Capture Myopathy and Stress Cardiomyopathy in a Live-Stranded Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in Rehabilitation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Evidence of Ethical Approval
2.2. Biochemical Analysis
2.3. Gross, Histological, Histochemical and Immuznohistochemical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biochemical Results
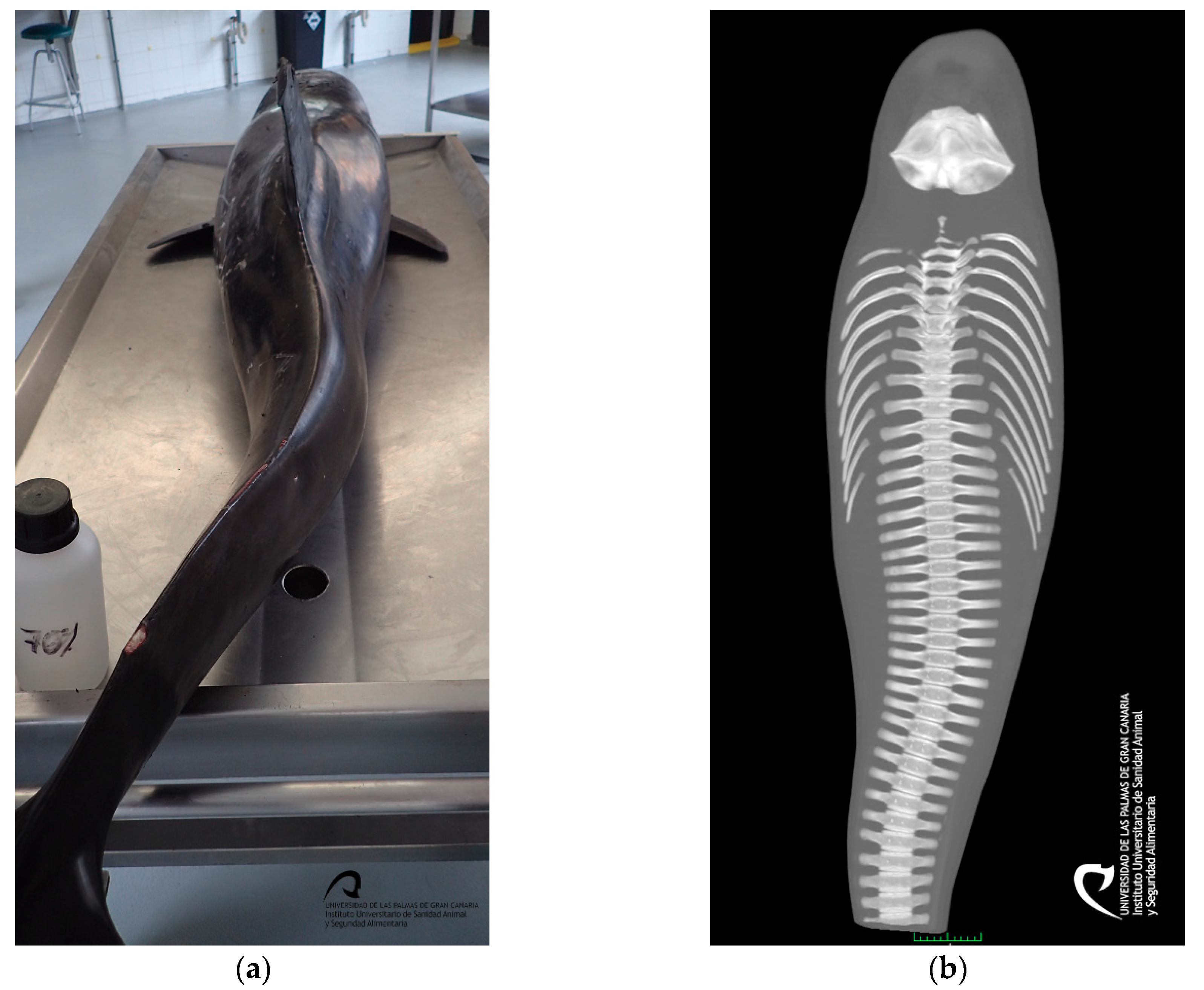
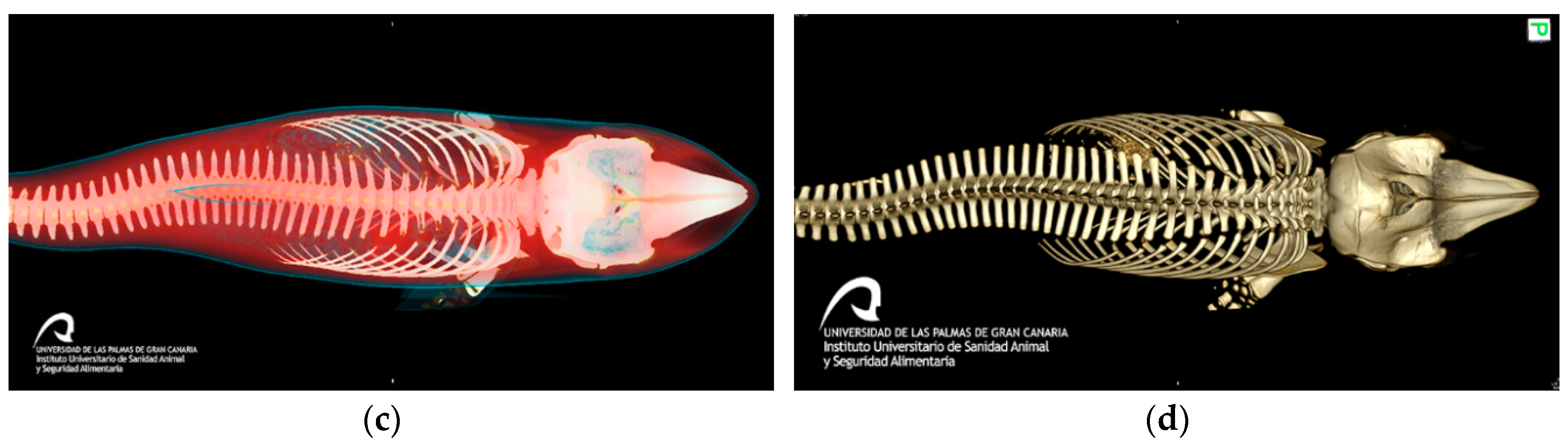
3.2. Gross Results
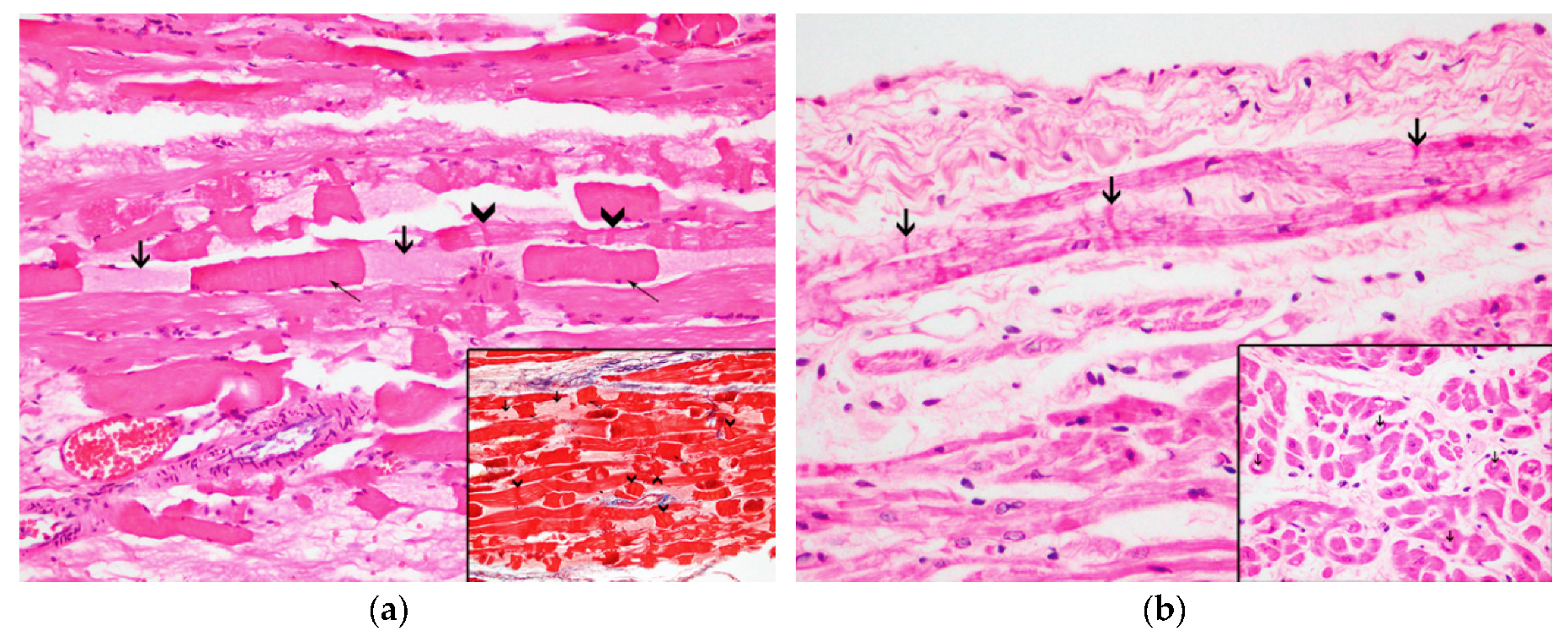
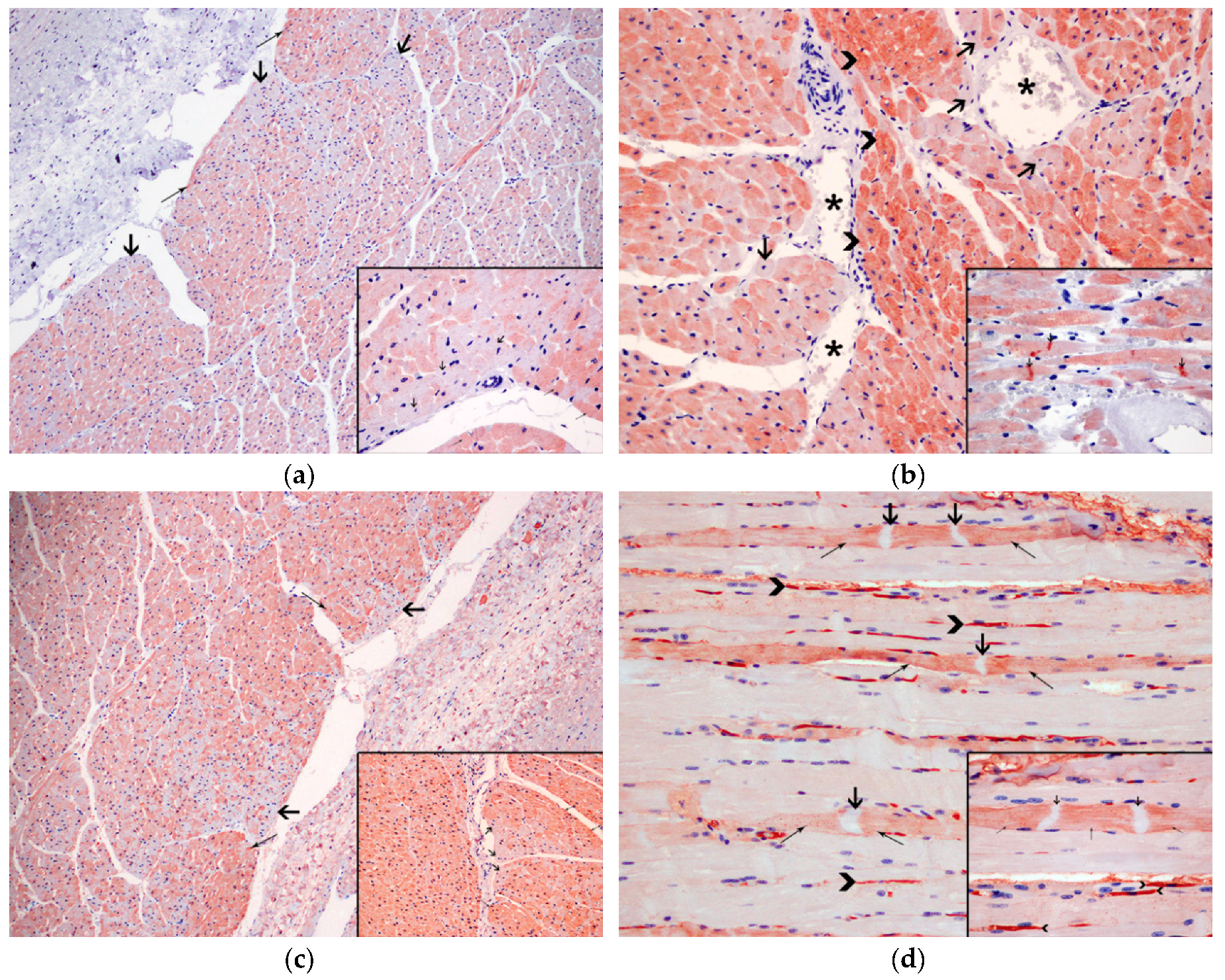
3.3. Histopathological Results
3.4. Immunohistochemical Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion of the Biochemical Results
4.2. Discussion of the Gross, Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Results
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yousef, M.K. Animal stress and strain: Definition and measurements. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1988, 20, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breazile, J.E. The physiology of stress and its relationship to mechanisms of disease and therapeutics. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 1988, 4, 441–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberg, G.P. Biological response to stress: Implications for animal welfare. In The Biology of Animal Stress: Basic Principles and Implications for Animal Welfare, 1st ed.; Moberg, G.P., Mench, J.A., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, Oxon, UK, 2000; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, A.; Lerman, A.; Rihal, C.S. Apical ballooning syndrome (tako-tsubo or stress cardiomyopathy): A mimic of acute myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. 2008, 3, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buja, L.M.; Butany, J. Cardiovascular Pathology, 4th ed.; Buja, L.M., Butany, J., Eds.; Elsevier Science: London, UK, 2015; pp. 245–249, 251, 477–478. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, A.R.; Bossone, E.; Schneider, B.; Sechtem, U.; Citro, R.; Underwood, S.R.; Sheppard, M.N.; Figtree, G.A.; Parodi, G.; Akashi, Y.J.; et al. Current state of knowledge on takotsubo syndrome: A position statement from the taskforce on takotsubo syndrome of the heart failure association of the european society of cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fineschi, V.; Michalodimitrakis, M.; D’Errico, S.; Neri, M.; Pomara, C.; Riezzo, I.; Turillazzi, E. Insight into stress-induced cardiomyopathy and sudden cardiac death due to stress: A forensic cardio-pathologist point of view. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 194, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Kawano, H.; Yoshida, T.; Yamagata, Y.; Nakata, T.; Koga, S.; Ikeda, S.; Kageyama, K.; Abe, K.; Maemura, K. The histological features of a myocardial biopsy specimen in a patient in the acute phase of reversible catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy due to pheochromocytoma. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herráez, P.; Sierra, E.; Arbelo, M.; Jaber, J.R.; Espinosa De Los Monteros, A.; Fernández, A. Rhabdomyolysis and myoglobinuric nephrosis (capture myopathy) in a striped dolphin. J. Wildl. Dis. Wildl. Dis. Assoc. 2007, 43, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herráez, P.; Espinosa de los Monteros, A.; Fernández, A.; Edwards, J.F.; Sacchini, S.; Sierra, E. Capture myopathy in live-stranded cetaceans. Vet. J. 2013, 196, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Delgado, J.; Fernández, A.; Sierra, E.; Sacchini, S.; Andrada, M.; Vela, A.I.; Quesada-Canales, Ó.; Paz, Y.; Zucca, D.; Groch, K.; et al. Pathologic findings and causes of death of stranded cetaceans in the Canary Islands (2006–2012). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbelo, M.; de los Monteros, A.; Herráez, P.; Andrada Borzollino, M.; Sierra, E.; Rodríguez Guisado, F.; Jepson, P.; Fernández, A. Pathology and causes of death of stranded cetaceans in the canary islands (1999–2005). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2013, 103, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, D.F.; Curry, B.E. Histopathological Assessment of Dolphins Necropsies Onboard Vesssels in the Eastern Tropical Pacific Tuna Fishery. 2020. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&ved=2ahUKEwj4v7DHoqXnAhUDBKYKHUWUDeoQFjABegQIARAB&url=https%3A%2F%2Fswfsc.noaa.gov%2FuploadedFiles%2FDivisions%2FPRD%2FPrograms%2FETP_Cetacean_Assessment%2FLJ_02_24C.pdf&usg=AOvVaw1ezGp_XRyF-XLVg4FGaZjG (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Cowan, D.F.; Curry, B.E. Histopathology of the Alarm Reaction in Small Odontocetes. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 139, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Câmara, N.; Sierra, E.; Fernández-Maldonado, C.; Espinosa de los Monteros, A.; Arbelo, M.; Fernández, A.; Herráez, P. Stress cardiomyopathy in stranded cetaceans: A histological, histochemical and immunohistochemical study. Vet. Rec. 2019, 185, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraci, J.R.; Lounsbury, V.J. Marine Mammals Ashore: A Field Guide for Strandings, 2nd ed.; Yates, N.S., Ed.; National Aquarium: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 39–48, 75–128, 167–252. [Google Scholar]
- Report to Assistant Administrator for Fisheries: Program Review of the Marine Mammal Stranding Networks. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/14920 (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Gulland, F.M.D.; Dierauf, L.A.; Whitman, K.L. CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine, 2nd ed.; Gulland, F.M.D., Dierauf, L.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 45–68, 253–270, 383–436, 449–470, 689–740. [Google Scholar]
- Bonsembiante, F.; Centelleghe, C.; Rossi, G.; Giglio, S.; Madeo, E.; Gelain, M.E.; Mazzariol, S. Clinico-pathological findings in a striped dolphin (stenella coeruleoalba) affected by rhabdomyolysis and myoglobinuric nephrosis (capture myopathy). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, B.S.; Cowan, D.F. Myocardial contraction band necrosis in stranded cetaceans. J. Comp. Pathol. 1998, 118, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguel, M.; Paredes, E.; Pavés, H.; Gottdenker, N.L. Capture-induced stress cardiomyopathy in south american fur seal pups (arctophoca australis gracilis). Mar. Mammal Sci. 2014, 30, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiken, T.; Hartmann, M.G. Dissection techniques and tissue sampling. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Cetacean Pathology, First European Cetacean Society, Leiden, The Netherlands, 13–14 September 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Normal Laboratory Values: Blood, Plasma, and Serum. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/resources/normal-laboratory-values/blood-tests-normal-values#v8508814 (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Wray, J. Canine Internal Medicine: What’s Your Diagnosis? 1st ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2017; pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Sleeper, M.M.; Clifford, C.A.; Laster, L.L. Cardiac troponin i in the normal dog and cat. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2001, 15, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtigall, P.E.; Pawloski, J.; Schroeder, J.P.; Sinclair, S. Successful maintenance and research with a formerly stranded risso’s dolphin (grampus griseus). Aquat. Mamm. 1990, 16, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Spraker, T. Stress and capture myopathy in artiodactylids. In Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine: Current Therapy, 3rd ed.; Fowler, M.E., Ed.; W. B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993; pp. 481–489. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandrowski, K.; Chen, A.; Januzzi, J. Cardiac markers for myocardial infarction: A brief review. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. Pathol. Patterns Rev. 2002, 118, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S. Diagnostic efficacy of cardiac troponin in post-mortem examination of acute myocardial infarction. Int. J. Eth. Trauma Vict. 2015, 1, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gough, A.; Murphy, K. Differential Diagnosis in Small Animal Medicine, 2nd ed.; Gough, A., Murphy, K., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2015; pp. 324, 338. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, R.S.; Fauquier, D.A.; Gulland, F.M.D.; Townsend, F.I.; DiGiovanni, R.A., Jr. Evaluating postintervention survival of free-ranging odontocete cetaceans. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2013, 29, 463–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, M.C.; Wang, T.; Matijasevic, M.; Hong, L.; Apple, F.S. Myocardial tissue troponins t and i: An immunohistochemical study in experimental models of myocardial ischemia. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2003, 12, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmann, C.; Pfeiffer, H.; Brinkmann, B. A comparative study on the immunohistochemical detection of early myocardial damage. Int. J. Legal Med. 2000, 113, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
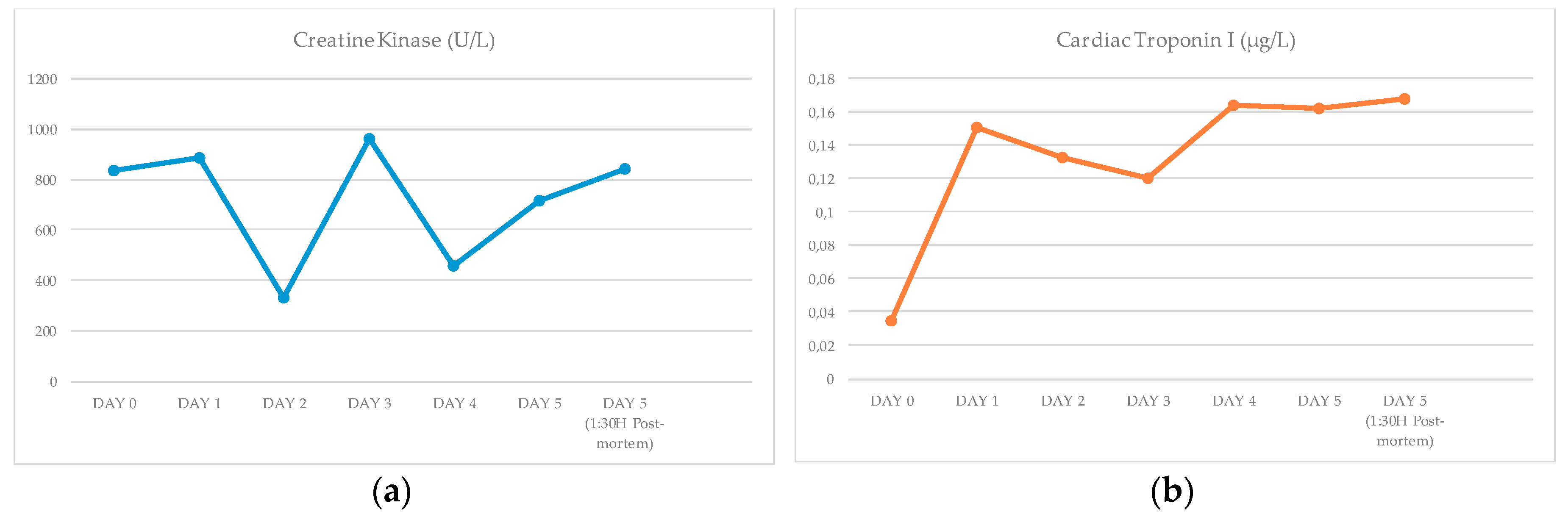

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Câmara, N.; Sierra, E.; Fernández, A.; Arbelo, M.; Bernaldo de Quirós, Y.; Arregui, M.; Consoli, F.; Herráez, P. Capture Myopathy and Stress Cardiomyopathy in a Live-Stranded Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in Rehabilitation. Animals 2020, 10, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020220
Câmara N, Sierra E, Fernández A, Arbelo M, Bernaldo de Quirós Y, Arregui M, Consoli F, Herráez P. Capture Myopathy and Stress Cardiomyopathy in a Live-Stranded Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in Rehabilitation. Animals. 2020; 10(2):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020220
Chicago/Turabian StyleCâmara, Nakita, Eva Sierra, Antonio Fernández, Manuel Arbelo, Yara Bernaldo de Quirós, Marina Arregui, Francesco Consoli, and Pedro Herráez. 2020. "Capture Myopathy and Stress Cardiomyopathy in a Live-Stranded Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in Rehabilitation" Animals 10, no. 2: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020220
APA StyleCâmara, N., Sierra, E., Fernández, A., Arbelo, M., Bernaldo de Quirós, Y., Arregui, M., Consoli, F., & Herráez, P. (2020). Capture Myopathy and Stress Cardiomyopathy in a Live-Stranded Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in Rehabilitation. Animals, 10(2), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020220




