Epidemiological and Bacteriological Investigations Using Whole-Genome Sequencing in a Recurrent Outbreak of Pullorum Disease on a Quail Farm in France
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Description
2.2. Epidemiological Investigations
2.3. Sampling Protocol
2.4. Bacteriological Analysis
2.5. Molecular Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiological Investigations and Follow-Up of Cleaning and Disinfection Effectiveness
3.2. Bacteriological Results
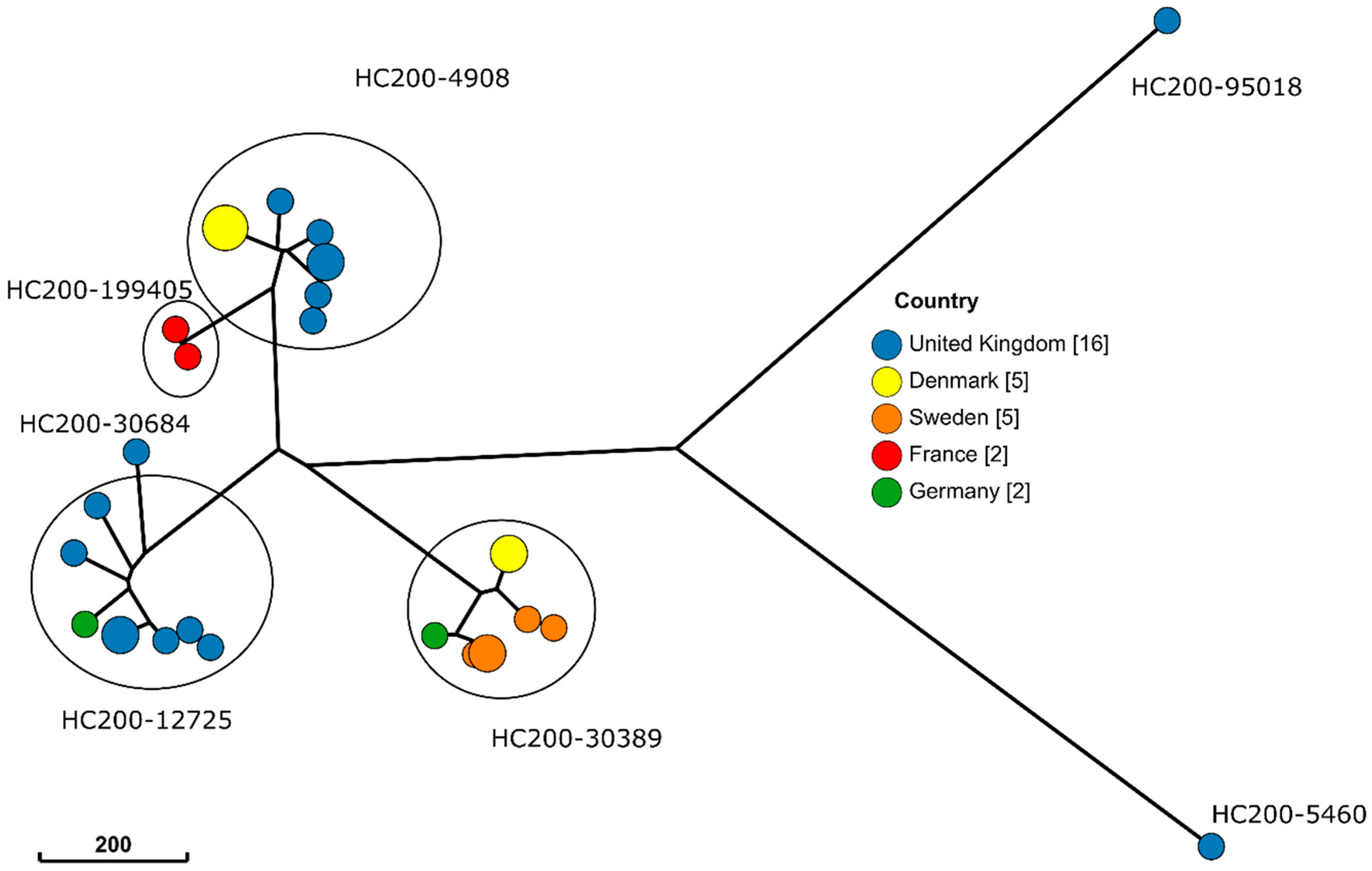
3.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OIE. Fowl_Typhoid And Pullorum Disease. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; OIE: Paris, France, 2018; Volume 8, pp. 914–930. [Google Scholar]
- Shivaprasad, H. Fowl typhoid and pullorum disease. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2000, 19, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprasad, H.L.; Barrow, P.A. Pullorum disease and fowl typhoid. In Diseases of Poultry; Swayne, D.E., Glisson, J.R., McDougald, L.R., Nolan, L.K., Suarez, D.L., Nair, V., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 678–693. [Google Scholar]
- Tadesse, S.; Ashenafi, H.; Aschalew, Z. Seroprevalence study of Newcastle disease in local chickens in central Ethiopia. Int. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2005, 3, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Teferi, M.; Nejash, A. Epidemiology and Economic Importance of Pullorum Disease in Poultry: A Review. Glob. Vet. 2016, 17, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, P.A.; Freitas, N.O.C. Pullorum disease and fowl typhoid—New thoughts on old diseases: A review. Avian Pathol 2011, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hassimiou, D.M.; Le Bouquin, S.; Vignaud, M.L.; Bonin, E.; Sadonès, H.; Michel, V.; Granier, S.; Moury, F.; Brisabois, A. Investigations épidémiologiques et microbiologiques de récents foyers de typhose et de pullorose chez les volailles en France. Bull. Épidémiol. Santé Anim. Aliment. 2012, 48, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, L.A.; Miller, D.A.; Trampel, D.W. Epidemiological investigation, cleanup, and eradication of pullorum disease in adult chickens and ducks in two small-farm flocks. Avian. Dis. 2006, 50, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, H.; Soderlund, R.; Ernholm, L.; Melin, L.; Jansson, D.S. Diagnostics, epidemiological observations and genomic subtyping in an outbreak of pullorum disease in non-commercial chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 217, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerial Decree Dated 29 March 2011, fixant les mesures techniques et administratives relatives à la lutte contre la pullorose, NOR AGRG1108929A. Available online: https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/eli/arrete/2011/3/29/AGRG1108929A/jo/texte (accessed on 30 March 2011).
- NF U47-101, Méthodes D’analyse en Santé Animale—Isolement et identification de tout sérovar ou de sérovar(s) spécifié(s) de salmonelles chez les oiseaux. Available online: https://www.boutique.afnor.org/norme/nf-u47-102/methodes-d-analyse-en-sante-animale-isolement-et-identification-de-tout-serovar-ou-de-serovars-specifies-de-salmonelles-chez-les/article/779142/fa155328 (accessed on 1 November 2007).
- Grimont, P.A.; Weill, F.X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars, 9th ed.; WHO Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Salmonella: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- NF U47-034, Méthodes D’analyse en Santé Animale—Recherche d’anticorps spécifiques de Salmonella Pullorum Gallinarum dans le sérum par agglutination rapide sur lame. Available online: https://www.boutique.afnor.org/norme/nf-u47-034/methodes-d-analyse-en-sante-animale-recherche-d-anticorps-specifiques-de-salmonella-pullorum-gallinarum-dans-le-serum-par-aggl/article/703819/fa159217 (accessed on 1 February 2009).
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Zhou, Z.; Sergeant, M.J.; Achtman, M.A. Genomic overview of the population structure of Salmonella. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Sergeant, M.J.; Luhmann, N.; Vaz, C.; Francisco, A.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Achtman, M. GrapeTree: Visualization of core genomic relationships among 100,000 bacterial pathogens. Genome Res. 2018, 9, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, M.; Mailund, T.; Pedersen, C.N.S. Rapid Neighbour-Joining. In Proceedings of the Algorithms in Bioinformatics, 8th International Workshop, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 14–19 September 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Toma, B.; Dufour, B.; Sanaa, M.; Bénet, J.-J.; Shaw, A.; Moutou, F.; Louza, A. Epidémiologie Appliquée à la Lutte Collective Contre les Maladies Animales Transmissibles Majeures; AEEMA: Maisons-Alfort, France, 2001; Volume 1, p. 697. [Google Scholar]
- Andino, A.; Hanning, I. Salmonella enterica: Survival, Colonization, and Virulence Differences among Serovars. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 520179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anses 2011 Opinion, AVIS de l’Agence Nationale de Sécurité Sanitaire de L’alimentation de L’environnement et du Travail Relatif à la Gestion Sanitaire D’un Foyer de Pullorose. Anses—Saisine n° 2011-SA-0059, 1–10. Available online: https://www.anses.fr/fr/system/files/SANT2011sa0059.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2011).
- Podolak, R.; Enache, E.; Stone, W.; Black, D.G.; Elliott, P.H. Sources and risk factors for contamination, survival, persistence, and heat resistance of Salmonella in low-moisture foods. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1919–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, C.F.; Wong, W.C.; Chai, L.C.; Robin, T.; Ponniah, J.; Hidayah, M.S.; Anyi, U.; Farinazleen, M.G.; Cheah, Y.K.; Son, R. Review Article Salmonella: A foodborne pathogen. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 465–473. [Google Scholar]
- Crippen, T.L.; Sheffield, C.L.; Beier, R.C.; Nisbet, D.J. The horizontal transfer of Salmonella between the lesser mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus) and poultry manure. Zoonoses Pub. Health 2018, 65, e23–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynants, E.; Frooninckx, L.; Van Miert, S.; Geeraerd, A.; Claes, J.; Van Campenhout, L. Risks related to the presence of Salmonella sp. during rearing of mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) for food or feed: Survival in the substrate and transmission to the larvae. Food Control 2019, 100, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbeck, D.H.; McLaughlin, B.G.; Singh, S.N. Pullorum disease with unusual signs in two backyard chicken flocks. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 895–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprasad, H.L. Pullorum disease and Fowl typhoid. In Manual of Poultry Diseases; Brugère-Picoux, J., Vaillancourt, J.P., Shivaprasad, H.L., Venne, D., Bouzouaia, M., Eds.; AFAS: Paris France, 2015; pp. 287–292. [Google Scholar]
| Location | Type of Samples | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Suspected site - on clinically suspect quail | Autopsies Bacteriology (heart, liver, caeca, etc.) Serology (60 blood samples/building) | Septicaemia Salmonella Infantis Salmonella Gallinarum 55 RSA neg, 5 RSA pos |
| Other poultry present on the farm - breeding quails | Autopsies Serology (2 × 60 blood samples taken 10 days apart) | RSA neg |
| Poultry farms in the vicinity - backyards - laying hen farm - broiler chicken farm | Serology (4 to 60 blood samples/building) | RSA neg |
| At the infected site after cleaning and disinfection operations | swabs lesser mealworm beetles | Salmonella Infantis Salmonella Infantis |
| cgMLST | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | Serotype | Year | Sector | HC0 | HC2 | HC5 | HC10 | HC20 |
| S18LNRS01-09 | Gallinarum | 2018 | Quails | 199405 | 199405 | 199405 | 199405 | 199405 |
| S19LNRS08-01 | Gallinarum | 2019 | Quails | 199407 | 199407 | 199407 | 199405 | 199405 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Bouquin, S.; Bonifait, L.; Thépault, A.; Ledein, T.; Guillon, F.; Rouxel, S.; Souillard, R.; Chemaly, M. Epidemiological and Bacteriological Investigations Using Whole-Genome Sequencing in a Recurrent Outbreak of Pullorum Disease on a Quail Farm in France. Animals 2021, 11, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010029
Le Bouquin S, Bonifait L, Thépault A, Ledein T, Guillon F, Rouxel S, Souillard R, Chemaly M. Epidemiological and Bacteriological Investigations Using Whole-Genome Sequencing in a Recurrent Outbreak of Pullorum Disease on a Quail Farm in France. Animals. 2021; 11(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Bouquin, Sophie, Laetitia Bonifait, Amandine Thépault, Thomas Ledein, François Guillon, Sandra Rouxel, Rozenn Souillard, and Marianne Chemaly. 2021. "Epidemiological and Bacteriological Investigations Using Whole-Genome Sequencing in a Recurrent Outbreak of Pullorum Disease on a Quail Farm in France" Animals 11, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010029
APA StyleLe Bouquin, S., Bonifait, L., Thépault, A., Ledein, T., Guillon, F., Rouxel, S., Souillard, R., & Chemaly, M. (2021). Epidemiological and Bacteriological Investigations Using Whole-Genome Sequencing in a Recurrent Outbreak of Pullorum Disease on a Quail Farm in France. Animals, 11(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010029




