-inflammatory effect of probiotics under challenged conditions by modulating the expression of cytokines. Probiotics improved villus height at certain ages in the small intestine while not influencing growth performance. Dietary metabolizable energy, crude protein, and days post-infection modified the effects of probiotics on the observed variables. Overall, meta-regressions support the beneficial effects of probiotics on gut integrity and structure in chickens.
1. Introduction
The use of antibiotic growth promoters in chicken farms has been banned in many countries worldwide. Probiotics are considered a promising alternative for livestock animals, including poultry, as they seem to exert a favorable effect on gut health [1]. To date, various microbial genera have been investigated for use as probiotics in poultry diets, including Lactobacillus, Bacillus, Enterococcus, Bifidobacterium, and Saccharomyces [1]. Several studies show potential beneficial effects of probiotics on growth performance, absorptive and secretory processes, as well as expression of genes related to host defense mechanisms, barrier function, and inflammation in broiler chickens [2,3,4]. For instance, dietary probiotics, such as B. subtilis and B. pumilus, have been shown to stimulate host defense mechanisms at the ileal epithelium by modulating tight junction protein expression in the grower and finisher phases [2]. Other probiotics, such as L. acidophilus and L. plantarum, have been reported to exert anti-inflammatory effects in the small intestine by moderating pro-inflammatory nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) signaling, which, in turn, leads to lower transcript levels pro-inflammatory cytokines in the jejunum and ileum [3,4]. However, the reported effects of probiotics on the gut epithelial response in chickens are inconsistent [5,6]. Multiple factors may be behind the controversial findings, including direct (e.g., strain and level of probiotics) and indirect factors (e.g., age of birds, intestinal sampling spot, and health status). Although the relationship between dietary probiotics and gene expression levels related to intestinal integrity and immunity in chickens has been described in recent qualitative reviews [7,8], the variation in results of the dependent variable due to influencing factors cannot be assessed in this manner [9]. The conductance of a meta-analysis is considered the most suitable method to address this complexity by generalizing the overall treatment effect, in our case, the effect of probiotics, presented in published studies [10,11]. To obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the efficacy of probiotics, investigations on each response variable were performed separately between original studies with or without pathogen challenge. Therefore, the present meta-analysis aimed to investigate the effects of dietary supplementation of probiotics on the expression of genes associated with intestinal barrier function and immune response, histomorphology, and growth performance in broiler chickens under non-challenged or pathogen-challenged conditions. Furthermore, we assessed the effects of dietary metabolizable energy, crude protein, and days post-infection as additional predictors to obtain a more accurate prediction on the observed variables.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
For the identification of original articles, a literature search was conducted using 5 public search generators, including Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science, Science Direct, and Google Scholar (Figure 1). Research articles investigating the effects of dietary probiotics on the expression levels of genes related to intestinal barrier function and immune response in broiler chickens that were published in scientific journals between January 2012 and July 2022 were considered for data extraction. To identify adequate articles, the following search terms were used in different combinations: probiotic, direct-fed microbes, gut, intestine, barrier function, gut permeability, gut integrity, tight junction proteins, immune response, inflammatory cytokines, gut inflammation, intestinal immunity, chicken, and broiler.
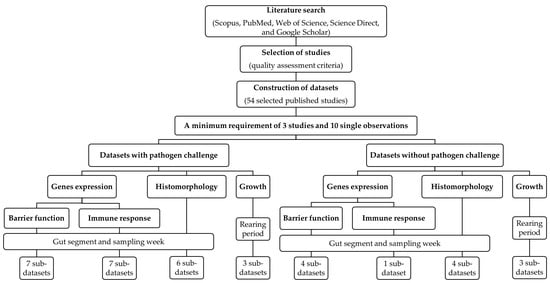
Figure 1.
Flowchart showing the process of the collection and selection of original studies as well as the construction of databases in the current meta-analysis.
2.2. Selection of Studies
Stringent criteria were applied in the decision to exclude or include the research articles in the present meta-analysis (Figure 1). The quality assessment criteria used in this study included detailed information on probiotics (type and level of dietary probiotics), chicken strain, body weight and age of chickens, rearing period, and number of chickens per treatment, diet composition, experimental design, including randomization of treatments, description of statistical analysis, and intra-study error (if standard deviation was provided, then it was converted to standard error). Only probiotics that were administered via the diet were considered in this study. In addition, studies investigating the combined effects of dietary probiotics with other treatments on target parameters were also included. From these studies, only data for control and probiotic treatments were considered. Regarding gene expression measurements, only studies that applied quantitative real-time PCR analysis and in which the relative gene expression was calculated using the 2−ddCt method were included. Moreover, only literature data from in vivo experiments was considered.
2.3. Construction of Database
After screening the literature, we identified 54 eligible research articles that met the quality criteria (Figure 1). A minimum requirement of 3 studies and 10 single observations (treatment means) along with the standard error (SE) for each dependent variable was set as requirement for calculating the combined effect size [10,11]. The main predictive variable was the dietary probiotic concentration. Information about the probiotic species used was mandatory. Reported expression levels of genes related to intestinal barrier function and immune response in various intestinal segments (e.g., duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and ceca) were extracted as dependent variables. Moreover, details provided on the chickens (strain, sex, age, and start body weight), experimental setup (experimental design, number of treatments, rearing period, number of chickens per group, and sampling days), pathogen challenge (species or strain of pathogen, administration route, and days post-infection), ingredients and nutritional composition of the diet, and gene expression analysis (e.g., reference genes) were extracted as probable additional prediction variables in the regression analysis. When available, histomorphology data such as villus height, crypt depth, and villus height/crypt depth ratio, as well as growth performance, including average daily feed intake (ADFI), average daily body weight gain (ADG), and feed conversion ratio (FCR) were also extracted. If data from the articles were presented in graphical form, they were extracted using Web Plot Digitizer software (Version 4.5; Ankit Rohatgi, Pacifica, CA, USA).
Two databases were constructed: one for data from research with pathogen challenge and the other for data from studies without pathogen challenge (Figure 1). The next step was to construct datasets for individual dependent variable categories separately for data with or without pathogen challenge, i.e., one dataset each for gut barrier and immune response-related gene expression, histomorphology measures (i.e., villus height, crypt depth, and villus height/crypt depth ratio), and growth performance (i.e., ADG, ADFI, and FCR). Datasets for gut barrier and immune-related gene expression and histomorphology were further subdivided; one sub-dataset was created for each gut segment. For each gut segment, the sub-sets were then grouped by age of the chicken. The dataset for growth performance was divided into sub-datasets based on the stage of the rearing period: starter (1–3 weeks), finisher (4–6 weeks), and overall (1–6 weeks) periods. As there were not enough studies available to investigate each probiotic strain or species separately, results for the various species/strains of probiotics were analyzed together in this meta-analysis. A reference list of the sub-datasets of broiler studies is presented in Table S1.
The screening for the non-challenge studies showed that the minimum number of studies and observations for gene expression variables related to intestinal barrier function and immune response were fulfilled for the jejunum and ileum at weeks 3 and 6 of life. Adequate numbers of studies and observations for histomorphology variables were available for the jejunum and ileum at weeks 3 and 6 of life. For growth performance variables, the extracted data for the starter, finisher, and entire rearing period also met the requirement. For the studies with pathogen challenge, with respect to the expression of genes related to the intestinal barrier, the variables for the jejunum at weeks 2 to 5 of life, ileum at weeks 3 and 4 of life, and ceca at week 4 of life provided the required number of studies and observations. The variables related to the immune response met the requirement for the jejunum and ileum at weeks 2 to 4 and ceca at week 2 of life. For histomorphology variables, the minimum requirement of studies and observations existed for the data with pathogen challenge for the duodenum at week 5 of life, jejunum at weeks 2, 3, and 5 of life, and ileum at weeks 3 and 5 of life. Adequate numbers of studies and observations were also available for growth variables of starter, finisher, and overall periods. Only dependent variables that met the minimum requirements will be presented.
To create comparability among response variables across studies, the log2fold values for the gene expression data were calculated in each sub-dataset between control and probiotic treatment for un-challenged and pathogen-challenged data. Positive and negative log2fold values indicate increased and decreased expression, respectively. Data were processed and displayed as fold change, which was calculated using logarithmic scale to base 2. As dietary metabolizable energy (ME) and crude protein (CP) can affect nutritional metabolism and growth performance, these variables were included as additional predictor variables for both databases. Specifically for the data from pathogen challenge studies, days post-infection (DPI), defined as the interval from the first day of pathogen administration to sample collection, was also incorporated as an additional predictor.
2.4. Data Analysis
Descriptive statistics on the predictive variable (dietary probiotic concentration) and dependent variables (expression of gut barrier and immune-related genes in the jejunum, ileum, and ceca; histomorphology measures in the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum; and growth parameters) were performed separately for the dataset with or without pathogen challenge using the SAS MEANS procedure (version 9.4; SAS Inst. Inc., Cary, NC, USA), as previously described [10,11]. Mixed modeling of each dependent variable was established using the MIXED procedure similar to Metzler-Zebeli et al. [10,11].
where = expected outcome for the dependent variable observed at level ( = 2, …, n) of the predictor variable in the study , whereas is the number of treatment means in study , = overall intercept across all studies (fixed effect), = overall regression coefficient of on across all studies (fixed effect), = the value of continuous variable in study , = random effect of the study ( = 1, …), = the random effect of study on the regression coefficient of on in study , and = the unexplained error. Thus, the model’s random effect components consist of , and the distributions are displayed below as follows:
which assumes that is normally distributed with a mean of 0 and constant variance and that and are normally distributed, have means of 0, and is their variance–covariance matrix:
As predictor variables for both study and dietary probiotic concentration were examined. The initial random effects included the slope and intercept based on the study and concentration of dietary probiotics. To prevent positive correlation between intercept and slope, an unstructured variance–covariance matrix (type = UN) was used [12]. The dependent variable was weighted by the inverse of its squared SE (SE of the treatment mean taken directly from the studies) to consider unequal variance between studies. The squared terms of the predictor variables were entered into the model to check for a quadratic relationship if significant (p < 0.05). The variance–covariance matrix, in this case, was modeled as variance components (TYPE = VC). For the current data set, there was no significant quadratic correlation; instead, the predictor and response variables showed only linear relationships. The GPLOT technique was used to display the data. To assess the quality of fit, estimates, root mean square error (RMSE), and R2 were calculated. For established relationships, alteration in the quantity of the dependent variables as affected by dietary probiotic concentration was shown for an assumed probiotic concentration in the diet of 4 log10 colony forming units (CFU)/kg.
We performed backward elimination analyses for the datasets with and without pathogen challenge to obtain more accurate predictions of the factors influencing the dependent variables that were affected by the dietary probiotic concentration [10,11]. This enabled us to simultaneously assess how the response variable was affected by the predictors of dietary probiotic concentration, dietary probiotic concentration squared, and dietary ME and CP level, as well as DPI specifically for pathogen challenge datasets. Consideration of variance inflation factors smaller than 10 (which presupposes no substantial multicollinearity among the tested predictor variables) for each continuous independent variable served to limit model over-parameterization [10,11].
3. Results
3.1. Database Description
The main characteristics of the 54 studies that met the selection criteria are presented in Table S1. Of the 54 studies, 14 and 28 studies were without and with pathogen challenge, respectively, whereas 12 studies provided data for challenged and un-challenged conditions. Overall, nine different genera and various species within these genera were administrated as probiotics in the included studies (Figure 2): Bacillus (29 studies) and Lactobacillus (19 studies) were predominantly used, followed by Enterococcus (6 studies), Saccharomyces (4 studies), Pediococcus (4 studies), Clostridium (3 studies), Bifidobacterium (3 studies), Paenibacillus (2 studies), and Streptococcus (1 study). Eight different Bacillus species (B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. coagulans, B. amyloliquefaciens, B. mesentericus, B. methylotrophicus, B. tequilensis, and B. pumilus), nine species for Lactobacillus (L. acidophilus, L. plantarum, L. fermentum, L. reuteri, L. casei, L. animalis, L. gallinarum, L. johnsonii, and L. salivarius), three species for Bifidobacterium (B. animalis, B. bifidum, and B. thermophilum), two species each for Enterococcus and Pediococcus (E. faecium, E. fecalis, P. acidilactici, and P. pentosaceus), one species each for Clostridium, Streptococcus, Paenibacillus, and Saccharomyces (C. butyricum, S. faecalis, P. polymyxa, and S. cerevisiae) were administered. In addition, 36 studies used only one mono-species probiotic, 7 studies used more than one mono-species probiotic, 8 studies used multi-species probiotics, and 3 studies used both mono- and multi-species probiotics. The experimental diets were mainly composed of corn, wheat, barley, bran, rice, distiller grain, and sorghum, with soybean meal, fish meal, corn gluten meal, corn protein powder, rapeseed meal, peanut meal, and cottonseed meal as protein feedstuffs (Table S1). The experimental diets did not contain other bioactive compounds. Dietary ME/CP ratios were constant, with a mean of 0.6 and 0.7 for the starter and finisher diets, respectively, for the various response variables.
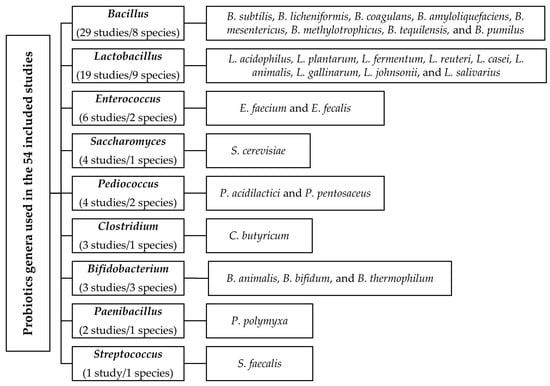
Figure 2.
Overview of genera and species within genera administered as probiotics in the included studies.
Descriptive statistical results of the predictor and dependent variables for the database without pathogen challenge are presented in Tables S2–S4. For these data, means of dietary probiotic concentrations across genera/species for the starter phase (1–3 weeks of age) ranged from 4.7 to 5.7 log10 CFU/kg, and those for the finisher phase (4–6 weeks of age) ranged from 5.7 to 6.2 log10 CFU/kg for the various categories of response variables. The means of dietary ME levels for the starter period were 12.3–12.5 MJ/kg, whereas those for the finisher period were 12.8–13.0 MJ/kg. Dietary CP levels for the starter and finisher phases showed means of 21.3–21.6% and 19.4–19.6%, respectively, for the various response variables.
The results of descriptive statistics for predictor variables and dependent variables of the database with pathogen challenge are presented in Tables S5–S8. Several pathogens were included in the original studies, such as Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, Eimeria (E. tenella, E. maxima, E. acervulina, E. mivati, E. brunetti, E. mitis, and E. praecox), Salmonella (S. enteritidis, S. pullorum, and S. minnesota), Listeria monocytogenes, as well as the fungi Fusarium graminearum and aflatoxins. For these data, the means of dietary probiotic concentrations across genera/species for the starter and finisher phases ranged from 4.6 to 5.6 log10 CFU/kg and 4.6 to 7.2 log10 CFU/kg, respectively, for the various categories of response variables. The respective means for the dietary ME level for starter and finisher periods were 12.0–12.6 MJ/kg and 12.4–12.8 MJ/kg for various dependent variables. The dietary CP levels in the starter phase showed a mean of 20.8–21.9%, whereas those in the finisher phase were 19.0–20.5% for a different category of response variables. In addition, the mean DPI for measuring gut barrier and immune gene expression for the starter and finisher ages ranged from 3.4 to 14.3 days and 7.6 to 28.7 days, respectively, for various intestinal segments. The mean DPI for the histomorphology variables were 5.2–10.3 days for the starter phase and 30.6–32.0 days for the finisher phase. For growth variables, the mean DPI for the starter and finisher ages were 10.8 and 33.2 days, respectively.
3.2. Probiotic Effects on Gut Barrier and Immune-Related Gene Expression
The results for the meta-regressions between probiotics and gut barrier and immune-related gene expression without pathogen challenge are presented in Table 1, whereas those with pathogen challenge can be found in Table 2. Irrespective of the pathogen challenge, most relationships between probiotics and gene expression levels were established for the jejunum and ileum.

Table 1.
Prediction of relative expression (fold change) of jejunal and ileal expression of genes related to gut barrier function and immune response in broiler chickens at weeks 3 to 6 of life without pathogen challenge.

Table 2.
Prediction of relative expression (fold change) of jejunal, ileal, and cecal expression of genes related to barrier function and immune response in broiler chickens from weeks 2 to 5 of life with pathogen challenge.
Without the pathogen challenge (Table 1), increasing probiotic concentrations linearly increased the jejunal expression of MUC2, ZO1, OCLN, and CLDN1 at week 3 of life (R2 = 0.32–0.46; p < 0.05). For a probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg, this would correspond to an increase in expression levels of these genes by 0.21-, 0.08-, 0.34-, and 0.16-fold, respectively. Likewise, at 6 weeks of life, increasing probiotic concentrations linearly increased the jejunal expression of MUC2 and ZO1 (R2 = 0.42–0.45; p < 0.05). Accordingly, the administration of a probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg in the diet would increase the jejunal MUC2 and ZO1 expression levels by 0.62- and 0.28-fold, respectively. In the ileum, increasing probiotic concentrations linearly increased the expression of MUC2 and OCLN of life at week 3 of life and of OCLN at week 6 of life (R2 = 0.26–0.57; p < 0.05), which corresponds to an upregulation of the MUC2 and OCLN expressions by 0.38-, 0.26- and 0.14-fold, respectively, for an assumed dietary probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg.
Regarding the meta-regressions with data from the pathogen challenge (Table 2), a positive linear relationship could be established between jejunal CLDN3 expression and probiotic concentration at week 2 of life (R2 = 0.97; p < 0.001). Here, an assumed dietary probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg would increase the jejunal CLDN3 expression by 0.41-fold. Meta-regressions showed that increasing probiotic concentrations linearly increased the jejunal ZO1 expression from weeks 2 to 4 of life (R2 = 0.31–0.51; p < 0.05) and that of OCLN from week 3 of life (R2 = 0.28; p = 0.028). Likewise, dietary probiotics positively influenced the expression of ZO1 and OCLN in the ileum at week 4 of life (R2 = 0.56–0.71; p < 0.05), amounting to an increase of 0.17- and 0.28-fold with an assumed probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg, respectively. In the ceca, expression of ZO1 linearly increased with increasing dietary probiotic concentrations at week 4 of life (R2 = 0.62; p = 0.007), which corresponded to a 0.48-fold increase with a probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg.
Under pathogen-challenged conditions, increasing dietary probiotic concentrations linearly decreased jejunal IFNG expression at week 2 of life (R2 = 0.82; p < 0.001; Table 2), which would correspond to a 0.15-fold decrease with a probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg in the diet. Similarly, a negative linear relationship existed between the jejunal IL1B expression with increasing probiotic concentrations at weeks 2 and 3 of life (R2 = 0.53–0.63; p < 0.05). In contrast, a dietary probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg would increase the jejunal IL10 expression by 0.61-fold at week 3 of life (R2 = 0.54; p = 0.004). Moreover, expression of jejunal IL6 and TNFA linearly decreased at week 3 of life (R2 = 0.35–0.45; p < 0.05), amounting to 0.12- and 0.10-fold, respectively, with a probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg. Like in the jejunum, increasing concentrations of dietary probiotics linearly downregulated the expression of TLR4 and IFNG in the ileum at weeks 2 and 3 of life, respectively (R2 = 0.71–0.75; p = 0.001; Table 2). At the cecal mucosa, higher probiotic concentrations decreased IL6 expression (R2 = 0.31; p = 0.017; Table 2) but increased the expression of IL10 (R2 = 0.47; p = 0.030) by 0.14- and 0.85-fold, respectively, at week 2 of life, with an assumed dietary probiotic concentration of 4 log10 CFU/kg.
3.3. Probiotic Effects on Gut Histomorphology
For the data without pathogen challenge (Table 3), increasing probiotic concentrations linearly increased jejunal villus height at weeks 3 and 6 of life (R2 = 0.28–0.66, p < 0.05), and the jejunal villus height/crypt depth ratio at week 3 of life (R2 = 0.42; p = 0.009). In the ileum, a similar positive linear relationship between the probiotic concentration and villus height was observed at week 6 of life (R2 = 0.58; p < 0.001) and ileal villus height/crypt depth ratio at week 3 and 6 of life (R2 = 0.41–0.65; p < 0.05). For the results with the pathogen challenge (Table 4), increasing probiotic concentrations linearly increased the villus height in the duodenum at week 5 of life (R2 = 0.53; p = 0.002). A similar relationship was found for the jejunal villus height at week 3 of life (R2 = 0.42; p = 0.005). Moreover, dietary probiotic concentrations showed a negative relationship with crypt depth (R2 = 0.28–0.71; p < 0.05) but a positive linear relationship with jejunal villus height/crypt depth ratio (R2 = 0.29–0.40; p < 0.05) at weeks 2, 3, and 5 of life. In the ileum, increasing probiotic concentrations linearly increased the crypt depth and decreased the villus height/crypt depth ratio at week 5 of life (R2 = 0.37–0.41; p < 0.05).

Table 3.
Prediction of jejunal and ileal histomorphology (fold change) in broiler chickens at weeks 3 and 6 of life without pathogen challenge.

Table 4.
Prediction of duodenal, jejunal, and ileal histomorphology (fold change) in broiler chickens from weeks 2 to 5 of life with pathogen challenge.
3.4. Probiotic Effects on Growth Performance
The meta-regression results for the growth performance in broiler chickens without and with pathogen challenges are presented in Table 5 and Table 6, respectively. Both under pathogen and non-pathogen challenges, dietary probiotics did not affect the ADFI, ADG, and FCR of broilers either in the starter, finisher, or overall phases.

Table 5.
Prediction of growth performance of broiler chickens at starter (weeks 1–3), finisher (weeks 4–6), and overall (weeks 1–6) periods without pathogen challenge.

Table 6.
Prediction of growth performance of broiler chickens at starter (week 1–3), finisher (week 4–6), and overall (week 1–6) periods with pathogen challenge.
3.5. Backward Elimination Analysis
The backward elimination analysis was conducted separately for data without (Table 7) and with pathogen challenge (Table 8 and Table 9). For the data of chickens without pathogen challenge, backward elimination analysis showed that dietary probiotic concentration was the main factor influencing the expression of MUC2, ZO1, and OCLN in jejunum and ileum and CLDN1 in jejunum at week 3 of life (= 0.36–0.57; p < 0.05). Moreover, increasing dietary ME levels counteracted the positive relationship between dietary probiotic concentration and jejunal MUC2 expression at week 6 of life (= 0.70; p < 0.05). In contrast, an increasing dietary CP level potentiated the increase in jejunal OCLN expression with increasing dietary probiotic concentrations at week 6 of life (R2 = 0.62; p < 0.05). The positive relationship between dietary probiotic concentration and jejunal ZO1 expression was potentiated by dietary ME but counteracted by dietary CP at week 6 of life (R2 = 0.70; p < 0.05). Both dietary ME and CP levels counteracted the increase in ileal ZO1 expression with increasing dietary probiotic concentrations at week 6 of life (R2 = 0.76; p < 0.05). For the gut histomorphology, backward elimination analysis showed that dietary probiotics were the only factor influencing the jejunal villus height at week 6 of life (R2 = 0.28; p = 0.02). A higher dietary ME level potentiated the increase in jejunal and ileal villus height/crypt depth ratio at week 3 of life (R2 = 0.68–0.72; p < 0.05) but counteracted the increase in ileal villus height/crypt depth ratio at week 6 of life (R2 = 0.76; p < 0.05) with higher concentrations of dietary probiotics. In addition, an increasing dietary CP level potentiated the positive relationship between dietary probiotic concentration and ileal villus height at week 6 of life (R2 = 0.72; p < 0.05).

Table 7.
Best-fit equations showing the response variables of gut barrier function-related gene expression and histomorphology (fold change) in relation to increasing dietary probiotics, metabolizable energy, and crude protein level in broiler chickens without pathogen challenge using backward elimination technique.

Table 8.
Best-fit equations showing the gut barrier and immune-related gene expression (fold change) in relation to increasing levels of dietary probiotics, metabolizable energy, and crude protein, as well as days post-infection in broiler chickens with pathogen challenge using backward elimination technique.

Table 9.
Best-fit equations showing the gut histomorphology response variables (fold change) in relation to increasing levels of dietary probiotics, metabolizable energy, and crude protein, as well as days post-infection in broiler chickens with pathogen challenge using backward elimination technique.
Backward elimination analysis for data from studies with pathogen challenge showed that the dietary probiotics concentration was a major factor influencing the expressions of CLDN3, IL6, IL10, IL1B, TNFA, and IFNG either in the jejunum, ileum, or ceca at week 2 and 3 of life (R2 = 0.31–0.97; p < 0.05; Table 8). In addition, an increasing dietary ME level counteracted the positive relationship between dietary probiotic concentration and ZO1 and IL10 expression either in the jejunum, ileum, or ceca at weeks 2 and 4 of life (R2 = 0.79–0.87; p < 0.05). Further results showed that dietary CP level counteracted the increased expression of ZO1, OCLN, and CLDN1 (R2 = 0.45–0.84; p < 0.05) as well as the decreased expression of IL6, IL1B, and TLR4 (R2 = 0.68–0.95; p < 0.05) with higher dietary probiotic concentrations in both the jejunum and ileum from weeks 2 to 4 of life. The positive relationship between dietary probiotic concentration and jejunal ZO1 expression was counteracted by a higher dietary ME but potentiated by increasing dietary CP at week 2 of life (R2 = 0.81; p < 0.05). Both dietary ME and CP levels counteracted the increase in jejunal ZO1 expression with higher concentrations of dietary probiotics at week 3 of life (R2 = 0.76; p < 0.05). Increasing DPI potentiated increased cecal ZO1 and IL10 expression (R2 = 0.79–0.96; p < 0.05) and decreased jejunal IL6 expression (R2 = 0.77; p < 0.05) with increasing dietary probiotic concentrations at weeks 2 and 4 of life.
For the gut histomorphology (Table 9), backward elimination analysis indicated that dietary probiotic concentration was the only factor influencing the villus height/crypt depth ratio in the jejunum and ileum at weeks 2 and 5 of life (R2 = 0.38–0.41; p < 0.05). A higher dietary ME level potentiated an increase in the jejunal villus height (R2 = 0.77; p < 0.05) but counteracted the decrease in jejunal crypt depth (R2 = 0.62; p < 0.05), with higher concentrations of dietary probiotics at week 3 or 5 of life. In contrast, increasing dietary CP levels counteracted the increase in jejunal villus height/crypt depth ratio (R2 = 0.60; p < 0.05) but potentiated the decrease in jejunal crypt depth (R2 = 0.51–88; p < 0.05) with increasing dietary probiotic concentrations at weeks 2 and 3 of life. Increasing DPI potentiated the increase in villus height in the duodenum and ileum at weeks 3 and 5 of life (R2 = 0.75–0.77; p < 0.05) but counteracted the increase in the jejunal villus height/crypt depth ratio and ileal crypt depth at week 5 of life (R2 = 0.57–0.75; p < 0.05) with increasing dietary probiotic concentrations.
4. Discussion
Factors such as type and dosage, chicken breed, rearing stage, the composition of the basal diet, and the health status of the bird can influence the physiological effects of probiotics in chickens, adding to the variation among individual studies. Due to that, literature results on the ability of dietary probiotics to modulate the expression of genes related to immune response and barrier function in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chickens are inconsistent [5,13,14]. Likewise, the effects of dietary probiotics on changes in histo-morphological parameters of the small intestine and performance in chickens also vary [15,16,17,18]. The original research included in this meta-analysis covers a wide scope of experimental settings, which should enable inferring predictions for the effect of probiotics on the target variables. However, it needs to be noted that the present meta-regressions only provide general trends for probiotic use in chicken diets. The data available for the individual probiotics did not meet the minimum requirements. Therefore, the data for the single and multi-species probiotics from the individual studies were combined to perform the meta-regression analysis. A similar limitation existed for the pathogens and aflatoxins administrated in the challenge studies. It also needs to be kept in mind that there is a chance that studies with no or adverse effects of probiotics were not published. From the parameters that met the minimum selection criteria, meta-regressions support the effectiveness of probiotics in sustaining small intestinal and cecal barrier function as well as structural components under non-challenged and challenged conditions while also controlling pro-inflammatory signaling under challenged conditions. The meta-regressions also supported that probiotics may effectively counteract potential damage caused by pathogens or mycotoxins in the lower part of the small intestine, such as oxidative stress and compromised barrier function. Regressions further indicated a beneficial effect of probiotics on absorptive and secretory functions by increasing villus height and decreasing crypt depth in the small intestine, especially under pathogen-challenged conditions. Our results also provided evidence for the gut segment- and age-specific effects. However, it needs to be kept in mind that sufficient data were not always available for the same parameters at the various ages of the birds. Consequently, our results provide a general idea about target variables that were modified by the addition of probiotics in the grower-finisher phase.
Mechanistically, there are several potential modes of action on how the probiotics can influence mucosal gene expression, depending on the actual species and strain of probiotics used. The administrated probiotics across the included non-challenge and challenge studies were Bacillus, Lactobacillus, Clostridium, Pediococcus, Bifidobacterium, Streptococcus, Paenibacillus, Enterococcus, and Saccharomyces. Bacteria interact with the host via microbial metabolites and microbe-associated molecular patterns, which represent specific cell surface structures [19,20]. Consequently, we can assume that parts of the mucosal signaling may have been mediated via the activation of G protein-coupled receptors, pattern recognition receptors, and microbe–microbe interactions, including the production of antimicrobial and fermentation metabolites [21,22,23]. Across the various species, the present meta-regressions supported the anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics under challenged conditions, which may have subsequently contributed to the upregulation of the mucosal barrier, including the expression of tight junction proteins and other first line of defense genes. Certain G protein-coupled receptors sense fermentation end products, such as short-chain and medium-chain fatty acids [24,25]. Due to the lack of data from the original studies, we can only speculate about the fermentation acids that changed locally in the gut due to the probiotic supplementation. Lactobacillus, Enterococcus, Pediococcus, Streptococcus, Paenibacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Bacillus produce lactic acid as a major fermentation product, but depending on the strain, they also produce short-chain fatty acids [26,27]. Clostridium is probably mainly signaled via short-chain fatty acids [28,29]. Short-chain fatty acid-induced G protein-coupled receptor activation may decrease the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines via the inhibition of NFKB expression [21]. Unfortunately, we could not extract sufficient data to assess the probiotic effect on NFKB expression under un-challenged and challenged conditions as well as on cytokine expression in non-challenged chickens. Nevertheless, moderation of the activation of the pro-inflammatory NF-kB signaling pathway may be behind the present findings for negative effects of probiotics on the expression of IL1B and INFG at the jejunal mucosa in week 2 of age and expression of IL1B, IL6, and TNFA in the challenged birds at week 3 of age. Moreover, based on the coefficient of determination for the cytokine expression under challenged conditions, probiotics seemed to be very efficient in the jejunum at week 2 of age and in the ileum at week 3 of age in the challenged chickens. Simultaneously, probiotics may act as anti-inflammatory agent by upregulating the expression of IL10 in innate and adaptive immune cells [30], as indicated by the present results for the jejunum at week 3 and ceca at week 2 of age. Moreover, Bacillus-based probiotics may not only act as an anti-inflammatory agent via fermentation acids but by producing quorum-sensing peptides, such as competence and sporulation factor, which signals via the Akt and p38 MAPK pathways [31,32]. Saccharomyces-based probiotics, especially Saccharomyces cereviceae, have been shown to effectively suppress inflammation by binding certain pathogens and toxins via mannose residues on their cell surface. This may be behind the efficacy of Sacharomyces to control Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. as well as and mitigate the effects of Fusarium-produced mycotoxins [33,34,35], which were the harmful agent used in the respective challenge studies.
Another mode of action in how fermentation metabolites (especially butyrate) can modulate pro-inflammatory signaling pathways is via inhibition of histone deacetylases in macrophages and dendritic cells [22,36]. From the included probiotics, mainly Clostridium butyricum produces butyrate [37,38,39]. The other genera as lactic acid-producing bacteria may have increased the intestinal butyrate levels via cross-feeding [40,41] and hence indirectly affected the activity of histone deacetylases and modified the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines as well as of genes related to the barrier function and host secretions. In the absence of actual data for intestinal butyrate levels, however, we can only speculate whether the presence of the probiotics led to physiologically relevant changes in intestinal butyrate production. Aside from interacting directly with the host, it can be assumed that part of the observed effects was mediated via the interaction of the probiotics with the commensal microbiota through fermentation acids and antimicrobials [42,43]. The latter metabolites can help shape the overall microbiota composition and inhibit the proliferation of pathogens and/or the expression of virulence factors [44,45]. For instance, reuterin produced by Limosilactobacillus reuteri is effective to control dysbiosis [46,47]. Similarly, antimicrobial compounds produced by certain Bacillus-based probiotics, such as surfactin, iturin, and fengycin, have also been reported to be effective against pathogenic bacteria [48]. Any alteration in the microbial composition automatically changes the composition of the microbial cell surface structures, which are recognized by pattern-recognition receptors at the gut mucosa and immune cells [49]. Unfortunately, not much data were available for the expression of pattern-recognition receptors in the included studies. In pathogen-challenged birds, our meta-regressions support a downregulating effect of the probiotics on TLR4 expression in the ileum at week 2 of age. In the respective original studies, the pathogens that were administrated were Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. [50,51], which comprise highly immune-reactive lipopolysaccharide recognized by TLR-4 [20]. This finding may indicate that probiotics effectively inhibited the proliferation of the administrated pathogens and/or moderated the TLR-4 activation. Harmful agents, such as Eimeria, fungi, and mycotoxins, likely signaled via different pattern recognition receptors than TLR-4. In general, it is thinkable that probiotics mediated their anti-inflammatory effect via lower ligand-specific activation of the respective pattern recognition receptors. This, in turn, probably led to a lower NFkB expression and/or gene expression within the AMP-activated protein kinase, MAPK, or Akt-signaling pathways [52,53], and ultimately to a downregulation in expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL1B, IL6, INFG, and TNFA) at the investigated gut sites.
The literature results suggested a protective effect of probiotics on intestinal integrity due to increased mucus production [54,55] and by stimulating the expression of tight junction proteins [55,56,57]. The present meta-regressions confirmed this assumption. However, fewer data were available for MUC2 expression from the challenge studies; therefore, the present findings mainly support the beneficial effects of probiotics in non-challenged birds. Moreover, the stimulating effect of probiotics on the MUC2 expression seemed to last longer in the jejunum than in the ileum of chickens under non-challenged conditions, which may be related to the length of the small intestine and age-related maturation of the immune system in the older chicken [42,58]. The aforementioned effects of probiotics on lower pro-inflammatory cytokine expression may explain their stimulatory effect on the expressions of CLDN3, OCLN, and ZO1 in the jejunum, OCLN and ZO1 in the ileum, and ZO1 in the ceca at week 2, 3, or 4 of age. However, the stimulatory effect was not consistent for all available tight junction protein genes, especially for the claudin genes, which might be related to developmental changes in the gut epithelial functioning and the actual role of the tight junction protein, which needs further investigation. When comparing the non-challenged with the challenged conditions, our meta-regressions indicated an upregulation of the expression of CLDN1 by the probiotics in non-challenged birds at week 3 of age. Under challenged conditions, however, probiotics did not modify the transcription of CLDN1 but that of CLDN3 at week 2 of age.
In individual studies, probiotics were shown to modulate gut histo-morphological parameters [37,59,60]. Our meta-regressions confirm that probiotics can effectively increase villus height and villus height/crypt ratio in non-pathogen- and pathogen-challenged conditions. Probiotics may increase villus height by inducing mitotic cell division and promoting epithelial cell proliferation [61]. Longer villi are associated with improved digestive and absorptive capabilities at the small intestinal mucosa [61]. In addition, probiotics seemed to have a stronger effect on crypt depth under pathogen-challenged conditions in both jejunum and ileum. A shallower crypt is associated with slower cell turnover [62], potentially indicating that the probiotics prevented the disruption of epithelial cells due to the administrated pathogens.
The backward elimination analysis was helpful in the assessment of the impact of certain dietary effects on the target variables. According to the best-fit model, higher dietary ME and CP levels were important influential factors that counteracted the efficacy of probiotics to increase the expression of MUC2, tight junction proteins, and anti-inflammatory cytokines and decrease pro-inflammatory cytokines in the small intestine and ceca. For instance, higher dietary CP may act pro-inflammatory in birds under challenged conditions by stimulating the proliferation of proteolytic taxa in the gut, which could lead to the activation of TLR4 expression. Of the administrated pathogens and toxins, Salmonella and Escherichia coli as Gram-negative and proteolytic bacteria, for instance, may have benefited from increased dietary CP levels. Higher dietary ME, most often caused by a higher starch content of the diet, has been shown to reduce the number of butyric acid-producing bacteria and increase Gram-negative bacteria [63,64], which may act as a pro-inflammatory agent. In contrast to the finding at the gene expression level, the best-fit model also indicated that higher levels of dietary ME and CP could enhance the effect of probiotics on intestinal villus height, which may be related to the stimulation of growth and proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells due to greater nutrient availability [65]. The backward elimination analysis also suggested a certain recovery of the gut mucosa after the pathogen challenge that was independent of the probiotics. Accordingly, with increasing time post-infection, the expression levels of genes for pro-inflammatory cytokines decreased, whereas those of genes coding for anti-inflammatory cytokines and tight junction proteins increased.
5. Conclusions
This present meta-analysis confirmed the results from individual studies at the gene expression level that probiotics can support intestinal barrier function in the small intestine under non-pathogen-challenged conditions in broiler chickens. From the available data that were used in this present analysis, it can be further deduced that under challenged conditions with pathogens and mycotoxins, probiotics do not only increase the expression of barrier function genes, but they mediate anti-inflammatory effects via modulation of cytokine expression in the small intestine and ceca. The effect of probiotics was not limited to the changes in gene expression but was also detectable at the structural level, where they improved villus height and crypt depth and hence influenced absorptive and secretory processes at the small intestinal epithelium. However, the present meta-regressions did not support the effect of probiotics on growth performance. Other sources of variation that could potentially influence or counteract the effects of probiotics in the diet included the dietary levels of ME and CP as well as the DPI in the challenge studies. Limitations of this present meta-analysis were that insufficient data were available from individual studies for the various probiotics and administrated pathogens and mycotoxins. Therefore, the present meta-regressions provide general trends that should be verified in the future when more data for the various single and multi-strain probiotics are available.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani13121970/s1, Table S1: List of references and the respective experimental variables included in the meta-analysis [66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98]; Table S2: Descriptive statistics for predictive and response variables of jejunal and ileal gene expression (fold change) related to barrier function and immune response in broiler chickens at weeks 3 and 6 of life without pathogen challenge; Table S3: Descriptive statistics for predictive and response variables of jejunal and ileal histomorphology (fold change) in broiler chickens at weeks 3 and 6 of life without pathogen challenge; Table S4: Descriptive statistics for predictors and response variables of growth performance in broiler chickens at starter, finisher, and overall periods without pathogen challenge; Table S5: Descriptive statistics for predictive and response variables of jejunal, ileal, and cecal gene expression (fold change) related to barrier function in broiler chickens from weeks 2 to 5 with pathogen challenge; Table S6: Descriptive statistics for predictive and response variables of jejunal, ileal, and cecal gene expression (fold change) related to immune response in broiler chickens from weeks 2 to 4 of life with pathogen challenge; Table S7: Descriptive statistics for predictive and response variables of duodenal, jejunal and ileal histomorphology (fold change) in broiler chickens at weeks 2, 3, and 5 of life with pathogen challenge; Table S8: Descriptive statistics for predictors and response variables of growth performance in broiler chickens at starter, finisher, and overall periods with pathogen challenge.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.U.M.-Z.; investigation, F.Y. and B.U.M.-Z.; statistical analysis, F.Y. and B.U.M.-Z.; data curation, F.Y and B.U.M.-Z.; writing—original draft preparation, F.Y.; writing—review and editing, B.U.M.-Z.; supervision, B.U.M.-Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Ernst Mach grant, ASEA-UNINET funded by the Austrian Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Research (BMBWF) with a reference number: MPC-2021-01736. Open Access Funding by the University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The first author would like to thank Austria’s Agency for Education and Internationalization, Mobility Programs and Cooperation (OeAD-GmbH) for awarding the Ernst Mach, ASEA-UNINET scholarship to pursue a Ph.D. program at the Unit of Nutritional Physiology, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna, Austria.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Popova, T. Effect of probiotics in poultry for improving meat quality. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 14, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Si, W.; Barbe, F.; Chevaux, E.; Sienkiewicz, O.; Zhao, X. Effects of novel probiotic strains of Bacillus pumilus and Bacillus subtilis on production, gut health, and immunity of broiler chickens raised under suboptimal conditions. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, K.; Zhang, A.; Chang, W.; Zheng, A.; Chen, Z.; Cai, H.; Liu, G. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus on the growth performance, immune response, and intestinal barrier function of broiler chickens challenged with Escherichia coli O157. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Q.; Jia, H.M.; Zeng, X.F.; Zhu, J.L.; Hou, C.L.; Liu, X.T.; Yang, F.J.; Qiao, S.Y. Prevention of Escherichia coli infection in broiler chickens with Lactobacillus plantarum B1. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2576–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus on the growth performance and intestinal health of broilers challenged with Clostridium perfringens. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Z. Effects of the dietary probiotic, Enterococcus faecium NCIMB11181, on the intestinal barrier and system immune status in Escherichia coli O78-challenged broiler chickens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neveling, D.P.; Dicks, L.M.T. Probiotics: An antibiotic replacement strategy for healthy broilers and productive rearing. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Das, R.; Oak, S.; Mishra, P. Probiotics (direct-fed microbials) in poultry nutrition and their effects on nutrient utilization, growth and laying performance, and gut health: A systematic review. Animals 2020, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, J. Effects of access to pasture on performance, carcass composition, and meat quality in broilers: A meta-analysis. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Trevisi, P.; Prates, J.A.M.; Tanghe, S.; Bosi, P.; Canibe, N.; Montagne, L.; Freire, J.; Zebeli, Q. Assessing the effect of dietary inulin supplementation on gastrointestinal fermentation, digestibility and growth in pigs: A meta-analysis. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 233, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Canibe, N.; Montagne, L.; Freire, J.; Bosi, P.; Prates, J.A.M.; Tanghe, S.; Trevisi, P. Resistant starch reduces large intestinal pH and promotes fecal lactobacilli and bifidobacteria in pigs. Animal 2019, 13, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, N.R. Invited review: Integrating quantitative findings from multiple studies using mixed model methodology. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, B.B.; Duan, Y.; Khawar, H.; Sun, Q.; Ren, Z.; Elsiddig Mohamed, M.A.; Abbasi, I.H.R.; Yang, X. Bacillus subtilis B21 and Bacillus licheniformis B26 improve intestinal health and performance of broiler chickens with Clostridium perfringens -induced necrotic enteritis. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib-Naseri, K.; de Paula Dorigam, J.C.; Doranalli, K.; Kheravii, S.; Swick, R.A.; Choct, M.; Wu, S.B. Modulations of genes related to gut integrity, apoptosis, and immunity underlie the beneficial effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CECT 5940 in broilers fed diets with different protein levels in a necrotic enteritis challenge model. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, K.; Li, C.-L.; Wang, J.; Qi, G.-H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.-J.; Wu, S.-G. Effects of dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis, as an alternative to antibiotics, on growth performance, serum immunity, and intestinal health in broiler chickens. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 786878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Wang, Z.; Dai, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, M.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, C.; Khalique, A.; Ni, X.; Zeng, D.; et al. Effects of Bacillus methylotrophicus SY200 supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant status, intestinal morphology, and immune function in broiler chickens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, L.; Guo, F.; Liu, Y.; Pham, V.H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z. Probiotics Bacillus licheniformis improves intestinal health of subclinical necrotic enteritis-challenged broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 623739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ni, X.; Qing, X.; Liu, L.; Lai, J.; Khalique, A.; Li, G.; Pan, K.; Jing, B.; Zeng, D. Probiotic enhanced intestinal immunity in broilers against subclinical necrotic enteritis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, C.; Tan, J.; Macia, L.; Mackay, C.R. The nutrition-gut microbiome-physiology axis and allergic diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, M.H.; Genovese, K.J.; Swaggerty, C.L.; He, H.; Broom, L. Inflammatory phenotypes in the intestine of poultry: Not all inflammation is created equal. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Ichimura, A.; Ohue-Kitano, R.; Igarashi, M. Free fatty acid receptors in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 171–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Guo, A. Biological function of short-chain fatty acids and its regulation on intestinal health of poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 736739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, X.; Yan, D.; Liu, S.; Gao, N.; Ma, Z.; Shi, Z.; Dong, N.; Shan, A. Host defense peptides in nutrition and diseases: A contributor of immunology modulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 3125–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U. The role of dietary and microbial fatty acids in the control of inflammation in neonatal piglets. Animals 2021, 11, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Osorio, L.M.; Yepes-Medina, V.; Ballou, A.; Parini, M.; Angel, R. Short and medium chain fatty acids and their derivatives as a natural strategy in the control of necrotic enteritis and microbial homeostasis in broiler chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 773372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessione, E. Lactic acid bacteria contribution to gut microbiota complexity: Lights and shadows. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakizimana, O.; Matabaro, E.; Lee, B.H. The current strategies and parameters for the enhanced microbial production of 2,3-butanediol. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 25, e00397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyoshi, T.; Hagihara, M.; Takahashi, M.; Mikamo, H. Effect of Clostridium butyricum on gastrointestinal infections. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zhang, K.; Ma, X.; He, P. Clostridium species as probiotics: Potentials and challenges. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, M.H.; Genovese, K.J.; He, H.; Arsenault, R.J. AMPK and mTOR: Sensors and regulators of immunometabolic changes during Salmonella infection in the chicken. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Fujiya, M.; Nata, T.; Ueno, N.; Inaba, Y.; Ishikawa, C.; Ito, T.; Moriichi, K.; Tanabe, H.; Mizukami, Y.; et al. Competence and sporulation factor derived from Bacillus subtilis improves epithelial cell injury in intestinal inflammation via immunomodulation and cytoprotection. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2012, 27, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suva, M.A.; Sureja, V.P.; Kheni, D.B. Novel insight on probiotic Bacillus subtilis: Mechanism of action and clinical applications. J. Curr. Res. Sci. Med. 2016, 2, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanello, G.; Meurens, F.; Berri, M.; Chevaleyre, C.; Melo, S.; Auclair, E.; Salmon, H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae decreases inflammatory responses induced by F4+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 141, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.S.; Elian, S.D.A.; Vieira, A.T.; Tiago, F.C.P.; Martins, A.K.S.; Silva, F.C.P.; Souza, É.L.S.; Sousa, L.P.; Araújo, H.R.C.; Pimenta, P.F.; et al. Oral treatment with Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain UFMG 905 modulates immune responses and interferes with signal pathways involved in the activation of inflammation in a murine model of typhoid fever. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhou, S.-N.; Wang, X.-D.; Wu, J.-E. Protective effect of Saccharomyces boulardii on deoxynivalenol-induced injury of porcine macrophage via attenuating p38 MAPK signal pathway. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 182, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; van Esch, B.C.A.M.; Wagenaar, G.T.M.; Garssen, J.; Folkerts, G.; Henricks, P.A.J. Pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of short chain fatty acids on immune and endothelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 831, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, S.; Olajide, J.S.; Qu, Z.; Gong, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, K.; et al. Clostridium butyricum supplement can ameliorate the intestinal barrier roles in broiler chickens experimentally infected with Clostridium perfringens. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.S.I.; Radey, R. Immunomodulation of antimicrobial peptides expression in the gastrointestinal tract by probiotics in response to stimulation by Salmonella minnesota Lipopolysaccharides. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ling, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Peng, N.; Zhao, S. Functional comparison of Clostridium butyricum and sodium butyrate supplementation on growth, intestinal health, and the anti-inflammatory response of broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 914212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Hooda, S.; Pieper, R.; Zijlstra, R.T.; van Kessel, A.G.; Mosenthin, R.; Gänzle, M.G. Nonstarch polysaccharides modulate bacterial microbiota, pathways for butyrate production, and abundance of pathogenic Escherichia coli in the pig gastrointestinal tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3692–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Zijlstra, R.T.; Mosenthin, R.; Gänzle, M.G. Dietary calcium phosphate content and oat β-glucan influence gastrointestinal microbiota, butyrate-producing bacteria and butyrate fermentation in weaned pigs. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 75, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broom, L.J.; Kogut, M.H. Gut immunity: Its development and reasons and opportunities for modulation in monogastric production animals. Anim. Heal. Res. Rev. 2018, 19, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shini, S.; Bryden, W.L. Probiotics and gut health: Linking gut homeostasis and poultry productivity. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2021, 62, 1090–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, M.; Pieper, R.; Rogel-Gaillard, C.; de Vries, H.; Bailey, M.; Smidt, H.; Lauridsen, C. Immunomodulating effects of probiotics for microbiota modulation, gut health and disease resistance in pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 233, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, G.E.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Lawlor, P.G. Impact of intestinal microbiota on growth and feed efficiency in pigs: A review. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Tavella, V.J.; Luo, X.M. Role of Lactobacillus reuteri in human health and diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, H.N.; Rebernick, R.J.; Goyert, J.; Singhal, R.; Kuljanin, M.; Kerk, S.A.; Huang, W.; Das, N.K.; Andren, A.; Solanki, S.; et al. Reuterin in the healthy gut microbiome suppresses colorectal cancer growth through altering redox balance. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 185–200.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaddad, S.A.; Almalki, M.H.K.; Alghamdi, O.A.; Sohrab, S.S.; Yasir, M.; Azhar, E.I.; Chouayekh, H. Bacillus species as direct-fed microbial antibiotic alternatives for monogastric production. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Groer, M.; Dutra, S.V.O.; Sarkar, A.; McSkimming, D.I. Gut microbiota and immune system interactions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateya, A.I.; Arafat, N.; Saleh, R.M.; Ghanem, H.M.; Naguib, D.; Radwan, H.A.; Elseady, Y.Y. Intestinal gene expressions in broiler chickens infected with Escherichia coli and dietary supplemented with probiotic, acidifier and synbiotic. Vet. Res. Commun. 2019, 43, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Teng, P.Y.; Lee, T.T.; Yu, B. Effects of multi-strain probiotic supplementation on intestinal microbiota, tight junctions, and inflammation in young broiler chickens challenged with Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Ajuwon, K.M. Butyrate modifies intestinal barrier function in IPEC-J2 cells through a selective upregulation of tight junction proteins and activation of the Akt signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.; Liang, L.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S. Modulatory effects of probiotics during pathogenic infections with emphasis on immune regulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 616713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.A.; Yalçın, S.; Latorre, J.D.; Basiouni, S.; Attia, Y.A.; Abd El-Wahab, A.; Visscher, C.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Huber, C.; Hafez, H.M.; et al. Probiotics, prebiotics, and phytogenic substances for optimizing gut health in poultry. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, W. Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum 16 and Paenibacillus polymyxa 10 against Clostridium perfringens infection in broilers. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 628374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, N.; Xin, J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, H.; Lei, L.; Ling, H.; et al. Dietary probiotic supplementation suppresses subclinical necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens in a microbiota-dependent manner. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 855426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Cai, W. Effects of novel microecologics combined with traditional Chinese medicine and probiotics on growth performance and health of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramasuriya, S.S.; Park, I.; Lee, K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W.H.; Nam, H.; Lillehoj, H.S. Role of physiology, immunity, microbiota, and infectious diseases in the gut health of poultry. Vaccines 2022, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calik, A.; Omara, I.I.; White, M.B.; Li, W.; Dalloul, R.A. Effects of dietary direct fed microbial supplementation on performance, intestinal morphology and immune response of broiler chickens challenged with coccidiosis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, T.; Daneshyar, M.; Allymehr, M.; Tukmechi, A.; Khalilvandi Behroozyar, H.; Shalizar Jalali, A. Combination of Lactobacillus species and yeast ameliorates adverse effect of deoxynivalenol contaminated diet on immune system, gut morphology and jejunal gene expression in broiler chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shafi, M.E.; Qattan, S.Y.A.; Batiha, G.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E.; Alagawany, M. Probiotics in poultry feed: A comprehensive review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1835–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.A.; Ghareeb, K.; Abdel-Raheem, S.; Böhm, J. Effects of dietary inclusion of probiotic and synbiotic on growth performance, organ weights, and intestinal histomorphology of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.-F.; He, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Alam, M.S. Effects of high carbohydrate diet-modulated microbiota on gut health in Chinese perch. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 575102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Shi, Z. The effects of dietary protein and fiber levels on growth performance, gout occurrence, intestinal microbial communities, and immunoregulation in the gut-kidney axis of goslings. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kim, W.K. Effects of dietary fiber on nutrients utilization and gut health of poultry: A review of challenges and opportunities. Animals 2021, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliakbarpour, H.R.; Chamani, M.; Rahimi, G.; Sadeghi, A.A.; Qujeq, D. The Bacillus subtilis and lactic acid bacteria probiotics influences intestinal mucin gene expression, histomorphology and growth performance in broilers. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 25, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.P.; Wu, A.M.; Ding, X.M.; Lei, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhang, K.Y.; Chio, J.S. Effects of probiotic-supplemented diets on growth performance and intestinal immune characteristics of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodinga, B.M.; Hayat, K.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Yang, X.; Ismaila, A.; Soomro, R.N.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.J. Effects of Bacillus Subtilis DSM 32315 on immunity, nutrient transporters and functional diversity of cecal microbiome of broiler chickens in necrotic enteritis challenge. J. World’s Poult. Res. 2020, 10, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wu, X.H.; Bai, Y.L.; Wu, X.Y.; Gu, S.B. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of probiotic powder containing Lactobacillus plantarum 1.2567 in necrotic enteritis model of broiler chickens. Livest. Sci. 2019, 223, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.A.; Lee, Y.; Lillehoj, H.S. Beneficial effects of dietary supplementation of Bacillus strains on growth performance and gut health in chickens with mixed coccidiosis infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 277, 109009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ishfaq, M.; Wang, J. Effects of Lactobacillus salivarius supplementation on the growth performance, liver function, meat quality, immune responses and Salmonella pullorum infection resistance of broilers challenged with Aflatoxin B1. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Shi, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, N. Effect of dietary Lactobacilli mixture on Listeria monocytogenes infection and virulence property in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3655–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.L.; Wang, Y.W.; Song, D.; Hou, Y.J.; Wang, W.W.; Qi, W.T.; Yun, T.T.; Li, A.K. The effects of dietary supplementation of pre-microencapsulated Enterococcus fecalis and the extract of Camellia oleifera seed on growth performance, intestinal morphology, and intestinal mucosal immune functions in broiler chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 212, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, N.K.; Calik, A.; White, M.B.; Kimminau, E.A.; Dalloul, R.A. Effect of probiotics and multi-component feed additives on microbiota, gut barrier and immune responses in broiler chickens during subclinical necrotic enteritis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, N.K.; Calik, A.; White, M.B.; Young, M.; Dalloul, R.A. Necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens: The role of tight junctions and mucosal immune responses in alleviating the effect of the disease. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Xi, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, B. Dietary Lactobacillus fermentum and Bacillus coagulans supplementation modulates intestinal immunity and microbiota of broiler chickens challenged by Clostridium perfringens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 680742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Long, S.; Mahfuz, S.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Piao, X. Effects of probiotics as antibiotics substitutes on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters, intestinal morphology, and barrier function of broilers. Animals 2019, 9, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.G.; Modarressi, M.H.; Mousavi, S.N.; Ebrahimi, M.T. Effects of indigenous spore-forming probiotic as feed supplement on performance and safety in broilers. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2019, 70, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Chamani, M.; Mousavi, S.N.; Hosseini, S.A.; Sadeghi, A.A. Growth performance, mucin2 gene expression, morphology of small intestine and intestinal lactobacillus population of broiler chicks fed with triticale-based diets: Effects of dietary physical form and dietary inclusion of enzyme and probiotic. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2018, 24, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczka, P.; Sandvang, D.; Kinsner, M.; Szkopek, D.; Szyryńska, N.; Jankowski, J. Bacillus-based probiotics affect gut barrier integrity in different ways in chickens subjected to optimal or challenge conditions. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 265, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Xun, X.Y.; Hu, Y.D.; Li, N.Z.; Yang, C.W.; Jiang, X.S.; Liu, Y.P. Research on the effect of Pediococcus pentosaceus on Salmonella enteritidis -infected chicken. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6416451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.P.; Yang, M.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Lu, Z.X.; Zhou, Y.M.; Wang, T. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens supplementation alleviates immunological stress and intestinal damage in lipopolysaccharide-challenged broilers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 208, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Lv, Z.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y. Bacillus subtilis and yeast cell wall improve the intestinal health of broilers challenged by Clostridium perfringens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2017, 58, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Z.; Liu, D. Supplemental Bacillus subtilis PB6 improves growth performance and gut health in broilers challenged with Clostridium perfringens. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 2549541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, F.U.; Yang, Y.; Leghari, I.H.; Lv, F.; Soliman, A.M.; Zhang, W.; Si, H. Transcriptome analysis revealed ameliorative effects of Bacillus based probiotic on immunity, gut barrier system, and metabolism of chicken under an experimentally induced Eimeria tenella infection. Genes 2021, 12, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsin, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, G. Effect of probiotics on the performance and intestinal health of broiler chickens infected with Eimeria tenella. Vaccines 2022, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mountzouris, K.C.; Palamidi, I.; Paraskeuas, V.; Griela, E.; Fegeros, K. Dietary probiotic form modulates broiler gut microbiota indices and expression of gut barrier genes including essential components for gut homeostasis. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 1143–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ishfaq, M.; Miao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hao, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Dietary administration of Bacillus subtilis KC1 improves growth performance, immune response, heat stress tolerance, and disease resistance of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Han, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, B.; D’inca, R. Dietary live yeast and mannan-oligosaccharide supplementation attenuate intestinal inflammation and barrier dysfunction induced by Escherichia coli in broilers. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhan, X. Bacillus subtilis DSM29784 alleviates negative effects on growth performance in broilers by improving the intestinal health under necrotic enteritis challenge. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Wang, F.; Guo, F.; Yan, F.; Yang, X.; Yang, X. Intestinal toxicity of deoxynivalenol is limited by supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum JM113 and consequentially altered gut microbiota in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, R.; Tang, L.; Gong, L.; Li, W. Effects of probiotics Lactobacillus plantarum 16 and Paenibacillus polymyxa 10 on intestinal barrier function, antioxidative capacity, apoptosis, immune response, and biochemical parameters in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5028–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Song, B.; Zhen, W.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Shahid, M.S.; Nie, W. Effects of Bacillus coagulans supplementation on the growth performance and gut health of broiler chickens with Clostridium perfringens-induced necrotic enteritis. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhen, W.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y. Pretreatment with probiotic Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 11181 ameliorates necrotic enteritis-induced intestinal barrier injury in broiler chickens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Memon, F.U.; Hao, K.; Jiang, M.; Guo, L.; Liu, T.; Lv, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Si, H. The combined use of Bacillus subtilis-based probiotic and anticoccidial herb had a better anti-Eimeria tenella efficiency. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2021, 30, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Yue, M.; Yang, C. Effects of Bacillus coagulans on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immunity function, and gut health in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.; Liang, C.; Zhai, Z. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BLCC1-0238 alone or in combination with mannan-oligosaccharides alleviates subclinical necrotic enteritis in broilers. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, W.; Shao, Y.; Gong, X.; Wu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y. Effect of dietary Bacillus coagulans supplementation on growth performance and immune responses of broiler chickens challenged by Salmonella enteritidis. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2654–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).