Determination of Efficacy of Single and Double 4.7 mg Deslorelin Acetate Implant on the Reproductive Activity of Female Pond Sliders (Trachemys scripta)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
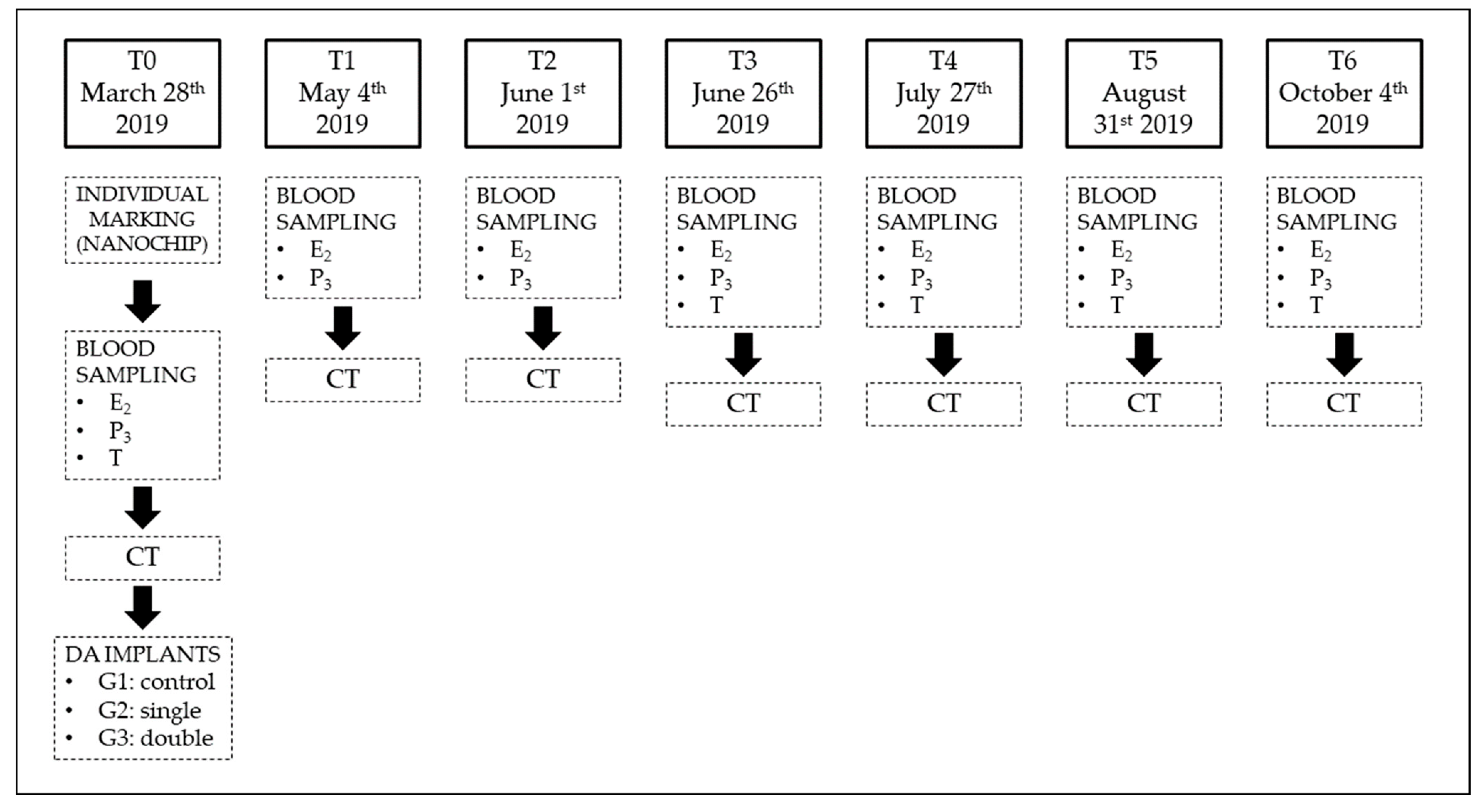
2. Materials and Methods
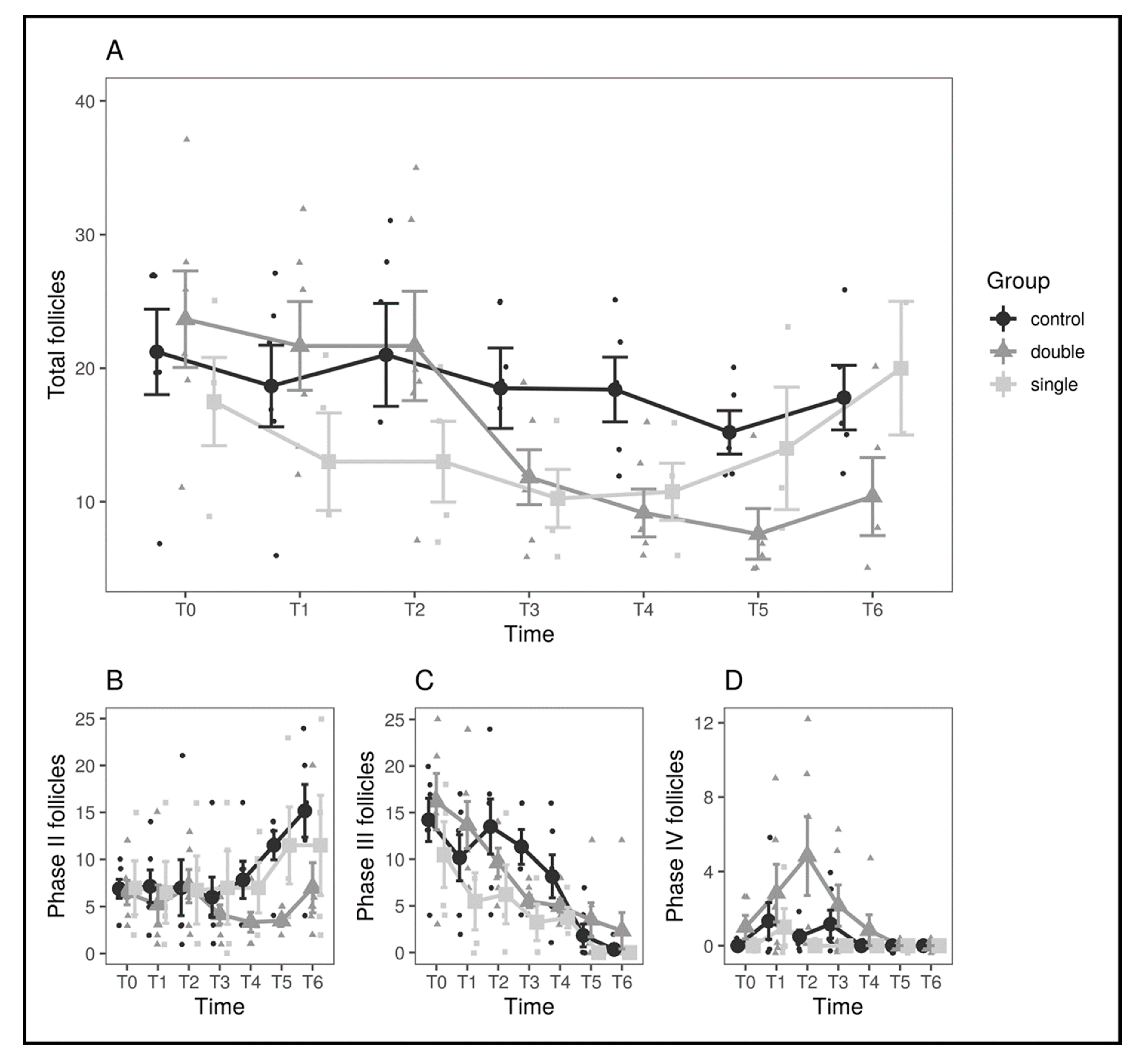
2.1. Ovarian Morphometric Evaluation
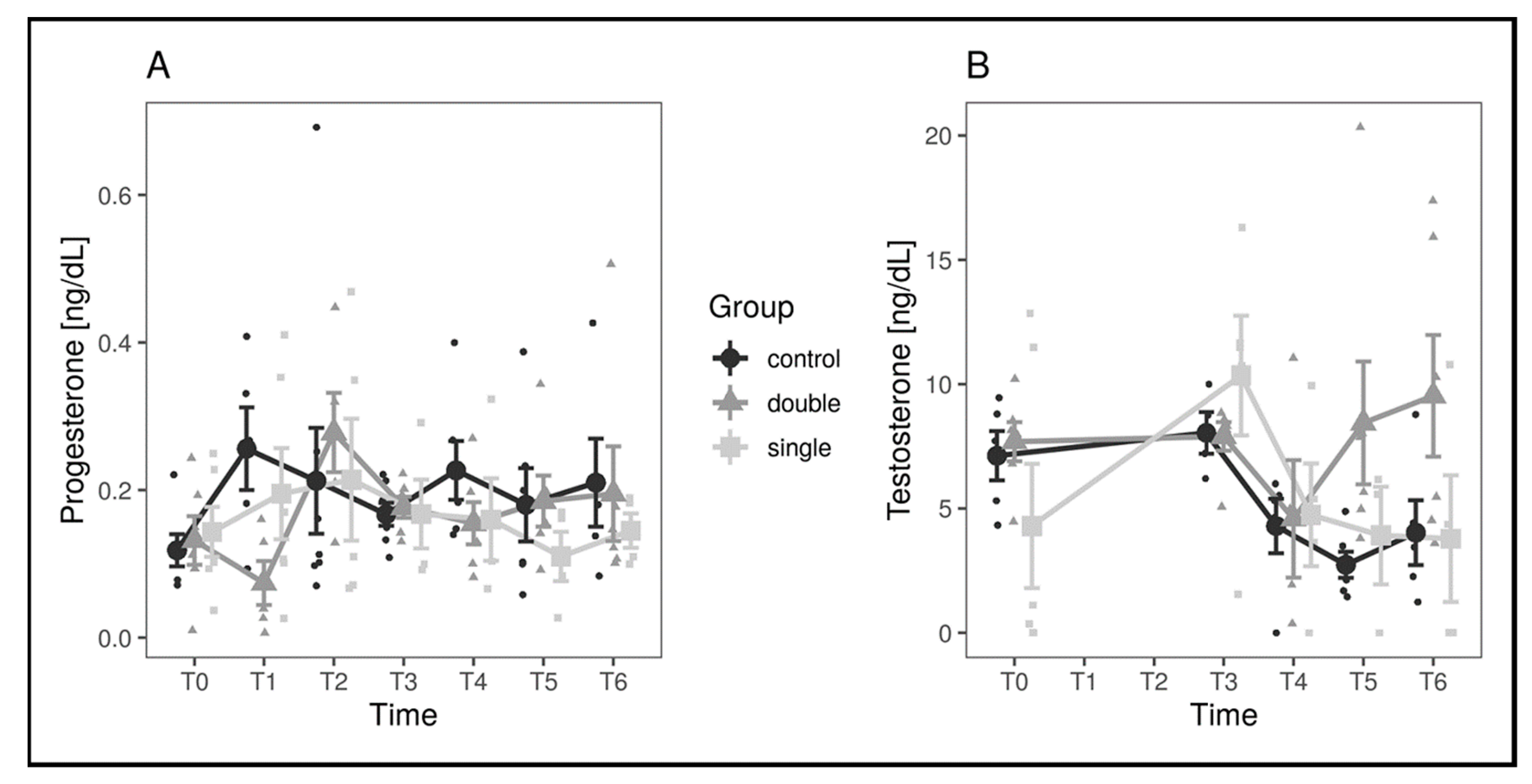
2.2. Plasmatic Hormones Concentration
2.3. Statistical Analysis
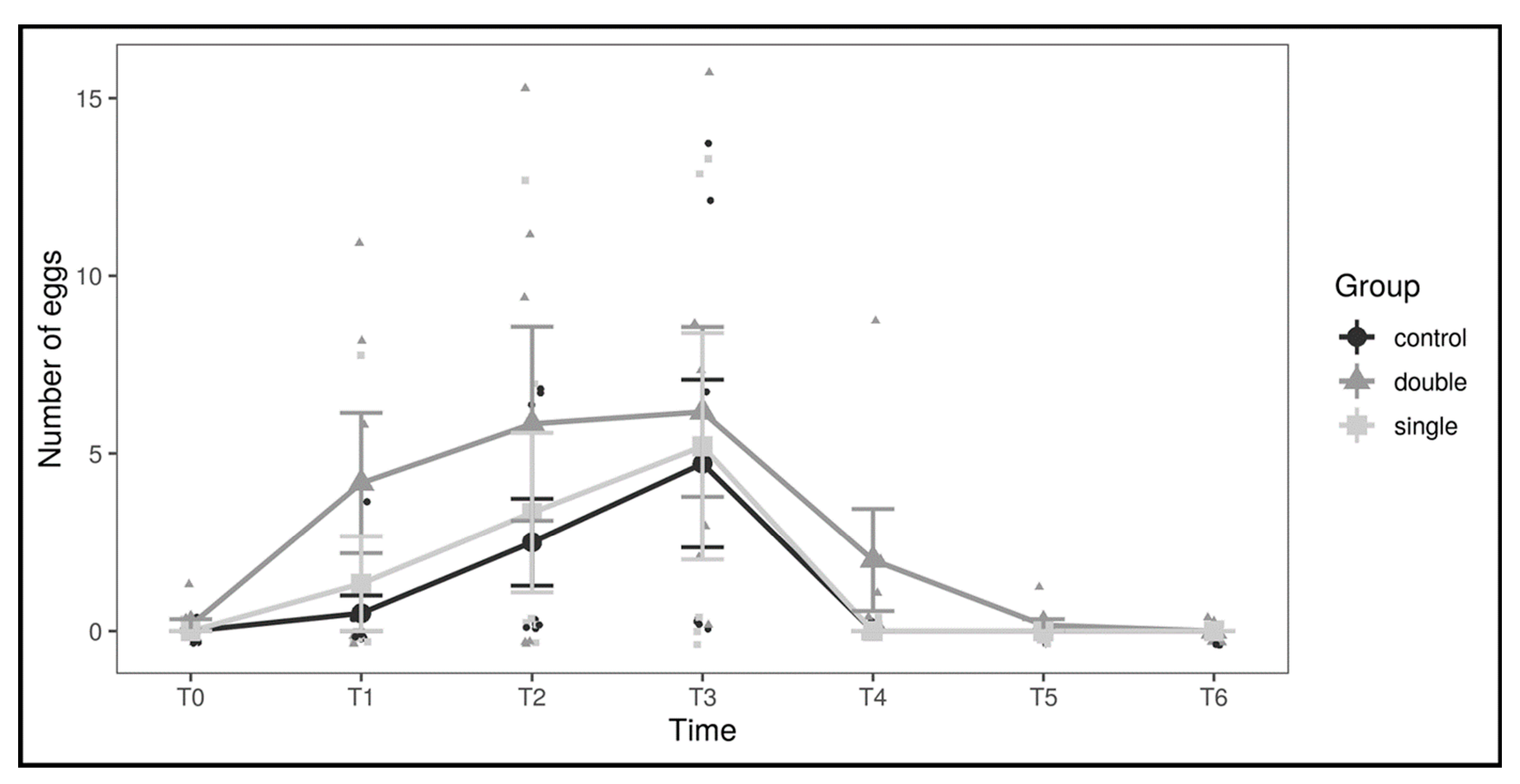
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferri, V.; Soccini, C. Riproduzione di Trachemys scripta elegans in condizioni seminaturali in Lombardia (Italia Settentrio-nale). Nat. Brescia. Ann. Mus. Civ. Sc. Nat. 2003, 33, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Cadi, A.; Delmas, V.; Prévot-Julliard, A.-C.; Joly, P.; Pieau, C.; Girondot, M. Successful reproduction of the introduced slider turtle(Trachemys scripta elegans) in the South of France. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2004, 14, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santigosa, P.N.; Paniagua, D.C.; Vila, H.J. The reproductive ecology of exotic Trachemys scripta elegans in an invaded area of southern Europe. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2008, 18, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Invasive Species Database. Species Profile: Trachemys Scripta Elegans. 2020. Available online: http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/speciesname/Trachemys+scripta+elegans (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Cadi, A.; Joly, P. Competition for basking places between the endangered European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis galloitalica) and the introduced red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans). Can. J. Zool. 2003, 81, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadi, A.; Joly, P. Impact of the introduction of the red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans) on survival rates of the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis). Biodivers. Conserv. 2004, 13, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavia, P.N.; López, P.; Martín, J. Competitive interactions during basking between native and invasive freshwater turtle species. Biol. Invasions 2009, 12, 2141–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavia, P.N.; López, P.; Martín, J. Aggressive interactions during feeding between native and invasive freshwater turtles. Biol. Invasions 2010, 13, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, S.H.; Avery, H.W.; Spotila, J.R. Juvenile invasive red-eared slider turtles negatively impact the growth of native turtles: Implications for global freshwater turtle populations. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 186, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; Du Preez, L.; Bonneau, E.; Héritier, L.; Quintana, M.; Valdeón, A.; Sadaoui, A.; Issad, K.N.; Palacios, C.; Verneau, O. Parasite host-switching from the invasive American red-eared slider, Trachemys scripta elegans, to the native Mediterranean pond turtle, Mauremys leprosa, in natural environments. Aquat. Invasions 2015, 10, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héritier, L.; Valdeón, A.; Sadaoui, A.; Gendre, T.; Ficheux, S.; Bouamer, S.; Kechemir-Issad, N.; Du Preez, L.; Palacios, C.; Verneau, O. Introduction and invasion of the red-eared slider and its parasites in freshwater ecosystems of Southern Europe: Risk assessment for the European pond turtle in wild environments. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 10, 33–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, H.J.; Paniagua, D.C.; Santigosa, P.N.; De Escobar, F.C.; Herrero, H.A. Salmonella in free-living exotic and native turtles and in pet exotic turtles from SW Spain. Res. Veter. Sci. 2008, 85, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.R.; Neil, K.P.; Behravesh, C.B.; Sotir, M.J.; Angulo, F.J. Recent Multistate Outbreaks of HumanSalmonellaInfections Acquired from Turtles: A Continuing Public Health Challenge. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzeżutka, A.; Kaupke, A.; Gorzkowski, B. Detection of Cryptosporidium parvum in a Red-Eared Slider Turtle (Trachemys scripta elegans), a Noted Invasive Alien Species, Captured in a Rural Aquatic Ecosystem in Eastern Poland. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species. IUCN/SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group; ISSG: Auckland, New Zealand, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rispoli, L.; Nett, T. Pituitary gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor: Structure, distribution and regulation of expression. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2005, 88, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesch, G.S. Long-term effects of GnRH agonists on fertility and behaviour. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2016, 52, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoemaker, N.J. Gonadotrophin-Releasing Hormone Agonists and Other Contraceptive Medications in Exotic Companion Animals. Veter. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2018, 21, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, M.L.; Martin, G.B.; Monks, D.J.; Johnston, S.D.; Doneley, R.J.T.; Blackberry, M.A. Inhibition of the Reproductive System by Deslorelin in Male and Female Pigeons (Columba livia). J. Avian Med. Surg. 2014, 28, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molter, C.M.; Fontenot, D.K.; Terrell, S.P. Use of Deslorelin Acetate Implants to Mitigate Aggression in Two Adult Male Domestic Turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo) and Correlating Plasma Testosterone Concentrations. J. Avian Med. Surg. 2015, 29, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petritz, O.A.; Guzman, D.S.-M.; Hawkins, M.G.; Kass, P.H.; Conley, A.J.; Murphy, P.J. Comparison of two 4.7-milligram to one 9.4-milligram deslorelin acetate implants on egg production and plasma progesterone concentrations in japanese quail (coturnix coturnix japonica). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2015, 46, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montani, A.; Collarile, T.; Selleri, P.; Speer, B.L.; Huynh, M.; Pecchia, F.; Di Girolamo, N. Evaluation of the efficacy and duration of single administration of 4.7-mg deslorelin acetate implant on follicular activity and plasma sex hormones in lovebird (Agapornis spp.) in a randomized controlled trial. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress for Avian, Reptile and Exotic Mammal, Venice, Italy, 25–29 March 2017; p. 508. [Google Scholar]
- Summa, N.M.; Guzman, D.S.-M.; Plotz, W.E.L.; Riedl, N.E.; Kass, P.H.; Hawkins, M.G. Evaluation of the effects of a 4.7-mg deslorelin acetate implant on egg laying in cockatiels (Nymphicus hollandicus). Am. J. Veter. Res. 2017, 78, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, M.; Möstl, E.; Knotkova, Z.; Knotek, Z. The use of synthetical GnRH agonist implants (deslorelin) for the suppression of reptile endocrine reproductive activity. In Proceedings of the 1st International Congress for Avian, Reptile and Exotic Mammal, Wiesbaden, Germany, 20–26 April 2013; p. 248. [Google Scholar]
- Knotek, Z.; Cermakova, E.; Oliveri, M. Reproductive Medicine in Lizards. Veter. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pr. 2017, 20, 411–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermakova, E.; Oliveri, M.; Knotkova, Z.; Knotek, Z. Effect of a GnRH agonist (deslorelin) on ovarian activity in leopard geckos (Eublepharis macularius). Veterinární Med. 2019, 64, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, K.M.; Mylniczenko, N.D.; Burns, C.M.; Bettinger, T.L.; Wheaton, C.J. Examining factors that may influence accurate measurement of testosterone in sea turtles. J. Veter. Diagn. Investig. 2015, 28, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannaccone, M.; Ulivi, V.; Campolo, M. Use and duration of Deslorelin acetate in a Testudo graeca to solve a chronic re-productive disorder. In Proceedings of the Zoo and Wildlife Health Conference, Berlin, Germany, 24–27 May 2017; pp. 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Potier, R.; Monge, E.; Loucachevsky, T.; Hermes, R.; Göritz, F.; Rochel, D.; Risi, E. Effects of deslorelin acetate on plasma testosterone concentrations in captive yellow-bellied sliders (Trachemys scripta sp.). Acta Veter. Hung. 2017, 65, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, C.; Schober, P.A. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of a sustained-release implant of deslorelin in companion animals. In Proceedings of the ISCFR/EVSSAR 7th International Symposium of Canine and Feline Reproduction, Whistler, Canada, 26–29 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.R.; Ernst, C.H.; Lovich, J.E.; Barbour, R.W. Turtles of the United States and Canada. Copeia 1995, 1995, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanvillain, G.; Owens, D.W.; Kuchling, G. Hormones and Reproductive Cycles in Turtles. In Hormones and Reproduction of Vertebrates; Norris, D.O., Lopez, K.H., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 277–303. [Google Scholar]
- Bermúdez, P.E.; Urquiola, R.A.; González, L.I.; Petric, B.; Cuenca, A.N.; Ochotorena, S.A.; López, E.G. Ovarian follicular development in the hawksbill turtle (Cheloniidae:Eretmochelys imbricataL.). J. Morphol. 2012, 273, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, R.; Boots, L.; MacGregor, R.; Marion, K. Plasma steroids associated with seasonal reproductive changes in a multiclutched freshwater turtle, Sternotherus odoratus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1982, 48, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, A.J.; Mendonca, M.T.; Horne, B.D.; Seigel, R.A. Seasonal Variation in Reproductive Steroids of Male and Female Yellow-Blotched Map Turtles, Graptemys flavimaculata. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2000, 119, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currylow, A.F.; Tift, M.S.; Meyer, J.L.; Crocker, D.E.; Williams, R.N. Seasonal variations in plasma vitellogenin and sex steroids in male and female Eastern Box Turtles, Terrapene carolina carolina. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 180, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, T.H.; Innis, C.J. Chelonian Taxonomy, Anatomy and Physiology. In Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery, 3rd ed.; Divers, S.J., Stahl, S.J., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2019; pp. 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Licht, P. Endocrine patterns in the reproductive cycles of turtles. Herpetologica 1982, 38, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, S.J.; DeNardo, D.F. Theriogenology. In Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 849–893. [Google Scholar]
| Control Group | Single-Implant Group | Double-Implant Group | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Follicles | Stage II Follicles | Total Follicles | Stage II Follicles | Total Follicles | Stage II Follicles | |||||||
| Mean (±SD) | Median | Mean (±SD) | Median | Mean (±SD) | Median | Mean (±SD) | Median | Mean (±SD) | Median | Mean (±SD) | Median | |
| T0 | 19 (±12) | 27 | 5 (±4) | 5 | 16 (±6) | 15 | 7 (±4) | 6 | 24 (±9) | 23 | 6 (±3) | 6 |
| T1 | 17 (±10) | 19 | 6 (±5) | 5 | 15 (±9) | 13 | 8 (±6) | 7 | 22 (±8) | 22 | 5 (±5) | 3 |
| T2 | 18 (±11) | 18 | 6 (±7) | 3 | 13 (±5) | 12 | 6 (±6) | 6 | 22 (±10) | 19 | 7 (±4) | 7 |
| T3 | 15 (±9) | 18 | 5 (±5) | 4 | 8 (±5) | 8 | 6 (±7) | 2 | 12 (±5) | 11 | 4 (±2) | 4 |
| T4 | 12 (±10) | 13 | 8 (±5) | 8 | 7 (±6) | 7 | 7 (±5) | 6 | 9 (±4) | 7 | 3 (±3) | 3 |
| T5 | 10 (±8) | 12 | 11 (±4) | 12 | 8 (±9) | 6 | 11 (±8) | 9 | 7 (±4) | 5 | 3 (±1) | 3 |
| T6 | 12 (±10) | 13 | 15 (±7) | 15 | 8 (±10) | 3 | 11 (±11) | 9 | 9 (±6) | 6 | 7 (±6) | 5 |
| Progesterone (ng/dL) | Testosterone (ng/dL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (±SD) | Median | Mean (±SD) | Median | |
| T0 | 0.13 (±0.07) | 0.11 | 7.17 (±3.53) | 7.96 |
| T1 | 1.82 (±3.68) | 0.18 | ||
| T2 | 1.53 (±4.81) | 0.22 | ||
| T3 | 0.23 (±0.26) | 0.19 | 8.75 (±3.31) | 8.59 |
| T4 | 0.18 (±0.09) | 0.15 | 4.92 (±3.28) | 5.15 |
| T5 | 0.16 (±0.10) | 0,16 | 5.63 (±4.72) | 4.93 |
| T6 | 0.19 (±0.12) | 0.15 | 7.11 (±5.14) | 4.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bardi, E.; Manfredi, M.; Capitelli, R.; Lubian, E.; Vetere, A.; Montani, A.; Bertoni, T.; Talon, E.; Ratti, G.; Romussi, S. Determination of Efficacy of Single and Double 4.7 mg Deslorelin Acetate Implant on the Reproductive Activity of Female Pond Sliders (Trachemys scripta). Animals 2021, 11, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030660
Bardi E, Manfredi M, Capitelli R, Lubian E, Vetere A, Montani A, Bertoni T, Talon E, Ratti G, Romussi S. Determination of Efficacy of Single and Double 4.7 mg Deslorelin Acetate Implant on the Reproductive Activity of Female Pond Sliders (Trachemys scripta). Animals. 2021; 11(3):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030660
Chicago/Turabian StyleBardi, Edoardo, Martina Manfredi, Raffaella Capitelli, Emanuele Lubian, Alessandro Vetere, Alessandro Montani, Tommaso Bertoni, Elisa Talon, Gabriele Ratti, and Stefano Romussi. 2021. "Determination of Efficacy of Single and Double 4.7 mg Deslorelin Acetate Implant on the Reproductive Activity of Female Pond Sliders (Trachemys scripta)" Animals 11, no. 3: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030660
APA StyleBardi, E., Manfredi, M., Capitelli, R., Lubian, E., Vetere, A., Montani, A., Bertoni, T., Talon, E., Ratti, G., & Romussi, S. (2021). Determination of Efficacy of Single and Double 4.7 mg Deslorelin Acetate Implant on the Reproductive Activity of Female Pond Sliders (Trachemys scripta). Animals, 11(3), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030660






