High Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slovenian Wild Boars (Sus scrofa)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Serological Methods
2.2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logar, J.; Kraut, A.; Stirn-Kranjc, B.; Vidovic-Valentincic, N. Seroprevalence of toxoplasma antibodies among patients with ocular disease in Slovenia. J. Infect. 2003, 46, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutterland, A.L.; Fond, G.; Kuin, A.; Koeter, M.W.J.; Lutter, R.; van Gool, T.; Yolken, R.; Szoke, A.; Leboyer, M.; de Haan, L. Beyond the association. Toxoplasma gondii in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and addiction: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2015, 132, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Seyyedtabaei, S.J.; Aghamolaie, S.; Behniafar, H.; Lasjerdi, Z.; Abdolrasouli, A.; Mehravar, S.; Alvarado-Esquivel, C. Seroprevalence and risk factors associated with toxoplasma gondii infection among rural communities in Northern Iran. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2016, 58, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiadeh, M.N.; Niyyati, M.; Fallahi, S.; Rostami, A. Human parasitic protozoan infection to infertility: A systematic review. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, S.; Rostami, A.; Birjandi, M.; Zebardast, N.; Kheirandish, F.; Spotin, A. Parkinson’s disease and Toxoplasma gondii infection: Sero-molecular assess the possible link among patients. Acta Trop. 2017, 173, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, V.O.; de Mendonça Lima, F.W.; de Carvalho, C.F.; Menezes-Filho, J.A. Toxoplasma gondii infection and behavioral outcomes in humans: A systematic review. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3059–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.J.C.; Gilbert, R.; Buffolano, W.; Zufferey, J.; Petersen, E.; Jenum, P.A.; Foulon, W.; Semprini, A.E.; Dunn, D.T.; Holliman, R. Sources of toxoplasma infection in pregnant women: European multicentre case-control study Commentary: Congenital toxoplasmosis—Further thought for food. BMJ 2000, 321, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P. Sources of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnancy. Until rates of congenital toxoplasmosis fall, control measures are essential. BMJ 2000, 321, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logar, J.; Petrovec, M.; Novak-Antolic, Z.; Premru-Srsen, T.; Cizman, M.; Arnez, M.; Kraut, A. Prevention of congenital toxoplasmosis in Slovenia by serological screening of pregnant women. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci-Goga, B.T.; Rossitto, P.V.; Sechi, P.; McCrindle, C.M.; Cullor, J.S. Toxoplasma in Animals, Food, and Humans: An Old Parasite of New Concern. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Giessen, J.; Fonville, M.; Bouwknegt, M.; Langelaar, M.; Vollema, A. Seroprevalence of Trichinella spiralis and Toxo-plasma gondii in pigs from different housing systems in the Netherlands. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slany, M.; Reslová, N.; Babak, V.; Lorencova, A. Molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in pork meat from different production systems in the Czech Republic. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 238, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Lindsay, D.; Sriranganathan, N. Wild boars as sources for infectious diseases in livestock and humas. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2697–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rostami, A.; Riahi, S.M.; Fakhri, Y.; Saber, V.; Hanifehpour, H.; Valizadeh, S.; Gholizadeh, M.; Pouya, R.H.; Gamble, H. The global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii among wild boars: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 244, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massei, G.; Kindberg, J.; Licoppe, A.; Gačić, D.; Šprem, N.; Kamler, J.; Baubet, E.; Hohmann, U.; Monaco, A.; Ozoliņš, J.; et al. Wild boar populations up, numbers of hunters down? A review of trends and implications for Europe. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grema, C.; Hotea, I.; Imre, M.; Dărăbus, G.; Pascu, C.; Mariş, C.; Herman, V. Seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis and swine infuenza in wild boars. Sci. Parasitol. 2015, 16, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Beral, M.; Rossi, S.; Aubert, D.; Gasqui, P.; Terrier, M.-E.; Klein, F.; Villena, I.; Abrial, D.; Gilot-Fromont, E.; Richomme, C.; et al. Environmental Factors Associated with the Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Boars (Sus scrofa), France. EcoHealth 2012, 9, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ); Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; et al. Public health risks associated with food-borne parasites. EFSA J 2018, 16, 5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiterová, K.; Špilovská, S.; Blaňarová, L.; Derdáková, M.; Čobádiová, A.; Hisira, V. Wild boar (Sus scrofa)—Reservoir host of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Slovakia. Acta Parasitol. 2016, 61, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halsby, K.D.; Walsh, A.L.; Smith, R.; Said, B.; Kirkbride, H.; Smyth, B.; Browning, L.; Larkin, L.; Morgan, D. The Health Burden of Orphan Zoonotic Disease in the United Kingdom, 2005–2009. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 61, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amici, A.; Cifuni, G.F.; Contò, M.; Esposito, L.; Failla, S. Hunting area affects chemical and physical characteristics and fatty acid composition of wild boar (Sus scrofa) meat. Rend. Lincei 2015, 26, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, N.S.; Stollberg, K.; Mayer-Scholl, A.; Johne, A.; Nöckler, K.; Richter, M. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild boar and deer in Brandenburg, Germany. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallander, C.; Frössling, J.; Vågsholm, I.; Uggla, A.; Lundén, A. Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Sweden and evaluation of ELISA test performance. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauss, C.; Dubey, J.; Vidal, D.; Ruiz, F.; Vicente, J.; Marco, I.; Lavin, S.; Gortazar, C.; Almería, S. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild pigs (Sus scrofa) from Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 131, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richomme, C.; Afonso, E.; Tolon, V.; Ducrot, C.; Halos, L.; Alliot, A.; Perret, C.; Thomas, M.; Boireau, P.; Gilot-Fromont, E. Seroprevalence and factors associated with Toxoplasma gondii infection in wild boar (Sus scrofa) in a Mediterranean island. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Closa-Sebastià, F.; Casas-Díaz, E.; Cuenca, R.; Lavrin, S.; Mentaberre, G.; Marco, I. Antibodies to selected pathogens in wild boar (Sus scrofa) from Catalonia (NE Spain). Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2011, 57, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Račka, K.; Bártova, E.; Budiková, M.; Vodrážka, P. Survey of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in meat juice of wild boar (Sus scrofa) in several districts of the Czech Republic. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adamič, M.; Jerina, K. Ungulate management in Europe in Slovenia. In European Ungulates and Their Management in the 21st Century; Apollonio, M., Andersen, R., Putman, R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 507–527. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Hayama, Y.; Yamaguchi, E.; Hanafusa, Y.; Osaki, M. First nantionwide survey of the seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild boars in Japan. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.; Rickard, L.; Zimmerman, G.; Mulrooney, D. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in llamas (Lama glama) in the northwest USA. Vet. Parasitol. 1992, 44, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolová, D.; Reiterová, K.; Dubinský, P. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in the Slovak Republic. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2007, 14, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jokelainen, P.; Velström, K.; Lassen, B. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in free-ranging wild boars hunted for human consumption in Estonia. Acta Vet. Scand. 2015, 57, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olsen, A.; Berg, R.; Tagel, M.; Must, K.; Deksne, G.; Enemark, H.L.; Alban, L.; Johansen, M.V.; Nielsen, H.V.; Sandberg, M.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in domestic pigs, sheep, cattle, wild boars, and moose in the Nordic-Baltic region: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasite Epidemiol. Control. 2019, 5, e00100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobić, B.; Nikolić, A.; Klun, I.; Djurkovic-Djakovic, O. Kinetics of Toxoplasma infection in the Balkans. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2011, 123, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Villa, L.; Riehn, K.; Hamedy, A.; Minazzi, S.; Olivieri, E.; Zanzani, S.A.; Manfredi, M.T. Occurrence of selected zoonotic food-borne parasites and first molecular identification of Alaria alata in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Wild Boar | Tested Animals (%) | T. gondii Positive (%) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.781 | ||
| male | 209 (59) | 132 (63) | |
| female | 144 (41) | 88 (61) | |
| Age (years) | 0.003 | ||
| 0–1 | 125 (35) | 64 (51) | |
| 1–2 | 162 (46) | 105 (65) | |
| 2–3 | 35 (10) | 29 (83) | |
| >3 | 31 (9) | 22 (71) | |
| Weight (kg) | 0.002 | ||
| 0–20 | 33 (9) | 12 (36) | |
| 20–40 | 137 (39) | 79 (58) | |
| 40–60 | 99 (28) | 66 (67) | |
| 60–80 | 55 (16) | 42 (76) | |
| >80 | 29 (8) | 21 (72) | |
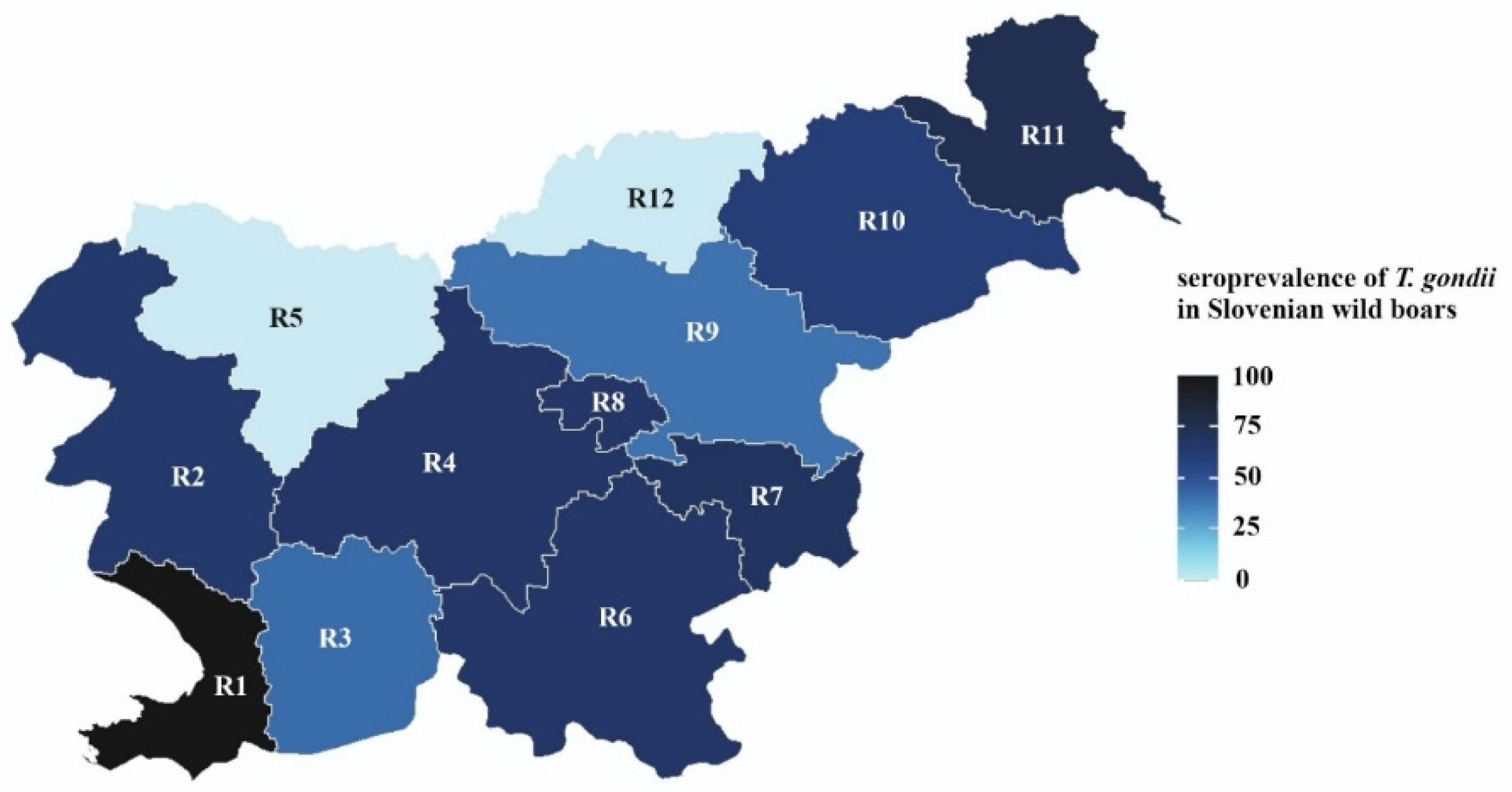
| Region | 0.043 | ||
| 1 obalno kraska | 2 (1) | 2 (100) | |
| 2 goriska | 20 (6) | 13 (65) | |
| 3 primorsko notranjska | 43 (12) | 18 (42) | |
| 4 osrednjeslovenska | 18 (5) | 12 (67) | |
| 5 gorenjska | 0 | 0 | |
| 6 jugovzhodna slovenija | 129 (36) | 87 (67) | |
| 7 posavska | 30 (8) | 21 (70) | |
| 8 zasavska | 12 (3) | 8 (67) | |
| 9 savinjska | 20 (6) | 8 (40) | |
| 10 podravska | 55 (16) | 33 (60) | |
| 11 pomurska | 24 (7) | 18 (75) | |
| 12 koroska | 0 | 0 |
| Wild Boar | Model 1 (AUC = 0.664) | Model 2 (AUC = 0.665) | Model 3 (AUC = 0.641) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | p = 0.963 | p = 0.911 | p = 0.915 |
| male vs. female | 1.01 (0.63–1.61) | 1.03 (0.65–1.63) | 0.98 (0.61–1.54) |
| Age (years) | p = 0.301 | p = 0.004 | |
| 1–2 vs. 0–1 | 1.24 (0.70–2.19) [p = 0.454] | / | 1.69 (1.02–2.77) [p = 0.038] |
| 2–3 vs. 1–2 | 2.19 (0.78–6.09) [p = 0.132] | / | 2.66 (1.03–6.85) [p = 0.042] |
| >3 vs. 2–3 | 0.47 (0.13–1.65) [p = 0.238] | / | 0.5 (0.15–1.63) [p = 0.249] |
| Weight (kg) | p = 0.094 | p = 0.001 | |
| 20–40 vs. 0–20 | 2.54 (1.11–5.84) [p = 0.028] | 2.74 (1.21–6.2) [p = 0.015] | / |
| 40–60 vs. 20–40 | 1.22 (0.66–2.23) [p = 0.52] | 1.42 (0.81–2.48) [p = 0.216] | / |
| 60–80 vs. 40–60 | 1.41 (0.61–3.24) [p = 0.417] | 1.58 (0.73–3.38) [p = 0.238] | / |
| >80 vs. 60–80 | 0.76 (0.24–2.36) [p = 0.64] | 0.8 (0.28–2.25) [p = 0.666] | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bandelj, P.; Vengušt, D.Ž.; Blagus, R.; Vergles Rataj, A.; Krt, B. High Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slovenian Wild Boars (Sus scrofa). Animals 2021, 11, 3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113139
Bandelj P, Vengušt DŽ, Blagus R, Vergles Rataj A, Krt B. High Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slovenian Wild Boars (Sus scrofa). Animals. 2021; 11(11):3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113139
Chicago/Turabian StyleBandelj, Petra, Diana Žele Vengušt, Rok Blagus, Aleksandra Vergles Rataj, and Branko Krt. 2021. "High Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slovenian Wild Boars (Sus scrofa)" Animals 11, no. 11: 3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113139
APA StyleBandelj, P., Vengušt, D. Ž., Blagus, R., Vergles Rataj, A., & Krt, B. (2021). High Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slovenian Wild Boars (Sus scrofa). Animals, 11(11), 3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113139






