Intestinal Ecology Changes in Diarrheic Père David’s Deer Revealed by Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. 16S rRNA Gene Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. UPLC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Metabolomics Data Analysis
2.6. Conventional PCR and Quantitative Real Time PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
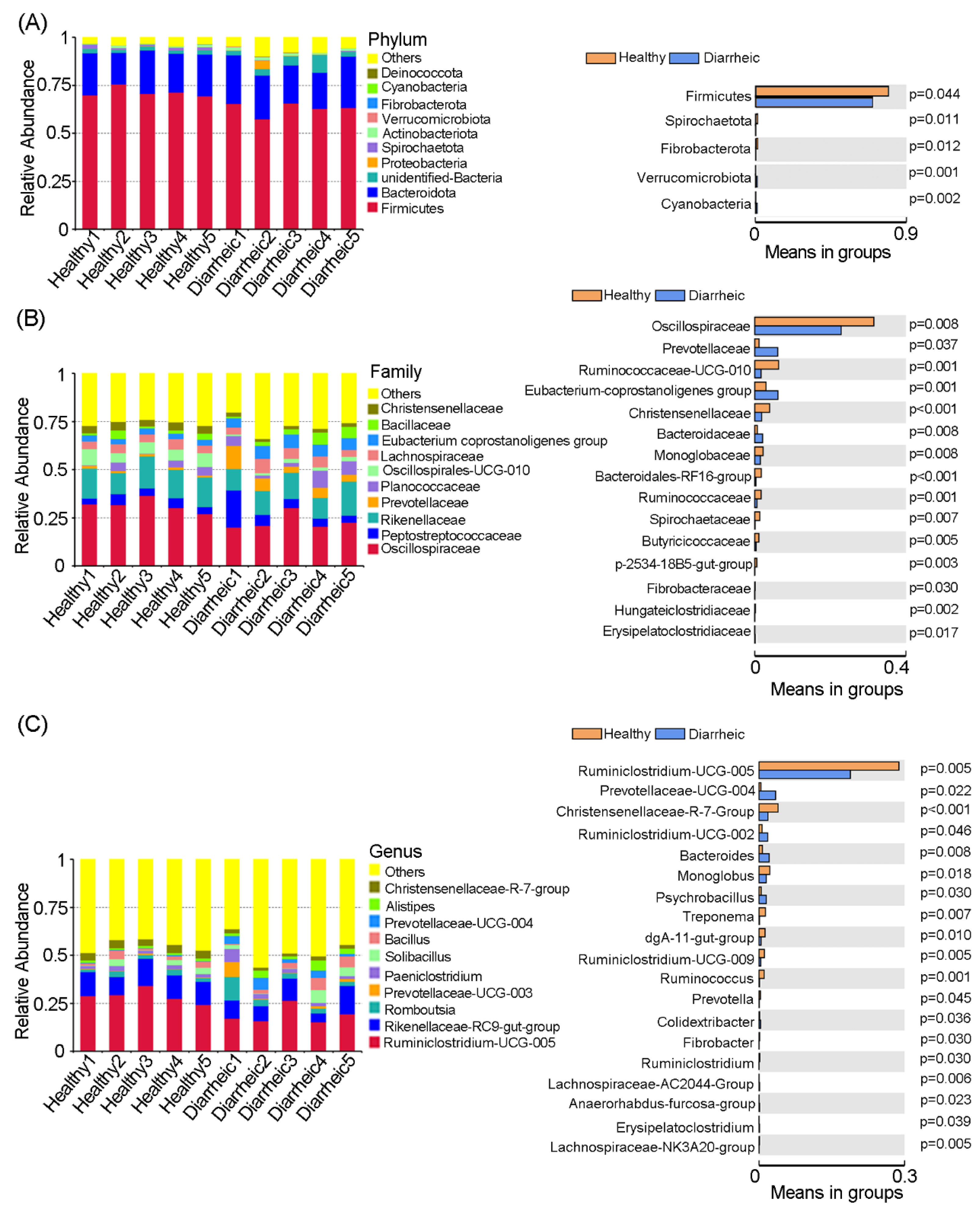
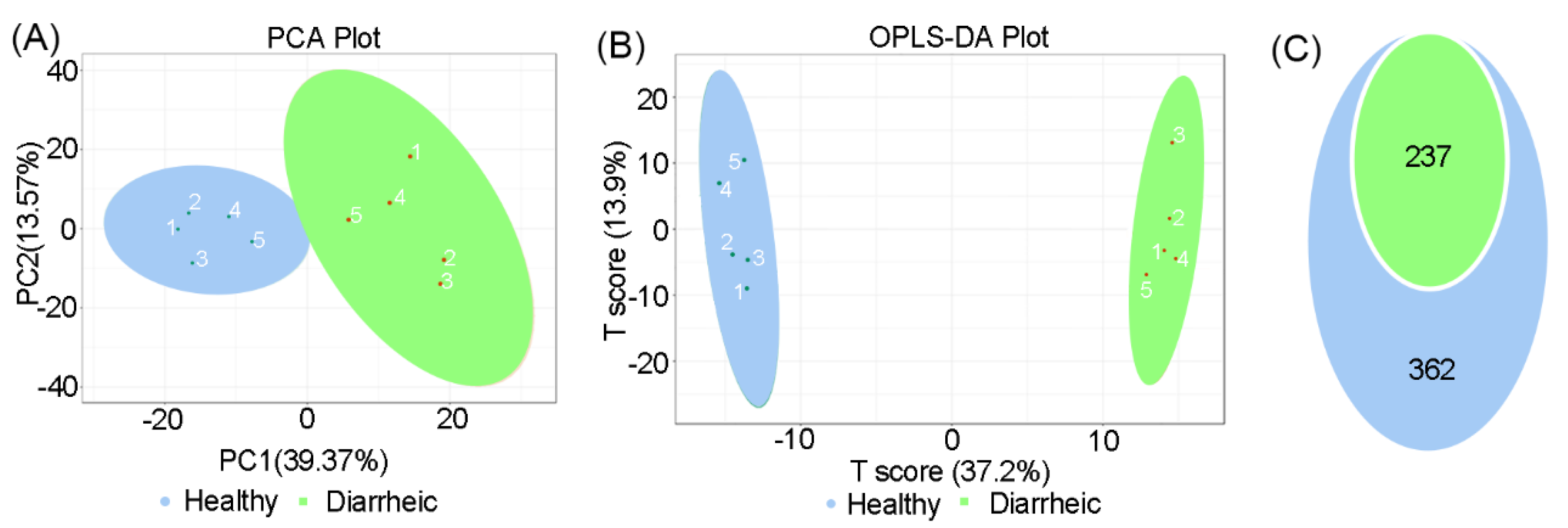
3.1. Gut Microbiome Differences and Diversity in Diarrheic Père David’s Deer
3.2. Altered Microbiota Composition in Diarrheic Père David’s deer
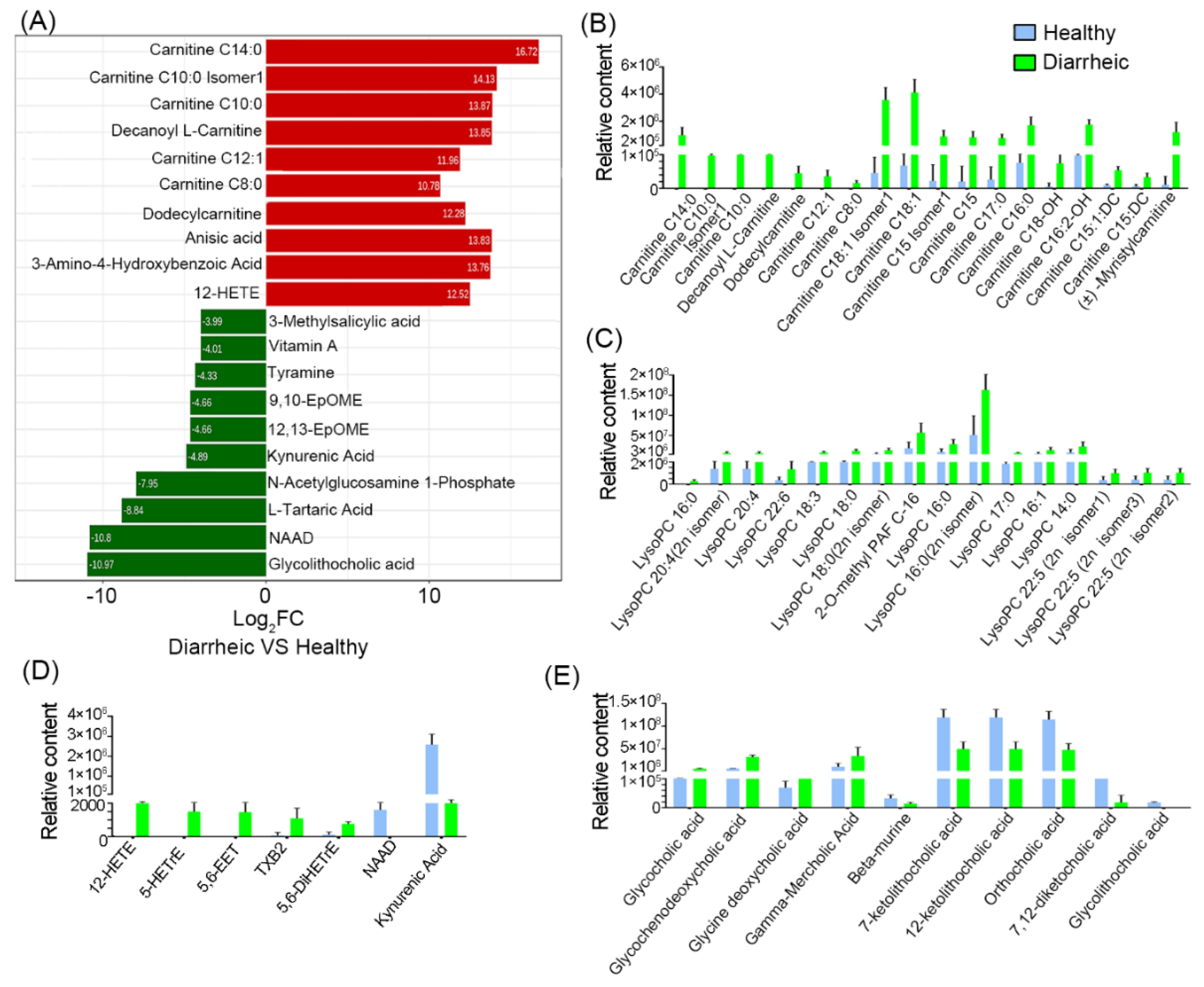
3.3. Altered Fecal in Diarrheic Père David’s deer
3.4. Altered Metabolites in Diarrheic Père David’s Deer
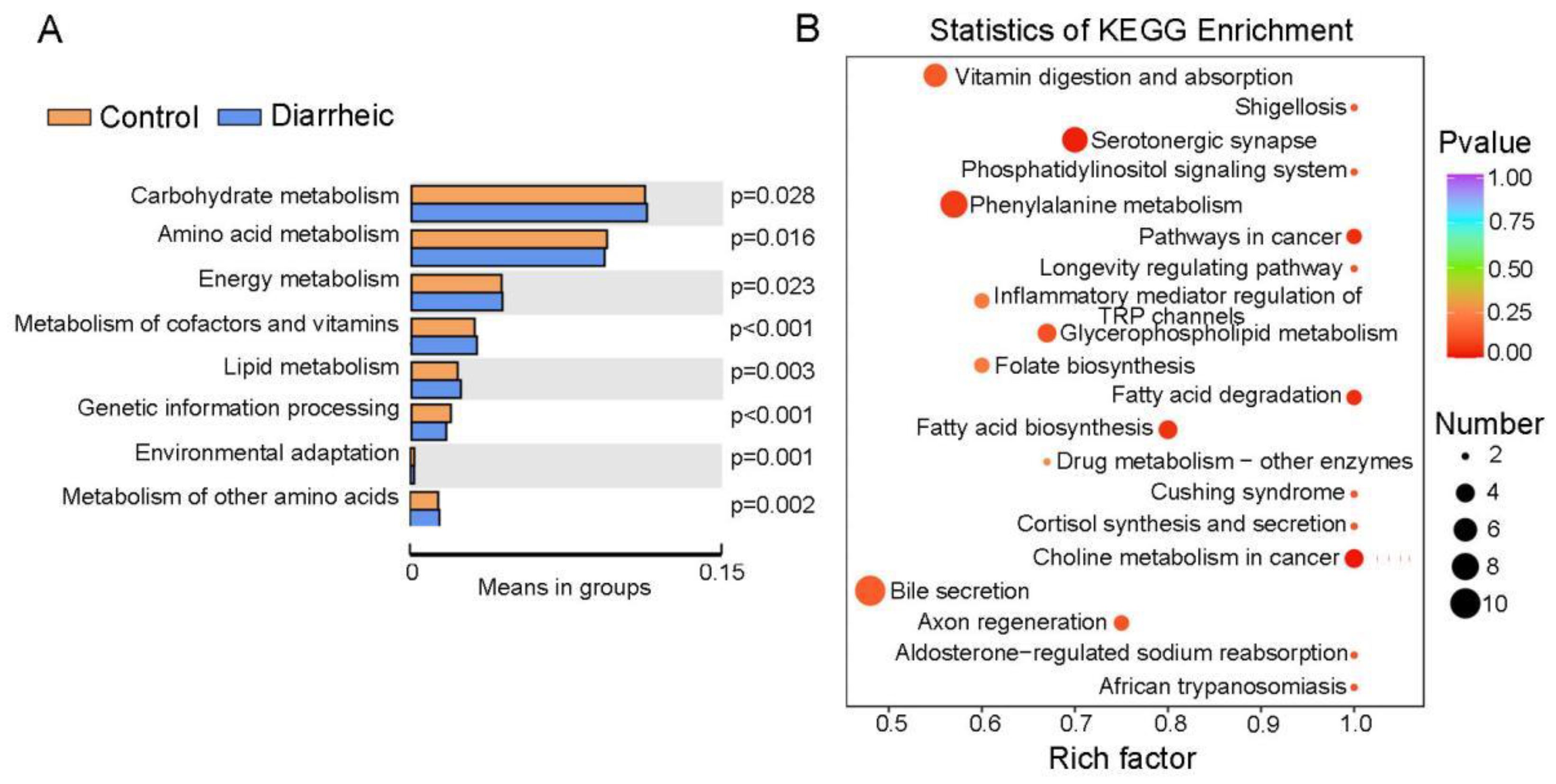
3.5. Altered Metabolic Pathways in Diarrheic Père David’s Deer
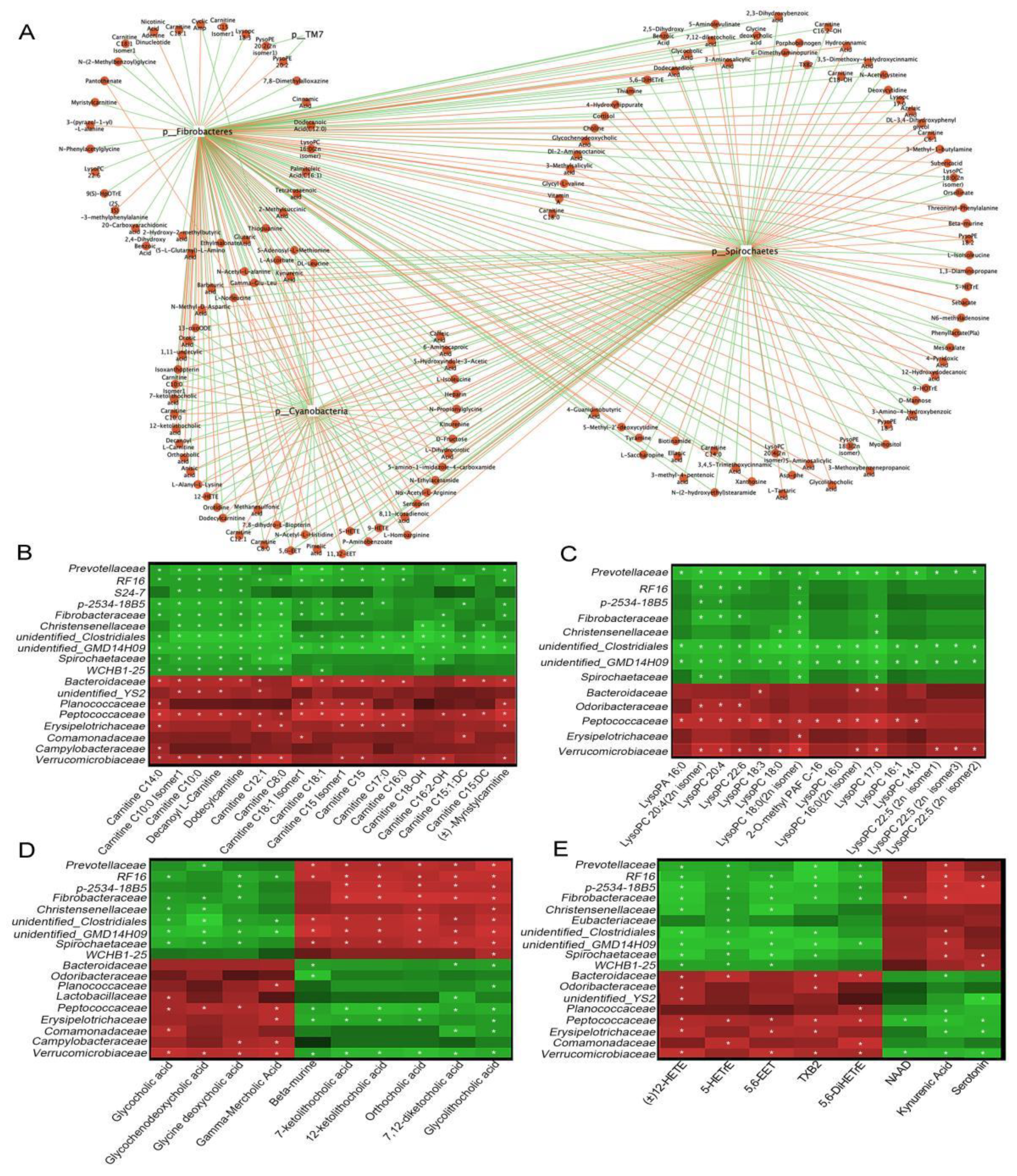
3.6. Functional Correlations between Fecal Metabolites and Main Gut Microbiota
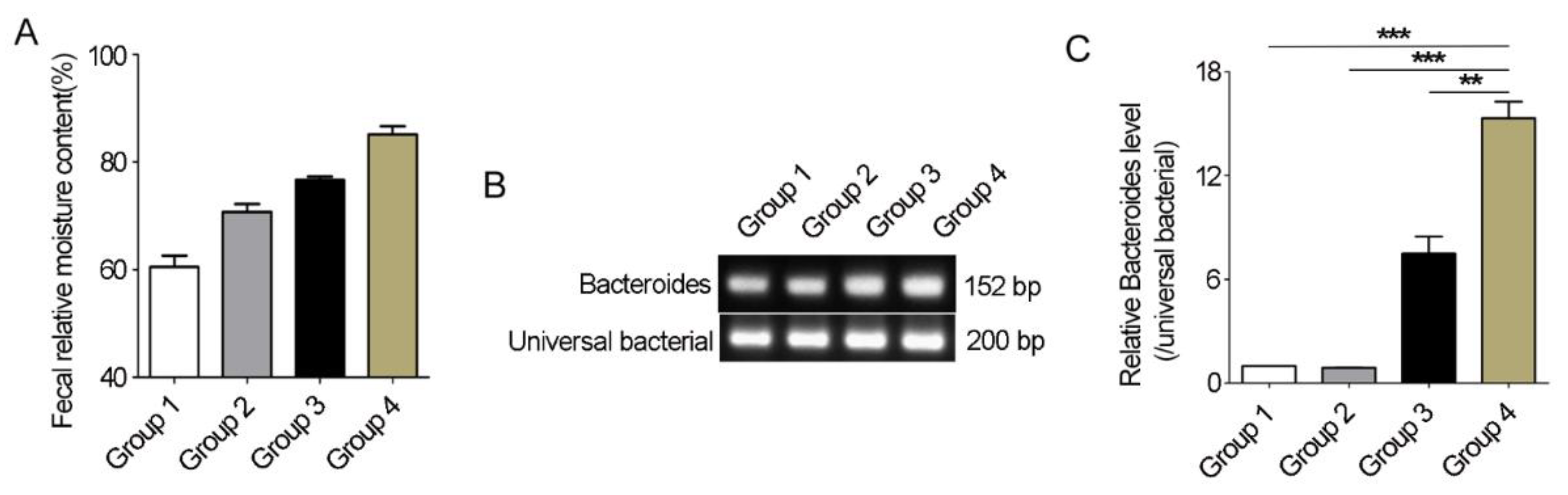
3.7. Bacteroides Abundance Comparison in Feces of Père David’s Deer with or without Diarrhea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hu, D.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Shan, Y.; Bai, J.; Liu, G. Genetic Differentiation of Reintroduced Père David’s Deer (Elaphurus davidianus) Based on Population Genomics Analysis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 705337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Liu, P.; Chen, Y. Effect of Different Dietary Regimes on the Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites of Père David’s Deer. Animals 2022, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C. Genetic Variability in Relocated Père David’s Deer (Elaphurus davidianus) Populations-Implications to Reintroduction Program. Conserv. Genet. 2007, 8, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, B.; Yang, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, D.; Bai, J. Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Gastrointestinal Parasite Infection in Père David’s Deer. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.Y.; Fan, Y.M.; Yao, N.; Yang, Y.; Pei, M.Y.; Ren, Y.J.; Gong, J.Z. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in the Endangered Père David’s Deer (Elaphurus davidianus) in China. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Fan, Y.M.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Y.J.; Gong, J.Z.; Yao, N.; Yang, B. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium Spp. in Père David’s Deer (Elaphurus davidianus) in Jiangsu, China. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2020, 29, e017919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Suding, Z.; Wang, L.; Hou, Z.; Liu, D.; Huang, S.; Xu, J.; Tao, J. A New Eimeria coccidian Species (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from Père David’s Deer (Elaphurus davidianus Milne-Edwards, 1866) in Dafeng Milu National Nature Reserve in Jiangsu Province, Eastern China. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Gong, J.Z.; Ren, Y.J.; Pan, M.; Cai, W.M.; Fan, Y.M.; Yao, N. First Report on the Prevalence of Fasciola hepatica in the Endangered Père David’s Deer (Elaphurus davidianus) in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Chen, F.; Leng, X.; Fei, R.; Wang, L. Toxinotyping of Clostridium perfringens Fecal Isolates of Reintroduced Père David’s Deer (Elaphurus davidianus) in China. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frölich, K.; Flach, E.J. Long-Term Viral Serology of Semi-Free-Living and Captive Ungulates. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1998, 29, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, M.; Fan, M.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Cha, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, Q.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiota Changes in Père David’s Deer Populations in Beijing Milu Park and Shishou, Hubei Province in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Liu, B.; Yuan, B.D.; Lu, C.H. Analysis of the Gut Microbiome of Wild and Captive Père David’s Deer. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.J.; Sun, D.M.; Yu, X.P.; Liu, B. Relationship between Growth and Disease of Milu Deer in Breast-Beeding Period. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2020, 11, 153–157. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, N.S.; Hendrickson, S.M.; Prongay, K.; Haertel, A.; Gill, L.; Edwards, R.A.; Garzel, L.; Slifka, M.K.; Messaoudi, I. Growth Faltering Regardless of Chronic Diarrhea is Associated with Mucosal Immune Dysfunction and Microbial Dysbiosis in the Gut lumen. Mucosal. Immunol. 2021, 14, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stedman, A.; van Vliet, A.H.M.; A Chambers, M.; Gutierrez-Merino, J. Gut Commensal Bacteria Show Beneficial Properties as Wildlife Probiotics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1467, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Lu, L.; Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Gut Microbiota and Sunitinib-Induced Diarrhea in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Pilot Study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 8663–8672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, S.; El-Mowafy, M.; Elgaml, A.; Ahmed, T.A.E.; Hassan, H.; Mottawea, W. Metabolic Influences of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis on Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 715506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passler, T.; Ditchkoff, S.S.; Walz, P.H. Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus (BVDV) in White-Tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, S.; Zhou, J.; Qi, L.; Sun, X.; Fan, M.; Xu, S.; Cha, M.; Zhang, M.; et al. Comparison Between the Fecal Bacterial Microbiota of Healthy and Diarrheic Captive Musk Deer. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.T.; Hansen, M.F.; Chriél, M.; Petersen, H.H. First Description of Onchocerca Flexuosa Infections in Danish Red Deer (Cervus elaphus). Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2022, 28, 100684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, G.; Cao, H.; Yu, D.; Fang, X.; de Vos, W.M.; Wu, H. Gut Dysbacteriosis and Intestinal Disease: Mechanism and Treatment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xia, S.; Jiang, X.; Feng, C.; Gong, S.; Ma, J.; Fang, Z.; Yin, J.; Yin, Y. Gut Microbiota and Diarrhea: An Updated Review. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Qin, X.; Song, Y.; Han, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Gut Microbial Alterations in Diarrheal Baer’s Pochards (Aythya baeri). Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 756486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Song, Y.; Qin, X.; Han, J.; Chang, Y.F. Microbiome Analysis Reveals the Dynamic Alternations in Gut Microbiota of Diarrheal Giraffa Camelopardalis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 649372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Ma, Y.; Rong, K.; Xu, Y.C.; Ma, J. Variations in Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolic Phenotype Associated with Fenbendazole and Ivermectin Tablets by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and LC/MS-Based Metabolomics in Amur Tiger. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierer, J.; Jackson, M.A.; Kastenmüller, G.; Mangino, M.; Long, T.; Telenti, A.; Mohney, R.P.; Small, K.S.; Bell, J.T.; Steves, C.J.; et al. The Fecal Metabolome as a Functional Readout of the Gut Microbiome. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, S.; Sen, P.; Dickens, A.M.; Orešič, M.; Bertram, H.C. Gut Metabolome Meets Microbiome: A Methodological Perspective to Understand the Relationship between Host and Microbe. Methods 2018, 149, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Arze, C.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Schirmer, M.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Poon, T.W.; Andrews, E.; Ajami, N.J.; Bonham, K.S.; Brislawn, C.J.; et al. Multi-Omics of the Gut Microbial Ecosystem in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Nature 2019, 569, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugerth, L.W.; Wefer, H.A.; Lundin, S.; Jakobsson, H.E.; Lindberg, M.; Rodin, S.; Engstrand, L.; Andersson, A.F. DegePrime, a Program for Degenerate Primer Design for Broad-Taxonomic-Range PCR in Microbial Ecology Studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5116–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Choi, S.H.; Nogoy, K.M.; Liang, S. The Development of the Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiota and Intervention in Neonatal Ruminants. Animal 2021, 15, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, K.; Bedrani, L.; Turpin, W.; Kabakchiev, B.; Stempak, J.; Borowski, K.; Nguyen, G.; Steinhart, A.H.; Smith, M.I.; Croitoru, K.; et al. Persistent Diarrhea in Patients with Crohn’s Disease after Mucosal Healing is Associated with Lower Diversity of the Intestinal Microbiome and Increased Dysbiosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yu, M.L.; Tao, X.; Cheng, M.H.; Liu, C.C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.G. Analysis of the Intestinal Microbial Community Altered During Rotavirus Infection in Suckling Mice. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiss, C.N.; Olofsson, L.E. Gut Microbiota-Dependent Modulation of Energy Metabolism. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Danska, J.; Parkinson, J. Metatranscriptomic Analysis of Diverse Microbial Communities Reveals Core Metabolic Pathways and Microbiome-Specific Functionality. Microbiome 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Yi, B.; Zhong, R.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Yin, Y.; Yin, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. From Gut Microbiota to Host Appetite: Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites as Key Regulators. Microbiome 2021, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portincasa, P.; Bonfrate, L.; Khalil, M.; Angelis, M.; Calabrese, F.M.; D’Amato, M.; Wang, D.Q.; Di Ciaula, A. Intestinal Barrier and Permeability in Health, Obesity and NAFLD. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The Influence of Probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, M.; Bahar Tokman, H.; Taner, Z.; Keskin, F.E.; Çağatay, P.; Ozturk Bakar, Y.; Özyazar, M.; Kiraz, N.; Kocazeybek, B.S. Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes Levels in Gut Microbiota and Effects of Hosts TLR2/TLR4 Gene Expression Levels in Adult Type 1 Diabetes Patients in Istanbul, Turkey. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2020, 34, 107449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Weirdt, R.; Van de Wiele, T. Micromanagement in the Gut: Microenvironmental Factors Govern Colon Mucosal Biofilm Structure and Functionality. NPJ Biofilms Microbiome 2015, 1, 15026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Shan, X.; Cai, C.; Hao, J.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Dietary Fucoidan Modulates the Gut Microbiota in Mice by Increasing the Abundance of Lactobacillus and Ruminococcaceae. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3224–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antharam, V.C.; Li, E.C.; Ishmael, A.; Sharma, A.; Mai, V.; Rand, K.H.; Wang, G.P. Intestinal Dysbiosis and Depletion of Butyrogenic Bacteria in Clostridium Difficile Infection and Nosocomial Diarrhea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2884–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Sim, J.; Lee, W.L.; Cui, L.; Chan, Y.; Chang, E.D.; Teh, Y.E.; Zhang, A.N.; Armas, F.; Chandra, F.; et al. Gut Ruminococcaceae Levels at Baseline Correlate with Risk of Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. iScience 2021, 25, 103644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, H.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Gut Bacteroides Species in Health and Disease. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Roles of Intestinal Bacteroides in Human Health and Diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3518–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zeng, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, N.; Zeng, B.; Niu, L.; Ni, X. Diarrhea-Associated Intestinal Microbiota in Captive Sichuan Golden Snub-Nosed Monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana). Microbes Environ. 2018, 33, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, N.; Lan, Y.; Lan, W.; Feng, J.; Yue, B.; He, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, A.; et al. The Gut Microbiome and Antibiotic Resistome of Chronic Diarrhea Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta) and its Similarity to the Human Gut Microbiome. Microbiome 2022, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Deng, B.; Yong, F.; Zhou, H.; Qu, C.; Zhou, Z. Comparison of the Fecal Microbiomes of Healthy and Diarrheic Captive Wild Boar. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Whitley, C.S.; Haribabu, B.; Jala, V.R. Regulation of Intestinal Barrier Function by Microbial Metabolites. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 1463–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Pang, Y.; Jiang, C. The Role of the Gut Microbiome and its Metabolites in Metabolic Diseases. Protein Cell. 2021, 12, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chiang, J.Y. Bile Acid Signaling in Metabolic Disease and Drug Therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 948–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Wang, W.; Hong, G.; Duan, C.; Zhu, S.; Tian, Y.; Han, C.; Qian, W.; Lin, R.; Hou, X. Gut Microbiota-Mediated Lysophosphatidylcholine Generation Promotes Colitis in Intestinal Epithelium-Specific Fut2 Deficiency. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoodi, M.; Pearl, D.S.; Eiden, M.; Shute, J.K.; Brown, J.F.; Calder, P.C.; Trebble, T.M. Altered Colonic Mucosal Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (PUFA) Derived Lipid Mediators in Ulcerative Colitis: New Insight Into Relationship with Disease Activity and Pathophysiology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Zheng, Y.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Hruby, A.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Clish, C.B.; Corella, D.; Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Fitó, M.; et al. Plasma Acylcarnitines and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: Effect of Mediterranean Diet Interventions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gander, J.; Carrard, J.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Borreggine, R.; Teav, T.; Infanger, D.; Colledge, F.; Streese, L.; Wagner, J.; Klenk, C.; et al. Metabolic Impairment in Coronary Artery Disease: Elevated Serum Acylcarnitines Under the Spotlights. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 792350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildreth, K.; Kodani, S.D.; Hammock, B.D.; Zhao, L. Cytochrome P450-Derived Linoleic Acid Metabolites EpOMEs and DiHOMEs: A Review of Recent Studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 86, 108484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, K.E.; Sitarik, A.R.; Havstad, S.; Lin, D.L.; Levan, S.; Fadrosh, D.; Panzer, A.R.; LaMere, B.; Rackaityte, E.; Lukacs, N.W.; et al. Neonatal Gut Microbiota Associates with Childhood Multisensitized Atopy and T Cell Differentiation. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnúsdóttir, S.; Ravcheev, D.; de Crécy-Lagard, V.; Thiele, I. Systematic Genome Assessment of B-Vitamin Biosynthesis Suggests Co-operation among Gut Microbes. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Bai, M.; Peng, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Intestinal Immunity Mediated by Tryptophan Metabolism. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, T.A.; Nguyen, J.C.; Polglaze, K.E.; Bertrand, P.P. Influence of Tryptophan and Serotonin on Mood and Cognition with a Possible Role of the Gut-Brain Axis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, A.A. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism: Regulatory and Functional Aspects. Int. J. Tryptophan. Res. 2016, 10, 1178646917691938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, L.G.; Rousseau, J.D.; Staempfli, H.R.; Weese, J.S. Suspected Clostridium Difficile-Associated Hemorrhagic Diarrhea in a 1-week-old Elk Calf. Can. Vet. J. 2005, 46, 1130–1131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhen, J.; Yuan, X.; Tao, L.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Y.; Xie, S.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y. Intestinal Ecology Changes in Diarrheic Père David’s Deer Revealed by Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites Analysis. Animals 2022, 12, 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233366
Zhen J, Yuan X, Tao L, Zhang H, Ren Y, Xie S, Wang L, Shen H, Chen Y. Intestinal Ecology Changes in Diarrheic Père David’s Deer Revealed by Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites Analysis. Animals. 2022; 12(23):3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233366
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhen, Junai, Xueli Yuan, Liping Tao, Huidan Zhang, Yijun Ren, Shengbin Xie, Libo Wang, Hua Shen, and Yuqing Chen. 2022. "Intestinal Ecology Changes in Diarrheic Père David’s Deer Revealed by Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites Analysis" Animals 12, no. 23: 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233366
APA StyleZhen, J., Yuan, X., Tao, L., Zhang, H., Ren, Y., Xie, S., Wang, L., Shen, H., & Chen, Y. (2022). Intestinal Ecology Changes in Diarrheic Père David’s Deer Revealed by Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites Analysis. Animals, 12(23), 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233366




