Molecular Detection of Gurltia paralysans by Semi-Nested PCR in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum Samples from Domestic Cats (Felis catus)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Patients
2.2. Neurological Examination and Sampling
2.3. Imaging Studies
2.4. Necropsy and Extraction of Nematodes
2.5. Extraction and Quantification of Gurltia paralysans DNA
2.6. Molecular Detection of Gurltia paralysans by Semi-Nested PCR
2.7. Internal Control Amplification by Real-Time PCR
2.8. Sequencing Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
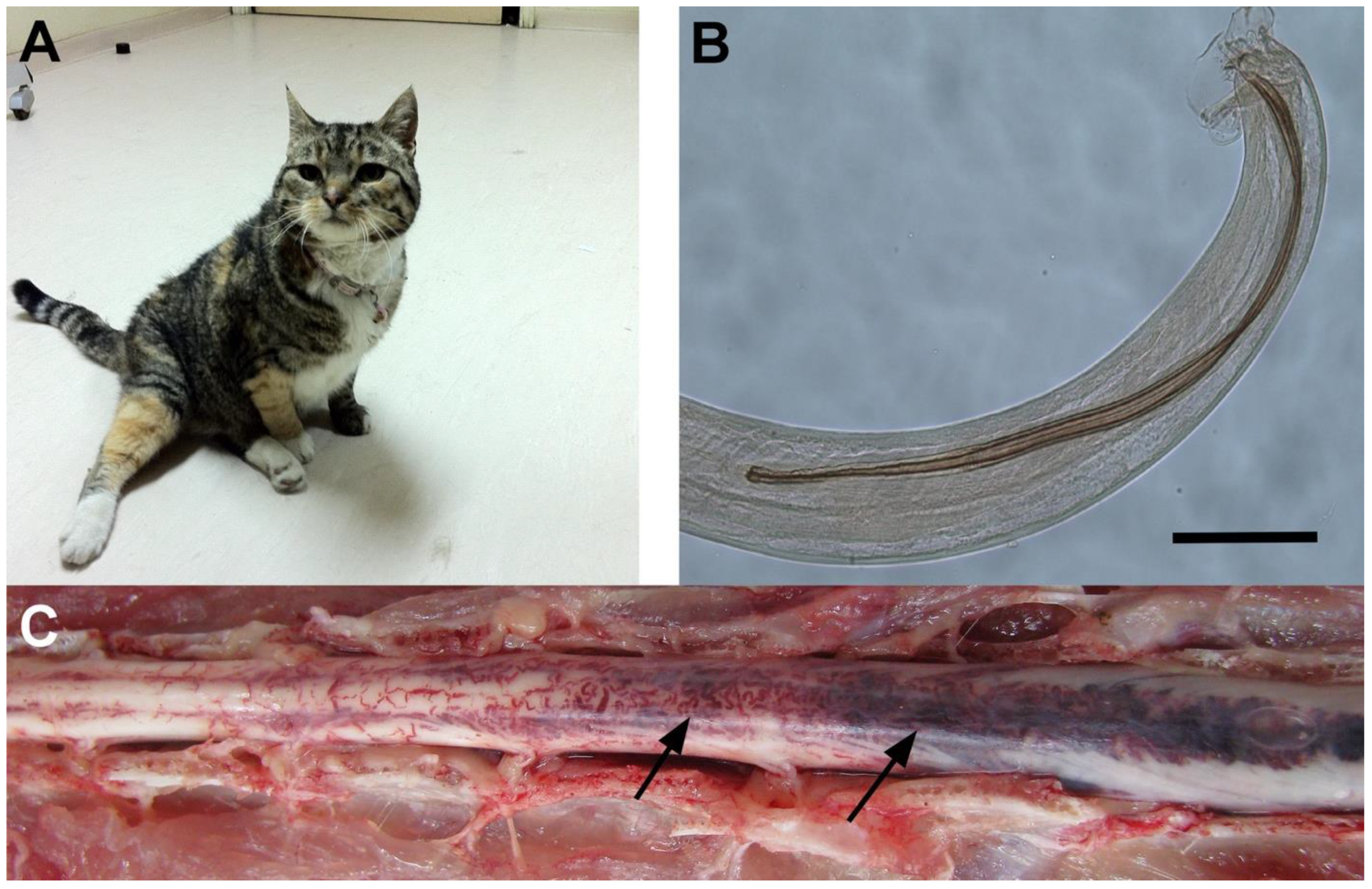
3.1. Biological Samples
3.2. Neurological Observations
3.3. Imaging Analysis
3.4. Pathological Findings
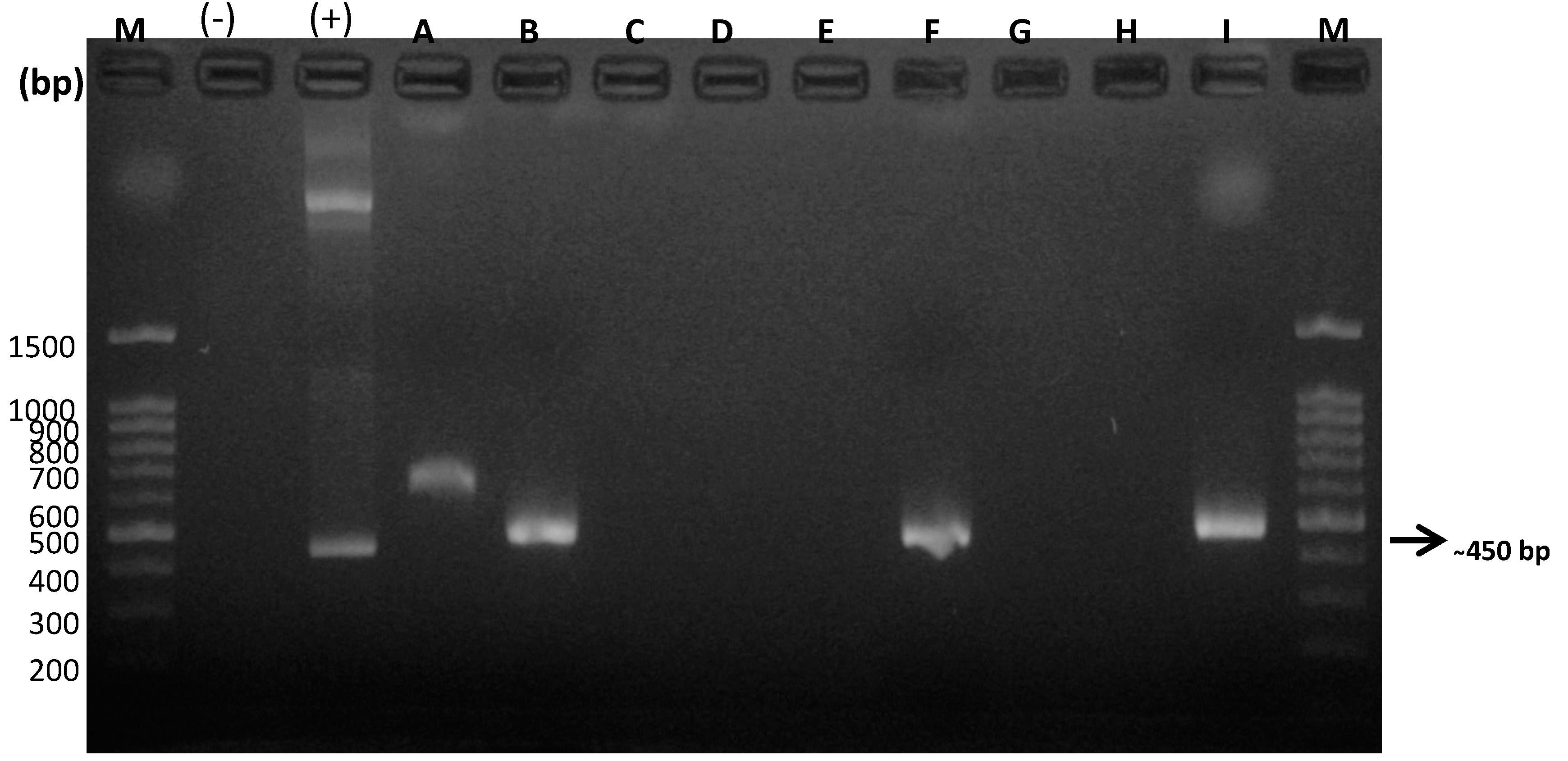
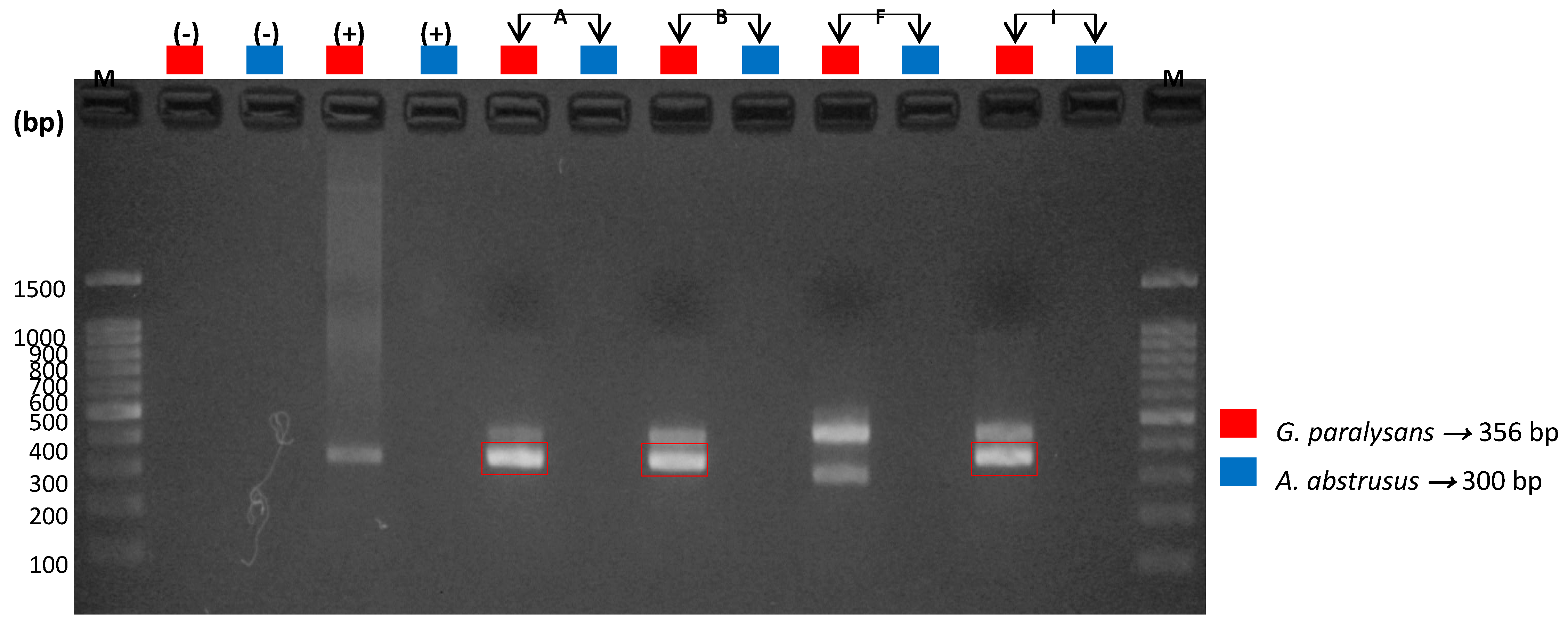
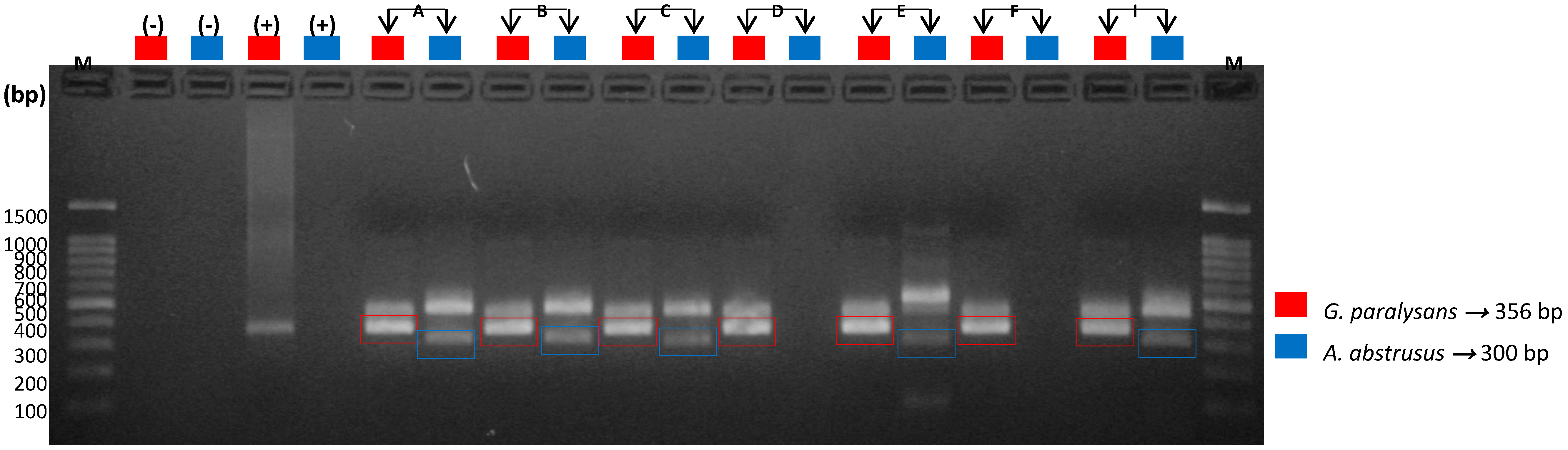
3.5. Molecular Detection of Feline Gurltiosis
3.6. Sequencing Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowman, D.; Hendrix, C.; Lindsay, D.; Barr, S. Feline Clinical Parasitology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Alzate, G.; Aranzazu, D.; Alzate, A.; Chaparro, J. Domestic cat paraplegia compatible with Gurltia paralysans nematode. First cases reported in Colombia. Rev. Colom. Cienc. Pecua. 2011, 24, 663–669. Available online: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=295022383010 (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Guerrero, I.; Paludi, A.; Saumell, L. Primera Descripción En Argentina De Gurltia Paralysans En Un Felino Doméstico. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Centro de la Provincia de Buenas Aires, Tandil, Argentina, 2011. Available online: http://www.biblioteca.unlpam.edu.ar/pubpdf/revet/v18n2a05pellegrino.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Moroni, M.; Muñoz, P.; Gómez, M.; Mieres, M.; Rojas, M.; Lillo, C.; Aguirre, F.; Acosta-Jammet, G.; Kaiser, M.; Lindsay, D. Gurltia paralysans: Description of adults and additional case reports of neurological diseases in three domestics cats from southern Chile. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 184, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, R.; Matto, C.; Adrien, M.; Nan, F.; Bell, T.; Gardiner, C. Parasite meningomyelitis in cats in Uruguay. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2011, 20, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togni, M.; Panziera, W.; Souza, T.; Oliveira, J.; Mazzanti, A.; Barros, C.; Fighera, A. Epidemiological, clinical and pathological aspects of Gurltia paralysans infection in cats. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2013, 33, 363–371. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udiz-Rodriguez, R.; García-Livia, K.; Valladares-Salmerón, M.; Dorta-Almenar, M.; Martín-Carrillo, N.; Martín-Alonso, A.; Izquierdo-Rodríguez, E.; Feliu, C.; Valladares, B.; Foronda, P. First ocular report of Gurltia paralysans (Wolffhügel, 1933) in cat. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 15, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, H. Parasitología, 1st ed.; Editorial Limusa: Balderas, México, 1984; pp. 367–390. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, M.; Mieres, M.; Moroni, M.; Mora, A.; Barrios, N.; Simeone, C.; Lindsay, D. Meningomyelitis due to nematode infection in four cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 170, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.; Hirzmann, J.; Rodriguez, E.; Moroni, M.; Taubert, A.; Gibbons, L.; Hermosilla, C.; Gómez, M. Redescription and first molecular characterization of the Little known feline neurotropic nematode Gurltia paralysans (Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea). Veter Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2017, 10, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolffhügel, K. Parasitic paraplegia in felines due to Gurltia paralysans gen. nov. sp. (Nematoda). Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 1933, 37, 190–192. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Mieres, M.; Gómez, M.; Lillo, C.; Rojas, M.; Moroni, M.; Muñoz, P.; Acosta-Jammet, G.; Wiegand, R. Clinical, imaging and pathologic characteristics of Gurltia paralysans myelopathy in domestic cats from Chile. Vet Radiol. Ultrasound 2013, 54, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.; Lorenz, M.; Kornegay, J. Handbook of Veterinary Neurology; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997; p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, R.; Bright, R.; Swartout, M. Small Animal Clinics, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Madrid, España, 2004; pp. 256–275. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Galeano, M.; Navarro, P.; Lluch, J. Hyla spp. (Amphibia, Hylidae) helminth fauna in some Spanish localities. Misc. Zool. 1990, 14, 1–6. Available online: http://other.museucienciesjournals.cat/files/MZ-vol-14-1990-pp-1-6 (accessed on 1 April 2020). (In Spanish).
- Sprent, J. On the invasion of the central nervous system by nematodes. I. The incidence and pathological significance of nematodes in the central nervous system. Parasitology 1955, 45, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helps, C.; Lait, P.; Damhuis, A.; Björnehammar, U.; Bolta, D.; Brovida, C.; Chabanne, L.; Egberink, H.; Ferrand, G.; Fontbonne, A.; et al. Factors associated with upper respiratory tract disease caused by feline herpesvirus, feline calicivirus, Chlamydophila felis and Bordetella bronchiseptica in cats; experience from 218 European catteries. Vet. Rec. 2005, 156, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, E.; Cornetta, A.; De Lahunta, A.; Center, S.; Kent, M. Clinical and clinicopathologic features in 11 cats with Cuterebra larvae myasis of the central nervous system. J. Vet. Int. Med. 1998, 12, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, D.; Dixon, M. Ribosomal DNA: Molecular evolution and phylogenetic inference. Q. Rev. Boil. 1991, 66, 411–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrin, A.; Cherubini, G.; Steeves, E. Angiostrongylus vasorum causing meningitis and detection of parasite larvae in the cerebrospinal fluid of a pug dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2008, 49, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.; Giese, E.; Melo, F.; Simões, R.; Thiengo, S.; Maldonado, A.; Santos, J. Endemic angiostrongyliasis in the Brazilian Amazon: Natural parasitism of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Rattus rattus and R. norvegicus, and sympatric giant African land snails, Achatina fulica. Acta Trop. 2013, 125, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.; Webster, P.; Willesen, J.; Deplazes, P.; Mathis, A.; Kapel, C. Detection of infection with Angiostrongylus vasorum (Nematoda, Strongylida) by PCR. Acta Vet. Scand. 2010, 52, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D.; Iorio, R.; Otranto, D. Diagnostic and clinical implications of a nested PCR specific for ribosomal DNA of the feline lungworm Aelurostrongylus abstrusus (Nematoda, Strongylida). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, R.; Morgan, E.; Shaw, S. A SYBR green real-time PCR assay for the detection of the nematode Angiostrongylus vasorum in definitive and intermediate hosts. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 166, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qvarnstrom, Y.; Sullivan, J.; Bishop, H.; Hollingsworth, R.; Da Silva, A. PCR-Based Detection of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Tissue and Mucus Secretions from Molluscan Hosts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Alonso, A.; Abreu-Yanes, E.; Feliu, C.; Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.D.; Valladares, B.; Foronda, P. Intermediate hosts of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Tenerife, Spain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jezewski, W.; Búnkowska-Gawlik, K.; Hildebrand, J.; Perec-Matysiak, A.; Laskowski, Z. Intermediate and paratenic hosts in the life cycle of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus in natural environment. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eamsobhana, P.; Wanachiwanawin, D.; Dechkum, N.; Parsartvit, A.; Yong, H. Molecular diagnosis of eosinophilic meningitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea) by polymerase chain reaction-DNA sequencing of cerebrospinal fluids of patients. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, A.; Graeff-Teixeira, C.; Zaha, A. Diagnosis of abdominal angiostrongyliasis by PCR from sera of patients. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2003, 45, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.H.; Lan, L.; Wu, F.-F.; Zhang, E.-P.; Song, Z.-M.; Huang, H.-C.; Luo, F.-J.; Pan, C.-W.; Tan, F. In vitro study of the effects of Angiostrongylus cantonensis larvae extracts on apoptosis and dysfunction in the blood-brain barrier (BBB). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Sequence (5′→3′) | Target Gene | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Universal, U1:AaGp28Sa1-R | AGGCATAGTTCACCATCT | Common sequence metastrongyloidea | ~450 bp |
| Universal 2, U2:AaGp28Ss1-F | CGAGTRATATGTATGCCATT | ||
| Specific 1, E1: Aa28Ss2-F | CGTTGATGTTGATGAGTATC | Aelurostrongylus abstrusus | 300 bp |
| Specific 2, E2: Gp28Sa3-R | TCTTGCCGCCATTATAGTA | Gurltia paralysans | 356 bp |
| rDNA specific for feline gene-Forward | AGCAGGAGGTGTTGGAAGAG | rDNA 28S | 100 bp |
| rDNA specific for feline gene-Reverse | AGGGAGAGAGCCTAATTCAAAGG |
| ID | Neurolocation | Neurological Examination | Macroscopic Findings | CSF PCR | Serum PCR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ataxia | Paraplegia | Superficial Pain | Deep Pain | Caudal/Anal Tone | |||||
| A | T3–L3, L4–Cd5 | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | Spinal cord inflammation Subarachnoid venous congestion Spinal cord deformation Presence of intravascular parasites | + | + |
| B | T3–L3, L4–Cd5 | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | Spinal cord inflammation Subarachnoid venous congestion Spinal cord deformation Presence of intravascular parasites | + | + |
| C | T3–L3 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | ND | − | + |
| D | T3–L3, L4–Cd5 | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | Spinal cord inflammation Subarachnoid venous congestion Spinal cord deformation | − | + |
| E | T3–L3, L4–Cd5 | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | Spinal cord inflammation Subarachnoid venous congestion Spinal cord deformation Presence of intravascular parasites | − | + |
| F | T3–L3, L4–Cd5 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | ND | + | + |
| G | T3–L3, L4–Cd5 | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | Spinal inflammation Subarachnoid venous congestion Spinal cord deformation | − | − |
| H | T3–L3, L4–Cd5 | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | Spinal cord inflammation Subarachnoid venous congestion Spinal cord deformation Presence of intravascular parasites | − | − |
| I | T3–L3, L4–Cd5 | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | Spinal cord inflammation Subarachnoid venous congestion Spinal deformation | + | + |
| J | L4–Cd5 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | ND | ND | − |
| K | L4–Cd5 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | ND | ND | − |
| L | L4–Cd5 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | ND | ND | − |
| Sample | Cat | Description | Max. Score | Total Score | Query Coverage | E-Value | % Identity | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSF | B | G. paralysans 18S rRNA gene, partial sequence; ITS 1, 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS 2, complete sequence; and 28S rRNA gene, partial sequence | 292 | 292 | 99% | 2 × 10−75 | 100% | JX975484.2 |
| CSF | F | G. paralysans 18S rRNA gene, partial sequence; ITS 1, 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS 2, complete sequence; and 28S rRNA gene, partial sequence | 468 | 468 | 100% | 6 × 10−128 | 100% | JX975484.2 |
| CSF | I | G. paralysans 18S rRNA gene, partial sequence; ITS 1, 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS 2, complete sequence; and 28S rRNA gene, partial sequence | 333 | 333 | 100% | 1 × 10−87 | 100% | JX975484.2 |
| Serum | A | A. abstrusus 28S rRNA gene | 246 | 246 | 85% | 4 × 10−61 | 96% | AM039759.1 |
| G. paralysans 18S rRNA gene, partial sequence; ITS 1, 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS 2, complete sequence; and 28S rRNA gene, partial sequence | 654 | 654 | 100% | 0 | 100% | JX975484.2 | ||
| Serum | B | G. paralysans 18S rRNA gene, partial sequence; ITS 1, 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS 2, complete sequence; and 28S rRNA gene, partial sequence | 501 | 501 | 100% | 6 × 10−138 | 100% | JX975484.2 |
| A. abstrusus 28S rRNA gene | 564 | 564 | 99% | 9 × 10−157 | 100% | AM039759.1 | ||
| Serum | D | G. paralysans 18S rRNA gene, partial sequence; ITS 1, 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS 2, complete sequence; and 28S rRNA gene, partial sequence | 222 | 222 | 100% | 2 × 10−54 | 100% | JX975484.2 |
| Serum | E | G. paralysans 18S rRNA gene, partial sequence; ITS 1, 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS 2, complete sequence; and 28S rRNA gene, partial sequence | 200 | 200 | 92% | 1 × 10−47 | 96,69% | JX975484.2 |
| A. abstrusus 28S rRNA gene | 176 | 176 | 89% | 1 × 10−47 | 98% | AM039759.1 | ||
| Serum | F | G. paralysans 18S rRNA gene, partial sequence; ITS 1, 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS 2, complete sequence; and 28S rRNA gene, partial sequence | 182 | 182 | 98% | 3 × 10−42 | 100% | JX975484.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Contreras, F.; Rojas-Barón, L.; Gómez, M.; Morera, F.; Sepúlveda, P.; Moroni, M.; Muñoz, P.; Acosta-Jammett, G.; Mieres, M.; Hirzmann, J.; et al. Molecular Detection of Gurltia paralysans by Semi-Nested PCR in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum Samples from Domestic Cats (Felis catus). Animals 2020, 10, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071169
López-Contreras F, Rojas-Barón L, Gómez M, Morera F, Sepúlveda P, Moroni M, Muñoz P, Acosta-Jammett G, Mieres M, Hirzmann J, et al. Molecular Detection of Gurltia paralysans by Semi-Nested PCR in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum Samples from Domestic Cats (Felis catus). Animals. 2020; 10(7):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071169
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Contreras, Freddy, Lisbeth Rojas-Barón, Marcelo Gómez, Francisco Morera, Paulina Sepúlveda, Manuel Moroni, Pamela Muñoz, Gerardo Acosta-Jammett, Marcelo Mieres, Jörg Hirzmann, and et al. 2020. "Molecular Detection of Gurltia paralysans by Semi-Nested PCR in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum Samples from Domestic Cats (Felis catus)" Animals 10, no. 7: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071169
APA StyleLópez-Contreras, F., Rojas-Barón, L., Gómez, M., Morera, F., Sepúlveda, P., Moroni, M., Muñoz, P., Acosta-Jammett, G., Mieres, M., Hirzmann, J., Hermosilla, C., & Taubert, A. (2020). Molecular Detection of Gurltia paralysans by Semi-Nested PCR in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum Samples from Domestic Cats (Felis catus). Animals, 10(7), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071169







