Sustainable Ornamental Fish Aquaculture: The Implication of Microbial Feed Additives
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
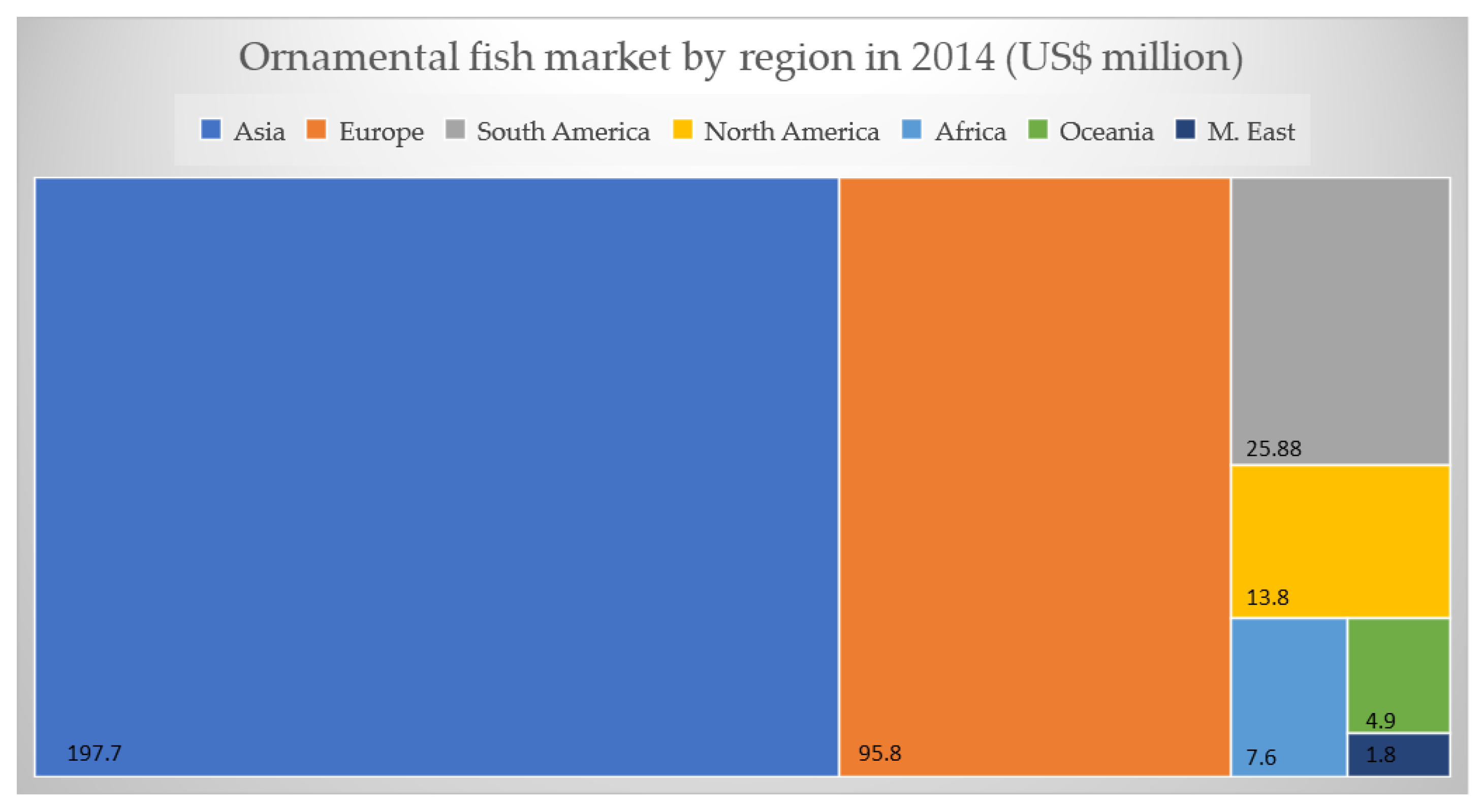
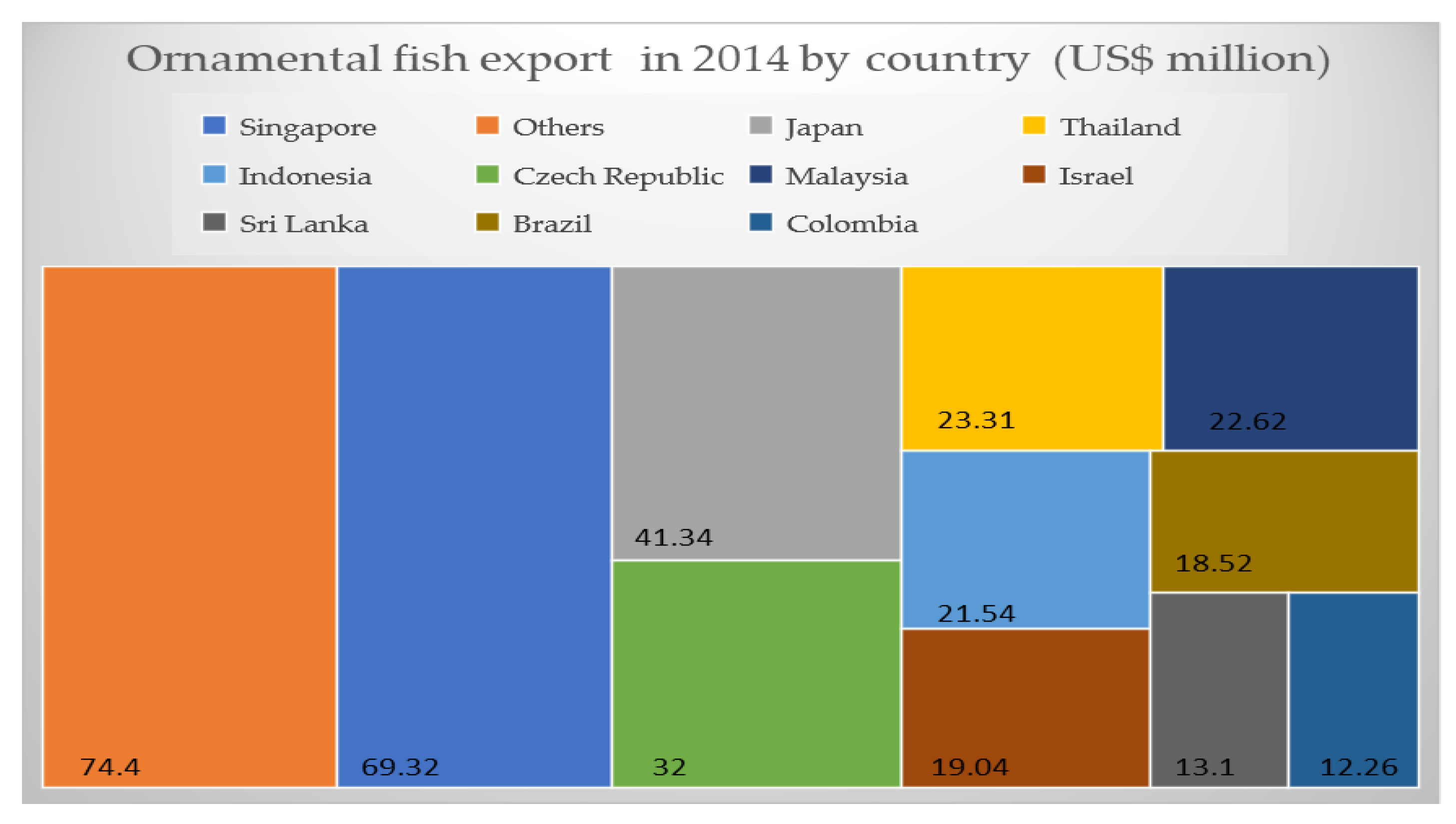
2. Economic Aspects of Ornamental Fish Trade
3. Effects of Microbial Feed Additives on Ornamental Fish Health
4. Effects of Microbial Feed Additives on Ornamental Fish Growth
5. Effects of Microbial Feed Additives on Ornamental Fish Reproduction
6. Role of Microbial Feed Additives in Maintaining Good Water Quality of Ornamental Fish Holding Systems
7. Current Knowledge Regarding Prebiotic and Synbiotic Use in Ornamental Fish
8. Research Gaps and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, T.A.; Gunasundari, V.; Prakash, S. Breeding and rearing of marine ornamentals. In Advances in Marine and Brackishwater Aquaculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Zeng, C.; Jerry, D.R.; Cobcroft, J.M. Recent advances of marine ornamental fish larviculture: Broodstock reproduction, live prey and feeding regimes, and comparison between demersal and pelagic spawners. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1518–1541. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, E.M. Exploitation of Coral Reef Fishes for the Aquarium Trade: A Report to the Marine Conservation Society; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1985; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Biondo, M.V.; Burki, R.P. Monitoring the trade in marine ornamental fishes through the European Trade Control and Expert System TRACES: Challenges and possibilities. Mar. Policy 2019, 108, 103620. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan, R.; Dahanukar, N.; Tlusty, M.F.; Rhyne, A.L.; Kumar, K.K.; Molur, S.; Rosser, A.M. Uncovering an obscure trade: Threatened freshwater fishes and the aquarium pet markets. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 164, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, S.; Kumar, T.T.A.; Raghavan, R.; Rhyne, A.; Tlusty, M.F.; Subramoniam, T. Marine aquarium trade in India: Challenges and opportunities for conservation and policy. Mar. Policy 2017, 77, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Novák, J.; Kalous, L.; Patoka, J. Modern ornamental aquaculture in Europe: Early history of freshwater fish imports. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2042–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Tlusty, M. The benefits and risks of aquacultural production for the aquarium trade. Aquaculture 2002, 205, 203–219. [Google Scholar]
- Evers, H.G.; Pinnegar, J.K.; Taylor, M.I. Where are they all from?–sources and sustainability in the ornamental freshwater fish trade. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 909–916. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderzwalmen, M.; Eaton, L.; Mullen, C.; Henriquez, F.; Carey, P.; Snellgrove, D.; Sloman, K.A. The use of feed and water additives for live fish transport. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 263–278. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, S.; Babu, T.; Nammalwar, P.; Jacob, C.; Dinesh, K. Potential of ornamental fish culture and marketing strategies for future prospects in India. Int. J. Biosci. Nanosci. 2014, 1, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Satam, S.; Sawant, N.; Ghughuskar, M.; Sahastrabuddhe, V.; Naik, V.; Pagarkar, A.; Chogale, N.; Metar, S.; Shinde, K.; Sadawarte, V. Ornamental fisheries: A new avenue to supplement farm income. Adv. Agric. Res. Technol. J. 2018, 2, 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, V. Ornamental Fish Trade–Recent Trends in Asia. In Souvenir, Ornamental; Department of Fisheries, Government of Kerala: Kerala, India, 2010; pp. 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, V. The global trade in ornamental fish. Infofish Int. 2016, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Pinnegar, J.K.; Murray, J.M. Understanding the United Kingdom marine aquarium trade–a mystery shopper study of species on sale. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evan, Y.; Putri, N.E. Status of aquatic animal health in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Promotion of Sustainable Aquaculture, Aquatic Animal Health, and Resource Enhancement in Southeast Asia, Iloilo, Philippines, 25–27 June 2019; pp. 138–149. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, Y. A systematic review on antibiotics misuse in livestock and aquaculture and regulation implications in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, W.M.; Liao, C.M. A risk-based approach for managing aquaculture used oxytetracycline-induced TetR in surface water across Taiwan regions. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 803499. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, S.; Hill, R.; Bermudez, L.; Miller-Morgan, T. Imported ornamental fish are colonized with antibiotic-resistant bacteria. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Preena, P.; Arathi, D.; Raj, N.S.; Arun Kumar, T.; Arun Raja, S.; Reshma, R.; Raja Swaminathan, T. Diversity of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens from a freshwater ornamental fish farm. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 71, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; MacKinnon, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Fridman, S.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Brun, E.; Le Groumellec, M.; Li, A.; Surachetpong, W.; Karunasagar, I. Review of alternatives to antibiotic use in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, D.M.; Stillwell, R.H. Probiotics: Growth-promoting factors produced by microorganisms. Science 1965, 147, 747–748. [Google Scholar]
- Kozasa, M. Toyocerin (Bacillus toyoi) as growth promotor for animal feeding. Microbiol. Aliment. Nutr. 1986, 4, 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ringø, E.; Gatesoupe, F.J. Lactic acid bacteria in fish: A review. Aquaculture 1998, 160, 177–203. [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Dimitroglou, A.; Foey, A.; Davies, S.J.; Baker, R.T.M.; Bøgwald, J.; Castex, M.; Ringø, E. The current status and future focus of probiotic and prebiotic applications for salmonids. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Carnevali, O.; Avella, M.; Gioacchini, G. Effects of probiotic administration on zebrafish development and reproduction. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 188, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as means of diseases control in aquaculture, A Review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soltani, M.; Ghosh, K.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Kumar, V.; Lymbery, A.J.; Roy, S.; Ringø, E. Genus bacillus, promising probiotics in aquaculture: Aquatic animal origin, bio-active components, bioremediation and efficacy in fish and shellfish. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2019, 27, 331–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Harikrishnan, R.; Soltani, M.; Ghosh, K. The Effect of Gut Microbiota and Probiotics on Metabolism in Fish and Shrimp. Animals 2022, 12, 3016. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ringø, E.; Shenavar Masouleh, A.; Esteban, M.Á. Probiotic, prebiotic and synbiotic supplements in sturgeon aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2016, 8, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevali, O.; Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G. Integrated control of fish metabolism, wellbeing and reproduction: The role of probiotic. Aquaculture 2017, 472, 144–155. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.A.; Duc, L.H.; Cutting, S.M. The use of bacterial spore formers as probiotics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 813–835. [Google Scholar]
- Ringø, E. Probiotics in shellfish aquaculture. Aquac. Fish. 2020, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, A.; Singh, R. Probiotics in aquaculture: A promising emerging alternative approach. Symbiosis 2019, 77, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Falcinelli, S.; Picchietti, S.; Rodiles, A.; Cossignani, L.; Merrifield, D.L.; Taddei, A.R.; Maradonna, F.; Olivotto, I.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O. Lactobacillus rhamnosus lowers zebrafish lipid content by changing gut microbiota and host transcription of genes involved in lipid metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falcinelli, S.; Rodiles, A.; Hatef, A.; Picchietti, S.; Cossignani, L.; Merrifield, D.L.; Unniappan, S.; Carnevali, O. Dietary lipid content reorganizes gut microbiota and probiotic L. rhamnosus attenuates obesity and enhances catabolic hormonal milieu in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falcinelli, S.; Rodiles, A.; Unniappan, S.; Picchietti, S.; Gioacchini, G.; Merrifield, D.L.; Carnevali, O. Probiotic treatment reduces appetite and glucose level in the zebrafish model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G.; Falcinelli, S.; Bertotto, D.; Radaelli, G.; Olivotto, I.; Carnevali, O. Probiotic supplementation promotes calcification in Danio rerio larvae: A molecular study. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e83155. [Google Scholar]
- Abid, A.; Davies, S.J.; Waines, P.; Emery, M.; Castex, M.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O.; Bickerdike, R.; Romero, J.; Merrifield, D.L. Dietary synbiotic application modulates Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) intestinal microbial communities and intestinal immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, G.; Giorgini, E.; Olivotto, I.; Maradonna, F.; Merrifield, D.L.; Carnevali, O. The influence of probiotics on zebrafish Danio rerio innate immunity and hepatic stress. Zebrafish 2014, 11, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Gioacchini, G.; Ciani, E.; Pessina, A.; Cecchini, C.; Silvi, S.; Rodiles, A.; Merrifield, D.L.; Olivotto, I.; Carnevali, O. Effects of Lactogen 13, a new probiotic preparation, on gut microbiota and endocrine signals controlling growth and appetite of Oreochromis niloticus juveniles. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, G.; Maradonna, F.; Lombardo, F.; Bizzaro, D.; Olivotto, I.; Carnevali, O. Increase of fecundity by probiotic administration in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Reproduction 2010, 140, 953–959. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgini, E.; Conti, C.; Ferraris, P.; Sabbatini, S.; Tosi, G.; Rubini, C.; Vaccari, L.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus on zebrafish oocyte maturation: An FTIR imaging and biochemical analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 3063–3072. [Google Scholar]
- Gioacchini, G.; Dalla Valle, L.; Benato, F.; Fimia, G.M.; Nardacci, R.; Ciccosanti, F.; Piacentini, M.; Borini, A.; Carnevali, O. Interplay between autophagy and apoptosis in the development of Danio rerio follicles and the effects of a probiotic. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2013, 25, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Vílchez, M.C.; Santangeli, S.; Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G.; Verdenelli, C.; Gallego, V.; Peñaranda, D.S.; Tveiten, H.; Pérez, L.; Carnevali, O. Effect of the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus on the expression of genes involved in European eel spermatogenesis. Theriogenology 2015, 84, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martínez Cruz, P.; Ibáñez, A.; Monroy Hermosillo, O.; Ramírez Saad, H. Use of probiotics in aquaculture. ISRN Microbiol. 2012, 916845, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Thongprajukaew, K.; Kovitvadhi, U.; Kovitvadhi, S.; Somsueb, P.; Rungruangsak-Torrissen, K. Effects of different modified diets on growth, digestive enzyme activities and muscle compositions in juvenile Siamese fighting fish (Betta splendens Regan, 1910). Aquaculture 2011, 322, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Roosta, Z.; Hajimoradloo, A.; Vakili, F. The effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus as feed supplement on skin mucosal immune parameters, intestinal microbiota, stress resistance and growth performance of black swordtail (Xiphophorus helleri). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, T.J.; Mondal, S.; Babu, C.S. Effect of Commercial Aquaculture Probiotic and Fish Gut Antagonistic Bacterial Flora on the Growth and Disease Resistance of Ornamental Fishes Carassius auratus and Xiphophorus helleri. Ege J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 25, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmaraj, S.; Dhevendaran, K. Evaluation of Streptomyces as a probiotic feed for the growth of ornamental fish Xiphophorus helleri. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 48, 497–504. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, A.; Sahu, C. Effect of probiotic on reproductive performance in female livebearing ornamental fish. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, A.; Sahu, C. Dietary probiotic supplementation in growth and health of live-bearing ornamental fishes. Aquac. Nutr. 2007, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, M.; Revathi, U. Role of probiotics in Ornamental fish Platy Xiphophorus maculates. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 5, 819–823. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A.; Ghosh, S.; Singh, D. Probiotics and nutrient supplement in artificial feed of gold fish (Carassius auratus). J. Indian Fish. Assoc. 2004, 31, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Anuar, N.S.; Omar, N.S.; Noordiyana, M.N.; Sharifah, N.E. Effect of commercial probiotics on the survival and growth performance of goldfish Carassius auratus. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2017, 10, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, L.; Barrera, T.; Mejia, J.; Mejia, G.; Del Carmen, M.; Dosta, M.; De Lara Andrade, R.; Sotres, J. Effects of the commercial probiotic Lactobacillus casei on the growth, protein content of skin mucus and stress resistance of juveniles of the Porthole livebearer Poecilopsis gracilis (Poecilidae). Aquac. Nutr. 2010, 16, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, K.; Isamma, A.; Ramasubramanian, V.; Sureshkumar, S.; Arunjith, T. Colonization of probiotic bacteria and its impact on ornamental fish Puntius conchonius. J. Environ. Biol. 2012, 33, 551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Illanjiam, S.; Sivakumar, J.; Sundaram, C.S.; Rao, U. Comparative study of Probiotic Bacteria on ornamental fish giant gourami, Osphronemus goramy for its survival and growth. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2019, 12, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, M.; Nayak, B.; Nanda, A. In vivo and in vitro characterization of probiotic organisms for their microbial adhesion property isolated from Coconut toddy. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2018, 4, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.K.; Nayak, B.K.; Nanda, A. In vivo characterization of probiotic organism isolated from coconut toddy using ornamental fish, Black molly. Der Pharm. Lett. 2016, 8, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, V.; Gomez-Chiarri, M.; Roy, C.; Smith, K.; Amaral-Zettler, L. Subtle microbiome manipulation using probiotics reduces antibiotic-associated mortality in fish. Msystems 2017, 2, e00133-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, I.; Radhakrishnan, D.K.; Venkatachalam, R.; Sathrajith, A.T.; Velayudhannair, K.; Sureshkumar, S. Studies on probiotics administration and its influence on gut microflora of ornamental fish Brachydanio rerio larvae. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 336–344. [Google Scholar]
- Avella, M.A.; Place, A.; Du, S.J.; Williams, E.; Silvi, S.; Zohar, Y.; Carnevali, O. Lactobacillus rhamnosus accelerates zebrafish backbone calcification and gonadal differentiation through effects on the GnRH and IGF systems. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Saputra, F.; Chen, Y.C.; Hu, S.Y. Dietary administration of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens R8 reduces hepatic oxidative stress and enhances nutrient metabolism and immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, G.; Rossi, G.; Carnevali, O. Host-probiotic interaction: New insight into the role of the endocannabinoid system by in vivo and ex vivo approaches. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.C.; Liu, C.H.; Chuang, K.P.; Chang, Y.T.; Hu, S.Y. A potential probiotic Chromobacterium aquaticum with bacteriocin-like activity enhances the expression of indicator genes associated with nutrient metabolism, growth performance and innate immunity against pathogen infections in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioacchini, G.; Giorgini, E.; Merrifield, D.L.; Hardiman, G.; Borini, A.; Vaccari, L.; Carnevali, O. Probiotics can induce follicle maturational competence: The Danio rerio case. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86, 65,1-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; He, S.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, Z. Comparison of fecundity and offspring immunity in zebrafish fed Lactobacillus rhamnosus CICC 6141 and Lactobacillus casei BL23. Reproduction 2014, 147, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcinelli, S.; Randazzo, B.; Vargas Abundez, J.A.; Cangiotti, G.; Olivotto, I.; Carnevali, O. Kluyveromyces fragilis RNA extract supplementation promotes growth, modulates stress and inflammatory response in zebrafish. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1521–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruffo, M.; Navarrete, N.C.; Salgado, O.A.; Faúndez, N.B.; Gajardo, M.C.; Feijóo, C.G.; Reyes-Jara, A.; García, K.; Navarrete, P. Protective yeasts control V. anguillarum pathogenicity and modulate the innate immune response of challenged zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avella, M.A.; Olivotto, I.; Silvi, S.; Place, A.R.; Carnevali, O. Effect of dietary probiotics on clownfish: A molecular approach to define how lactic acid bacteria modulate development in a marine fish. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R359–R371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadifard, N.; Rezaei Aminlooi, V.; Tukmechi, A.; Agh, N. Evaluation of the impacts of long-term enriched Artemia with Bacillus subtilis on growth performance, reproduction, intestinal microflora, and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila of ornamental fish Poecilia latipinna. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamloo, K.; Akhavan, S.R.; Henry, M.A. Effects of dietary administration of Bacillus probiotics on the non-specific immune responses of tinfoil barb, Barbonymus schwanenfeldii (Actinopterygii: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae). Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2013, 43, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.C.; Brinn, R.P.; Marcon, J.L.; Dantas, L.A.; Brandão, F.R.; Sampaio de Abreu, J.; McComb, D.M.; Baldisserotto, B. Using Efinol® L during transportation of marbled hatchetfish, Carnegiella strigata (Günther). Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.C.; Brinn, R.P.; Marcon, J.L.; Dantas, L.A.; Brandão, F.R.; De Abreu, J.S.; Lemos, P.E.M.; McComb, D.M.; Baldisserotto, B. Benefits of using the probiotic Efinol® L during transportation of cardinal tetra, Paracheirodon axelrodi (Schultz), in the Amazon. Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neissi, A.; Rafiee, G.; Nematollahi, M.; Safari, O. The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici bacteria used as probiotic supplement on the growth and non-specific immune responses of green terror, Aequidens rivulatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1976–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimirad, M.; Meshkini, S.; Ahmadifard, N.; Hoseinifar, S.H. The effects of feeding with synbiotic (Pediococcus acidilactici and fructooligosaccharide) enriched adult Artemia on skin mucus immune responses, stress resistance, intestinal microbiota and performance of angelfish (Pterophyllum danio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, J.A.R.; Abe, H.A.; Sousa, N.C.; Silva, R.D.F.; Cordeiro, C.A.M.; Gomes, G.F.E.; Ready, J.S.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Martins, M.L.; Carneiro, P.C.F. Enterococcus faecium as potential probiotic for ornamental neotropical cichlid fish, Pterophyllum scalare (Schultze, 1823). Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan Girijakumari, N.; Ethiraja, K.; Narayanasamy Marimuthu, P. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of probiotic properties of Enterobacter cloacae in Kenyi cichlid, Maylandia lombardoi. Aquac. Int. 2018, 26, 959–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzbakhsh, F.; Noori, F.; Khalesi, M.K.; Jani-Khalili, K. Effects of a probiotic, protexin, on the growth performance and hematological parameters in the Oscar (Astronotus ocellatus) fingerlings. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 37, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Aminlooi, V.; Ahmadifard, N.; Tukmechi, A.; Agh, N. Improvement of reproductive indices, lysozyme activity, and disease resistance in live-bearing ornamental fish, Poecilia latipinna using Artemia supplementation with treated yeast cell, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasundari, V.; Kumar, T.A.; Ghosh, S.; Kumaresan, S. An ex vivo loom to evaluate the brewer’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae in clownfish aquaculture with special reference to Amphiprion percula (Lacepede, 1802). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 13, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.B.; Iversen, S.L.; Sørensen, K.I.; Johansen, E. The long and winding road from the research laboratory to industrial applications of lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Pingitore, E.V.; Mozzi, F.; Saavedra, L.; M Villegas, J.; M Hebert, E. Lactic acid bacteria as cell factories for the generation of bioactive peptides. Protein Pept. Lett. 2017, 24, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoli, R.; Bosco, F.; Mizrahi, I.; Bayer, E.A.; Pessione, E. Towards lactic acid bacteria-based biorefineries. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1216–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas-Ortega, M.G.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Martínez-Hernández, J.L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Nevárez-Moorillón, G.V. Production of bioactive peptides from lactic acid bacteria: A sustainable approach for healthier foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieco-Saiz, N.; Belguesmia, Y.; Raspoet, R.; Auclair, E.; Gancel, F.; Kempf, I.; Drider, D. Benefits and inputs from lactic acid bacteria and their bacteriocins as alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters during food-animal production. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, N.; Maqsood, S.; Masud, T.; Ahmad, A.; Sohail, A.; Momin, A. Lactobacillus acidophilus: Characterization of the species and application in food production. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, M.; Plummer, S.; Marchesi, J.; Mahenthiralingam, E. The life history of Lactobacillus acidophilus as a probiotic: A tale of revisionary taxonomy, misidentification and commercial success. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 349, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, A.; Grimaldi, A.; Walker, M.; Bartowsky, E.; Grbin, P.; Jiranek, V. Lactic acid bacteria as a potential source of enzymes for use in vinification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5715–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, C.; Jänsch, A.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Toelstede, S.; Vogel, R.F. Characterization of cinnamoyl esterases from different Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojan, J.M.; Gioacchini, G.; Giorgini, E.; Orlando, P.; Tiano, L.; Maradonna, F.; Carnevali, O. Zebrafish caudal fin as a model to investigate the role of probiotics in bone regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Kruger, R.; Inglis, V. Augmentation of non-specific protection in African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell), by the long-term oral administration of immunostimulants. J. Fish Dis. 1995, 18, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstad, R.E.; Robertsen, B.; Frivold, E. Yeast glucan induces increase in lysozyme and complement-mediated haemolytic activity in Atlantic salmon blood. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1992, 2, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwicki, A.K.; Anderson, D.P.; Rumsey, G.L. Dietary intake of immunostimulants by rainbow trout affects non-specific immunity and protection against furunculosis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 41, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katya, K.; Yun, Y.-h.; Park, G.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yoo, G.; Bai, S.C. Evaluation of the efficacy of fermented by-product of mushroom, Pleurotus ostreatus, as a fish meal replacer in juvenile Amur Catfish, Silurus asotus: Effects on growth, serological characteristics and immune responses. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, A.J.; Romero, A.; Gonzalez-Stegmaier, R.; Dantagnan, P. The effects of supplemented diets with a phytopharmaceutical preparation from herbal and macroalgal origin on disease resistance in rainbow trout against Piscirickettsia salmonis. Aquaculture 2016, 454, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Sukumaran, V.; Oviya, M. Potential probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum VSG3 improves the growth, immunity, and disease resistance of tropical freshwater fish, Labeo rohita. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringø, E.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ghosh, K.; Doan, H.V.; Beck, B.R.; Song, S.K. Lactic Acid Bacteria in Finfish—An Update. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Doeschate, K.; Coyne, V. Improved growth rate in farmed Haliotis midae through probiotic treatment. Aquaculture 2008, 284, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanka, K.M.; Damerau, T.; Costas, B.; Krueger, A.; Schulz, C.; Wuertz, S. Isolation and characterization of native probiotics for fish farming. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcázar, J.L.; De Blas, I.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Cunningham, D.; Vendrell, D.; Muzquiz, J.L. The role of probiotics in aquaculture. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 114, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Dadar, M.; Ringø, E. Modulation of nutrient digestibility and digestive enzyme activities in aquatic animals: The functional feed additives scenario. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 3987–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, T.L.; Lim, C. Use of probiotics in diets of tilapia. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, 1, 014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K.; Ghosh, K.; Ringø, E. Enzyme-producing bacteria isolated from fish gut: A review. Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahem, M.D. Evolution of probiotics in aquatic world: Potential effects, the current status in Egypt and recent prospectives. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 765–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, W.; Ren, P.; Marubashi, T.; Ringø, E. Evaluation of probiotic strain Bacillus subtilis C-3102 as a feed supplement for koi carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, S1, 005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irianto, A.; Austin, B. Probiotics in aquaculture. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Miandare, H.K.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Yarahmadi, P. Dietary Lactobacillus acidophilus modulated skin mucus protein profile, immune and appetite genes expression in gold fish (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 59, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miandare, H.K.; Farvardin, S.; Shabani, A.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ramezanpour, S.S. The effects of galactooligosaccharide on systemic and mucosal immune response, growth performance and appetite related gene transcript in goldfish (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 55, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, O.; Atash, M. Study on the effects of probiotic, Pediococcus acidilactici in the diet on some biological indices of Oscar Astronauts ocellatus. Int. Res. J. Appl. Basic Sci. 2013, 4, 3458–3464. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezani, F.; Moghaddasi, B. Dietary effects of the probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici on growth and feeding indices in the convict cichlid fish (Amatitlania nigrofasciata). J. Anim. Biol. 2017, 9, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Rosovitz, M.; Voskuil, M.; Chambliss, G. Bacillus Systematic Bacteriology; Arnold Press: London, UK, 1998; pp. 709–720. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanaraj, M.; Haniffa, M.; Singh, S.A.; Arockiaraj, A.J.; Ramakrishanan, C.M.; Seetharaman, S.; Arthimanju, R. Effect of probiotics on growth performance of koi carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Appl. Aquac. 2010, 22, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miest, J.J.; Arndt, C.; Adamek, M.; Steinhagen, D.; Reusch, T.B. Dietary β-glucan (MacroGard®) enhances survival of first feeding turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) larvae by altering immunity, metabolism and microbiota. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 48, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitorus, H.; Ramija, K.E.; Akhir, I.S. Effect of probiotic em-4 in feeds on the growth and survival rate of goldfish (Carrasius auratus). Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2018, 6, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Sahandi, J.; Jafaryan, H.; Moradi, P.; Tadiri, C. Effect of in-feed probiotic blend on growth performance and infection resistance of the guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2013, 16, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, T.J.; Babu, S.; Banerjee, T. Influence of a fish bacterium Lactobacillus sp. on the production of swordtail Xiphophorus helleri (Heckel 1848). Bangladesh J. Fish. Res. 2007, 11, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, F.; Mousavi, S.M.; Zakeri, M.; Ahmadmoradi, E. Effect of dietary probiotic, Saccharomyces cerevisiae on growth performance, survival rate and body biochemical composition of three spot cichlid (Cichlasoma trimaculatum). Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2016, 9, 451–457. [Google Scholar]
- Gumus, E.; Aydin, B.; Kanyilmaz, M. Growth and feed utilization of goldfish (Carassius auratus) fed graded levels of brewers yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2016, 15, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, M.; Arockiaselvi, J.J. Isolation of intestinal microflora and its probiotic effect on feed utilization and growth of gold fish Carassius auratus. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 685–688. [Google Scholar]
- Subharanjani, S.; Gunarani, R.; Prema, P.; Immanuel, G. Potential influence of probiotic bacteria on the growth gut microflora of Carassius auratus. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2015, 2, 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Chitra, G.; Krishnaveni, N. Effect of probiotics on reproductive performance in female livebearing ornamental fish Poecilia sphenops. Int. J. Pure Appl. Zool. 2013, 1, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Ahilan, B.; Shine, G.; Santhanam, R. Influence of probiotics on the growth and gut microbial load of juvenile goldfish (Carassius auratus). Asian Fish. Sci. 2004, 17, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahire, J.; Mokashe, N.; Chaudhari, B. Effect of dietary probiotic Lactobacillus helveticus on growth performance, antioxidant levels, and absorption of essential trace elements in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.L.; Akhter, S.; Mallik, M.K.M.; Rashid, I. Probiotic enrich dietary effect on the reproduction of butter catfish, Ompok pabda (Hamilton, 1872). Int. J. Curr. Res. Life Sci. 2018, 7, 866–873. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, F.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O. Probiotic-based nutritional effects on killifish reproduction. Fish. Aquac. J. 2011, 27, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Valcarce, D.G.; Riesco, M.F.; Martínez-Vázquez, J.M.; Robles, V. Diet supplemented with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory probiotics improves sperm quality after only one spermatogenic cycle in zebrafish model. Nutrients 2019, 11, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdinejad, N.; Imanpour, M.R.; Jafari, V. Combined or individual effects of dietary probiotic, Pediococcus acidilactici and nucleotide on reproductive performance in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giommi, C.; Habibi, H.R.; Candelma, M.; Carnevali, O.; Maradonna, F. Probiotic administration mitigates bisphenol A reproductive toxicity in zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibiene, G.; Zibas, A. Impact of commercial probiotics on growth parameters of European catfish (Silurus glanis) and water quality in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.K.; Swarnakumar, N.; Sivakumar, K.; Thangaradjou, T.; Kannan, L. Probiotics in aquaculture: Importance and future perspectives. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmin, G.; Kathiresan, K.; Purushothaman, A. Effect of probiotics on bacterial population and health status of shrimp in culture pond ecosystem. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 39, 939–942. [Google Scholar]
- Jahangiri, L.; Esteban, M.Á. Administration of probiotics in the water in finfish aquaculture systems: A review. Fishes 2018, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Zhang, X.-H.; Boon, N.; Bossier, P. Probiotics in aquaculture of China—Current state, problems and prospect. Aquaculture 2009, 290, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, T.N.; Duc, P.M.; Hatai, K. Overview of the use of probiotics in aquaculture. Int. J. Res. Fish. Aquac. 2013, 3, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, S.; Ali, M.L.; Alam, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Jørgensen, N.O. Effect of probiotic and sand filtration treatments on water quality and growth of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and pangas (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) in earthen ponds of southern Bangladesh. J. Appl. Aquac. 2016, 28, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalloo, R.; Ramchuran, S.; Ramduth, D.; Görgens, J.; Gardiner, N. Isolation and selection of Bacillus spp. as potential biological agents for enhancement of water quality in culture of ornamental fish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanailides, C.; Kolygas, M.; Choremi, K.; Mavraganis, T.; Gouva, E.; Vidalis, K.; Athanassopoulou, F. Probiotics have the potential to significantly mitigate the environmental impact of freshwater fish farms. Fishes 2021, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Pan, Y.; Luo, L.; Luo, L. Effects of dietary β-1, 3-glucan, chitosan or raffinose on the growth, innate immunity and resistance of koi (Cyprinus carpio koi). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, A.; Bakhsh, J.A.; Irshad, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Xiong, H. The functionality of prebiotics as immunostimulant: Evidences from trials on terrestrial and aquatic animals. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 76, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Gastrointestinal infections and the protective role of probiotics and prebiotics. Food Sci. Technol. Bull. Funct. Foods 2003, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Paknejad, H.; Hajimoradloo, A. The effects of dietary supplement of galactooligosaccharide on innate immunity, immune related genes expression and growth performance in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 73, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Azevedo, R.V.; da Silva-Azevedo, D.K.; dos Santos-Júnior, J.M.; Fosse-Filho, J.C.; de Andrade, D.R.; Tavares-Braga, L.G.; Vidal-Júnior, M.V. Effects of dietary mannan oligosaccharide on the growth, survival, intestinal morphometry and nonspecific immune response for Siamese fighting fish (Betta splendens Regan, 1910) larvae. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 44, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanadevi, V.; Muthazhagan, K.; Ajithkumar, T.; Thangaraj, M. The efficacy of dietary yeast mannan oligosaccharide on growth and survival rate in Amphiprion ocellaris fingerlings. Eur. J. Biotechnol. Biosci. 2013, 1, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Forsatkar, M.N.; Nematollahi, M.A.; Rafiee, G.; Farahmand, H.; Lawrence, C. Effects of the prebiotic mannan-oligosaccharide on the stress response of feed deprived zebrafish (Danio rerio). Physiol. Behav. 2017, 180, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzapour-Rezaee, S.; Farhangi, M.; Rafiee, G. Combined effects of dietary mannan-and fructo-oligosaccharide on growth indices, body composition, intestinal bacterial flora and digestive enzymes activity of regal peacock (Aulonocara stuartgranti). Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Khalili, M.; Sun, Y.-Z. Intestinal histomorphology, autochthonous microbiota and growth performance of the oscar (Astronotus ocellatus Agassiz, 1831) following dietary administration of xylooligosaccharide. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2016, 32, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, Q. Effect of prebiotic xylooligosaccharides on growth performances and digestive enzyme activities of allogynogenetic crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abasali, H.; Mohamad, S. Effect of prebiotic immunogen on reproductive performance in female swordtail Xiphophorus helleri. Agric. J. 2011, 6, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Abasali, H.; Mohamad, S. Effect of dietary probiotic level on the reproductive performance of female platy Xiphophorus maculatus. Agric. J. 2011, 6, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Akrami, R.; Rahnama, B.; Chitsaz, H.; Razeghi Mansour, M. Effects of dietary inulin on growth performance, survival, body composition, stress resistance and some hematological parameters of Gibel carp juveniles (Carassius auratus gibelio). Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2015, 14, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Safari, R.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Nejadmoghadam, S.; Jafar, A. Transciptomic study of mucosal immune, antioxidant and growth related genes and non-specific immune response of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fed dietary Ferula (Ferula assafoetida). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 55, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, O.; Sarkheil, M. Dietary administration of eryngii mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) powder on haemato-immunological responses, bactericidal activity of skin mucus and growth performance of koi carp fingerlings (Cyprinus carpio koi). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, L.C.; Gamin, D.M., 3rd. Evaluation of dairy-yeast prebiotic supplementation in the diet of juvenile goldfish in the presence or absence of phytoplankton and zooplankton. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2009, 21, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghashlaghi, P.; Rashidian, G.; Chardeh Baladehi, E.; Ghafari Farsani, H. Effect of synbiotic biomin imbo on growth parameters, survival, digestive enzymes and mucus parameters of banded cichlide (Heros severus). Aquat. Physiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 49–74. [Google Scholar]
- Mahghani, F.; Gharaei, A.; Ghaffari, M.; Akrami, R. Dietary synbiotic improves the growth performance, survival and innate immune response of Gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) juveniles. Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2014, 2, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nekoubin, H.; Gharedaashi, E.; Imanpour, M.R.; Nowferesti, H.; Asgharimoghadam, A. The influence of synbiotic (Biomin Imbo) on growth factors and survival rate of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae via supplementation with biomar. Glob. Vet. 2012, 8, 503–506. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Mao, S.; Guan, Y.; Luo, L.; Luo, L.; Pan, Y. Effects of dietary chitosan oligosaccharides and Bacillus coagulans on the growth, innate immunity and resistance of koi (Cyprinus carpio koi). Aquaculture 2012, 342, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.D.; Wang, K.; Li, F.D.; Sun, Y.Z. Single or combined effects of fructo- and mannan oligosaccharide supplements and Bacillus clausii on the growth, feed utilization, body composition, digestive enzyme activity, innate immune response and lipid metabolism of the Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquac. Nutr. 2011, 17, e902–e911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iger, Y.; Abraham, M. The process of skin healing in experimentally wounded carp. J. Fish Biol. 1990, 36, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezuela, R.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M. Current Knowledge in Synbiotic Use for Fish Aquaculture: A Review. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimnejad, S.; Guardiola, F.A.; Leclercq, E.; Esteban, M.Á.; Castex, M.; Sotoudeh, E.; Lee, S.-M. Effects of dietary supplementation with Pediococcus acidilactici MA18/5M, galactooligosaccharide and their synbiotic on growth, innate immunity and disease resistance of rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli). Aquaculture 2018, 482, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpou, A.; Papadaki, P.; Lappa, I.K.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Bosnea, L.A.; Kopsahelis, N. Probiotics in Food Systems: Significance and Emerging Strategies Towards Improved Viability and Delivery of Enhanced Beneficial Value. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Occurrence | Reason | Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ichthyobodo necator | Flagellates (Costia) | Skin, gills | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus |
| Spironucleus vortens | Binucleate flagellate | Gastrointestinal tracts | Poor water quality, malnutrition, overcrowding, fluctuating temperatures | Pterophyllum sp. |
| Cryptobia lubilans | Cryptobia | Gastrointestinal tracts, abdominal organs | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus, Herichthys yanoguttatus, Cichlasoma cyanoguttatum, Cichlasoma meeki |
| Amyloodinium ocellatum | Dinoflagellates | Gill, fins, skin | Poor water quality | Amphiprion sp. |
| Oodinium pilluarius | Dinoflagellates | Gill, skin | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus |
| Ichthyophthirius multifilis | Holotrichous ciliate | Gill, eyes, skin | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus |
| Cryptocaryon irritans | Marine white spot (Ich) | Gill, skin | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus, Zebrasoma xanthurum, Chaetodon adiergastos, Paracanthurus hepatus |
| Trichodina sp. | Monogenean | Gill, skin | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus, Betta splendens, Pterophyllum sp., Paracheirodon innesi, Trichopodus trichopterus, Xiphophorus hellerii, Betta splendens |
| Trichodonella sp. | Monogenean | Gill, skin | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus, Betta splendens, Pterophyllum sp., Paracheirodon innesi, Trichopodus trichopterus |
| Tripartiella sp. | Monogenean | Gill, skin | Poor water quality | Xiphophorus hellerii, Betta splendens |
| Epistylis (Heteropolaria) sp. | Monogenean | Skin, fins, gills | High organic content waters | Astronotus ocellatus, Carassius auratus, Poecilia reticulata, Cichlasoma nigrofasciatum, Pterophyllum scalare, Poecilia sphenops |
| Tricodina sp. | Monogenean | Gill, skin | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus, Poecilia reticulata, Pterophyllum scalare, Symphsodon discus, Poecilia latipinna |
| Chilodonella | Ciliate | Gill, skin | Poor water quality | Astronotus ocellatus, Carassius auratus, Poecilia reticulata, Cichlasoma nigrofasciatum, Pterophyllum scalare, Poecilia sphenops |
| Hexamita | Flagellate | Gastrointestinal duct | Poor water quality | Poecilia reticulata, Pterophyllum scalare |
| Dactylogyrus sp. | Monogenean | Skin, fins, gills | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus |
| Gyrodactylus sp. | Monogenean | Skin, fins, gills | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus |
| Bothriocephalus sp. | Tapeworms | Digestive tract, coelomic cavity | Poor water quality | Xiphophorus hellerii |
| Eustrongylides sp. | Nematode | Muscle, liver, intestinal, Abdomens, guts | Poor water quality | Poecilia reticulata, Danio rerio, Pterophyllum scalare |
| Capillaria pterophylli | Nematode | Intestinal tract | Poor water quality | Archocentrus nigrofasciatus, Pelvicachromis pulcher, Carassius auratus, Trichogaster trichopterus, Hyphessobrycon anisitsi |
| Pentastomids | Tongue worms | Skin, body cavity, connective tissue, muscle | Poor water quality | Archocentrus nigrofasciatus, Xiphophorus hellerii, Poecilia sphenops, Xiphophorus maculatus |
| Argulus | Fish louse | Skin | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus |
| Lernaea | Anchor worm | Skin | Poor water quality | Carassius auratus |
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Symptoms | Reason | Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aeromonas hydrophila | Aeromonas Septicemia (MAS) | Hemorrhagic septicemia in skin, fin, oral cavity, ulceration in epidermis | Stress, overcrowding, contaminated water | Carassius auratus, Xiphophorus hellerii, Colisa lalia, Molliensia sphenops |
| Aeromonas caviae | Gastroenteritis | Hemorrhagic septicemia | Contaminated water | Carassius auratus, Datnioides polota, Poecilia sphenops, Xiphophorus hellerii, Carassius auratus, Datnioides polota, Poecilia sphenops |
| Aeromonas salmonicida | Furunculosis | Hemorrhage in skin, fin, oral cavity, muscles | Contaminated water | Carassius auratus, Puntius conchonius |
| Flexibactor columnar | Columnaris | Skin, gills lesions and necrosis | Crowded unhygienic conditions, cold snaps stress | Carassius auratus, Paracheirodon innesi |
| Streptococci iniae | Streptocosis | Erratic swimming, darkening of skin, hemorrhages in eye, gill, vent, ascites, dropsy, | Contaminated water | Pethia conchonius, Danio rerio |
| Edwardsiella ictaluri | Edwardsiellosis | Ulcer in skin, spiral and erratic swimming, hemorrhage and inflammation in tissues | Contaminated water | Danio devario, Puntius conchonius, Molliensia sphenops |
| Vibrio vulnificus | Vibriosis | Erratic swimming, hemorrhage | Contaminated water | Poecilia sphenops |
| Name | Symptoms | Host |
|---|---|---|
| Carp pox viral disease (CYHV—1) | Grey lesions on the body and fins | Carassius auratus |
| Cyprinid herpesviral disease (CYHV—2) | Hematopoietic necrosis | Carassius auratus |
| Herpesviral hematopoietic necrosis (HVHN/CyHV-2) | Softening and discoloration of the spleen and kidney, necrotic foci in the hematopoietic tissue, splenic pulp, pancreas | Carassius auratus |
| Spring Viremia of Carp (SVC) | Darkening of the skin, exophthalmia, ascites, pale gills, hemorrhage and a protruding vent with thick mucoid fecal casts | Carassius auratu |
| Viral hemorrhagic septicemia (VHS) | lethargy, darkening of the skin, exophthalmia, anemia (pale gills), hemorrhages at the base of the fins, gills, eyes, skin | Pterophyllumscalare |
| Banggai Cardinalfish Iridovirus (BCIR) | Lethargy. respiratory distress (rapid movement of opercula) | Barbus graellsii |
| Dwarf Gourami Iridovirus (DGIR) | Necrosis in spleen and kidney, pale coloration, loss of appetite, lesions on the body ascites (abdominal swelling) | Pterapogon kauderni |
| Reovirus (head and lateral line erosion, HLLE) | Hemorrhagic | Trichogaster lalius |
| Koi herpesviral disease (KHV) | Necrosis of gill epithelium copious secretion of mucus on the gills and skins and necrosis of gill tissue, lethargy, anorexia, excessive gill necrosis, gill and body mucus and signs such as ulceration, skin hemorrhages, petechial ecchymosis and fin rot, erosion of primary lamellae, fusion of secondary lamellae and swelling at the tips of the primary and secondary lamellae | Pterophyllum sp., Pterophyllum scalare |
| Iridovirus | Abdominal distention exophthalmia and pale gills abdominal swellings | Poecilia reticulata, Osphronemus goramy, Pterophyllum sp. |
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Condition | Host |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saprolegnia sp. | Saprolegniasis | Poor water quality | Pterophyllum sp., |
| Icthyophonus hoferi | Ichthyophoniasis | Skin a sandpaper texture | Gymnocorymbus ternetzi, Pentius tetrazona |
| Aphanomyces invadans | Epizootic ulcerative syndrome (EUS) | Erode underlying tissues, unilateral or bilateral clouding of the eye, red spots or small hemorrhagic lesions on the surface of fish, ulcers and eventually large necrotic erosions | Barbus thamalakanensis, Glossogobius giuris, Carassius auratus |
| Species | Probiotic Strain | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siamese fighting fish (B. splendens) | L. plantarum KKU CRIT5 | Lack of evident beneficial effects. Timing and dose of administration are under review | [47] |
| Green swordtail (X. helleri) | L. acidophilus | Positively modulated mucosal immune parameters | [48] |
| Commercial formulation (Lactobacillus sp., Bacillus sp., S. faecium and S. cereviasiae) | No beneficial effect observed against bacterial challenges | [49] | |
| Streptomyces sp. | Improves food conversion efficiency and conversion rate | [50] | |
| B. subtilis | Increases the GSI, fertility and fecundity. Decreases morphological alteration of the larvae | [51,52] | |
| B. subtilis | Increases the GSI, fertility and fecundity. Decreases morphological alteration of the larvae | [51,52,53] | |
| Platy fish (X. maculatus) | Commercial formulation containing Lactobacillus sp. | Increase of muscle mass due to protein increase and fat decrease | [54] |
| Goldfish (C. auratus) | Commercial formulation (Lactobacillus sp., Bacillus sp., S. faecium and S. cereviasiae) | No beneficial effect observed against bacterial challenges | [49] |
| Mix of Lactobacillus sp. and Bacillus sp. | No beneficial effect observed against Pseudomonas fuorescens | [49] | |
| Commercial mix (B. subtilis and B. licheniformis) | Improvement of food digestibility, stress resistance and immune response | [55] | |
| L. casei | Faster recovery after the air-dive/stress test | [56] | |
| Porthole livebearer (P. gracilis) | B. coagulans (L. sporogens), B. mesentericus | Scarce colonization of the gut but induction of significant microflora composition | [57] |
| Rosy barb (P. conchonius) | mixture of Bacillus sp. and Lactobacillus sp. | Decreases mortality due to improvement in the quality of rearing waters | [58] |
| Giant gourami (O. goramy) | L. fermentum (KT183369) and B. subtilis sp. inaquasporium (KR816099) | Good capacity to colonize the host gut | [59,60] |
| Black molly (P. sphenops) | B. pumilus RI06-95Sm | Gut colonization; increases protection against pathogens | [61] |
| P. inhibens S4Sm | Increases tolerance to antibiotic treatment | [61] | |
| L. rhamnosus | Decreases the number of gut pathogenic CFU/mL | [62] | |
| Zebrafish (D. rerio) | L. rhamnosus | Skeletogenesis acceleration | [38] |
| L. rhamnosus | Affects lipid and vitamin D metabolism, with a positive role in backbone calcification | [63] | |
| B. amyloliquefaciens R8 | Increases xylanase activity, 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase and citrate synthase. Increases mRNA of glycolysis-related and anti-apoptotic signals | [64] | |
| Commercial mixture (S. thermophilus DSM 24731, B. longum DSM 24736, B. breve DSM 24732, B. infantis DSM 24737, L. acidophilus DSM 24735, L. plantarum DSM 24730, L. paracasei DSM 24733, L. delbrueckii sp. bulgaricus DSM 24734), | Increased expression of Toll-like receptors and other immune factors. Decreases number of apoptotic cells | [65] | |
| L. rhamnosus IMC 501 | Upregulation of genes involved in innate immune responses and decrease in the abundance of stress- and apoptotic-related genes | [40] | |
| B. infantis and B. longum | Decreased number of pathogenic species, but scarce gut colonization | [62] | |
| C. aquaticum | Increased hepatic mRNA expression of carbohydrate metabolism-related- and Innate immune-related genes | [66] | |
| L. rhamnosus | Increased fertility, fecundity and follicle maturation | [26,42,67] | |
| L. rhamnosus CIC6141 L. casei BL23 | Improved reproduction | [68] | |
| K. fragilis | Decreases stress biomarkers | [69] | |
| Yarrowia lipolytica 242 (Yl242) and Debaromyces hansenii 97 (Dh97) | Improved the immune system (downregulation of 1b, tnfa, il10, c3, mpx) | [70] | |
| L. rhamnosus | Positive modulation of signal involved in lipid and vitamin D metabolism | [71] | |
| Clownfish (A. ocellaris) | B. subtilis | Higher survival in antibiotic-treated fish, increased fertility and fecundity | [72] |
| Sailfin Molly (P. latipinna) | B. subtilis and B. licheniformis | Increase in peroxidase and trypsin levels and resistance against bacterial challenges | [73] |
| Tinfoil barb (B. schwanenfeldii) | Commercial mixture (B. subtilis, B. licheniformes, L. acidophilus and S. cerevisiae) | Improved water quality by reducing metabolic waste and stress response | [74] |
| Marbled hatchetfish (C. strigata) | Commercial mixture (B. subtilis, B. licheniformes, L. acidophilus and S. cerevisiae) | Improved water quality by reducing metabolic waste and stress response | [75] |
| Cardinal tetra (P. axelrodi) | P. acidilactici | Significant increase in all non-specific immune system biomarkers (lysozyme activity, total immunoglobulin and alternative complement activity) | [76] |
| Green terror (A. rivulatus) | P. acidilactici | Improved stress response (modulation of lysozyme activity, immunoglobulin and protease levels) | [77] |
| Angelfish (P. danio) | |||
| Angelfish (P. scalare) | E. faecium | Improved fish viability | [78] |
| E. cloacae | Improved resistance against P.shigelloides challenge (increased blood cell counts and respiratory activity) | [79] | |
| Kenyi cichlid (M. lombardoi) | B. infantis | Alteration of gut microbiota composition | [57] |
| Rosy barb (P. conchonius) | Commercial mixture (Lactobacillus sp, B. bacterium, S. silivarius, E. faecium, A. oryzae, C. pintolopesii | Positive effects on hematological factors | [80] |
| Oscar (A. ocellatus) | B. subtilis | Increase in the GSI, fertility and fecundity. Decreased morphological alteration of the larvae | [51] |
| Guppy (P. reticulata) | B. subtilis | Increase in the GSI, fertility and fecundity. Decreased morphological alteration of the larvae | [51] |
| Gold black molly (P. sphenops) | S. cerevisiae | Improvement of reproduction, stress response and resistance against pathogens | [81] |
| Sailfish molly (P. latipinna) | S. cerevisiae | Improvement of growth performance, feed utilization and disease resistance | [82] |
| Orange clownfish (A. percula) |
| Probiotic Strain | Fish Name | Parameters | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Probiotic preparation A * | Astronotus ocellatus | SGR | [80] |
| L. acidophilus (LAD) and/or brewer’s yeast | Cyprinus carpio koi | SGR | [114] |
| Lactobacillus sp. | Xiphophorus hellerii | SGR | [118] |
| Probiotic preparation B ** | Carassius auratus | SGR, SR | [116] |
| S. cerevisiae | Cichlasoma trimaculatum | SGR, SR | [119] |
| Streptomyces | Xiphophorus helleri | SGR, AGR, RGR, FCR | [50] |
| Commercial probiotics | Carassius auratus | SGR, WG, SR, FCR | [55] |
| S. cerevisiae | Carassius auratus | SGR, WG, FCR, PER | [120] |
| Pseudomonas sp. | Carassius auratus | SGR, FCR, RGR | [121] |
| B. cereus | Trichogaster trichopterus | SGR, SR | [122] |
| Lactobacillus | Carassius auratus | SGR, SR | [54] |
| Bacillus, S. cerevisiae | Poecilia reticulata | SR | [117] |
| Probiotic preparation C *** | Poecilia sphenops | SR | [123] |
| L. sporogenes | Carassius auratus | WG | [124] |
| L. helveticus | Carassius auratus | SGR | [125] |
| Prebiotic Substances | Target Species | Measured Responses | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOS | Betta splendens | GP, IR↑, IHM | [144] |
| Danio rerio | GP↑, SR↑ | [146] | |
| Aulonocara stuartgranti | GP↑, BC, DEA↑, IM | [147] | |
| Amphiprion ocellaris | GP, SR↑ | [145] | |
| XOS | Astronotus ocellatus | GP↑, IM, IHM, SR↑ | [148] |
| Carassius auratus | GP↑, DEG↑, SR | [149] | |
| β-glucan, chitosan and raffinose | Cyprinus carpio koi | GP↑, IR↑, DR↑ | [140] |
| Preparation D * | Xiphophorus maculatus Xiphophorus hellerii | GSI↑, RP↑, SR↑ | [150,151] |
| Inulin | Carassius auratus | GP↑, FU↑, BC, IM, HP, SR↑ | [152] |
| GOS | Carassius auratus | GP, IR↑, SR | [110] |
| Danio rerio | GP, IR↑ | [143] | |
| FOS | Aulonocara stuartgranti | GP↑, BC, DEA↑, IM | [147] |
| Ferula (Ferula asafoetida) powder | Cyprinus carpio koi | GP↑, FU↑, IR↑, HP↑, DEA↑, IM, DR↑, SR↑ | [153] |
| Eryngii mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) | Cyprinus carpio koi | GP↑, FU↑, IR↑, HP↑, DEA↑, IM, DR↑, SR↑ | [154] |
| Preparation E ** | Carassius auratus | GP, IR, DEA, IM, DR | [155] |
| Synbiotic (Pre/Pro) | Target Species | Measured Responses | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| FOS/P. acidilactici | Pterophyllum scalare | GP↑, IR↑, IM, SR↑ | [78] |
| FOS/E. faecium | Heros severus | GP↑, FU↑, IR↑, DEA↑, SR↑ | [156] |
| Carassius auratus gibelio | GP↑, IR↑, SR | [157] | |
| Danio rerio | GP↑, FU↑, RP↑, SR↑ | [158] | |
| COS/B. coagulans | Cyprinus carpio koi | GP↑, IR↑, HP↑, DR↑, SR↑ | [159] |
| FOS, MOS/B. clausii | Paralichthys olivaceus | GP↑, FU↑, BC, IR↑, HP, DEA↑, SR↑ | [160] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoseinifar, S.H.; Maradonna, F.; Faheem, M.; Harikrishnan, R.; Devi, G.; Ringø, E.; Van Doan, H.; Ashouri, G.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O. Sustainable Ornamental Fish Aquaculture: The Implication of Microbial Feed Additives. Animals 2023, 13, 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101583
Hoseinifar SH, Maradonna F, Faheem M, Harikrishnan R, Devi G, Ringø E, Van Doan H, Ashouri G, Gioacchini G, Carnevali O. Sustainable Ornamental Fish Aquaculture: The Implication of Microbial Feed Additives. Animals. 2023; 13(10):1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101583
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoseinifar, Seyed Hossein, Francesca Maradonna, Mehwish Faheem, Ramasamy Harikrishnan, Gunapathy Devi, Einar Ringø, Hien Van Doan, Ghasem Ashouri, Giorgia Gioacchini, and Oliana Carnevali. 2023. "Sustainable Ornamental Fish Aquaculture: The Implication of Microbial Feed Additives" Animals 13, no. 10: 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101583
APA StyleHoseinifar, S. H., Maradonna, F., Faheem, M., Harikrishnan, R., Devi, G., Ringø, E., Van Doan, H., Ashouri, G., Gioacchini, G., & Carnevali, O. (2023). Sustainable Ornamental Fish Aquaculture: The Implication of Microbial Feed Additives. Animals, 13(10), 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101583










