Comparative Effects of Using New Multi-Strain Synbiotics on Chicken Growth Performance, Hematology, Serum Biochemistry and Immunity
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Birds, Diets and Experimental Design
2.2. Determination of Chicken Production Parameters
2.3. Determination of Blood Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Dietary Treatment on Production Parameters
3.2. The Effect of Dietary Treatment on Chicken Biochemical Parameters
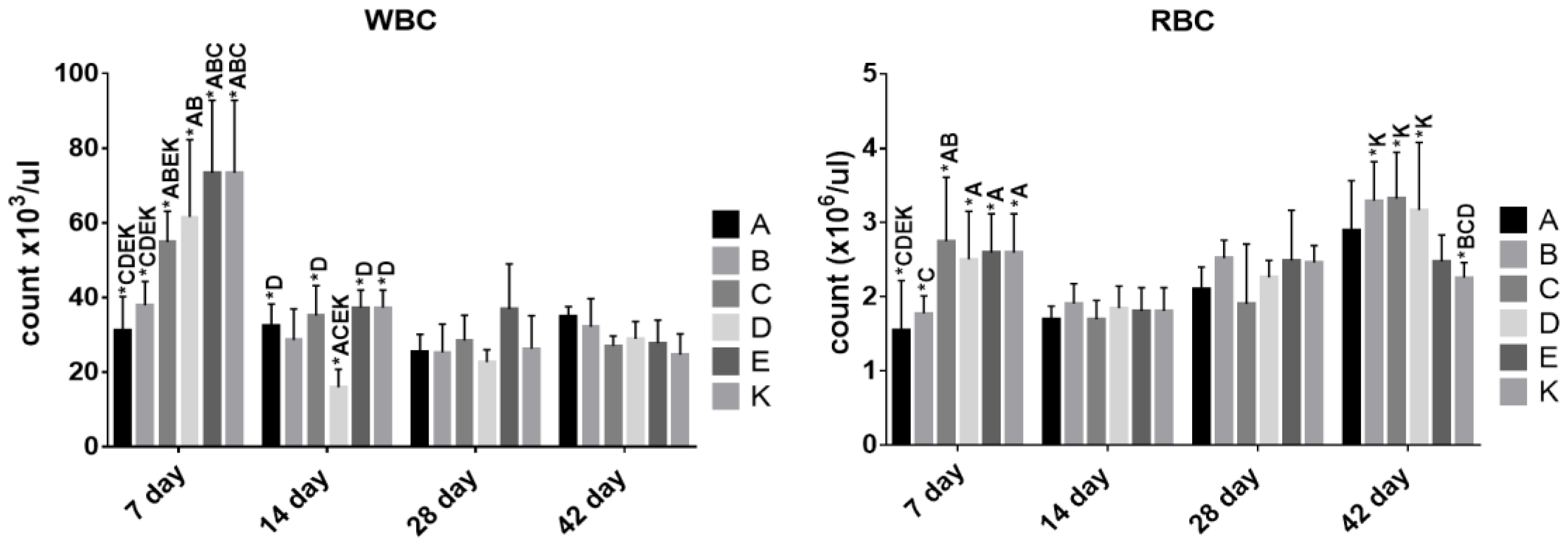
3.3. The Effect of Dietary Treatment on Chicken Hematology
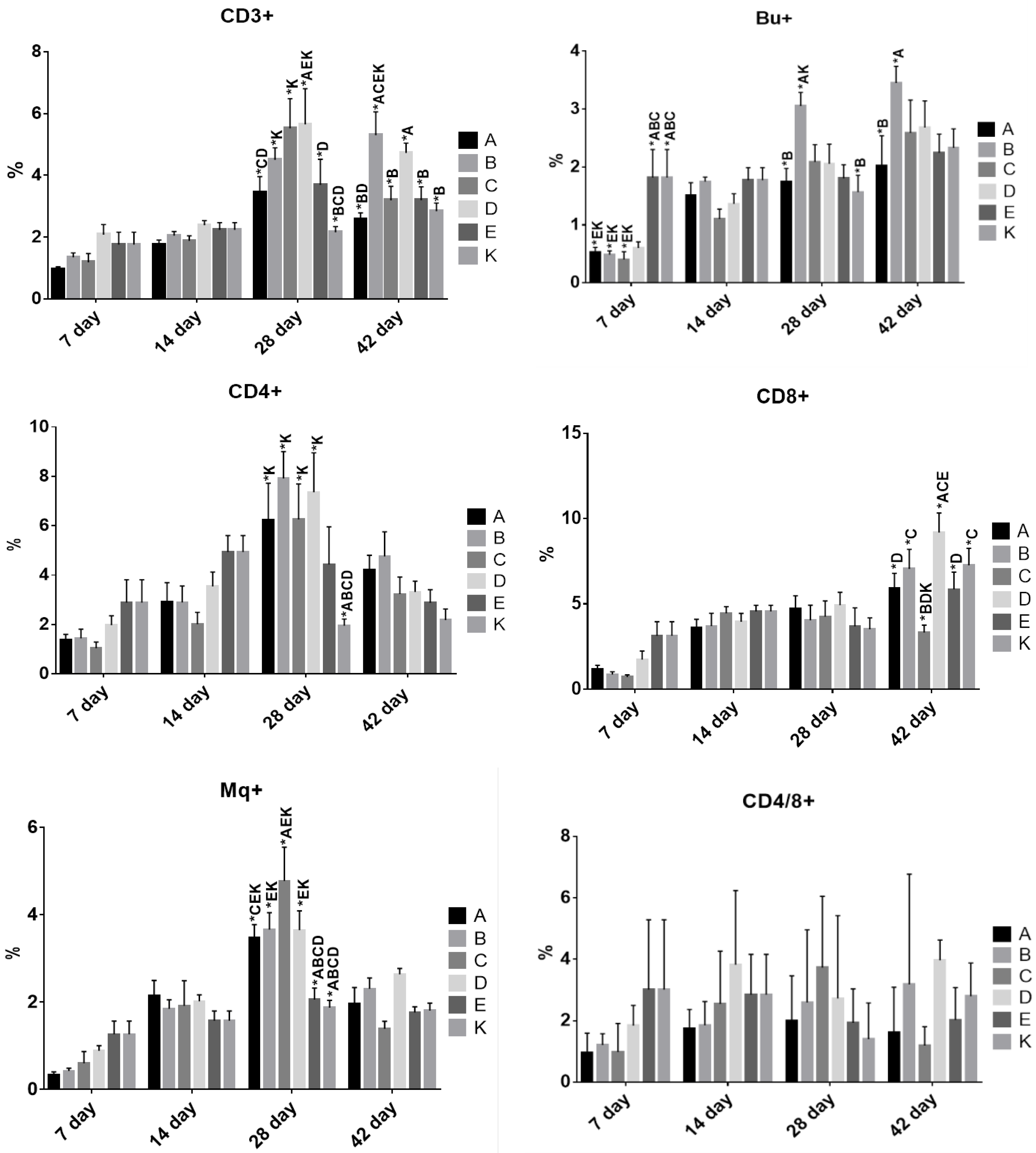
3.4. The Effect of Dietary Treatment on Chicken Lymphocyte and Monocyte Populations
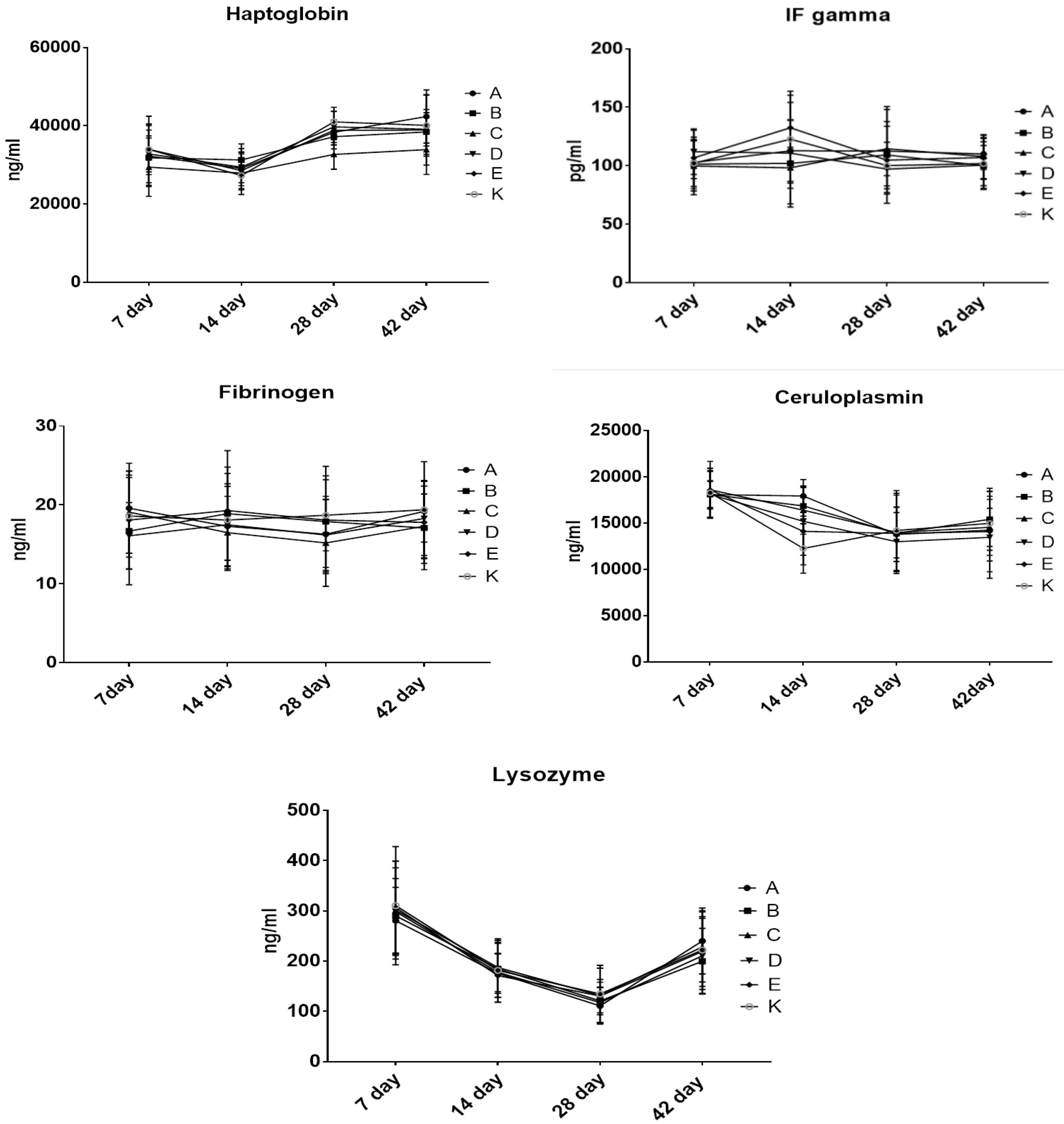
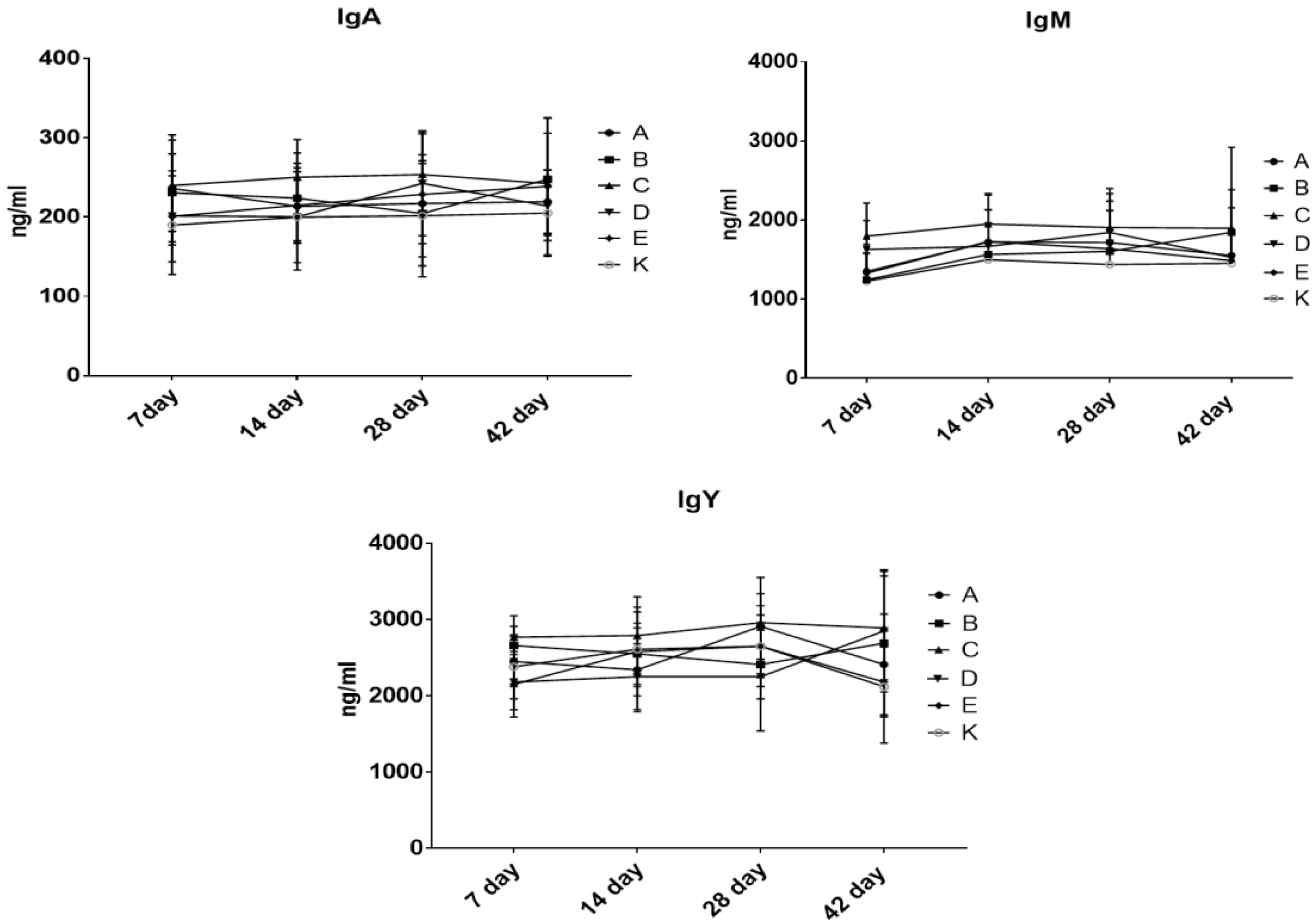
3.5. The Effect of Dietary Treatment on Chicken Acute Phase Proteins and Immunoglobulins
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Performance of Broilers
4.2. Serum Biochemistry and Immunity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdel-Hafeez, H.M.; Saleh, E.S.E.; Tawfeek, S.S.; Youssef, I.M.I.; Abdel-Daim, A.S.A. Effects of probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic with and without feed restriction on performance, hematological indices and carcass characteristics of broiler chickens. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, B.; Hernandez-Patlan, D.; Solis-Cruz, B.; Kwon, Y.M.; Arreguin, M.A.; Latorre, J.D.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Hargis, B.M.; Tellez-Isaias, G. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial and Anti-inflammatory Properties of Bacillus-DFM (Norum™) in Broiler Chickens Infected With Salmonella Enteritidis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ateya, A.I.; Arafat, N.; Saleh, R.M.; Ghanem, H.M.; Naguib, D.; Radwan, H.A.; Elseady, Y.Y. Intestinal gene expressions in broiler chickens infected with Escherichia coli and dietary supplemented with probiotic, acidifier and synbiotic. Vet. Res. Commun. 2019, 43, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dec, M.; Nowaczek, A.; Urban-Chmiel, R.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Wernicki, A. Probiotic potential of Lactobacillus isolates of chicken origin with anti-Campylobacter activity. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, H.; Tahoun, A.; Rizk, A.M.; Suzuki, T.; Elmonir, W.; Nassef, E.; Shukry, M.; Germoush, M.O.; Farrag, F.; Bin-Jumah, M.; et al. Evaluation of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus Probiotics as Alternative Therapy for Salmonella typhimurium Infection in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2020, 10, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Vahjen, W.; Dadi, T.; Saliu, E.M.; Goodarzi, Boroojeni, F.; Zentek, J. Synergistic Effects of Probiotics and Phytobiotics on the Intestinal Microbiota in Young Broiler Chicken. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedek, B.; Kirchgessner, M. The nutritive effect of Bacillus cereus as a probiotic in the raising of piglets. Effect and microbial count, composition and resistance determination of gastrointestinal and fecal microflora. Arch. Tier. 1993, 44, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloui, M.; Szczurek, W.; Świstkiewicz, S. The usefulness of prebiotics and probiotics in modern poultry nutrition: A review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2013, 13, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhama, K.; Tiwari, R.; Khan, R.U.; Chakraborty, S.; Gopi, M.; Karthik, K.; Saminathan, M. Growth promoters and novel feed additives improving poultry production and health, bioactive principles and beneficial applications: The trends and advances—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 10, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadde, U.; Kim, W.H.; Oh, S.T.; Lillehoj, H.S. Alternatives to antibiotics for maximizing growth performance and feed efficiency in poultry: A review. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 18, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, D.M.; Stillwell, R.H. Probiotics: Growth-promoting factors produced by microorganisms. Science 1965, 12, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food. In Proceedings of the Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Working Group on Drafting Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food, London, ON, Canada, 30 April–1 May 2002; Available online: https://www.who.int/foodsafety/fs_management/en/probiotic_guidelines.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Vineetha, P.G.; Tomar, S.; Saxena, V.K.; Kapgate, M.; Suvarna, A.; Adil, K. Effect of laboratory-isolated Lactobacillus plantarum LGFCP4 from gastrointestinal tract of guinea fowl on growth performance, carcass traits, intestinal histomorphometry and gastrointestinal microflora population in broiler chicken. J. Anim. Phys. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, J.; Burkholder, K.M. Application of prebiotics and probiotics in poultry production. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookiah, S.; Sieo, C.C.; Ramasamy, K.; Abdullah, N.; Ho, Y.W. Effects of dietary prebiotics, probiotic and synbiotics on performance, caecal bacterial populations and caecal fermentation concentrations of broiler chickens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, H.; Moghaddam, A.Z.; Khosravi, M.; Mayahi, M. Effects of synbiotic on the intestinal morphology and humoral immune response in broiler chickens. Livest. Sci. 2013, 153, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, A.; Amirzadeh, B.; Mokhtari, B.; Gahri, H. Effects of a multi-strain probiotic (PrimaLac) on performance and antibody responses to Newcastle disease virus and infectious bursal disease virus vaccination in broiler chickens. Avian Path. 2008, 37, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, A.; Amani, A.; Pourmahmod, M.; Saghaei, P.; Rezaie, R. Synbiotic enhances immune responses against infectious bronchitis, infectious bursal disease, Newcastle disease and avian influenza in broiler chickens. Vet. Res. Forum 2015, 6, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Saiyed, M.A.; Joshi, R.S.; Savaliya, F.P.; Patel, A.B.; Mishra, R.K.; Bhagora, N.J. Study on inclusion of probiotic, prebiotic and its combination in broiler diet and their effect on carcass characteristics and economics of commercial broilers. Vet. World 2015, 8, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, N.R.; Babu, L.K.; Kumar, A.; Pradhan, C.R.; Pati, P.K.; Mishra, J.P. Effect of dietary supplementation of prebiotic, probiotic, and synbiotic on growth performance and carcass characteristics of broiler chickens. Vet. World 2016, 9, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didari, T.; Solki, S.; Mozaffari, S.; Nikfar, S.; Abdollahi, M. A systematic review of the safety of probiotics. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2014, 13, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, S.; Newberry, S.; Ruelaz, A.; Wang, Z.; Miles, J.N.V.; Suttorp, J.M.; Johnsen, B.; Shanman, R.; Slusser, W.; Fu, N.; et al. Safety of Probiotics to Reduce Risk and Prevent or Treat Disease. Evid. Rep. Technol. Assess. 2011, 200, 1–645. [Google Scholar]
- Śliżewska, K.; Markowiak-Kopeć, P.; Żbikowski, A.; Szeleszczuk, P. The effect of synbiotic preparations on the intestinal microbiota and her metabolism in broiler chickens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śliżewska, K.; Motyl, I.; Libudzisz, Z.; Otlewska, A.; Burchardt, H.; Klecha, J.; Henzler, J. Lactobacillus Plantarum Lactic Bacteria Strain. Patent Application no. 401554; Patent type C12N 1/20, C12R 1/25; Patent no. PL221959, 2012. Available online: https://ewyszukiwarka.pue.uprp.gov.pl/search/pwp-details/P.401554 (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Lactic Bacterial Strain of Lactobacillus Pentosus. Patent Application no. 422589; Patent type C12N 1/20, C12R 1/225; Patent no. PL233261, 2017. Available online: https://ewyszukiwarka.pue.uprp.gov.pl/search/pwp-details/P.422589 (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Lactic Bacterial Strain of Lactobacillus Reuteri. Patent Application no. 422593; Patent type C12N 1/20, C12R 1/225, A61K 35/747; Patent Description no. PL2332631, 2017. Available online: https://ewyszukiwarka.pue.uprp.gov.pl/search/pwp-details/P.422593 (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Lactic Bacterial Strain of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus. Patent Application no. 422602; Patent type C12N 1/20, C12R 1/225, A61K 35/747; Patent no. PL233582, 2017. Available online: https://ewyszukiwarka.pue.uprp.gov.pl/search/pwp-details/P.422602 (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Strain of Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Patent Application no. 422709; Patent type C12N 1/18, C12R 1/865; Patent no. PL233581, 2017. Available online: https://ewyszukiwarka.pue.uprp.gov.pl/search/pwp-details/P.422709 (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Lactic Bacterial Strain of Lactobacillus Paracasei. Patent Application no. 422603; Patent type C12N 1/20, C12R 1/225, A61K 35/747; Patent no. PL233262, 2017. Available online: https://ewyszukiwarka.pue.uprp.gov.pl/search/pwp-details/P.422603 (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Opinion of the Scientific Committee on a request from EFSA related to a generic approach to the safety assessment by EFSA of microorganisms used in food/feed and the production of food/feed additives. EFSA J. 2005, 226, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Midilli, M.; Alp, M.; Kocabach, N.; Muglah, O.H.; Turan, N.; Yilmaz, H.; Cakir, S. Effects of dietary probiotic and prebiotic supplementation on growth performance and serum IgG concentration of broilers. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 38, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.A.; Ghareeb, K.; Abdel-Raheem, S.; Bohm, J. Effects of dietary inclusion of probiotic and synbiotic on growth performance, organ weights, and intestinal histomorphology of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashayerizadeh, A.; Dabiri, N.; Ashayerizadeh, O.; Mirzadeh, K.H.; Roshanfekr, H.; Mamooee, M. Effect of dietary antibiotic, probiotic and prebiotic as growth promoters, on growth performance, carcass characteristics and hematological indices of broiler chickens. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 12, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, H.A.; Shivazad, M.; Esmaeilnia, K.; Kohram, H.; Karim, M.A. The effects of a synbiotic containing Enterococcus faecium and inulin on growth performance and resistance to Coccidiosis in broiler chickens. J. Poult. Sci. 2010, 47, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.K.; Haldar, S.; Bedford, M.R.; Muthusami, N.; Samanta, I. Assessment of yeast cell wall as replacements for antibiotic growth promoters in broiler diets: Effects on performance, intestinal histo-morphology and humoral immune responses. J. Anim. Phys. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 96, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, H.M.; Kang, H.K.; Akter, N.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Na, J.C.; Jong, H.B.; Choi, H.C.; Suh, O.S.; et al. Supplementation of direct-fed microbials as an alternative to antibiotic on growth performance, immune response, cecal microbial population, and ileal morphology of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohamadi, K.; Taherpour, K.; Ghasemi, H.A.; Fatahnia, F. Comparative effects of using black seed (Nigella sativa), cumin seed (Cuminum cyminum), probiotic or prebiotic on growth performance, blood haematology and serum biochemistry of broiler chicks. J. Anim. Phys. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 98, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, H.A.; Kasani, N.; Taherpour, K. Effects of black cumin seed (Nigella sativa L.), a probiotic, a prebiotic and a synbiotic on growth performance, immune response and blood characteristics of male broilers. Livest. Sci. 2014, 164, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Chen, Y.P.; Cheng, Y.F.; Yang, W.L.; Wen, C.; Zhou, Y.M. Effect of yeast cell wall powder with different particle sizes on the growth performance, serum metabolites, immunity and oxidative status of broilers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 212, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.N.; Yang, H.L.; Xu, Y.X.; Gao, Y.P. Effects of dietary supplementation of synbiotics on growth performance, intestinal morphology, sIgA content and antioxidant capacities of broilers. J. Anim. Phys. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehimanesh, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Roostaei-Ali Mehr, M. Effect of dietary probiotic, prebiotic and synbiotic supplementation on performance, immune responses, intestinal morphology and bacterial populations in broilers. J. Anim. Phys. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Wen, C.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Y. Effects of synbiotic supplementation on growth performance, carcass characteristics, meat quality and muscular antioxidant capacity and mineral contents in broilers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3699–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhamare, K.S.; Dildeep, V.; Senthil-Murugan, S.; Chavan, S.J. Nutritive evaluation of cashew apple waste in broilers. Int. J. Sci. Nat. 2016, 7, 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczuk-Vasilev, E.; Grela, E.R.; Samolińska, W.; Klebaniuk, R.; Kiczorowska, B.; Krusiński, R.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A.; Kępka, K.; Kwiecień, M. Blood metabolic profile of broiler chickens fed diets with different types and levels of inulin. Med. Weter. 2017, 73, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lewandowski, A.H.; Campbell, T.W.; Harrison, G.J. Clinical chemistries. In Clinical Avian Medicine and Surgery; Harrison, G.J., Harrison, L.R., Eds.; WB Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1986; pp. 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Harr, K.E. Clinical chemistry of companion avian species: A review. Vet. Clin. Path. 2002, 31, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kassie, G.A.M.; Al-Jumaa, Y.M.F.; Jameel, Y.J. Effect of probiotic (Aspergillus niger) and prebiotic (Taraxacum officinale) on blood picture and biochemical properties of broiler chicks. Int. J. Poul. Sci. 2008, 7, 1182–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanamanta, N.; Narayana, M.; Veena, T.; Narayana, H.D.; Jayakumar, K. Effect of prebiotic, probiotic and G-probiotic SPL® on certain haematological parameters in broiler chickens. Vet. World 2009, 9, 344–346. [Google Scholar]
- Beski, S.S.M.; Al-Sardary, S.Y.T. Effects of dietary supplementation of probiotic and synbiotic on broiler chickens hematology and intestinal integrity. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2015, 14, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, R.; Vasiljevic, T.; Day, S.; Smith, S.; Donkor, O. Lactic acid bacteria and probiotic organisms induce different cytokine profile and regulatory T cells mechanisms. J. Funct. Food. 2014, 6, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balevi, T.; Ucan, U.S.; Coskun, B.; Kurtoglu, V.; Cetingul, I.S. Effect of dietary probiotic on performance and humoral immune response in layer hens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2001, 42, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mountzouris, K.C.; Tsitrsikos, P.; Palamidi, I.; Arvaniti, A.; Mohnl, M.; Schatzmayr, G.; Fegeros, K. Effects of probiotic inclusion levels in broiler nutrition on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, plasma immunoglobins, and cecal microflora composition. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Experimental Groups | Composition | |
|---|---|---|
| Synbiotic preparation | A | Lactobacillus plantarum (ŁOCK 0860) |
| Lactobacillus reuteri (ŁOCK 1092) | ||
| Lactobacillus pentosus (ŁOCK 1094) | ||
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ŁOCK 0119) | ||
| B | Lactobacillus plantarum (ŁOCK 0860) | |
| Lactobacillus reuteri (ŁOCK 1092) | ||
| Lactobacillus pentosus (ŁOCK 1094) | ||
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus (ŁOCK 1087) | ||
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ŁOCK 0119) | ||
| C | Lactobacillus plantarum (ŁOCK 0860) | |
| Lactobacillus reuteri (ŁOCK 1092) | ||
| Lactobacillus pentosus (ŁOCK 1094) | ||
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus (ŁOCK 1087) | ||
| Lactobacillus paracasei (ŁOCK 1091) | ||
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ŁOCK 0119) | ||
| Probiotics | D | Bioplus® YC: |
| Bacillus licheniformis (DSM 5749) | ||
| Bacillus subtilis (DSM 5750) | ||
| E | Cylactin®: | |
| Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 10415 (SF68), LBC ME10, DSM | ||
| Control | K | Without additives |
| Type of Feed | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Broiler Starter Prestige | Broiler Grower Prestige | Broiler Finisher Prestige |
| Composition | wheat, corn, post-extraction soya meal *, hemoglobin (from swine blood), rapeseed cake, soybean oil *, calcium carbonate, palm oil derived fatty acids, monocalcium phosphate, sodium chloride | wheat, corn, post-extraction soya meal *, hemoglobin (from swine blood), rapeseed cake, post-extraction sunflower meal, palm oil derived fatty acids, soybean oil *, calcium carbonate, swine fat, monocalcium phosphate, sodium chloride | wheat, corn, post-extraction soya meal * rapeseed cake, soybean oil *, calcium carbonate, monocalcium phosphate, sodium chloride |
| Component amount in 1 kg of feed | |||
| Total proteins (Kjeldahl method) | 225 g | 205 g | 187.5 g |
| Oil and crude fats | 48 g | 55 g | 75 g |
| Fiber | 27 g | 30 g | 33 g |
| Lysine | 13.6 g | 12.9 g | 12.2 g |
| Methionine | 6 g | 5.8 g | 5.6 g |
| Calcium | 8 g | 6.2 g | 4.9 g |
| Phosphorus | 6 g | 5.2 g | 4.6 g |
| Sodium | 1.5 g | 1.5 g | 1.4 g |
| Ash | 55 g | 47 g | 40 g |
| Dietetic additives in 1 kg of feed | |||
| Vitamin A (3a672a) | 10,000 IU | ||
| Vitamin D3 (E671) | 5000 IU | ||
| Vitamin E (dl-α-tocopherol) | 75 mg | ||
| Fe (iron sulphate, E1) | 40 mg | ||
| J (potassium iodide, 3b201) | 1.25 mg | ||
| Cu (copper sulphate, E4) | 16 mg | ||
| Mn (manganese oxide, E5) | 120 mg | ||
| Zn (zinc oxide, E6) | 100 mg | ||
| Se (sodium selenite, E8) | 0.3 mg | ||
| Zootechnics additives in 1 kg of feed | |||
| 6-phytase (EC 3.1.3.26) 500 FTU/g, 4a19 | 1000 FTU | 1000 FTU | - |
| 6-phytase (EC 3.1.26) 2500 OTU/g, 4a16 | - | - | 250 OTU/g |
| Endo-1,4-β-xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8), 12,500 VU/mL, 4a22 | 1250 VU | 1250 VU | - |
| Endo-1,4-β-xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8), 30,000 EPU/g, 4a1617 | - | - | 1500 EPU |
| Endo-1,3 (4)-β-gluconate (EC 3.2.1.6), 8600 VU/mL, 4a22 | 860 VU | 860 VU | - |
| Serine protease (EC 3.4.21), 75,000 PROT/g 4a13 | 15000 PROT | - | - |
| Age of Birds | Feed Additives | Body Weight (Mean ± SD) (g) | Average Cumulative Feed Consumption (g) | Feed Converse Ratio (FCR) | European Production Efficiency Factor (EPEF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 days | Synbiotic A | 110.71 ± 12.02 *DK | 96.00 ± 9.78 *DEK | 0.87 ± 0.03 | 182.66 ± 23.29 *EK |
| Synbiotic B | 107.53 ± 11.82 *DEK | 95.00 ± 9.78 *DEK | 0.89 ± 0.10 | 175.99 ± 39.36 *EK | |
| Synbiotic C | 108.32 ± 7.81 *DEK | 95.93 ± 2.52 *DEK | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 175.33 ± 23.22 *EK | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 134.43 ± 7.53 *ABCE | 116.00 ± 6.75 *ABCE | 0.86 ± 0.05 | 223.21 ± 22.03 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 120.66 ± 10.35 *BCDK | 105.00 ± 7.38 *ABCDK | 0.87 ± 0.03 | 198.23 ± 20.97 *ABCK | |
| Without (K) | 137.93 ± 8.48 *ABCE | 117.00 ± 6 *ABCE | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 232.41 ± 18.04 *ABC | |
| 14 days | Synbiotic A | 288.65 ± 23.01 | 323.17 ± 23.44 | 1.12 ± 0.02 | 182.19 ± 16.27 |
| Synbiotic B | 298.69 ± 17.19 | 330.67 ± 14.68 | 1.11 ± 0.05 *K | 193.01 ± 17.77 | |
| Synbiotic C | 305.60 ± 26.73 | 334.33 ± 16.69 | 1.10 ± 0.05 *K | 199.86 ± 25.85 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 308.42 ± 23.60 | 338.33 ± 19.81 | 1.10 ± 0.04 | 198.85 ± 20.55 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 299.80 ± 38.32 | 334.83 ± 36.84 | 1.12 ± 0.02 *K | 189.71 ± 27.80 | |
| Without (K) | 302.90 ± 17.04 | 361.67 ± 30.96 | 1.19 ± 0.08 *BCE | 179.94 ± 16.44 | |
| 28 days | Synbiotic A | 1121.33 ± 130.45 | 1608.5 ± 234.84 | 1.43 ± 0.07 | 279.78 ± 28.53 |
| Synbiotic B | 1087.50 ± 64.17 | 1510.17 ± 130.63 | 1.39 ± 0.06 | 276.87 ± 17.13 | |
| Synbiotic C | 1096.33 ± 116.77 | 1493.5 ± 139.34 | 1.36 ± 0.04 | 284.23 ± 35.70 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 1180.17 ± 79.61 | 1643.29 ± 88.55 | 1.39 ± 0.04 | 307.75 ± 26.60 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 1130.00 ± 122.76 | 1568.33 ± 143.08 | 1.39 ± 0.05 | 290.06 ± 37.82 | |
| Without (K) | 1113.67 ± 134.02 | 1540.14 ± 202.76 | 1.39 ± 0.05 | 280.04 ± 29.93 | |
| 42 days | Synbiotic A | 1944.00 ± 66.28 *BCDEK | 3168.50 ± 114.51 *BCDEK | 1.63 ± 0.03 *K | 280.96 ± 11.52 *BCK |
| Synbiotic B | 2095.33 ± 18.14 *AK | 3352.17 ± 45.67 *ADEK | 1.60 ± 0.01 *DEK | 304.43 ± 2.52 *A | |
| Synbiotic C | 2096.17 ± 12.43 *AK | 3374.00 ± 26.5 *ADEK | 1.61 ± 0.01 *DEK | 306.70 ± 2.37 *A | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 2176.50 ± 56.95 *AK | 3677.33 ± 87.71 *ABC | 1.69 ± 0.05 *BC | 299.62 ± 14.79 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 2119.67 ± 39.51 *A | 3561.50 ± 133.74 *ABCK | 1.68 ± 0.05 *BC | 297.31 ± 9.48 | |
| Without (K) | 2235.00 ± 67.71 *ABCD | 3798.00 ± 43.82 *ABCE | 1.70 ± 0.04 *ABC | 309.90 ± 16.67 *A |
| Age of Birds | Feed Additives | AST (U/L) | ALT (U/L) | AP (U/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 days | Synbiotic A | 261.6 ± 42.7 | 9.8 ± 5.2 | 2839.1 ± 397.6 *DEK |
| Synbiotic B | 228.1 ± 33.3 | 8.9 ± 3.3 | 3051.0 ± 572.0 *DEK | |
| Synbiotic C | 263.3 ± 63.9 | 6.2 ± 3.7 | 3556.2 ± 1345.3 *EK | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 248.7 ± 24.3 | 6.0 ± 1.9 | 4763.9 ± 708.7 *AB | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 239.6 ± 42.7 | 5.7 ± 2.2 | 5032,6 ± 104.1 *ABC | |
| Without (K) | 220.6 ± 21.1 | 6.0 ± 3.0 | 4957.2 ± 165.3 *ABC | |
| 14 days | Synbiotic A | 237.3 ± 22.7 | 6.9 ± 4.2 | 4718.0 ± 627.3 |
| Synbiotic B | 228.3 ± 16.9 | 3.7 ± 3.3 | 4266.4 ± 535.6 | |
| Synbiotic C | 234.1 ± 15.1 | 6.6 ± 4.7 | 4021.2 ± 819.9 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 247.0 ± 31.1 | 6.1 ± 4.3 | 3883.8 ± 1272.6 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 225.6 ± 15.7 | 8.7 ± 3.2 | 4684.9 ± 616.6 | |
| Without (K) | 224.8 ± 9.7 | 9.1 ± 4.6 | 4602.5 ± 1061.2 | |
| 28 days | Synbiotic A | 264.1 ± 42.4 | 8.6 ± 6.6 | 2067.8 ± 506.9 |
| Synbiotic B | 304.1 ± 63.8 | 7.3 ± 5.2 | 1567.6 ± 308.0 | |
| Synbiotic C | 307.5 ± 73.4 | 7.6 ± 4.2 | 2462.9 ± 339.8 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 277.9 ± 33.9 | 8.3 ± 4.0 | 2025.1 ± 799.8 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 253.3 ± 46.8 | 5.4 ± 3.3 | 1874.0 ± 710.1 | |
| Without (K) | 279.0 ± 53.6 | 8.8 ± 2.6 | 2250.3 ± 1686.2 | |
| 42 days | Synbiotic A | 299.8 ± 107.4 *K | 3.9 ± 1.6 | 1255.7 ± 286.6 |
| Synbiotic B | 384.2 ± 31.1 *K | 4.8 ± 3.6 | 940.2 ± 264.2 | |
| Synbiotic C | 376.6 ± 63.5 *K | 6.0 ± 2.8 | 792.1 ± 276.8 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 365.2 ± 91.5 *K | 7.4 ± 4.5 | 1774.9 ± 320.8 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 402.4 ± 20.0 *K | 8.0 ± 4.8 | 1057.0 ± 326.8 | |
| Without (K) | 834.6 ± 123.7 *ABCDE | 5.0 ± 2.0 | 1728.0 ± 303.7 |
| Age of Birds | Feed Additives | Glucose (mg/dL) | Uric Acid (mg/dL) | Bilirubin (mg/dL) | Cholesterol (mg/dL) | Triglycerides (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 days | Synbiotic A | 270.8 ± 31.9 *D | 6.3 ± 1.1 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 211.4 ± 20.4 | 80.8 ± 39.1 *EK |
| Synbiotic B | 250.3 ± 26.8 | 7.9 ± 2.8 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 193.0 ± 9.9 | 82.5 ± 26.0 *EK | |
| Synbiotic C | 244.9 ± 14.0 | 5.4 ± 2.1 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 193.8 ± 11.7 | 44.2 ± 11.1 *EK | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 214.1 ± 17.6 *A | 5.7 ± 1.1 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 175.2 ± 21.3 | 68.2 ± 32.2 *EK | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 239.1 ± 28.2 | 6.0 ± 1.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 181.4 ± 26.9 | 132.9 ± 32.9 *ABCD | |
| Without (K) | 228.3 ± 23.4 | 5.9 ± 1.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 178.2 ± 25.2 | 135.0 ± 28.5 *ABCD | |
| 14 days | Synbiotic A | 225.9 ± 12.5 | 5.6 ± 0.9 | 0.2 ± 0.1 *D | 158.5 ± 36.2 | 75.2 ± 67.9 |
| Synbiotic B | 242.5 ± 42.5 | 6.3 ± 0.8 | 0.3 ± 0.1 *D | 152.7 ± 21.7 | 67.7 ± 42.6 | |
| Synbiotic C | 220.2 ± 30.3 | 5.9 ± 1.6 | 0.3 ± 0.1 *D | 174.0 ± 12.0 | 54.7 ± 10.3 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 220.9 ± 29.3 | 7.4 ± 3.5 | 0.7 ± 0.3 *ABCEK | 153.6 ± 7.9 | 52.1 ± 6.1 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 217.9 ± 22.8 | 7.0 ± 2.4 | 0.4 ± 0.1 *D | 164.0 ± 16.5 | 64.2 ± 23.2 | |
| Without (K) | 217.1 ± 18.8 | 7.6 ± 2.7 | 0.4 ± 0.1 *D | 166.0 ± 15.5 | 68.4 ± 24.1 | |
| 28 days | Synbiotic A | 261.3 ± 13.7 *BCD | 3.1 ± 0.9 *CK | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 140.2 ± 22.0 | 27.9 ± 10.8 |
| Synbiotic B | 209.0 ± 22.0 *AE | 6.8 ± 3.7 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 155.6 ± 15.4 | 34.0 ± 7.6 | |
| Synbiotic C | 207.7 ± 22.4 *AE | 7.8 ± 3.2 *A | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 171.5 ± 49.8 | 34.2 ± 24.8 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 210.1 ± 33.3 *AE | 5.1 ± 4.4 *K | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 135.4 ± 14.8 | 32.4 ± 5.7 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 268.2 ± 14.7 *BCD | 4.3 ± 1.0 *K | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 147.3 ± 16.2 | 46.3 ± 4.7 | |
| Without (K) | 250.4 ± 16.9 | 9.9 ± 6.0 *ADE | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 156.1 ± 20.1 | 54.1 ± 14.4 | |
| 42 days | Synbiotic A | 170.2 ± 72.6 | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 135.6 ± 24.0 | 27.8 ± 7.3 |
| Synbiotic B | 213.8 ± 23.6 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 0.2 ± 0.1 *D | 146.4 ± 18.8 | 28.8 ± 7.0 | |
| Synbiotic C | 210.2 ± 14.6 | 2.5 ± 0.8 | 0.2 ± 0.1 *DE | 144.3 ± 34.4 | 27.2 ± 8.9 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 215.9 ± 61.2 | 3.5 ± 1.5 | 0.6 ± 0.2 *BCE | 123.9 ± 14.5 | 29.6 ± 7.8 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 197.5 ± 15.0 | 4.8 ± 1.5 | 0.2 ± 0.1 *D | 143.5 ± 12.6 | 38.3 ± 13.8 | |
| Without (K) | 196.5 ± 15.8 | 3.8 ± 1.1 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 145.8 ± 20.6 | 37.0 ± 14.6 |
| Age of Birds | Feed Additives | Total Protein (g/L) | Albumin (g/L) | Globulin (g/L) | A:G ratio (Albumin:Globulin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 days | Synbiotic A | 22.5 ± 3.9 | 13.2 ± 1.2 | 9.3 ± 3.1 | 1.7 ± 1.1 |
| Synbiotic B | 24.0 ± 2.5 | 14.3 ± 2.4 | 9.7 ± 2.7 | 1.6 ± 0.8 | |
| Synbiotic C | 24.0 ± 2.8 | 13.2 ± 1.8 | 10.8 ± 1.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 23.5 ± 2.1 | 12.7 ± 0.5 | 10.8 ± 1.8 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 22.2 ± 2.3 | 12.5 ± 1.5 | 9.7 ± 2.9 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | |
| Without (K) | 21.7 ± 2.2 | 11.3 ± 1.0 | 10.3 ± 1.4 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | |
| 14 days | Synbiotic A | 23.0 ± 2.6 | 13.3 ± 1.6 | 9.7 ± 2.3 | 1.5 ± 0.5 |
| Synbiotic B | 23.0 ± 2.8 | 12.7 ± 1.2 | 10.3 ± 1.6 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | |
| Synbiotic C | 23.5 ± 2.1 | 13.0 ± 1.4 | 10.5 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 23.5 ± 1.2 | 13.5 ± 0.5 | 10.0 ± 1.4 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 24.2 ± 2.6 | 13.5 ± 1.5 | 10.7 ± 1.8 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | |
| Without (K) | 24.3 ± 2.9 | 13.5 ± 1.4 | 10.8 ± 2.3 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | |
| 28 days | Synbiotic A | 28.0 ± 4.8 | 14.8 ± 1.9 *BCDEK | 13.2 ± 5.5 | 1.3 ± 0.6 |
| Synbiotic B | 30.2 ± 2.9 | 16.2 ± 1.5 *A | 14.0 ± 1.9 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | |
| Synbiotic C | 32.5 ± 12.1 *EK | 18.2 ± 6.9 *A | 14.3 ± 5.3 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 27.7 ± 2.0 | 15.5 ± 1.0 *A | 12.2 ± 1.2 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 26.3 ± 1.9 *C | 15.3 ± 1.2 *A | 11.0 ± 2.5 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | |
| Without (K) | 25.8 ± 2.4 *C | 15.3 ± 1.0 *A | 10.5 ± 1.5 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | |
| 42 days | Synbiotic A | 28.2 ± 8.3 | 13.8 ± 3.9 | 14.3 ± 4.7 | 1.0 ± 0.1 |
| Synbiotic B | 33.0 ± 2.1 | 15.8 ± 3.3 | 17.2 ± 3.1 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | |
| Synbiotic C | 30.8 ± 2.9 | 16.7 ± 2.0 | 14.2 ± 1.8 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 31.7 ± 2.3 | 16.2 ± 0.8 | 15.5 ± 1.5 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 30.7 ± 1.9 | 15.5 ± 0.8 | 15.2 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | |
| Without (K) | 29.7 ± 3.7 | 15.3 ± 1.5 | 14.3 ± 2.2 | 1.1 ± 0.1 |
| Age of Birds | Feed Additives | Ca (mg/dL) | P (mg/dL) | Ca:P Ratio | K (mmol/L) | Na (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 days | Synbiotic A | 12.7 ± 1.7 *CEK | 5.7 ± 1.0 | 2.3 ± 0.5 | 5.9 ± 0.9 *D | 142.8 ± 2.7 |
| Synbiotic B | 11.3 ± 2.4 *EK | 4.4 ± 1.2 *EK | 2.8 ± 1.0 | 4.9 ± 0.5 *DEK | 151.0 ± 7.1 *D | |
| Synbiotic C | 9.4 ± 1.2 *ADEK | 4.8 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 5.5 ± 2.1 *DEK | 141.9 ± 3.9 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 13.2 ± 1.3 *C | 6.4 ± 1.3 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 7.5 ± 0.7 *ABC | 137.8 ± 3.7 *B | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 12.1 ± 2.3 *ABC | 6.2 ± 0.9 *B | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 6.2 ± 0.8 *BC | 139.4 ± 5.2 | |
| Without (K) | 14.9 ± 1.5 *ABC | 7.0 ± 0.9 *B | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 7.2 ± 0.6 *BC | 141.5 ± 1.8 | |
| 14 days | Synbiotic A | 11.8 ± 1.3 *CDEK | 5.2 ± 0.8 | 2.3 ± 0.4 | 8.0 ± 0.5 | 140.7 ± 2.3 |
| Synbiotic B | 13.2 ± 2.0 *CDEK | 5.0 ± 0.9 | 2.7 ± 0.8 | 7.1 ± 0.7 | 141.6 ± 1.4 | |
| Synbiotic C | 16.5 ± 1.2 *AB | 4.5 ± 0.9 | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 7.2 ± 0.4 | 142.1 ± 2.9 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 16.4 ± 2.1 *AB | 6.6 ± 1.9 | 2.7 ± 1.1 | 7.9 ± 1.2 | 146.1 ± 3.6 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 14.8 ± 2.3 *AB | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 7.6 ± 0.7 | 147.2 ± 3.2 | |
| Without (K) | 15.8 ± 1.1 *AB | 6.5 ± 1.3 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 7.8 ± 0.8 | 142.8 ± 10.1 | |
| 28 days | Synbiotic A | 10.9 ± 1.0 | 6.7 ± 1.8 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 5.6 ± 1.2 | 145.2 ± 3.1 |
| Synbiotic B | 9.7 ± 1.0 | 7.7 ± 1.4 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 5.4 ± 0.5 | 146.2 ± 1.9 | |
| Synbiotic C | 10.2 ± 2.1 | 7.7 ± 2.6 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 6.0 ± 0.6 *EK | 146.6 ± 1.8 | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 9.7 ± 0.7 | 8.9 ± 0.5 *K | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 6.4 ± 0.4 *EK | 145.2 ± 1.5 | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 8.6 ± 0.8 | 7.1 ± 0.9 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.2 *CD | 146.4 ± 4.1 | |
| Without (K) | 10.7 ± 0.7 | 5.7 ± 1.4 *D | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 4.1 ± 0.6 *CD | 150.0 ± 2.3 | |
| 42 days | Synbiotic A | 10.3 ± 0.4 | 7.5 ± 1.0 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 8.3 ± 1.3 | 131.2 ± 24.3 *BCDEK |
| Synbiotic B | 10.1 ± 0.7 | 7.0 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 8.2 ± 1.2 | 145.0 ± 1.0 *A | |
| Synbiotic C | 9.6 ± 0.7 | 8.1 ± 3.2 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 7.8 ± 1.1 | 142.5 ± 2.5 *A | |
| Bioplus® YC (D) | 9.9 ± 0.9 | 7.9 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 8.0 ± 1.4 | 143.7 ± 1.8 *A | |
| Cylactin® (E) | 9.6 ± 0.6 | 7.6 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 7.7 ± 0.8 | 145.0 ± 2.3 *A | |
| Without (K) | 9.5 ± 0.5 | 7.9 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 7.8 ± 1.2 | 145.8 ± 2.5 *A |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Żbikowski, A.; Pawłowski, K.; Śliżewska, K.; Dolka, B.; Nerc, J.; Szeleszczuk, P. Comparative Effects of Using New Multi-Strain Synbiotics on Chicken Growth Performance, Hematology, Serum Biochemistry and Immunity. Animals 2020, 10, 1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091555
Żbikowski A, Pawłowski K, Śliżewska K, Dolka B, Nerc J, Szeleszczuk P. Comparative Effects of Using New Multi-Strain Synbiotics on Chicken Growth Performance, Hematology, Serum Biochemistry and Immunity. Animals. 2020; 10(9):1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091555
Chicago/Turabian StyleŻbikowski, Artur, Karol Pawłowski, Katarzyna Śliżewska, Beata Dolka, Joanna Nerc, and Piotr Szeleszczuk. 2020. "Comparative Effects of Using New Multi-Strain Synbiotics on Chicken Growth Performance, Hematology, Serum Biochemistry and Immunity" Animals 10, no. 9: 1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091555
APA StyleŻbikowski, A., Pawłowski, K., Śliżewska, K., Dolka, B., Nerc, J., & Szeleszczuk, P. (2020). Comparative Effects of Using New Multi-Strain Synbiotics on Chicken Growth Performance, Hematology, Serum Biochemistry and Immunity. Animals, 10(9), 1555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091555







