Automated Cardiac Chamber Size and Cardiac Physiology Measurement in Water Fleas by U-Net and Mask RCNN Convolutional Networks
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Flea Culture
2.2. Chemical Exposure
2.3. Video Acquisition
2.4. Training Dataset Preparation
2.5. Performance Validation
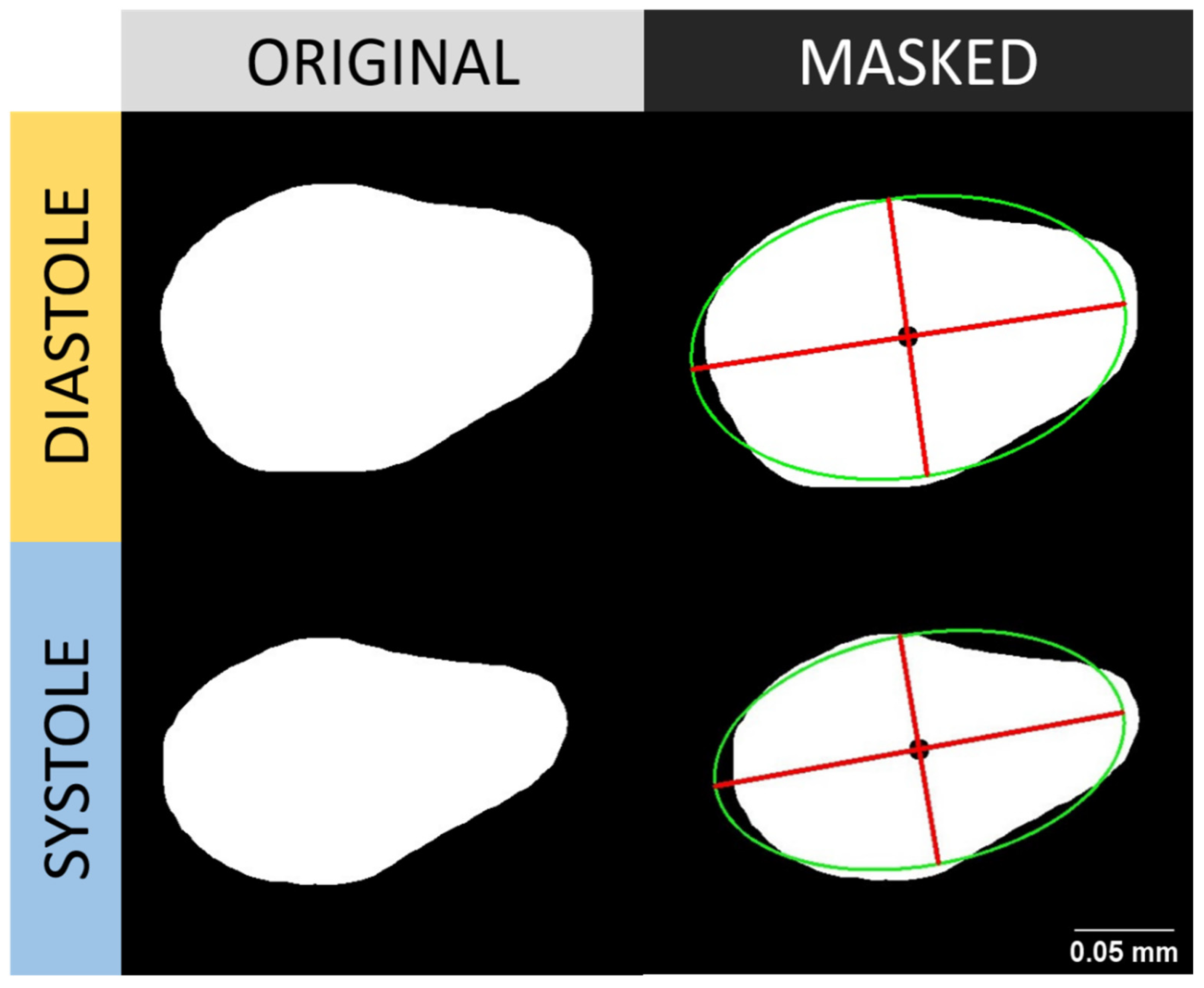
2.6. Volumetric Estimation of Water Flea’s Heart
2.7. Computer Hardware Requirement
2.8. Cardiac Performance Analysis
2.9. Statistical Calculation
3. Results
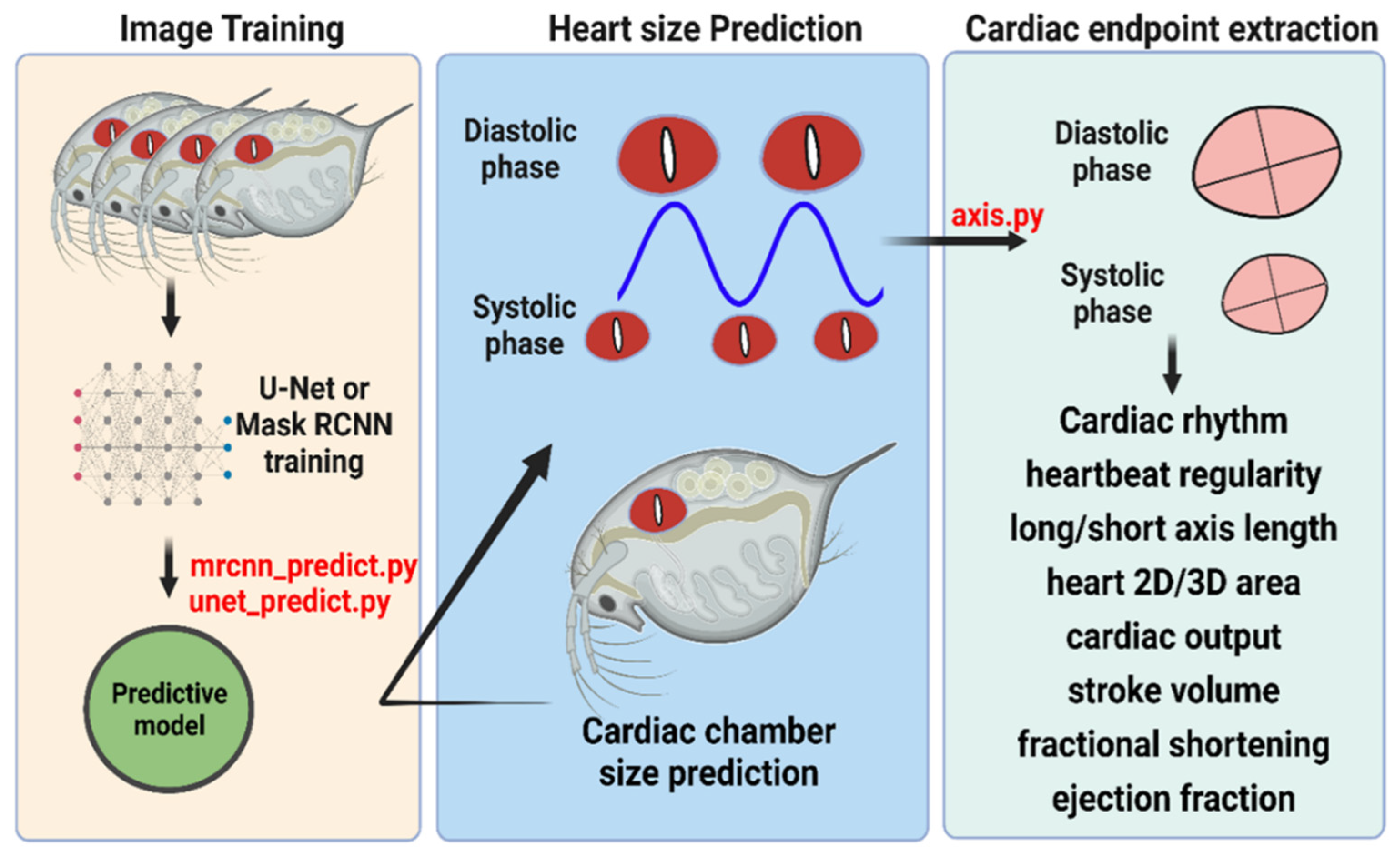
3.1. Overview of Experimental Design and Training Dataset Preparation
3.2. Training and Validation Performance
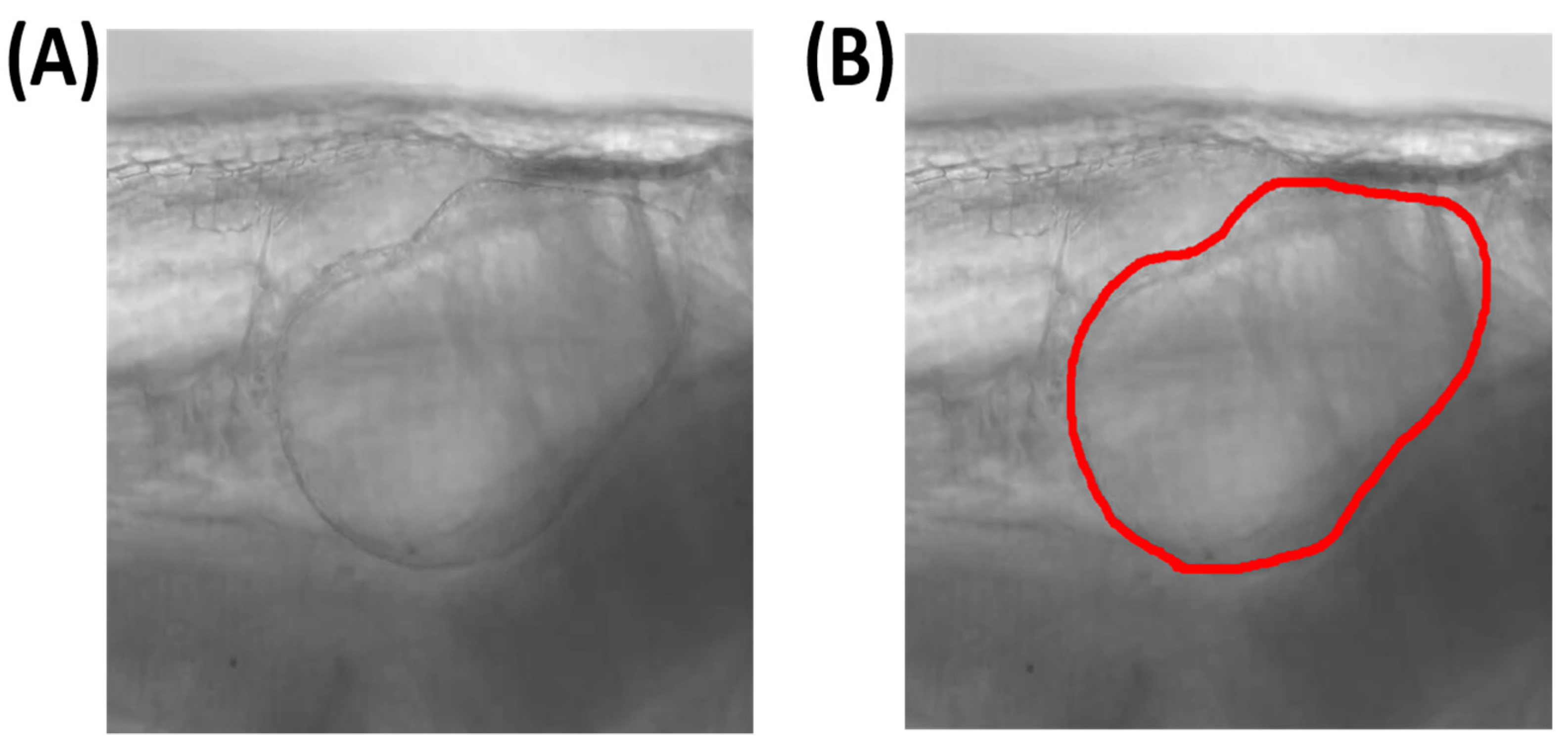
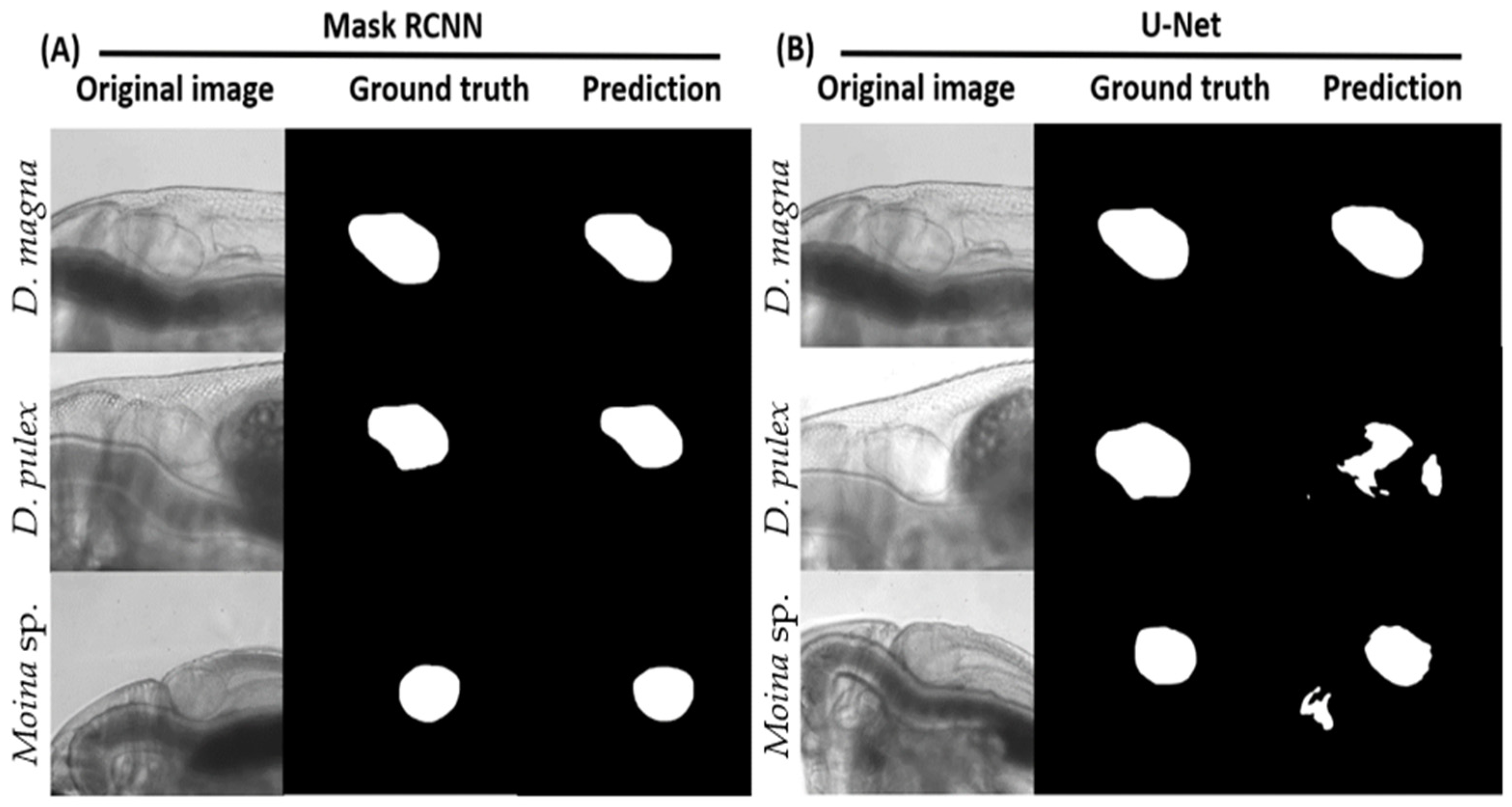
3.3. Testing Process
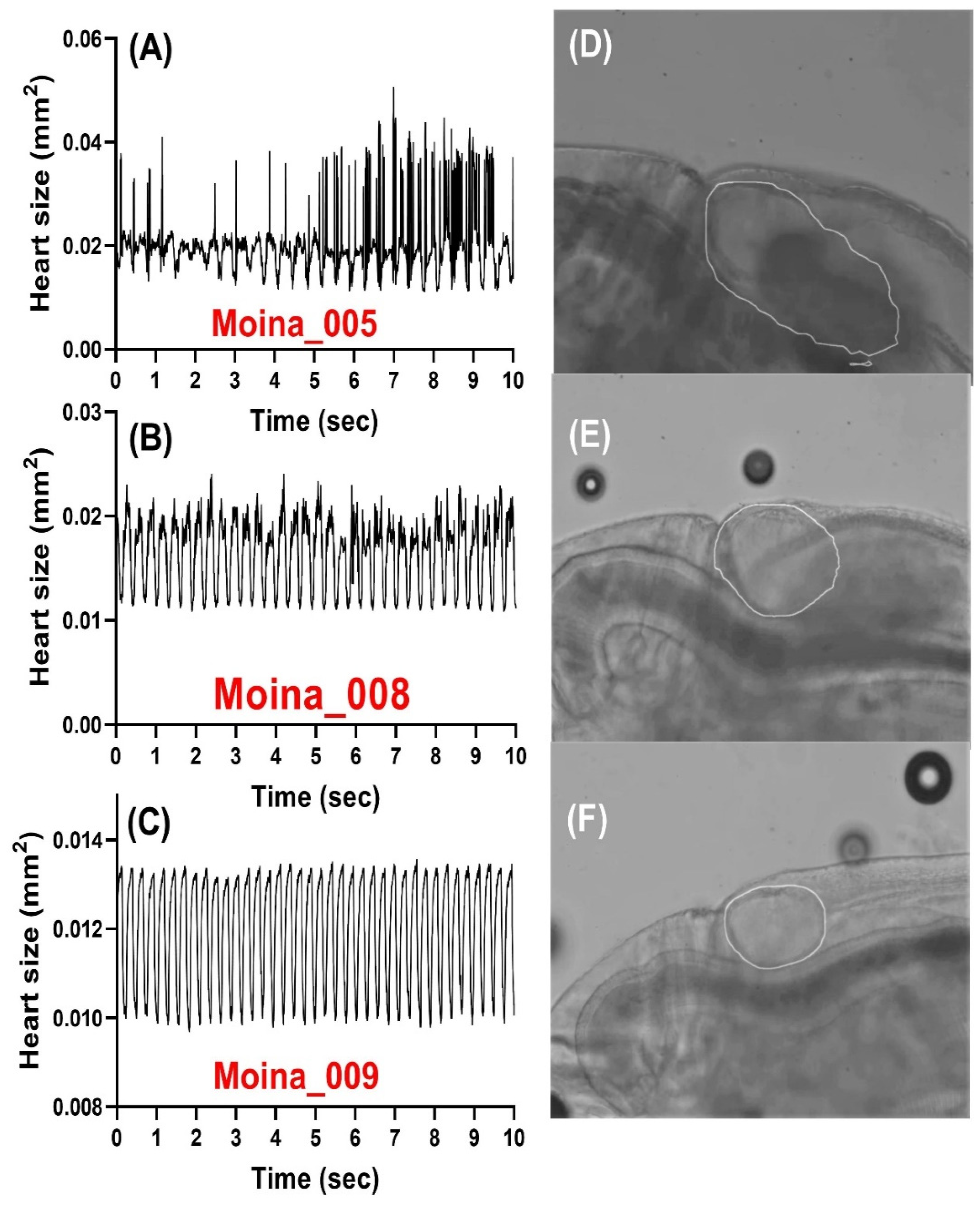
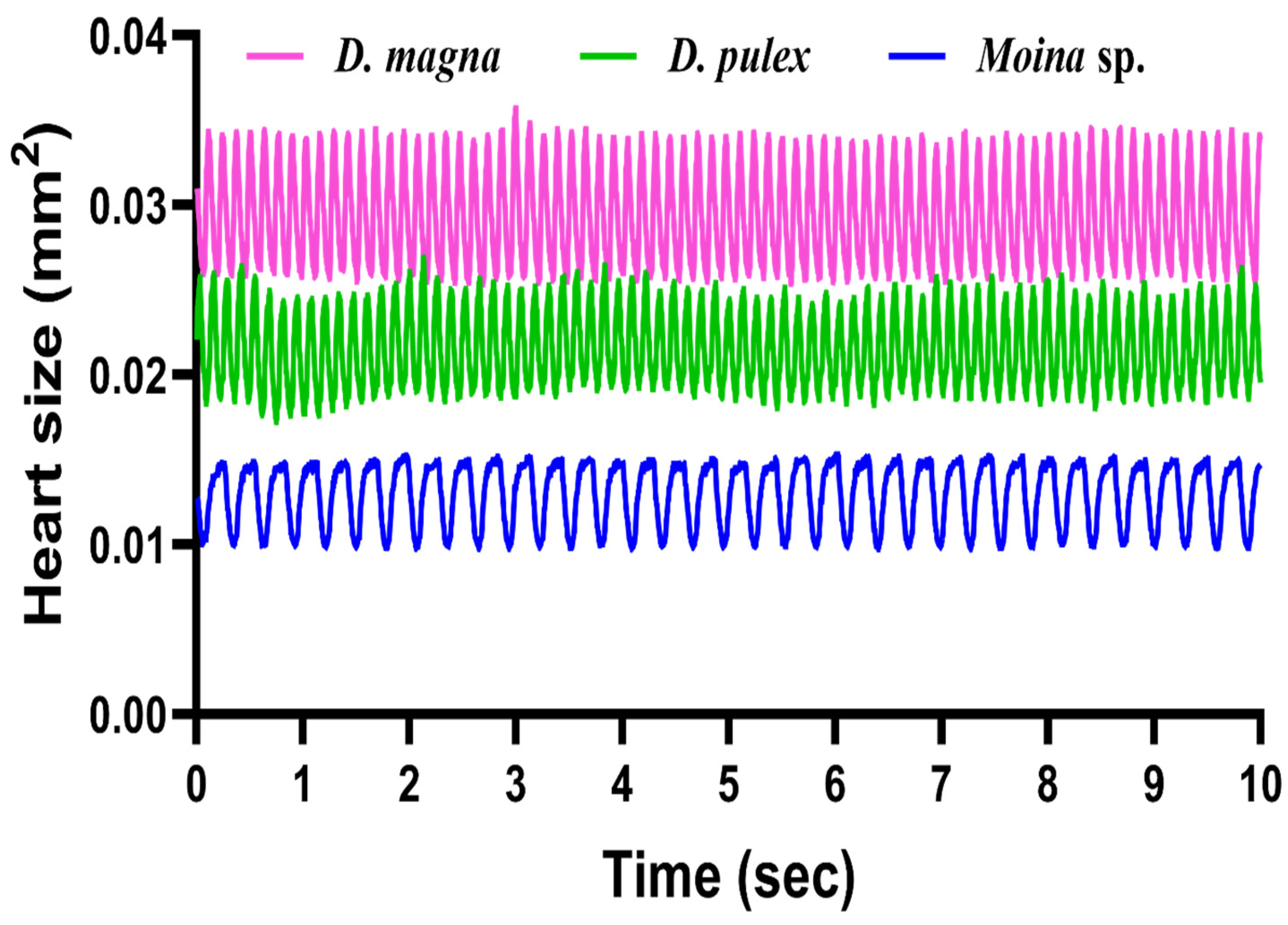
3.4. Analysis of Heart Cardiac Size Change over Time in Three Water Fleas by Mask RCNN
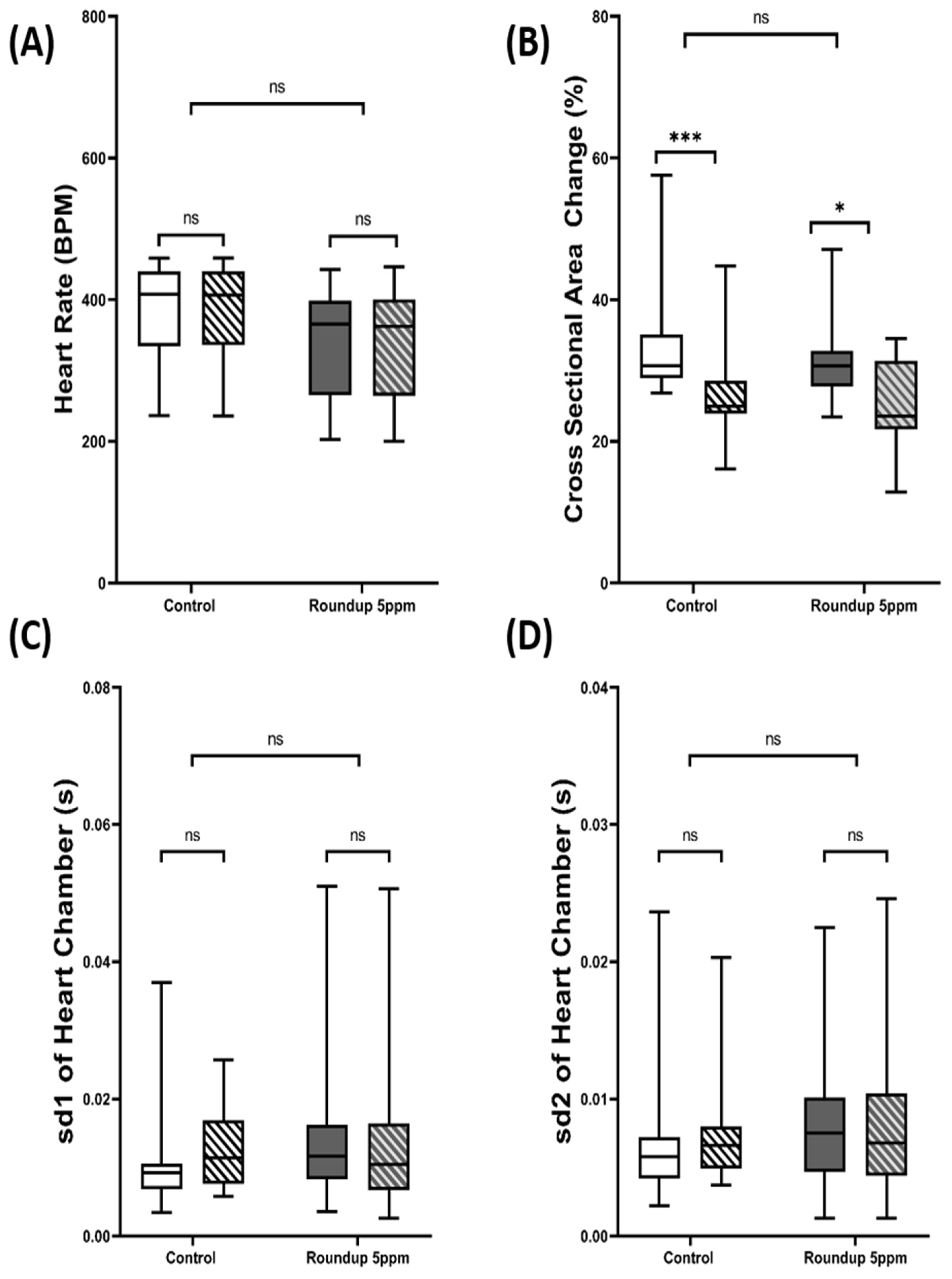
3.5. Validation of Cardiac Physiology Alterations in D. magna after Herbicide Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Smirnov, N.N. Physiology of the Cladocera; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karuthapandi, M.; Rao, D. Cladoceran diversity, distribution and ecological significance. In Arthropod Diversity and Conservation in the Tropics and Sub-Tropics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Berta, C.; Tóthmérész, B.; Wojewódka, M.; Augustyniuk, O.; Korponai, J.; Bertalan-Balázs, B.; Nagy, A.S.; Grigorszky, I.; Gyulai, I. Community response of cladocera to trophic stress by biomanipulation in a shallow oxbow lake. Water 2019, 11, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, C.B.; Somparn, A.; Noller, B. Using zooplankton, Moina micrura Kurz to evaluate the ecotoxicology of pesticides used in paddy fields of Thailand. In Pesticides in the Modern World—Risks and Benefits; INTECH Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 267–280. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Jung, D.; Kho, Y.; Ji, K.; Kim, P.; Ahn, B.; Choi, K. Ecotoxicological assessment of cimetidine and determination of its potential for endocrine disruption using three test organisms: Daphnia magna, Moina macrocopa, and Danio rerio. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.-H.; Shin, Y.-J.; An, Y.-J. Accelerated ecotoxicity of photoreactive nanoparticles on Moina macrocopa. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2017, 32, e2017007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkaczyk, A.; Bownik, A.; Dsudka, J.; Kowal, K.; Ślaska, B. Daphnia magna model in the toxicity assessment of pharmaceuticals: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 763, 143038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.D.; Bartlett, N.J.; Lloyd, V.K. Daphnia as an emerging epigenetic model organism. Genet. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 147892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.L.D.; Antunes, S.C.; Gonçalves, F.; Rocha, O.; Nunes, B. Acute and chronic ecotoxicological effects of four pharmaceuticals drugs on cladoceran Daphnia magna. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 39, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pociecha, A.; Wojtal, A.Z.; Szarek-Gwiazda, E.; Cieplok, A.; Ciszewski, D.; Kownacki, A. Response of Cladocera fauna to heavy metal pollution, based on sediments from subsidence ponds downstream of a mine discharge (S. Poland). Water 2019, 11, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Nandini, S. Review of recent ecotoxicological studies on cladocerans. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2006, 41, 1417–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhett, A.L.; Santangelo, J.M.; Bozelli, R.L.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Farjalla, V.F. An overview of the contribution of studies with cladocerans to environmental stress research. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2015, 27, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [OECD] Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Guideline for testing of chemicals. Daphnia sp., Acute immobilisation test. In OECD Guidel. No 202; OECD: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Peake, B.M.; Braund, R.; Tong, A.Y.; Tremblay, L.A. Impact of pharmaceuticals on the environment. In The Life-Cycle of Pharmaceuticals in the Environment; Peake, B.M., Braund, R., Tong, A.Y.C., Tremblay, L.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 109–152. [Google Scholar]
- Santoso, F.; Krylov, V.V.; Castillo, A.L.; Saputra, F.; Chen, H.-M.; Lai, H.-T.; Hsiao, C.-D. Cardiovascular performance measurement in water fleas by utilizing high-speed videography and imagej software and its application for pesticide toxicity assessment. Animals 2020, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, J.M.; Krijgsman, B. Physiological investigations into the heart function of Daphnia. J. Physiol. 1951, 115, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bownik, A. Physiological endpoints in daphnid acute toxicity tests. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, B.; Gulliver, T.A.; Alzahir, S. Image splicing detection using mask-RCNN. Signal Image Video Process. 2020, 14, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Gan, Z.; Henao, R.; Yuan, X.; Li, C.; Stevens, A.; Carin, L. Variational autoencoder for deep learning of images, labels and captions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, T.; Mai, D.; Bensch, R.; Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Marrakchi, Y.; Böhm, A.; Deubner, J.; Jäckel, Z.; Seiwald, K. U-Net: Deep learning for cell counting, detection, and morphometry. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Kido, S.; Hirano, Y.; Hashimoto, N. Detection and classification of lung abnormalities by use of convolutional neural network (CNN) and regions with CNN features (R-CNN). In Proceedings of the 2018 International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 7–9 January 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Song, B.; Jung, C.; Huang, L. Automatic segmentation and cardiopathy classification in cardiac mri images based on deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 1020–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Ünver, H.M.; Ayan, E. Skin lesion segmentation in dermoscopic images with combination of YOLO and grabcut algorithm. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zuo, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. A value recognition algorithm for pointer meter based on improved Mask-RCNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Information Science and Technology (ICIST), Hulunbuir, China, 2–5 August 2019; pp. 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Karatzas, P.; Melagraki, G.; Ellis, L.J.A.; Lynch, I.; Varsou, D.D.; Afantitis, A.; Tsoumanis, A.; Doganis, P.; Sarimveis, H. Development of deep learning models for predicting the effects of exposure to engineered nanomaterials on Daphnia Magna. Small 2020, 16, 2001080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wei, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wong, K.K. A novel U-Net approach to segment the cardiac chamber in magnetic resonance images with ghost artifacts. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Z.; Deng, J.; Shi, Y.; Tian, M.; Zhuo, C. DeU-Net: Deformable U-Net for 3D Cardiac MRI Video Segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.E.S.; Ferreira, L.D.C.; Peixoto, L.B.; Monaco, C.G.; Gil, M.A.; Ortiz, J. Study of the myocardial contraction and relaxation velocities through Doppler tissue imaging echocardiography: A new alternative in the assessment of the segmental ventricular function. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2002, 78, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baylor, E. Cardiac pharmacology of the cladoceran, Daphnia. Biol. Bull. 1942, 83, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Navarro, A.; Rosas, L.E.; Reyes, J.L. The heart of Daphnia magna: Effects of four cardioactive drugs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 136, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FernáNdez-GonzáLez, M.A.; Gonzalez-Barrientos, J.; Carter, M.J.; Ramos-Jiliberto, R. Parent-to-offspring transfer of sublethal effects of copper exposure: Metabolic rate and life-history traits of Daphnia. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2011, 84, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Shukla, S.; Chopra, A. Physiological responses of heart of tailless fresh water flea Simocephalus vetulus (Crustacea-cladocera) under copper sulphate stress. CIBTech J. Zool 2016, 5, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Bownik, A. Protective effects of ectoine on physiological parameters of Daphnia magna subjected to clove oil-induced anaesthesia. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 16, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.-Y.; Asselman, J.; De Schamphelaere, K.A.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Deforce, D.; Kim, S.D. Effect of β-adrenergic receptor agents on cardiac structure and function and whole-body gene expression in Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnia, K.A.; Saputra, F.; Roldan, M.J.M.; Castillo, A.L.; Huang, J.-C.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Lai, H.-T.; Hsiao, C.-D. Measurement of Multiple Cardiac Performance Endpoints in Daphnia and Zebrafish by Kymograph. Inventions 2021, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Kurnia, K.A.; Saputra, F.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Huang, J.-C.; Roldan, M.J.M.; Lai, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-D. An OpenCV-Based Approach for Automated Cardiac Rhythm Measurement in Zebrafish from Video Datasets. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid-Adar, M.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Goldberger, J.; Greenspan, H. Synthetic data augmentation using GAN for improved liver lesion classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buslaev, A.; Iglovikov, V.I.; Khvedchenya, E.; Parinov, A.; Druzhinin, M.; Kalinin, A.A. Albumentations: Fast and flexible image augmentations. Information 2020, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zedong, H.; Yuan, L. Software implementation of corn grain morphology detection based on OpenCV. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th IEEE International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Yangzhou, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 412–415. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, K.A.; Rimoli, J.J. MicroStructPy: A statistical microstructure mesh generator in Python. SoftwareX 2020, 12, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengoni, M.; Stringhini, D. High level computer vision using opencv. In Proceedings of the 2011 24th SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns, and Images Tutorials, Alagoas, Brazil, 28–30 August 2011; pp. 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ryoo, D.; Balusek, C.; Acharya, A.; Rydmark, M.O.; Linke, D.; Gumbart, J.C. Inward-facing glycine residues create sharp turns in β-barrel membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Chintala, S.; Chanan, G.; Yang, E.; DeVito, Z.; Lin, Z.; Desmaison, A.; Antiga, L.; Lerer, A. Automatic Differentiation in Pytorch. Available online: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=BJJsrmfCZ (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- MacFarland, T.W.; Yates, J.M. Introduction to Nonparametric Statistics for the Biological Sciences Using R; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, T.A.; McCleery, R.H.; Hart, T. Introduction to Statistics for Biology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q. Automatic whole heart segmentation using a two-stage u-net framework and an adaptive threshold window. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 83628–83636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.-H.; Nian, F.-D.; Yu, M.-H.; Li, X. An improved mask R-CNN model for multiorgan segmentation. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8351725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Ning, M.; Si, W.; Liao, X.; Qin, J. 3D deeply-supervised U-net based whole heart segmentation. In International Workshop on Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart, Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop, STACOM 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Quebec City, Canada, 10–14 September 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Du, J.; Liu, H.; Hou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, M. LU-NET: An Improved U-Net for ventricular segmentation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 92539–92546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; An, G.; Liu, Y. Mask R-CNN with feature pyramid attention for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 14th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Beijing, China, 12–16 August 2018; pp. 1194–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, R.O.; Dogan, H.; Bayrak, C.; Kayikcioglu, T. A Two-Phase Approach using Mask R-CNN and 3D U-Net for High-Accuracy Automatic Segmentation of Pancreas in CT Imaging. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 207, 106141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopczyński, T.; Heiman, R.; Woźnicki, P.; Gniewek, P.; Duvernoy, M.-C.; Hallatschek, O.; Hesser, J. Instance Segmentation of Densely Packed Cells Using a Hybrid Model of U-Net and Mask R-CNN. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing, Proceedings of the19th International Conference, ICAISC 2020, Zakopane, Poland, 12–14 October 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 626–635. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Feng, J. CFUN: Combining faster R-CNN and U-net network for efficient whole heart segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.04914. [Google Scholar]
- Vuola, A.O.; Akram, S.U.; Kannala, J. Mask-RCNN and U-net ensembled for nuclei segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; pp. 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Durkee, M.S.; Abraham, R.; Ai, J.; Fuhrman, J.D.; Clark, M.R.; Giger, M.L. Comparing Mask R-CNN and U-Net architectures for robust automatic segmentation of immune cells in immunofluorescence images of Lupus Nephritis biopsies. In Proceedings of the Imaging, Manipulation, and Analysis of Biomolecules, Cells, and Tissues XIX, Online Only, CA, USA, 6–12 March 2021; p. 116470X. [Google Scholar]
- Quoc, T.T.P.; Linh, T.T.; Minh, T.N.T. Comparing U-Net Convolutional Network with Mask R-CNN in Agricultural Area Segmentation on Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th NAFOSTED Conference on Information and Computer Science (NICS), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 26–27 November 2020; pp. 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, A.K.; Wann, K.T.; Matthews, S.B. Lactose causes heart arrhythmia in the water flea Daphnia pulex. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 139, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. Ecology, Epidemiology, and Evolution of Parasitism in Daphnia; National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2005.


| Reference | Recording Instrument | Software/Tools | Animal model | Obtainable Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | High-speed CCD camera mounted to an inverted microscope | U-Net and Mask RCNN convolutional Networks | D. magna, D. pulex, and Moina sp. | Cross sectional area change, heart rate, stroke volume, ejection fraction, fraction shortening, cardiac output, and heartbeat regularity |
| [31] | Spencer microscope devised with stroboscope | Stroboscope or stopwatch for manual counting with the naked eye | D. magna | Heart rate |
| [32] | Inverted microscope, digital video camera, and videotape recorder assembled to computer | Echocardiography | D. magna | Irregularity of cardiac rhythm, cardiac area in systole/diastole, and beats per min. |
| [33] | Digital camera attached to a microscope | Manual counting | D. pulex | Heart rate |
| [34] | Panasonic DMC-LZ8 camera | Movie maker was used to play the recording video in slow motion, then manual counting (beats/min) was conducted | Simocephalus vetulus | Heart rate |
| [35] | a digital camera Nikon D3100 mounted on a microscope. | Tracker® software | D. magna | Heart rate, diastole/systole heart area ratio, duration of diastole |
| [36] | microscope (CKX41SF, Olympus) equipped with a digital camera | GOM player and ImageJ software | D. magna | Heart size, contraction capacity, and heart rate |
| [27] | Nikon stereomicroscope, model SMZ800 Digital Sight, fitted with a D5-Fi2 camera | Image capture by NIS-Elements software and image analysis by machine learning (R-CNN) | D. magna | Heart malformation detection |
| [15] | High-speed CCD camera mounted to an inverted microscope | ImageJ Time Series Analyzer plug-in | D. magna, D. similis, and Moina sp. | Heart rate, blood flow rate, stroke volume, ejection fraction, fractional shortening, cardiac output, and heartbeat regularity |
| [37] | High-speed CCD camera mounted to an inverted microscope | ImageJ Kymograph plug-in | D. magna | Heart rate, stroke volume, ejection fraction, fraction shortening, cardiac output, and heartbeat regularity |
| [38] | High-speed CCD camera mounted to an inverted microscope | OpenCV | D. magna | Heart rate and heartbeat regularity |
| Dice Coefficient | IOU | Sensitivity | Specificity | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | |||||
| D. magna | 0.930 ± 0.042 | 0.872 ± 0.070 | 0.946 ± 0.084 | 0.987 ± 0.009 | 60 |
| D. pulex | 0.817 ± 0.124 | 0.707 ± 0.161 | 0.804 ± 0.173 | 0.989 ± 0.006 | 100 |
| Moina sp. | 0.659 ± 0.209 | 0.526 ± 0.228 | 0.732 ± 0.207 | 0.970 ± 0.029 | 100 |
| Mask RCNN | |||||
| D. magna | 0.969 ± 0.008 | 0.940 ± 0.015 | 0.967 ± 0.019 | 0.995 ± 0.005 | 60 |
| D. pulex | 0.958 ± 0.011 | 0.919 ± 0.020 | 0.945 ± 0.025 | 0.998 ± 0.001 | 100 |
| Moina sp. | 0.930 ± 0.054 | 0.874 ± 0.083 | 0.961 ± 0.032 | 0.994 ± 0.009 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saputra, F.; Farhan, A.; Suryanto, M.E.; Kurnia, K.A.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Vasquez, R.D.; Roldan, M.J.M.; Huang, J.-C.; Lin, Y.-K.; Hsiao, C.-D. Automated Cardiac Chamber Size and Cardiac Physiology Measurement in Water Fleas by U-Net and Mask RCNN Convolutional Networks. Animals 2022, 12, 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131670
Saputra F, Farhan A, Suryanto ME, Kurnia KA, Chen KH-C, Vasquez RD, Roldan MJM, Huang J-C, Lin Y-K, Hsiao C-D. Automated Cardiac Chamber Size and Cardiac Physiology Measurement in Water Fleas by U-Net and Mask RCNN Convolutional Networks. Animals. 2022; 12(13):1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131670
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaputra, Ferry, Ali Farhan, Michael Edbert Suryanto, Kevin Adi Kurnia, Kelvin H.-C. Chen, Ross D. Vasquez, Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, Jong-Chin Huang, Yih-Kai Lin, and Chung-Der Hsiao. 2022. "Automated Cardiac Chamber Size and Cardiac Physiology Measurement in Water Fleas by U-Net and Mask RCNN Convolutional Networks" Animals 12, no. 13: 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131670
APA StyleSaputra, F., Farhan, A., Suryanto, M. E., Kurnia, K. A., Chen, K. H.-C., Vasquez, R. D., Roldan, M. J. M., Huang, J.-C., Lin, Y.-K., & Hsiao, C.-D. (2022). Automated Cardiac Chamber Size and Cardiac Physiology Measurement in Water Fleas by U-Net and Mask RCNN Convolutional Networks. Animals, 12(13), 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131670












