NF-κB–Dependent Snail Expression Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Mastitis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Collection
2.2. GMEC Isolation and Culture
2.3. EMT Induction
2.4. TAK-242 and QNZ Treatment
2.5. RNA Preparation and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
2.6. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. siRNA Transfection
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
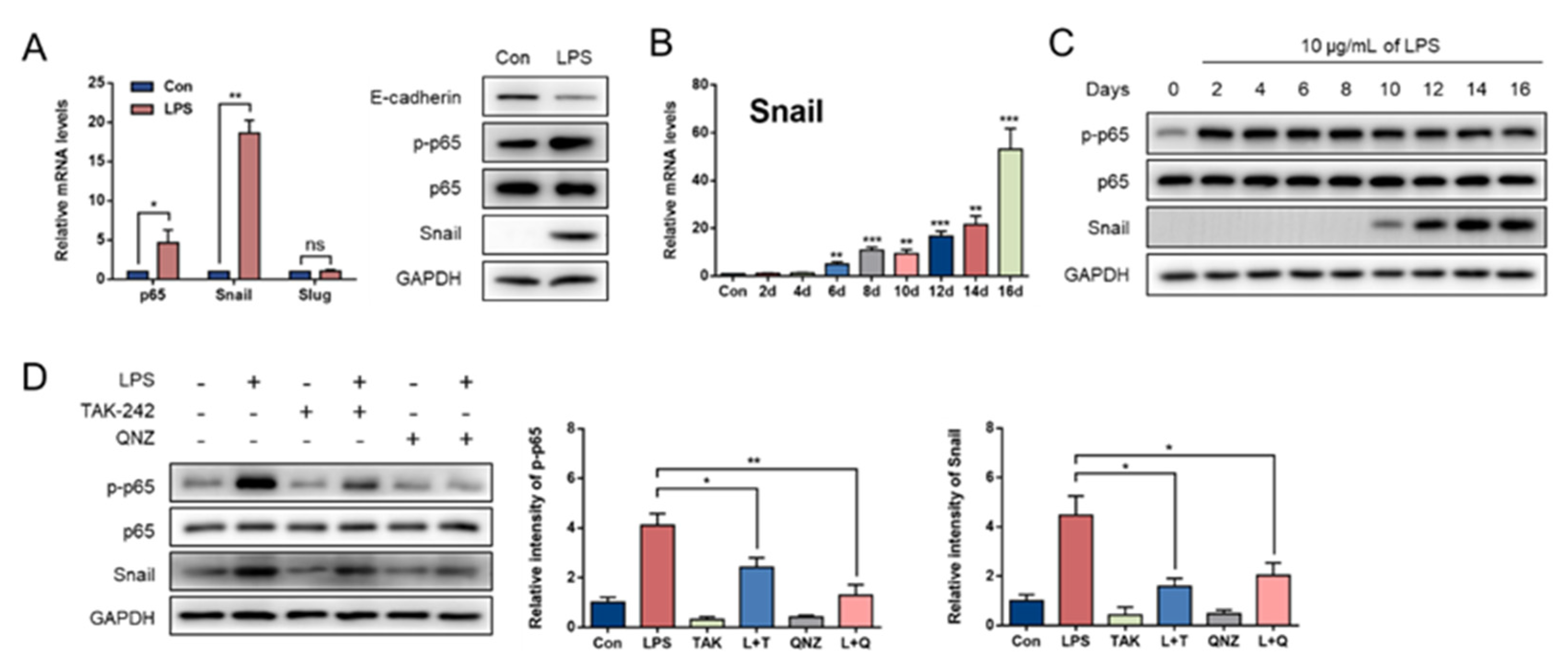
3.1. LPS Induces EMT in GMECs
3.2. NF-κB/Snail Signaling Pathway Mediates LPS-Induced EMT in GMECs
3.3. p65 Nuclear Translocation Is Required for LPS-Induced Snail Expression
3.4. Knockdown of Snail Attenuates LPS-Induced EMT
3.5. Snail Is Expressed in Mastitis Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A





| Gene ID | Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 100860784 | β-casein | ACAGCCTCCCACAAAACATC AGGAAGGTGCAGCTTTTCAA |
| 100860872 | GAPDH | TGCCCGTTCGACAGATAGC ACGATGTCCACTTTGCCAGTA |
| 100860955 | TLR4 | TTCAACCGTATCACGGCCTC TGACCCACTGCAGGAAACTC |
| 102174883 | MyD88 | TTGAGAAGAGGTGCCGTCG CAGACAGTGATGAAGCGCAG |
| 100861232 | TNF-α | CAACAGGCCTCTGGTTCAGAC GGACCTGCGAGTAGATGAGG |
| 100860816 | IL-1β | TCCACCTCCTCTCACAGGAAA TACCCAAGGCCACAGGGATCT |
| 100860785 | IL-6 | CCTCTTCACAAGCGCCTTCA TGCTTGGGGTGGTGTCATTC |
| 102178438 | IL-8 | AAGCTGGCTGCTCTCTTG GGGTGGAAAGGTGTGGAATG |
| 102174096 | NF-κB p65 | ACAACCCCTTCCAAGTTCCC AGTTCCGATTTACCCGGCAG |
| 102191364 | TGF-β1 | TTTCCGTGGGATACCGAGA CTGTTTGCGGGGAGAGTTG |
| 102172917 | Snail | CTCTTCTCCAGAGCTCACTTTC AGAGAGTCCCAGATGAGTGT |
| 102178744 | Slug | CCTTCGCAGACAGGTCCAAT CTCAGAGGCGGAGTGACAAG |
| Antibody | Manufactory | Catalog Number | Dilution Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | Cell Signaling Technology | 2118 | 1:2000 for WB |
| β-actin | Boster | BM5422 | 1:1000 for WB |
| CK18 | abcam | ab668 | 1:100 for IF |
| CK14 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-53253 | 1:100 for IF |
| E-cadherin | abcam | ab76055 | 1:2000 for WB or 1:100 for IF |
| N-cadherin | abcam | ab76057 | 1:2000 for WB or 1:100 for IF |
| Vimentin | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-80975 | 1:1000 for WB or 1:100 for IF |
| α-SMA | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-56499 | 1:1000 for WB |
| Collagen III | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-271249 | 1:1000 for WB |
| NF-κB p65 | Cell Signaling Technology | 8242 | 1:2000 for WB or 1:100 for IF |
| p-p65 (Ser536) | Cell Signaling Technology | 3033 | 1:2000 for WB |
| Snail | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-393172 | 1:100 for IF or IHC |
| Snail | Cell Signaling Technology | 3879 | 1:1000 for WB |
| Histone H3 | abcam | ab176842 | 1:2000 for WB |
References
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Predisposing factors for bacterial mastitis in ewes. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2019, 54, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.R.M.; Feitosa, M.L.T.; Rocha, A.R.; Bezerra, D.O.; Leite, Y.K.C.; Argolo Neto, N.M.; Rodrigues, H.W.S.; Sousa, A., Jr.; Silva, A.S.; Sarmento, J.L.R.; et al. Adipose stem cells in reparative goat mastitis mammary gland. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.W.; Fourcaudot, A.B.; Yamane, K.; You, T.; Chan, R.K.; Leung, K.P. Exacerbated and prolonged inflammation impairs wound healing and increases scarring. Wound Repair Regen. 2016, 24, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzora, A.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Linde, K. The effects of inoculation of Listeria monocytogenes into the ovine mammary gland. Vet. Microbiol. 1998, 59, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.; Barcelos, M.M.; Cue, R.I.; Anderson, K.L.; Santos, M.V.D.; Gonçalves, J.L. Chronic subclinical mastitis reduces milk and components yield at the cow level. J. Dairy Res. 2020, 87, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiitiö, H.; Vakkamäki, J.; Simojoki, H.; Autio, T.; Junnila, J.; Pelkonen, S.; Pyörälä, S. Prevalence of subclinical mastitis in Finnish dairy cows: Changes during recent decades and impact of cow and herd factors. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, M.; Sun, S.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M. Virulence factors impair epithelial junctions during bacterial infection. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, F.T.; Melo, S.A.; Özdemir, B.C.; Kato, N.; Revuelta, I.; Miller, C.A.; Gattone, V.H.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. TGF-β1–containing exosomes from injured epithelial cells activate fibroblasts to initiate tissue regenerative responses and fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lovisa, S.; LeBleu, V.S.; Tampe, B.; Sugimoto, H.; Vadnagara, K.; Carstens, J.L.; Wu, C.C.; Hagos, Y.; Burckhardt, B.C.; Pentcheva-Hoang, T. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induces cell cycle arrest and parenchymal damage in renal fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Jiang, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Jiang, J.; Yan, P.; Wang, F.; Tu, K.; Wang, D.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4 shRNA attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Mao, Y.F.; Dong, W.W.; Zhu, X.Y.; Jiang, L. Resveratrol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis through suppression of oxidative stress and transforming growth factor-β1 signaling. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Yeh, W.C.; Ohashi, P.S. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 2008, 42, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, A.; Humeres, C.; Frangogiannis, N.G. The role of Smad signaling cascades in cardiac fibrosis. Cell. Signal 2021, 77, 109826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sun, L.; Kato, T.; Okuda, K.; Martino, M.B.; Abzhanova, A.; Lin, J.M.; Gilmore, R.C.; Batson, B.D.; O’Neal, Y.K. IL-1β dominates the promucin secretory cytokine profile in cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 4433–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.D.; Zhou, B.P. Snail: More than EMT. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2010, 4, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, M.T.; Sánchez-Laorden, B.; López-Blau, C.; De Frutos, C.A.; Boutet, A.; Arévalo, M.; Rowe, R.G.; Weiss, S.J.; López-Novoa, J.M.; Nieto, M.A. Snail1-induced partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition drives renal fibrosis in mice and can be targeted to reverse established disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.D.; Zhou, B.P. TNF-α/NF-κB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matuozzo, M.; Spagnuolo, M.S.; Hussein, H.A.; Gomaa, A.M.; Scaloni, A.; D’Ambrosio, C. Novel Biomarkers of Mastitis in Goat Milk Revealed by MALDI-TOF-MS-Based Peptide Profiling. Biology 2020, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Sharma, N.; Singh, D.D.; Gururaj, K.; Abhishek; Kumar, V.; Sharma, D.K. Prevalence and bacterial etiology of subclinical mastitis in goats reared in organized farms. Vet. World 2018, 11, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaninelli, M.; Tangorra, F.M.; Costa, A.; Rossi, L.; Dell’Orto, V.; Savoini, G. Improved Fuzzy Logic System to Evaluate Milk Electrical Conductivity Signals from On-Line Sensors to Monitor Dairy Goat Mastitis. Sensors 2016, 16, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Miao, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Q.; Ma, B. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of goat mammary epithelial cells via NF-κB signalling pathway. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2021, 56, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Shang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, A.; Jin, Y.; Lin, P. Transcriptomic Analysis of STAT1/3 in the Goat Endometrium During Embryo Implantation. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 757759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strandberg, Y.; Gray, C.; Vuocolo, T.; Donaldson, L.; Broadway, M.; Tellam, R. Lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid induce different innate immune responses in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Cytokine 2005, 31, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ji, S.; Zhang, W.; Kang, J.; Li, J.; Fei, G. Melatonin prevents LPS-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human alveolar epithelial cells via the GSK-3β/Nrf2 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Qiu, Y.B.; Gao, Z.Q.; Wu, Y.X.; Wan, B.B.; Liu, G.; Chen, J.L.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, R.Q.; Pang, Q.F. Sodium Propionate Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6554–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B. Depression of lncRNA NEAT1 Antagonizes LPS-Evoked Acute Injury and Inflammatory Response in Alveolar Epithelial Cells via HMGB1-RAGE Signaling. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 8019467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Dong, G. The Synergism of PGN, LTA and LPS in Inducing Transcriptome Changes, Inflammatory Responses and a Decrease in Lactation as Well as the Associated Epigenetic Mechanisms in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkidasamy, B.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Thirupathi, P.; Subramanian, U. Inhibition of histone deacetylases is the major pathway mediated by astaxanthin to antagonize LPS-induced inflammatory responses in mammary epithelial cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxic 2020, 34, e22507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.P.; Deng, J.; Xia, W.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.M.; Gunduz, M.; Hung, M.C. Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhu, R.; Luo, A.; Zhou, H.; Ding, F.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z. EIF3H promotes aggressiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating Snail stability. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberà, M.J.; Puig, I.; Domínguez, D.; Julien-Grille, S.; Guaita-Esteruelas, S.; Peiró, S.; Baulida, J.; Francí, C.; Dedhar, S.; Larue, L.; et al. Regulation of Snail transcription during epithelial to mesenchymal transition of tumor cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7345–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.T.; Li, C.Y.; Xu, D.W.; Zhu, J.J.; Wei, S.; Zhong, A.; Sheng, M.W.; Duarte, S.; Coito, A.J.; Busuttil, R.W.; et al. Jagged1-mediated myeloid Notch1 signaling activates HSF1/Snail and controls NLRP3 inflammasome activation in liver inflammatory injury. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Qi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.Q. TGF-β1 Induces EMT in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells Through the TGFβ1/Smad Signaling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salem, S.; Harris, T.; Mok, J.S.; Li, M.Y.; Keenan, C.R.; Schuliga, M.J.; Stewart, A.G. Transforming growth factor-β impairs glucocorticoid activity in the A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 2036–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, J.; Morgani, S.M.; David, C.J.; Wang, Q.; Er, E.E.; Huang, Y.H.; Basnet, H.; Zou, Y.; Shu, W.; Soni, R.K.; et al. TGF-β orchestrates fibrogenic and developmental EMTs via the RAS effector RREB1. Nature 2020, 577, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Ma, Y.; Shen, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L.; Bu, X.; Guo, Z.; Qin, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. NDRG2 regulates adherens junction integrity to restrict colitis and tumourigenesis. eBioMedicine 2020, 61, 103068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Li, Q.; Wu, X.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.; Zou, X.; et al. Deubiquitinase USP29 promotes gastric cancer cell migration by cooperating with phosphatase SCP1 to stabilize Snail protein. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6802–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kage, H.; Borok, Z. EMT and interstitial lung disease: A mysterious relationship. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2012, 18, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.; Simoes, E.; de Castro, G.; Morais, M.; de Matos-Neto, E.M.; Alves, M.J.; Pinto, N.I.; Figueredo, R.G.; Zorn, T.M.T.; Felipe-Silva, A.S.; et al. Tumour-derived transforming growth factor-β signalling contributes to fibrosis in patients with cancer cachexia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piersma, B.; Hayward, M.K.; Weaver, V.M. Fibrosis and cancer: A strained relationship. BBA Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang-Gillam, A.; Yu, J.; Head, R.; Liu, J.; Ruzinova, M.B.; Lim, K.H. Tumor-Stroma IL1β-IRAK4 Feedforward Circuitry Drives Tumor Fibrosis, Chemoresistance, and Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.X.; Li, P.; Chen, Z.; Lin, H.; Cai, Z.; Liao, W.; Pan, Z. Impact of liver fibrosis score on prognosis after common therapies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, C.; Wu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, L. Snail-mediated partial epithelial mesenchymal transition augments the differentiation of local lung myofibroblast. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Adeyanju, O.; Roy, S.; Sunil, C.; Jeffers, A.; Guo, X.; Ikebe, M.; Idell, S.; Tucker, T.A. DOCK2 Promotes Pleural Fibrosis by Modulating Mesothelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossberg, A.J.; Lei, X.; Xu, T.; Shaitelman, S.F.; Hoffman, K.E.; Bloom, E.S.; Stauder, M.C.; Tereffe, W.; Schlembach, P.J.; Woodward, W.A.; et al. Association of Transforming Growth Factor β Polymorphism C-509T With Radiation-Induced Fibrosis Among Patients With Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, I.R.; Camassa, J.A.; Bordelo, J.A.; Babo, P.S.; Viegas, C.A.; Dourado, N.; Reis, R.L.; Gomes, M.E. Preclinical and Translational Studies in Small Ruminants (Sheep and Goat) as Models for Osteoporosis Research. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.Y.; Wu, Y.X.; Li, R.; Li, G.S.; Hu, Y. A translational study of somatosensory evoked potential time-frequency components in rats, goats, and humans. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 2269–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvites, R.D.; Branquinho, M.V.; Sousa, A.C.; Lopes, B.; Sousa, P.; Mendonça, C.; Atayde, L.M.; Maurício, A.C. Small Ruminants and Its Use in Regenerative Medicine: Recent Works and Future Perspectives. Biology 2021, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Q.; Ma, B. NF-κB–Dependent Snail Expression Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Mastitis. Animals 2021, 11, 3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123422
Liu H, Zhao Y, Wu Y, Yan Y, Zhao X, Wei Q, Ma B. NF-κB–Dependent Snail Expression Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Mastitis. Animals. 2021; 11(12):3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123422
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haokun, Ying Zhao, Yanfang Wu, Yutong Yan, Xiaoe Zhao, Qiang Wei, and Baohua Ma. 2021. "NF-κB–Dependent Snail Expression Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Mastitis" Animals 11, no. 12: 3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123422
APA StyleLiu, H., Zhao, Y., Wu, Y., Yan, Y., Zhao, X., Wei, Q., & Ma, B. (2021). NF-κB–Dependent Snail Expression Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Mastitis. Animals, 11(12), 3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123422






