Intelligent-Responsive Enrofloxacin-Loaded Chitosan Oligosaccharide–Sodium Alginate Composite Core-Shell Nanogels for On-Demand Release in the Intestine
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material
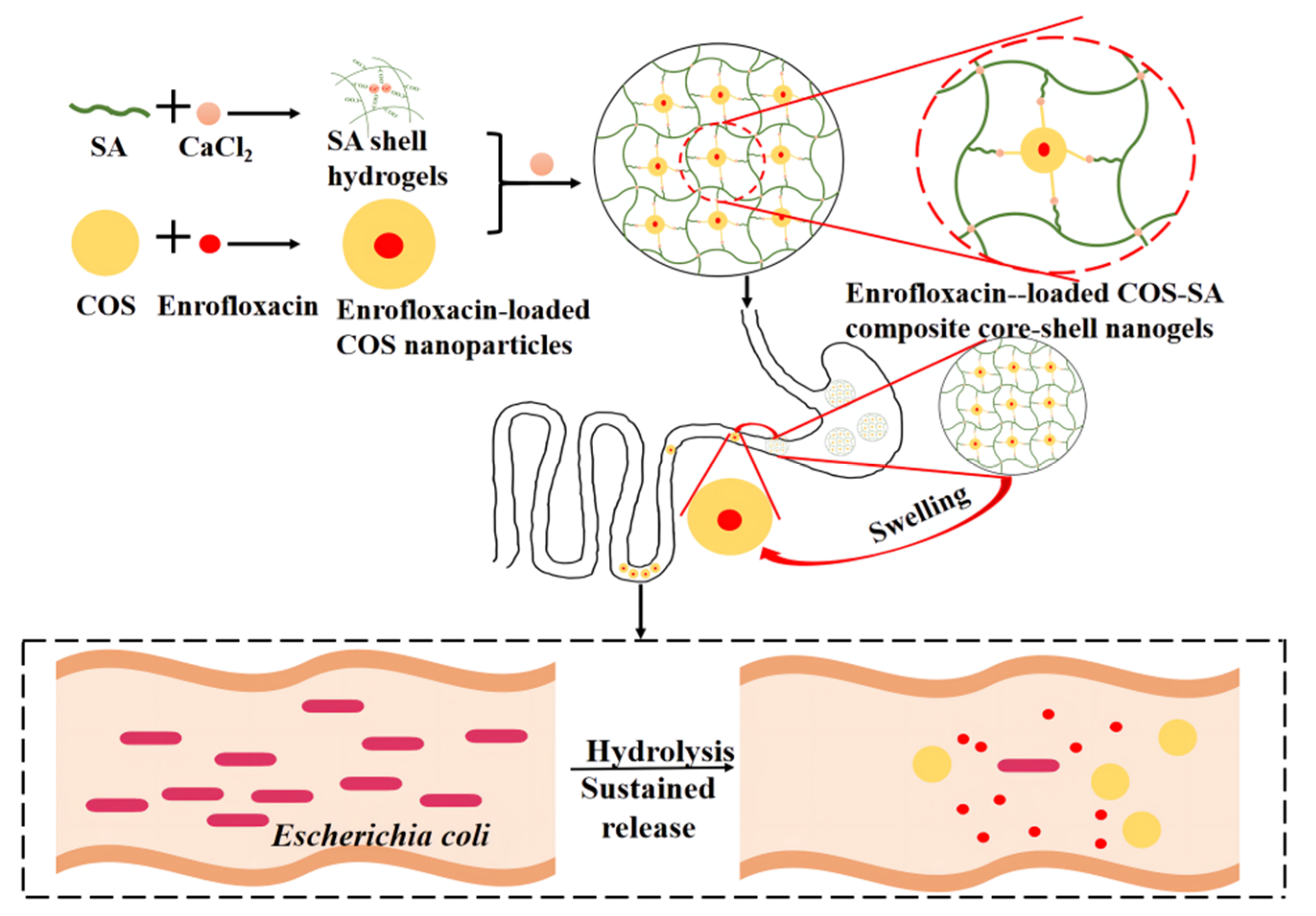
2.2. Preparation
2.3. Characterization
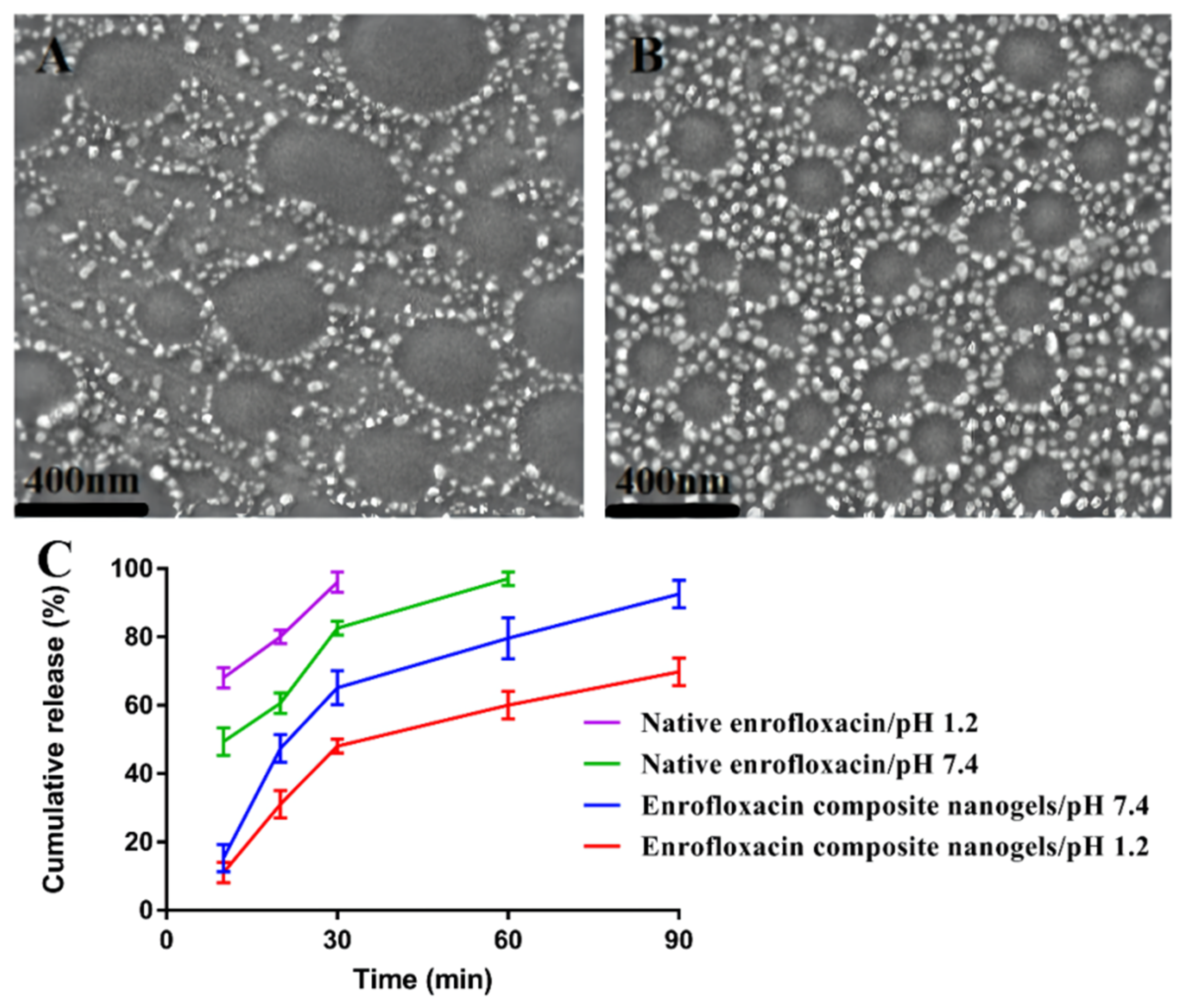
2.3.1. Surface Morphology
2.3.2. Zeta Potential (ZP), Polydispersity Index (PDI), and Particle Diameter
2.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.4. pH-Responsive Performances
2.5. Antibacterial Activity Studies
2.5.1. Broth Microdilution Method
2.5.2. Time-Kill Curves
2.6. Animal Experiment
2.6.1. Mouse Infection Model
2.6.2. Treatment Schedules
2.7. Safety Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Formula
3.2. Properties
3.3. pH-Responsive Performances
3.4. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity Test
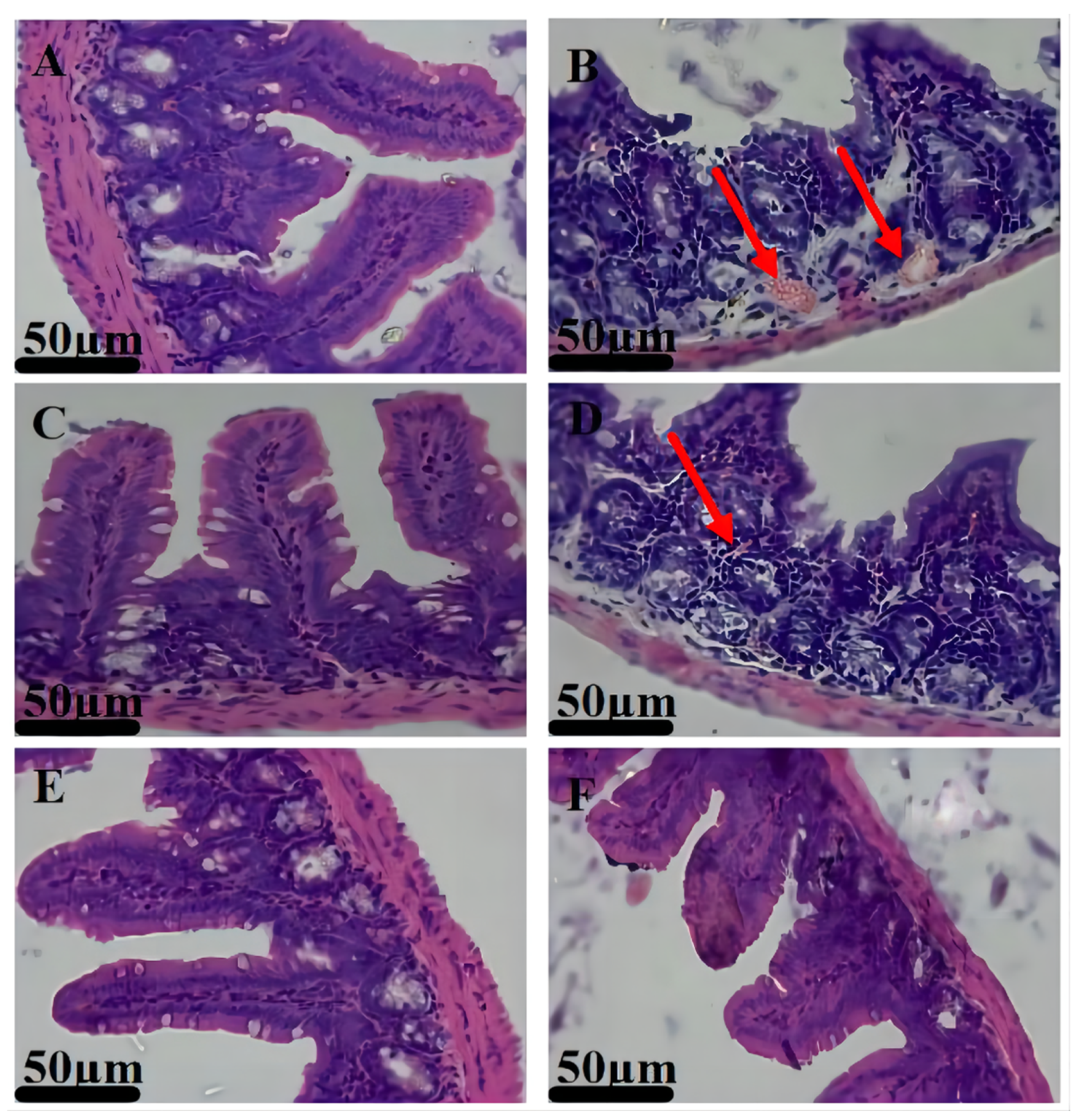
3.5. Therapeutic Effects
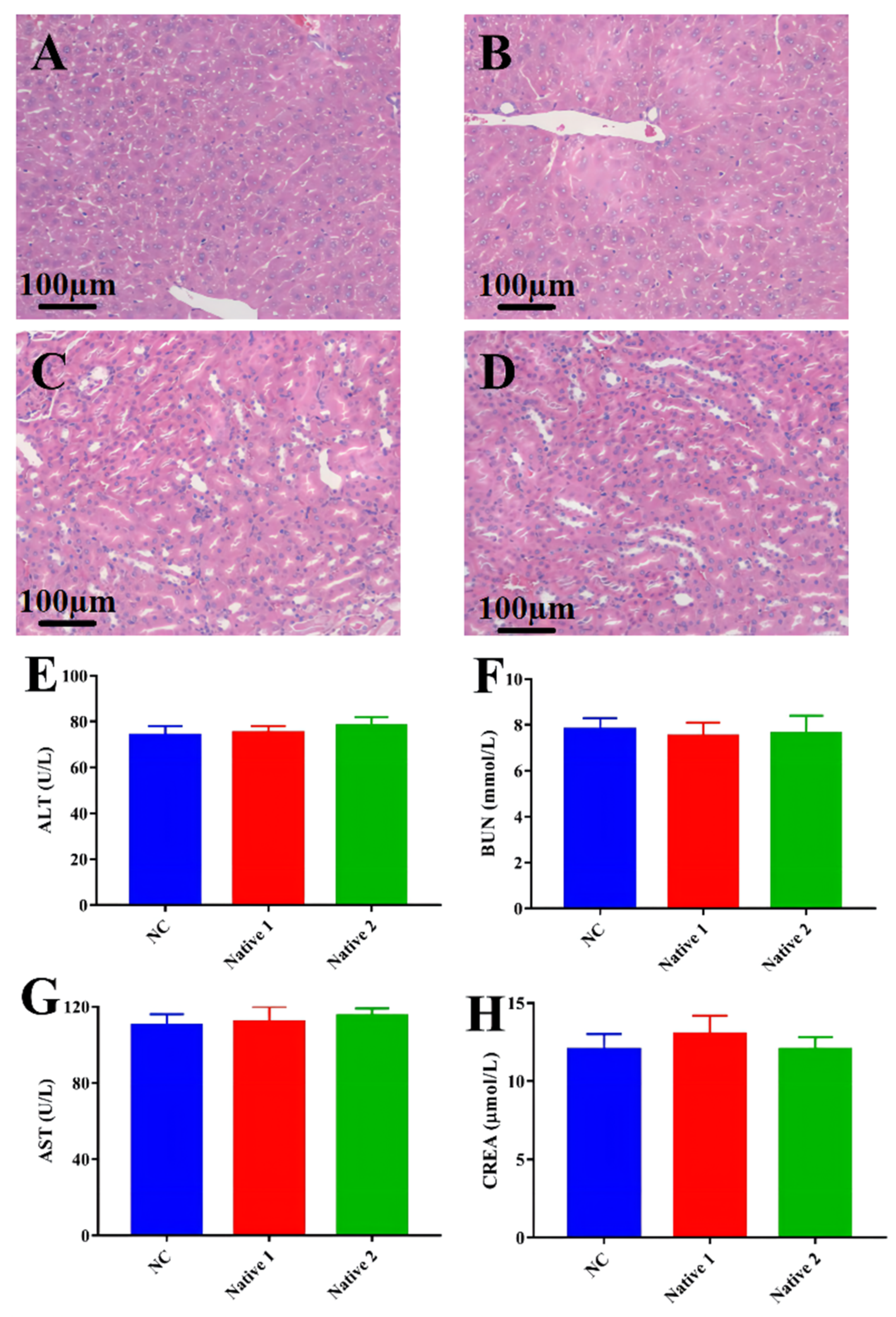
3.6. Biosafety Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, W.; Qin, H.; Chen, D.; Wu, M.; Meng, K.; Zhang, A.; Pan, Y.; Qu, W.; Xie, S. The dose regimen formulation of tilmicosin against Lawsonia intracellularis in pigs by pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, N.; Ju, M.; Jiang, Y.; Guan, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Algharib, S.A.; Dawood, A.; Luo, W. The therapeutic effect of florfenicol-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan-gelatin shell nanogels against Escherichia coli infection in mice: Running title: Therapeutic effect of florfenicol shell nanogels. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1269, 133847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.; Kim, J.; Acharya, D.; Bajgain, B.; Park, J.; Yoo, S.; Lee, K. A Diarrhoeagenic Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) Infection Outbreak That Occurred among Elementary School Children in Gyeongsangbuk-Do Province of South Korea Was Associated with Consumption of Water-Contaminated Food Items. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Huo, M.; Ma, W.; Mi, K.; Xu, X.; Algharib, S.A.; Xie, S.; Huang, L. Application of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Develop a Veterinary Amorphous Enroflfloxacin Solid Dispersion. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, A.; Algharib, S.A.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, T.; Qi, M.; Delai, K.; Hao, Z.; Marawan, M.A.; Shirani, I.; Guo, A. Mycoplasmas as Host Pantropic and Specific Pathogens: Clinical Implications, Gene Transfer, Virulence Factors, and Future Perspectives. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 855731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, H.; Guo, B.; Dong, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, P.X. Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials 2017, 122, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, H.; Hussain, M.; Wang, H.; Zhou, N.; Tao, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, J. Injectable and pH-Sensitive Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels with On-Demand Release of Antimicrobial Peptides for Infected Wound Healing. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 3049–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Xiong, H.; Zhou, D.; Jing, X.; Huang, Y. Ion-assisted fabrication of neutral protein crosslinked sodium alginate nanogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.V.; Boppana, R.; Krishna, M.G.; Mutalik, S.; Kalyane, N.V. pH-responsive interpenetrating network hydrogel beads of poly(acrylamide)-g-carrageenan and sodium alginate for intestinal targeted drug delivery: Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algharib, S.A.; Dawood, A.; Zhou, K.; Chen, D.; Li, C.; Meng, K.; Zhang, A.; Luo, W.; Ahmed, S.; Huang, L.; et al. Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles by ionotropic gelation technique: Effects of formulation parameters and in vitro characterization. J. Mol. Struc. 2022, 1252, 132129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Phil, L.; Sohail, M.; Hasnat, M.; Baig, M.; Ihsan, A.U.; Shumzaid, M.; Kakar, M.U.; Mehmood, K.T.; Akabar, M.D.; et al. Chitosan oligosaccharide (COS): An overview. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 827–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, K.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Tao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Meng, K.; Shabbir, M.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; et al. Solid lipid nanoparticles with enteric coating for improving stability, palatability, and oral bioavailability of enrofloxacin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhao, L. Chitosan Nanoparticles to Enhance the Inhibitory Effect of Natamycin on Candida albicans. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 6644567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Liu, J.; Algharib, S.A.; Chen, W. Antibacterial activity of enrofloxacin loaded gelatin-sodium alginate composite nanogels against intracellular Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 23, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Lu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Hao, Z.; Dawood, A.; Chen, Y.; Schieck, E.; Hu, C.; et al. Novel mycoplasma nucleomodulin MbovP475 decreased cell viability by regulating expression of CRYAB and MCF2L2. Virulence 2022, 13, 1590–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraich, G.S.; Sidhu, P.K.; Daundkar, P.S.; Kaur, G.; Sharma, S.K. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characterization of ceftiofur crystalline-free acid following subcutaneous administration in domestic goats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 40, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Du, J.F.; Hu, M.; Qi, J.; Cai, Y.; Niu, W.; Liu, Y. Analysis of mechanisms of resistance and tolerance of Escherichia coli to enrofloxacin. Ann. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, K.; Hao, H.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z. Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Enrofloxacin Against Escherichia coli in Broilers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Luo, W.; Pan, Y.; Qu, W.; Xie, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y. Antibacterial activity of combined aditoprim and sulfamethoxazole against Escherichia coli from swine and a dose regimen based on pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 45, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, X.; Pang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Liu, J. Biointerfacial self-assembly generates lipid membrane coated bacteria for enhanced oral delivery and treatment. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakstad, O.G.; Aasbakk, K.; Maeland, J.A. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, A.; Xiao, M.; Li, Z.; Luo, W.; Pan, Y.; Qu, W.; Xie, S. Composite inclusion complexes containing hyaluronic acid/chitosan nanosystems for dual responsive enrofloxacin release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algharib, S.A.; Dawood, A.; Zhou, K.; Chen, D.; Li, C.; Meng, K.; Maa, M.K.; Ahmed, S.; Huang, L.; Xie, S. Designing, structural determination and biological effects of rifaximin loaded chitosan-carboxymethyl chitosan nanogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 248, 116782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, Y.; Assis, R.Q.; Tupuna-Yerovi, D.S.; Rios, A. Influence of ph on the properties of sodium alginate films with norbixin salt. J. Food Process. Pres. 2020, 44, e14475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alborzi, S.; Lim, L.T.; Kakuda, Y. Release of folic acid from sodium alginate-pectin-poly(ethylene oxide) electrospun fibers under in vitro conditions. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisha, P.; Ranjana, G.; Ashok, R.; Kymonil, K.M.; Shubhini, S.A. Controlled release theophylline loaded bouyant sodium alginate microbeads for prolonged drug delivery to gastric mucosa. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 4, 758–762. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Song, R.; Sun, G.; Kong, M.; Bao, Z.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Cha, D.; Park, H.; Chen, X. Immobilization of coacervate microcapsules in multilayer sodium alginate beads for efficient oral anticancer drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ju, M.; Guan, D.; Song, W.; Algharib, S.A.; Luo, W. Composite inclusion complexes containing sodium alginate composite nanogels for ph-responsive valnemulin hydrochloride release. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1263, 133054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algharib, S.A.; Dawood, A.; Xie, S. Nanoparticles for treatment of bovine Staphylococcus aureus mastitis. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cheng, C.; Nie, S.; Wang, L.; Nie, C.; Sun, S.; Zhao, C. Graphene oxide linked sulfonate-based polyanionic nanogels as biocompatible, robust and versatile modifiers of ultrafiltration membranes. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6143–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, C.A.S.; Correa, D.S.; Zucolotto, V. Polycaprolactone nanofiber mats decorated with photoresponsive nanogels and silver nanoparticles: Slow release for antibacterial control. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hao, H.; Huang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, D.; Yuan, Z. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Integration and Modeling of Enrofloxacin in Swine for Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Chitosan Oligosaccharide (mg/mL) | Sodium Alginate (mg/mL) | CaCl2 (mg/mL) | Enrofloxacin (mg/mL) | Loading Capacity (%) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 2 | 0.1 | 5 | 15.3 ± 0.8 | 63.7 ± 0.7 |
| 4 | 2 | 0.2 | 15 | 18.5 ± 0.3 | 65.2 ± 0.4 |
| 8 | 2 | 0.4 | 10 | 25.7 ± 0.9 | 68.3 ± 0.2 |
| 8 | 8 | 0.2 | 5 | 26.6 ± 0.5 | 72.4 ± 0.8 |
| 12 | 4 | 0.2 | 10 | 21.5 ± 1.3 | 71.3 ± 1.3 |
| 8 | 4 | 01 | 15 | 20.1 ± 0.5 | 65.8 ± 0.5 |
| 4 | 2 | 0.1 | 10 | 21.4 ± 0.4 | 61.4 ± 0.8 |
| 12 | 8 | 0.4 | 15 | 20.1 ± 1.7 | 71.4 ± 0.9 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.1 | 10 | 23.9 ± 1.5 | 63.2 ± 1.1 |
| pH Value | Mean Particles Diameter (nm) | Polydispersity Index | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 | 168.6 ± 4.2 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | 38.7 ± 0.75 |
| 7.4 | 134.4 ± 3.2 | 0.65 ± 0.03 | −36.5 ± 0.43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, W.; Ju, M.; Liu, J.; Algharib, S.A.; Dawood, A.S.; Xie, S. Intelligent-Responsive Enrofloxacin-Loaded Chitosan Oligosaccharide–Sodium Alginate Composite Core-Shell Nanogels for On-Demand Release in the Intestine. Animals 2022, 12, 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192701
Luo W, Ju M, Liu J, Algharib SA, Dawood AS, Xie S. Intelligent-Responsive Enrofloxacin-Loaded Chitosan Oligosaccharide–Sodium Alginate Composite Core-Shell Nanogels for On-Demand Release in the Intestine. Animals. 2022; 12(19):2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192701
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Wanhe, Mujie Ju, Jinhuan Liu, Samah Attia Algharib, Ali Sobhy Dawood, and Shuyu Xie. 2022. "Intelligent-Responsive Enrofloxacin-Loaded Chitosan Oligosaccharide–Sodium Alginate Composite Core-Shell Nanogels for On-Demand Release in the Intestine" Animals 12, no. 19: 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192701
APA StyleLuo, W., Ju, M., Liu, J., Algharib, S. A., Dawood, A. S., & Xie, S. (2022). Intelligent-Responsive Enrofloxacin-Loaded Chitosan Oligosaccharide–Sodium Alginate Composite Core-Shell Nanogels for On-Demand Release in the Intestine. Animals, 12(19), 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192701







