Optimalisation of the Activation Medium and Effect of Inhibiting Activities of Acid Phosphatase, Lactate Dehydrogenase and β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase on the Fertilisation Success of Eurasian Perch (Perca fluviatilis L.)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Origin and Broodstock Management
- Stage I
- The germinal vesicle (GV) was situated in the oocyte centre, oil droplets were poorly visible;
- Stage II
- Beginning of GV migration, beginning of coagulation of oil droplets, which were clearly visible;
- Stage III
- Migrating GV (above half of the oocyte diameter), oil droplets were clearly visible;
- Stage IV
- The GV was at the oocyte periphery, a large forming oil droplet was clearly visible (the droplet diameter was greater than the GV diameter and it reached the size of about 1/3 of the oocyte diameter) with visible smaller droplets;
- Stage V
- The GV was situated at the oocyte edge, one large (size of about half the oocyte diameter) oil droplet was clearly visible;
- Stage VI
- Oocyte samples taken for analysis were macroscopically transparent; there was no visible GV after they were placed in Serra’s solution (following GVBD), oocytes at the preovulation stage.
2.2. Determination of Optimal Activating Solution for Perch Gametes
2.2.1. Determination of the Optimal Activating Solution for the Perch Sperm Motility Parameters
2.2.2. Determination of the Optimal Activating Solution for Perch Fertilisation
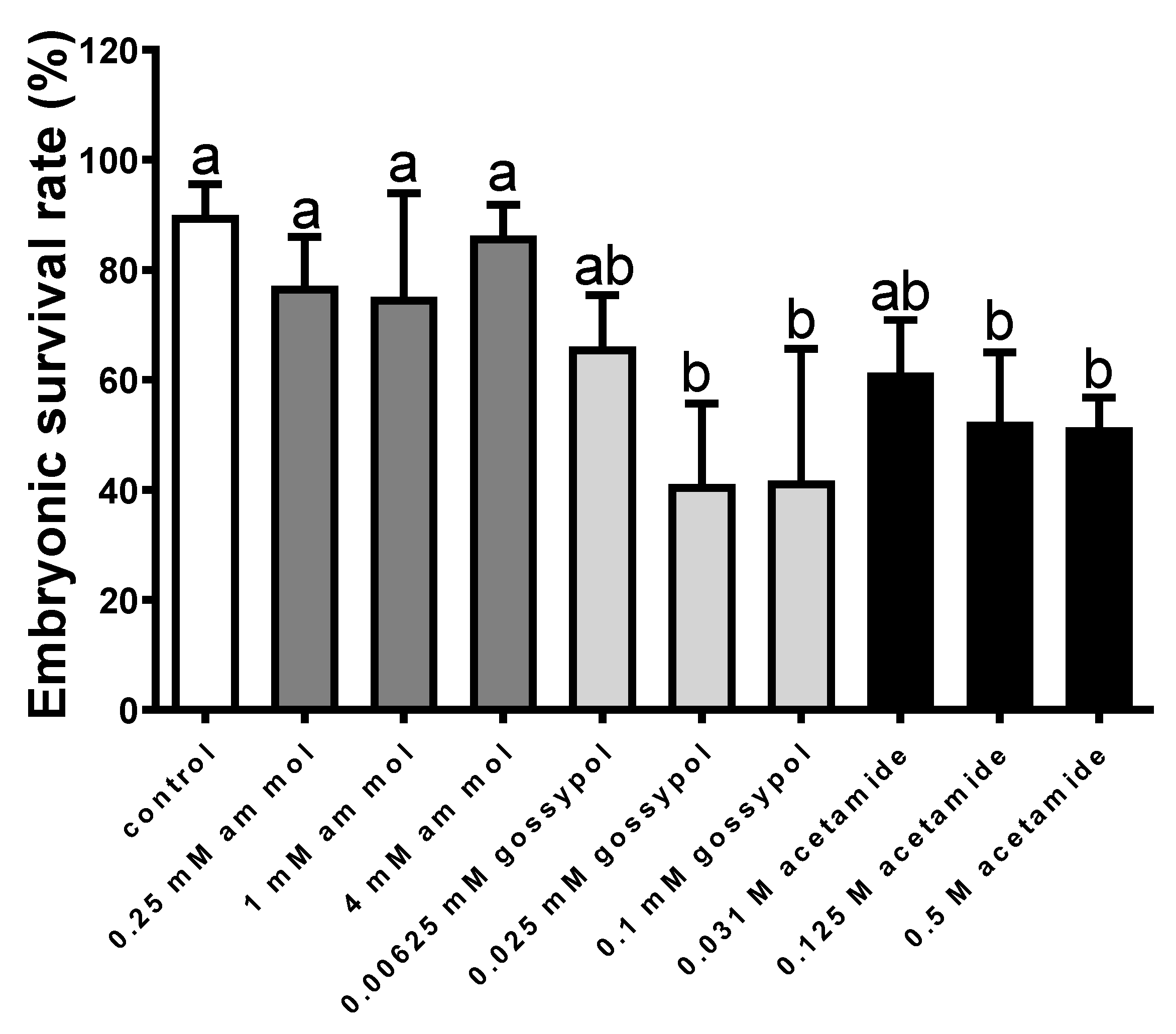
2.3. Effect of Inhibitors on Enzymatic Activities
2.3.1. Determination of the Effect of the Enzyme Inhibitors on Sperm Motility
2.3.2. Eurasian Perch Fertilisation with Enzyme Inhibitors
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Determination of the Optimal Activating Solution for Perch Gametes
4.2. Effect of Inhibitors on Enzymatic Activities, Sperm Motility Parameters and Fertilisation
4.2.1. The Effect of Enzyme Inhibitors on Perch Gametes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Żarski, D.; Palinska-Zarska, K.; Targońska, K.; Bokor, Z.; Kotrik, L.; Krejszeff, S.; Kupren, K.; Horvath, A.; Urbányi, B.; Kucharczyk, D. Oocyte quality indicators in Eurasian perch, Perca fluviatilis L., during reproduction under controlled conditions. Aquaculture 2011, 313, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żarski, D.; Horváth, A.; Kotrik, L.; Targońska, K.; Palińska, K.; Krejszeff, S.; Bokor, Z.; Urbányi, B.; Kucharczyk, D. Effect of different activating solutions on the fertilization ability of Eurasian perch, Perca fluviatilis L., eggs. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 28, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żarski, D.; Horváth, A.; Held, J.A.; Kucharczyk, D. Artificial reproduction of percid fishes. In Biology and Culture of Percid Fishes; Kestemont, P., Dabrowski, K., Summerfelt, R.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 123–161. [Google Scholar]
- Żarski, D.; Horváth, A.; Bernáth, G.; Krejszeff, S.; Radóczi, J.; Palińska-Żarska, K.; Bokor, Z.; Kupren, K.; Urbányi, B. Controlled reproduction of wild Eurasian perch. In A Hatchery Manual; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2017; p. 101. ISBN1 978-3-319-49375-6. ISBN2 978-3-319-49375-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahnsteiner, F.; Berger, B.; Weismann, T.; Patzner, R. Fine structure and motility of spermatozoa and composition of the seminal plasma in the perch. J. Fish Biol. 1995, 47, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urner, F.; Sakkas, D. Protein phosphorylation in mammalian spermatozoa. Reproduction 2006, 125, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahnsteiner, F.; Berger, B.; Weismann, T.; Patzner, R.A. Determination of semen quality of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, by sperm motility, seminal plasma parameters, and spermatozoal metabolism. Aquaculture 1998, 163, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosiek, B.; Glogowski, J.; Cejko, B.I.; Kujawa, R.; Szczepkowski, M.; Kuźmiński, H.; Dobosz, S.; Kowalski, R. Inhibition of β-N-acetylglucosaminidase by acetamide affects sperm motility and fertilization success of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Theriogenology 2013, 81, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosiek, B.; Dryl, K.; Palińska-Żarska, K.; Żarski, D. The influence of inhibition of acid phosphatase, β-N-acetylglucosamindase and lactate dehydrogenase present in the sperm of ide (Leuciscus idus) on the percentage of fertilized eggs. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 195, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żarski, D.; Krejszeff, S.; Horváth, A.; Bokor, Z.; Palińska, K.; Szentes, K.; Łuczyńska, J.; Targońska, K.; Kupren, K.; Urbányi, B.; et al. Dynamics of composition and morphology in oocytes of Eurasian perch, Perca fluviatilis L., during induced spawning. Aquaculture 2012, 364–365, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woynarovich, E.; Woynarovich, A. Modified technology for elimination of stickiness of common carp Cyprinus carpio eggs. Aquac. Hung. 1980, 2, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki, P.; Strzeżek, J. Isolation and biochemical characteristics of a molecular form of epididymal acid phosphatase of boar seminal plasma. Theriogenology 2006, 66, 2152–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciereszko, A.; Dabrowski, K. In vitro effect of gossypol acetate on yellow perch (Perca flavescens) spermatozoa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 49, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glogowski, J.; Babiak, I.; Goryczko, K.; Dobosz, S. Activity of aspartate aminotransferase and acid phosphatase in cryopreserved trout semen. Reprod. Fert. Dev. 1996, 8, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassault, A. (Ed.) Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jauhiainen, A.; Vanha-Perttula, T. β-N-acetylglucosaminidase in the reproductive organs and seminal plasma of the bull. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1986, 76, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, T.; Fushiki, S.; Ueno, K. Improvement of sperm motility of sex-reversed male rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, by incubation in high-pH artificial seminal plasma. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2004, 69, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perchec, G.P.; Cosson, J.; Andrc, F.; Billard, R. Degradation of the quality of carp sperm by urine contamination during stripping. Aquaculture 1995, 129, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, S.M.H.; Rodina, M.; Policar, T.; Kozak, P.; Psenicka, M.; Linhart, O. Semen of Perca fluviatilis L. sperm volume and density, seminal plasma indices and effects of dilution ratio, ions and osmolality on sperm motility. Theriogenology 2007, 68, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, L.; Wysocki, P.; Ciereszko, A.; Płucienniczak, G.; Kotłowska, M.; Kordan, W.; Wojtczak, M.; Dietrich, G.; Strzezek, J. Application of biochemical markers for identification of biological properties of animal semen. Reprod. Biol. 2006, 6, 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.J.; Gong, X.; Shur, B.D. Sperm require beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase to penetrate through the egg zona pellucida. Development 1993, 118, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.D. Physiological impact of acute molybdenum exposure in juvenile kokanee salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 133, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhnke, I.; Luedemann, D. Results of the investigation of 200 chemical compounds for acute fish toxicity with the golden orfe test [Ergebnisse der Untersuchung von 200 Chemischen Verbindungen auf Akute Fischtoxizitat mit dem Goldorfentest]. Z. Wasser Abwasser-Forsch 1978, 11, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Sarosiek, B.; Dryl, K.; Judycka, S.; Szczepkowski, M.; Kowalski, R.K. Influence of acid phosphatase and arylsulfatase inhibitor additions on fertility rate of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii Brandt, 1869). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, M.J.; Macfarlane, C.P.; Yeates, S.; Ward, R.G.; Searle, J.B.; Parker, G.A. Spermatozoal Traits and Sperm Competition in Atlantic Salmon: Relative Sperm Velocity Is the Primary Determinant of Fertilization Success. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, H.P. An electron microscope study of spermiogenesis in the teleost fish Oligocottus maculosus. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1969, 27, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
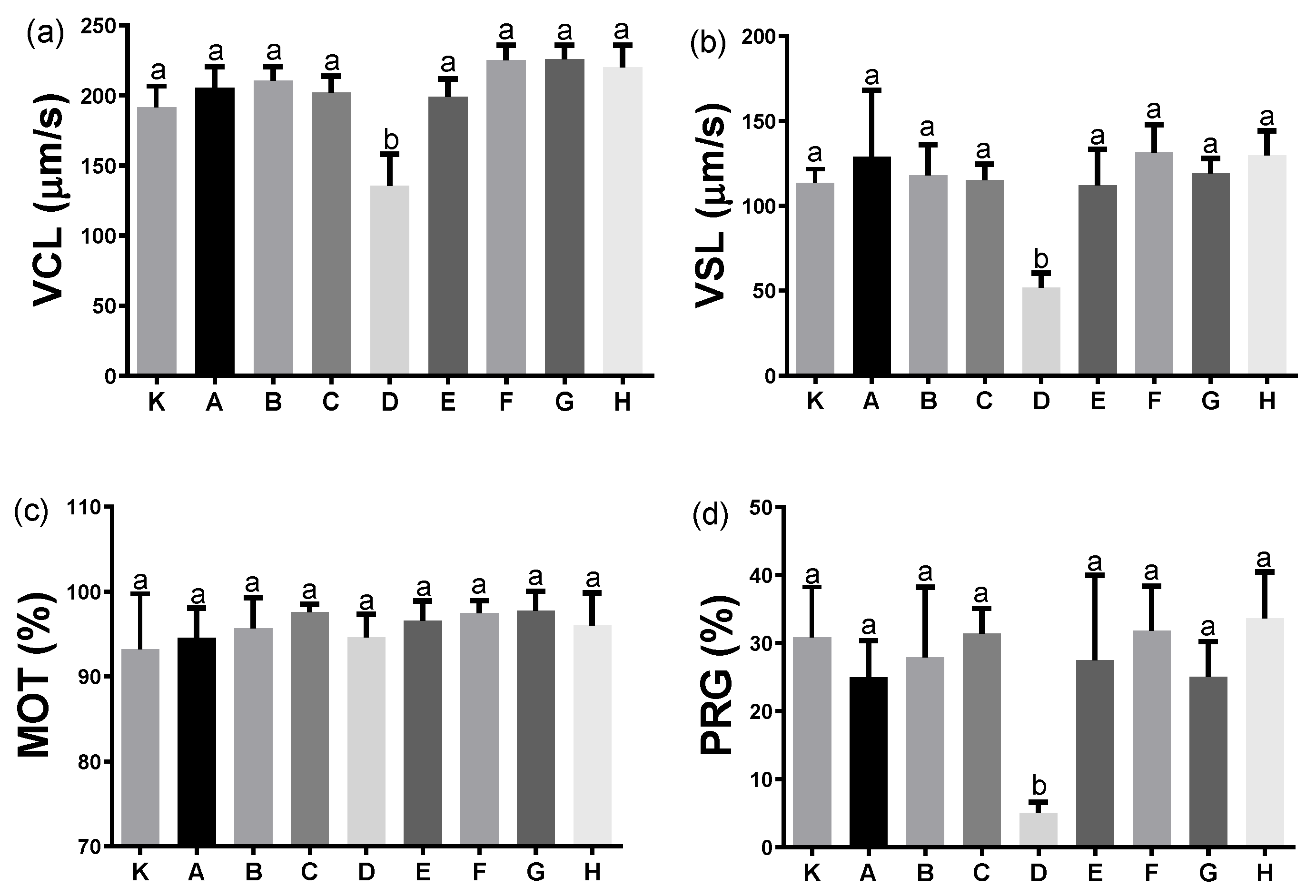
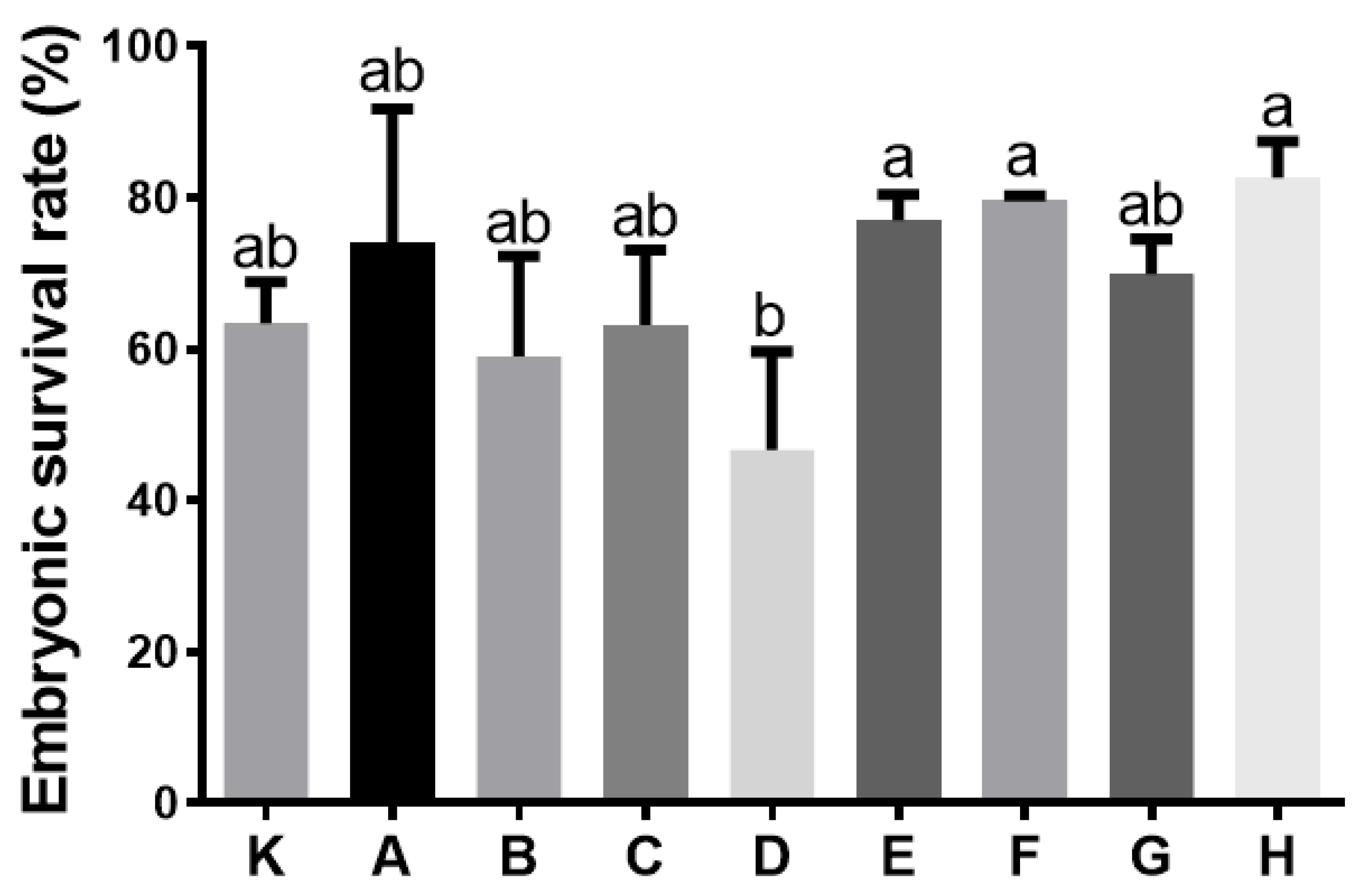

| Composition | pH | Osmolality (mOsm × kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| K | Hatchery water | 6.9 | 4 |
| A | 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris | 7.0 | 199 |
| B | 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris | 8.0 | 198 |
| C | 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris | 9.0 | 199 |
| D | 10 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris | 8.5 | 35 |
| E | 20 mM Tris, 40 mM NaHCO3 | 8.5 | 101 |
| F | 0.3% urea, 0.4% NaCl | 7.7 | 181 |
| G | 10 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl | 8.0 | 204 |
| H | 80 mM NaCl, 20 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris | 8.0 | 206 |
| Ammonium Molybdate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mM | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 |
| Seminal plasma Sperm extract | 39.8 ± 5.2 30.1 ± 4.9 | 46.5 ± 4.8 39.2 ± 5.2 | 51.6 ± 6.7 58.8 ± 6.1 | 60.1 ± 7.6 65.3 ± 7.0 | 85.5 ± 8.4 81.7 ± 6.3 |
| Gossypol | |||||
| mM | 0.00625 | 0.0125 | 0.025 | 0.05 | 0.1 |
| Seminal plasma Sperm extract | 37.2 ± 3.9 30.9 ± 3.8 | 40.5 ± 3.8 37.1 ± 5.5 | 50.4 ± 5.8 41.3 ± 5.4 | 55.4 ± 5.9 48.8 ± 5.4 | 61.2 ± 7.1 64.9 ± 6.9 |
| Acetamide | |||||
| M | 0.0313 | 0.0625 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| Seminal plasma Sperm extract | 31.2 ± 4.0 35.1 ± 5.1 | 58.3 ± 5.5 44.9 ± 5.9 | 69.0 ± 7.3 56.3 ± 6.5 | 73.4 ± 8.1 69.9 ± 7.8 | 84.6 ± 8.1 77.9 ± 7.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarosiek, B.; Dryl, K.; Kowalski, R.K.; Palińska-Żarska, K.; Żarski, D. Optimalisation of the Activation Medium and Effect of Inhibiting Activities of Acid Phosphatase, Lactate Dehydrogenase and β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase on the Fertilisation Success of Eurasian Perch (Perca fluviatilis L.). Animals 2022, 12, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030307
Sarosiek B, Dryl K, Kowalski RK, Palińska-Żarska K, Żarski D. Optimalisation of the Activation Medium and Effect of Inhibiting Activities of Acid Phosphatase, Lactate Dehydrogenase and β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase on the Fertilisation Success of Eurasian Perch (Perca fluviatilis L.). Animals. 2022; 12(3):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030307
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarosiek, Beata, Katarzyna Dryl, Radosław K. Kowalski, Katarzyna Palińska-Żarska, and Daniel Żarski. 2022. "Optimalisation of the Activation Medium and Effect of Inhibiting Activities of Acid Phosphatase, Lactate Dehydrogenase and β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase on the Fertilisation Success of Eurasian Perch (Perca fluviatilis L.)" Animals 12, no. 3: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030307
APA StyleSarosiek, B., Dryl, K., Kowalski, R. K., Palińska-Żarska, K., & Żarski, D. (2022). Optimalisation of the Activation Medium and Effect of Inhibiting Activities of Acid Phosphatase, Lactate Dehydrogenase and β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase on the Fertilisation Success of Eurasian Perch (Perca fluviatilis L.). Animals, 12(3), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030307







