Synergism of Dietary Co-Supplementation with Lutein and Bile Salts Improved the Growth Performance, Carotenoid Content, Antioxidant Capacity, Lipid Metabolism, and Lipase Activity of the Marbled Spinefoot Rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Culture Condition
2.2. Experimental Diets Formulation
2.3. Samples Collection
2.3.1. Fish Sampling
2.3.2. Tissues Sampling
2.4. Measured Parameters
2.4.1. Growth Index and Feed Efficiency
2.4.2. Proximate Chemical Analysis
2.4.3. Analysis of Total Carotenoids in Fish and Diets
2.4.4. Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth and Feed Efficiency
3.2. Whole-Body Proximate Composition
3.3. Carotenoid Content in Fish and Experimental Diets.
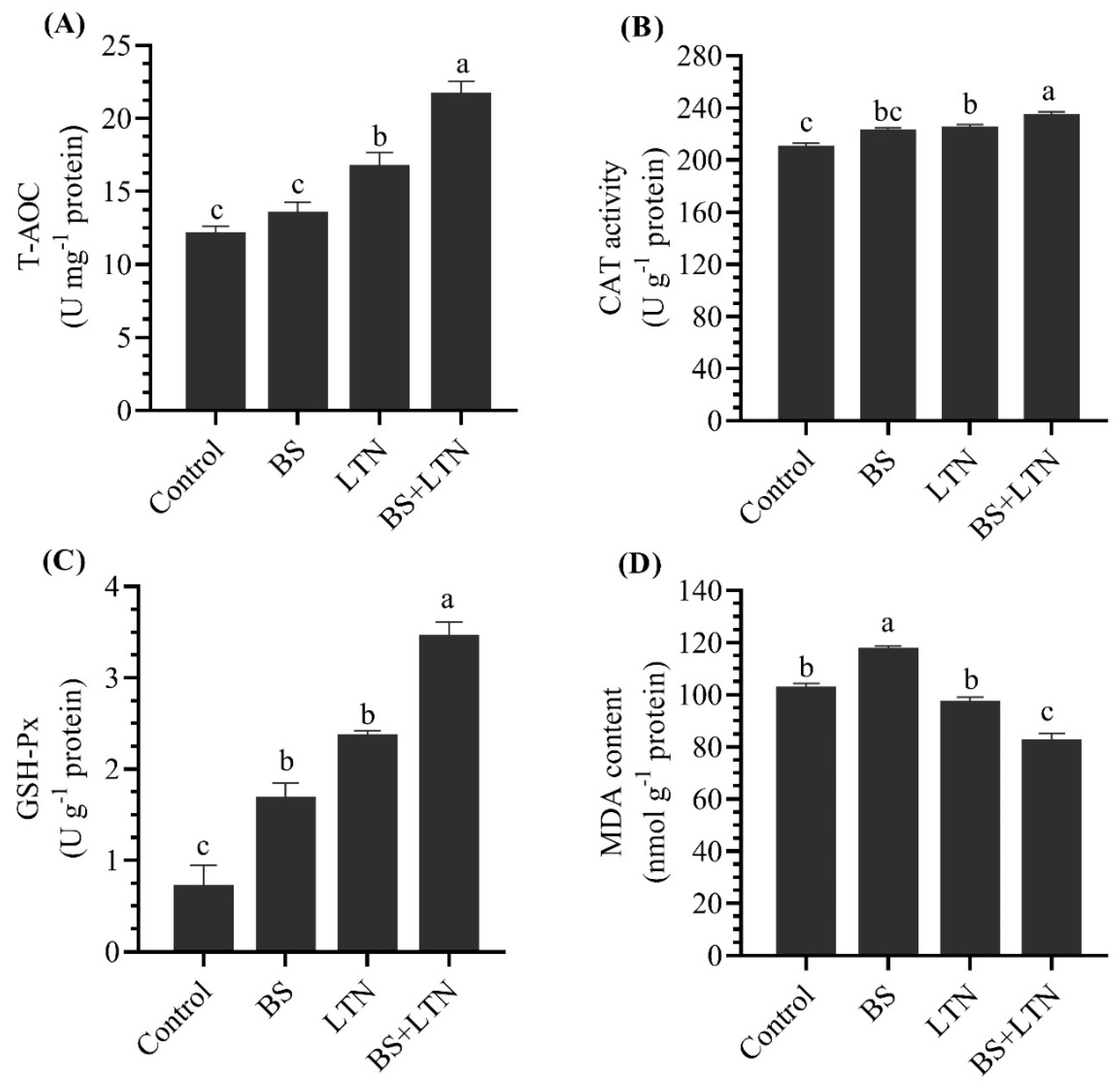
3.4. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
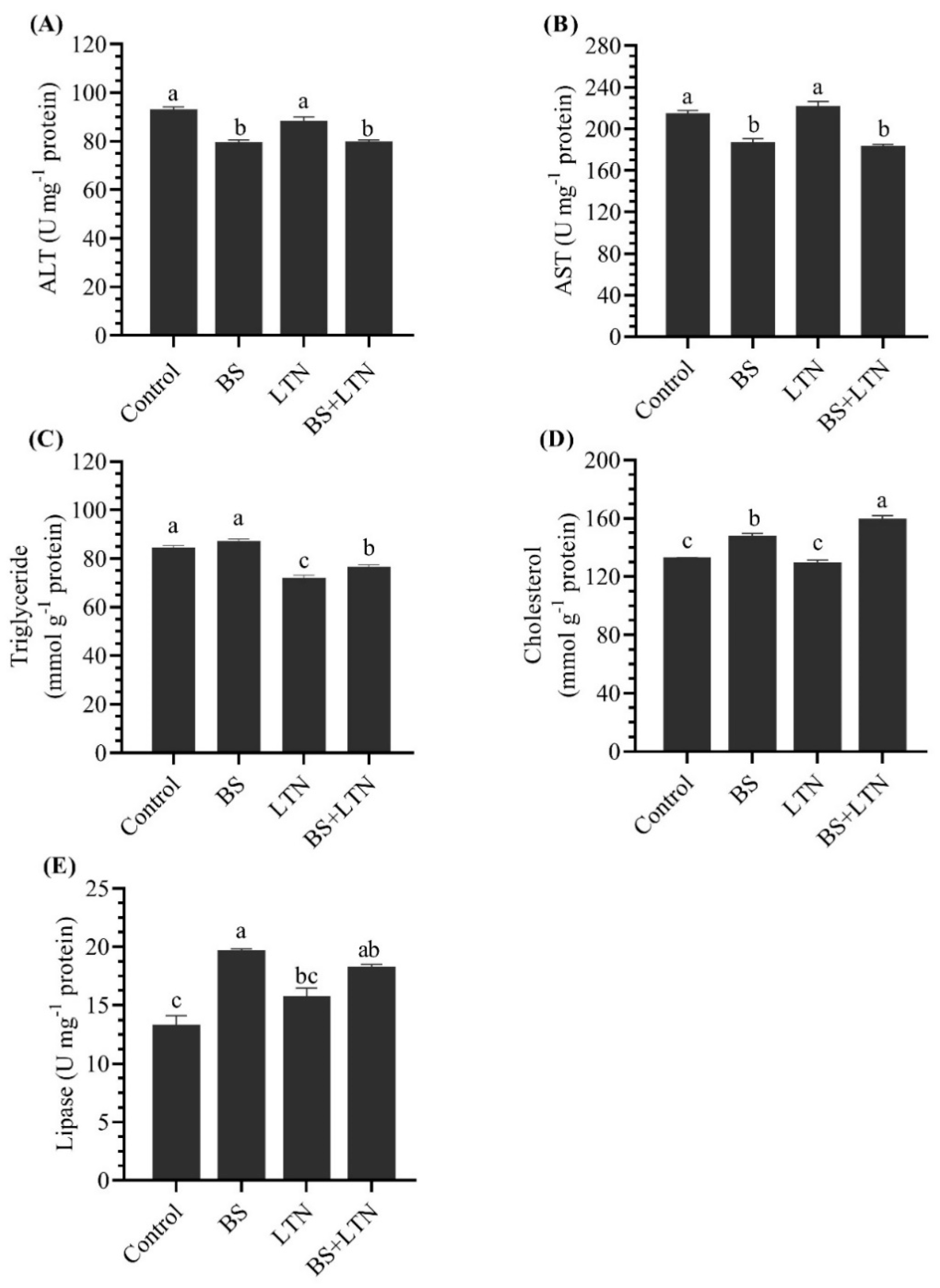
3.5. Liver Function and Lipase Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. El Estado Mundial de la Pesca y la Acuicultura, 2016. Contribucion a la Seguridad Alimentaria y la Nutricion para Todos; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016; p. 224. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Sallam, A.E.; Mansour, A.T.; Srour, T.M.; Goda, A.M.A. Effects of different carotenoid supplementation sources with or without sodium taurocholate on growth, feed utilization, carotenoid content and antioxidant status in fry of the European seabass, Dicentrarchus Labrax. Aquacult. Res. 2017, 48, 3848–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Mansour, A.; Goda, A.; El-Hammady, A.; Omar, E. Effect of Poly-Unsaturated Fatty Acids Fortification on Growth Performance, Survival, Fatty Acid Composition and Antioxidant Balance of Meagre, Argyrosomus regius Larvae. J. Aquac. Res. Development 2018, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.S.; Mansour, A.T.; Goda, A.M.A.; Omar, E.A. Effect of selenium yeast supplementation on growth performance, feed utilization, lipid profile, liver and intestine histological changes, and economic benefit in meagre, Argyrosomus regius, fingerlings. Aquaculture 2019, 501, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, E.C.; Galuch, M.B.; Silveira, R.d.; Santos, H.; Sary, C.; Magon, T.F.; Figueiredo, I.L.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Visentainer, J.V.; Santos, O.O. Fatty acid composition and carotenoids in raw and grilled tilapia GIFT fillets supplemented with lycopene, β-carotene and lutein. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Yu, W.; Liu, J. Comparison of effect of dietary supplementation with Haematococcus pluvialis powder and synthetic astaxanthin on carotenoid composition, concentration, esterification degree and astaxanthin isomers in ovaries, hepatopancreas, carapace, epithelium of adult female Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735146. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, P.S.; Li, B.; Vachali, P.P.; Gorusupudi, A.; Shyam, R.; Henriksen, B.S.; Nolan, J.M. Lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin: The basic and clinical science underlying carotenoid-based nutritional interventions against ocular disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 50, 34–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansour, A.; Omar, E.; Srour, T.; Yousef, M. Effect of three natural phytochemicals supplementation on growth performance, testosterone level and feed utilization of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquacult. Nutr. 2018, 24, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.T.; Miao, L.; Espinosa, C.; García-Beltrán, J.M.; Francisco, D.C.C.; Esteban, M.Á. Effects of dietary inclusion of Moringa oleifera leaves on growth and some systemic and mucosal immune parameters of seabream. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 1223–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.T.; Espinosa, C.; García-Beltrán, J.M.; Miao, L.; Francisco, D.C.C.; Alsaqufi, A.S.; Esteban, M.Á. Dietary supplementation of drumstick tree, Moringa oleifera, improves mucosal immune response in skin and gills of seabream, Sparus aurata, and attenuates the effect of hydrogen peroxide exposure. Fish. Physiol. Bioch. 2020, 46, 981–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmann, G. Carotenoids of biotechnological importance. In Biotechnology of Isoprenoids; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, M.O.; Contreras, L.M.; Lo, M.H.; Díaz, J.M.; Herrera, G.C. Lutein as a functional food ingredient: Stability and bioavailability. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, A.A.E.-S.; Sallam, A.E.; Srour, T.M. Evaluation of natural and synthetic carotenoid supplementation on growth, survival, total carotenoids content, fatty acids profile and stress resistance of European Seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax, Fry. Aquacult. Stud. 2018, 18, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- McWilliams, A. The Global Market for Carotenoids; BCC Research: Wellesley, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Molino, A.; Mehariya, S.; Karatza, D.; Chianese, S.; Iovine, A.; Casella, P.; Marino, T.; Musmarra, D. Bench-scale cultivation of microalgae Scenedesmus almeriensis for CO2 capture and lutein production. Energies 2019, 12, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, A.T.; da Costa, D.C.; Vieira, A.A.H.; Antoniosi Filho, N.R. Analysis of major carotenoids and fatty acid composition of freshwater microalgae. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alves-Rodrigues, A.; Shao, A. The science behind lutein. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 150, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Tsao, R.; Zhang, S.; Dong, Z.; Yang, R.; Gong, J.; Pei, Y. Antioxidant activity, mutagenicity/anti-mutagenicity, and clastogenicity/anti-clastogenicity of lutein from marigold flowers. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajizadeh-Sharafabad, F.; Ghoreishi, Z.; Maleki, V.; Tarighat-Esfanjani, A. Mechanistic insights into the effect of lutein on atherosclerosis, vascular dysfunction, and related risk factors: A systematic review of in vivo, ex vivo and in vitro studies. Pharmacol. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, R.W.; Leanderson, P.; Lundberg, A.K.; Jonasson, L. Lutein exerts anti-inflammatory effects in patients with coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2017, 262, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, H.; Deng, H.; Zhang, B. Differential expression of CuZnSOD gene under low temperature stress in noble scallop Chlamys nobilis with different carotenoid content. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejas, J.R.; Almansa, E.; Tejera, N.; Jerez, S.; Bolaños, A.; Lorenzo, A. Effect of dietary supplementation with shrimp on skin pigmentation and lipid composition of red porgy (Pagrus pagrus) alevins. Aquaculture 2003, 218, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besen, K.P.; Melim, E.W.H.; da Cunha, L.; Favaretto, E.D.; Moreira, M.; Fabregat, T.E.H.P. Lutein as a natural carotenoid source: Effect on growth, survival and skin pigmentation of goldfish juveniles (Carassius auratus). Aquacult. Res. 2019, 50, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Fan, S.; Yu, D. High carotenoids content can enhance resistance of selected Pinctada fucata families to high temperature stress. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 61, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meilisza, N.; Jusadi, D.; Zairin, M., Jr.; Artika, I.M.; Priyo Utomo, N.B.; Kadarini, T.; Suprayudi, M.A. Digestibility, growth and pigmentation of astaxanthin, canthaxanthin or lutein diets in Lake Kurumoi rainbowfish, Melanotaenia parva (Allen) cultured species. Aquacult. Res. 2017, 48, 5517–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.R.; Want, E.J.; Geier, F.M.; Spagou, K.; Wilson, I.D.; Sidaway, J.E.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E. Systemic gut microbial modulation of bile acid metabolism in host tissue compartments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4523–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.S.; Teshima, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Koshio, S. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on growth and digestive enzyme activities of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck & Schlegel). Aquacult. Res. 2001, 32, 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, J.; Ribeiro, L.; Aragão, C. Bile salts regulate ion transport in the intestine of Senegalese sole. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y. Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Pan, T.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, T.T.; Sun, P.; Zhou, F.; Ding, X.; Zhou, Q. Effects of supplemental dietary L-carnitine and bile acids on growth performance, antioxidant and immune ability, histopathological changes and inflammatory response in juvenile black seabream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) fed high-fat diet. Aquaculture 2019, 504, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, H.; Ji, H.; Shi, X.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Du, Z.; Yu, H. Effect of dietary bile acids on growth, body composition, lipid metabolism and microbiota in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquacult. Nutr. 2018, 24, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wen, H.; Gou, G.; Liu, T.; Lu, X.; Deng, D. Preliminary study to evaluate the effects of dietary bile acids on growth performance and lipid metabolism of juvenile genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed plant ingredient-based diets. Aquacult. Nutr. 2018, 24, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashita, K.; Rønnestad, I.; Furuita, H.; Matsunari, H.; Oku, H.; Yamamoto, T. Effects of dietary soybean meal on the bile physiology in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoud, I.P.; Kreydiyyeh, S.; Chalfoun, A.; Fakih, M. Influence of salinity on survival, growth, plasma osmolality and gill Na+–K+–ATPase activity in the rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 348, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, T.V.R.; Kutty, M.N. Aquaculture: Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Monzer, S.; Nasser, N.; Babikian, J.; Saoud, I.P. Substitution of fish meal by soybean meal in diets for juvenile marbled spinefoot, Siganus rivulatus. J. Appl. Aquac. 2017, 29(2), 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Roumieh, R.; Abdel Meguid, N.; Ghanawi, J.; Patrick Saoud, I. Feed regimen affects growth, condition index, proximate analysis and myocyte ultrastructure of juvenile spinefoot rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. Aquacult. Nutr. 2011, 17, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T. Siganids: Their biology and mariculture potential. Aquaculture 1974, 3, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.E.; Mansour, A.T.; Alsaqufi, A.S.; Salem, M.E.-S.; El-Feky, M.M. Growth performance, anti-oxidative status, innate immunity, and ammonia stress resistance of Siganus rivulatus fed diet supplemented with zinc and zinc nanoparticles. Aquacult. Rep. 2020, 18, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoud, I.P.; Ghanawi, J.; Lebbos, N. Effects of stocking density on the survival, growth, size variation and condition index of juvenile rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. Aquacult. Int. 2008, 16, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanou, D.; Georgiou, G. Recent experiences on the culture of rabbitfish Siganus rivulatus in Cyprus. Cah. Options Mediterr. 2000, 47, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Parazo, M.M. An artificial diet for larval rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus Bloch. In Fish Nutrition Research in Asia. Proceedings of the Fourth Asian Fish Nutrition Workshop; De Silva, S.S., Ed.; Asian Fisheries Society: Manila, Philippines, 1991; Volume 5, pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Saoud, I.P.; Mohanna, C.; Ghanawi, J. Effects of temperature on survival and growth of juvenile spinefoot rabbitfish (Siganus rivulatus). Aquacult. Res. 2008, 39, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanawi, J.; Roy, L.; Davis, D.A.; Saoud, I.P. Effects of dietary lipid levels on growth performance of marbled spinefoot rabbitfish Siganus rivulatus. Aquaculture 2011, 310, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dakar, A.; Shalaby, S.; Saoud, I. Assessing the use of a dietary probiotic/prebiotic as an enhancer of spinefoot rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus, survival and growth. Aquacult. Nutr. 2007, 13, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Daoud, Y.; Ghanawi, J.; Farran, M.; Davis, D.; Saoud, I. Effect of dietary protein level on growth performance and blood parameters of marbled spinefoot, Siganus rivulatus. J. Appl. Aquac. 2014, 26, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Fish and Shrimp; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, TX, USA; Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, J.A. A simple dual assay for vitamin A and carotenoids in human liver. Nutr. Rep. Int. 1979, 19, 807–813. [Google Scholar]
- Draper, H.; Squires, E.; Mahmoodi, H.; Wu, J.; Agarwal, S.; Hadley, M. A comparative evaluation of thiobarbituric acid methods for the determination of malondialdehyde in biological materials. Free Radical Biol. Med. 1993, 15, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Verdon, C.P.; Wu, A.; Wang, H.; Prior, R.L. Automated assay of oxygen radical absorbance capacity with the COBAS FARA II. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 1738–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Cantor, A.H.; Scott, M.L. Mode of action of selenium and vitamin E in prevention of exudative diathesis in chicks. J. Nutr. 1973, 103, 1502–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.K. Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal. Biochem. 1972, 47, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, P.; Prencipe, L. Serum triglycerides determined colorimetrically with an enzyme that produces hydrogen peroxide. Clin. Chem. 1982, 28, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allain, C.; Poon, L.; Chan, C.; Richmond, W.; Fu, P. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin. Chim. Acta 1974, 20, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, B.W.; Khalil, H.S.; Mansour, A.T.; Srour, T.M.; Omar, E.A.; Nour, A.A.M. Impact of substitution of fish meal by high protein distillers dried grains on growth performance, plasma protein and economic benefit of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, A.G.; Fernandez, M.L. Potential of dietary non-provitamin A carotenoids in the prevention and treatment of diabetic microvascular complications. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Brown, J.A. Carotenoid pigments in seafoods and aquaculture. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 38, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuangsoi, B.; Jintasathaporn, O. Carotenoids digestibility of free astaxanthin and lutein by fancy carp (Cyprinus carprio). Kasetsart J. Nat. Sci. 2011, 45, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.G.; McEvoy, J.; Tocher, D.R.; Sargent, J.R. Depletion of α-tocopherol and astaxanthin in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) affects autoxidative defense and fatty acid metabolism. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amar, E.; Kiron, V.; Satoh, S.; Watanabe, T. Influence of various dietary synthetic carotenoids on bio-defence mechanisms in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Aquacult. Res. 2001, 32, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, E.C.; Kiron, V.; Satoh, S.; Watanabe, T. Enhancement of innate immunity in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) associated with dietary intake of carotenoids from natural products. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 16, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, T.L.M.; Paiva, N.M.; Oliveira, D.L.; Taniwaki, F.; Cavazzana, J.F.; da Costa Camargo, G.C.R.; Diniz, J.C.P.; Bermejo-Poza, R.; Borghesi, R.; Villarroel, M. Growth performance and flesh quality of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed low concentrations of Rubrivivax gelatinosus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Spirulina platensis. Aquacul. Int. 2020, 28, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.E.S.; Abdel-Ghany, H.M.; Sallam, A.E.; El-Feky, M.M.; Almisherfi, H.M. Effects of dietary orange peel on growth performance, antioxidant activity, intestinal microbiota and liver histology of Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) larvae. Aquacult. Nutr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilannejad, N.; de las Heras, V.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Moyano, F.J.; Yúfera, M.; Martínez-Rodríguez, G. Ontogeny of Expression and Activity of Digestive Enzymes and Establishment of gh/igf1 Axis in the Omnivorous Fish Chelon labrosus. Animals 2020, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarça, L.G.; Murakami, F.Y.; Félix, A.P.; Krabbe, E.L.; Oliveira, S.G.d.; Silva, S.A.B.d. Dietary lutein supplementation on diet digestibility and blood parameters of dogs. Ciência Rural 2016, 46, 2195–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, X.-R.; Feng, L.; Jiang, W.-D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Kuang, S.-Y.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.-Q. Supplementation exogenous bile acid improved growth and intestinal immune function associated with NF-κB and TOR signalling pathways in on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Enhancement the effect of protein-sparing by dietary lipid. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Goto, T.; Tanaka, N.; Furuita, H.; Sugita, T.; Suzuki, N. Supplemental effects of essential amino acids and bile salts to a high-fat diet containing soybean meal, corn gluten meal and squid meal for rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquacult. Sci. 2007, 55, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.-X.; Jiao, J.-H.; Li, Z.-Y.; Liu, R.-R.; Shi, Q.; Ma, L. Lutein supplementation reduces plasma lipid peroxidation and C-reactive protein in healthy nonsmokers. Atherosclerosis 2013, 227, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, C.; Zhu, J.; Gao, K.; Fang, J.; Li, H. Lutein suppresses oxidative stress and inflammation by Nrf2 activation in an osteoporosis rat model. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.F.; Hagey, L.R.; Krasowski, M.D. Bile salts of vertebrates: Structural variation and possible evolutionary significance. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, W.; Wen, X.; Meng, Q.; Liu, L.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Everaert, N. Running Head: Heat Affects Cholesterol and Bile Acid Alterations in Cholesterol and Bile Acids Metabolism in Large White Pigs during Short-Term Heat Exposure. Animals 2020, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grosell, M.; Farrell, A.P.; Brauner, C.J. Fish. Physiology: The Multifunctional Gut of Fish; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, E.; Dias, J.; Silva, P.; Valente, L.; Empis, J.; Gouveia, L.; Bowen, J.; Young, A. Utilization of natural and synthetic sources of carotenoids in the skin pigmentation of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2002, 214, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Effects of dietary lutein/canthaxanthin ratio on the growth and pigmentation of large yellow croaker Larimichthys croceus. Aquacult. Nutr. 2016, 22, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, B.-S.; Kweon, M.-J.; Park, M.-Y.; Baek, S.-H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Baek, I.-O.; Kang, S.-J. Comparison of dietary carotenoids metabolism and effects to improve the body color of cultured fresh-water fishes and marine fishes. Korean J. Food Nutr. 1997, 26, 270–284. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.H.; Robinson, E.H.; Oberle, D.F.; Lucas, P.M.; Peterson, B.C.; Bates, T.D. Clearance of yellow pigments lutein and zeathanxin in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, reared at different water temperatures. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2011, 42, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, A.G.; Aguilar, D.; Norris, G.H.; DiMarco, D.M.; Missimer, A.; Hu, S.; Smyth, J.A.; Gannon, S.; Blesso, C.N.; Luo, Y. Compared with powdered lutein, a lutein nanoemulsion increases plasma and liver lutein, protects against hepatic steatosis, and affects lipoprotein metabolism in guinea pigs. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.; Kiessling, A.; Milley, J.; Ross, N.; Lall, S. Effect of lipid source and bile salts in diet of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., on astaxanthin blood levels. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatani, A.J.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Abuohashish, H.M.; Al-Assaf, A.; Parmar, M.Y.; Ahmed, M.M. Lutein dietary supplementation attenuates streptozotocin-induced testicular damage and oxidative stress in diabetic rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R. Lutein supplementation alters inflammatory cytokine production and antioxidant status in F-line turkeys. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Qin, T.; Liu, Z.; Caceres, M.A.; Ronchi, C.F.; Chen, C.O.; Yeum, K.-j.; Taylor, A.; Blumberg, J.B.; Liu, Y. Lutein and zeaxanthin supplementation reduces H2O2-induced oxidative damage in human lens epithelial cells. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 3180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ahmed, F.; Bernstein, P.S. Studies on the singlet oxygen scavenging mechanism of human macular pigment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 504, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krinsky, N.I.; Yeum, K.-J. Carotenoid–radical interactions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 305, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subczynski, W.K.; Wisniewska, A.; Widomska, J. Location of macular xanthophylls in the most vulnerable regions of photoreceptor outer-segment membranes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 504, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wisniewska, A.; Subczynski, W.K. Distribution of macular xanthophylls between domains in a model of photoreceptor outer segment membranes. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Cao, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Effect of high dose of bile acids supplementation in broiler feed on growth performance, clinical blood metabolites, and organ development. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2018, 27, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, F.A.; Roushdy, E.M.; Kishawy, A.T.; Zaglool, A.W.; Tukur, H.A.; Saadeldin, I.M. Growth performance, antioxidant capacity, lipid-related transcript expression and the economics of broiler chickens fed different levels of rutin. Animals 2019, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, M.; Bai, N.; Kortner, T.M. Taurocholate supplementation attenuates the changes in growth performance, feed utilization, lipid digestion, liver abnormality and sterol metabolism in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) fed high level of plant protein. Aquaculture 2017, 468, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Ingredients | Diets (g kg−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | BS | LTN | BS+LTN | |
| Soybean seed meal, 48% | 362.00 | 362.00 | 362.00 | 362.00 |
| Fishmeal anchovy, 65% | 70.00 | 70.00 | 70.00 | 70.00 |
| Sunflower seed meal | 70.00 | 70.00 | 70.00 | 70.00 |
| Soya protein concentrate | 87.00 | 87.00 | 87.00 | 87.00 |
| Whole wheat flour | 190.00 | 190.00 | 190.00 | 190.00 |
| Corn starch | 107.00 | 106.85 | 106.90 | 106.75 |
| Sunflower oil | 80.00 | 80.00 | 80.00 | 80.00 |
| Binder (Carboxy methyl cellulose) | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Vitamin premix a | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Mineral premix b | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Monocalcium phosphate | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 |
| Attractant (1 glycine and 2 betaine) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Bile salt (BS) c | - | 0.15 | - | 0.15 |
| Lutein (LTN) d | - | - | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Proximate analysis (g kg−1) | ||||
| Dry matter (DM) | 875.10 | 874.30 | 866.30 | 879.00 |
| Crude protein (CP) | 343.70 | 349.00 | 334.80 | 345.80 |
| Ether extract (EE) | 98.10 | 96.20 | 99.60 | 93.10 |
| Ash | 58.50 | 58.10 | 61.20 | 55.80 |
| Nitrogen free extract (NFE) e | 499.70 | 496.70 | 504.40 | 505.30 |
| Gross energy (GE; kJ g−1) f | 20.57 | 20.57 | 20.50 | 20.52 |
| Diets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | BS | LTN | BS+LTN | |
| Final body weight (g fish−1) | 1.97 ± 0.02 b | 2.06 ± 0.07 b | 2.01 ± 0.01 b | 2.35 ± 0.03 a |
| Weight gain (g fish−1) | 1.79 ± 0.01 b | 1.88 ± 0.07 b | 1.83 ± 0.01 b | 2.18 ± 0.02 a |
| Specific growth rate (% day−1) | 3.94 ± 0.05 b | 4.01 ± 0.08 b | 4.02 ± 0.03 b | 4.37 ± 0.04 a |
| Final body length (cm fish−1) | 5.43 ± 0.03 | 5.47 ± 0.03 | 5.53 ± 0.07 | 5.83 ± 0.03 |
| Body length growth rate (% day−1) | 1.29 ± 0.04 | 1.32 ± 0.03 | 1.40 ± 0.06 | 1.40 ± 0.02 |
| Feed efficiency (%) | 35.76 ± 1.13 b | 38.60 ± 2.60 b | 37.08 ± 0.86 b | 46.55 ± 1.46 a |
| Feeding rate (% BW day−1) | 7.74 ± 0.23 ab | 7.27 ± 0.46 ab | 7.51 ± 0.16 a | 6.20 ± 0.22 b |
| Condition factor | 1.26 ± 0.02 | 1.23 ± 0.01 | 1.19 ± 0.04 | 1.19 ± 0.01 |
| Survival (%) | 86.67 ± 3.85 b | 91.11 ± 2.22 ab | 93.33 ± 3.85 ab | 97.78 ± 2.22 a |
| Nutrient Component | Diets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | BS | LTN | BS+LTN | |
| Moisture (%) | 75.89 ± 0.48 a | 75.59 ± 0.28 ab | 75.64 ± 0.06 ab | 74.71 ± 0.28 b |
| Crude protein (%) | 14.61 ± 0.26 ab | 14.48 ± 0.06 b | 15.34 ± 0.04 ab | 15.63 ± 0.28 a |
| Crude lipid (%) | 4.97 ± 0.06 ab | 5.55 ± 0.0 ab | 4.81 ± 0.22 b | 5.59 ± 0.13 a |
| Ash (%) | 3.93 ± 0.41 | 4.43 ± 0.41 | 4.22 ± 0.28 | 3.97 ± 0.14 |
| Carotenoids Content (µg g−1) | Diets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | BS | LTN | BS+LTN | |
| Feed | 13.88 ± 1.38 b | 14.51 ± 1.62 b | 107.55 ± 3.91 a | 110.75 ± 2.55 a |
| Fish | ||||
| Skin | 5.42 ± 0.22 b | 7.14 ± 0.70 b | 52.64 ± 3.72 a | 57.62 ± 2.70 a |
| Muscle | 0.20 ± 0.07 c | 0.54 ± 0.16 c | 8.01 ± 0.81 b | 13.43 ± 1.67 a |
| Whole body | 1.45 ± 0.05 c | 1.57 ± 0.20 c | 20.19 ± 2.47 b | 22.33 ± 3.79 a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansour, A.T.; El-feky, M.M.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Sallam, A.E. Synergism of Dietary Co-Supplementation with Lutein and Bile Salts Improved the Growth Performance, Carotenoid Content, Antioxidant Capacity, Lipid Metabolism, and Lipase Activity of the Marbled Spinefoot Rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. Animals 2020, 10, 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091643
Mansour AT, El-feky MMM, El-Beltagi HS, Sallam AE. Synergism of Dietary Co-Supplementation with Lutein and Bile Salts Improved the Growth Performance, Carotenoid Content, Antioxidant Capacity, Lipid Metabolism, and Lipase Activity of the Marbled Spinefoot Rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. Animals. 2020; 10(9):1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091643
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansour, Abdallah Tageldein, Mohamed M. M. El-feky, Hossam S. El-Beltagi, and Ahmed Elsayed Sallam. 2020. "Synergism of Dietary Co-Supplementation with Lutein and Bile Salts Improved the Growth Performance, Carotenoid Content, Antioxidant Capacity, Lipid Metabolism, and Lipase Activity of the Marbled Spinefoot Rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus" Animals 10, no. 9: 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091643
APA StyleMansour, A. T., El-feky, M. M. M., El-Beltagi, H. S., & Sallam, A. E. (2020). Synergism of Dietary Co-Supplementation with Lutein and Bile Salts Improved the Growth Performance, Carotenoid Content, Antioxidant Capacity, Lipid Metabolism, and Lipase Activity of the Marbled Spinefoot Rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. Animals, 10(9), 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091643








