Enhanced Virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila Is Induced by Stress and Serial Passaging in Mice
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compliance with Ethical Standards
2.2. Bacterial Isolates and Reference Strain
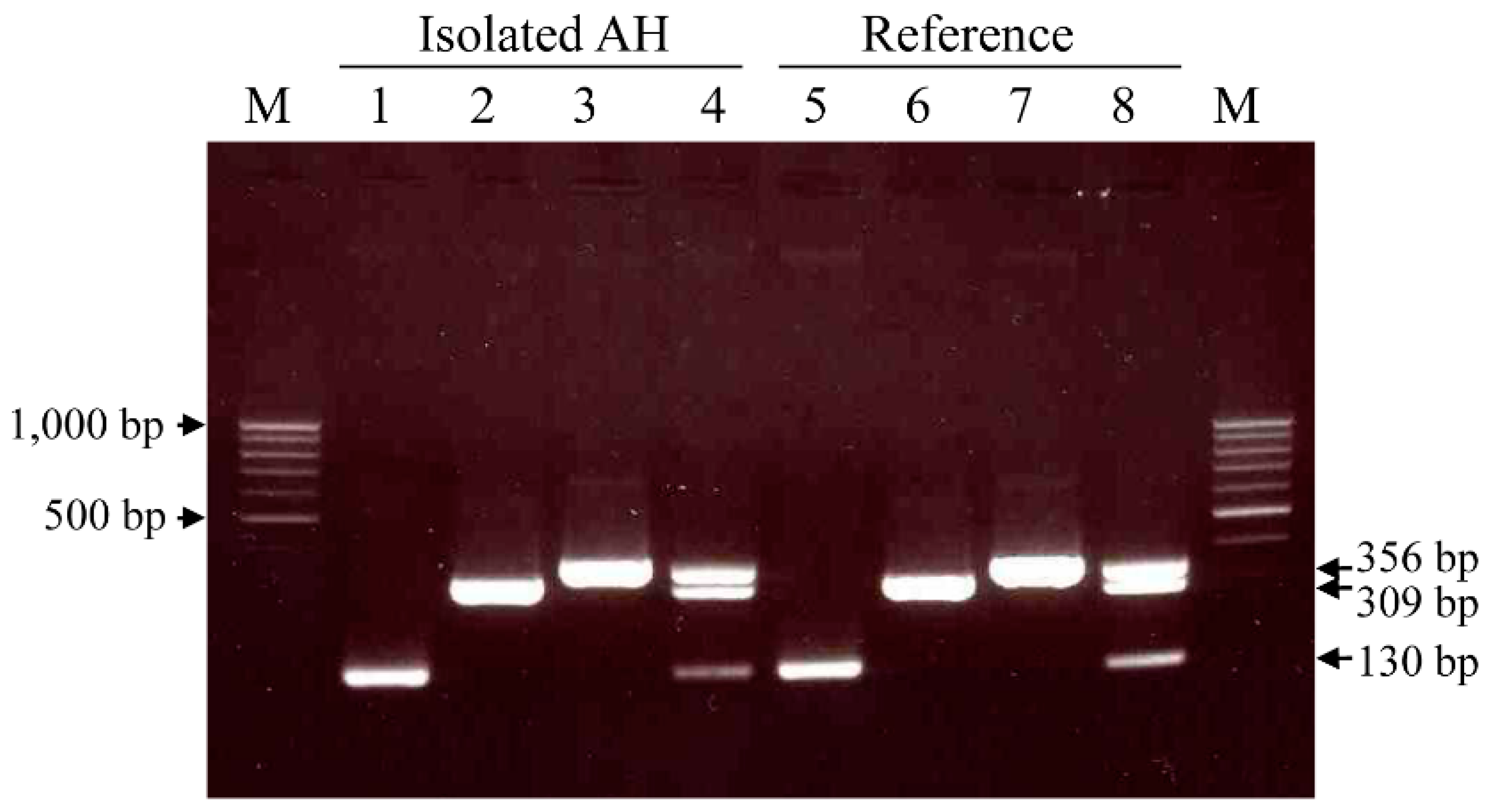
2.3. Singleplex and Multiplex PCR for A. hydrophila Identification and Virulence Genes
2.4. Hemolytic Activity and Cytotoxicity of the Isolate
2.5. Effect of Stress Hormones on the In Vitro Growth of A. hydrophila
2.6. Effect of Stressors on A. hydrophila Virulence
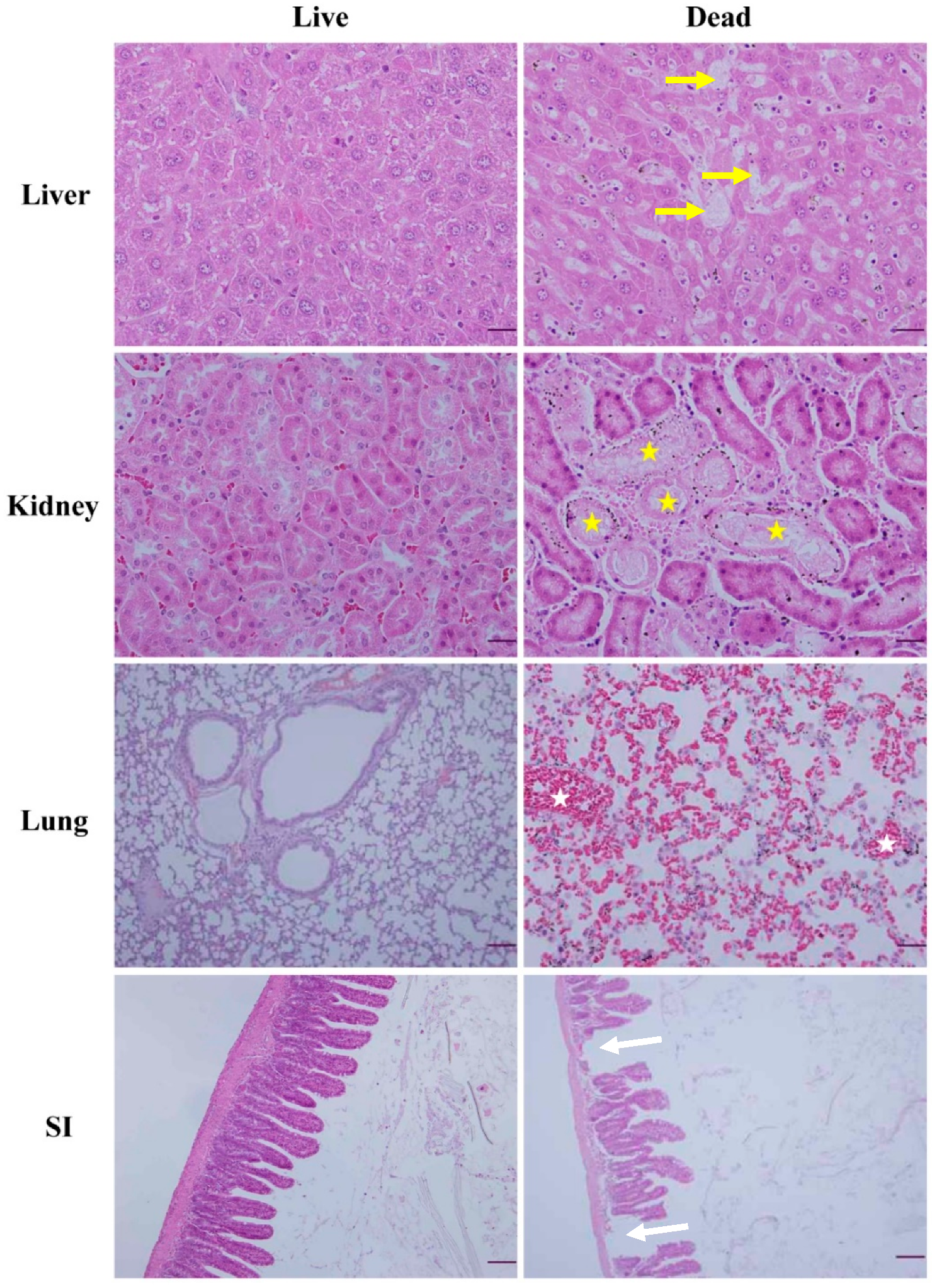
2.7. Necropsy and Histopathology
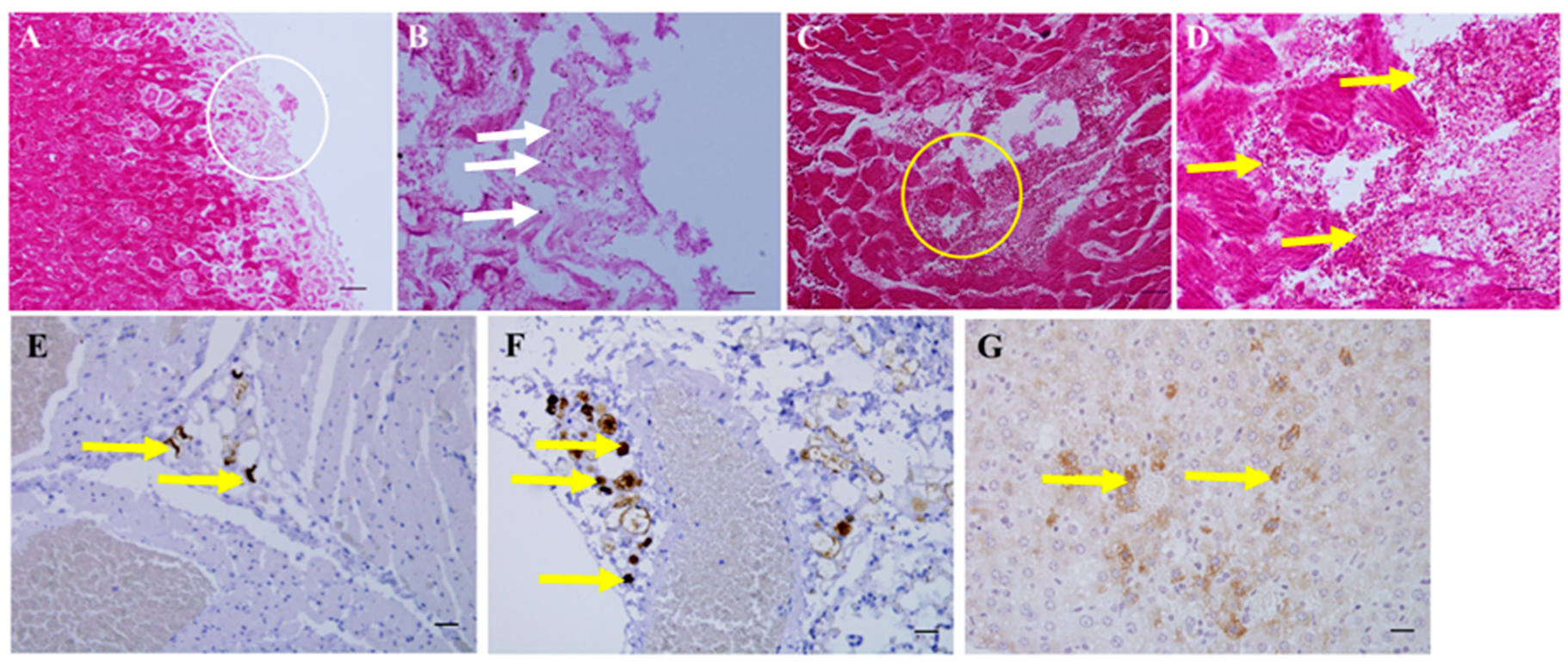
2.8. In Situ PCR
2.9. Effect of Serial Passaging on Virulence
3. Results
3.1. Singleplex and Multiplex PCR for A. hydrophila Identification and Virulence Genes
3.2. Hemolytic Activity and Cytotoxicity Assay
3.3. Effect of Stress Hormones on the In Vivo Growth of A. hydrophila
3.4. Effect of Stressors on A. hydrophila Virulence
3.5. Necropsy and Histopathology
3.6. Effect of Serial Passaging on Virulence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colwell, R.R.; MacDonell, M.T.; De Ley, J. Proposal to recognize the family Aeromonadaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1986, 36, 473–477. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, J.M. Recent advances in the study of the taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infectious syndromes associated with the genus Aeromonas. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 4, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An update on the genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A.; Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Bacterial Fish Pathogens; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cusick, P.K.; Bullock, B.C. Ulcerative dermatitis and pneumonia associated with Aeromonas hydrophila infection in the bottle-nosed dolphin. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1973, 163, 578–579. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.T.; Cho, S.W.; Son, H.Y.; Ryu, S.Y. Aeromonas hydrophilia infection in Jackass Penguins (Spheniscus demersus). Korean J. Vet. Res. 2005, 45, 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.T.; Kwak, D. A case of Aeromonas hydrophila infection due to captivity-induced stress in a spectacled caiman (Caiman crocodilus). J. Anim. Plant. Sci. 2013, 23, 1761–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, M.D.; Lemos, L.S.; Roges, E.M.; de Moura, J.F.; Tavares, D.C.; Matias, C.A.R.; Rodrigues, D.P.; Siciliano, S.A. Comprehensive survey of Aeromonas sp. and Vibrio sp. in seabirds from southeastern Brazil: Outcomes for public health. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirov, S.M. The public health significance of Aeromonas spp. in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1993, 20, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.K.; Houston, C.W. Enterotoxins in Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Microbes Infect. 1999, 1, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, K.S.; Austin, C.E.; Morton, D.S.; Sonnenfeld, G. Catecholamine enhancement of Aeromonas hydrophila growth. Microb. Pathog. 1999, 26, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuge, T.; Takahashi, K.; Barcs, I.; Hayashi, F. Aeromonus hydrophila, a Causative Agent of Mass Mortality in Cultured Japanese Catfish Larvae (Silurus asotus). Fish Pathol. 1992, 27, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thune, R.L.; Stanley, L.A.; Cooper, R.K. Pathogenesis of gram-negative bacterial infections in warmwater fish. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1993, 3, 37–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angka, S.L.; Lam, T.J.; Sin, Y.M. Some virulence characteristics of Aeromonas hydrophila in walking catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Aquaculture 1995, 130, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, D.; Krause, G.; Knabner, D.; Weber, H.; Beutin, L. Isolation and characterization of potentially human pathogenic, cytotoxin-producing Aeromonas strains from retailed seafood in Berlin, Germany. J. Vet. Med. B 2005, 52, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granum, P.E.; O’Sullivan, K.; Tomas, J.M.; Ormen, O. Possible virulence factors of Aeromonas spp. from food and water. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1998, 21, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Clark, C.G.; Liu, C.; Pucknell, C.; Munro, C.K.; Kruk, T.M.; Caldeira, R.; Woodward, D.L.; Rodgers, F.G. Detection and characterization of the hemolysin genes in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria by multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Agarwal, R.K.; Bist, B. Comparison of ELISA and PCR vis-a-vis cultural methods for detecting Aeromonas spp. in foods of animal origin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 106, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köbölkuti, L.; Czirjak, G.A.; Spinu, M. Effects of malnutrition and improper captive maintenance on European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis): A case report. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2016, 26, 874–879. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, L.M.; Marquez, R.F.; Yano, T. Incidence of toxic Aeromonas isolated from food and human infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 32, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, M.L.; Arnould, J.P.; Dann, P.; Trathan, P.; Groscolas, R.; Smith, S. Interspecific variations in the gastrointestinal microbiota in penguins. Microbiologyopen 2013, 2, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkodie, E.K.; Zhou, S.; Baidoo, S.A.; Chu, W. Influences of stress hormones on microbial infections. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, M.; Takahashi, A.; Sakai, Y.; Nakaya, Y. Modulation of pathogenicity with norepinephrine related to the type III secretion system of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yang, M.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Q.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y. QseBC controls flagellar motility, fimbrial hemagglutination and intracellular virulence in fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, G.J.; Chen, T.H. Incidence and toxigenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila in seafood. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 31, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsoi, A.; Quinteiro-Filho, W.M.; Calefi, A.S.; Piantino Ferreira, A.J.; Astolfi-Ferreira, C.S.; Florio, J.C.; Palermo-Neto, J. Effects of cold stress and Salmonella Heidelberg infection on bacterial load and immunity of chickens. Avian Pathol. 2015, 44, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzymińska, S.; Mokracka, J.; Laganowska, M.; Włodarczak, K.; Guszczyńska, E.; Liszkowska, J.; Popkowska, E.; Lima, I.; Lemańska, I.; Wendt, M. Enhancement of the virulence of Aeromonas caviae diarrhoeal strains by serial passages in mice. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.V.; Sanyal, S.C. Enterotoxicity of clinical and environmental isolates of Aeromonas spp. J. Med. Microbiol. 1992, 36, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlstead, K.; Shepherdson, D. Alleviating stress in zoo animals with environmental enrichment. In The Biology of Animal Stress: Basic Principles and Implications for Animal Welfare; Moberg, G.P., Mench, J.A., Eds.; CABI Publishing: London, UK, 2000; pp. 337–354. [Google Scholar]
- Munson, L.; Nesbit, J.W.; Meltzer, D.G.A.; Colly, L.P.; Bolton, L.; Kriek, N.P.J. Diseases of captive cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus jubatus) in South Africa: A 20-year retrospective survey. J. Wildl. Dis. 1999, 30, 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- St Aubin, D.J.; Dierauf, L.A. Stress and marine mammals. In CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine: Health, Disease, and Rehabilitation, 2nd ed.; Dierauf, L.A., Gulland, F.M.D., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 253–269. [Google Scholar]

| Strain | Rabbit Erythrocytes | Vero Cells | BHK Cells | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 3 h | 24 h | 0 h | 3 h | 24 h | ||
| Isolate | 64 | 0 | 32 | 256 | 0 | 32 | 512 |
| Reference 1 | 256 | 0 | 16 | 256 | 0 | 16 | 256 |
| PBS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| No. of Dead Mice/No. of Mice Alive at the Day after Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group * | Day 0 | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 |
| AH + N | 0/10 | 6/4 | 4/0 | - | - |
| AH + P | 0/10 | 2/8 | 0/8 | 2/6 | 0/6 |
| AH + F | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 4/6 | 6/0 |
| AH + L | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| AH + S | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| AH alone | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| PBS | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| Passage Number | Route of Inoculation | No. of Dead Mice/No. of Mice Alive Post Infection | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 12 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | ||
| 1st | Oral | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 1/9 |
| Intraperitoneal | 0/10 | 0/10 | 8/2 | 2/0 | - | |
| PBS * | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | |
| 2nd | Oral | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 1/9 | 1/8 |
| Intraperitoneal | 0/10 | 2/8 | 8/0 | - | - | |
| PBS | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | |
| 3rd | Oral | 0/10 | 10/0 | - | - | - |
| Intraperitoneal | 0/10 | 10/0 | - | - | - | |
| PBS | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.-T.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, K.-K.; Han, J.E.; Kwak, D. Enhanced Virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila Is Induced by Stress and Serial Passaging in Mice. Animals 2021, 11, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020508
Kim K-T, Lee S-H, Lee K-K, Han JE, Kwak D. Enhanced Virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila Is Induced by Stress and Serial Passaging in Mice. Animals. 2021; 11(2):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020508
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyoo-Tae, Seung-Hun Lee, Kyoung-Ki Lee, Jee Eun Han, and Dongmi Kwak. 2021. "Enhanced Virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila Is Induced by Stress and Serial Passaging in Mice" Animals 11, no. 2: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020508
APA StyleKim, K.-T., Lee, S.-H., Lee, K.-K., Han, J. E., & Kwak, D. (2021). Enhanced Virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila Is Induced by Stress and Serial Passaging in Mice. Animals, 11(2), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020508








