Alleviating Effects of Vitamins C and E Supplementation on Oxidative Stress, Hematobiochemical, and Histopathological Alterations Caused by Copper Toxicity in Broiler Chickens
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Birds, Design
2.2. Determination of Hematological and Biochemical Parameters
2.3. Histopathological Investigations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hematological Parameters
3.2. Serum Biochemical Parameters
3.3. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Status
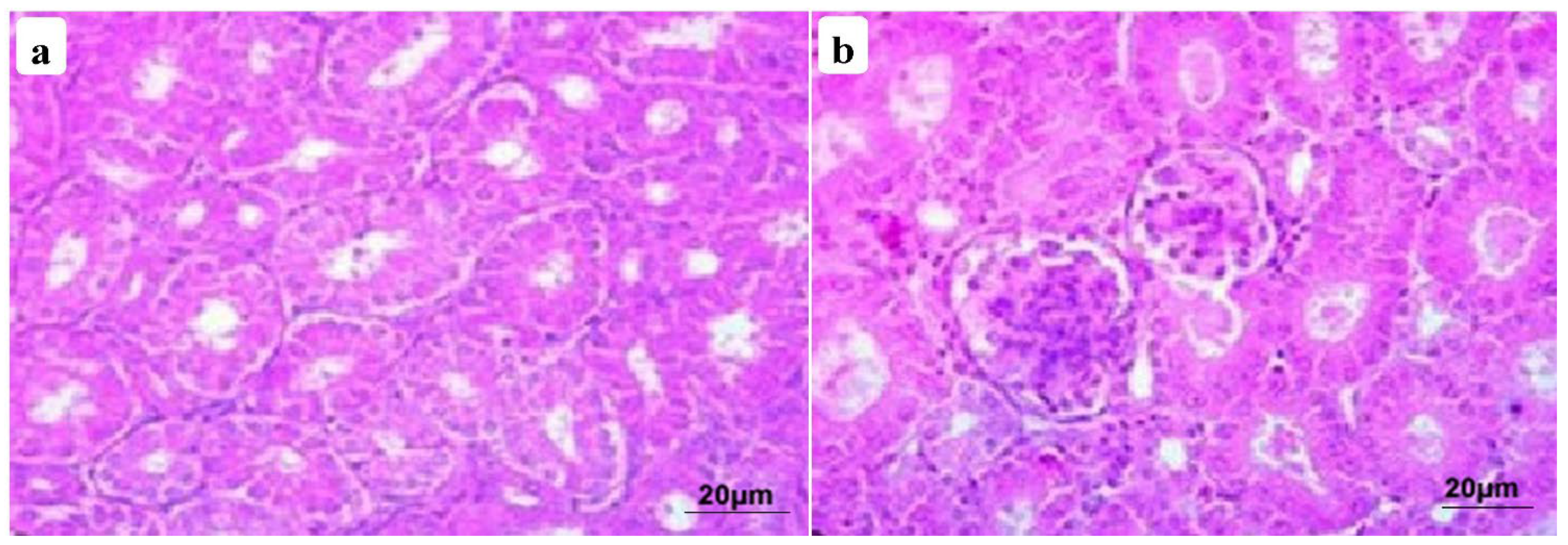
3.4. Histopathological Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, R.C. Veterinary Toxicology: Basic and Clinical Principles; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gaetke, L.M.; Chow, C.K. Copper toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology 2003, 189, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Mondal, M.; Biswas, P.; Bairagi, B.; Samanta, C. Influence of level of dietary inorganic and organic copper and energy level on the performance and nutrient utilization of broiler chickens. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 23, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, B.; Biswas, A.; Ghosh, P. Effects of dietary copper supplementation on production performance and plasma biochemical parameters in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2011, 52, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, B.; Ghosh, P.; Biswas, A.; Das, S. The effects of copper supplementation on the performance and hematological parameters of broiler chickens. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 24, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Y.; Abdalah, A.; Zeweil, H.; Bovera, F.; El-Din, A.T.; Araft, M. Effect of inorganic or organic copper additions on reproductive performance, lipid metabolism and morphology of organs of dual-purpose breeding hens. Arch. Geflugelk. 2011, 3, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, Y.; Qota, E.; Zeweil, H.; Bovera, F.; Abd Al-Hamid, A.; Sahledom, M. Effect of different dietary concentrations of inorganic and organic copper on growth performance and lipid metabolism of White Pekin male ducks. Br. Poult. Sci. 2012, 53, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, A.; Dai, S.; Wu, X.; Cai, Z. Copper bioavailability, mineral utilization, and lipid metabolism in broilers. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 64, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, M.; Baker, D. Toxicity and tissue accumulation of copper in chicks fed casein and soy-based diets. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 4505–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Besbasi, F.; Afan, A.; Bengali, E.; Zendah, M.; Hilmy, M.; Mukhtar, M.; Jaspal, S.; Aslam, N. Effects of copper supplement on haematological profiles and broiler meat composition. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2001, 3, 203–205. [Google Scholar]
- Yigit, A.; Cinar, M.; Yildirim, E. The effects of levamisole on oxidative stress induced by copper intoxication in broilers. N. Z. Vet. J. 2012, 60, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, M.; Yildirim, E.; Yigit, A.A.; Yalcinkaya, I.; Duru, O.; Kisa, U.; Atmaca, N. Effects of dietary supplementation with vitamin C and vitamin E and their combination on growth performance, some biochemical parameters, and oxidative stress induced by copper toxicity in broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 158, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wideman, R., Jr.; Kirby, Y.K.; Barton, T.; Clark, D.; Bayyari, G.; Huff, W.; Moore, P., Jr.; Dunn, P. Excess dietary copper triggers enlargement of the proventriculus in broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 1996, 5, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardej, D.; Trombetta, L.D. Clinical Toxicology Principles and Mechanism; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, M.; Abd El Hamied, S.; Ahmed, E. Mitigation Effects of Vitamin C and E Against Copper Toxicity in Broiler Chickens, with Reference to Biochemical, Genotoxicity and Pathological Studies; Research Square: Durham, NC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, M.; Portmann, B.; Mowat, A.; Williams, R.; Pandit, A.; Mills, C.; Bremner, I. Increased hepatic copper concentration in Indian childhood cirrhosis. Lancet 1979, 313, 1203–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Cui, W.; Peng, X.; Bai, C.; Cui, H. Effect of dietary high copper on the antioxidase activities of brain tissue in chickens. Chin. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2010, 41, 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Liao, J.; Pei, R.; Yu, W.; Han, Q.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Hu, L.; Pan, J.; Tang, Z. Autophagy attenuates copper-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by regulating oxidative stress in chicken hepatocytes. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, F.; Peng, X.; Deng, J.; Cui, H. Effects of high copper on the production of the hydroxy radical and nitrogen monoxide in liver of ducklings. Chin. Vet. Sci. 2008, 38, 787–790. [Google Scholar]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkuş, İ. Serbest radikaller ve fizyopatolojik etkileri. Mimoza Yayınları Konya 1995, 1, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, I. Manifestations of copper excess. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67, 1069S–1073S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B.; Chirico, S. Lipid peroxidation: Its mechanism, measurement, and significance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1993, 57, 715S–725S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, M.; Yigit, A.; Eraslan, G. Effects of vitamin C or vitamin E supplementation on cadmium induced oxidative stress and anaemia in broilers. Rev. Méd. Vétér. 2010, 161, 449–454. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, R.E.; Amer, S.A.; Farroh, K.Y.; Al-Gabri, N.A.; Ahmed, A.I.; El-Araby, D.A.; Ahmed, S.A. The effects of chitosan-vitamin C nanocomposite supplementation on the growth performance, antioxidant status, immune response, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings. Aquaculture 2021, 534, 736269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.A.; Mohamed, W.A.; Gharib, H.S.; Al-Gabri, N.A.; Gouda, A.; Elabbasy, M.T.; Abd El-Rahman, G.I.; Omar, A.E. Changes in the growth, ileal digestibility, intestinal histology, behavior, fatty acid composition of the breast muscles, and blood biochemical parameters of broiler chickens by dietary inclusion of safflower oil and vitamin C. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, A.; Amer, S.A.; Gabr, S.; Tolba, S.A. Effect of dietary supplemental ascorbic acid and folic acid on the growth performance, redox status, and immune status of broiler chickens under heat stress. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, R.E.; Ahmed, S.A.; Amer, S.A.; Al-Gabri, N.A.; Ahmed, A.I.; Abdel-Warith, A.-W.A.; Younis, E.-S.M.; Metwally, A.E. Influence of vitamin C feed supplementation on the growth, antioxidant activity, immune status, tissue histomorphology, and disease resistance in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovec, J.; Levart, A.; Svete, A.N.; Perić, L.; Stojčić, M.Đ.; Žikić, D.; Salobir, J.; Rezar, V. Effects of supplementation with α-tocopherol, ascorbic acid, selenium, or their combination in linseed oil-enriched diets on the oxidative status in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, L.R. Vitamins in Animal and Human Nutrition; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Niki, E. Interaction of ascorbate and α-tocopherol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1987, 498, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, Q.; Yang, X. Effect of in ovo feeding of vitamin C on antioxidation and immune function of broiler chickens. Animal 2019, 13, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, O.; Braimah, S. Mitigating Effect of Vitamin-E on Copper Sulphate-Induced Toxicity in African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Eur. J. Med. Res. 2020, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Ibrahim, R.E.; Farroh, K.Y.; Moustafa, A.A.; Al-Gabri, N.A.; Alkafafy, M.; Amer, S.A. Chitosan vitamin E nanocomposite ameliorates the growth, redox, and immune status of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reared under different stocking densities. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajuwon, O.R.; Idowu, O. Vitamin C attenuates copper-induced oxidative damage in broiler chickens. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 7525–7530. [Google Scholar]
- Vantress, C. Cobb Broiler Management Guide. Cobb Vantress. Siloam Springs USA. 2012. Available online: https://www.cobb-vantress.com/assets/5c7576a214/Broiler-guide-R1.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Giambrone, J.; Clay, R.P. Vaccination of day-old broiler chicks against Newcastle disease and infectious bursal disease using commercial live and/or inactivated vaccines. Avian Dis. 1986, 30, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, K.; Sahin, N.; Yaralioglu, S. Effects of vitamin C and vitamin E on lipid peroxidation, blood serum metabolites, and mineral concentrations of laying hens reared at high ambient temperature. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2002, 85, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinder, P. Determination of blood glucose using an oxidase-peroxidase system with a non-carcinogenic chromogen. J. Clin. Pathol. 1969, 22, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, R. Determination of serum creatinine. In Clinical Chemistry: Principles and Techniques, 2nd ed.; Harper and Row Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, G.; Pasman, A.; Hoek, F. Determination of uric acid with uricase and peroxidase. Clin. Chim. Acta 1980, 101, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, D.E.; Valentine, W.N. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1967, 70, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.P., Jr.; Dailey, M.; Sugarman, E. Negative and positive assays of superoxide dismutase based on hematoxylin autoxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1987, 255, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, S.; Layton, C.; Bancroft, J. The hematoxylins and eosin. In Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 7th ed.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2013; pp. 172–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhu, J.; Liu, B.; Qiu, J.; Lu, X.; Curtin, B.; Ji, F.; Yu, D. Effects of High-Dose of Copper Amino Acid Complex on Laying Performance, Hematological and Biochemical Parameters, Organ Index, and Histopathology in Laying Hens. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Ji, F.; Lin, Y.; Steward, F.; Lu, L.; Liu, B.; Yu, S. Effects of dietary supplementation with copper sulfate or tribasic copper chloride on broiler performance, relative copper bioavailability, and oxidation stability of vitamin E in feed. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cerrate, S.; Coto, C.; Yan, F.; Waldroup, P. Evaluation of Mintrex copper as a source of copper in broiler diets. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2007, 6, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarski, B.; Gortat, M.; Lechowski, J.; Zukiewicz-Sobczak, W.; Sobczak, P.; Zawislak, K. Impact of copper (Cu) at the dose of 50 mg on haematological and biochemical blood parameters in turkeys, and level of Cu accumulation in the selected tissues as a source of information on product safety for consumers. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2014, 21, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ozcelik, D.; Toplan, S.; Ozdemir, S.; Akyolcu, M. Effects of excessive copper intake on hematological and hemorheological parameters. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2002, 89, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.; Rennert, O. The role of copper in iron metabolism. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1980, 10, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Selim, N.; Youssef, S.; Abdel-Salam, A.; Nada, S.A. Evaluations of some natural antioxidant sources in broiler diets: 1-effect on growth, physiological and immunological performance of broiler chicks. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2013, 12, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baruah, S.; Goswami, S.; Kalita, D. Haematobiochemical and Pathological Alterations of Chronic Copper Toxicity in Ducks. J. Anim. Res. 2018, 8, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Kalavathi, S.; Kumar, A.A.; Reddy, A.G.; Srilatha, C.; Reddy, A.R. Sodium Arsenite Toxicity in Broiler Chicks and its Amelioration: Haemato-Biochemical and Pathological Studies; AGRIS: Chatham, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kandpal, V.; Kumar, D.; Bisht, R. Protective effect of vitamin E on haematological parameters in chronic toxicity of hexavalent chromium in laboratory chicks. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 388–392. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, R.R.; Kumar, P.; Mondal, T.K. Effect of vitamin E and selenium on haematological parameters in sub-acute toxicity of hexavalent chromium in broiler chick. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 3, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.C.; Nogueira-Pedro, A.; Santos, E.W.; Hastreiter, A.; Silva, G.B.; Borelli, P.; Fock, R.A. A review of select minerals influencing the haematopoietic process. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2018, 31, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazon, A.; Monteiro, E.; Pinheiro, G.; Fernadez, M. Hematological and physiological changes induced by short-term exposure to copper in the freshwater fish, Prochilodus scrofa. Braz. J. Biol. 2002, 62, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.-H.; Liu, P.-J.; Hsia, S.; Chuang, C.-J.; Chen, P.-C. Role of certain trace minerals in oxidative stress, inflammation, CD4/CD8 lymphocyte ratios and lung function in asthmatic patients. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 48, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kazaz, S.E.; Hafez, M.H. Evaluation of copper nanoparticles and copper sulfate effect on immune status, behavior, and productive performance of broilers. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2020, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ognik, K.; Sembratowicz, I.; Cholewińska, E.; Jankowski, J.; Kozłowski, K.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Zduńczyk, Z. The effect of administration of copper nanoparticles to chickens in their drinking water on the immune and antioxidant status of the blood. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eo, J.; Lee, K.-J. Effect of dietary ascorbic acid on growth and non-specific immune responses of tiger puffer, Takifugu rubripes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.; Maggini, S. Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afaghi, A.; Zare, S.; Heidari, R.; Asadpoor, Y.; Viayeh, R.M. Effects of copper sulfate (CuSO4) on the levels of glucose and cortisol in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2007, 10, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Long, X.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, S. The potential toxicity of copper nanoparticles and copper sulphate on juvenile Epinephelus coioides. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 152, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Shaikh, M.U.; Ali, N.; Riaz, M. Copper sulphate toxicity in a young male complicated by methemoglobinemia, rhabdomyolysis and renal failure. J. Coll. Phys. Surg. Pak. 2010, 20, 490–491. [Google Scholar]
- Lierz, M. Avian renal disease: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Vet. Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2003, 6, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Sharaf, R.; Khan, M.; Saleemi, M.K.; Mahmood, F. Arsenic toxicity in broiler chicks and its alleviation with ascorbic acid: A toxico-patho-biochemical study. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2013, 15, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseintabar, B.; Dadashbeiki, M.; Bouyeh, M.; Seidavi, A.; van den Hoven, R.; Gamboa, S. Effect of different levels of L-carnitine and lysine-methionine on broiler blood parameters. Rev. MVZ Córdoba 2015, 20, 4698–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Torki, M.; Habibian, M.; Rostami, T.; Moradi, A. Effects of High Dietary Levels of Selenium and Copper on Growth Performance, Selected Blood Biochemical Parameters and Antibody Production Against Newcastle Disease Vaccine Virus in Broiler Chickens; Scientific Information Database: Tehran, Iran, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Apsîte, M.; Berzina, N.; Basova, N. Effects of high but non-toxic dietary intake of selenium and copper on indices of the antioxidant defence system and on accumulation of trace elements in chicks. Proc. Latvian Acad. Sci. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Xing, M. Copper or/and arsenic induce oxidative stress-cascaded, nuclear factor kappa B-dependent inflammation and immune imbalance, trigging heat shock response in the kidney of chicken. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 98103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Iqbal, R.; Malik, F.; Aziz, T.; Sarfraz, I.; Ahmed, Z.; Shafqat, S. The study of histopathological changes upon exposure to vinegerized copper sulphate in liver and kidney of broiler chick. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2012, 12, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Rasool, A.; Javed, M.T.; Akhtar, M.; Bhatti, S.S.; Shahzad, M.; Hussain, R. Effects of urea and copper sulphate on some serum biochemical and meat parameters in broiler chicken. Pak. Vet. J. 2012, 33, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Newsome, C.; Williams, J.; Glass, K. Copper-induced cytotoxicity and transcriptional activation of stress genes in human liver carcinoma (HepG2) cells. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Metal Ions in Biology and Medicine (Les Ions Metalliques en Biologie et en Medecine, Symposium International Sur Les Ions Metalliques), Lisbon, Portugal, 21–24 May 2008; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Oguz, E.O.; Yuksel, H.; Enli, Y.; Tufan, A.C.; Turgut, G. The effects of copper sulfate on liver histology and biochemical parameters of term ross broiler chicks. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 133, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oğuz, E.; Enli, Y.; Tufan, A.; Turgut, G. Toxic effects of copper sulfate on the brains of term Hubbard broiler chicks: A stereological and biochemical study. Biotech. Histochem. 2014, 89, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajuwon, O.; Idowu, O.; Afolabi, S.; Kehinde, B.; Oguntola, O.; Olatunbosun, K. The effects of dietary copper supplementation on oxidative and antioxidant systems in broiler chickens. Arch. Zootec. 2011, 60, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, R.S.; Gupta, E.S.; Dhakal, B.K.; Thakur, A.R.; Ahnn, J. Vitamin C and vitamin E protect the rat testes from cadmium-induced reactive oxygen species. Mol. Cells 2004, 17, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Jian, Z.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Copper induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in the mouse liver. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ademuyiwa, O.; Ugbaja, R.; Ojo, D.; Owoigbe, A.; Adeokun, S. Reversal of aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD) inhibition and reduction of erythrocyte protoporphyrin levels by vitamin C in occupational lead exposure in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 20, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattie, M.D.; Freedman, J.H. Protective effects of aspirin and vitamin E (α-tocopherol) against copper-and cadmium-induced toxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ingredients | Starter Stage (1–10 Day) | Grower Stage (11–22 Day) | Finisher Stage (23–42 Day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean meal, 48% | 34.65 | 28.1 | 24.9 |
| Corn gluten, 60% | 1.5 | 3 | 3 |
| Yellow corn | 58.1 | 62.1 | 63.6 |
| Wheat bran | - | 1.10 | 1.80 |
| Soy oil | 2.00 | 2.00 | 3.26 |
| Calcium carbonate | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Calcium dibasic phosphate | 1.80 | 1.70 | 1.50 |
| Premix * | 0.300 | 0.300 | 0.300 |
| Common salt | 0.300 | 0.300 | 0.300 |
| DL-Methionine, 98% | 0.180 | 0.140 | 0.110 |
| Lysine, Hcl, 78% | 0.160 | 0.160 | 0.130 |
| Anti-mycotoxin | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.100 |
| Proximate composition (%) | |||
| ME, Kcal/Kg | 3047.53 | 3090.13 | 3178.59 |
| Crude protein | 22.14 | 20.40 | 19.07 |
| Crude fiber | 2.60 | 2.61 | 2.63 |
| Fat | 4.50 | 4.61 | 5.87 |
| Available P | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.42 |
| Calcium | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.87 |
| Lysine | 1.38 | 1.21 | 1.09 |
| Methionine | 0.56 | 0.49 | 0.47 |
| Parameters | CON | CuSO4 | CuSO4 + vitamin C | CuSO4 + vitamin E | CuSO4 + vitamin C + vitamin E | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At the 3rd week | RBCs (×106/µL) | 2.15 ± 0.068 a | 1.85 ± 0.094 b | 2.08 ± 0.058 a | 2.09 ± 0.066 a | 2.11 ± 0.052 a | 0.00 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 9.73 ± 0.228 a | 8.05 ± 0.545 c | 9.00 ± 0.158 b | 9.15 ± 0.145 b | 9.41 ± 0.303 a,b | 0.00 | |
| HCT (%) | 25.1 ± 0.47 a | 21.5 ± 1.32 b | 23.9 ± 0.54 a | 24.1 ± 0.66 a | 24.5 ± 0.61 a | 0.00 | |
| MCV (fL) | 116 ± 1.8 | 116 ± 2.5 | 115 ± 1.8 | 1151 ± 1.4 | 116 ± 1.0 | 0.59 | |
| MCH (Pg) | 45.1 ± 1.83 | 43.4 ± 1.77 | 43.1 ± 1.06 | 43.8 ± 1.13 | 44.5 ± 0.48 | 0.12 | |
| MCHC (%) | 38.8 ± 1.10 | 37.3 ± 0.97 | 37.6 ± 0.71 | 38.0 ± 0.82 | 38.3 ± 0.73 | 0.05 | |
| At the 6th week | RBCs (×106/µL) | 2.79 ± 0.124 a | 2.42 ± 0.045 d | 2.55 ± 0.049 c,d | 2.60 ± 0.088 b,c | 2.70 ± 0.077 a,b | 0.00 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 10.98 ± 0.184 a | 9.54 ± 0.383 c | 9.93 ± 0.109 b,c | 10.18 ± 0.268 b | 10.68 ± 0.226 a | 0.00 | |
| HCT (%) | 28.4 ± 0.56 a | 26.0 ± 0.73 c | 27.1 ± 0.51 b | 27.5 ± 0.60 a,b | 28.1 ± 0.84 a,b | 0.00 | |
| MCV (fL) | 101 ± 1.6 | 107 ± 1.6 | 106 ± 1.7 | 106 ± 1.7 | 103 ± 1.0 | 0.51 | |
| MCH (Pg) | 40.1 ± 2.55 | 38.7 ± 1.11 | 38.6 ± 0.84 | 39.1 ± 0.89 | 39.5 ± 0.94 | 0.37 | |
| MCHC (%) | 38.2 ± 0.51 a | 36.1 ± 0.69 c | 36.5 ± 0.53 c | 37.0 ± 0.51 b,c | 37.9 ± 1.04 a,b | 0.00 |
| Parameters | CON | CuSO4 | CuSO4 + Vitamin C | CuSO4 + Vitamin E | CuSO4 + Vitamin C + Vitamin E | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At the 3rd week | WBCs (×103/µ L) | 20.4 ± 1.33 a | 17.2 ± 1.21 c | 18.0 ± 0.88 b,c | 18.7 ± 0.77 a,b,c | 19.7 ± 1.33 a,b | 0.001 |
| Heterophils (×103/µ L) | 6.79 ± 0.459 | 6.23 ± 0.393 | 6.30 ± 0.312 | 6.56 ± 0.379 | 6.70 ± 0.459 | 0.09 | |
| Lymphocytes (×103/µ L) | 10.54 ± 0.425 a | 8.32 ± 0.927 c | 9.03 ± 0.654 b,c | 9.41 ± 0.685 a,b,c | 0.15 ± 0.758 a,b | 0.00 | |
| Monocytes (×103/µ L) | 1.59 ± 0.157 a | 1.16 ± 0.340 b | 1.27 ± 0.071 a,b | 1.30 ± 0.084 a,b | 1.44 ± 0.105 a,b | 0.007 | |
| Eosinophils (×103/µ L) | 0.980 ± 0.0604 | 1.03 ± 0.288 | 0.970 ± 0.0484 | 0.982 ± 0.1042 | 0.992 ± 0.1308 | 0.95 | |
| Basophils (×103/µ L) | 0.506 ± 0.0493 | 0.468 ± 0.0497 | 0.472 ± 0.0396 | 0.472 ± 0.0438 | 0.486 ± 0.0461 | 0.57 | |
| At the 6th week | WBCs (×103/µ L) | 21.1 ± 1.90 a | 15.8 ± 1.68 c | 16.8 ± 0.87 c | 17.9 ± 0.58 b,c | 19.9 ± 1.25 a,b | 0.00 |
| Heterophils (×103/µ L) | 7.12 ± 0.674 a | 5.26 ± 1.088 b | 5.99 ± 0.321 a,b | 6.14 ± 0.571 a,b | 6.75 ± 0.447 a | 0.001 | |
| Lymphocytes (×103/µ L) | 10.84 ± 0.993 a | 7.86 ± 0.616 b | 8.16 ± 0.532 b | 9.01 ± 0.564 b | 10.20 ± 0.700 a | 0.00 | |
| Monocytes (×103/µ L) | 1.60 ± 0.150 a | 1.18 ± 0.340 b | 1.29 ± 0.071 a,b | 1.34 ± 0.084 a,b | 1.45 ± 0.102 a,b | 0.008 | |
| Eosinophils (×103/µ L) | 1.00 ± 0.090 | 1.05 ± 0.388 | 0.980 ± 0.0484 | 0.992 ± 0.1042 | 1.08 ± 0.130 | 0.83 | |
| Basophils (×103/µ L) | 0.518 ± 0.0476 b | 0.450 ± 0.0509 | 0.462 ± 0.0396 | 0.472 ± 0.0438 | 0.506 ± 0.0461 | 0.07 |
| Parameters | CON | CuSO4 | CuSO4 + Vitamin C | CuSO4 + Vitamin E | CuSO4 + Vitamin C + Vitamin E | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At the 3rd week | Glucose (mg/dL) | 157 ± 10.01 a | 117 ± 7.20 b | 127 ± 8.00 a,b | 136 ± 7.5 a,b | 150 ± 9.7 a | 0.009 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 3.29 ± 0.553 | 3.70 ± 0.266 | 3.19 ± 0.158 | 3.39 ± 0.503 | 3.14 ± 0.479 | 0.25 | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.508 ± 0.0679 | 0.618 ± 0.1160 | 0.566 ± 0.0585 | 0.532 ± 0.0438 | 0.528 ± 0.0759 | 0.13 | |
| At the 6th week | Glucose (mg/dL) | 159 ± 17.9 a | 122 ± 9.8 b | 135 ± 13.6 a,b | 143 ± 11.3 a,b | 152 ± 14.0 a | 0.003 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 4.41 ± 0.570 b | 5.18 ± 0.362 a | 4.85 ± 0.352 a,b | 4.83 ± 0.651 a,b | 4.54 ± 0.405 b | 0.008 | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.614 ± 0.0665 b | 0.784 ± 0.0971a | 0.688 ± 0.0664 a,b | 0.624 ± 0.0646 b | 0.586 ± 0.1059 b | 0.009 |
| Parameters | CON | CuSO4 | CuSO4 + Vitamin C | CuSO4 + Vitamin E | CuSO4 + Vitamin C + Vitamin E | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At the 3rd week | MDA (nmol/mL) | 1.28 ± 0.177 c | 1.78 ± 0.094 a | 1.64 ± 0.134 a,b | 1.53 ± 0.182 a,b,c | 1.44 ± 0.131 b,c | 0.00 |
| GSH-Px (U/mL) | 37.3 ± 5.71 | 30.3 ± 3.50 | 31.5 ± 3.13 | 34.0 ± 8.00 | 36.1 ± 6.38 | 0.07 | |
| SOD (U/mL) | 4.04 ± 0.114 a | 2.48 ± 0.211 c | 2.95 ± 0.124 b | 3.08 ± 0.174 b | 3.10 ± 0.234 b | 0.00 | |
| At the 6th week | MDA (nmol/mL) | 1.34 ± 0.157 c | 2.01 ± 0.222 a | 1.84 ± 0.152 a,b | 1.74 ± 0.147 a,b | 1.65 ± 0.249 b | 0.00 |
| GSH-Px (U/mL) | 57.0 ± 6.70 a | 37.6 ± 3.60 c | 43.6 ± 3.57 b | 46.3 ± 11.23 b | 50.4 ± 4.97 a,b | 0.00 | |
| SOD (U/mL) | 4.99 ± 0.234 a | 2.91 ± 0.177 d | 3.24 ± 0.350 c,d | 3.61 ± 0.165 b,c | 3.85 ± 0.350 b | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hashem, M.A.; Abd El Hamied, S.S.; Ahmed, E.M.A.; Amer, S.A.; Hassan, A.M. Alleviating Effects of Vitamins C and E Supplementation on Oxidative Stress, Hematobiochemical, and Histopathological Alterations Caused by Copper Toxicity in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061739
Hashem MA, Abd El Hamied SS, Ahmed EMA, Amer SA, Hassan AM. Alleviating Effects of Vitamins C and E Supplementation on Oxidative Stress, Hematobiochemical, and Histopathological Alterations Caused by Copper Toxicity in Broiler Chickens. Animals. 2021; 11(6):1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061739
Chicago/Turabian StyleHashem, Mohamed A., Sahar S. Abd El Hamied, Eman M. A. Ahmed, Shimaa A. Amer, and Aziza M. Hassan. 2021. "Alleviating Effects of Vitamins C and E Supplementation on Oxidative Stress, Hematobiochemical, and Histopathological Alterations Caused by Copper Toxicity in Broiler Chickens" Animals 11, no. 6: 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061739
APA StyleHashem, M. A., Abd El Hamied, S. S., Ahmed, E. M. A., Amer, S. A., & Hassan, A. M. (2021). Alleviating Effects of Vitamins C and E Supplementation on Oxidative Stress, Hematobiochemical, and Histopathological Alterations Caused by Copper Toxicity in Broiler Chickens. Animals, 11(6), 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061739







