Validation of NEDAP Monitoring Technology for Measurements of Feeding, Rumination, Lying, and Standing Behaviors, and Comparison with Visual Observation and Video Recording in Buffaloes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
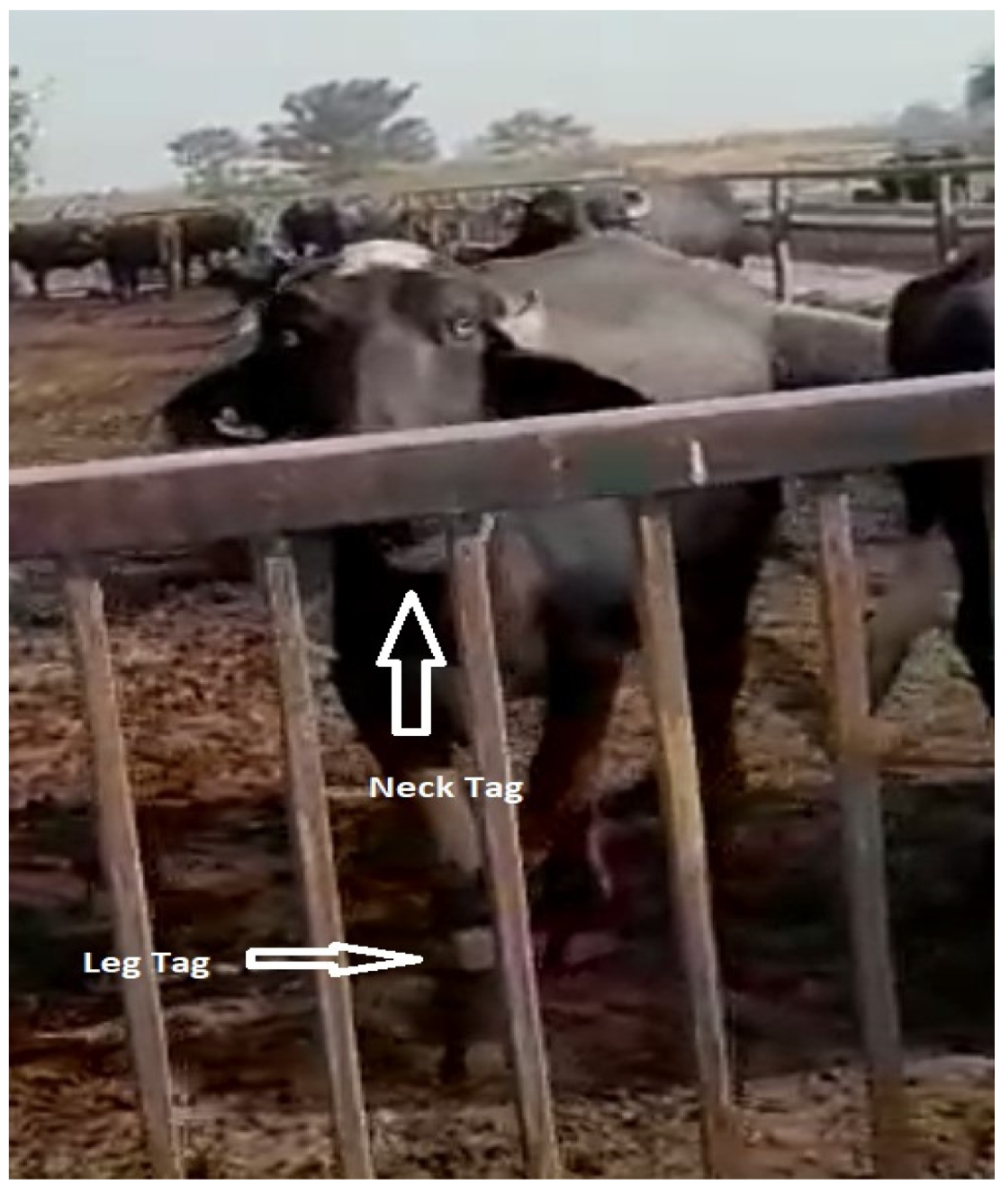
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
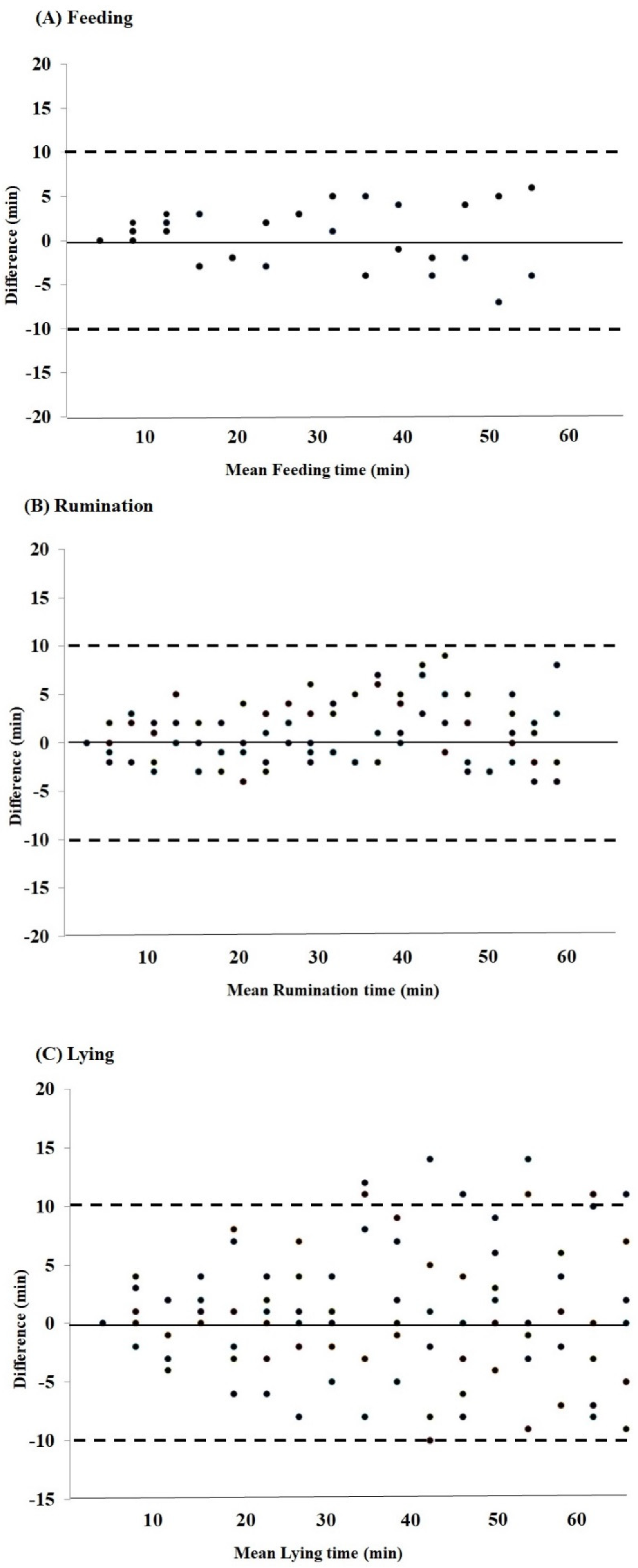
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Assessing agreement between methods of measurement. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 1653–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, M.M.; Zeitoun, M.M.; Hussein, F.M. Mastitis outcomes on pre-ovulatory follicle diameter, estradiol concentrations, subsequent luteal profiles and conception rate in Buffaloes. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 181, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkema, H.W.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.; Kastelic, J.P.; Lam, T.; Luby, C.; Roy, J.-P.; LeBlanc, S.J.; Keefe, G.P.; Kelton, D.F. Invited review: Changes in the dairy industry affecting dairy cattle health and welfare. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7426–7445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bikker, J.; Van Laar, H.; Rump, P.; Doorenbos, J.; Van Meurs, K.; Griffioen, G.; Dijkstra, J. Evaluation of an ear-attached movement sensor to record cow feeding behavior and activity. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 2974–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambriz-Vilchis, V.; Jessop, N.; Fawcett, R.; Shaw, D.; Macrae, A. Comparison of rumination activity measured using rumination collars against direct visual observations and analysis of video recordings of dairy cows in commercial farm environments. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gusterer, E.; Kanz, P.; Krieger, S.; Schweinzer, V.; Süss, D.; Lidauer, L.; Kickinger, F.; Öhlschuster, M.; Auer, W.; Drillich, M. Sensor technology to support herd health monitoring: Using rumination duration and activity measures as unspecific variables for the early detection of dairy cows with health deviations. Theriogenology 2020, 157, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merenda, V.R.; Marques, O.; Miller-Cushon, E.K.; Dilorenzo, N.; Laporta, J.; Chebel, R.C. Validation of a system for monitoring individual behavior in beef heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 4732–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, G.; Sharpe, K.; Heins, B. Evaluation of the RumiWatch system as a benchmark to monitor feeding and locomotion behaviors of grazing dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 3736–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamari, L.; Soriani, N.; Panella, G.; Petrera, F.; Minuti, A.; Trevisi, E. Rumination time around calving: An early signal to detect cows at greater risk of disease. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 3635–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, M.; Gavigan, S.; Harbers, A.; Bewley, J. An evaluation of a novel device for measuring eating, rumination, and inactive behaviors in lactating Holstein dairy cattle. Animal 2021, 15, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehner, N.; Umstätter, C.; Niederhauser, J.J.; Schick, M. System specification and validation of a noseband pressure sensor for measurement of ruminating and eating behavior in stable-fed cows. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 136, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, Z.; Diosdado, J.V.; Codling, E.; Bell, N.; Hodges, H.; Croft, D.; Amory, J. Use of novel sensors combining local positioning and acceleration to measure feeding behavior differences associated with lameness in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6310–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schirmann, K.; Chapinal, N.; Weary, D.; Vickers, L.; Von Keyserlingk, M. Rumination and feeding behavior before and after calving in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 7088–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriani, N.; Trevisi, E.; Calamari, L. Relationships between rumination time, metabolic conditions, and health status in dairy cows during the transition period. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 4544–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, G.; Heins, B.; Endres, M. Validation of an ear-tag accelerometer sensor to determine rumination, eating, and activity behaviors of grazing dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2492–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diosdado, J.A.V.; Barker, Z.E.; Hodges, H.R.; Amory, J.R.; Croft, D.P.; Bell, N.J.; Codling, E.A. Classification of behaviour in housed dairy cows using an accelerometer-based activity monitoring system. Anim. Biotelemetry 2015, 3, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Navon, S.; Mizrach, A.; Hetzroni, A.; Ungar, E.D. Automatic recognition of jaw movements in free-ranging cattle, goats and sheep, using acoustic monitoring. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 114, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, S.; Borda, C.; Diugan, E.A.; Niculae, M.; Stefan, R.; Sandru, C.D. The effect of the housing system on the welfare quality of dairy cows. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 13, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, D.E.; Wiersma, W.; Jurs, S.G. Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences; Houghton Mifflin College Division: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Borchers, M.; Chang, Y.; Tsai, I.; Wadsworth, B.; Bewley, J. A validation of technologies monitoring dairy cow feeding, ruminating, and lying behaviors. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7458–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.H.; Cantor, M.C.; Neave, H.W. Symposium review: Precision technologies for dairy calves and management applications. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1203–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhawk, C.; Schwartzkopf-Genswein, K.; Beauchemin, K. Validation of rumination collars for beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 2858–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shepley, E.; Berthelot, M.; Vasseur, E. Validation of the ability of a 3D pedometer to accurately determine the number of steps taken by dairy cows when housed in tie-stalls. Agriculture 2017, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, A.; Cook, N. Time budgets of lactating dairy cattle in commercial freestall herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5772–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | NEDAP | Visual Observation | Video | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Min | Max | Mean ± SD | Min | Max | Mean ± SD | Min | Max | ||
| Feeding | FB | 2.1 ± 1.8 | 0 | 8 | 2.3 ± 0.6 | 0 | 6 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | 0 | 7 |
| AFB | 10.8 ± 3.7 a | 0 | 84.0 | 8.5 ± 1.1 b | 0 | 42.1 | 10.2 ± 1.6 a | 0 | 60 | |
| FT | 25.2 ± 2.7 a | 0 | 84.0 | 24.6 ± 2.6 b | 0 | 75.5 | 23.1 ± 2.9 c | 0 | 76.6 | |
| Rumination | RB | 1.8 ± 1.5 | 0 | 7 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 0 | 6 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 0 | 6 |
| ARB | 7.9 ± 1.1 a | 0 | 30.8 | 6.8 ± 1.2 c | 0 | 20.5 | 7.1 ± 1.1 b | 0 | 23.1 | |
| RT | 18.5 ± 2.1 b | 0 | 90.4 | 18.6 ± 1.1 b | 0 | 85.2 | 19.8 ± 1.7 a | 0 | 71 | |
| Lying | LB | 1 ± 0.4 | 0 | 3 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 0 | 3 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 0 | 3 |
| ALB | 20.8 ± 3.6 a | 0 | 89.4 | 16.4 ± 2.5 b | 0 | 89.7 | 19.2 ± 2.5 ab | 0 | 89 | |
| LT | 26.9 ± 2.5 b | 0 | 89.4 | 26.4 ± 2.8 b | 0 | 89.7 | 27.5 ± 2.2 a | 0 | 89.3 | |
| Standing | SB | 3.5 ± 0.1 a | 0 | 4 | 2.9 ± 0.1 b | 0 | 5 | 3.5 ± 0.7 a | 0 | 4 |
| ASB | 17.6 ± 1.4 | 0 | 36.2 | 18.2 ± 2.3 | 0 | 32 | 17.9 ± 1.4 | 0 | 29.8 | |
| ST | 53.8 ± 2.5 c | 1 | 77.5 | 57.5 ± 7.8 a | 1 | 90 | 55.4 ± 4.3 b | 0 | 89.6 | |
| Variables | Pearson Correlation (r) | p Value | Bias Correlation (Cb) | Location Shift (V) | Scale Shift (µ) | CCC (95% Cl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feeding | 0.91 | 0.001 | 1.00 | −0.003 | 0.98 | 0.85 (0.81 0.92) |
| Rumination | 0.85 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 0.002 | 1.01 | 0.91 (0.88 0.93) |
| Lying | 0.93 | 0.001 | 0.99 | 0.16 | 0.91 | 0.88 (0.91 0.94) |
| Standing | 0.87 | 0.01 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.89 | 0.91 (0.88 0.93) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quddus, R.A.; Ahmad, N.; Khalique, A.; Bhatti, J.A. Validation of NEDAP Monitoring Technology for Measurements of Feeding, Rumination, Lying, and Standing Behaviors, and Comparison with Visual Observation and Video Recording in Buffaloes. Animals 2022, 12, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050578
Quddus RA, Ahmad N, Khalique A, Bhatti JA. Validation of NEDAP Monitoring Technology for Measurements of Feeding, Rumination, Lying, and Standing Behaviors, and Comparison with Visual Observation and Video Recording in Buffaloes. Animals. 2022; 12(5):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050578
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuddus, Ray Adil, Nisar Ahmad, Anjum Khalique, and Jalees Ahmed Bhatti. 2022. "Validation of NEDAP Monitoring Technology for Measurements of Feeding, Rumination, Lying, and Standing Behaviors, and Comparison with Visual Observation and Video Recording in Buffaloes" Animals 12, no. 5: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050578
APA StyleQuddus, R. A., Ahmad, N., Khalique, A., & Bhatti, J. A. (2022). Validation of NEDAP Monitoring Technology for Measurements of Feeding, Rumination, Lying, and Standing Behaviors, and Comparison with Visual Observation and Video Recording in Buffaloes. Animals, 12(5), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050578





