Impact of Ambient Temperature Sample Storage on the Equine Fecal Microbiota
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Animals
2.3. Sample Size Calculation
2.4. Sample Storage and Processing
2.5. Data Analysis and Bioinformatics
3. Results
3.1. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis
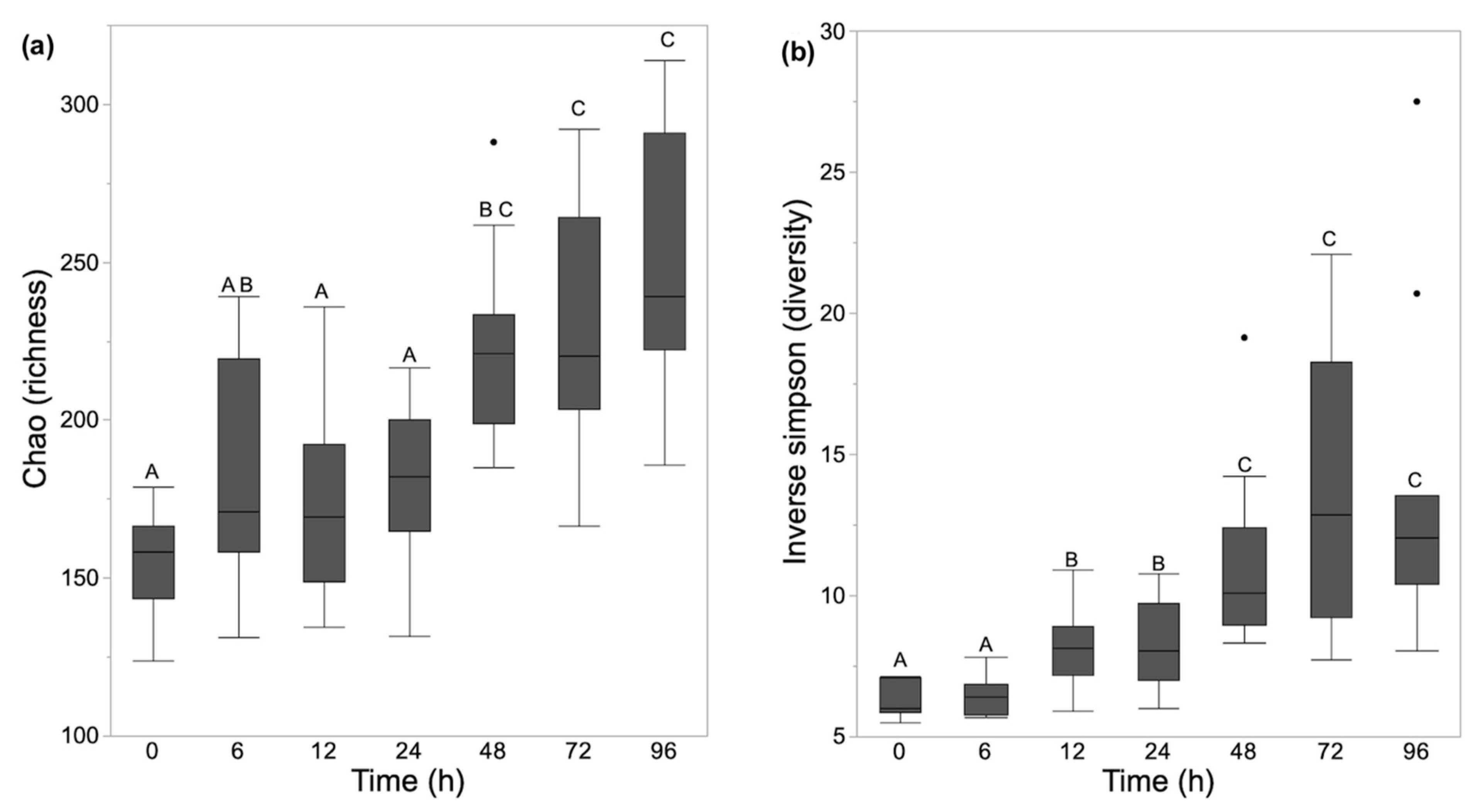
3.2. Alpha Diversity
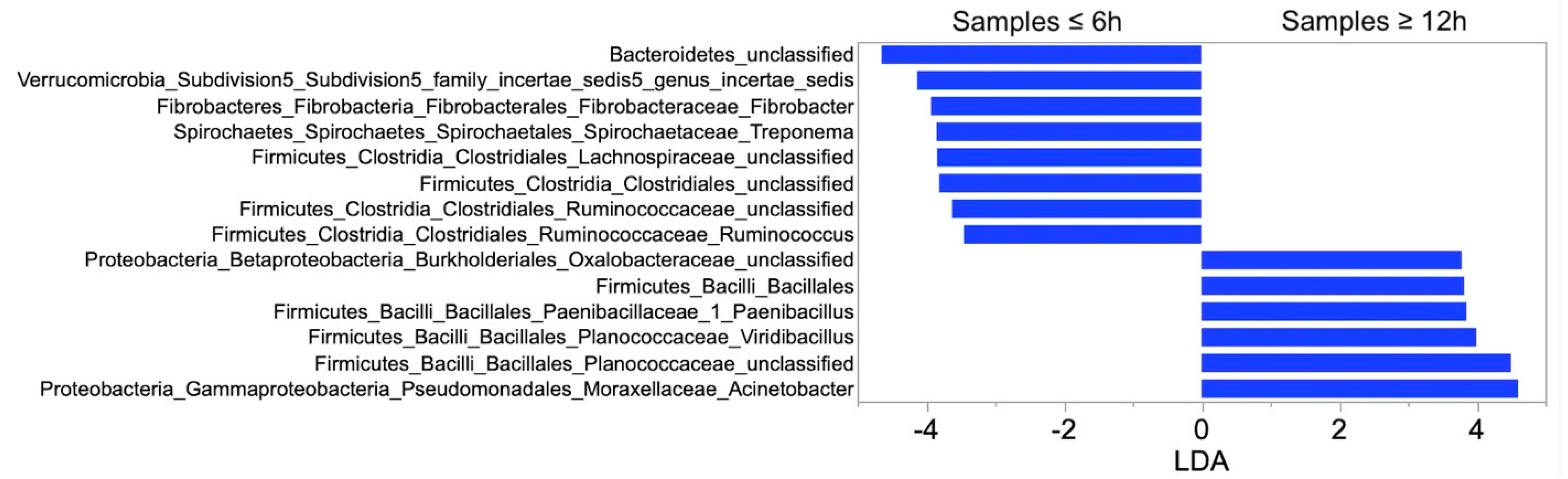
3.3. Relative Abundance and LEfSe Analysis
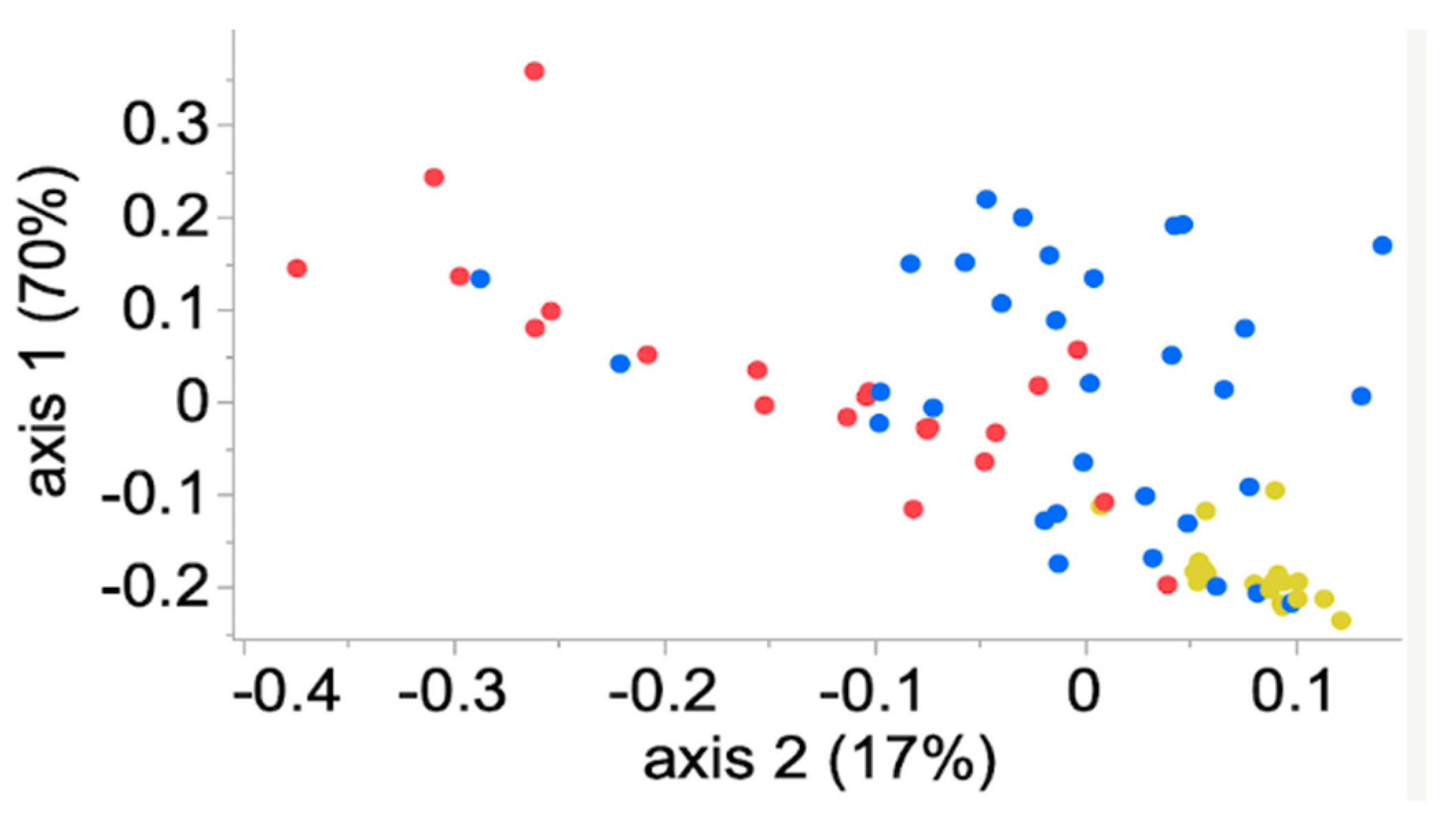
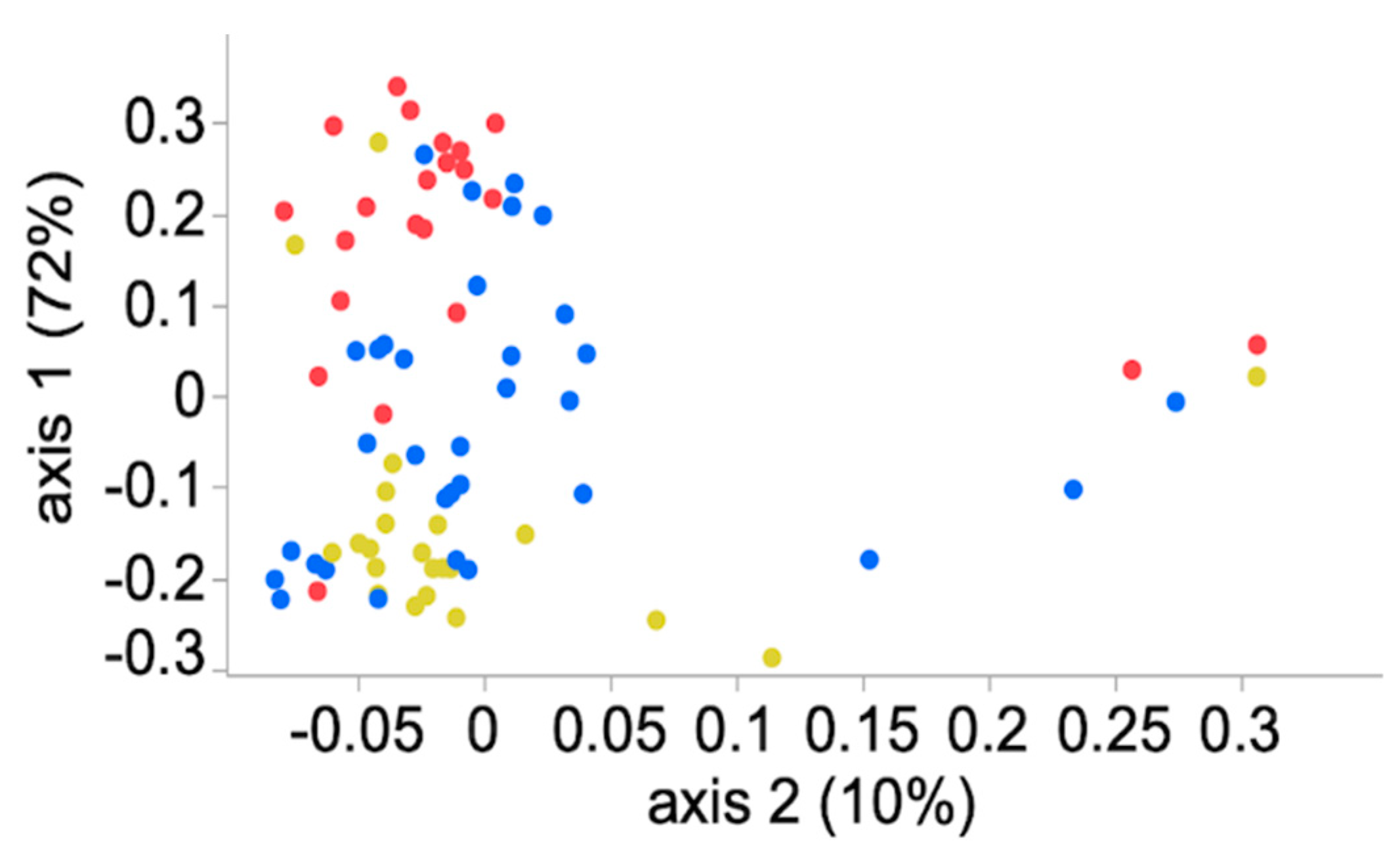
3.4. Community Membership and Structure
3.5. Meta-Communities Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, M.C.; Weese, J.S. Understanding the Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. Veter. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2018, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Weese, J.S. The equine intestinal microbiome. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2012, 13, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, J.M.; Leong, L.E.X.; Rogers, G.B. Sample storage conditions significantly influence faecal microbiome profiles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.; Clark, J.; Doré, J. Fecal microbiota analysis: An overview of sample collection methods and sequencing strategies. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1485–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, I.M.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Siddle, J.P.; Klaenhammer, T.R.; Ringel, Y. Characterization of the Fecal Microbiota Using High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals a Stable Microbial Community during Storage. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouhy, F.; Deane, J.; Rea, M.C.; O’Sullivan, Ó.; Ross, R.P.; O’Callaghan, G.; Plant, B.J.; Stanton, C. The Effects of Freezing on Faecal Microbiota as Determined Using MiSeq Sequencing and Culture-Based Investigations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Room Temperature. The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language; Houghton Mifflin Harcourt: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tal, M.; Verbrugghe, A.; Gomez, D.E.; Chau, C.; Weese, J.S. The effect of storage at ambient temperature on the feline fecal microbiota. BMC Veter. Res. 2017, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlčková, K.; Mrázek, J.; Kopečný, J.; Petrželková, K.J. Evaluation of different storage methods to characterize the fecal bacterial communities of captive western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla gorilla). J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 91, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, M.I.; Bergström, A.; Licht, T.R. Freezing fecal samples prior to DNA extraction affects the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio determined by downstream quantitative PCR analysis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 329, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.; Shaw, T.I.; Oladeinde, A.; Glenn, T.C.; Oakley, B.; Molina, M. Rapid Microbiome Changes in Freshly Deposited Cow Feces under Field Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al, K.F.; Bisanz, J.E.; Gloor, G.B.; Reid, G.; Burton, J.P. Evaluation of sampling and storage procedures on preserving the community structure of stool microbiota: A simple at-home toilet-paper collection method. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 144, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedjo, D.I.; Jonkers, D.M.A.E.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Masclee, A.A.; Van Best, N.; Pierik, M.J.; Penders, J. The Effect of Sampling and Storage on the Fecal Microbiota Composition in Healthy and Diseased Subjects. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, K.F.; Schulz, C.J.; Childers, G.W. Rapid regrowth and detection of microbial contaminants in equine fecal microbiome samples. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, H.L.; Pitta, D.; Indugu, N.; Vecchiarelli, B.; Engiles, J.B.; Southwood, L.L. Characterization of the fecal microbiota of healthy horses. Am. J. Veter. Res. 2018, 79, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muiños-Bühl, A.; González-Recio, O.; Muñoz, M.; Óvilo, C.; García-Casco, J.; Fernández, A.I. Evaluating Protocols for Porcine Faecal Microbiome Recollection, Storage and DNA Extraction: From the Farm to the Lab. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyma, J.F.; Epstein, K.L.; Whitfield-Cargile, C.M.; Cohen, N.D.; Giguère, S. Investigation of effects of omeprazole on the fecal and gastric microbiota of healthy adult horses. Am. J. Veter. Res. 2019, 80, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Stämpfli, H.R.; Arroyo, L.G.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Gomes, R.G.; Weese, J.S. Changes in the equine fecal microbiota associated with the use of systemic antimicrobial drugs. BMC Veter. Res. 2015, 11, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Arroyo, L.G.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Stämpfli, H.R.; Kim, P.T.; Sturgeon, A.; Weese, J.S. Comparison of the Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Horses and Horses with Colitis by High Throughput Sequencing of the V3-V5 Region of the 16S rRNA Gene. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.E.; Arroyo, L.G.; Poljak, Z.; Viel, L.; Weese, J.S. Implementation of an algorithm for selection of antimicrobial therapy for diarrhoeic calves: Impact on antimicrobial treatment rates, health and faecal microbiota. Veter. J. 2017, 226, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.; Arroyo, L.; Costa, M.; Viel, L.; Weese, J. Characterization of the Fecal Bacterial Microbiota of Healthy and Diarrheic Dairy Calves. J. Veter. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a Dual-Index Sequencing Strategy and Curation Pipeline for Analyzing Amplicon Sequence Data on the MiSeq Illumina Sequencing Platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compo, N.R.; Gomez, D.E.; Tapscott, B.; Weese, J.S.; Turner, P.V. Fecal bacterial microbiota of Canadian commercial mink (Neovison vison): Yearly, life stage, and seasonal comparisons. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, I.; Harris, K.; Quince, C. Dirichlet Multinomial Mixtures: Generative Models for Microbial Metagenomics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesch, L.F.; Casella, G.; Simell, O.; Krischer, J.; Wasserfall, C.H.; Schatz, D.; Atkinson, M.A.; Neu, J.; Triplett, E.W. Influence of Fecal Sample Storage on Bacterial Community Diversity. Open Microbiol. J. 2009, 3, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, A.; McDonald, D.; Navas-Molina, J.A.; Debelius, J.; Morton, J.T.; Hyde, E.; Robbins-Pianka, A.; Knight, R. Correcting for Microbial Blooms in Fecal Samples during Room-Temperature Shipping. mSystems 2017, 2, e00199-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Zhou, N.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Effect of storage conditions on the assessment of bacterial community structure in soil and human-associated samples. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 307, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, J.S.; Jalali, M. Evaluation of the impact of refrigeration on next generation sequencing-based assessment of the canine and feline fecal microbiota. BMC Veter. Res. 2014, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Horse | Breed | Age (year) | Sex | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Thoroughbred | 12 | F | 581 |
| 2 | Thoroughbred | 12 | M | 543 |
| 3 | Thoroughbred | 5 | M | 536 |
| 4 | Thoroughbred | 5 | M | 529 |
| 5 | Thoroughbred | 5 | M | 572 |
| 6 | Thoroughbred | 11 | F | 514 |
| 7 | Thoroughbred | 4 | F | 481 |
| 8 | Thoroughbred | 9 | M | 618 |
| 9 | Thoroughbred | 8 | F | 508 |
| 10 | Thoroughbred | 5 | F | 505 |
| 11 | Thoroughbred | 12 | F | 492 |
| Time (Hours) | Phylum | Genus | LDA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Bacteroidetes | Bacteroidetes (unclassified) | 4.86 |
| Bacteroidales (unclassified) | 3.98 | ||
| Fibrobacteres | Fibrobacter | 4.11 | |
| Firmicutes | Lachnospiraceae (unclassified) | 4.11 | |
| Firmicutes (unclassified) | 3.67 | ||
| Clostridia (unclassified) | 3.43 | ||
| Pseudobutyrivibrio | 3.11 | ||
| Cellulosilyticum | 2.24 | ||
| Proteobacteria | Vampirovibrio | 2.73 | |
| Spirochaetes | Treponema | 4.09 | |
| Verrucomicrobia | 5 genus (incertae sedis) | 4.44 | |
| 6 | Firmicutes | Clostridiales (unclassified) | 3.99 |
| Ruminococcus | 3.65 | ||
| Saccharofermentans | 2.89 | ||
| Weissella | 2.65 | ||
| Lentisphaerae | Victivallis | 2.80 | |
| Verrucomicrobia | Verrucomicrobia (unclassified) | 2.81 | |
| 12 | Firmicutes | Acidaminococcaceae (unclassified) | 3.30 |
| Tenericutes | Anaeroplasma | 3.00 | |
| 24 | Firmicutes | Caryophanon | 3.20 |
| Proteobacteria | Sphingomonas | 4.70 | |
| 48 | Actinobacteria | Arthrobacter | 2.97 |
| Micrococcaceae (unclassified) | 2.78 | ||
| Cellulosimicrobium | 2.59 | ||
| Firmicutes | Bacillales unclassified | 4.23 | |
| Viridibacillus | 4.19 | ||
| Rummeliibacillus | 3.86 | ||
| Kurthia | 3.70 | ||
| Lysinibacillus | 3.41 | ||
| Proteobacteria | Acinetobacter | 4.78 | |
| 72 | Actinobacteria | Nocardioides | 3.04 |
| Micromonospora | 2.17 | ||
| Firmicutes | Paenibacillus | 4.15 | |
| Tumebacillus | 3.88 | ||
| Cohnella | 3.72 | ||
| Brevibacillus | 2.50 | ||
| Proteobacteria | Oxalobacteraceae (unclassified) | 4.12 | |
| Sphingomonas | 4.03 | ||
| Rhizobiales (unclassified) | 4.02 | ||
| Sandarakinorhabdus | 3.87 | ||
| Enterobacteriaceae (unclassified) | 3.52 | ||
| Alcaligenaceae (unclassified) | 2.87 | ||
| Sphingopyxis | 2.03 | ||
| 96 | Actinobacteria | Leifsonia | 3.19 |
| Actinomycetales (unclassified) | 2.73 | ||
| Coriobacteriaceae (unclassified) | 2.49 | ||
| Sanguibacter | 2.28 | ||
| Bacteroidetes | Sphingobacterium | 3.14 | |
| Segetibacter | 2.89 | ||
| Firmicutes | Clostridium_sensu_stricto | 3.23 | |
| Sedimentibacter | 3.13 | ||
| Bacillaceae 1 (unclassified) | 2.92 | ||
| Planococcaceae (incertae sedis) | 2.58 | ||
| Mogibacterium | 2.56 | ||
| Peptococcaceae 1 (unclassified) | 2.34 | ||
| Clostridiaceae 1 (unclassified) | 2.22 | ||
| Parasporobacterium | 2.18 | ||
| Sporobacter | 2.14 | ||
| Bacillus | 2.12 | ||
| Desulfitobacterium | 2.08 | ||
| Proteobacteria | Brevundimonas | 3.92 | |
| Xanthomonadaceae (unclassified) | 3.81 | ||
| Massilia | 3.41 | ||
| Burkholderiales (unclassified) | 3.33 | ||
| Pseudomonas | 3.21 | ||
| Sphingomonadaceae (unclassified) | 3.14 | ||
| Azospirillum | 3.14 | ||
| Magnetospirillum | 3.08 | ||
| Ensifer | 3.06 | ||
| Pseudomonadaceae (unclassified) | 3.02 | ||
| Myxococcales (unclassified) | 2.71 | ||
| Devosia | 2.25 | ||
| Hyphomicrobium | 2.10 | ||
| TM7 | TM7 (incertae sedis) | 2.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin de Bustamante, M.; Plummer, C.; MacNicol, J.; Gomez, D. Impact of Ambient Temperature Sample Storage on the Equine Fecal Microbiota. Animals 2021, 11, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030819
Martin de Bustamante M, Plummer C, MacNicol J, Gomez D. Impact of Ambient Temperature Sample Storage on the Equine Fecal Microbiota. Animals. 2021; 11(3):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030819
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin de Bustamante, Michelle, Caryn Plummer, Jennifer MacNicol, and Diego Gomez. 2021. "Impact of Ambient Temperature Sample Storage on the Equine Fecal Microbiota" Animals 11, no. 3: 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030819
APA StyleMartin de Bustamante, M., Plummer, C., MacNicol, J., & Gomez, D. (2021). Impact of Ambient Temperature Sample Storage on the Equine Fecal Microbiota. Animals, 11(3), 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030819






