Does Exposure of Broodstock to Dietary Soybean Meal Affect Its Utilization in the Offspring of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)?
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Broodstock Rearing and Spawning
2.2. Diet Preparation
2.3. Experimental Groups and Feeding Regime
- A progeny obtained from FM-fed broodstock that received FM diet (FMBS-FM, +control);
- A progeny obtained from FM-fed broodstock that received PP diet (FMBS-PP, −control);
- A progeny obtained from “nutritionally programmed” broodstock that received PP diet (PPBS-PP);
- A progeny obtained from “nutritionally programmed” broodstock that received FM diet (PPBS-FM) (Figure 1).
2.4. Sampling and Measurements
2.5. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.6. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance and Survival
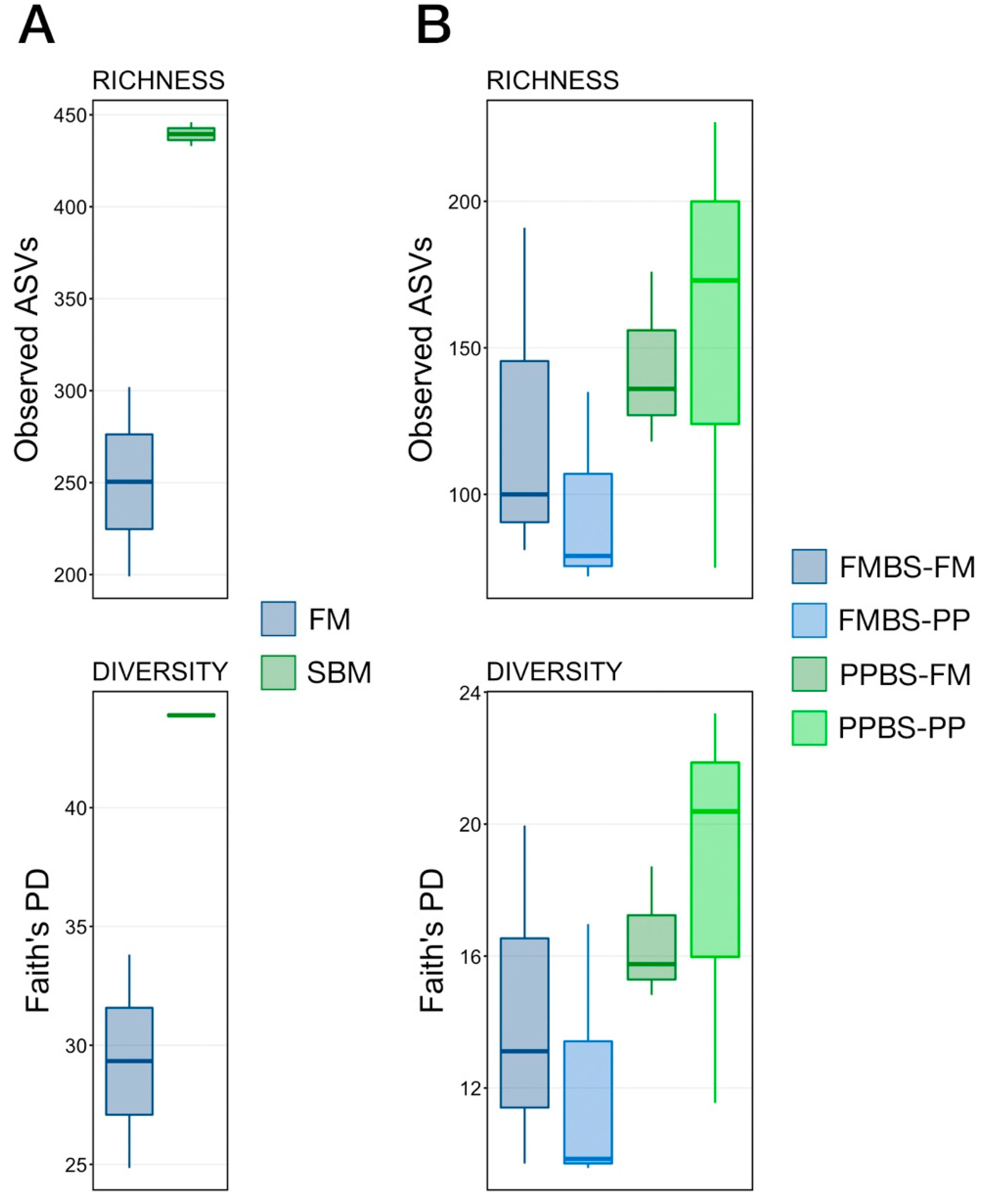
3.2. Microbial Richness and Diversity
3.3. Microbial Community Composition
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Performance
4.2. Gut Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cashion, T.; Le Manach, F.; Zeller, D.; Pauly, D. Most fish destined for fishmeal production are food-grade fish. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action. 2020. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/ca9229en/CA9229EN.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- Glencross, B.D.; Baily, J.; Berntssen, M.H.; Hardy, R.; MacKenzie, S.; Tocher, D.R. Risk assessment of the use of alternative animal and plant raw material resources in aquaculture feeds. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 703–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Olsen, R.E.; Myklebust, R.; Ringø, E.; El-Shemy, H. Dietary effect of soybean (Glycine max) products on gut histology and microbiota of fish. Soybean Nutr. 2011, 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- Geurden, I.; Borchert, P.; Balasubramanian, M.N.; Schrama, J.W.; Dupont-Nivet, M.; Quillet, E.; Kaushik, S.J.; Panserat, S.; Médale, F. The positive impact of the early-feeding of a plant-based diet on its future acceptance and utilisation in rainbow trout. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjevic, B.; Morales-Lange, B.; Øverland, M.; Mercado, L.; Lagos, L. Immune and proteomic responses to the soybean meal diet in skin and intestine mucus of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyf, M.; McGowan, P.; Meaney, M.J. The social environment and the epigenome. Environ. Mol. Mutagenesis 2008, 49, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.; Mørkøre, T.; Robinson, N. Epigenetics—Potential for programming fish for aquaculture? J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabory, A.; Attig, L.; Junien, C. Epigenetic mechanisms involved in developmental nutritional programming. World J. Diabetes 2011, 2, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, M.N.; Panserat, S.; Dupont-Nivet, M.; Quillet, E.; Montfort, J.; Le Cam, A.; Medale, F.; Kaushik, S.J.; Geurden, I. Molecular pathways associated with the nutritional programming of plant-based diet acceptance in rainbow trout following an early feeding exposure. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwasek, K.; Wojno, M.; Iannini, F.; McCracken, V.J.; Molinari, G.S.; Terova, G. Nutritional programming improves dietary plant protein utilization in zebrafish Danio rerio. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molinari, G.S.; Wojno, M.; Kwasek, K. The use of live food as a vehicle of soybean meal for nutritional programming of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patula, S.; Wojno, M.; Pinnell, L.J.; Oliaro, F.; Cabay, C.; Molinari, G.S.; Kwasek, K. Nutritional Programming with Dietary Soybean Meal and Its Effect on Gut Microbiota in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Zebrafish 2021, 18, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemski, M.; Wick, M.; Dabrowski, K. Nutritional programming effects on growth and reproduction of broodstock and embryonic development of progeny in yellow perch (Perca flavescens) fed soybean meal-based diets. Aquaculture 2018, 497, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.S.; Turkmen, S.E.; Montero, D.; Zamorano, M.J.; Afonso, J.M.; Karalazos, V.; Fernández-Palacios, H. Nutritional programming through broodstock diets to improve utilization of very low fishmeal and fish oil diets in gilthead sea bream. Aquaculture 2015, 449, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmen, S.; Zamorano, M.J.; Fernández-Palacios, H.; Hernández-Cruz, C.M.; Montero, D.; Robaina, L.; Izquierdo, M. Parental nutritional programming and a reminder during juvenile stage affect growth, lipid metabolism and utilisation in later developmental stages of a marine teleost, the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallo, B.D.; Farrell, J.M.; Leydet, B.F. Fish Gut Microbiome: A Primer to an Emerging Discipline in the Fisheries Sciences. Fisheries 2020, 45, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, W.Z.; Burns, A.R.; Stagaman, K.; Wong, S.; Rawls, J.F.; Guillemin, K.; Bohannan, B.J.M. The composition of the zebrafish intestinal microbial community varies across development. ISME J. 2016, 10, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Feng, W.; Yan, Q.; Gong, Y. Host species as a strong determinant of the intestinal microbiota of fish larvae. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, P.; Magne, F.; Araneda, C.; Fuentes, P.; Barros, L.; Opazo, R.; Espejo, R.; Romero, J. PCR-TTGE analysis of 16S rRNA from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) gut microbiota reveals host-specific communities of active bacteria. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedrera, M.I.; Galdames, J.A.; Jimenez-Reyes, M.F.; Reyes, A.E.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Romero, J.; Feijóo, C.G. Soybean meal induces intestinal inflammation in zebrafish larvae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brugman, S. The zebrafish as a model to study intestinal inflammation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 64, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulloa, P.E.; Iturra, P.; Neira, R.; Araneda, C. Zebrafish as a model organism for nutrition and growth: Towards comparative studies of nutritional genomics applied to aquacultured fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2011, 21, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, A.L.; Ikeda-Ohtsubo, W.; Sipkema, D.; Peggs, S.; McGurk, G.; Forlenza, M.; Wiegertjes, G.F.; Brugman, S. Feed, Microbiota, and Gut Immunity: Using the Zebrafish Model to Understand Fish Health. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, M.; Varga, Z.M. Anesthesia and euthanasia in zebrafish. ILAR J. 2012, 53, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raz, E. Primordial germ-cell development: The zebrafish perspective. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, T.; Imanpoor, M.R.; Jafari, V.; Bennetau-Pelissero, C. Reproductive impairment and endocrine disruption in goldfish by feeding diets containing soybean meal. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2013, 139, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish. Available online: http://zfin.Org/zf_info/zfbook/zfbk.Html (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- Molinari, G.S.; McCracken, V.J.; Wojno, M.; Rimoldi, S.; Terova, G.; Kwasek, K. Can intestinal absorption of dietary protein be improved through early exposure to plant-based diet? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, H.; Peres, H.; Carvalho, A.P. Dietary protein requirement during juvenile growth of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Zebrafish 2016, 13, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, M. National Research Council. In Nutrient Requirements of Fish and Shrimp; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lovell, T. Dietary requirements. In Nutrition and Feeding of Fish; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 13–70. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, W.; Hyde, E.R.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Ackermann, G.; Humphrey, G.; Parada, A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Caporaso, J.G.; Fuhrman, J.A.; et al. Improved bacterial 16S rRNA gene (V4 and V4–5) and fungal internal transcribed spacer marker gene primers for microbial community surveys. Msystems 2016, 1, e00009–e00015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, J.N.; Stine, O.C.; Bravo, H.C.; Pop, M. Differential abundance analysis for microbial marker-gene surveys. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version, 2.5-5 Ed. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- Arbizu, P.M. PairwiseAdonis: Pairwise Multilevel Comparison Using Adonis. Available online: https://github.com/pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- Murtagh, F.; Legendre, P. Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: Which algorithms implement Ward’s criterion? J. Classif. 2014, 31, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarotto, V.; Corraze, G.; Larroquet, L.; Mazurais, D.; Médale, F. Does broodstock nutritional history affect the response of progeny to different first-feeding diets? A whole-body transcriptomic study of rainbow trout alevins. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 2079–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seiliez, I.; Vélez, E.J.; Lutfi, E.; Dias, K.; Plagnes-Juan, E.; Marandel, L.; Panserat, S.; Geurden, I.; Skiba-Cassy, S. Eating for two: Consequences of parental methionine nutrition on offspring metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2017, 471, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.C.; Rosenlund, G.; Karlsen, Ø.; Koppe, W.; Hemre, G.I. Total replacement of fish meal with plant proteins in diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) I—Effects on growth and protein retention. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Han, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Bian, P.; Wang, Y.; Cai, X. Effects of replacing fish meal with soybean meal on growth performance, feed utilization and physiological status of juvenile redlip mullet Liza haematocheila. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Bian, Y.; Huang, L.; Lan, Q.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Leng, X. Effects of replacing fish meal with fermented soybean meal on the growth performance, intestinal microbiota, morphology and disease resistance of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 22, 100954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Liufu, Z. Effects of replacing fish meal with soy protein concentrate on feed intake and growth of juvenile Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sink, T.D.; Lochmann, R.T.; Pohlenz, C.; Buentello, A.; Gatlin, D., III. Effects of dietary protein source and protein–lipid source interaction on channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) egg biochemical composition, egg production and quality, and fry hatching percentage and performance. Aquaculture 2010, 298, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, A.A.; Olaleye, V.F.; Adesulu, E.A. Egg and sperm quality of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell) broodstock fed differently heated soybean-based diets. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2005, 1, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Pastore, M.R.; Negrato, E.; Poltronieri, C.; Barion, G.; Messina, M.; Tulli, F.; Ballarin, C.; Maccatrozzo, L.; Radaelli, G.; Bertotto, D. Effects of dietary soy isoflavones on estrogenic activity, cortisol level, health and growth in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain, F.É.; Derome, N. Vertically and horizontally transmitted microbial symbionts shape the gut microbiota ontogenesis of a skin-mucus feeding discus fish progeny. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eichmiller, J.J.; Hamilton, M.J.; Staley, C.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Sorensen, P.W. Environment shapes the fecal microbiome of invasive carp species. Microbiome 2016, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarnecki, A.M.; Burgos, F.A.; Ray, C.L.; Arias, C.R. Fish intestinal microbiome: Diversity and symbiosis unravelled by metagenomics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desai, A.R.; Links, M.G.; Collins, S.A.; Mansfield, G.S.; Drew, M.D.; Van Kessel, A.G.; Hill, J.E. Effects of plant-based diets on the distal gut microbiome of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2012, 350, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, P.P.; Turnbull, J.F.; Dawson, K.A.; Crumlish, M. Effects of low-level dietary microalgae supplementation on the distal intestinal microbiome of farmed rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 2438–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Mai, K.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, Q. Effects of fish meal replacement by soybean meal with supplementation of functional compound additives on intestinal morphology and microbiome of Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 2186–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, H.M.; Bridgman, S.L.; Chari, R.; Field, C.J.; Guttman, D.S.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; Sears, M.R.; et al. Roles of birth mode and infant gut microbiota in intergenerational transmission of overweight and obesity from mother to offspring. JAMA Pediatrics 2018, 172, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.L.; Cox, W.T.; Levine, R.P. Evidence that the causal agent of bacterial cold-water disease Flavobacterium psychrophilum is transmitted within salmonid eggs. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1997, 29, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Kempher, M.L.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liao, L.; et al. Environmental filtering decreases with fish development for the assembly of gut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4739–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.F. Alien invasions and gut “island biogeography”. Cell 2014, 159, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galindo-Villegas, J.; García-Moreno, D.; De Oliveira, S.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. Regulation of immunity and disease resistance by commensal microbes and chromatin modifications during zebrafish development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2605–E2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roeselers, G.; Mittge, E.K.; Stephens, W.Z.; Parichy, D.M.; Cavanaugh, C.M.; Guillemin, K.; Rawls, J.F. Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rawls, J.F.; Mahowald, M.A.; Ley, R.E.; Gordon, J.I. Reciprocal gut microbiota transplants from zebrafish and mice to germ-free recipients reveal host habitat selection. Cell 2006, 127, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwasek, K.; Wojno, M.; Patula, S.; Oliaro, F.; Cabay, C.; Pinnell, L.J. The Effect of First Feeding Exposure of Larval Largemouth Bass to a Formulated Soybean Meal-Based or Soy Saponin-Supplemented Diet on Fish Growth Performance and Gut Microbiome. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2021, 83, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, I.; Coward, E.; Andersen, T.; Vadstein, O. Selection in the host structures the microbiota associated with developing cod larvae (Gadus morhua). Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullam, K.E.; Rubin, B.E.; Dalton, C.M.; Kilham, S.S.; Flecker, A.S.; Russell, J.A. Divergence across diet, time and populations rules out parallel evolution in the gut microbiomes of Trinidadian guppies. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1508–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Zhu, Y.J.; Yan, Q.Y.; Ringø, E.; Yang, D.G. Do the intestinal microbiotas differ between paddlefish (Polyodon spathala) and bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) reared in the same pond? J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ingredient | FM | SBM |
|---|---|---|
| Fish Meal 1 | 63.8 | - |
| Soybean Meal 2 | - | 46.3 |
| Soy Protein Isolate 3 | - | 15.4 |
| Krill Meal 4 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| CPSP 5 | 5.8 | 5.7 |
| Dextrin 6 | 5.3 | - |
| Fish Oil 7 | 3.9 | 7.1 |
| Soy Lecithin 8 | 4.7 | 4.7 |
| Mineral Mix 9 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| CaHPO4 6 | - | 1.4 |
| Vitamin Mix 10 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Vitamin C 11 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Choline Chloride 6 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Methionine 6 | - | 0.5 |
| Lysine 6 | - | 2.3 |
| Threonine 6 | - | 0.1 |
| Taurine 6 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Guar Gum 6 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Sum | 100 | 100 |
| Analyzed composition | ||
| Crude protein (N × 6.25) | 54.51 ± 0.57 | 53.30 ± 0.13 |
| Crude lipids | 17.25 ± 0.47 | 16.89 ± 0.08 |
| Ash | 15.39 ± 0.09 | 9.10 ± 0.27 |
| Group | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Final Weighing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMBS-FM | 100 | 92.3 (±8.4) | 92.3 (±8.4) | 79.0 (±11.0) | 79.0 (±11.0) |
| FMBS-PP | 100 | 99.2 (±1.3) | 96.7 (±3.8) | 83.1 (±3.0) | 83.1 (±3.0) |
| PPBS-FM | 100 | 100.0 (±0.0) | 97.1 (±5.1) | 82.6 (±5.3) | 82.6 (±5.3) |
| PPBS-PP | 100 | 95.9 (±3.6) | 95.9 (±3.6) | 80.7 (±4.1) | 80.7 (±4.1) |
| Treatment | Weight Gain (g) | Weight Gain (%) | Average Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FMBS-FM | 0.157 a (±0.029) | 1281.27 (±298.17) | 0.170 a (±0.032) |
| FMBS-PP | 0.090 b (±0.028) | 745.84 (±459.84) | 0.104 b (±0.025) |
| PPBS-FM | 0.164 a (±0.010) | 1289.81 (±20.54) | 0.177 a (±0.011) |
| PPBS-PP | 0.114 ab (±0.028) | 852.50 (±452.53) | 0.130 ab (±0.023) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwasek, K.; Patula, S.; Wojno, M.; Oliaro, F.; Cabay, C.; Pinnell, L.J. Does Exposure of Broodstock to Dietary Soybean Meal Affect Its Utilization in the Offspring of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)? Animals 2022, 12, 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121475
Kwasek K, Patula S, Wojno M, Oliaro F, Cabay C, Pinnell LJ. Does Exposure of Broodstock to Dietary Soybean Meal Affect Its Utilization in the Offspring of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)? Animals. 2022; 12(12):1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121475
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwasek, Karolina, Samuel Patula, Michal Wojno, Frank Oliaro, Chrissy Cabay, and Lee J. Pinnell. 2022. "Does Exposure of Broodstock to Dietary Soybean Meal Affect Its Utilization in the Offspring of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)?" Animals 12, no. 12: 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121475
APA StyleKwasek, K., Patula, S., Wojno, M., Oliaro, F., Cabay, C., & Pinnell, L. J. (2022). Does Exposure of Broodstock to Dietary Soybean Meal Affect Its Utilization in the Offspring of Zebrafish (Danio rerio)? Animals, 12(12), 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121475






