Screening of Swiss Pig Herds for Hepatitis E Virus: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.1.1. Evaluation of Different Sample Types
2.1.2. Sock Swab Screening
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.2.1. Homogenisation of Floor and Dust Swabs
2.2.2. Homogenisation of Slurry Samples
2.2.3. Homogenisation of Individual Faecal Samples
2.2.4. Homogenisation of Sock Swabs
2.2.5. RNA Mini Kit
2.3. RT-qPCR
2.4. Typing PCR
2.5. NGS
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. RT-qPCR
3.1.1. Evaluation of Different Sample Types
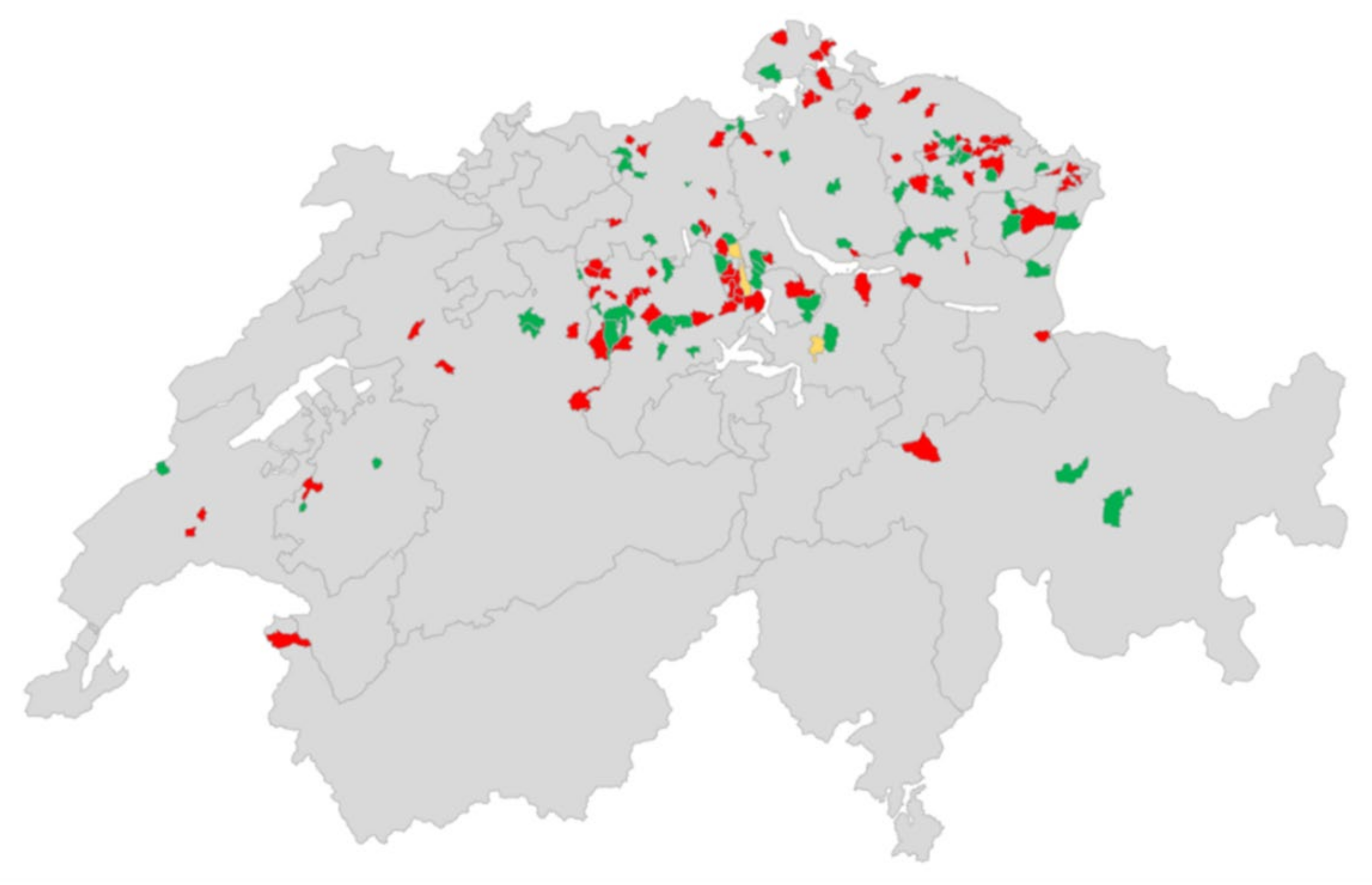
3.1.2. Sock Swab Screening
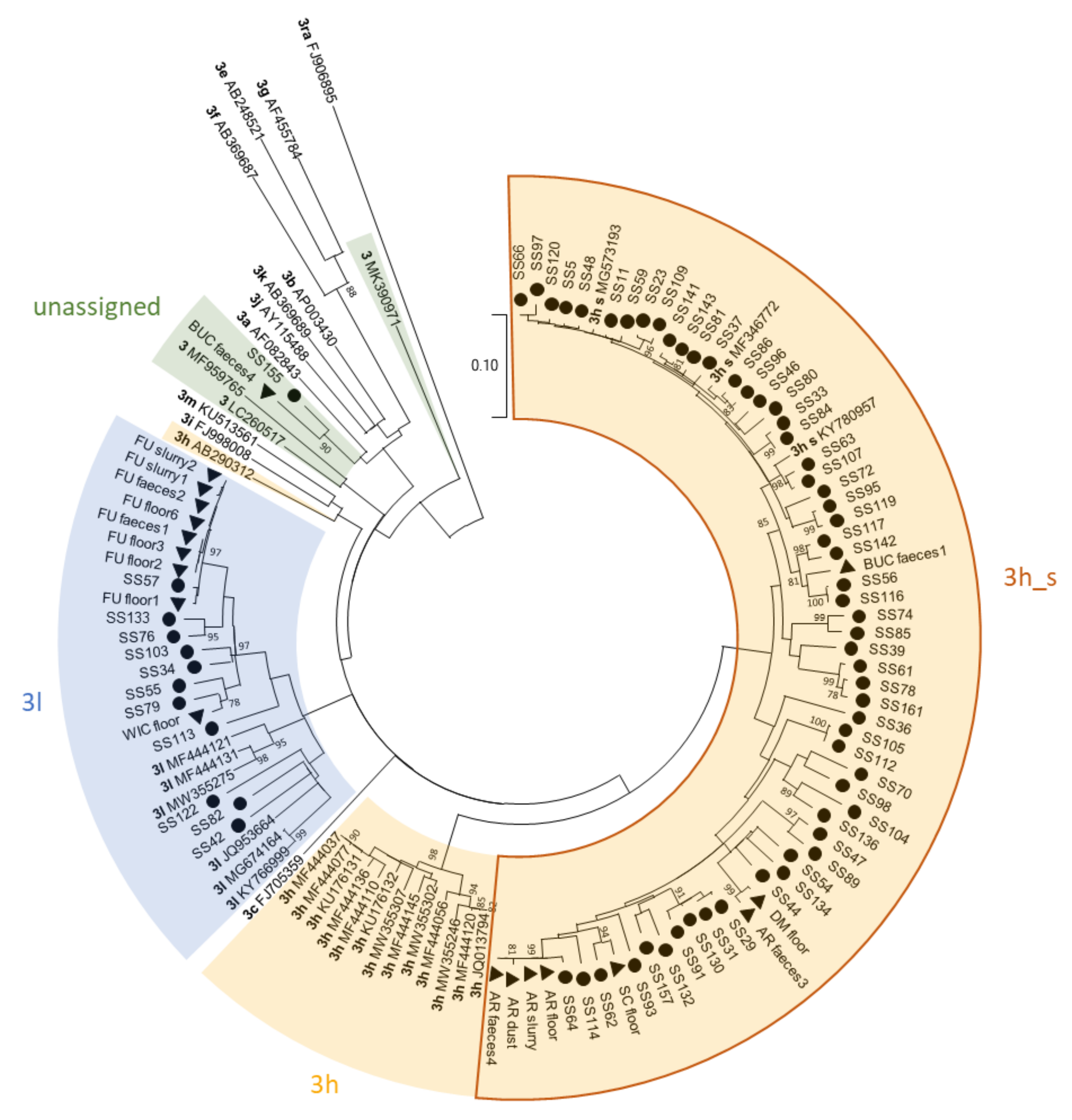
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. NGS
3.4. Questionnaire
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purdy, M.A.; Harrison, T.J.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.J.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Smith, D.B.; ICTV Report Consortium. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2645–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, H.; Hoshino, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Jirintai, F.; Mizuo, H.; Yazaki, Y.; Takagi, T.; Azuma, M.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) strains in serum samples can replicate efficiently in cultured cells despite the coexistence of HEV antibodies: Characterization of HEV virions in blood circulation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, Z.; Hirai-Yuki, A.; McKnight, K.L.; Lemon, S.M. Naked Viruses That Aren’t Always Naked: Quasi-Enveloped Agents of Acute Hepatitis. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2014, 1, 539–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.J. From barnyard to food table: The omnipresence of hepatitis E virus and risk for zoonotic infection and food safety. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavio, N.; Doceul, V.; Bagdassarian, E.; Johne, R. Recent knowledge on hepatitis E virus in Suidae reservoirs and transmission routes to human. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Hepatitis E in the EU/EEA, 2005–2015; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hogema, B.M.; Molier, M.; Slot, E.; Zaaijer, H.L. Past and present of hepatitis E in the Netherlands. Transfusion 2014, 54, 3092–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holm, D.K.; Moessner, B.K.; Engle, R.E.; Zaaijer, H.L.; Georgsen, J.; Purcell, R.H.; Christensen, P.B. Declining prevalence of hepatitis E antibodies among Danish blood donors. Transfusion 2015, 55, 1662–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, M.; Willrich, N.; Schemmerer, M.; Rauh, C.; Kuhnert, R.; Stark, K.; Wenzel, J.J. Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence, seroincidence and seroreversion in the German adult population. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederhauser, C.; Widmer, N.; Hotz, M.; Tinguely, C.; Fontana, S.; Allemann, G.; Borri, M.; Infanti, L.; Sarraj, A.; Sigle, J.; et al. Current hepatitis E virus seroprevalence in Swiss blood donors and apparent decline from 1997 to 2016. Euro Surveill. 2018, 23, 1700616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andraud, M.; Dumarest, M.; Cariolet, R.; Aylaj, B.; Barnaud, E.; Eono, F.; Pavio, N.; Rose, N. Direct contact and environmental contaminations are responsible for HEV transmission in pigs. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasorndorkbua, C.; Guenette, D.K.; Huang, F.F.; Thomas, P.J.; Meng, X.J.; Halbur, P.G. Routes of transmission of swine hepatitis E virus in pigs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5047–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Barredo, S.; Galiana, C.; García, A.; Vega, S.; Gómez, M.T.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T. Detection of hepatitis E virus shedding in feces of pigs at different stages of production using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2006, 18, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ward, P.; Müller, P.; Letellier, A.; Quessy, S.; Simard, C.; Trottier, Y.L.; Houde, A.; Brassard, J. Molecular characterization of hepatitis E virus detected in swine farms in the province of Quebec. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 72, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Halbur, P.G.; Lehman, J.R.; Webb, D.M.; Tsareva, T.S.; Haynes, J.S.; Thacker, B.J.; Emerson, S.U. A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9860–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.J.; Halbur, P.G.; Haynes, J.S.; Tsareva, T.S.; Bruna, J.D.; Royer, R.L.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Experimental infection of pigs with the newly identified swine hepatitis E virus (swine HEV), but not with human strains of HEV. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salines, M.; Andraud, M.; Rose, N. From the epidemiology of hepatitis E virus (HEV) within the swine reservoir to public health risk mitigation strategies: A comprehensive review. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Bartolo, I.; Martelli, F.; Inglese, N.; Pourshaban, M.; Caprioli, A.; Ostanello, F.; Ruggeri, F.M. Widespread diffusion of genotype 3 hepatitis E virus among farming swine in Northern Italy. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 132, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wacheck, S.; Werres, C.; Mohn, U.; Dorn, S.; Soutschek, E.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Märtlbauer, E. Detection of IgM and IgG against hepatitis E virus in serum and meat juice samples from pigs at slaughter in Bavaria, Germany. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiry, D.; Mauroy, A.; Saegerman, C.; Thomas, I.; Wautier, M.; Miry, C.; Czaplicki, G.; Berkvens, D.; Praet, N.; van der Poel, W.; et al. Estimation of hepatitis E virus (HEV) pig seroprevalence using ELISA and Western blot and comparison between human and pig HEV sequences in Belgium. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, M.; Cortés, R.; Pina, S.; Peralta, B.; Allepuz, A.; Cortey, M.; Casal, J.; Martín, M. Longitudinal study of hepatitis E virus infection in Spanish farrow-to-finish swine herds. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burri, C.; Vial, F.; Ryser-Degiorgis, M.P.; Schwermer, H.; Darling, K.; Reist, M.; Wu, N.; Beerli, O.; Schöning, J.; Cavassini, M.; et al. Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus in domestic pigs and wild boars in Switzerland. Zoonoses Public Health 2014, 61, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wacheck, S.; Sarno, E.; Märtlbauer, E.; Zweifel, C.; Stephan, R. Seroprevalence of anti-hepatitis E virus and anti-Salmonella antibodies in pigs at slaughter in Switzerland. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1483–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Simmonds, P.; Izopet, J.; Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Ulrich, R.G.; Johne, R.; Koenig, M.; Jameel, S.; Harrison, T.J.; Meng, X.J.; et al. Proposed reference sequences for hepatitis E virus subtypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, F.; Jeanne, N.; Roulet, A.; Lefebvre, C.; Carcenac, R.; Manno, M.; Dubois, M.; Kamar, N.; Lhomme, S.; Abravanel, F.; et al. Diversity of hepatitis E virus genotype 3. Rev. Med. Virol. 2018, 28, e1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, F.; Dimeglio, C.; Migueres, M.; Jeanne, N.; Latour, J.; Abravanel, F.; Ranger, N.; Harter, A.; Dubois, M.; Lameiras, S.; et al. Classification of the Zoonotic Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 Into Distinct Subgenotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 634430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Harms, D.; Hofmann, J.; Ciardo, D.; Kneubühl, A.; Bock, C.T. Identification of a Novel Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 Strain Isolated from a Chronic Hepatitis E Virus Infection in a Kidney Transplant Recipient in Switzerland. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00345-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubacki, J.; Fraefel, C.; Jermini, M.; Giannini, P.; Martinetti, G.; Ripellino, P.; Bernasconi, E.; Sidler, X.; Stephan, R.; Bachofen, C. Complete Genome Sequences of Two Swiss Hepatitis E Virus Isolates from Human Stool and Raw Pork Sausage. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00888-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wist, V.; Kubacki, J.; Lechmann, J.; Steck, M.; Fraefel, C.; Stephan, R.; Bachofen, C. Complete Genome Sequence of a Swiss Hepatitis E Virus Isolate from the Liver of a Fattening Pig. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e00113-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.B.; Izopet, J.; Nicot, F.; Simmonds, P.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; et al. Update: Proposed reference sequences for subtypes of hepatitis E virus (species Orthohepevirus A). J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahli, R.; Fraga, M.; Semela, D.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. Rabbit HEV in immunosuppressed patients with hepatitis E acquired in Switzerland. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stalder, H.; Hug, C.; Zanoni, R.; Vogt, H.R.; Peterhans, E.; Schweizer, M.; Bachofen, C. A nationwide database linking information on the hosts with sequence data of their virus strains: A useful tool for the eradication of bovine viral diarrhea (BVD) in Switzerland. Virus Res. 2016, 218, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, G.C.; Grant, D.M.; Lycett, S.; Bachofen, C.; Caldow, G.L.; Burr, P.D.; Davie, K.; Ambrose, N.; Gunn, G.J.; Zadoks, R.N. Analysis of bovine viral diarrhoea virus: Biobank and sequence database to support eradication in Scotland. Vet. Rec. 2017, 180, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulder, A.C.; Kroneman, A.; Franz, E.; Vennema, H.; Tulen, A.D.; Takkinen, J.; Hofhuis, A.; Adlhoch, C.; HEVnet, M.O. HEVnet: A One Health, collaborative, interdisciplinary network and sequence data repository for enhanced hepatitis E virus molecular typing, characterisation and epidemiological investigations. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24, 1800407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsler, M.L. Occurrence of Escherichia Coli Non-Susceptible to Quinolones in Fecal and Environmental Samples from Pigs at Different Ages after Fluoroquinolone Treatment in Piglets or Their Dams. DVM Thesis, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jothikumar, N.; Cromeans, T.L.; Robertson, B.H.; Meng, X.J.; Hill, V.R. A broadly reactive one-step real-time RT-PCR assay for rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 131, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garson, J.A.; Ferns, R.B.; Grant, P.R.; Ijaz, S.; Nastouli, E.; Szypulska, R.; Tedder, R.S. Minor groove binder modification of widely used TaqMan probe for hepatitis E virus reduces risk of false negative real-time PCR results. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 186, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxman, I.L.A.; Jansen, C.C.C.; Hägele, G.; Zwartkruis-Nahuis, A.; Cremer, J.; Vennema, H.; Tijsma, A.S.L. Porcine blood used as ingredient in meat productions may serve as a vehicle for hepatitis E virus transmission. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 257, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubacki, J.; Fraefel, C.; Bachofen, C. Implementation of next-generation sequencing for virus identification in veterinary diagnostic laboratories. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 33, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhire, B.M.; Varsani, A.; Martin, D.P. SDT: A virus classification tool based on pairwise sequence alignment and identity calculation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risalde, M.A.; Rivero-Juarez, A.; Frias, M.; Olivas, I.; Lopez-Lopez, P.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Brieva, T.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Camacho, A.; Fernández-Molera, V.; et al. Evaluation of a non-invasive screening approach to determine hepatitis E virus status of pig farms. Vet. Rec. 2020, 187, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, K.S.; Okholm, E.; Johansen, M.; Angen, Ø.; Jorsal, S.E.; Nielsen, J.P.; Bækbo, P. Clinical utility and performance of sock sampling in weaner pig diarrhoea. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 120, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinde, H.; Goodluck, H.A.; Pitesky, M.; Friend, T.D.; Campbell, J.A.; Hill, A.E. Validation of Single and Pooled Manure Drag Swabs for the Detection of Salmonella Serovar Enteritidis in Commercial Poultry Houses. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, A.J.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Soares, M.o.C.; Pinho, J.R.; Malheiros, A.P.; Carneiro, L.A.; dos Santos, D.R.; Pereira, W.L. HEV infection in swine from Eastern Brazilian Amazon: Evidence of co-infection by different subtypes. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 35, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandadam, M.; Tebbal, S.; Caron, M.; Siriwardana, M.; Larouze, B.; Koeck, J.L.; Buisson, Y.; Enouf, V.; Nicand, E. Evidence for hepatitis E virus quasispecies. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3189–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Karlsson, M.; Lindberg, M.; Nyström, K.; Norder, H. Hepatitis E virus strains infecting Swedish domestic pigs are unique for each pig farm and remain in the farm for at least 2 years. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, C.; Stalder, H.; Sidler, X.; Renzullo, S.; Gurtner, C.; Grahofer, A.; Schweizer, M. Long-Term Circulation of Atypical Porcine Pestivirus (APPV) within Switzerland. Viruses 2019, 11, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Mansuy, J.M.; Dubois, M.; Kamar, N.; Peron, J.M.; Rostaing, L.; Izopet, J. Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 diversity, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Schlosser, J.; Becher, D.; Kaden, V.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 diversity: Phylogenetic analysis and presence of subtype 3b in wild boar in Europe. Viruses 2015, 7, 2704–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milojević, L.; Velebit, B.; Teodorović, V.; Kirbiš, A.; Petrović, T.; Karabasil, N.; Dimitrijević, M. Screening and Molecular Characterization of Hepatitis E Virus in Slaughter Pigs in Serbia. Food Environ. Virol. 2019, 11, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdy, M.A.; Sue, A. The effect of phylogenetic signal reduction on genotyping of hepatitis E viruses of the species Orthohepevirus A. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baylis, S.A.; Adlhoch, C.; Childs, L.; HEV sequencing study group. An Evaluation of Hepatitis E Virus Molecular Typing Methods. Clin. Chem. 2021. accepted. [Google Scholar]


| Number of Farms | Environmental Samples | Individual Faecal Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Floor Swab | Slurry | Dust Swab | ||
| 6 | + 1 | + | + | + |
| 3 | + | + | − 2 | + |
| 1 | + | + | − | − |
| 2 | − | + | − | − |
| 2 | − | − | − | + |
| 1 | − | − | − | − |
| Mean Ct value | 36.4 | 37.8 | 37.5 | 37.5 |
| Range of the Ct | 32.7–39.9 | 32.4–41.1 | 35.0–39.6 | 27.5–42.6 |
| Age of Pigs Tested | No. of Total Samples | Positive Samples | Mean Ct Value | Range of the Ct Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | ||||
| 4–10 weeks | 12 | 3 | 25.0 | 33.8 | 28.5–40.6 |
| >10 weeks–6 months | 130 | 76 | 58.5 | 34.8 | 25.9–43.2 |
| >6 months | 3 | 1 | 33.3 | 40.3 | |
| Mixed age groups | 8 | 3 | 37.5 | 34.6 | 29.0–37.5 |
| Total | 153 | 83 | 54.2 | 34.8 | 25.9–43.2 |
| Farm | 4–10 Weeks | >10 Weeks–6 Months | >6 Months | One-for-All Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | + | − | + | − |
| B | − | − | Not sampled | − |
| C | − | − | – | − |
| Sample Material | No. of Samples Submitted to Typing PCR | No. of Typing PCR Positive Samples | No. of Successfully Sequenced Samples | Subtype 3h | Subtype 3l | Unassigned Genotype 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Floor swabs | 13 | 12 | 11 | 4 | 7 | - |
| Slurry | 5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 3 | - |
| Dust swabs | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - |
| Individual faeces | 12 | 11 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 1 |
| Sock swabs | 83 | 71 | 70 | 58 | 11 | 1 |
| Total | 115 | 100 | 96 | 71 | 23 | 2 |
| Sample Type | AR | BUC | LE | FU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Floor swab | A | C + D | C | E |
| Slurry | A | C + D | − 1 | E |
| Dust swab | A | − | − | − |
| Individual faeces | 3 × A, 1 × B | 3 × C, 1 × D | − | 2 × E, 1 × F |
| Sample | Method | Ct Value | HEV Coverage (%) | Reads 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS48 | TRIzol | 31.5 | 99.4 1 | 3259 |
| SS48 | RNA kit with BME | 31.0 | 50.6 2 | 43 |
| SS48 | RNA kit with DTT | 30.5 | 60.6 1 | 65 |
| SS66 | TRIzol | 34.1 | 65.5 1 | 105 |
| SS66 | RNA kit with BME | 32.0 | 18.6 1 | 10 |
| SS66 | RNA kit with DTT | 32.0 | 3.0 3 | 33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lienhard, J.; Vonlanthen-Specker, I.; Sidler, X.; Bachofen, C. Screening of Swiss Pig Herds for Hepatitis E Virus: A Pilot Study. Animals 2021, 11, 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113050
Lienhard J, Vonlanthen-Specker I, Sidler X, Bachofen C. Screening of Swiss Pig Herds for Hepatitis E Virus: A Pilot Study. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113050
Chicago/Turabian StyleLienhard, Julia, Isabelle Vonlanthen-Specker, Xaver Sidler, and Claudia Bachofen. 2021. "Screening of Swiss Pig Herds for Hepatitis E Virus: A Pilot Study" Animals 11, no. 11: 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113050
APA StyleLienhard, J., Vonlanthen-Specker, I., Sidler, X., & Bachofen, C. (2021). Screening of Swiss Pig Herds for Hepatitis E Virus: A Pilot Study. Animals, 11(11), 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113050






