Towards Efficient Early Warning: Pathobiology of African Swine Fever Virus “Belgium 2018/1” in Domestic Pigs of Different Age Classes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Animal Trials
2.2.1. Trial A
2.2.2. Trial B
2.3. Virus Inoculum
2.3.1. Trial A
2.3.2. Trial B
2.4. Cells for Virus Titration
2.4.1. Trial A
2.4.2. Trial B
2.5. Pathology
2.5.1. Trial A
2.5.2. Trial B
2.6. Processing of Samples
2.6.1. Trial A
2.6.2. Trial B
2.7. Pathogen Detection—Nucleic Acid Extraction and Real-Time PCR
2.7.1. Trial A
2.7.2. Trial B
2.8. Antibody Detection
2.8.1. Trial A
2.8.2. Trial B
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
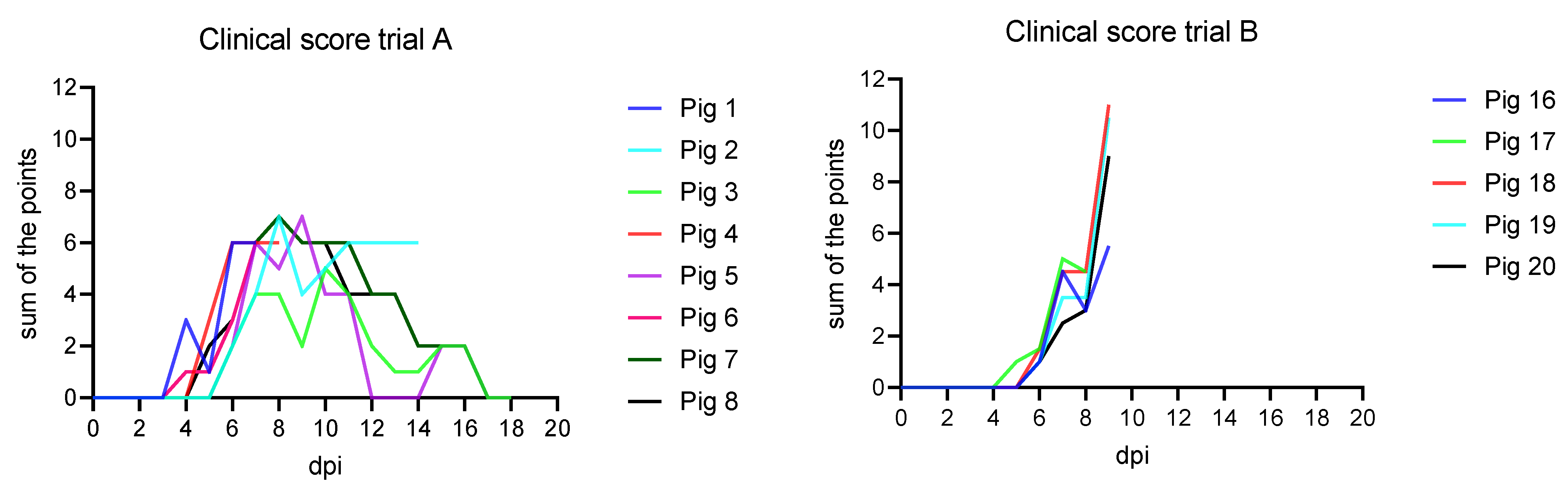
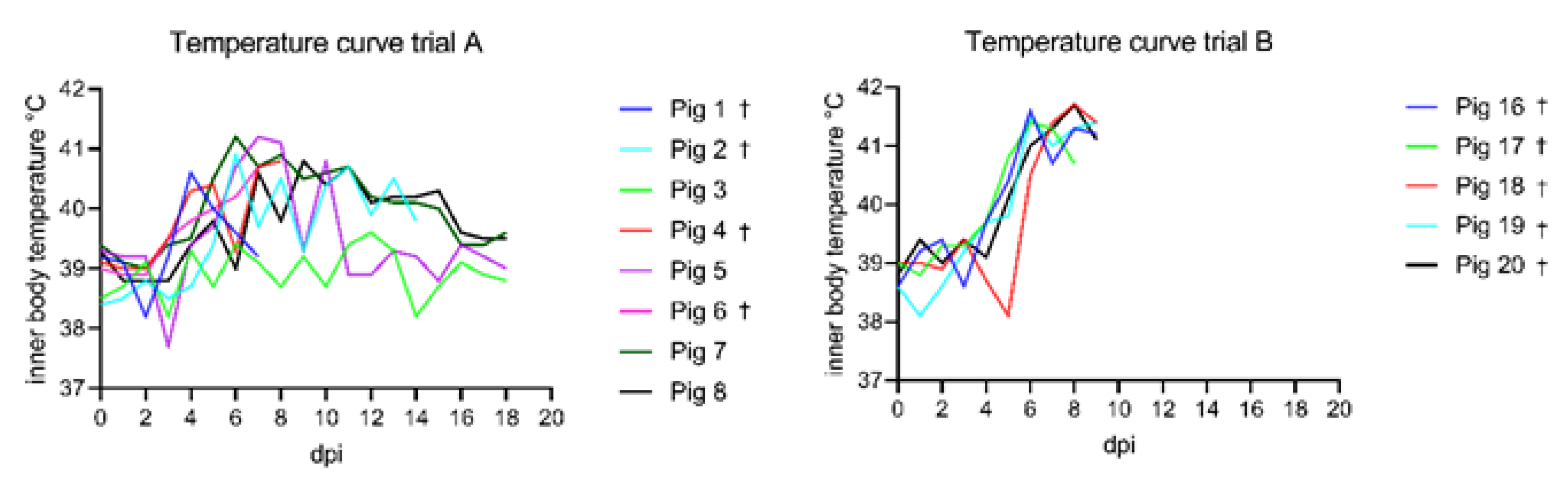
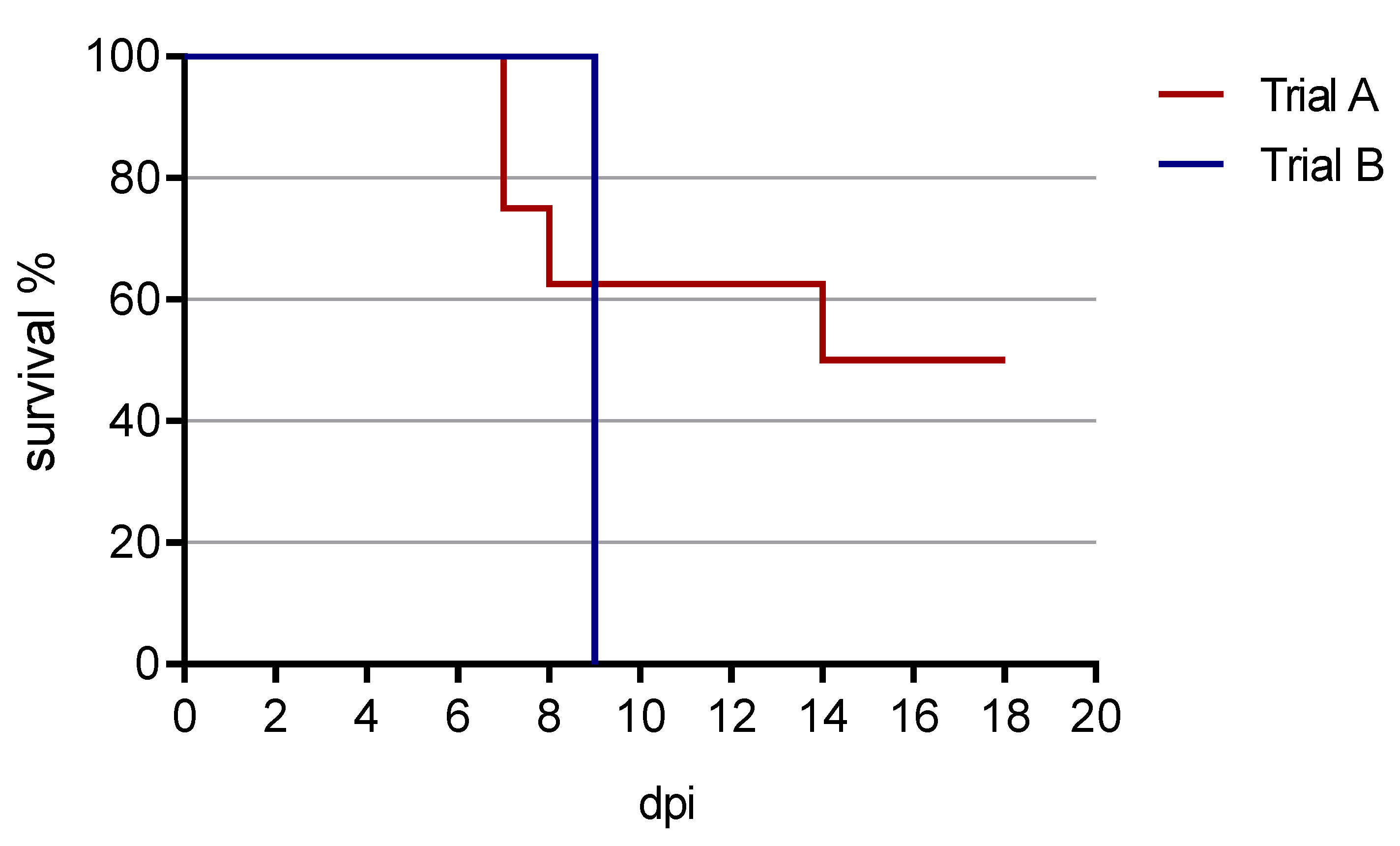
3.1. Clinical Findings
3.1.1. Trial A
3.1.2. Trial B
3.2. Pathomorphological Findings
3.2.1. Trial A
3.2.2. Trial B
3.3. Pathogen Detection
3.3.1. Trial A
3.3.2. Trial B
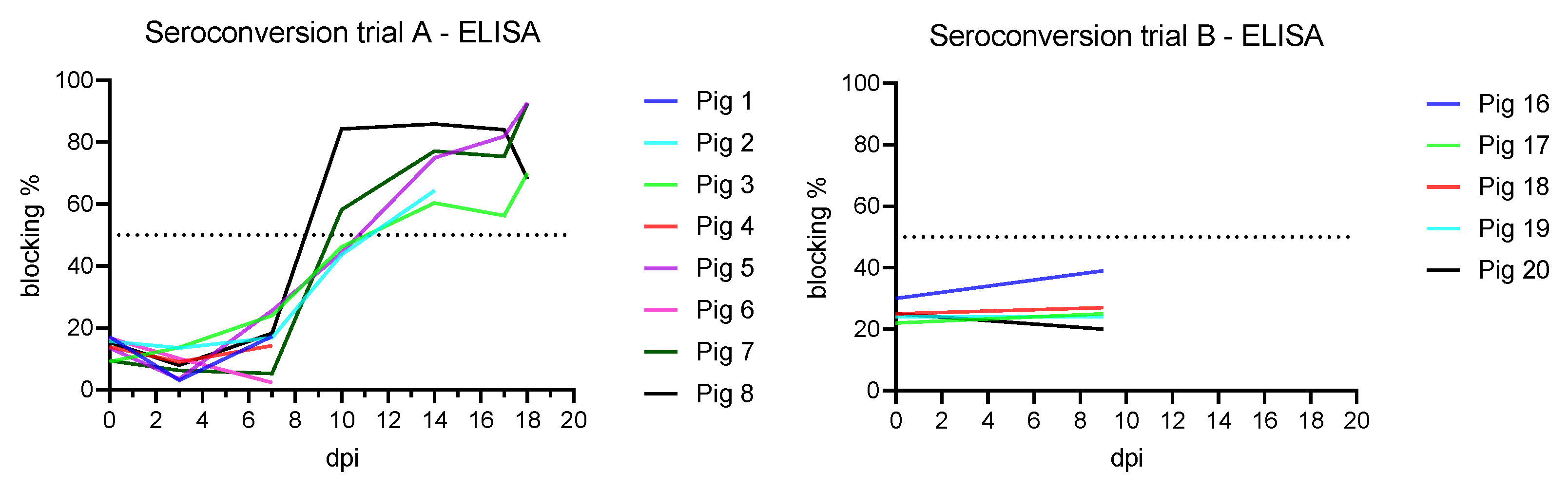
3.4. Antibody Detection
3.4.1. Trial A
3.4.2. Trial B
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallardo, C.; Fernández-Pinero, J.; Pelayo, V.; Gazaev, I.; Markowska-Daniel, I.; Pridotkas, G.; Nieto, R.; Fernández-Pacheco, P.; Bokhan, S.; Nevolko, O.; et al. Genetic Variation among African Swine Fever Genotype II Viruses, Eastern and Central Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1544–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallardo, C.; Soler, A.; Nieto, R.; Cano, C.; Pelayo, V.; Sánchez, M.A.; Pridotkas, G.; Fernandez-Pinero, J.; Briones, V.; Arias, M. Experimental Infection of Domestic Pigs with African Swine Fever Virus Lithuania 2014 Genotype II Field Isolate. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 64, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, A.; Licoppe, A.; Volpe, R.; Paternostre, J.; Lesenfants, C.; Cassart, D.; Garigliany, M.; Tignon, M.; Berg, T.V.D.; Desmecht, D.; et al. Summer 2018: African swine fever virus hits north-western Europe. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forth, J.H.; Tignon, M.; Cay, A.B.; Forth, L.F.; Höper, D.; Blome, S.; Beer, M. Comparative analysis of whole-genome sequence of African swine fever virus Belgium 2018/1. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikalo, J.; Schoder, M.E.; Sehl, J.; Breithaupt, A.; Tignon, M.; Cay, A.B.; Gager, A.M.; Fischer, M.; Beer, M.; Blome, S. The African swine fever virus isolate Belgium 2018/1 shows high virulence in European wild boar. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1654–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sehl, J.; Pikalo, J.; Schäfer, A.; Franzke, K.; Pannhorst, K.; Elnagar, A.; Blohm, U.; Blome, S.; Breithaupt, A. Comparative Pathology of Domestic Pigs and Wild Boar Infected with the Moderately Virulent African Swine Fever Virus Strain “Estonia 2014”. Pathogens 2020, 9, 662. [Google Scholar]
- Pikalo, J.; Zani, L.; Hühr, J.; Beer, M.; Blome, S. Pathogenesis of African swine fever in domestic pigs and European wild boar—Lessons learned from recent animal trials. Virus Res. 2019, 271, 197614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.; Weesendorp, E.; Montoya, M.; Loeffen, W.L. Influence of age and dose of African swine fever virus infections on clinical outcome and blood parameters in pigs. Viral Immunol. 2017, 30, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Żmudzki, J.; Mazur-Panasiuk, N.; Juszkiewicz, M.; Woźniakowski, G. Analysis of the Clinical Course of Experimental Infection with Highly Pathogenic African Swine Fever Strain, Isolated from an Outbreak in Poland. Aspects Related to the Disease Suspicion at the Farm Level. Pathogens 2020, 9, 237. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschmann, J.; Guinat, C.; Beer, M.; Pronin, V.; Tauscher, K.; Petrov, A.; Keil, G.; Blome, S. Course and transmission characteristics of oral low-dose infection of domestic pigs and European wild boar with a Caucasian African swine fever virus isolate. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Cardiel, I.; Ballester, M.; Solanes, D.; Nofrarías, M.; López-Soria, S.; Argilaguet, J.M.; Lacasta, A.; Accensi, F.; Rodríguez, F.; Segalés, J. Standardization of pathological investigations in the framework of experimental ASFV infections. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tignon, M.; Gallardo, C.; Iscaro, C.; Hutet, E.; Van der Stede, Y.; Kolbasov, D.; De Mia, G.M.; Le Potier, M.-F.; Bishop, R.P.; Arias, M.; et al. Development and inter-laboratory validation study of an improved new real-time PCR assay with internal control for detection and laboratory diagnosis of African swine fever virus. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 178, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoder, M.-E.; Tignon, M.; Linden, A.; Vervaeke, M.; Cay, A.B. Evaluation of seven commercial African swine fever virus detection kits and three Taq polymerases on 300 well-characterized field samples. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 280, 113874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.P.; Reid, S.M.; Hutchings, G.H.; Grierson, S.S.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Dixon, L.K.; Bastos, A.D.; Drew, T.W. Development of a TaqMan® PCR assay with internal amplification control for the detection of African swine fever virus. J. Virol. Methods 2003, 107, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blome, S.; Gabriel, C.; Dietze, K.; Breithaupt, A.; Beer, M. High Virulence of African Swine Fever Virus Caucasus Isolate in European Wild Boars of All Ages. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Replication and virulence in pigs of the first African swine fever virus isolated in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blome, S.; Gabriel, C.; Beer, M. Pathogenesis of African swine fever in domestic pigs and European wild boar. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, A.; Forth, J.H.; Zani, L.; Beer, M.; Blome, S. No evidence for long-term carrier status of pigs after African swine fever virus infection. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1318–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howey, E.B.; O’Donnell, V.; Ferreira, H.C.D.C.; Borca, M.; Arzt, J. Pathogenesis of highly virulent African swine fever virus in domestic pigs exposed via intraoropharyngeal, intranasopharyngeal, and intramuscular inoculation, and by direct contact with infected pigs. Virus Res. 2013, 178, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omondi, E.A. Determination Of Optimal Viral Dos Immunological Response And Survival Rate In Local And Exotic Pigs Experimentally Infected with Africans Swine Fever Virus. Master’s Thesis, University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mujibi, F.D.; Okoth, E.; Cheruiyot, E.K.; Onzere, C.; Bishop, R.P.; Fevre, E.; Thomas, L.; Masembe, C.; Plastow, G.; Rothschild, M. Genetic diversity, breed composition and admixture of Kenyan domestic pigs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Navas, M.J.; Costa-Hurtado, M.; Almagro, V.; Bosch-Camós, L.; López, E.; Cuadrado, R.; Accensi, F.; Pina-Pedrero, S.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation from warthog to pig confirms the influence of the gut microbiota on African swine fever susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Animal | Day of Euthanasia | Cause | Major Pathological Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 dpi | humane endpoint |
|
| 2 | 14 dpi | humane endpoint |
|
| 3 | 18 dpi | end of experiment |
|
| 4 | 8 dpi | humane endpoint |
|
| 5 | 18 dpi | end of experiment |
|
| 6 | 7 dpi | humane endpoint |
|
| 7 | 18 dpi | end of experiment |
|
| 8 | 18 dpi | end of experiment |
|
| Animal | Day of Euthanasia | Cause | Major Pathological Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 9 dpi | humane endpoint |
|
| 17 | 9 dpi | died acutely over night |
|
| 18 | 9 dpi | humane endpoint |
|
| 19 | 9 dpi | humane endpoint |
|
| 20 | 9 dpi | humane endpoint |
|
| Animal | 0 dpi | 3 dpi | 7 dpi | 10 dpi | 14 dpi | 18 dpi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nd | 0.3 | 29,200 | |||
| 2 | nd | nd | 1270 | NA | 4260 | |
| 3 | nd | nd | nd | 19 | 15 | 8 |
| 4 | nd | 0.7 | 15,100 | |||
| 5 | nd | nd | 202 | 1290 | 353 | 284 |
| 6 | nd | 22 | 68,000 | |||
| 7 | nd | nd | 401 | 1660 | 525 | 127 |
| 8 | nd | nd | 2810 | 2810 | 870 | 20 |
| Animal | Day of Euthanasia | Blood | Serum | Spleen | Tonsil | Lymph Node | Lung | Liver | Kidney |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 dpi | 29,200 | 1140 | 37,100 | 21,000 | 33,300 | 20,100 | 13,200 | 734 |
| 2 | 14 dpi | 4260 | 595 | 4520 | 855 | 6600 | 820 | 2630 | 120 |
| 3 | 18 dpi | 8 | nd | 4 | 57 | 43 | 479 | 2 | 1 |
| 4 | 8 dpi | 15,100 | 1000 | 18,700 | 13,100 | 8760 | 9540 | 30,600 | 894 |
| 5 | 18 dpi | 248 | 0.2 | 5 | 514 | 132 | 5 | nd | 2 |
| 6 | 7 dpi | 68,000 | 15,200 | 43,000 | 56,700 | 37,000 | 59,600 | 224,000 | 13,800 |
| 7 | 18 dpi | 127 | 0.1 | 3 | 423 | 319 | 8 | 2 | 1 |
| 8 | 18 dpi | 20 | 0.02 | 10 | 102 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 3 |
| Animal | Day of Euthanasia | Blood | Serum | Spleen | Tonsil | Lymph Node | Lung | Liver | Kidney |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 9 dpi | 10,200 | 2320 | 4510 | 164 | 42 | 122 | 359 | 49 |
| 17 | 9 dpi | 66,400 | 15,800 | 15,400 | 8560 | 9770 | 4520 | 48,600 | 3780 |
| 18 | 9 dpi | 103,000 | 22,500 | 14,000 | 1900 | 589 | 5810 | 22,000 | 707 |
| 19 | 9 dpi | 61,900 | 13,900 | 4610 | 3360 | 587 | 552 | 4040 | 500 |
| 20 | 9 dpi | 78,000 | 27,100 | 23,000 | 18,900 | 3120 | 5680 | 11,000 | 987 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pikalo, J.; Schoder, M.-E.; Sehl-Ewert, J.; Breithaupt, A.; Cay, A.B.; Lhoëst, C.; van Campe, W.; Mostin, L.; Deutschmann, P.; Roszyk, H.; et al. Towards Efficient Early Warning: Pathobiology of African Swine Fever Virus “Belgium 2018/1” in Domestic Pigs of Different Age Classes. Animals 2021, 11, 2602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092602
Pikalo J, Schoder M-E, Sehl-Ewert J, Breithaupt A, Cay AB, Lhoëst C, van Campe W, Mostin L, Deutschmann P, Roszyk H, et al. Towards Efficient Early Warning: Pathobiology of African Swine Fever Virus “Belgium 2018/1” in Domestic Pigs of Different Age Classes. Animals. 2021; 11(9):2602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092602
Chicago/Turabian StylePikalo, Jutta, Marie-Eve Schoder, Julia Sehl-Ewert, Angele Breithaupt, Ann Brigitte Cay, Coline Lhoëst, Willem van Campe, Laurent Mostin, Paul Deutschmann, Hanna Roszyk, and et al. 2021. "Towards Efficient Early Warning: Pathobiology of African Swine Fever Virus “Belgium 2018/1” in Domestic Pigs of Different Age Classes" Animals 11, no. 9: 2602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092602
APA StylePikalo, J., Schoder, M.-E., Sehl-Ewert, J., Breithaupt, A., Cay, A. B., Lhoëst, C., van Campe, W., Mostin, L., Deutschmann, P., Roszyk, H., Beer, M., Blome, S., & Tignon, M. (2021). Towards Efficient Early Warning: Pathobiology of African Swine Fever Virus “Belgium 2018/1” in Domestic Pigs of Different Age Classes. Animals, 11(9), 2602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092602








