The Multi-Omics Analysis Revealed Microbiological Regulation of Rabbit Colon with Diarrhea Fed an Antibiotic-Free Diet
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals Feeding Condition
2.3. Samples Collection
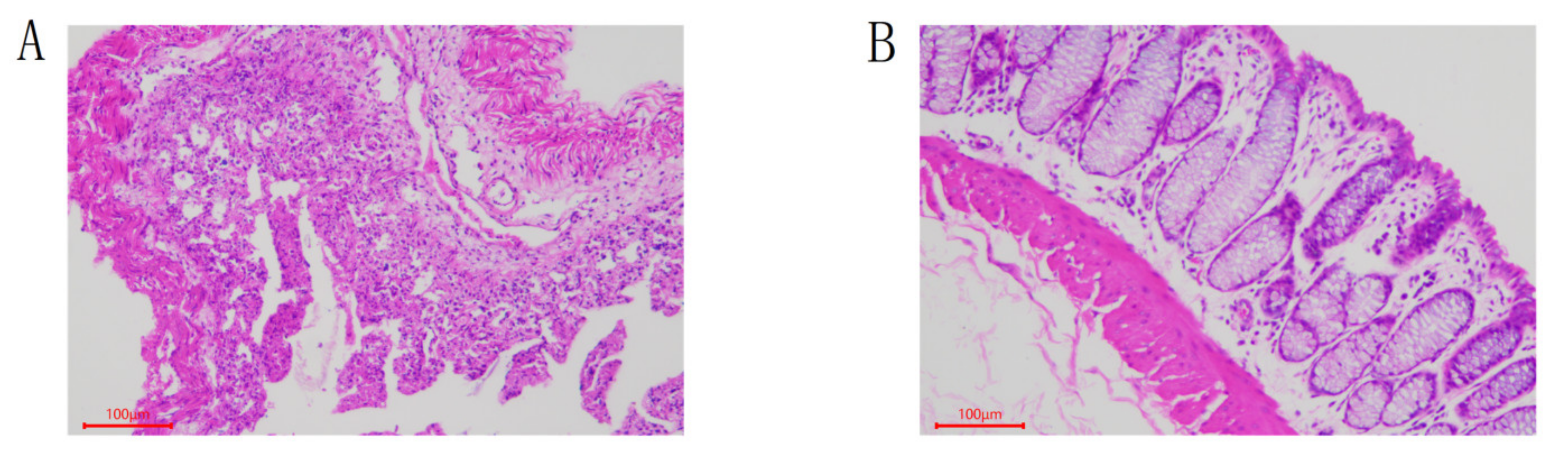
2.4. Morphological Section Analysis of Rabbit Colon
2.5. Microbial Genomic16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Sequencing Analysis
2.6. RNA-Seq Data and Differential Expression Analysis
2.7. Metabolome Analysis
2.8. Association Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Colon Tissue Sections
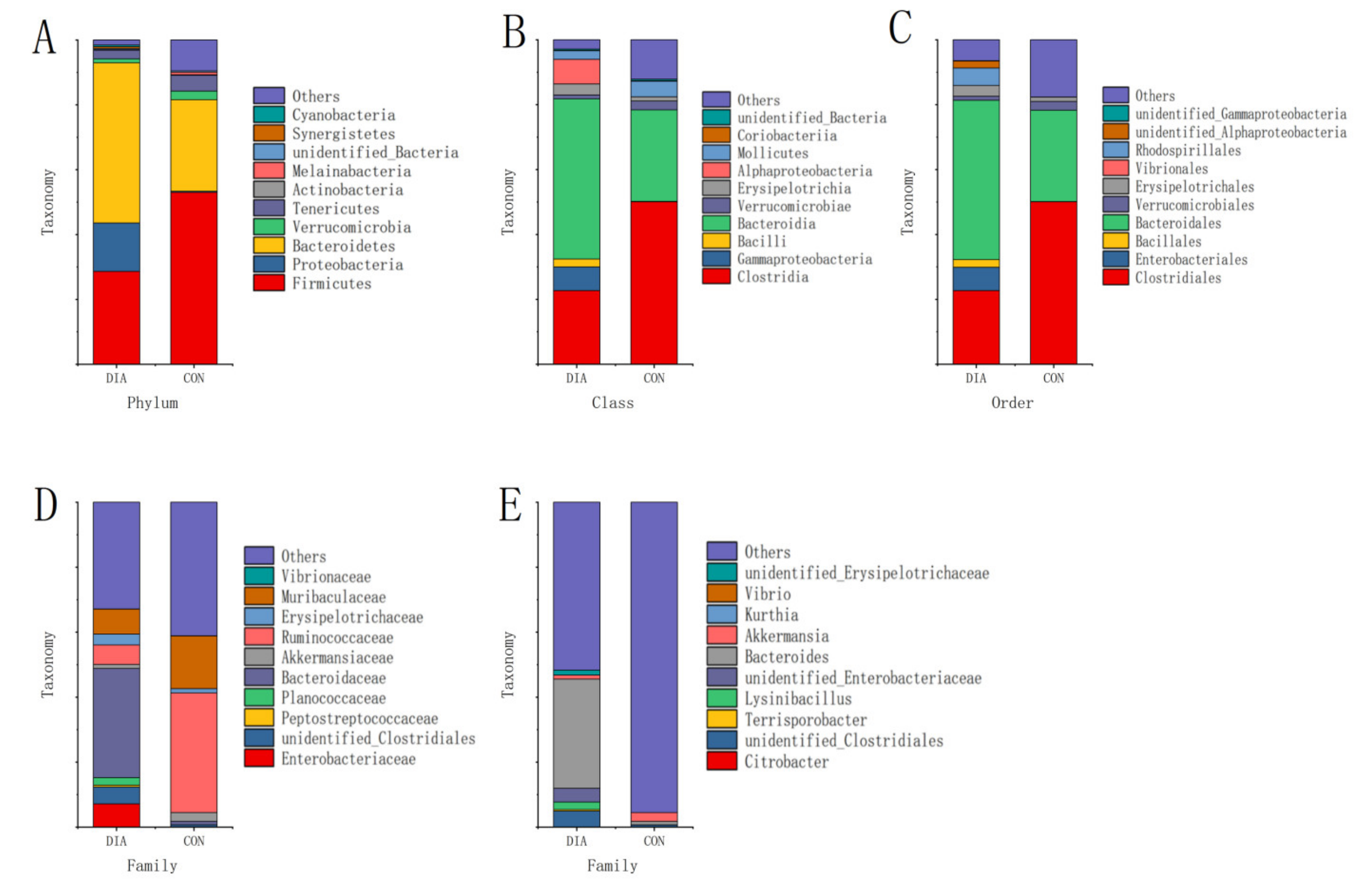
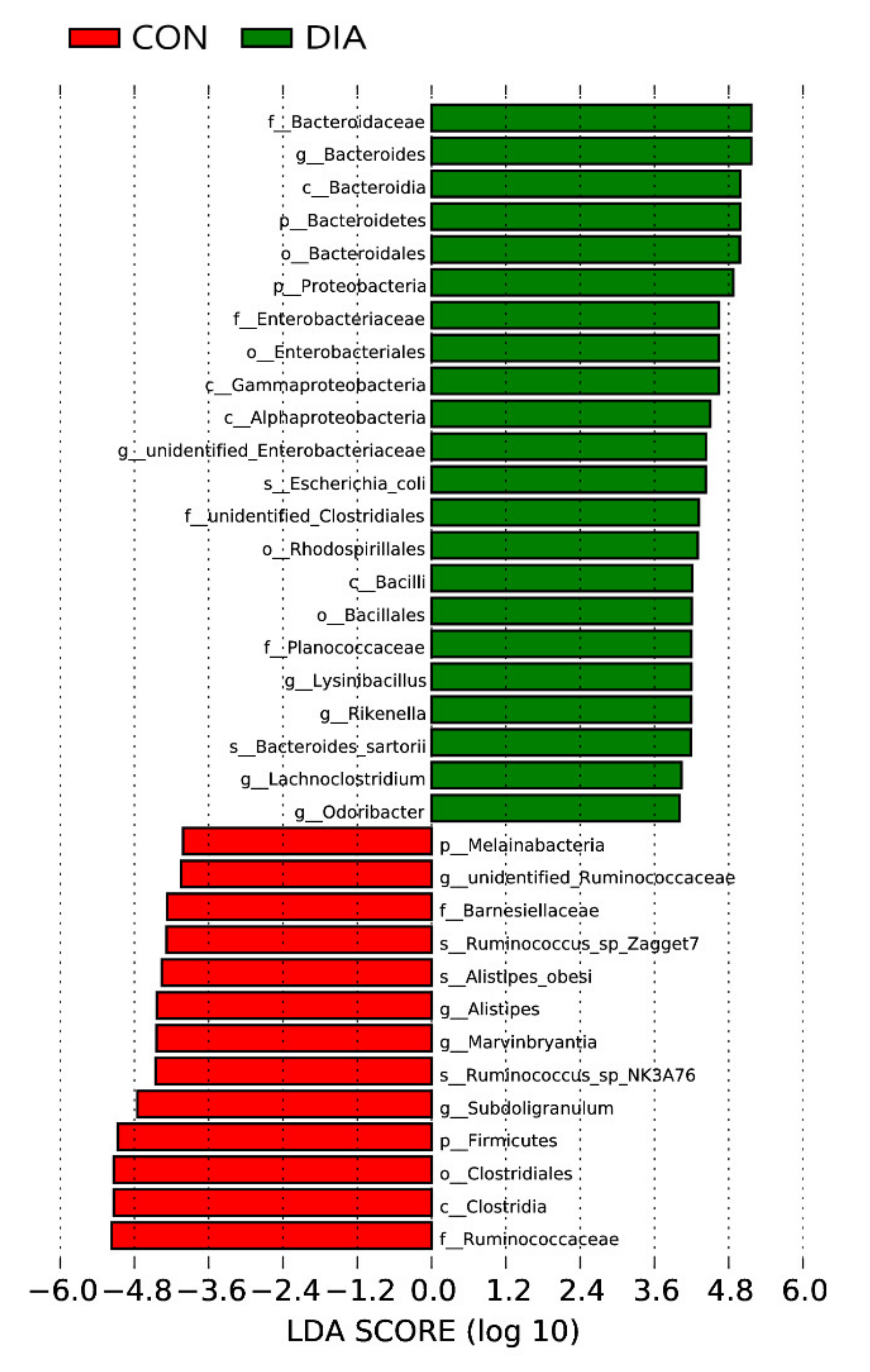
3.2. Microbial Community Imbalance
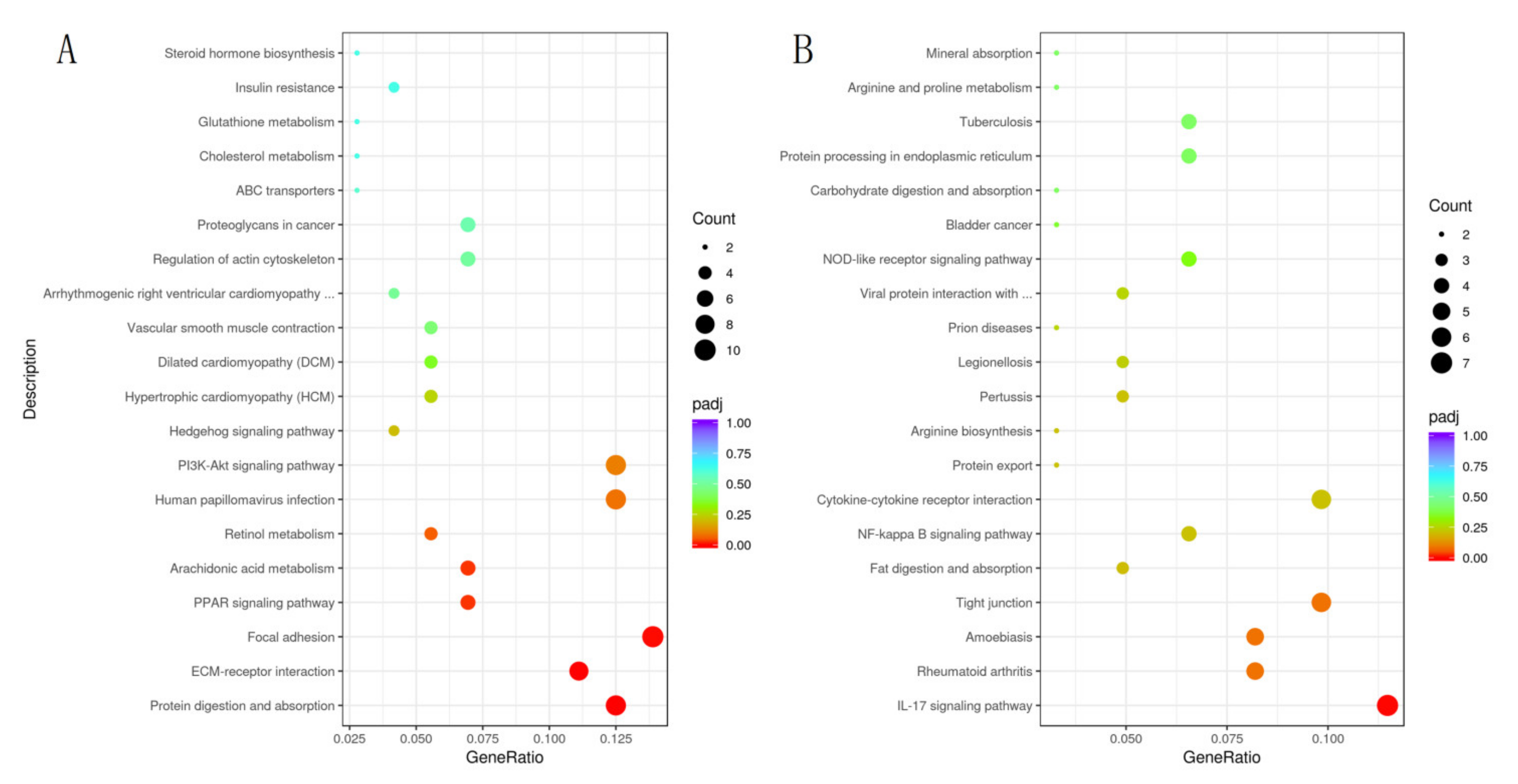
3.3. Differential Expression of Genes in Colon
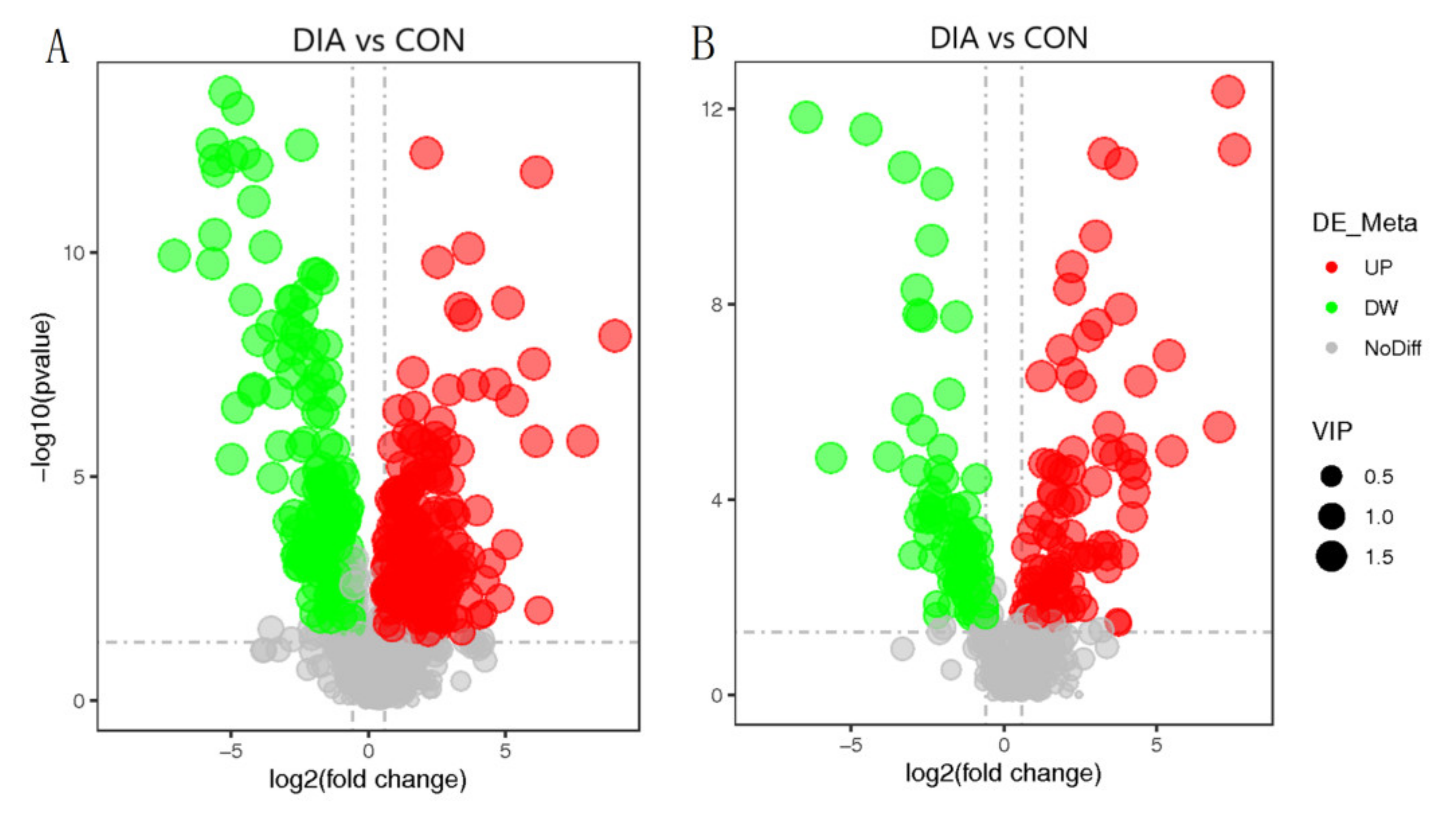
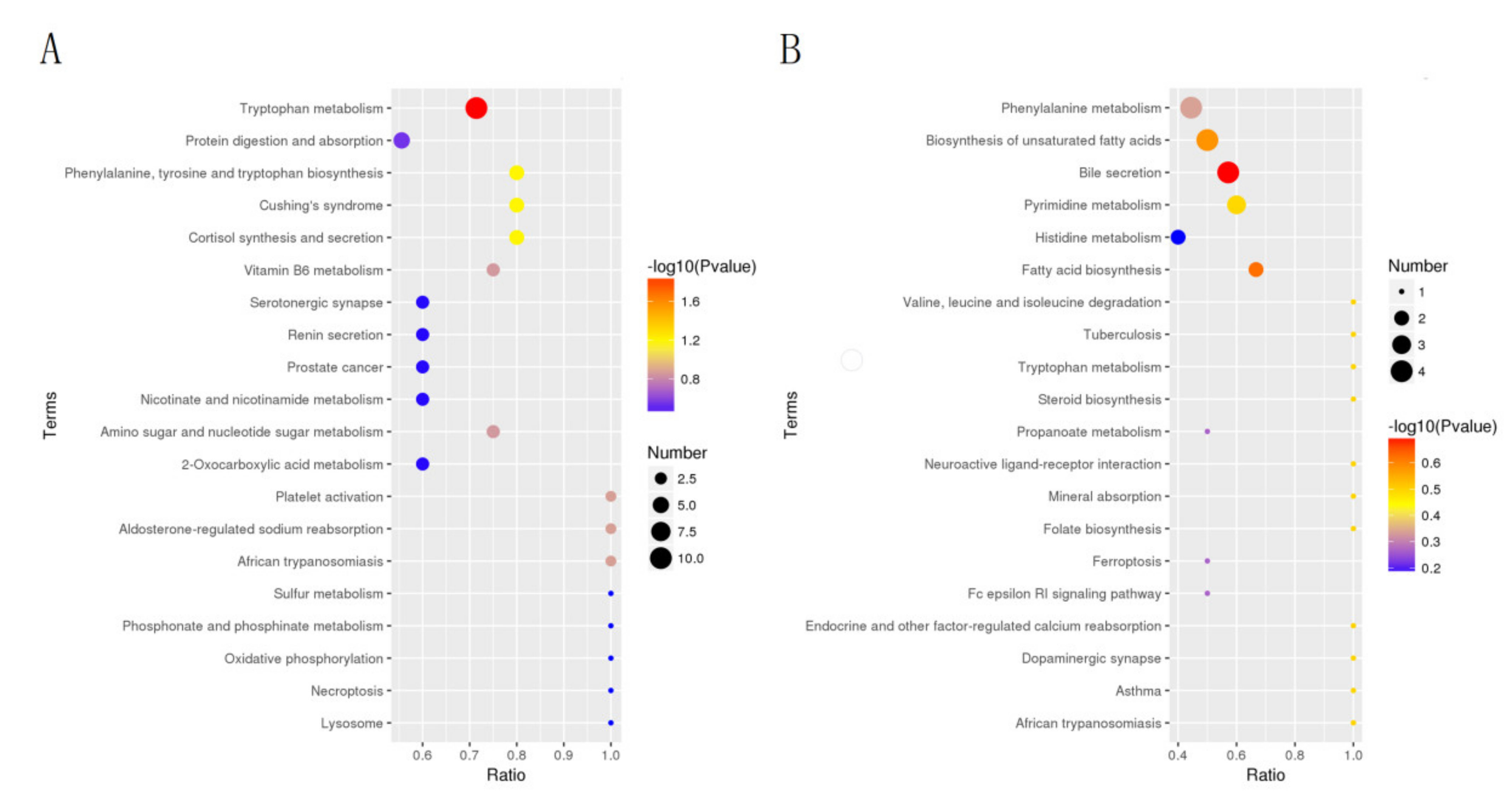
3.4. Differential Metabolite Analysis
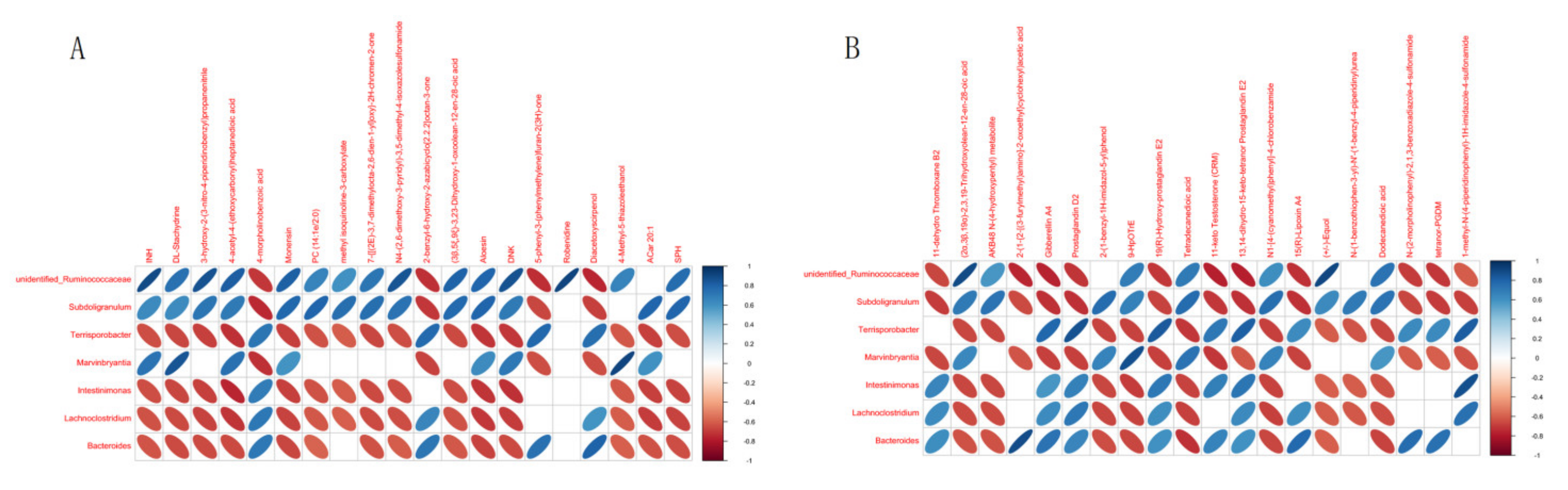
3.5. Metabolite-Centric Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosen, G.D. Antibacterials in poultry and pig nutrition. In Biotechnology in Animal Feeds and Animal Feeding; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1995; pp. 143–172. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, M. Antibiotic use in animal feed and its impact on human healt. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2001, 13, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bell, B.G.; Schellevis, F.; Stobberingh, E.; Goossen, H.; Pringle, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of antibiotic consumption on antibiotic resistance. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van, T.; Yidana, Z.; Smooker, P.M.; Coloe, P.J. Antibiotic Use in Food Animals in the World with Focus on Africa: Pluses and Minuses. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 20, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Paruch, L.; Chen, X.; Eerde, A.V.; Clarke, J.L. Antibiotic Application and Resistance in Swine Production in China: Current Situation and Future Perspectives. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seal, B.S.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Donovan, D.M.; Gay, C.G. Alternatives to antibiotics: A symposium on the challenges and solutions for animal production. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2013, 14, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, K.; Mu, C.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhu, W.Y. Segment specific responses of intestinal epithelium transcriptome to in-feed antibiotics in pigs. Physiol. Genom. 2017, 49, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikram, A.; Rovira, P.; Agga, G.E.; Arthur, T.M.; Bosilevac, J.M.; Wheeler, T.L.; Morley, P.S.; Belk, K.E.; Schmidt, J.W. Impact of “Raised Without Antibiotics” Beef Cattle Production Practices On Occurrences of Antimicrobial Resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01682-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A.; Schütte, A.; Ermund, A.; Boysen, P.; Bemark, M.; Sommer, F.; Bckhed, F.; Hansson, G.C.; Johansson, M.E. The composition of the gut microbiota shapes the colon mucus barrier. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Y.; Hu, S.; Wu, X. Impacts of diarrhea on the immune system, intestinal environment, and expression of PGRPs in New Zealand rabbits. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4100. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, R.S. Inflammation in the Intestinal Tract: Pathogenesis and Treatment. Dig. Dis. 2009, 27, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhouma, R.B.; Jouini, A.; Klibi, A.; Hamrouni, S.; Maaroufi, A. Molecular characterisation of antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes in Escherichia coli strains isolated from diarrhoeic and healthy rabbits in Tunisia. World Rabbit Sci. 2020, 28, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maioli, T.U.; Trindade, L.M.; Souza, A.; Torres, L.; Andrade ME, R.; Cardoso, V.N.; Generoso, S.V. Non-pharmacologic strategies for the management of intestinal inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmuthuge, N.; Liang, G.; Guan, L.L. Regulation of rumen development in neonatal ruminants through microbial metagenomes and host transcriptomes. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Sun, J. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Shows Marked Shifts in the Multi-Omic Profiles of Porcine Post-weaning Diarrhea. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 619460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Elzo, M.A.; Lai, S. Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Intestinal Pathogenesis and Self-Repair in Rabbits Fed an Antibiotic-Free Diet. Animals 2021, 11, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J. DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borodina, T.; Adjaye, J.; Sultan, M. A strand-specific library preparation protocol for RNA sequencing. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 500, 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, I.D.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K.; Want, E.J. Global metabolic profiling procedures for urine using UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Anne-Laure, B.; Korbinian, S. Partial least squares: A versatile tool for the analysis of high-dimensional genomic data. Brief. Bioinform. 2007, 8, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, G.; Huang, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Shi, Y.; Zhi, F. An IRF1-dependent Pathway of TNFα-induced Shedding in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2021, 16, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, K.; Yu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Xylooligosaccharide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal injury in piglets via suppressing inflammation and modulating cecal microbial communities. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molist, F.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Pérez, J.F.; Nyachoti, C.M. Coarse, but not finely ground, dietary fibre increases intestinal Firmicutes:Bacteroidetes ratio and reduces diarrhoea induced by experimental infection in piglets. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Natividad, J.M.; Pinto-Sanchez, M.I.; Galipeau, H.J.; Jury, J.; Verdu, E.F. Ecobiotherapy Rich in Firmicutes Decreases Susceptibility to Colitis in a Humanized Gnotobiotic Mouse Model. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.; Yu, J.; Luo, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, D. Dietary pea fibre alters the microbial community and fermentation with increase in fibre degradation-associated bacterial groups in the colon of pigs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 102, e254–e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abigail, R.B.; Adrian, G.N.; Alexandria, L.S.; Ludovica, B.; Danielle, K.; Alexandra, W.; Luca, D.M.; Gina, P.; Abdullah, O.; Alexander, R.P. Replacing Animal Protein with Soy-Pea Protein in an “American Diet” Controls Murine Crohn Disease-Like Ileitis Regardless of Firmicutes: Bacteroidetes Ratio. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 579–590. [Google Scholar]
- Koliada, A.; Syzenko, G.; Moseiko, V.; Budovska, L. Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in an adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nomura, K.; Dai, I.; Okahara, K.; Ito, S.; Nagahara, A. Bacteroidetes Species Are Correlated with Disease Activity in Ulcerative Colitis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.L.; Heaver, S.L.; Walters, W.A.; Ley, R.E. Microbiome and metabolic disease: Revisiting the bacterial phylum Bacteroidetes. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 95, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrncirova, L.; Machova, V.; Trckova, E.; Krejsek, J.; Hrncir, T. Food Preservatives Induce Proteobacteria Dysbiosis in Human-Microbiota Associated Nod2-Deficient Mice. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litvak, Y.; Byndloss, M.; Tsolis, R.; Bäumler, A. Dysbiotic Proteobacteria expansion: A microbial signature of epithelial dysfunction. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.P.; Li, P.; Du, T.; Du, X.J.; Wang, S. Protective effect and mechanism of Monascus-fermented red yeast rice against colitis caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium ATCC 14028. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6363–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Trukelj, B. The Influence of Probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, I.; Sarra, M.; Pallone, F.; Monteleone, G. Th17-Related Cytokines in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Friends or Foes? Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, M.; Julie, B.; Paul, S.; Kolls, J.K. Critical role of IL-17 receptor signaling in acute TNBS-induced colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 12, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Dong, C. Signaling of interleukin-17 family cytokines in immunity and inflammation. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, W.; Kolls, J.K.; Zheng, Y. The Biological Functions of T Helper 17 Cell Effector Cytokines in Inflammation. Immunity 2008, 28, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Ding, L.; Bao, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Co-infection of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Escherichia coli Triggers Inflammatory Injury Involving the IL-17 Signaling Pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugerette, F.; Vors, C.; Géloën, A.; Chauvin, M.A.; Soulage, C.; Lambert-Porcheron, S.; Peretti, N.; Alligier, M.; Burcelin, R.; Laville, M. Emulsified lipids increase endotoxemia: Possible role in early postprandial low-grade inflammation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marozzi, M.; Parnigoni, A.; Negri, A.; Viola, M.; Rizzi, F. Inflammation, Extracellular Matrix Remodeling, and Proteostasis in Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Piao, L. Chlorogenic acid-enriched extract of Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng tea inhibits neutrophil recruitment in injured zebrafish by promoting reverse migration via the focal adhesion pathway. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, A.; Shields, M.A.; David, N.; Gwon, P.C.; Alexandra, A.; Poindexter, M.E.; Priya, U.; Uyeminami, D.L.; Arnaud, P.; Victoria, K. Neutrophil extracellular traps produced during inflammation awaken dormant cancer cells in mice. Science 2018, 361, eaao4227. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Sun, S.; Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, N.; Wu, Z.; Wu, G.; Dai, Z. Dietary L-Tryptophan Regulates Colonic Serotonin Homeostasis in Mice with Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1966–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.K.; Cheng, H.H.; Chang, T.C. 5-methoxyindole metabolites of L-tryptophan: Control of COX-2 expression, inflammation and tumorigenesis. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papadimitriou, N.; Gunter, M.J.; Murphy, N.; Gicquiau, A.; Achaintre, D.; Brezina, S.; Gumpenberger, T.; Baierl, A.; Ose, J.; Geijsen, A.J.M.R.; et al. Circulating tryptophan metabolites and risk of colon cancer: Results from case-control and prospective cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenniger, L.; Beuers, U. Bile salts and cholestasis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.W. The enzymes, regulation, and genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 137–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negroni, A.; Fiaschini, N.; Palone, F.; Vitali, R.; Colantoni, E.; Laudadio, I.; Oliva, S.; Aloi, M.; Cucchiara, S.; Stronati, L. Intestinal Inflammation Alters the Expression of Hepatic Bile Acid Receptors Causing Liver Impairment. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 71, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, B. Bile acid–microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis: A role for bifidobacteria and lactobacilli? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.L.; Takeda, K.; Sundrud, M.S. Emerging roles of bile acids in mucosal immunity and inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gadaleta, R.M.; Mil, S.; Oldenburg, B.; Siersema, P.D.; Klomp, L.; Erpecum, K. Bile acids and their nuclear receptor FXR: Relevance for hepatobiliary and gastrointestinal disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Umar, S.; Rust, B.; Lazarova, D.; Bordonaro, M. Secondary Bile Acids and Short Chain Fatty Acids in the Colon: A Focus on Colonic Microbiome, Cell Proliferation, Inflammation, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Group | Species | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIA | 89 | 4.06 | 0.812 | 124.49 | 0.96 |
| CON | 146 | 5.44 * | 0.936 | 215.25 * | 0.93 |
| Group | A | Observed-Delta | Expected-Delta | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON.VS.DIA | 0.2053 | 0.6475 | 0.8147 | 0.002 |
| Level | Name | avg(DIA) | sd(DIA) | avg(CON) | sd(CON) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| phylum | Firmicutes | 0.286470 | 0.083302 | 0.530045 | 0.110976 | 0.001857 |
| Proteobacteria | 0.149093 | 0.078586 | 0.003590 | 0.003954 | 0.006152 | |
| Bacteroidetes | 0.493764 | 0.147044 | 0.281935 | 0.083914 | 0.015600 | |
| Melainabacteria | 0.000377 | 0.000585 | 0.007936 | 0.006042 | 0.027750 | |
| class | Clostridia | 0.227135 | 0.067548 | 0.500944 | 0.127411 | 0.001879 |
| Bacteroidia | 0.493764 | 0.147044 | 0.281935 | 0.083914 | 0.015600 | |
| order | Bacteroidales | 0.025132 | 0.038578 | 0.281746 | 0.083690 | 0.000243 |
| Verrucomicrobiales | 0 | 0 | 0.027021 | 0.016279 | 0.009673 | |
| family | Peptostreptococcaceae | 0.005480 | 0.003822 | 0 | 0 | 0.017071 |
| Bacteroidaceae | 0.335978 | 0.262398 | 0.010959 | 0.009849 | 0.028913 | |
| Ruminococcaceae | 0.059901 | 0.039701 | 0.368102 | 0.103267 | 0.000356 | |
| genus | Terrisporobacter | 0.004535 | 0.003286 | 0 | 0 | 0.019661 |
| Bacteroides | 0.335978 | 0.262398 | 0.010959 | 0.009849 | 0.028913 | |
| Lachnoclostridium | 0.021542 | 0.016209 | 0 | 0 | 0.022563 | |
| unidentified_Ruminococcaceae | 0.002834 | 0.003344 | 0.012093 | 0.005203 | 0.005681 | |
| Intestinimonas | 0.003590 | 0.002626 | 0 | 0 | 0.020366 | |
| Subdoligranulum | 0 | 0 | 0.001322 | 0.000853 | 0.012676 | |
| Marvinbryantia | 0 | 0 | 0.001889 | 0.001373 | 0.019868 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Fan, H.; Xia, S.; Zhao, K.; Chen, G.; Li, Y. The Multi-Omics Analysis Revealed Microbiological Regulation of Rabbit Colon with Diarrhea Fed an Antibiotic-Free Diet. Animals 2022, 12, 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121497
Chen Y, Wang J, Fan H, Xia S, Zhao K, Chen G, Li Y. The Multi-Omics Analysis Revealed Microbiological Regulation of Rabbit Colon with Diarrhea Fed an Antibiotic-Free Diet. Animals. 2022; 12(12):1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121497
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yang, Jie Wang, Huimei Fan, Siqi Xia, Kaisen Zhao, Guanhe Chen, and Yuchao Li. 2022. "The Multi-Omics Analysis Revealed Microbiological Regulation of Rabbit Colon with Diarrhea Fed an Antibiotic-Free Diet" Animals 12, no. 12: 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121497
APA StyleChen, Y., Wang, J., Fan, H., Xia, S., Zhao, K., Chen, G., & Li, Y. (2022). The Multi-Omics Analysis Revealed Microbiological Regulation of Rabbit Colon with Diarrhea Fed an Antibiotic-Free Diet. Animals, 12(12), 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121497






