Experimental Horizontal Transmission of Enterospora nucleophila (Microsporea: Enterocytozoonidae) in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Donors and Naïve Recipient Fish
2.2. Samplings and Parasite Diagnosis
2.3. Experimental Transmission Trials
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Trial 1
3.2. Trial 2
3.3. Trial 3
3.4. Trial 4
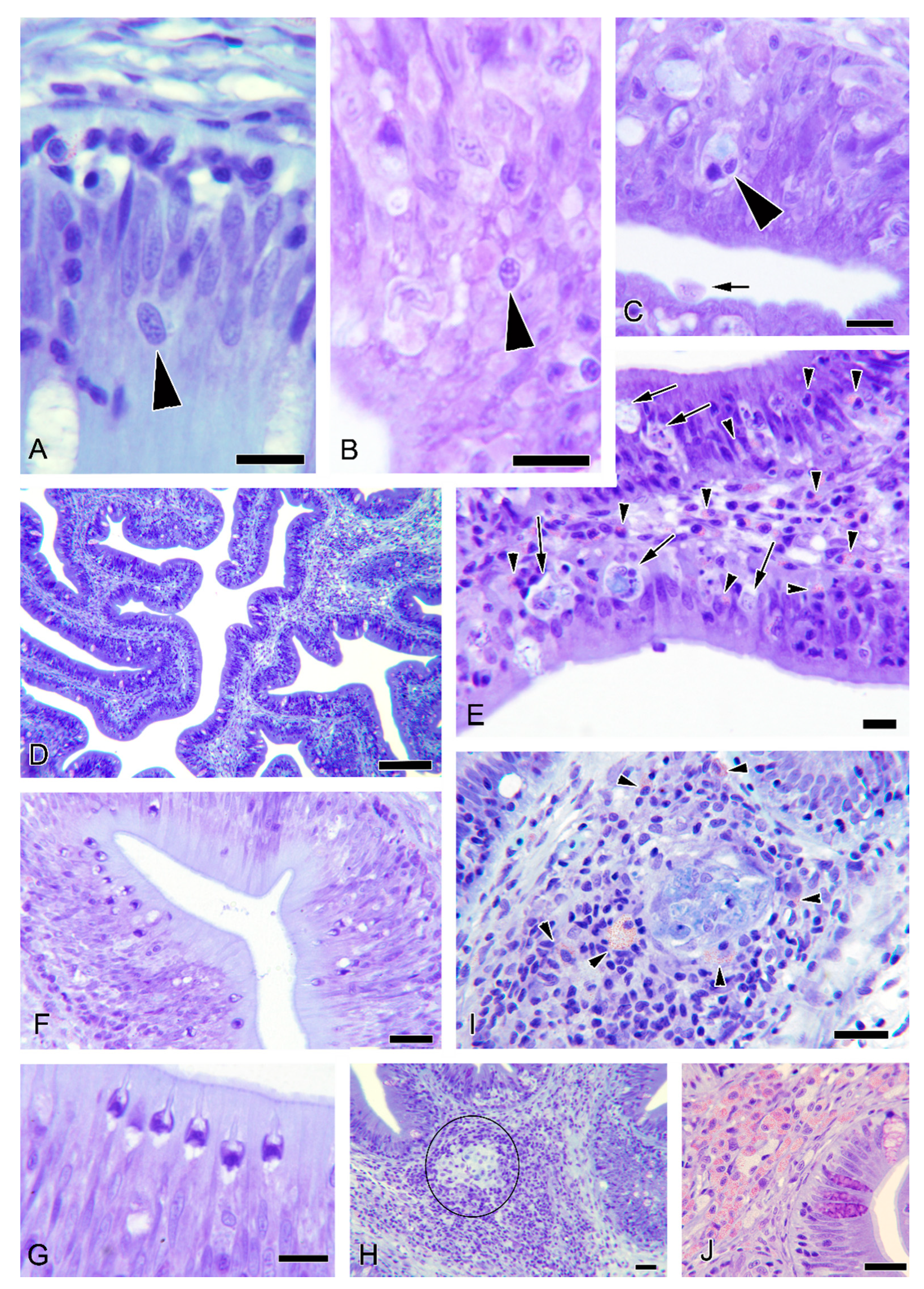
3.5. Histopathological Observations
3.6. Additional Observations in Donor Fish
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szumowski, S.C.; Troemel, E.R. Microsporidia-host interactions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 26, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, M.L.; Shaw, R.W.; Sanders, J.L. Microsporidia in Fish. In Microsporidia: Pathogens of Opportunity, 1st ed.; Weiss, L.M., Becnel, J.J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2014; pp. 493–520. [Google Scholar]
- Lom, J.; Dyková, I. Microsporidia (Phylum Microspora Sprague, 1977). In Protozoan Parasites of Fishes Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Lom, J., Dyková, I., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; Volume 26, pp. 125–157. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, L.M.; Delbac, F.; Russell Hayman, J.; Pan, G.; Dang, X.; Zhou, Z. The Microsporidian polar tube and spore wall. In Microsporidia: Pathogens of Opportunity, 1st ed.; Weiss, L.M., Becnel, J.J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2014; pp. 261–306. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Pan, L.; Chen, Z.; Du, H.; Luo, B.; Luo, J.; Pan, G. The roles of microsporidia spore wall proteins in the spore wall formation and polar tube anchorage to spore wall during development and infection processes. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 187, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fayer, R. Infectivity of microsporidian spores exposed to temperature extremes and chemical disinfectants. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2006, 53, S77–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiro, J.M.; Piazzon, C.; Domínguez, B.; Mallo, N.; Lamas, J. Evaluation of some physical and chemical treatments for inactivating microsporidian spores isolated from fish. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 156, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.; Kent, M.L.; Adamson, M. Viability of Loma salmonae (Microspora) under laboratory conditions. Parasitol. Res. 2001, 86, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, A.; Smith, J. Microsporidian life cycles and diversity: The relationship between virulence and transmission. Microb. Infect. 2001, 3, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Vicar, A.H. Infection of plaice Pleuronectes platessa L. with Glugea (Nosema) stephani (Hagenmüller 1899) (Protozoa: Microsporidia) in a fish farm and under experimental conditions. J. Fish Biol. 1975, 7, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, J.M.; Speare, D.J.; Daley, J. Timing of changes in growth rate, feed intake and feed conversion in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), experimentally infected with Loma salmonae (Microspora). J. Fish Dis. 2004, 27, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.W.; Kent, M.L.; Adamson, M.L. Modes of transmission of Loma salmonae (Microsporidia). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1998, 33, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.L.; Lawrence, C.; Nichols, D.K.; Brubaker, J.F.; Peterson, T.S.; Murray, K.N.; Kent, M.L. Pleistophora hyphessobryconis (Microsporidia) infecting zebrafish Danio rerio in research facilities. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 91, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.; Peterson, T.; Kent, M.L. Early development and tissue distribution of Pseudoloma neurophilia in the Zebra fish, Danio rerio. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2014, 61, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, M.; Bishop-Stewart, J. Transmission and tissue distribution of Pseudoloma neurophilia (Microsporidia) of zebrafish, Danio rerio (Hamilton). J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, R.A.; Matthews, B.F. Cell and tissue reactions of turbot Scophthalmus maximus (L.) to Tetramicra brevifilum gen. n., sp. n. (Microspora). J. Fish Dis. 1980, 3, 495–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxa, D.; Groff, J.; Hedrick, R. Experimental horizontal transmission of Enterocytozoon salmonis to Chinook Salmon, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha. J. Protozool. 1992, 39, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissenberg, R. Intracellular development of the microsporidan Glugea anomala Moniez in hypertrophying migratory cells of the fish Gasterosteus aculeatus L., an example of the formation of “xenoma” tumors. J. Protozool. 1968, 15, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Yokoyama, H.; Ogawa, K. Modes of transmission of Glugea plecoglossi (Microspora) via the skin and digestive tract in an experimental infection model using rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Fish Dis. 2004, 27, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.E. Laboratory and field studies on Glugea stephani (Hagenmuller), a microsporidan parasite of pleuronectid flatfishes. J. Protozool. 1976, 23, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micieli, M.V.; García, J.J.; Becnel, J.J. Horizontal transmission of Amblyospora albifasciati García and Becnel, 1994 (Microsporidia: Amblyosporidae), to a copepod intermediate host and the neotropical mosquito, Aedes albifasciatus (Macquart, 1837). J. Invert. Pathol. 2000, 75, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becnel, J. Horizontal transmission and subsequent development of Amblyospora californica (Microsporidia: Amblyosporidae) in the intermediate and definitive hosts. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1992, 13, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palenzuela, O.; Redondo, M.J.; Cali, A.; Takvorian, P.M.; Alonso-Naveiro, M.; Álvarez-Pellitero, P.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. A new intranuclear microsporidium, Enterospora nucleophila n. sp., causing an emaciative syndrome in a piscine host (Sparus aurata), prompts the redescription of the family Enterocytozoonidae. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard-Sánchez, A.; Piazzon, M.C.; Ahmed, N.H.; Del Pozo, R.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Palenzuela, O. Enterospora nucleophila (Microsporidia) in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata): Pathological effects and cellular immune response in natural infections. Vet. Patholol. 2020, 57, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.H.; Caffara, M.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Fioravanti, M.L.; Mazzone, A.; Aboulezz, A.S.; Metwally, A.M.; Omar, M.A.; Palenzuela, O.R. Detection of the intranuclear microsporidian Enterospora nucleophila in gilthead sea bream by in situ hybridization. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estensoro, I.; Redondo, M.J.; Álvarez-Pellitero, P.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Novel horizontal transmission route for Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa) by anal intubation of gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 92, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, G.; Matthews, R.A. Immunosuppression of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) to ichthyophthiriasis using the corticosteroid triamcinolone acetonide. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1986, 12, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Connaughey, M.B. Physical Chemical Properties of Fungi. In XPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Enna, S.J., Bylund, D.B., Eds.; Elservier Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, K.; Bashtar, A.R.; Abdel-Ghaffar, F.; Al-Quraishy, S. Morphological and phylogenetic description of a new xenoma-inducing microsporidian, Microsporidium aurata nov. sp., parasite of the gilthead seabream Sparus aurata from the Red Sea. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3905–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassopoulou, F. A case report of Pleistophora sp. infection in cultured sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) in Greece. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1998, 18, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Abela, M.; Brinch-Iversen, J.; Tanti, J.; Le Breton, A. Occurrence of a new histozoic microsporidian (Protozoa, Microspora) in cultured gilt head sea bream Sparus aurata L. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1996, 16, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Ghaffar, F.; Bashtar, A.R.; Morsy, K.; Mehlhorn, H.; Al Quraishy, S.; Al-Rasheid, K.; Abdel-Gaber, R. Morphological and molecular biological characterization of Pleistophora aegyptiaca sp. nov. infecting the Red Sea fish Saurida tumbil. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard-Sánchez, A.; Estensoro, I.; Del Pozo, R.; Palenzuela, O.R.; Piazzon, M.C.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Water temperature, time of exposure and population density are key parameters in Enteromyxum leei fish-to-fish experimental transmission. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.R. The Microsporidia of Vertebrates. Parasitology 1987, 94, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Becnel, J.J.; Weiss, L.M.; Keeling, P.J.; Didier, E.S.; Williams, B.A.P.; Bjornson, S.; Kent, M.L.; Freeman, M.A.; Brown, M.J.F.; et al. Microsporidia-Emergent pathogens in the global food chain. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vávra, J.; Lukeš, J. Microsporidia and ‘the art of living together’. Adv. Parasitol. 2013, 82, 253–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Didier, E. Insights into the immune responses to Microsporidia. In Opportunistic Infections: Toxoplasma, Sarcocystis, and Microsporidia, 1st ed.; Weiss, L.M., Lindsay, D.S., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 9, pp. 135–158. [Google Scholar]
- Abram, Q.H.; Dixon, B.; Katzenback, B.A. Impacts of low temperature on the teleost immune system. Biology 2017, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, J.M.; Watral, V.; Schreck, C.B.; Kent, M.L. Pseudoloma neurophilia infections in zebrafish Danio rerio: Effects of stress on survival, growth, and reproduction. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2009, 88, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, S.T.; Sanders, J.L.; Watral, V.; Kent, M.L. Pseudoloma neurophilia infection combined with gamma irradiation causes increased mortality in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) compared to infection or irradiation alone: New implications for studies involving immunosuppression. Zebrafish 2016, 13, S107–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovy, J.; Speare, D.J.; Stryhn, H.; Wright, G.M. Effects of dexamethasone on host innate and adaptive immune responses and parasite development in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss infected with Loma salmonae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.; Speare, D.; Markham, R.; Wright, G.; Kibenge, F. Localization of the initial developmental stages of Loma salmonae in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Vet. Pathol. 2001, 38, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial | Challenge | Mean Water Temperature (Range) (°C) | Initial Number of Fish | Samplings (Weeks Post-Challenge) | Prevalence of Infection (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | O-1 | 17.2 (10.4–26.0) | 15R 10D | 8, 20 | 14.3, 0 |
| CH-1 | 16.9 (10.4–25.0) | 15R 15D | 12, 20 | 0, 8.3 | |
| 2 | O-2 | 17.0 (13.4–20.1) | 30R 15D | 4, 8 | 70, 55.2 |
| EF-1 | 22.4 (13.4–22.9) | 31R 31D | 4, 10 | 66.7, 87.1 | |
| EF-2 | 25.0 (21.5–26.8) | 31R 20C 20D | 4, 8 | 80.6, 11.8 | |
| 3 | O-3 | 19.8 (15.0–25.6) | 30R 11C 22D 1 | 4, 12 | 0, 5.5 |
| O-3-I | 19.8 (15.0–25.6) | 40R 20C 22D 1 | 4, 12 | 10, 0 | |
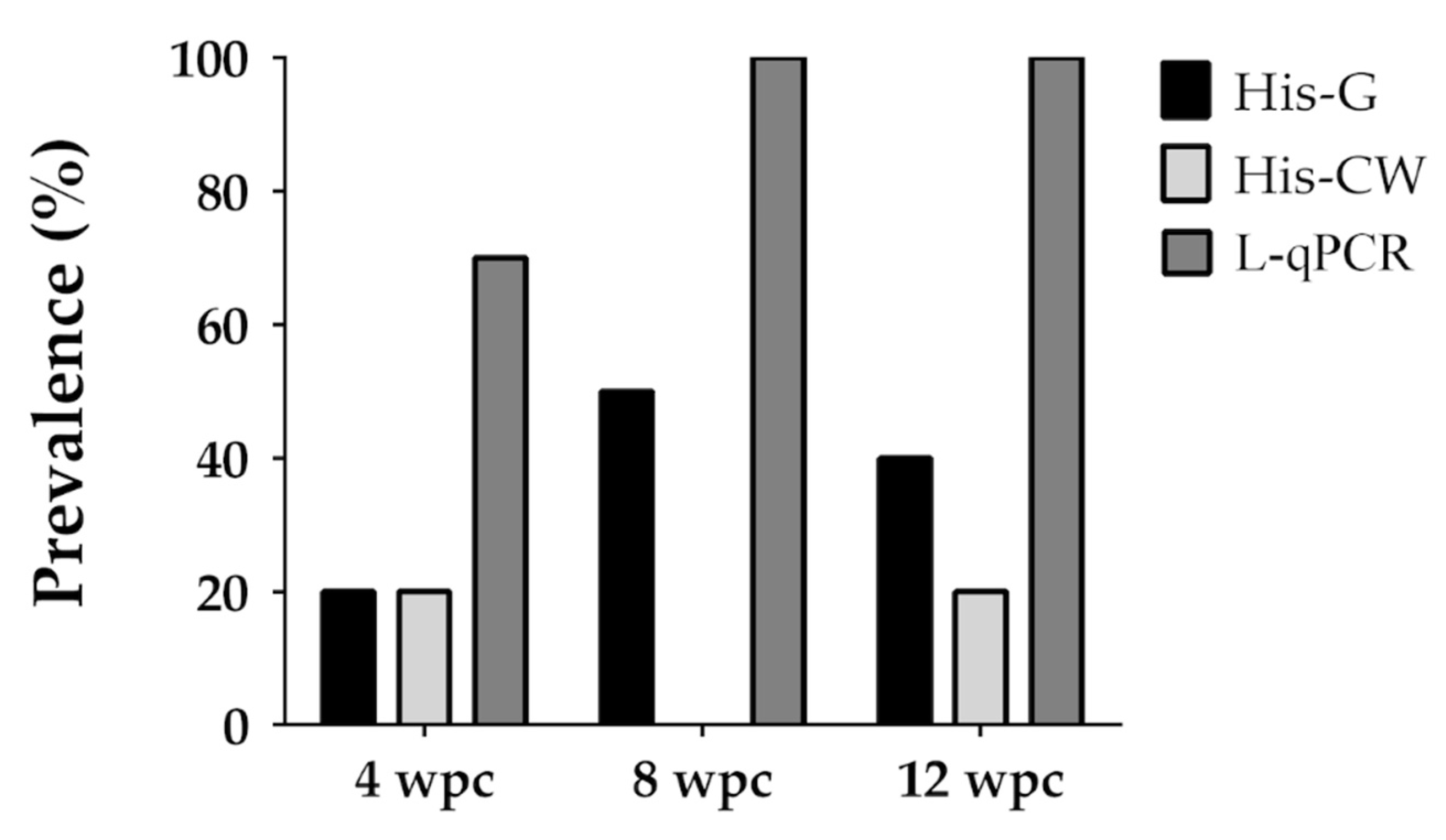
| 4 | A-1 | 16.2 (13.7–18.1) | 30R 37C 11D | 4, 8, 12 | 70, 100, 100 |
| Item | O-2 | EF-1 | EF-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence at S1 (%) | |||
| NL-qPCR-Blood | 0/10 (0%) | 28/30 (93.3%) | |
| NL-qPCR-Intestine | 21/30 (70%) | 10/30 (66.7%) | 25/31 (80.6%) |
| Median Ct (range) at S1 | |||
| NL-qPCR-Blood | - | 35.8 (34.3–36.9) | |
| NL-qPCR-Intestine | 33.5 (28.7–36.0) | 35.8 (34.7–37.9) | 36.2 (33.4–37.9) |
| Prevalence at S2 (%) | |||
| NL-qPCR-Blood | 4/10 (40%) | 3/10 (30%) | |
| NL-qPCR-Intestine | 16/29 (55.2%) | 27/31 (87.1%) | |
| L-qPCR-Intestine (whole) | 6/10 (60%) | 10/10 (100%) | 2/17 (11.8%) |
| Median Ct (range) at S2 | |||
| NL-qPCR-Blood | 36.0 (34.5–37.8) | 36.8 (35.1–37.5) | |
| NL-qPCR-Intestine | 36.7 (31.2–37.6) | 35.1 (30.3–37.8) | |
| L-qPCR-Intestine (whole) | 36.3 (35.7–37.3) | 33.3 (32.8–34.4) | 37.3 (36.7–37.9) |
| Biometry at S1 | |||
| Weight (g) C | 135 ± 4.71 | ||
| Weight (g) R | 43.0 ± 1.35 | 48.1 ± 2.03 | 101.0 ± 3.79 *** |
| Length (cm) C | 17.6 ± 0.18 | ||
| Length (cm) R | 12.6 ± 0.14 | 13.1 ± 0.17 | 16.1 ± 0.19 *** |
| CF C | 2.5 ± 0.05 | ||
| CF R | 2.2 ± 0.03 | 2.1 ± 0.04 | 2.1 ± 0.14 * |
| Biometry at S2 | |||
| Weight (g) C | 176.1 ± 5.72 *** | ||
| Weight (g) R | 44.4 ± 1.49 | 48.1 ± 2.07 | 115.9 ± 5.89 *** |
| Length (cm) C | 19.2 ± 0.21 *** | ||
| Length (cm) R | 12.8 ± 0.15 | 13.3 ± 0.19 | 17.0 ± 0.25 *** |
| CF C | 2.5 ± 0.03 | ||
| CF R | 2.1 ± 0.03 | 2.1 ± 0.12 | 2.3 ± 0.02 * |
| Final Mortality (%) | |||
| C | 1/20 (5%) | ||
| R | 1/30 (3.3%) | 1/31 (3.2%) | 4/15 (12.9%) |
| D | n.a. | 17/31 (54.8%) | 5/20 (25%) |
| Item | O-3 | O-3-I |
|---|---|---|
| Prevalence at S1 (%) | ||
| NL-qPCR-Intestine | 0/10 (0%) | 1/10 (10%) |
| Median Ct (range) at S1 | ||
| NL-qPCR-Intestine | - | 34.5 (34.5) |
| Prevalence at S2 (%) | ||
| L-qPCR-Intestine | 1/18 (5.5%) | 0/2 (0%) |
| Median Ct (range) at S2 | ||
| L-qPCR-Intestine | 32.4 (32.4) | - |
| Biometry at t0 | ||
| Weight (g) C | 9.5 ± 0.46 | 9.5 ± 0.35 |
| Weight (g) R | 10.1 ± 0.34 | 9.4 ± 0.27 |
| Length (cm) C | 7.7 ± 0.10 | 7.8 ± 0.11 |
| Length (cm) R | 8.2 ± 0.17 | 7.9 ± 0.08 |
| CF C | 2.1 ± 0.06 | 2.0 ± 0.04 |
| CF R | 2.1 ± 0.06 | 2.0 ± 0.02 |
| Biometry at S1 | ||
| Weight (g) C | n.a. | 11.0 ± 0.65 |
| Weight (g) R | 10.5 ± 0.38 | 8.9 ± 0.28 * |
| Length (cm) C | No data | 8.3 ± 0.18 |
| Length (cm) R | 8.1 ± 0.09 | 7.9 ± 0.08 * |
| CF C | n.a. | 1.9 ± 0.06 |
| CF R | 2.0 ± 0.05 | 1.8 ± 0.03 |
| Biometry at S2 | ||
| Weight (g) C | 46.6 ± 2.45 | 33.6 ± 1.53 |
| Weight (g) R | 26.0 ± 1.60*** | 10.3 ± 1.02 *** |
| Length (cm) C | 12.5 ± 0.15 | 11.5 ± 0.16 |
| Length (cm) R | 10.8 ± 0.23*** | 8.4 ± 0.10 *** |
| CF C | 2.4 ± 0.06 | 2.2 ± 0.04 |
| CF R | 2.0 ± 0.03*** | 1.7 ± 0.11 *** |
| Final Mortality (%) | ||
| C | 1/11 (9.1%) | 4/20 (20%) |
| R | 12/30 (40%) | 34/40 (85%) |
| Sampling Time | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue | 4 wpc | 8 wpc | 12 wpc | |||
| Ct Median (range) | Prevalence (%) | Ct Median (range) | Prevalence (%) | Ct Median (range) | Prevalence (%) | |
| Blood | - | 0/10 (0%) | 37.2 (37.2) | 1/10 (10%) | 37.0 (36.0–37.0) | 3/10 (30%) |
| Brain | 36.7 (36.7) | 1/10 (10%) | - | 0/10 (0%) | - | 0/10 (0%) |
| Gallbladder | - | 0/10 (0%) | 36.0 (36.0) | 1/10 (10%) | 37.2 (36.5–37.6) | 2/10 (20%) |
| Gills | 36.2 (35.4–37.8) | 8/10 (80%) | 36.3 (36.3) | 1/10 (10%) | 37.5 (36.5–37.8) | 4/10 (40%) |
| Heart | 34.3 (33.3–37.3) | 5/10 (50%) | 37.0 (36.1–37.8) | 4/10 (40%) | 37.3 (36.0–37.7) | 3/10 (30%) |
| Head kidney | 37.3 (36.6–37.9) | 3/10 (30%) | 37.1 (37.1) | 1/10 (10%) | 37.6 (37.6) | 1/10 (10%) |
| Intestine | 32.0 (27.5–37.2) | 7/10 (70%) | 33.5 (26.3–35.7) | 10/10 (100%) | 30.9 (26.1–37.6) | 10/10 (100%) |
| Liver | 33.4 (31.8–37.6) | 7/10 (70%) | 37.0 (35.7–37.5) | 8/10 (80%) | 35.4 (33.0–37.7) | 2/10 (20%) |
| Posterior kidney | – | 0/10 (0%) | 37.5 (37.5) | 1/10 (10%) | 36.0 (35.0–37.0) | 2/10 (20%) |
| Spleen | 34.6 (33.1–35.5) | 2/10 (20%) | 37.0 (36.7–37.3) | 2/10 (20%) | 36.0 (36.0) | 1/10 (10%) |
| Stomach | 34.2 (26.2–37.9) | 8/10 (80%) | 34.4 (31.7–37.4) | 6/10 (60%) | 36.4 (35.5–37.3) | 2/10 (20%) |
| Swim bladder | n.a. | n.a. | 35.7 (34.8–37.9) | 4/10 (40%) | 37.5 (36.5–37.6) | 3/10 (30%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Picard-Sánchez, A.; Piazzon, M.C.; Estensoro, I.; Del Pozo, R.; Hossameldin Ahmed, N.; Palenzuela, O.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Experimental Horizontal Transmission of Enterospora nucleophila (Microsporea: Enterocytozoonidae) in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Animals 2021, 11, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020362
Picard-Sánchez A, Piazzon MC, Estensoro I, Del Pozo R, Hossameldin Ahmed N, Palenzuela O, Sitjà-Bobadilla A. Experimental Horizontal Transmission of Enterospora nucleophila (Microsporea: Enterocytozoonidae) in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Animals. 2021; 11(2):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020362
Chicago/Turabian StylePicard-Sánchez, Amparo, M. Carla Piazzon, Itziar Estensoro, Raquel Del Pozo, Nahla Hossameldin Ahmed, Oswaldo Palenzuela, and Ariadna Sitjà-Bobadilla. 2021. "Experimental Horizontal Transmission of Enterospora nucleophila (Microsporea: Enterocytozoonidae) in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata)" Animals 11, no. 2: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020362
APA StylePicard-Sánchez, A., Piazzon, M. C., Estensoro, I., Del Pozo, R., Hossameldin Ahmed, N., Palenzuela, O., & Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. (2021). Experimental Horizontal Transmission of Enterospora nucleophila (Microsporea: Enterocytozoonidae) in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Animals, 11(2), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020362









