Humane Euthanasia of Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) with a Penetrating Spring-Loaded Captive Bolt
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
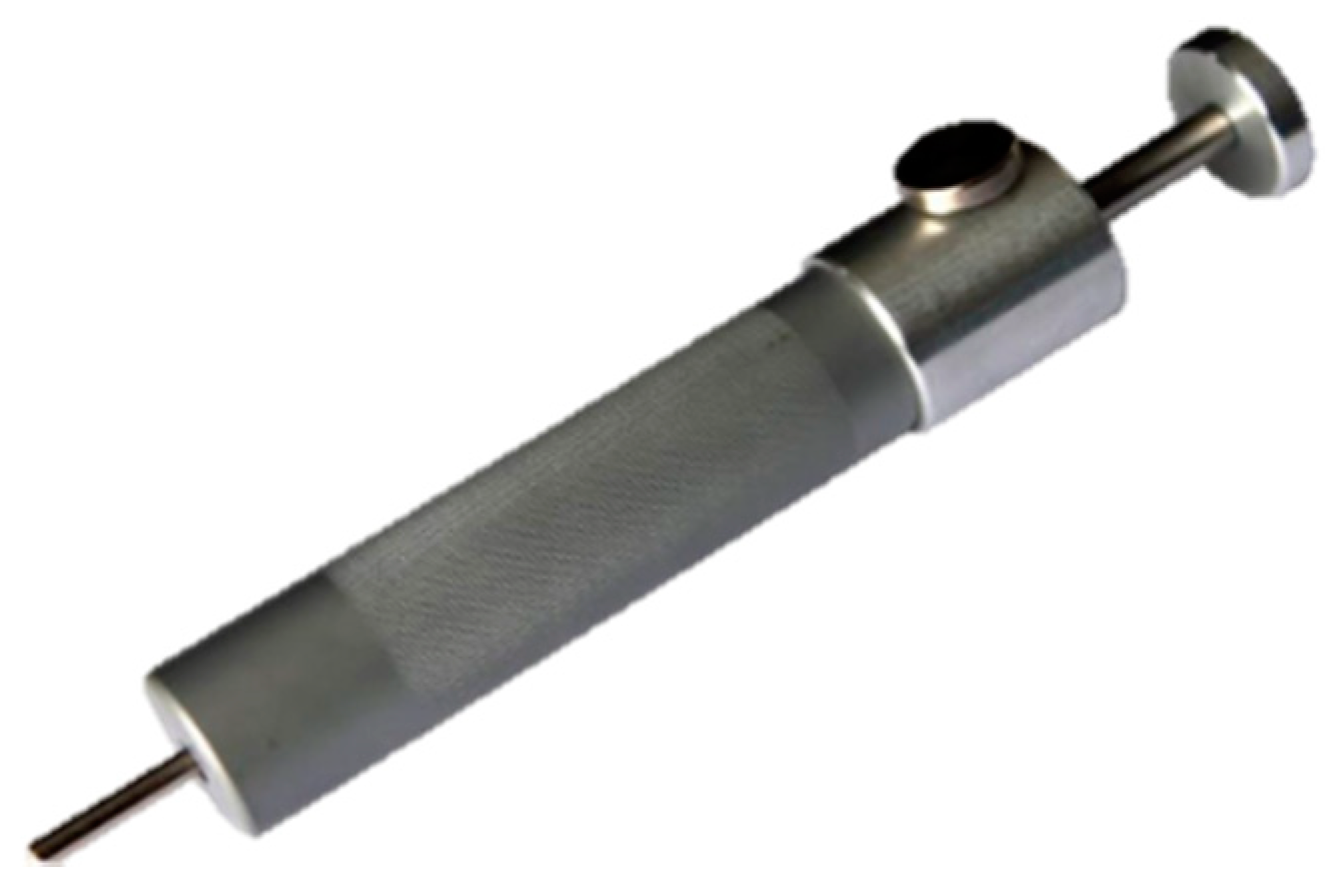
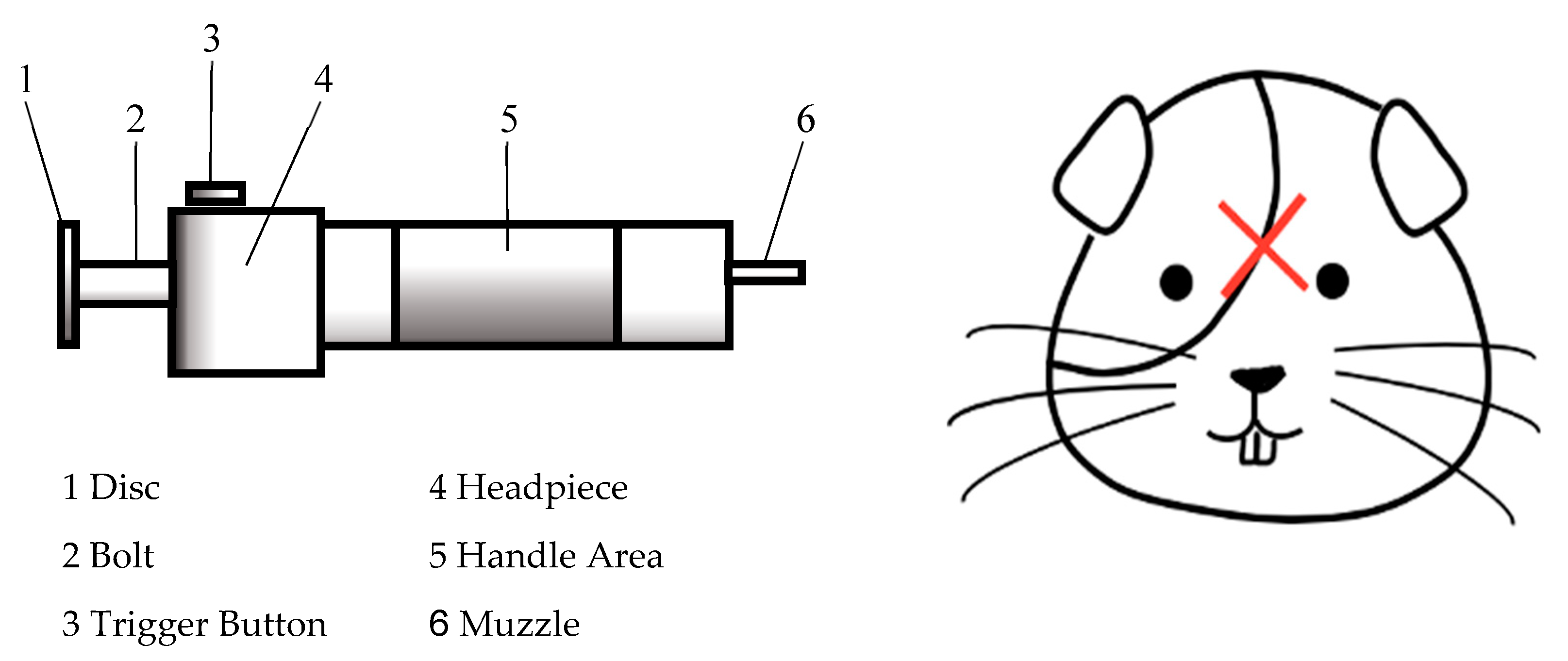
2. Materials and Methods
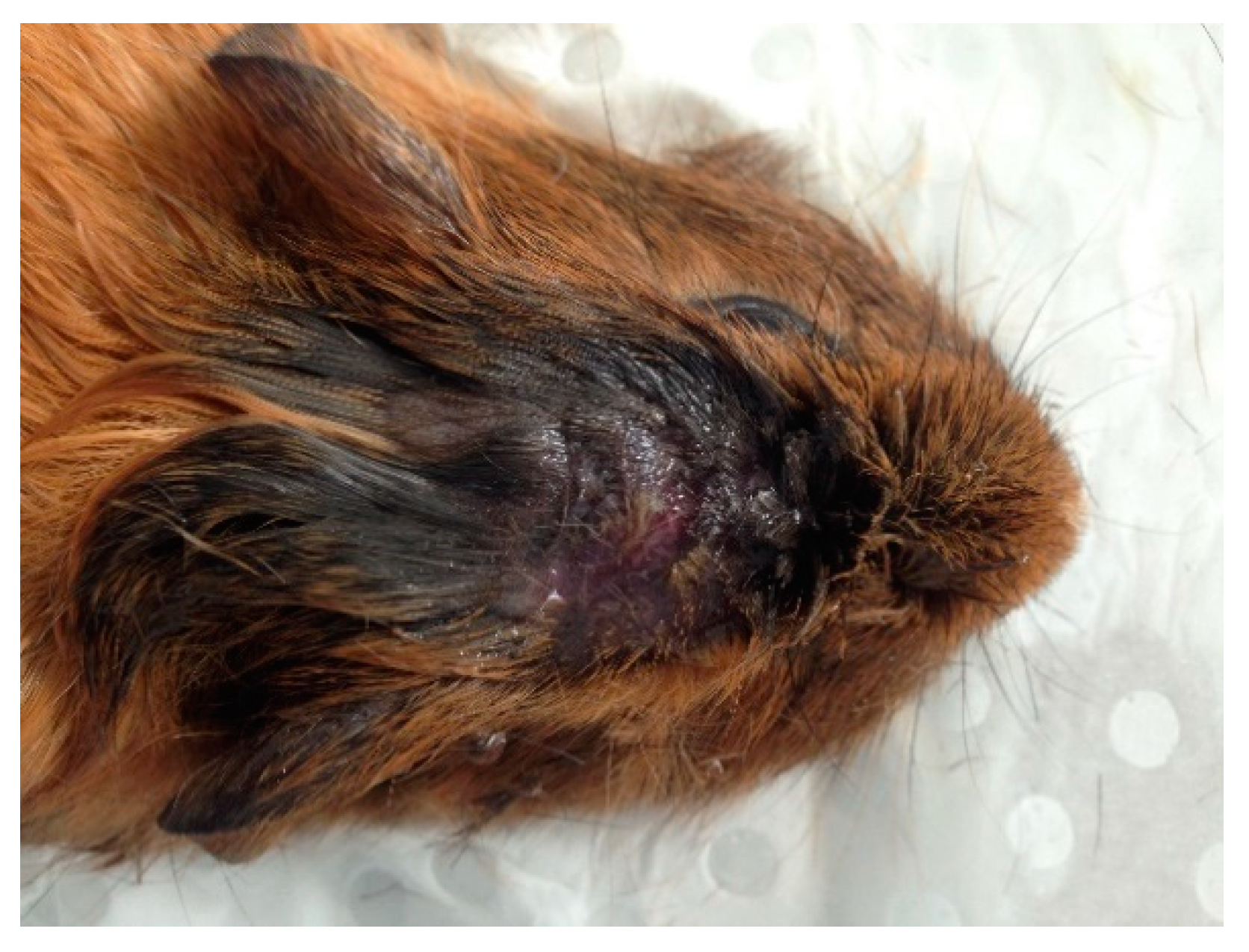
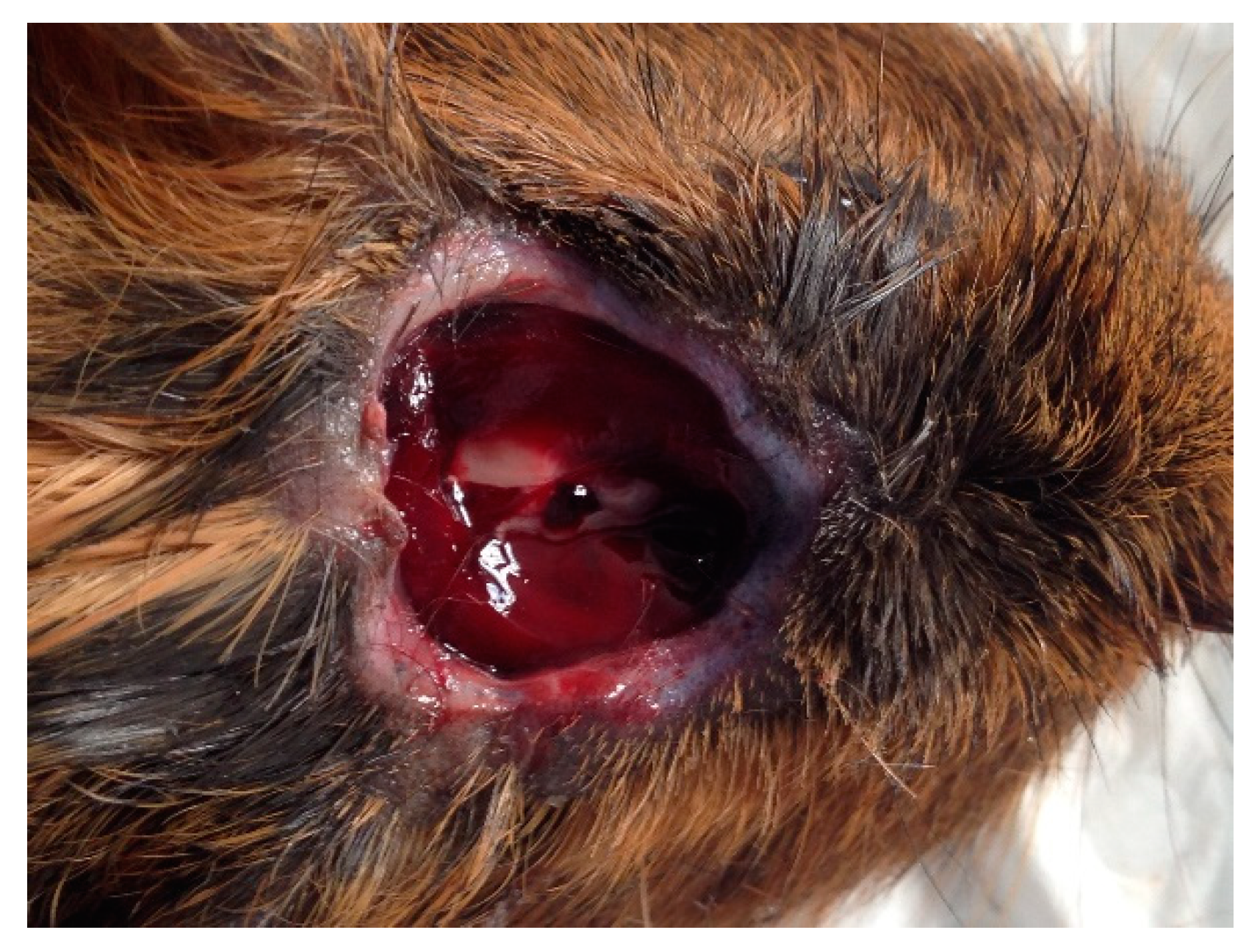
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Effectiveness of Captive Bolt in Animals
4.2. Uncontaminated Tissues
4.3. Physical, Emotional and Compassion Fatigue
4.4. Limitations and the Future
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padilla-Carlin, D.J.; McMurray, D.N.; Hickey, A.J. The guinea pig as a model of infectious diseases. Comp. Med. 2008, 58, 324–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.K.; Lee, V.K. Chapter 25—Guinea Pigs as Experimental Models. In The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents; Suckow, M.A., Stevens, K.A., Wilson, R.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 705–744. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Chapter 5—Humane Endpoints for Animals in Pain. In Recognition and Alleviation of Pain and Distress in Laboratory Animals; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 102–116. [Google Scholar]
- Grandin, T. Euthanasia and slaughter of livestock. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1994, 204, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leary, S.L.; Underwood, W.; Anthony, R.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.; Poison, A.; Meyer, R. AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals: 2013 edition. In Proceedings of American Veterinary Medical Association; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2013; pp. 18–50. Available online: https://www.avma.org/sites/default/files/2020-01/2020-Euthanasia-Final-1-17-20.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2020).
- Russell, W.M.S.; Burch, R.L. The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique; Methuen: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Grandin, T. Recommended Captive Bolt Stunning Techniques for Cattle. Available online: https://www.grandin.com/humane/cap.bolt.tips.html (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- Casey-Trott, T.; Millman, S.; Turner, P.; Nykamp, S.; Widowski, T. Effectiveness of a nonpenetrating captive bolt for euthanasia of piglets less than 3 d of age. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 5477–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandin, T. Captive Bolt Stunning of Cattle, Sheep, and Pigs. Available online: http://www.grandin.com/humane/captive.bolt.html (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- Finnie, J.; Manavis, J.; Summersides, G.; Blumbergs, P. Brain damage in pigs produced by impact with a nonpenetrating captive bolt pistol. Aust. Vet. J. 2003, 81, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampton, J.O. Gunpowder-powered captive bolts for the euthanasia of kangaroo pouch young. Aust. Mammal. 2018, 41, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlouw, C.; Bourguet, C.; Deiss, V. Consciousness, unconsciousness and death in the context of slaughter. Part I. Neurobiological mechanisms underlying stunning and killing. Meat Sci. 2016, 118, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limon, G.; Gonzales-Gustavson, E.A.; Gibson, T.J. Investigation Into the Humaneness of Slaughter Methods for Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcelus) in the Andean Region. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. Jaaws 2016, 19, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, J.; Manavis, J.; Blumbergs, P.; Summersides, G. Brain damage in sheep from penetrating captive bolt stunning. Aust. Vet. J. 2002, 80, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandin, T. How to Determine Insensibility (Unconsciousness) in Cattle, Pigs, and Sheep in Slaughter Plants. Available online: https://www.grandin.com/humane/insensibility.html (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- Leary, S.L.; Underwood, W.; Anthony, R.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.; Grandin, T.; Meyer, R. AVMA Guidelines for the Humane Slaughter of Animals: 2016 Edition. In Proceedings of the American Veterinary Medical Association; AVMA: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2016; pp. 24–39. Available online: https://www.avma.org/sites/default/files/resources/Humane-Slaughter-Guidelines.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2020).
- Walsh, J.L.; Percival, A.; Turner, P.V. Efficacy of Blunt Force Trauma, a Novel Mechanical Cervical Dislocation Device, and a Non-Penetrating Captive Bolt Device for On-Farm Euthanasia of Pre-Weaned Kits, Growers, and Adult Commercial Meat Rabbits. Animals 2017, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grist, A.; Lines, J.A.; Knowles, T.G.; Mason, C.W.; Wotton, S.B. The Use of a Non-Penetrating Captive Bolt for the Euthanasia of Neonate Piglets. Animals 2018, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey-Trott, T.M.; Millman, S.T.; Turner, P.V.; Nykamp, S.G.; Lawlis, P.C.; Widowski, T.M. Effectiveness of a nonpenetrating captive bolt for euthanasia of 3 kg to 9 kg pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 5166–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widowski, T.; Elgie, R.; Lawlis, P. Assessing the effectiveness of a non-penetrating captive bolt for euthanasia of newborn piglets. In Proceedings of the Allen D. Leman Swine Conference, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 22 September 2020; pp. 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Chevillon, P.; Mircovich, C.; Dubroca, S.; Fleho, J.-Y. Comparison of different pig euthanasia methods available to the farmers. Proc. Int. Soc. Anim. Hyg. 2004, 11, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Whiting, T.; G Steele, G.; Wamnes, S.; Green, C. Evaluation of methods of rapid mass killing of segregated early weaned piglets. Can. Vet. J. 2011, 52, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharp, T.M.; McLeod, S.R.; Leggett, K.E.A.; Gibson, T.J. Evaluation of a spring-powered captive bolt gun for killing kangaroo pouch young. Wildl. Res. 2015, 41, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, J.; Blumbergs, P.; Manavis, J.; Summersides, G.; Davies, R. Evaluation of brain damage resulting from penetrating and non-penetrating captive bolt stunning using lambs. Aust. Vet. J. 2000, 78, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, T.; Ridler, A.; Lamb, C.; Williams, A.; Giles, S.; Gregory, N. Preliminary evaluation of the effectiveness of captive-bolt guns as a killing method without exsanguination for horned and unhorned sheep. Anim. Welf. 2012, 21, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grist, A.; Lines, J.A.; Knowles, T.G.; Mason, C.W.; Wotton, S.B. The Use of a Mechanical Non-Penetrating Captive Bolt Device for the Euthanasia of Neonate Lambs. Animals 2018, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grist, A.; Lines, J.A.; Knowles, T.G.; Mason, C.W.; Wotton, S.B. Use of a Non-Penetrating Captive Bolt for Euthanasia of Neonate Goats. Animals 2018, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; O’Callaghan, M. Evaluation of a pneumatically operated captive bolt for stunning/killing broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2001, 42, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figley, C. Compassion Fatigue in the Animal-Care Community; The Humane Society of the United States: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.P. Compassion Fatigue and the Veterinary Health Team. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 37, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, V.; Bennett, P. Perpetration-induced Traumatic Stress in Persons Who Euthanize Nonhuman Animals in Surgeries, Animal Shelters, and Laboratories. Soc. Anim. Soc. Sci. Stud. Hum. Exp. Other Anim. 2005, 13, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotney, R.; McLaughlin, D.; Keates, H. A systematic review of the effects of euthanasia and occupational stress in personnel working with animals in animal shelters, veterinary clinics, and biomedical research facilities. J. Am. Vet. Med Assoc. 2015, 247, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arluke, A. Trapped in a guilt cage. New Sci. 1992, 134, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Close, B.; Banister, K.; Baumans, V.; Bernoth, E.M.; Bromage, N.; Bunyan, J.; Erhardt, W.; Flecknell, P.; Gregory, N.; Hackbarth, H.; et al. Recommendations for euthanasia of experimental animals: Part 1. Lab. Anim. 1996, 30, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, T.; Saunders, G. GEN001 Methods of Euthanasia. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/53fd/4a5923b24bd0696a4140e42ef715b3524d83.pdf?_ga=2.130248399.190541707.1566051564-314654895.1566051564 (accessed on 5 January 2019).
- Close, B.; Banister, K.; Baumans, V.; Bernoth, E.-M.; Bromage, N.; Bunyan, J.; Erhardt, W.; Flecknell, P.; Gregory, N.; Hackbarth, H. Recommendations for euthanasia of experimental animals: Part 2. Lab. Anim. 1997, 31, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey-Trott, T. Effectiveness of a Non-Penetrating Captive Bolt for Euthanasia of Suckling and Weaned Piglets; University of Guelph: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sivula, C.P.; Suckow, M.A. Chapter 35-Euthanasia. In Management of Animal Care and Use Programs in Research, Education, and Testing; Weichbrod, R.H., Thompson, G.A.H., Norton, J.N., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 869–882. [Google Scholar]
- Reeve, C.L.; Rogelberg, S.G.; Spitzmüller, C.; Digiacomo, N. The Caring-Killing Paradox: Euthanasia-Related Strain Among Animal-Shelter Workers. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2005, 35, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.T.; Hard, L.A. Human-animal bonds in the laboratory: How animal behavior affects the perspective of caregivers. ILAR J. 2002, 43, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, T.L.; Marion, C.R. Perpetration-induced traumatic stress—A risk for veterinarians involved in the destruction of healthy animals. Can. Vet. J. 2011, 52, 794–796. [Google Scholar]
- Agriculture Victoria. Appendix 2: Methods Of Euthanasia for Post-Neonatal Laboratory Mice, Rats, Guinea Pigs and Rabbits. Available online: http://agriculture.vic.gov.au/agriculture/animal-health-and-welfare/animal-welfare/animal-welfare-legislation/victorian-codes-of-practice-for-animal-welfare/code-of-practice-for-the-housing-and-care-of-laboratory-mice,-rats,-guinea-pigs-and-rabbits/appendix-2-methods-of-euthanasia-for-post-neonatal-laboratory-mice,-rats,-guinea-pigs-and-rabbits (accessed on 13 February 2019).
- Gagea-Iurascu, M.; Craig, S. Chapter 4—Euthanasia and Necropsy. In The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents; Suckow, M.A., Stevens, K.A., Wilson, R.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, S.H.; Gografe, S.I.; Kohn, D.F.; Swindle, M.M. Methods of Euthanasia. In Laboratory Mouse Handbook; Gografe, S.I., Ed.; American Association for Laboratory Animal Science: Memphis, TN, USA, 2010; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- Hau, J.; Schapiro, S.J. Laboratory Animal Analgesia, Anesthesia, and Euthanasia. In Handbook of Laboratory Animal Science: Volume I—Essential Principles and Practices, 3rd ed.; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Conlee, K.; Stephens, M.; Rowan, A.; Kin, L. Carbon dioxide for euthanasia: Concerns regarding pain and distress, with special reference to mice and rats. Lab. Anim. 2005, 39, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, J.M.; Pang, D.S.J. Assessment of Carbon Dioxide, Carbon Dioxide/Oxygen, Isoflurane and Pentobarbital Killing Methods in Adult Female Sprague-Dawley Rats. PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.B.M.; Johnson, S.P.; Wotton, S.B.; McInstry, J.L. Welfare implications of gas stunning pigs: The time to loss of somatosensory evoked potential and spontaneous electrocorticogram of pigs during exposure to gases. Vet. J. 1997, 153, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, M.C.; Bowell, V.A.; Allan, T.F.; Morton, D.B. Aversion to gaseous euthanasia agents in rats and mice. Comp. Med. 2002, 52, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anton, F.; Euchner, I.; Handwerker, H.O. Psychophysical examination of pain induced by defined CO2 pulses applied to the nasal mucosa. Pain 1992, 49, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnyrancher. Which Bolt Gun Is Best for Me? Available online: https://www.bunnyrancher.com/why-bolt-guns.html (accessed on 6 June 2019).
- Stewart, A. (University of Melbourne Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Melbourne, Australia). Personal Communication, 2019.
- Claudia Terlouw, E.M.; Bourguet, C.; Deiss, V.; Mallet, C. Origins of movements following stunning and during bleeding in cattle. Meat Sci. 2015, 110, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandin, T. Auditing animal welfare at slaughter plants. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guertin, P.A. The mammalian central pattern generator for locomotion. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 62, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierozan, P.; Jernerén, F.; Ransome, Y.; Karlsson, O. The Choice of Euthanasia Method Affects Metabolic Serum Biomarkers. Basic Clin. Pharm. Toxicol. 2017, 121, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, J.O.; Adams, P.J.; Forsyth, D.M.; Cowled, B.D.; Stuart, I.G.; Hyndman, T.H.; Collins, T. Improving animal welfare in wildlife shooting: The importance of projectile energy: Projectile Energy and Wildlife Shooting. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandin, T. Improving Animal Welfare: A Practical Approach; Colorado State University Fort Collins: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, M.D.; Lombardi, M.E.; Benson, E.R.; Alphin, R.L.; Malone, G.W. Using Accelerometers to Determine the Cessation of Activity of Broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2007, 16, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.D.; Johnson, K.J.; Benson, E.R.; Alphin, R.L.; Seta, S.; Malone, G.W. Determining cessation of brain activity during depopulation or euthanasia of broilers using accelerometers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2009, 18, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sade, R.M. Brain death, cardiac death, and the dead donor rule. J. South Carol. Med. Assoc. 2011, 107, 146–149. [Google Scholar]

| Euthanasia Method | Disadvantages | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Anesthetic Gas Overdose | ||
| Barbiturates |
| |
| Carbon Dioxide Stunning |
|
|
| Cervical Dislocation |
| |
| Decapitation |
|
|
| Blunt Force Trauma |
|
|
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cohen, S.; Kwok, M.; Huang, J. Humane Euthanasia of Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) with a Penetrating Spring-Loaded Captive Bolt. Animals 2020, 10, 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081356
Cohen S, Kwok M, Huang J. Humane Euthanasia of Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) with a Penetrating Spring-Loaded Captive Bolt. Animals. 2020; 10(8):1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081356
Chicago/Turabian StyleCohen, Shari, Melody Kwok, and Joel Huang. 2020. "Humane Euthanasia of Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) with a Penetrating Spring-Loaded Captive Bolt" Animals 10, no. 8: 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081356
APA StyleCohen, S., Kwok, M., & Huang, J. (2020). Humane Euthanasia of Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) with a Penetrating Spring-Loaded Captive Bolt. Animals, 10(8), 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081356




