Investigation of the Impacts of Antibiotic Exposure on the Diversity of the Gut Microbiota in Chicks
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics and Approval Statement
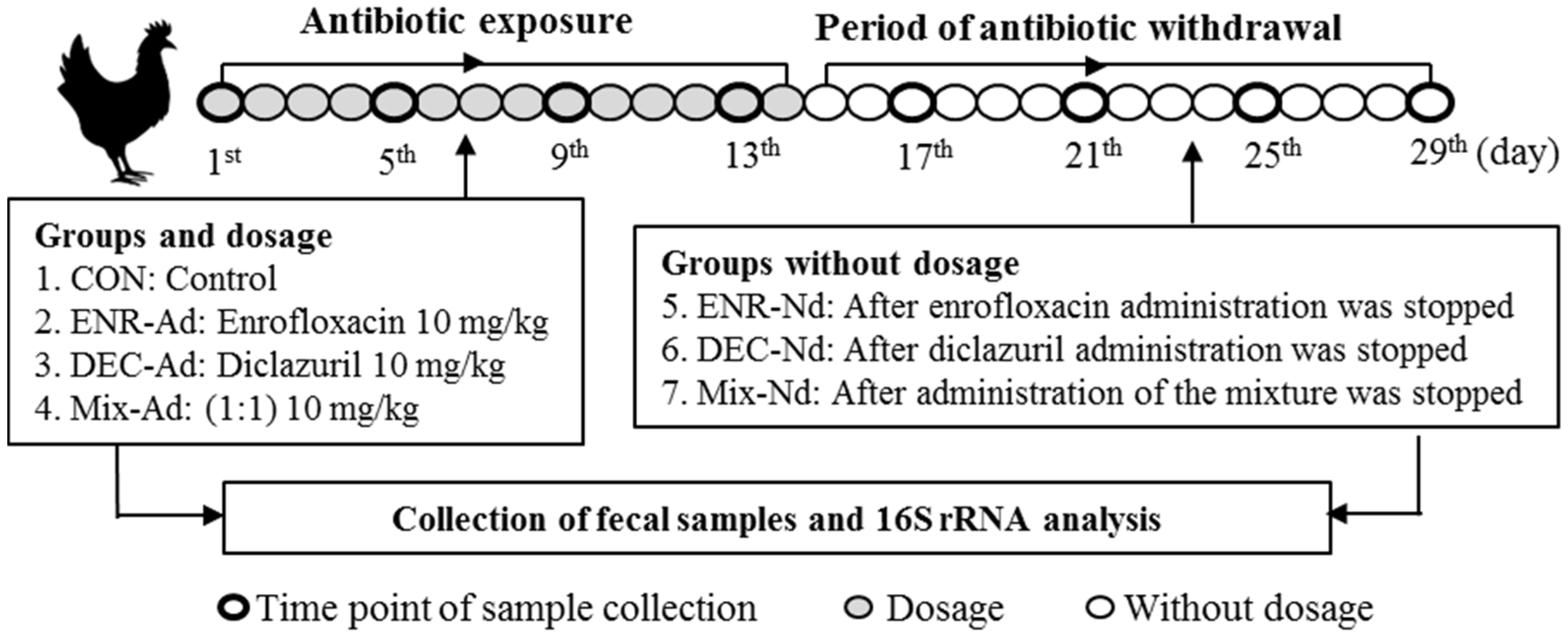
2.2. Experimental Design and Fecal Sample Collection
2.3. Microbial DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and 16S rRNA Analysis
2.4. Sequence Quality and OTU Calculation
2.5. Annotation of Microbial Composition
2.6. Annotation of Microbial Function
2.7. Accession Number
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effective Sequence Quality Assessment
3.2. Impact of Antibiotics on the Microbial Diversity Analysis of Exposed Chicks
3.3. Antibiotic-Exposed Chicks Alter their Gut Microbiota Community Structure
3.4. Microbiota that Associate with Antibiotic-Exposed Chicks
3.5. Comparison of the KEGG Pathways of the Gut Microbiota among Groups of Antibiotic-Exposed Chicks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Philippe, P.; Alzieu, J.P.; Taylor, M.A.; Dorchies, P. Comparative efficacy of diclazuril (Vecoxan ®) and toltrazuril (Baycox bovis ®) against natural infections of Eimeria bovis and Eimeria zuernii in French calves. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 206, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hao, H.; Cheng, G.; Wang, X.; Ahmed, S.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; Liu, Z.; Dai, M.; Yuan, Z. The effects of different enrofloxacin dosages on clinical efficacy and resistance development in chickens experimentally infected with Salmonella Typhimurium. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, C.; Tang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Tang, X.; Suo, J.; Jia, Y.; Saeed, E.A. Influence of Eimeria falciformis Infection on Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Pathways in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00073-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaus, U.G.; Hertzberger, R.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Yousefi, S.P.; Branco, D.S.F. Pathogen control at the intestinal mucosa - H2O2 to the rescue. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, N.; Chen, G.Y.; Inohara, N.; Núñez, G. Control of pathogens and pathobionts by the gut microbiota. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harp, J.A.; Chen, W.; Harmsen, A.G. Resistance of severe combined immunodeficient mice to infection with Cryptosporidium parvum: The importance of intestinal microflora. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 3509–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brestoff, J.R.; Artis, D. Commensal bacteria at the interface of host metabolism and the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.R.; Collins, J.J.; Relman, D.A. Antibiotics and the gut microbiota. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4212–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Cecilia, J.; Andersson, A.F.; Maria, S.L.K.; Jansson, J.K.; Lars, E. Short-term antibiotic treatment has differing long-term impacts on the human throat and gut microbiome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingtao, C.; Jing, Y.; Xu, F.; Hong, W.; Wei, H. Effects of enrofloxacin on the human intestinal microbiota in vitro. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 37, 567–571. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.; Chiller, T.; Powers, J.H.; Angulo, F. Fluoroquinolone-resistant Campylobacter species and the withdrawal of fluoroquinolones from use in poultry: A public health success story. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Banna, H.A.; El-Bahy, M.M.; El-Zorba, H.Y.; El-Hady, M. Anticoccidial efficacy of drinking water soluble diclazuril on experimental and field coccidiosis in broiler chickens. J. Vet. Med. 2010, 52, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schokker, D.; Jansman, A.J.M.; Veninga, G.; Bruin, N.D.; Vastenhouw, S.A.; Bree, F.M.D.; Bossers, A.; Rebel, J.M.J.; Smits, M.A. Perturbation of microbiota in one-day old broiler chickens with antibiotic for 24 hours negatively affects intestinal immune development. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmody, R.; Gerber, G.; Jr, J.L.; Gatti, D.; Somes, L.; Svenson, K.; Turnbaugh, P. Diet Dominates Host Genotype in Shaping the Murine Gut Microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisavljević, S.; Čepić, A.; Bojić, S.; Veljović, K.; Mihajlović, S.; Đedović, N.; Jevtić, B.; Momčilović, M.; Lazarević, M.; Mostarica Stojković, M.; et al. Oral neonatal antibiotic treatment perturbs gut microbiota and aggravates central nervous system autoimmunity in Dark Agouti rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.; Guo, J.; Pu, F.; Wan, C.; Shi, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, M.; He, F. Loading ceftriaxone, vancomycin, and Bifidobacteria bifidum TMC3115 to neonatal mice could differently and consequently affect intestinal microbiota and immunity in adulthood. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, L.V.; Charbonneau, M.R.; Salih, T.; Barratt, M.J.; Venkatesh, S.; Ilkaveya, O.; Subramanian, S.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Jorgensen, J.M. Gut bacteria that prevent growth impairments transmitted by microbiota from malnourished children. Science 2016, 351, aad3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, M.; Mann, J.; Chapman, T.; Thomas, F.; Whitton, C.; Floyd, R.; Abebe, E. Defining operational taxonomic units using DNA barcode data. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Shen, T.-J. Nonparametric prediction in species sampling. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 2004, 9, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alban, R. Multivariate analyses in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 62, 142–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethlefsen, L.; Huse, S.; Sogin, M.L.; Relman, D.A. The Pervasive Effects of an Antibiotic on the Human Gut Microbiota, as Revealed by Deep 16S rRNA Sequencing. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzępa, A.; Majewskaszczepanik, M.; Lobo, F.M.; Wen, L.; Szczepanik, M. Broad spectrum antibiotic enrofloxacin modulates contact sensitivity through gut microbiota in a murine model. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, S0091674917300568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearden, D.T.; Danziger, L.H. Mechanism of action of and resistance to quinolones. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.; Hughes, R.J.; Moore, R.J. Microbiota of the chicken gastrointestinal tract: Influence on health, productivity and disease. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4301–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.R.; Tuohy, K.M.; Peter, L.; Brown, D.T.; Gibson, G.R.; Wilson, I.D.; James, S.; Nicholson, J.K.; Elaine, H. Variation in antibiotic-induced microbial recolonization impacts on the host metabolic phenotypes of rats. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3590–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.H.; Chen, Z.L.; Yun, L.I.; Liu, Y.W. Effects of Low Concentration Enrofloxacin on SPF Mice Intestinal Microflora. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2005, 38, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Su, Y.; Shi, D.; Xiao, H.; Tian, Y. High-throughput sequencing technology to reveal the composition and function of cecal microbiota in Dagu chicken. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Ma, C.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.; Su, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Feed-additive probiotics accelerate yet antibiotics delay intestinal microbiota maturation in broiler chicken. Microbiome 2017, 5, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, L.; Leplae, R.; Summers, A.O.; Toussaint, A. Mobile genetic elements: The agents of open source evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.R.; Lee, H.H.; Spina, C.S.; Collins, J.J. Antibiotic treatment expands the resistance reservoir and ecological network of the phage metagenome. Nature 2013, 499, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Costa, V.M.; King, C.E.; Kalan, L.; Morar, M.; Sung, W.W.L.; Schwarz, C.; Froese, D.; Zazula, G.; Calmels, F.; Debruyne, R.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is ancient. Nature 2011, 477, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Oluwasegun, R.D.; Church, G.M. Bacteria subsisting on antibiotics. Science 2008, 320, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, E.K.; Keaton, S.; Les, D.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Relman, D.A. The application of ecological theory toward an understanding of the human microbiome. Science 2012, 336, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Phulum and Genuse 1 | Enrofloxacin (ENR) | Declazuril (DEC) | Mix 1:1 (MIX) | Control | SEM | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENR.Ad | ENR.Nd | DEC.Ad | DEC.Nd | Mix.Ad | Mix.Nd | CON | |||
| Firmicutes (P) | 76.840 bc | 73.530 c | 64.880 d | 73.530 c | 50.670 f | 78.740 b | 83.980 a | 1.530 | 0.001 |
| Lactobacillus | 1.960 d | 0.580 f | 0.700 e | 2.170 c | 0.200 g | 2.330 b | 5.520 a | 0.020 | 0.001 |
| Lactococcus | 0.030 c | 0.012 b | 0.002 c | 0.003 c | 0.020 d | 0.02 d | 0.087 a | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Enterococcus | 0.300 a | 0.006 f | 0.300 b | 0.031 e | 0.087 c | 0.061 d | 0.009 g | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Ruminococcus | 0.040 b | 0.003 c | 0.037 a | 0.007 c | 0.041 a | 0.005 d | 0.029 b c | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Facklamia | 0.060 c | 0.020 e | 0.160 a | 0.05 d | 0.070 b | 0.010f | 0.001 g | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Arthromitus | 0.391 d | 0.0567 b | 0.774 a | 0.361 e | 0.480 c | 0.174f | 0.178 f | 0.004 | 0.001 |
| Clostridium | 0.005 c | 0.005 c | 0.008 a | 0.007 b | 0.004 c d | 0.003 d | 0.003 d | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Erysipelothrix | 0.179 e | 2.444 a | 0.272 d | 1.850 b | 0.258 d | 1.082 c | 0.183 e | 0.183 | 0.011 |
| Bacteroidetes (P) | 10.870 a | 8.120 b | 4.880 b | 7.720 b | 7.080 b | 7.610 b | 11.770 b | 2.260 | 0.090 |
| S24-7 | 0.014 c | 0.008 e | 0.009 d | 0.019 b | 0.009 d | 0.009 d | 0.078 a | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| F/B ratio | 4.590 b | 12.270 a b | 14.840 a | 13.380 a | 7.090 a b | 6.600 a b | 7.760 a b | 2.450 | 0.050 |
| Actinobacteria (P) | 3.970 c | 2.950 d | 3.880 c | 3.690 c | 1.860 e | 4.440 b | 9.910 a | 0.140 | 0.001 |
| Corynebacterium | 0.023 d | 0.007 e | 0.031 c | 0.008 e | 0.002f | 0.310 a | 0.087 b | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Arthrobacter | 0.0290 c | 0.0140 d | 0.0760 b | 0.0120 e | 0.107 a | 0.008f | 0.001 g | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| Bifidobacterium | 0.008 b | 0.006 c | 0.006 c | 0.009 d | 0.006 b | 0.008 b | 0.001 e | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Proteobacteria (P) | 4.130 b | 4.240 b | 5.430 a | 5.810 a | 4.340 b | 1.510 c | 0.330 d | 1.350 | 0.040 |
| Sphingobium | 0.112 b | 0.023 c | 0.097 b | 0.077 d | 3.871 a | 0.012 c | 0.003 e | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Pseudomonas | 0.259 b | 0.025 e | 0.13 b | 0.074 c | 0.339 a | 0.040 d | 0.003 g | 0.000 | 0.050 |
| Acinetobacter | 0.352 b | 0.028 c | 1.030 a | 0.348 b | 0.022 c d | 0.0130 d | 0.016 d | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| Cyanobacteria (P) | 0.960 a | 0.560 b | 0.970 a | 0.030f | 0.210 d | 0.340 c | 0.103 e | 0.006 | 0.020 |
| MLE1-12 | 0.008 b | 0.008 b | 0.009 a | 0.001 c | 0.008 b | 0.008 b | 0.008 b | 0.001 | 0.050 |
| Streptophyta | 0.103 a | 0.062 c | 0.101 b | 0.004 g | 0.009 e | 0.036 d | 0.007 f | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Chloroflexi (P) | 0.004 c | 0.004 c | 0.289 a | 0.005 c | 0.003 c | 0.103 b | 0.007 c | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| CFB-26 | 0.009 c | 0.008 e | 0.009 c | 0.008 d | 0.013 a | 0.011 b | 0.005 f | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| JG30-KF-CM45 | 0.012 f | 0.017 e | 0.031 b | 0.033 a | 0.021 d | 0.028 c | 0.006 g | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| Deferribacteres (P) | 0.046 b | 0.045 b | 0.046 b | 0.046 b | 0.047 b | 0.045 b | 0.07 a | 0.005 | 0.051 |
| Schaedleri | 0.008 c | 0.008 d | 0.011 b | 0.006 f | 0.013 a | 0.007 e | 0.008 d | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Fusobacteria (P) | 0.484 c | 0.007 d | 0.001 d | 1.309 b | 0.004 d | 1.926 a | 0.004 d | 0.020 | 0.001 |
| Fusobacterium | 0.051 c | 0.003 f | 0.002 f | 0.138 b | 0.017 d | 0.204 a | 0.007 e | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Tenericutes (P) | 0.498 a | 0.002 g | 0.263 b | 0.043 e | 0.149 d | 0.025 f | 0.190 c | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| RF39 | 0.055 a | 0.002 g | 0.026 b | 0.005 e | 0.016 d | 0.002 f | 0.021 c | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Verrucomicrobia (P) | 0.001 b | 0.001 b | 0.004 b | 0.005 b | 0.005 b | 0.004 b | 0.159 a | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| muciniphila | 0.006 b | 0.007 b | 0.002 d | 0.004 c | 0.002 d | 0.003 c | 0.016 a | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Thermi (P) | 0.060 b | 0.034 c | 0.029 d | 0.027 de | 0.024 e | 0.025 e | 0.127 a | 0.001 | 0.050 |
| Thermus | 0.006 b | 0.003 c | 0.003 c | 0.002 d | 0.002 d | 0.002 d | 0.011 a | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Alpha Diversity Index | Enrofloxacin (ENR) | Declazuril (DEC) | Mix 1:1 (MIX) | Control | SEM | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENR-Ad | ENR-Nd | DEC-Ad | DEC-Nd | MIX-Ad | MIX-Nd | CON | |||
| Observed OTUs | 6285.00 a | 4527.25 b | 6302.75 a | 6030.75 a | 4413.50 b | 5451.50 ab | 4115.41 b | 275.54 | 0.001 |
| Simpson | 0.94 a | 0.91 a | 0.96 a | 0.94 a | 0.80 b | 0.94 a | 0.94 a | 0.020 | 0.039 |
| Chao1 | 1516.94 a | 1055.91 cd | 1511.53 a | 1447.44 ab | 1140.58 bcd | 1319.29 abc | 925.53 d | 69.70 | 0.001 |
| ACE | 1579.58 a | 1071.84 bc | 1554.66 a | 1483.48 a | 1166.55 bc | 1331.12 ab | 935.19 d | 70.18 | 0.001 |
| Shannon | 7.24 a | 6.41 ab | 7.64 a | 7.05 a | 5.43 a | 6.87 b | 6.65 ab | 0.270 | 0.048 |
| Categories and Levels of KEGG Pathways 1 | The Relative Abundance for Predicting of Functional Microbiome (%) | SEM | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENR-Ad | ENR-Nd | DEC-Ad | DEC-Nd | MIX-Ad | MIX-Nd | CON | |||
| Cellular Processes | |||||||||
| Cell growth and death | 0.51 b | 0.46 b | 0.51 b | 0.48 b | 0.64 a | 0.46 b | 0.45 b | 0.032 | 0.003 |
| Cell motility | 2.63 bc | 3.69 a | 2.38 bc | 2.72 bc | 3.18 ab | 3.01 b | 1.97 c | 0.037 | 0.002 |
| Transport and catabolism | 0.19 b | 0.21 ab | 0.25 ab | 0.23 ab | 0.28 ab | 0.19 b | 0.29 a | 0.028 | 0.023 |
| Environmental Information Processing | |||||||||
| Membrane transport | 13.49 a | 12.97 a | 12.74 ab | 12.6 ab | 11.06 a | 12.79 ab | 13.73 a | 0.082 | 0.074 |
| Signaling molecules and interaction | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.016 | 0.973 |
| Signal transduction | 1.69 | 2.06 | 1.82 | 1.89 | 2.02 | 1.94 | 1.64 | 0.146 | 0.132 |
| Genetic Information Processing | |||||||||
| Folding, sorting, and degradation | 2.33 ab | 2.32 ab | 2.32 ab | 2.36 a | 2.21 a | 2.25 ab | 2.34 ab | 0.043 | 0.041 |
| DNA replication and repair | 8.36 a | 8.04 b | 7.99 bc | 8.34 ab | 7.89 b | 8.35 a | 6.92 c | 0.348 | 0.021 |
| Transcription | 2.86 | 2.74 | 2.68 | 2.71 | 2.74 | 2.91 | 2.76 | 0.094 | 0.601 |
| Translation | 5.41 ab | 5.16 ab | 5.17 ab | 5.37 ab | 4.73 b | 5.33 ab | 5.69 a | 0.283 | 0.035 |
| Immune Information Processing | |||||||||
| Immune system diseases | 0.06 a | 0.05 a | 0.05 a | 0.06 a | 0.04 b | 0.05 ab | 0.06 a | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| Infectious diseases | 0.42 a | 0.44 a | 0.41 ab | 0.43 a | 0.47 a | 0.44 a | 0.4 b | 0.021 | 0.049 |
| Metabolic diseases | 0.09 ab | 0.09 b | 0.08 b | 0.08 b | 0.08 b | 0.09 ab | 0.11 a | 0.006 | 0.002 |
| Neurodegenerative diseases | 0.17 b | 0.22 b | 0.23 b | 0.22 b | 0.44 a | 0.17 b | 0.16 b | 0.050 | 0.004 |
| Metabolism Processing | |||||||||
| Amino acid metabolism | 9.56 ab | 9.91 ab | 9.95 ab | 9.74 ab | 10.49 a | 9.30 b | 9.35 b | 0.364 | 0.043 |
| Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 0.81 b | 0.78 b | 0.77 b | 0.73 b | 0.96 a | 0.76 b | 0.79 b | 0.040 | 0.012 |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | 10.53 ab | 9.73 c | 10.38 abc | 9.98 bc | 10.4 abc | 10.17 bc | 10.92 a | 0.244 | 0.003 |
| Energy metabolism | 5.35 ab | 5.3a b | 5.36 ab | 5.27 ab | 5.55 a | 5.17 b | 5.41 ab | 0.094 | 0.061 |
| Enzyme families | 2.13 | 2.03 | 1.96 | 2.01 | 2.01 | 2.11 | 2.15 | 0.069 | 0.199 |
| Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism | 1.55 b | 1.55 b | 1.66 ab | 1.68 ab | 1.41 b | 1.56 b | 1.92 a | 0.110 | 0.005 |
| Lipid metabolism | 3.07 b | 3.2 ab | 3.5 ab | 3.41 a b | 3.63 a | 3.03 b | 3.14 ab | 0.168 | 0.089 |
| Cofactors and vitamins | 4.00 | 4.05 | 3.93 | 3.92 | 4.08 | 3.98 | 3.97 | 0.120 | 0.953 |
| Other amino acids | 1.67 ab | 1.67 ab | 1.78 ab | 1.71 ab | 1.93 a | 1.61 b | 1.62 b | 0.086 | 0.025 |
| Terpenoids and polyketides | 1.86 ab | 1.85 ab | 2.06 a | 1.99 ab | 2.09 a | 1.74 b | 1.75 b | 0.097 | 0.028 |
| Nucleotide metabolism | 3.95 a b | 3.71 b | 3.67 b | 3.88 a b | 3.42 b | 3.87 a b | 4.26 a | 0.171 | 0.005 |
| Xenobiotic biodegradation | 3.62 a | 3.63 a | 3.28 b | 3.01 c | 3.03 c | 2.42 d | 2.49 cd | 0.302 | 0.047 |
| Organismal Systems | |||||||||
| Circulatory system | 0.01 b | 0.02 ab | 0.02 b | 0.02 b | 0.04 a | 0.01 b | 0.01 b | 0.007 | 0.018 |
| Digestive system | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.005 | 0.139 |
| Endocrine system | 0.25 b | 0.25 b | 0.30 b | 0.25 b | 0.4 a | 0.23 b | 0.26 b | 0.032 | 0.015 |
| Excretory system | 0.04 ab | 0.03 ab | 0.03 ab | 0.04 a | 0.03 b | 0.03 ab | 0.03 ab | 0.004 | 0.032 |
| Immune system | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.007 | 0.609 |
| Nervous system | 0.09 b | 0.09 ab | 0.08 b | 0.09 b | 0.08 b | 0.09 b | 0.11 b | 0.005 | 0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elokil, A.A.; Abouelezz, K.F.M.; Ahmad, H.I.; Pan, Y.; Li, S. Investigation of the Impacts of Antibiotic Exposure on the Diversity of the Gut Microbiota in Chicks. Animals 2020, 10, 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050896
Elokil AA, Abouelezz KFM, Ahmad HI, Pan Y, Li S. Investigation of the Impacts of Antibiotic Exposure on the Diversity of the Gut Microbiota in Chicks. Animals. 2020; 10(5):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050896
Chicago/Turabian StyleElokil, Abdelmotaleb A., Khaled F.M. Abouelezz, Hafiz I. Ahmad, Yuanhu Pan, and Shijun Li. 2020. "Investigation of the Impacts of Antibiotic Exposure on the Diversity of the Gut Microbiota in Chicks" Animals 10, no. 5: 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050896
APA StyleElokil, A. A., Abouelezz, K. F. M., Ahmad, H. I., Pan, Y., & Li, S. (2020). Investigation of the Impacts of Antibiotic Exposure on the Diversity of the Gut Microbiota in Chicks. Animals, 10(5), 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050896





