Changes in Stereotypies: Effects over Time and over Generations
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
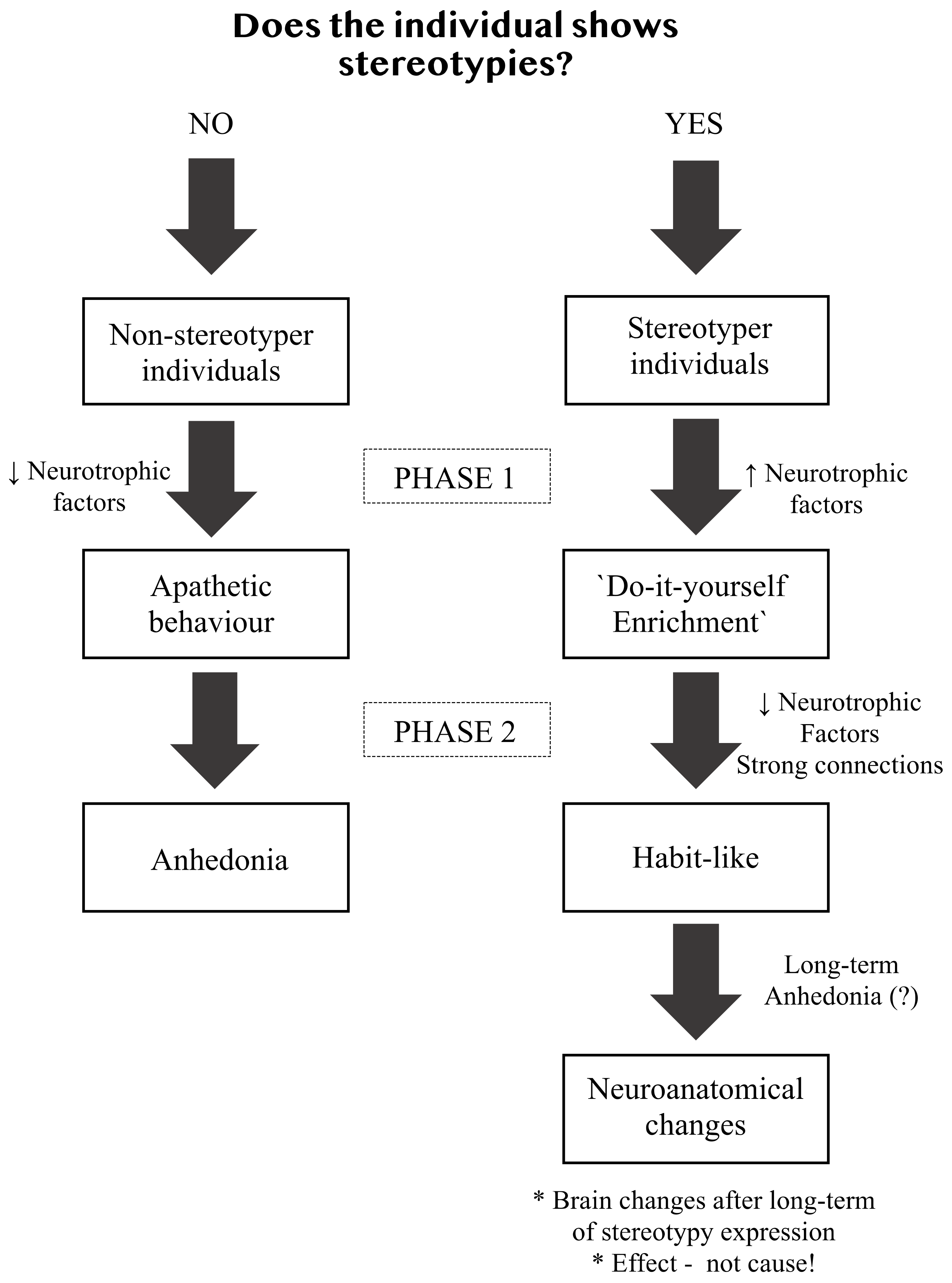
2. Stereotypies as Animal Welfare Indicators
3. Why Environmental Enrichment Reduces Stereotypies
4. Are There Consequences in the Offspring?
5. Epigenetic Processes Driving Fetal Programming
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broom, D.M. Stereotypies as Animal Welfare Indicators BT. In Indicators Relevant to Farm Animal Welfare: A Seminar in the CEC Programme of Coordination of Research on Animal Welfare, Organized by Dr. D. Smidt, and Held in Mariensee, Germany, 9–10 November 1982; Smidt, D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 81–87. ISBN 978-94-009-6738-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dantzer, R. Stress, Stereotypies and Welfare. Behav. Process. 1991, 25, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.J. Stereotypies and Suffering. Behav. Process. 1991, 25, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, D.M.; Johnson, K.G. Assessing Welfare: Long-Term Responses. In Stress and Animal Welfare; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 111–144. [Google Scholar]
- Broom, D.M. Broom and Fraser’s Domestic Animal Behaviour and Welfare, 6th ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2022; p. 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, D.M.; Johnson, K.G. Stress and Animal Welfare; Animal Welfare; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 19, ISBN 978-3-030-32152-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, D. The Effect of Straw on the Behaviour of Sows in Tether Stalls. Anim. Prod. 1975, 21, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.; Rushen, J. Stereotypic Animal Behaviour: Fundamentals and Applications to Welfare; CABI Pub: Wallingford, UK, 2006; ISBN 1845934652. [Google Scholar]
- Newberry, R.C. Environmental Enrichment: Increasing the Biological Relevance of Captive Environments. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1995, 44, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, C.; Bateson, M.; Walsh, C.; Bédué, A.; Edwards, S.A. Environmental Enrichment Induces Optimistic Cognitive Biases in Pigs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 139, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandi, Ε.; Kalamari, A.; Touloumi, O.; Lagoudaki, R.; Nousiopoulou, E.; Simeonidou, C.; Spandou, E.; Tata, D.A. Beneficial Effects of Environmental Enrichment on Behavior, Stress Reactivity and Synaptophysin/BDNF Expression in Hippocampus Following Early Life Stress. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 67, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.J.; Nicol, C.J. The “coping” Hypothesis of Stereotypic Behaviour: A Reply to Rushen. Anim. Behav. 1993, 45, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushen, J. The “coping” Hypothesis of Stereotypic Behaviour. Anim. Behav. 1993, 45, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, K.M.D.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.; Donald, R.D.; Robson, S.K.; Ison, S.H.; Jarvis, S.; Brunton, P.J.; Russell, J.A.; Lawrence, A.B. Prenatal Stress Produces Anxiety Prone Female Offspring and Impaired Maternal Behaviour in the Domestic Pig. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 129, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, E.M.; Mulligan, J.; Hall, S.A.; Donbavand, J.E.; Palme, R.; Aldujaili, E.; Zanella, A.J.; Dwyer, C.M. Positive and Negative Gestational Handling Influences Placental Traits and Mother-Offspring Behavior in Dairy Goats. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 157, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardino, T.; Tatemoto, P.; Morrone, B.; Rodrigues, P.H.M.; Zanella, A.J. Piglets Born from Sows Fed High Fibre Diets during Pregnancy Are Less Aggressive Prior to Weaning. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hales, C.N.; Barker, D.J.P. The Thrifty Phenotype Hypothesis: Type 2 Diabetes. Br. Med. Bull. 2001, 60, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, D.M.; Johnson, K.G. Stress and Animal Welfare; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; ISBN 978-0-412-39580-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.H.; Liu, H.G.; Li, J.H.; Bao, J. Effects of Confinement Duration and Parity on Stereotypic Behavioral and Physiological Responses of Pregnant Sows. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 179, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlouw, E.M.C.; Lawrence, A.B.; Ladewig, J.; De Passille, A.M.; Rushen, J.; Schouten, W.G.P. Relationship between Plasma Cortisol and Stereotypic Activities in Pigs. Behav. Process. 1991, 25, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, D. Cortisol: Often Not the Best Indicator of Stress and Poor Welfare. Physiol. News 2017, 107, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.J.; Latham, N.R. Can’t Stop, Won’t Stop: Is Stereotypy a Reliable Animal Welfare Indicator? Anim. Welf. 2004, 13, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Dantzer, R.; Gonyou, H.W.; Curtis, S.E.; Kelley, K.W. Changes in Serum Cortisol Reveal Functional Differences in Frustration-Induced Chain Chewing in Pigs. Physiol. Behav. 1987, 39, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, A.R.K.; Campbell, D.L.M.; Mason, J. Boredom-like States in Mink and Their Behavioural Correlates: A Replicate Study. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 197, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, L.; Buchanan-Smith, H.M. Effects of Predictability on the Welfare of Captive Animals. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 102, 223–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, G.M.; Wiepkema, P.R.; van Ree, J.M. Endogenous Opioids Are Involved in Abnormal Stereotyped Behaviours of Tethered Sows. Neuropeptides 1985, 6, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushen, J.; De Passillé, A.M.; Schouten, W. Stereotypic Behavior, Endogenous Opioids, and Postfeeding Hypoalgesia in Pigs. Physiol. Behav. 1990, 48, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savory, C.J.; Seawright, E.; Watson, A. Stereotyped Behaviour in Broiler Breeders in Relation to Husbandry and Opioid Receptor Blockade. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1992, 32, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fureix, C.; Walker, M.; Harper, L.; Reynolds, K.; Saldivia-Woo, A.; Mason, G. Stereotypic Behaviour in Standard Non-Enriched Cages Is an Alternative to Depression-like Responses in C57BL/6 Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 305, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broom, D.M. Stereotypies and Responsiveness as Welfare Indicators in Stall-Housed Sows. Anim. Prod. 1986, 15, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, A.J.; Broom, D.M.; Hunter, J.C.; Mendl, M.T. Brain Opioid Receptors in Relation to Stereotypies, Inactivity, and Housing in Sows. Physiol. Behav. 1996, 59, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, M.C.; Lawrence, A.B. Food Restriction as a Cause of Stereotypic Behaviour in Tethered Gilts. Anim. Prod. 1987, 45, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaibold, U.; Pillay, N. Stereotypic Behaviour Is Genetically Transmitted in the African Striped Mouse Rhabdomys pumilio. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2001, 74, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, L.; Heller, K.; Bildsøe, M. Stereotypies in Female Farm Mink (Mustela vison) May Be Genetically Transmitted and Associated with Higher Fertility Due to Effects on Body Weight. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2004, 86, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijichi, C.L.; Collins, L.M.; Elwood, R.W. Evidence for the Role of Personality in Stereotypy Predisposition. Anim. Behav. 2013, 85, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Pillay, N. Association between Personality and Stereotypic Behaviours in the African Striped Mouse Rhabdomys dilectus. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 174, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Pillay, N. Is Wheel Running a Re-Directed Stereotypic Behaviour in Striped Mice Rhabdomys dilectus? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 204, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, L.A.; Tribe, A. Prevalence and Cause of Stereotypic Behaviour in Common Wombats (Vombatus ursinus) Residing in Australian Zoos. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 105, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Duan, H.; Wang, C. Effects of Ambient Environmental Factors on the Stereotypic Behaviors of Giant Pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.; Stojanovski, K.; Melotti, L.; Reichlin, T.S.; Palme, R.; Würbel, H. Effects of Stereotypic Behaviour and Chronic Mild Stress on Judgement Bias in Laboratory Mice. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 174, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Uramura, K.; Nambu, T.; Yada, T.; Goto, K.; Yanagisawa, M.; Sakurai, T. Orexin-Induced Hyperlocomotion and Stereotypy Are Mediated by the Dopaminergic System. Brain Res. 2000, 873, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.J.; Nicol, C.J. Stereotypic Behaviour Affects Environmental Preference in Bank Voles, Clethrionomys glareolus. Anim. Behav. 1991, 41, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-León, M.; Bowman, J.; Bursian, S.; Filion, H.; Galicia, D.; Kanefsky, J.; Napolitano, A.; Palme, R.; Schulte-Hostedde, A.; Scribner, K.; et al. Environmentally Enriched Male Mink Gain More Copulations than Stereotypic, Barren-Reared Competitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebelt, D.; Zanella, A.J.; Unshelm, J. Physiological Correlates Associated with Cribbing Behaviour in Horses: Changes in Thermal Threshold, Heart Rate, Plasma β-Endorphin and Serotonin. Equine Vet. J. 1998, 30, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmkvist, J.; Brix, B.; Henningsen, K.; Wiborg, O. Hippocampal Neurogenesis Increase with Stereotypic Behavior in Mink (Neovison vison). Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 229, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, D.T.; Lucki, I. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Regulation, Functional Implications, and Contribution to Disease Pathology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 232–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, D.M.; Fonseca, R.S.; Kokovay, E. The Role of Adult Neurogenesis in Psychiatric and Cognitive Disorders. Brain Res. 2017, 1655, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briefer Freymond, S.; Bardou, D.; Briefer, E.F.; Bruckmaier, R.; Fouché, N.; Fleury, J.; Maigrot, A.-L.; Ramseyer, A.; Zuberbühler, K.; Bachmann, I. The Physiological Consequences of Crib-Biting in Horses in Response to an ACTH Challenge Test. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 151, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svendsen, P.M.; Palme, R.; Malmkvist, J. Novelty Exploration, Baseline Cortisol Level and Fur-Chewing in Farm Mink with Different Intensities of Stereotypic Behaviour. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 147, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.A.; van Lierop, M.; Mason, G.; Pillay, N. Increased Reproductive Output in Stereotypic Captive Rhabdomys Females: Potential Implications for Captive Breeding. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2010, 123, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, J.P.; Mason, G.J. Evidence for a Relationship between Cage Stereotypies and Behavioural Disinhibition in Laboratory Rodents. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 136, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, P.E.; Pijoan, C.; Jacobson, L.D.; Algers, B. Stereotyped Behaviour, Social Interactions and Suckling Pattern of Pigs Housed in Groups or in Single Crates. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1992, 35, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyne, A. Meta-Analytic Review of the Effects of Enrichment on Stereotypic Behavior in Zoo Mammals. Zoo Biol. 2006, 25, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.; Clubb, R.; Latham, N.; Vickery, S. Why and How Should We Use Environmental Enrichment to Tackle Stereotypic Behaviour? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 102, 163–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.A.; Mason, G.; Pillay, N. Early Environmental Enrichment Protects Captive-Born Striped Mice against the Later Development of Stereotypic Behaviour. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2011, 135, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simpson, J.; Kelly, J.P. The Impact of Environmental Enrichment in Laboratory Rats—Behavioural and Neurochemical Aspects. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 222, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suemaru, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Aso, H.; Watanabe, M. Environmental Enrichment Alleviates Cognitive and Behavioral Impairments in EL Mice. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 85, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griñán-Ferré, C.; Izquierdo, V.; Otero, E.; Puigoriol-Illamola, D.; Corpas, R.; Sanfeliu, C.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D.; Pallàs, M. Environmental Enrichment Improves Cognitive Deficits, AD Hallmarks and Epigenetic Alterations Presented in 5xFAD Mouse Model. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadry, V.O.; Barreto, R.E. Environmental Enrichment Reduces Aggression of Pearl Cichlid, Geophagus brasiliensis, during Resident-Intruder Interactions. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2010, 8, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, F.; Winblad, B.; Mohammed, A.H. Psychological Stress and Environmental Adaptation in Enriched vs. Impoverished Housed Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 73, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotrschal, A.; Taborsky, B. Environmental Change Enhances Cognitive Abilities in Fish. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbesson, L.O.E.; Braithwaite, V.A. Environmental Effects on Fish Neural Plasticity and Cognition. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 81, 2151–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gro, A.; Salvanes, V.; Moberg, O.; Ebbesson, L.O.E.; Nilsen, O.; Jensen, K.H.; Braithwaite, V.A. Environmental Enrichment Promotes Neural Plasticity and Cognitive Ability in Fish. Proc. R Soc. B 2013, 280, 20131331. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.M.; Luo, Y.; Ward, C.; Redd, K.; Gibson, R.; Kuczaj, S.A.; McCoy, J.G. Environmental Enrichment: Effects on Spatial Memory and Hippocampal CREB Immunoreactivity. Physiol. Behav. 2001, 73, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro-Piquero, P.; Zancada-Menendez, C.; Begega, A.; Rubio, S.; Arias, J.L. Effects of Environmental Enrichment on Anxiety Responses, Spatial Memory and Cytochrome c Oxidase Activity in Adult Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2013, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, G.P.; Olin, A.; O’Riordan, K.; Hullinger, R.; Burger, C. Environmental Enrichment Improves Hippocampal Function in Aged Rats by Enhancing Learning and Memory, LTP, and MGluR5-Homer1c Activity. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohline, S.M.; Abraham, W.C. Environmental Enrichment Effects on Synaptic and Cellular Physiology of Hippocampal Neurons. Neuropharmacology 2018, 145, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mychasiuk, R.; Zahir, S.; Schmold, N.; Ilnytskyy, S.; Kovalchuk, O.; Gibb, R. Parental Enrichment and Offspring Development: Modifications to Brain, Behavior and the Epigenome. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 228, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, K.M.; McLaughlin, K.J.; Wright, R.L.; Bryce Ortiz, J.; Anouti, D.P.; Mika, A.; Diamond, D.M.; Conrad, C.D. Environmental Enrichment Protects against the Effects of Chronic Stress on Cognitive and Morphological Measures of Hippocampal Integrity. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2012, 97, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedro-Piquero, P.; De Bartolo, P.; Petrosini, L.; Zancada-Menendez, C.; Arias, J.L.; Begega, A. Astrocytic Plasticity as a Possible Mediator of the Cognitive Improvements after Environmental Enrichment in Aged Rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2014, 114, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroncelli, L.; Braschi, C.; Spolidoro, M.; Begenisic, T.; Sale, A.; Maffei, L. Nurturing Brain Plasticity: Impact of Environmental Enrichment. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 17, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampon, C.; Jiang, C.H.; Dong, H.; Tang, Y.-P.; Lockhart, D.J.; Schultz, P.G.; Tsien, J.Z.; Hu, Y. Effects of Environmental Enrichment on Gene Expression in the Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12880–12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggio, M.G.; Mandolesi, L.; Federico, F.; Spirito, F.; Ricci, B.; Gelfo, F.; Petrosini, L. Environmental Enrichment Promotes Improved Spatial Abilities and Enhanced Dendritic Growth in the Rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 163, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia, G.; Yage, A.G.; Garca-Verdugo, J.M.; Mora, F. Environmental Enrichment Promotes Neurogenesis and Changes the Extracellular Concentrations of Glutamate and GABA in the Hippocampus of Aged Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 70, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidar, J.; Campderrich, I.; Jansson, E.; Wichman, A.; Winberg, S.; Keeling, L.; Løvlie, H. Environmental Complexity Buffers against Stress-Induced Negative Judgement Bias in Female Chickens. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goes, T.C.; Antunes, F.D.; Teixeira-Silva, F. Environmental Enrichment for Adult Rats: Effects on Trait and State Anxiety. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.A.; Souza, T.M.O.; de Andrade, J.S.; Silva, M.F.S.; Antunes, H.K.M.; Le Sueur-Maluf, L.; Céspedes, I.C.; Viana, M.B. Environmental Enrichment Decreases Avoidance Responses in the Elevated T-Maze and Delta FosB Immunoreactivity in Anxiety-Related Brain Regions. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 344, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuaid, R.J.; Dunn, R.; Jacobson-Pick, S.; Anisman, H.; Audet, M.-C. Post-Weaning Environmental Enrichment in Male CD-1 Mice: Impact on Social Behaviors, Corticosterone Levels and Prefrontal Cytokine Expression in Adulthood. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rault, J.-L.; Lawrence, A.J.; Ralph, C.R. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Serum as an Animal Welfare Indicator of Environmental Enrichment in Pigs. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2018, 65, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosaferi, B.; Babri, S.; Mohaddes, G.; Khamnei, S.; Mesgari, M. Post-Weaning Environmental Enrichment Improves BDNF Response of Adult Male Rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2015, 46, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novkovic, T.; Mittmann, T.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. BDNF Contributes to the Facilitation of Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity and Learning Enabled by Environmental Enrichment. Hippocampus 2015, 25, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, A.M.; Kelly, Á.M. Lifelong Environmental Enrichment in the Absence of Exercise Protects the Brain from Age-Related Cognitive Decline. Neuropharmacology 2018, 145, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.M.; Bush, S.J.; Summers, K.M.; Hume, D.A.; Lawrence, A.B. Environmentally Enriched Pigs Have Transcriptional pro Fi Les Consistent with Neuroprotective Effects and Reduced Microglial Activity. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 350, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, D.L. Sensory Stimulation as Environmental Enrichment for Captive Animals: A Review. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 118, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, M.; Woo, C. Environmental Enrichment and Successful Aging. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakubo, A.; Jarskog, L.F.; Lieberman, J.A.; Gilmore, J.H. Prenatal Exposure to Maternal Infection Alters Cytokine Expression in the Placenta, Amniotic Fluid, and Fetal Brain. Schizophr. Res. 2001, 47, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnaudéry, M.; Maccari, S. Epigenetic Programming of the Stress Response in Male and Female Rats by Prenatal Restraint Stress. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 57, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulon, M.; Wellman, C.L.; Marjara, I.S.; Janczak, A.M.; Zanella, A.J. Early Adverse Experience Alters Dendritic Spine Density and Gene Expression in Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus in Lambs. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, U.; Feldon, J.; Fatemi, S.H. In-Vivo Rodent Models for the Experimental Investigation of Prenatal Immune Activation Effects in Neurodevelopmental Brain Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 1061–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatemoto, P.; Bernardino, T.; Alves, L.; Zanella, A.J. Sham-Chewing in Sows Is Associated with Decreased Fear Responses in Their Offspring. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemoto, P.; Bernardino, T.; Morrone, B.; Queiroz, M.R. Stereotypic Behavior in Sows Is Related to Emotionality Changes in the Offspring. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemoto, P.; Bernardino, T.; Alves, L.; Cristina, A.; Souza, D.O.; Palme, R.; José, A. Environmental Enrichment for Pregnant Sows Modulates HPA-Axis and Behavior in the o Ff Spring. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2019, 220, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, R.; Steibel, J.P.; Siegford, J.M.; Zanella, A.J. Effects of Early Weaning and Social Isolation on the Expression of Glucocorticoid and Mineralocorticoid Receptor and 11beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase 1 and 2 MRNAs in the Frontal Cortex and Hippocampus of Piglets. Brain Res. 2006, 1067, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, M. The Long-Term Behavioural Consequences of Prenatal Stress. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mychasiuk, R. Epigenetics of Brain Plasticity and Behavior. Int. Encycl. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 2, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolvi, S.; Karlsson, L.; Bridgett, D.J.; Korja, R.; Huizink, A.C.; Kataja, E.-L.; Karlsson, H. Maternal Prenatal Stress and Infant Emotional Reactivity Six Months Postpartum. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 199, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattane, N.; Richetto, J.; Cattaneo, A. Prenatal Exposure to Environmental Insults and Enhanced Risk of Developing Schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Focus on Biological Pathways and Epigenetic Mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 117, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moisiadis, V.G.; Matthews, S.G. Glucocorticoids and Fetal Programming Part 2: Mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowden, A.L.; Valenzuela, O.A.; Vaughan, O.R.; Jellyman, J.K.; Forhead, A.J. Glucocorticoid Programming of Intrauterine Development. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, S121–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupien, S.J.; Lepage, M. Stress, Memory, and the Hippocampus: Can’t Live with It, Can’t Live without It. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 127, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcewen, B.S. Stress and Hippocampal LTD. Neuroscience 1997, 3, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, T.; Powell, T.L. Role of the Placenta in Fetal Programming: Underlying Mechanisms and Potential Interventional Approaches. Clin. Sci. 2007, 113, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckl, J.R. Prenatal Glucocorticoids and Long-Term Programming. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 151, U49–U62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welberg, L.A.M.; Thrivikraman, K.V.; Plotsky, P.M. Chronic Maternal Stress Inhibits the Capacity to Up-Regulate Placental 11-Beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 2 Activity. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 186, R7–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Hidaka, N.; Kawagoe, C.; Odagiri, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Ishizuka, Y.; Hashiguchi, H.; Takeda, R.; Nishimori, T.; et al. Prenatal Psychological Stress Causes Higher Emotionality, Depression-like Behavior, and Elevated Activity in the Hypothalamo-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 59, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkman, B.; Boissy, A.; Meunier-Salaün, M.C.; Canali, E.; Jones, R.B. A Critical Review of Fear Tests Used on Cattle, Pigs, Sheep, Poultry and Horses. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 340–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, R.D.; Healy, S.D.; Lawrence, A.B.; Rutherford, K.M.D. Emotionality in Growing Pigs: Is the Open Field a Valid Test? Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijn, L.; Antonides, A.; Aalderink, D.; Nordquist, R.E.; van der Staay, F.J. Does Litter Size Affect Emotional Reactivity, Spatial Learning and Memory in Piglets? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 178, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, K.M.D.; Donald, R.D.; Lawrence, A.B.; Wemelsfelder, F. Qualitative Behavioural Assessment of Emotionality in Pigs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 139, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogi, K.; Nagasawa, M.; Kikusui, T. Developmental Consequences and Biological Significance of Mother-Infant Bonding. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branchi, I.; Curley, J.P.; Andrea, I.D.; Cirulli, F.; Champagne, F.A.; Alleva, E.; Regina, V. Early Interactions with Mother and Peers Independently Build Adult Social Skills and Shape BDNF and Oxytocin Receptor Brain Levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Lei, L.; de Rooij, S.R.; King, S.; Matthews, S.G.; Metz, G.A.S.; Roseboom, T.J.; Szyf, M. Prenatal Stress and Epigenetics. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 117, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsankova, N.; Renthal, W.; Kumar, A.; Nestler, E.J. Epigenetic Regulation in Psychiatric Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, K.D.; Connor, C.M.; Campan, M.; Long, T.I.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Biniszkiewicz, D.; Jaenisch, R.; Laird, P.W.; Akbarian, S. DNA Methylation in the Human Cerebral Cortex Is Dynamically Regulated throughout the Life Span and Involves Differentiated Neurons. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankiewicz, A.M.; Swiergiel, A.H.; Lisowski, P. Epigenetics of Stress Adaptations in the Brain. Brain Res. Bull. 2013, 98, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Siyahhan Julnes, P.; Chen, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Walton, E.; Calhoun, V.D. The Association of DNA Methylation and Brain Volume in Healthy Individuals and Schizophrenia Patients. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 169, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.-S.; Yang, J.-J.; Morey, T.E.; Gravenstein, N.; Seubert, C.N.; Resnick, J.L.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Martynyuk, A.E. Role of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Transmitting the Effects of Neonatal Sevoflurane Exposure to the next Generation of Male, but Not Female, Rats. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 121, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall’Aglio, L.; Muka, T.; Cecil, C.A.M.; Bramer, W.M.; Verbiest, M.M.P.J.; Nano, J.; Hidalgo, A.C.; Franco, O.H.; Tiemeier, H. The Role of Epigenetic Modifications in Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Systematic Review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 94, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isles, A.R.; Davies, W.; Wilkinson, L.S. Genomic Imprinting and the Social Brain. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.A.; Sweatt, J.D. Covalent Modification of DNA Regulates Memory Formation. Neuron 2007, 53, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gräff, J.; Mansuy, I.M. Epigenetic Codes in Cognition and Behaviour. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 192, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kader, F.; Ghai, M.; Maharaj, L. The Effects of DNA Methylation on Human Psychology. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 346, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSocio, J.E. Epigenetics, Maternal Prenatal Psychosocial Stress, and Infant Mental Health. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2018, 32, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ho, S.-M. Epigenetics Meets Endocrinology. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 46, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, K.J.; Li, X.; Kobor, M.S.; Kippin, T.E.; Bredy, T.W. Epigenetic Mechanisms Mediating Vulnerability and Resilience to Psychiatric Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, M.J. An Epigenetic Framework for Neurodevelopmental Disorders: From Pathogenesis to Potential Therapy. Neuropharmacology 2013, 68, 2–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, S.B.; Szyszkowicz, J.K.; Luheshi, G.N.; Lutz, P.E.; Turecki, G. Plasticity of the Epigenome during Early-Life Stress. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 77, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouliaras, L.; Rutten, B.P.F.; Kenis, G.; Peerbooms, O.; Visser, P.J.; Verhey, F.; van Os, J.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; van den Hove, D.L.A. Epigenetic Regulation in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 90, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griñán-Ferré, C.; Sarroca, S.; Ivanova, A.; Puigoriol-Illamola, D.; Aguado, F.; Camins, A.; Sanfeliu, C.; Pallàs, M. Epigenetic Mechanisms Underlying Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease Hallmarks in 5XFAD Mice. Aging 2016, 8, 664–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Morales, R.; Esteller, M. Opening up the DNA Methylome of Dementia. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, C.J. Insights from Epigenetic Studies on Human Health and Evolution. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 53, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tatemoto, P.; Broom, D.M.; Zanella, A.J. Changes in Stereotypies: Effects over Time and over Generations. Animals 2022, 12, 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192504
Tatemoto P, Broom DM, Zanella AJ. Changes in Stereotypies: Effects over Time and over Generations. Animals. 2022; 12(19):2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192504
Chicago/Turabian StyleTatemoto, Patricia, Donald M. Broom, and Adroaldo J. Zanella. 2022. "Changes in Stereotypies: Effects over Time and over Generations" Animals 12, no. 19: 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192504
APA StyleTatemoto, P., Broom, D. M., & Zanella, A. J. (2022). Changes in Stereotypies: Effects over Time and over Generations. Animals, 12(19), 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192504





