Comparative Analysis of Saliva and Plasma Proteins Patterns in Pregnant Cows—Preliminary Studies
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Saliva and Blood Collection and Processing
2.3. Two-Dimensional Analysis
2.4. Isoelectric Focusing
2.5. Gels Staining and Analysis
2.6. Mass Spectrometry-Based Protein Identification
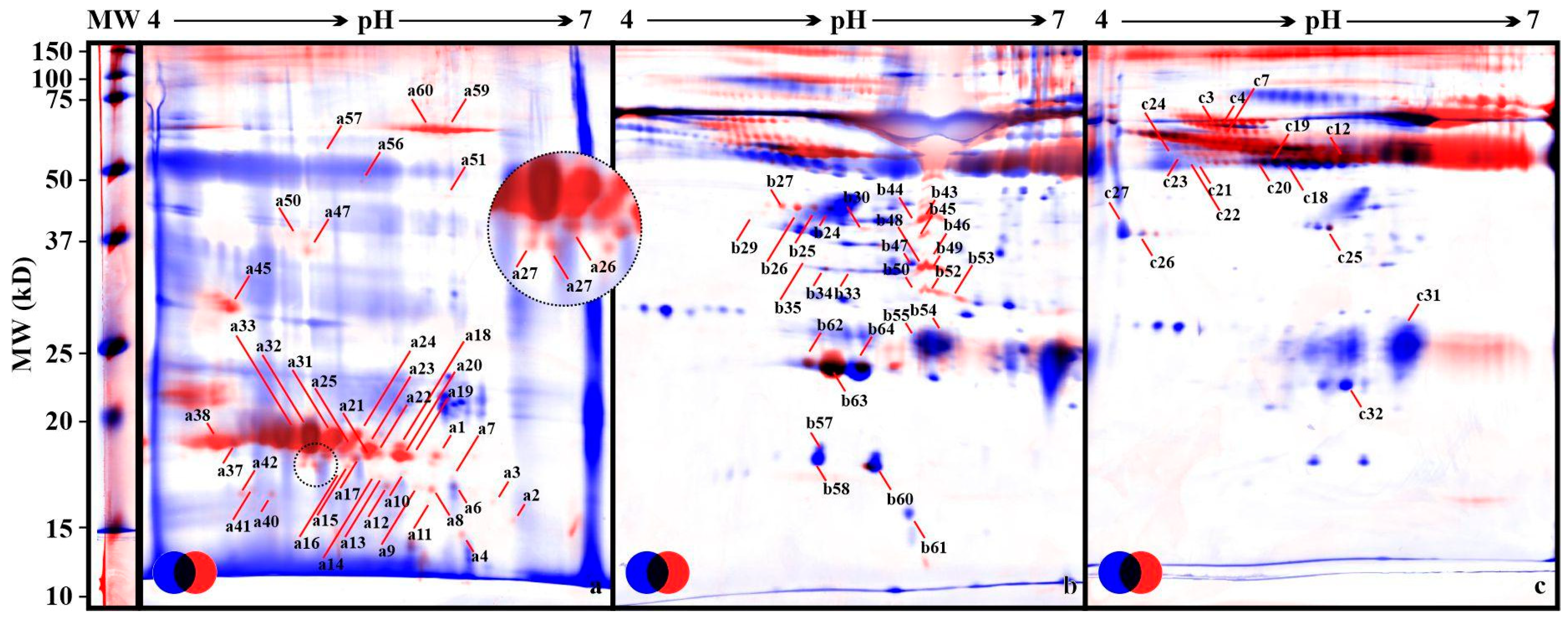
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balhara, A.K.; Gupta, M.; Singh, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Singh, I. Early pregnancy diagnosis in bovines: Current status and future directions. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 958540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.S.; Singh, R.P.; Karsauliya, K.; Sonker, A.K.; Reddy, P.J.; Mehrotra, D.; Gupta, S.; Singh, S.; Kumar, R.; Singh, S.P. Label-free plasma proteomics for the identification of the putative biomarkers of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Proteom. 2022, 259, 104541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.K.; Pandey, M.; Baithalu, R.K.; Fernandes, A.; Ali, S.A.; Jaiswal, L.; Pannu, S.; Neeraj; Mohanty, T.K.; Kumaresan, A.; et al. Comparative Proteome Profiling of Saliva Between Estrus and Non-Estrus Stages by Employing Label-Free Quantitation (LFQ) and Tandem Mass Tag (TMT)-LC-MS/MS Analysis: An Approach for Estrus Biomarker Identification in Bubalus bubalis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Contreras-Aguilar, M.D.; Cerón, J.J.; Ayala, I.; Martin-Cuervo, M.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, J.C.; Jacobsen, S.; Kuleš, J.; Beletić, A.; Rubić, I.; et al. Changes in Proteins in Saliva and Serum in Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome Using a Proteomic Approach. Animals 2022, 12, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsina, S.S.; Jolly, P.; Durr, N.; Yafia, M.; Ingber, D.E. Enabling Multiplexed Electrochemical Detection of Biomarkers with High Sensitivity in Complex Biological Samples. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 3529–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, R.; Piras, C.; Kovačić, M.; Samardžija, M.; Ahmed, H.; De Canio, M.; Urbani, A.; Meštrić, Z.F.; Soggiu, A.; Bonizzi, L.; et al. Proteomics of inflammatory and oxidative stress response in cows with subclinical and clinical mastitis. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4412–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaradia, E.; Avellini, L.; Tartaglia, M.; Gaiti, A.; Just, I.; Scoppetta, F.; Czentnar, Z.; Pich, A. Proteomic evaluation of sheep serum proteins. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, I.; Preßlmayer-Hartler, A.; Wait, R.; Hummel, K.; Sensi, C.; Eberini, I.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E.; Gianazza, E. In between—Proteomics of dog biological fluids. J. Proteom. 2014, 106, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceciliani, F.; Eckersall, D.; Burchmore, R.; Lecchi, C. Proteomics in Veterinary Medicine. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talamo, F.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Arena, S.; Del Vecchio, P.; Ledda, L.; Zehender, G.; Ferrara, L.; Scaloni, A. Proteins from bovine tissues and biological fluids: Defining a reference electrophoresis map for liver, kidney, muscle, plasma and red blood cells. Proteomics 2003, 3, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendixen, E.; Danielsen, M.; Hollung, K.; Gianazza, E.; Miller, I. Farm animal proteomics—A review. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, M.; Codrea, M.C.; Ingvartsen, K.L.; Friggens, N.C.; Bendixen, E.; Røntved, C.M. Quantitative milk proteomics—Host responses to lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation of bovine mammary gland. Proteomics 2010, 10, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.X.; Kim, H.R.; Diao, Y.F.; Lee, M.G.; il Jin, D. Detection of early pregnancy-specific proteins in Holstein milk. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 3221–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, C.-S.; Binos, S.; Knight, M.I.; Moate, P.J.; Cocks, B.G.; McDonagh, M.B. Global Survey of the Bovine Salivary Proteome: Integrating Multidimensional Prefractionation, Targeted, and Glycocapture Strategies. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 5059–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, E.; Mau, M. Saliva proteomics as an emerging, non-invasive tool to study livestock physiology, nutrition and diseases. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmerhorst, E.J.; Oppenheim, F.G. Saliva: A Dynamic Proteome. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, M.; Palicki, O.; Lucchi, G.; Ducoroy, P.; Chambon, C.; Salles, C.; Morzel, M. Inter-individual variability of protein patterns in saliva of healthy adults. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, R.G.; Silletti, E.; Vingerhoeds, M.H. Saliva as research material: Biochemical, physicochemical and practical aspects. Arch. Oral Biol. 2007, 52, 1114–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, O.; Menchetti, L.; Brecchia, G.; Barile, V.L. Using Pregnancy-Associated Glycoproteins (PAGs) to Improve Reproductive Management: From Dairy Cows to Other Dairy Livestock. Animals 2022, 12, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, O.; Menchetti, L.; Sousa, N.M.; Malfatti, A.; Brecchia, G.; Canali, C.; Beckers, J.F.; Barile, V.L. Pregnancy-associated glycoproteins (PAGs) concentrations in water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) during gestation and the postpartum period. Theriogenology 2017, 97, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carolis, M.; Barbato, O.; Acuti, G.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M.; de Sousa, N.M.; Canali, C.; Moscati, L. Plasmatic profile of pregnancy-associated glycoprotein (PAG) during gestation and postpartum in sarda and lacaune sheep determined with two radioimmunoassay systems. Animals 2020, 10, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during Assembly of Head of Bacteriophage-T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Vorm, O.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.N.; Pappin, D.J.C.; Creasy, D.M.; Cottrell, J.S. Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 3551–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.; Menze, B.H.; Kirchner, M.; Monigatti, F.; Parker, K.C.; Patterson, T.; Steen, J.J.; Hamprecht, F.A.; Steen, H. Robust prediction of the MASCOT score for an improved quality assessment in mass spectrometric proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3708–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shu, S.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Xia, C.; Xu, C. Plasma Protein Comparison between Dairy Cows with Inactive Ovaries and Estrus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurpińska, A.K.; Jarosz, A.; Ożgo, M.; Skrzypczak, W.F. Analysis of protein expression changes in the blood plasma of cows during the last month before parturition and 2 months after calving. Turkish J. Biol. 2016, 40, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzykowski, J.; Franczyk, M.; Hoedemaker, M.; Pries, M.; Streuff, B.; Kankofer, M. Preliminary data on possible protein markers of parturition in cows. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2018, 53, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.P.; Diniz, D.G.; Moimaz, S.A.S.; Sumida, D.H.; Okamoto, A.C. Saliva: Reflection of the body. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e184–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Córdoba, B.; Santiago-García, J. Saliva: A Fluid of Study for OMICS. Omi. A J. Integr. Biol. 2014, 18, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, E.; da Costa, G.; Santos, R.; Capela e Silva, F.; Potes, J.; Pereira, A.; Coelho, A.V.; Sales Baptista, E. Sheep and goat saliva proteome analysis: A useful tool for ingestive behavior research? Physiol. Behav. 2009, 98, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, A.M.; Miller, I.; Hummel, K.; Nöbauer, K.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E.; Gemeiner, M.; Cerón, J.J. Proteomic analysis of porcine saliva. Vet. J. 2011, 187, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri, B.; Tagesson, C.; Lindahl, M. Mapping of proteins in human saliva using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and peptide mass fingerprinting. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-M. Comparative proteomic analysis of human whole saliva. Arch. Oral Biol. 2004, 49, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorino, R.; Lobo, M.J.C.; Ferrer-Correira, A.J.; Dubin, J.R.; Tomer, K.B.; Domingues, P.M.; Amado, F.M.L. Identification of human whole saliva protein components using proteomics. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, F.M.L.; Vitorino, R.M.P.; Domingues, P.M.D.N.; Lobo, M.J.C.; Duarte, J.A.R. Analysis of the human saliva proteome. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2005, 2, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xie, Y.; Ramachandran, P.; Ogorzalek Loo, R.R.; Li, Y.; Loo, J.A.; Wong, D.T. Large-scale identification of proteins in human salivary proteome by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2005, 5, 1714–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Loo, J.A.; Wong, D.T. Human Saliva Proteome Analysis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1098, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Apweiler, R.; Balgley, B.M.; Boontheung, P.; Bundy, J.L.; Cargile, B.J.; Cole, S.; Fang, X.; Gonzalez-Begne, M.; Griffin, T.J.; et al. Systematic comparison of the human saliva and plasma proteomes. PROTEOMICS-Clin. Appl. 2009, 3, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, J.; Yan, W.; Ramachandran, P.; Wong, D. Comparative human salivary and plasma proteomes. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Laster, D.B. Development of the Bovine Fetus1. J. Anim. Sci. 1979, 48, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfarrer, C.; Ebert, B.; Miglino, M.A.; Klisch, K.; Leiser, R. The three-dimensional feto-maternal vascular interrelationship during early bovine placental development: A scanning electron microscopical study. J. Anat. 2001, 198, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Tang, F.L.; Lee, D.; Zhao, Y.; Song, H.; Zhu, X.J.; Mei, L.; Xiong, W.C. Ependymal Vps35 promotes ependymal cell differentiation and survival, suppresses microglial activation, and prevents neonatal hydrocephalus. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 3862–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczubiał, M.; Wawrzykowski, J.; Dąbrowski, R.; Krawczyk, M.; Kankofer, M. Preliminary study on plasma proteins in pregnant and non-pregnant female dogs. Theriogenology 2017, 97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Lei, Y.P.; Zhou, Y.L.; Okamoto, C.T.; Snead, M.L.; Paine, M.L. Structural organization and cellular localization of tuftelin-interacting protein 11 (TFIP11). Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, V.; Lu, H.; Killeen, M.; Greenblatt, J.; Burton, Z.F.; Reinberg, D. The small subunit of transcription factor IIF recruits RNA polymerase II into the preinitiation complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9999–10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proud, C.G. Regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2B. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 2001, 26, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franczak, A.; Wojciechowicz, B.; Kolakowska, J.; Zglejc, K.; Kotwica, G. Transcriptomic analysis of the myometrium during peri-implantation period and luteolysis–the study on the pig model. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2014, 14, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashikumar, N.G.; Baithalu, R.K.; Bathla, S.; Ali, S.A.; Rawat, P.; Kumaresan, A.; Kumar, S.; Maharana, B.R.; Singh, G.; Puneeth Kumar, D.S.; et al. Global proteomic analysis of water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) saliva at different stages of estrous cycle using high throughput mass spectrometry. Theriogenology 2018, 110, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzio, W.; Chrobak, Ł.; Rutkowski, M.; Franczyk, M.; Kankofer, M. Antioxidative and oxidative profiles in plasma and saliva of cows in different ages and hormonal status. Vet. Ital. 2019, 55, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopucki, M.; Wawrzykowski, J.; Gęca, T.; Miturski, A.; Franczyk, M.; Kankofer, M. Preliminary analysis of the protein profile in saliva during physiological term and preterm delivery. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 8253–8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; McIntyre, J.O.; Matrisian, L.M.; Fortunato, S.J. Salivary proteinase activity: A potential biomarker for preterm premature rupture of the membranes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 194, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wait, R.; Miller, I.; Eberini, I.; Cairoli, F.; Veronesi, C.; Battocchio, M.; Gemeiner, M.; Gianazza, E. Strategies for proteomics with incompletely characterized genomes: The proteome of Bos taurus serum. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 3418–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairoli, F.; Battocchio, M.; Veronesi, M.C.; Brambilla, D.; Conserva, F.; Eberini, I.; Wait, R.; Gianazza, E. Serum protein pattern during cow pregnancy: Acute-phase proteins increase in the peripartum period. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Kang, J.K.; Yoon, J.T.; Seong, H.H.; Jung, J.K.; Lee, H.M.; Park, C.S.; Jin, D.I. Protein profiles of bovine placenta derived from somatic cell nuclear transfer. Proteomics 2005, 5, 4264–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Shin, H.Y.; Lin, T.; Jin, D. Il Proteomic analysis of bovine pregnancy-specific serum proteins by 2D fluorescence difference gel electrophoresis. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pyo, J.; Hwang, S.-I.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.-J.; Kang, S.-C.; Kim, J.-S.; Lim, J. Characterization of a bovine pregnancy-associated protein using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis,N-terminal sequencing and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2003, 3, 2420–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mojsym, W.; Wawrzykowski, J.; Jamioł, M.; Chrobak, Ł.; Kankofer, M. Comparative Analysis of Saliva and Plasma Proteins Patterns in Pregnant Cows—Preliminary Studies. Animals 2022, 12, 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202850
Mojsym W, Wawrzykowski J, Jamioł M, Chrobak Ł, Kankofer M. Comparative Analysis of Saliva and Plasma Proteins Patterns in Pregnant Cows—Preliminary Studies. Animals. 2022; 12(20):2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202850
Chicago/Turabian StyleMojsym, Wioleta, Jacek Wawrzykowski, Monika Jamioł, Łukasz Chrobak, and Marta Kankofer. 2022. "Comparative Analysis of Saliva and Plasma Proteins Patterns in Pregnant Cows—Preliminary Studies" Animals 12, no. 20: 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202850
APA StyleMojsym, W., Wawrzykowski, J., Jamioł, M., Chrobak, Ł., & Kankofer, M. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Saliva and Plasma Proteins Patterns in Pregnant Cows—Preliminary Studies. Animals, 12(20), 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202850




