Correlation Analysis between AK1 mRNA Expression and Inosine Monophosphate Deposition in Jingyuan Chickens
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Material
2.2. Determination of Inosine and IMP Content
2.3. Screening of the Differential Expression of AK1
2.4. Protein Network Analysis of AK1
2.5. Extraction and Reverse Transcription of Total RNA
2.6. Primer Design
2.7. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR
2.8. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Determination of Inosine and IMP Content
3.2. Screening of the AK1 Gene in Transcriptome Data
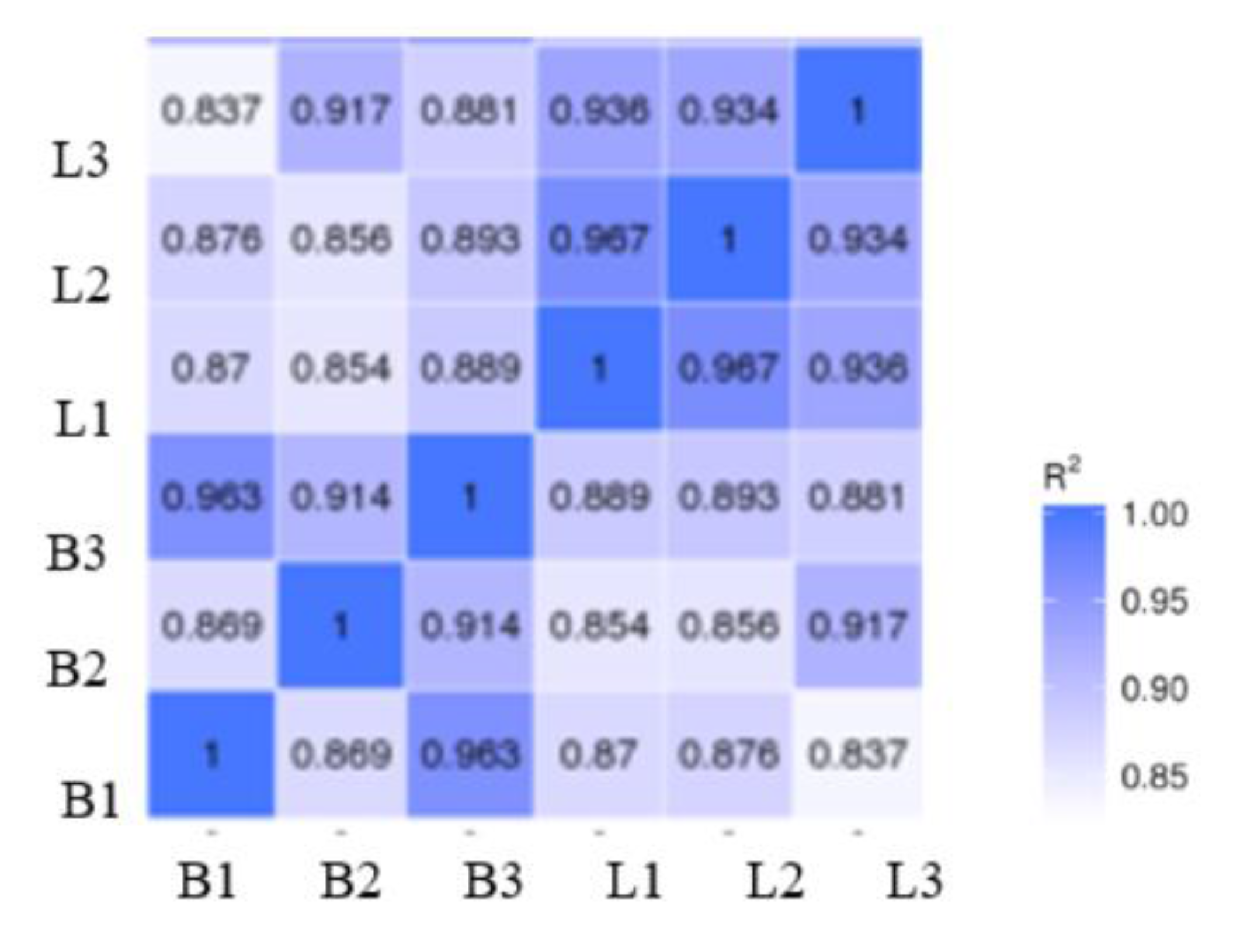
3.2.1. RNA-Seq Correlation Analysis
3.2.2. AK1 Gene Screening
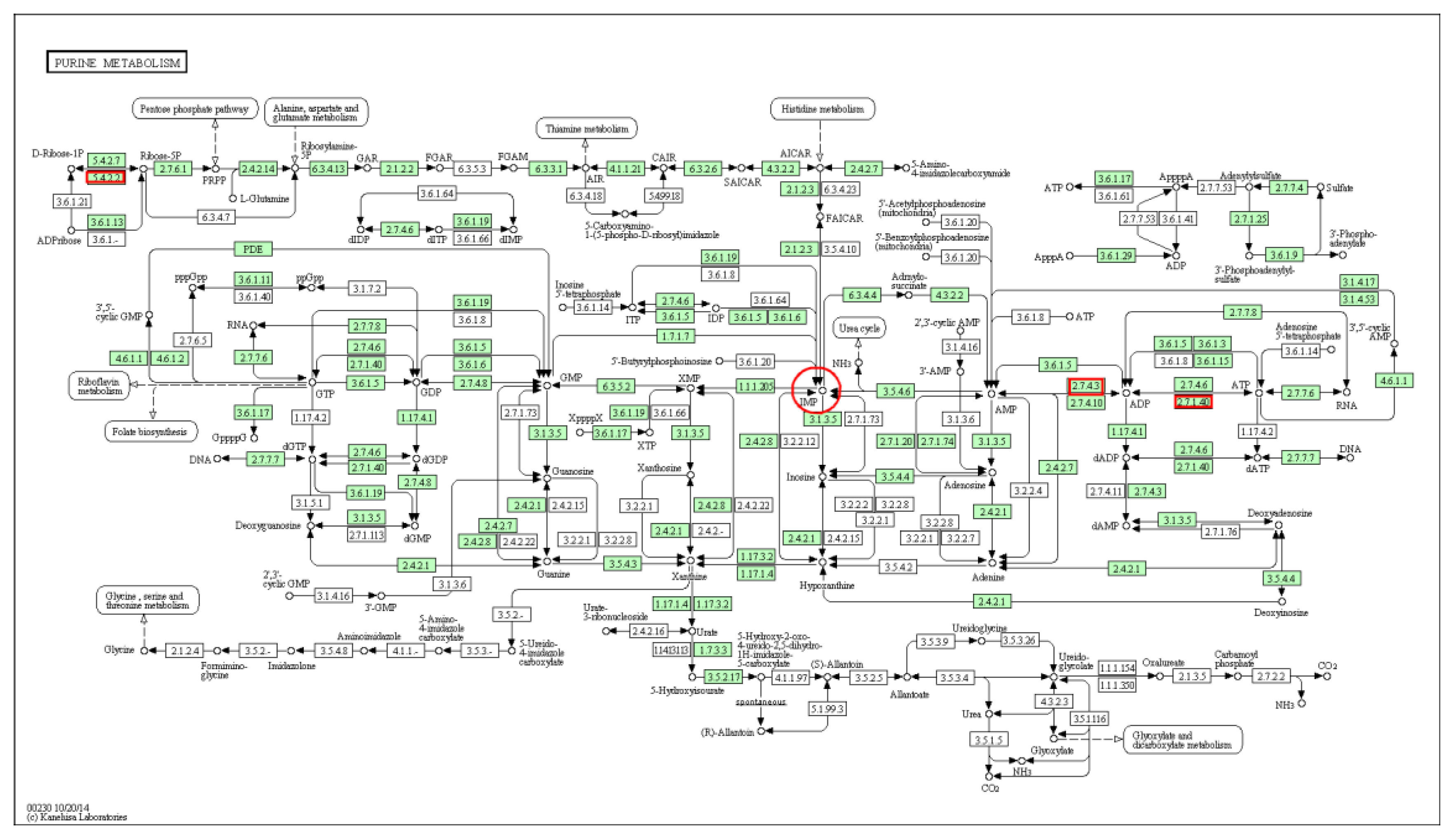
3.2.3. Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analysis of AK1
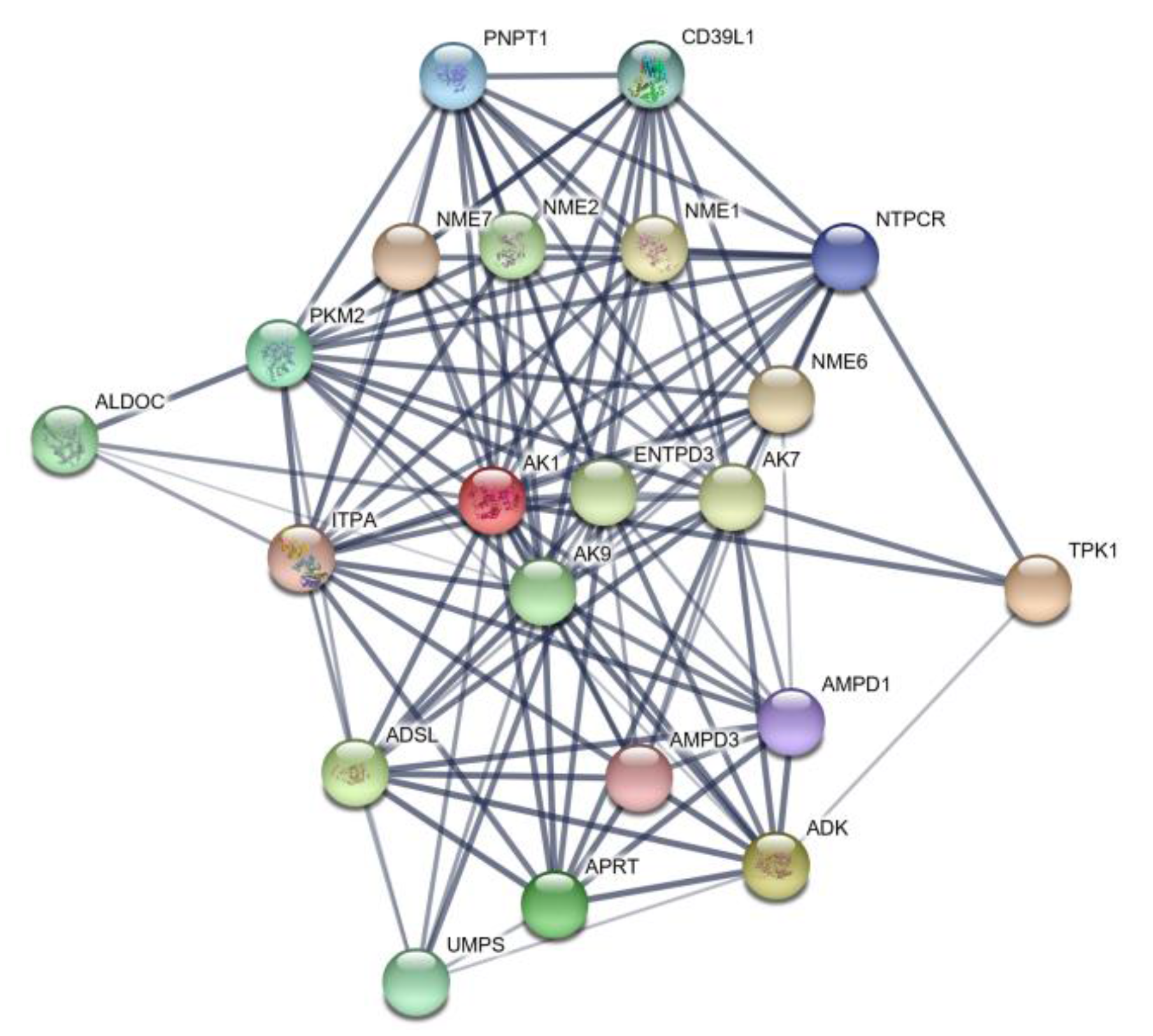
3.2.4. Protein Network Analysis of AK1
3.3. qRT-PCR Amplification Product Specificity Analysis
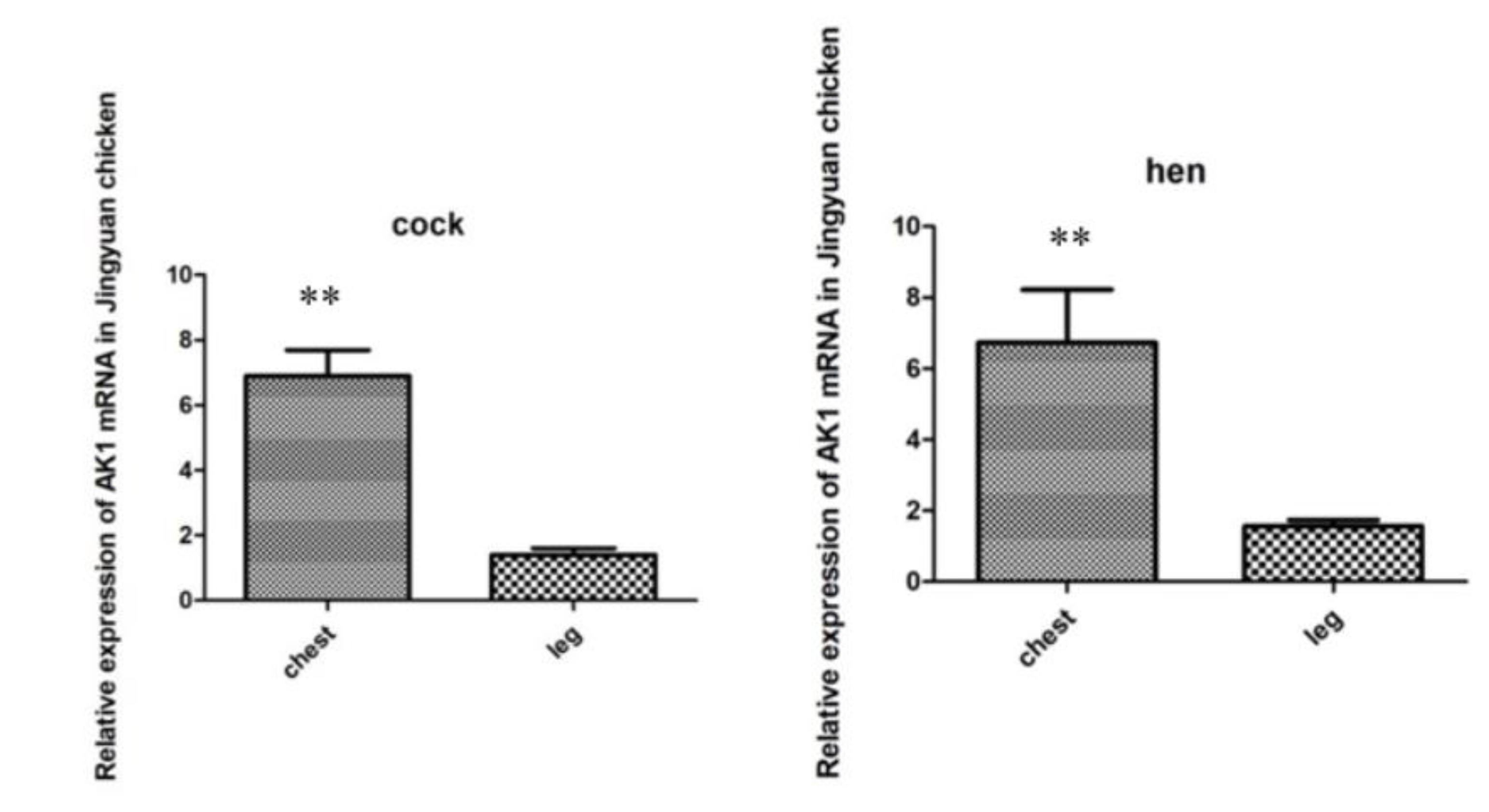
3.4. mRNA Expression of the AK1 Gene in the Breast and Leg Muscles of Jingyuan Chickens
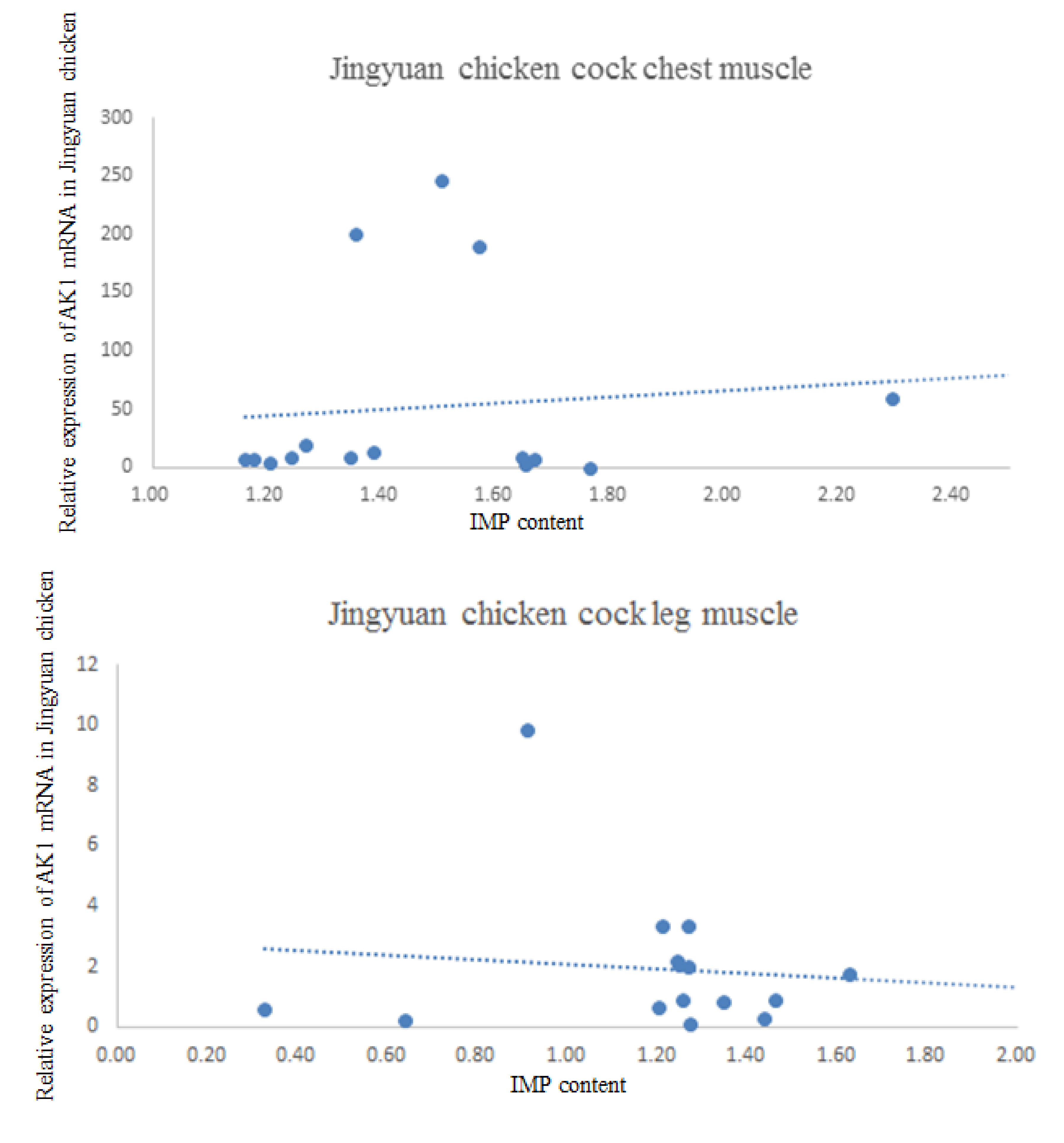
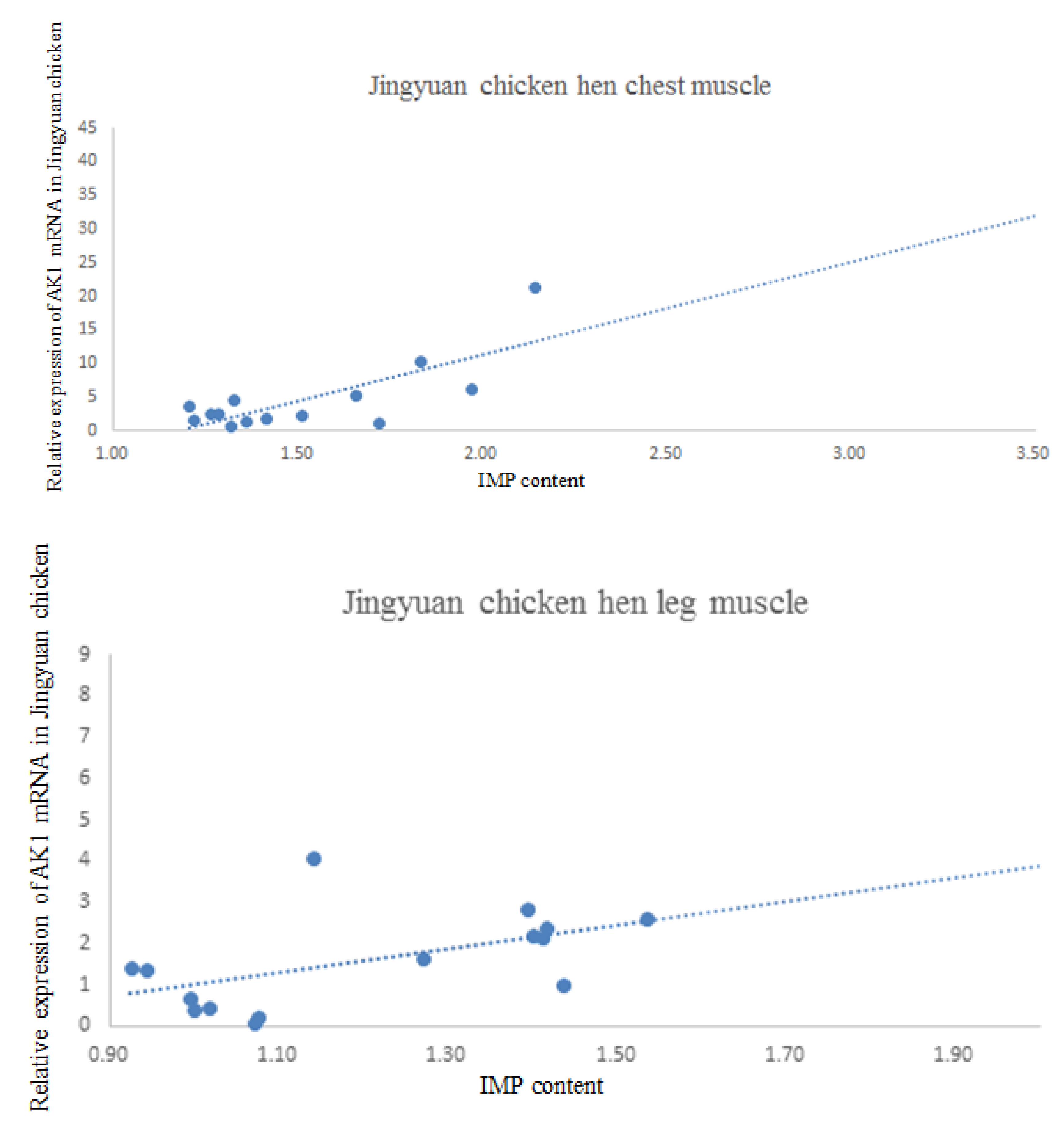
3.5. Correlation between AK1 mRNA Expression and IMP Content in the Breast and Leg Muscles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dou, T.F.; Wang, S.R.; Tong, H.Q.; Liu, L.X.; Gu, D.H.; Xu, Z.Q.; Li, Q.H.; Jia, J.J.; Ge, C.R. Study oninosinic acid content and ADSL gene expression in Wuding chicken and Daweishan mini chicken. China Poult. 2017, 39, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, C.D.; Russell, S.M.; Fletcher, D.L. The relationship of broiler breast meat color and pH to shelf-life and odor development. Poult. Sci. 1997, 76, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Q.; Chen, G.H. Main factors affecting chicken quality. Chin. Poult. 2002, 24, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena, D.D.; Ahn, D.U.; Nam, K.C.; Jo, C. Flavour chemistry of chicken meat: A review. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Nakashima, K.; Ishida, A.; Ashihara, A.; Katsumata, M. Effects of low protein diet and low protein diet supplemented with synthetic essential amino acids on meat quality of broiler chickens. Anim. Sci. J. 2013, 84, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Motoyama, M.; Mitsumoto, M. Changes in the amounts of water-soluble umami-related substances in porcine longissimus and biceps femoris muscles during moist heat cooking. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masic, U.; Yeomans, M.R. Umami flavor enhances appetite but also increases satiety. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narukawa, M.; Morita, K.; Hayashi, Y. L-Theanineelicits an umami taste with inosine 5′-monophosphate. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 3015–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.N.; Homma, A.; Fukuda, T. Effect of high pressure treatment on the flavor-related components. Meat Sci. 1994, 37, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuijmura, S. Identification of tastractive components in the meat of the Japanese native chicken, Hinaidori and broilers and the effect of feeding treatments on tastractive component. Anim. Food Sci. 1998, 50, 99–158. [Google Scholar]
- Davidek, J.; Khan, A.W. Estimation of inosinic acid in chicken muscle and its formation and degradation during postmortem aging. J. Food Sci. 1967, 32, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.W.; Davidek, J.; Lentz, C. Degradation of inosinic acid in chicken muscle during a septics to rage and its possible use as an index of quality. J. Food Sci. 1968, 33, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Wen, J.; Chen, J.L.; Zhen, M.Q. The effect of strain and age on the contents of taste compounds and aroma precursors. Poult. Meat 2003, 34, 548–553. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.S.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Yang, Q.; Li, D.Y.; Wu, H.L.; Yi, H.D.; Shu, G.; Liu, Y.P.; Jiang, X.S.; Zhao, X. Analysis of intramuscular fat and inosine monophosphate content in different strains chickens. China Anim. Husb. Vet. 2011, 38, 230–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zeleznikar, R.J.; Heyman, R.A.; Graeff, R.M.; Walseth, T.F.; Dawis, S.M.; Butz, E.A.; Goldberg, N.D. Evidence for compartmentalized adenylate kinase catalysis serving a high energy phosphoryl transfer function in rat skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 300–311. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rompay, A.R.; Johansson, M.; Karlsson, A. Phosphorylation of nucleosides and nucleoside analogs by mammalian nucleoside monophosphate kinases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 87, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suminami, Y.; Kishi, F.; Torigoe, T. Structure and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding chicken cytosolic adenylate kinase. J. Biochem. 1988, 103, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, T.; Yamada, M.; Noma, T.; Kajii, T.; Nakazawa, A. Tissue-Specific and developmentally regulated expression of the genes encoding adenylate kinase isozymes. J. Biochem. 1993, 113, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Kwon, O.B. Secretion of adenylate kinase 1 is required for extracellular ATP synthesis in C2C12 myotubes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2008, 40, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.J. Problems and countermeasures on the development of chicken industry in Pengyang county. Anim. Breed. Feed 2011, 10, 59–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Mu, T.; Zhao, P.; Chen, J.P.; Feng, X.F.; Guo, P.; Wu, Z.W.; Liu, L.Y.; Jiang, Q.F.; Gu, Y.L. Polymorphism of ELOVL5 gene in Jingyuan chicken. Zhejiang Nongye Xuebao Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2019, 31, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Li, W.Y.; Xie, M. Determination of inosine acid in animal muscles by HPLC, Shipin Kexue. Food Sci. 2005, 26, 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Huo, K.K.; Zhang, T.; Lu, H.C. Comparison of muscle inosinic acid content between Lueyang black chicken and Liangfeng flower chicken. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 195–197. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.W.; Wang, H.; Ren, B.B.; Jiang, L.; Wang, K.H.; Xiong, Y.L.; Xu, Y.O. Comparative analysis of inosine acid and intramuscular fat content in some local chicken breeds in Sichuan. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2014, 42, 218–221. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.G.; Tong, H.Q.; Li, Q.H.; Jia, J.J.; Liu, L.X.; Ge, C.R. Comparative analysis of muscle inosine content in Wuding chicken and Daweishan miniature chicken. Chin. Poult. 2018, 40, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.J.; Zhu, N.H.; Zhang, R.J. Effect of variety, age and feeding mode on Inosine acid and intramuscular fat content in chicken. J. Anim. Nutr. 2010, 22, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L. Changes of inosine content in muscle of Lueyang black chickens of different ages. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 277–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.Q.; Du, B.W.; Li, D.H.; Li, N.B.; Yang, F.X. Comparison of IMP content and related gene expression at different time in Yellow Broilers. Food Ferment. Ind. 2015, 41, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.L.; Wen, J.; Wang, S.B.; Zhao, G.P.; Zhen, M.Q.; Li, X. Studies on the characteristics of deposition of chicken IMP and IMF. J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2005, 36, 843–845. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Studies on Biochemical and Molecular Mechanism of Intramuscular Fat and Inosinic-5 & Apos-Monophosphate Contents in Chicken Meat; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.Y.; Zhu, L.F.; Weng, Z.F.; Shen, H. A comparative study of inosinic acid contents in chicken muscle. China Agric. Sci. 1980, 04, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.F.; Huang, M.N. Comparison of Inosinic acid content in different types of chicken breast. In Proceedings of Selection and Matching of High Quality Yellow Feather Broiler Strains; Institute of Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China; Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1995; pp. 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.F.; Chen, K.W. Comparison of Inosinic acid and fatty acid contents of muscle in different chicken. J. Yangzhou Univ. 2004, 3, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, C.R.; Janssen, E.; Terjung, R.L. Skeletal muscle contractile performance and ADP accumulation in adenylate kinase-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005, 288, C1287–C1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucar, D.; Bast, P.; Gumina, R.J.; Lim, L.; Drahl, C.; Juranic, N. Adenylate kinase AK1 knockout heart: Energetics and functional performance under ischemia-reperfusion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 283, H776–H782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrasco, A.J.; Dzeja, P.P.; Alekseev, A.E.; Pucar, D.; Zingman, L.V.; Abraham, M.R.; Hodgson, D.; Bienengraeber, M.; Puceat, M.; Janssen, E.; et al. Adenylate kinase phosphotransfer communicates cellular energetic signals to ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7623–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.J. Screening of Differentially Expressed Genes in the Longissimusdorsi Muscles of the Wannanhua Pig and the Yorkshire Pig Based on RNA-Seq Technology. Thesis for Master’s, Anhui Agricultural University, Anhui, China, 2015; pp. 34–35. [Google Scholar]



| Gene | Accession Number | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK1 | M37901 | F: GGCTACCGAACCCGTCAT | 185 |
| R: TAAGGCCACTTCCGCTGT | |||
| β-actin | L08165 | F: ATATTGCTGCGCTCGTTGT | 191 |
| R: CAGGGTCAGGATACCTCTTTT |
| Step | Time | Temperature | Ramp Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCR initial heat activation | 2 min | 95 °C | Maximal/fast mode |
| Denaturation | 5 s | 95 °C | Maximal/fast mode |
| Combined annealing/extension | 10 s | 56.9 °C | Maximal/fast mode |
| Number of cycles | 42 | ||
| Melting curve | 0.05 s | 60 to 90 °C | Increment 0.5 °C |
| Gender | Tissue | IMP Content (g/kg) | Inosine Content (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cock | Breast | 1.484 ± 0.298 a | 0.359 ± 0.079 A |
| Leg | 1.179 ± 0.329 b | 0.181 ± 0.096 B | |
| Leg + breast | 1.287 ± 0.247 | 0.270 ± 0.066 | |
| Hen | Breast | 1.525 ± 0.294 A | 0.327 ± 0.067 A |
| Leg | 1.200 ± 0.213 B | 0.181 ± 0.063 B | |
| Leg + breast | 1.362 ± 0.157 | 0.254 ± 0.035 |
| Term | Sample Number | Background Number | p-Value | Corrected p-Value | UniGenes | KO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purine metabolism | 3 | 148 | 0.769096085 | 0.993035152 | ENSGALG00000001992 ENSGALG00000011016 ENSGALG00000029150 * | gga:396456 gga:424691 gga:396002 * |
| Molecular Function (GO) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO Accession | Description | Term Type | Over-Represented | Corrected | DEG Item | DEG List |
| p-Value | p-Value | |||||
| GO:0016301 | kinase activity | molecular_function | 0.000506 | 0.16646 | 145 | 1683 |
| GO:0043167 | ion binding | molecular_function | 0.004572 | 0.46911 | 564 | 1683 |
| GO:0003824 | catalytic activity | molecular_function | 0.004688 | 0.46911 | 755 | 1683 |
| GO:0016787 | hydrolase activity | molecular_function | 0.009348 | 0.59761 | 370 | 1683 |
| GO:0043168 | anion binding | molecular_function | 0.010458 | 0.62516 | 273 | 1683 |
| GO:0016772 | transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups | molecular_function | 0.033078 | 0.91083 | 182 | 1683 |
| GO:0001882 | nucleoside binding | molecular_function | 0.035078 | 0.91083 | 226 | 1683 |
| GO:0016740 | transferase activity | molecular_function | 0.042141 | 0.97629 | 312 | 1683 |
| GO:0035639 | purine ribonucleoside triphosphate binding | molecular_function | 0.043127 | 0.97629 | 224 | 1683 |
| GO:0001883 | purine nucleoside binding | molecular_function | 0.045535 | 0.98066 | 224 | 1683 |
| GO:0032549 | ribonucleoside binding | molecular_function | 0.045535 | 0.98066 | 224 | 1683 |
| GO:0032550 | purine ribonucleoside binding | molecular_function | 0.045535 | 0.98066 | 224 | 1683 |
| GO:0032555 | purine ribonucleotide binding | molecular_function | 0.048628 | 0.98066 | 224 | 1683 |
| GO:0000166 | nucleotide binding | molecular_function | 0.049591 | 0.98066 | 256 | 1683 |
| GO:1901265 | nucleoside phosphate binding | molecular_function | 0.049591 | 0.98066 | 256 | 1683 |
| GO:0017076 | purine nucleotide binding | molecular_function | 0.052362 | 0.99569 | 226 | 1683 |
| GO:0036094 | small molecule binding | molecular_function | 0.052961 | 0.99569 | 260 | 1683 |
| GO:0032553 | ribonucleotide binding | molecular_function | 0.061359 | 1 | 225 | 1683 |
| GO:0005524 | ATP binding | molecular_function | 0.086411 | 1 | 194 | 1683 |
| GO:0032559 | adenyl ribonucleotide binding | molecular_function | 0.09077 | 1 | 194 | 1683 |
| GO:0030554 | adenyl nucleotide binding | molecular_function | 0.095447 | 1 | 196 | 1683 |
| GO:0005488 | binding | molecular_function | 0.10168 | 1 | 1139 | 1683 |
| GO:0097367 | carbohydrate derivative binding | molecular_function | 0.10857 | 1 | 232 | 1683 |
| GO:0016817 | hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides | molecular_function | 0.13552 | 1 | 117 | 1683 |
| GO:0097159 | organic cyclic compound binding | molecular_function | 0.22511 | 1 | 516 | 1683 |
| GO:1901363 | heterocyclic compound binding | molecular_function | 0.22511 | 1 | 516 | 1683 |
| GO:0016462 | pyrophosphatase activity | molecular_function | 0.31183 | 1 | 97 | 1683 |
| GO:0043531 | ADP binding | molecular_function | 0.33714 | 1 | 6 | 1683 |
| GO:0003674 | molecular function | molecular_function | 0.3384 | 1 | 1509 | 1683 |
| GO:0017111 | nucleoside-triphosphatase activity | molecular_function | 0.34628 | 1 | 95 | 1683 |
| GO:0016818 | hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, in | molecular_function | 0.39208 | 1 | 99 | 1683 |
| phosphorus-containing anhydrides | ||||||
| GO:0004127 | cytidylate kinase activity | molecular_function | 0.57225 | 1 | 2 | 1683 |
| GO:0019205 | nucleobase-containing compound kinase activity | molecular_function | 0.57356 | 1 | 8 | 1683 |
| GO:0019201 | nucleotide kinase activity | molecular_function | 0.59085 | 1 | 6 | 1683 |
| GO:0016887 | ATPase activity | molecular_function | 0.86048 | 1 | 38 | 1683 |
| Biological Process (GO) | ||||||
| GO:0044238 | primary metabolic process | biological_process | 0.0046851 | 0.46911 | 696 | 1683 |
| GO:0071704 | organic substance metabolic process | biological_process | 0.0075438 | 0.56007 | 723 | 1683 |
| GO:0008152 | metabolic process | biological_process | 0.034676 | 0.91083 | 828 | 1683 |
| GO:0044237 | cellular metabolic process | biological_process | 0.047786 | 0.98066 | 652 | 1683 |
| GO:0046483 | heterocycle metabolic process | biological_process | 0.18179 | 1 | 392 | 1683 |
| GO:1901360 | organic cyclic compound metabolic process | biological_process | 0.20756 | 1 | 395 | 1683 |
| GO:0006725 | cellular aromatic compound metabolic process | biological_process | 0.26552 | 1 | 387 | 1683 |
| GO:0034641 | cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process | biological_process | 0.30598 | 1 | 424 | 1683 |
| GO:0006139 | nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process | biological_process | 0.31487 | 1 | 368 | 1683 |
| GO:0006807 | nitrogen compound metabolic process | biological_process | 0.32063 | 1 | 447 | 1683 |
| GO:0008150 | biological process | biological_process | 0.54104 | 1 | 1216 | 1683 |
| GO:0009987 | cellular process | biological_process | 0.76378 | 1 | 937 | 1683 |
| Gender | Tissue | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| Cock | Breast IMP | −0.404 |
| Leg IMP | 0.271 | |
| Hen | Breast IMP | 0.534 |
| Leg IMP | 0.538 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Hu, H.; Mu, T.; Wang, W.; Yu, B.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Z.; et al. Correlation Analysis between AK1 mRNA Expression and Inosine Monophosphate Deposition in Jingyuan Chickens. Animals 2020, 10, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030439
Zhang J, Hu H, Mu T, Wang W, Yu B, Guo J, Wang Y, Zhou Z, Gu Y, Huang Z, et al. Correlation Analysis between AK1 mRNA Expression and Inosine Monophosphate Deposition in Jingyuan Chickens. Animals. 2020; 10(3):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030439
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Juan, Honghong Hu, Tong Mu, Weizhen Wang, Baojun Yu, Ju Guo, Ying Wang, Zihang Zhou, Yaling Gu, Zengwen Huang, and et al. 2020. "Correlation Analysis between AK1 mRNA Expression and Inosine Monophosphate Deposition in Jingyuan Chickens" Animals 10, no. 3: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030439
APA StyleZhang, J., Hu, H., Mu, T., Wang, W., Yu, B., Guo, J., Wang, Y., Zhou, Z., Gu, Y., Huang, Z., Cai, Z., & Xin, G. (2020). Correlation Analysis between AK1 mRNA Expression and Inosine Monophosphate Deposition in Jingyuan Chickens. Animals, 10(3), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030439





