Exploring the Diversity of Active Ureolytic Bacteria in the Rumen by Comparison of cDNA and gDNA
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sampling
2.2. gDNA Extraction and cDNA Reverse Transcription
2.3. PCR Amplification and Sequencing of UreC Genes
2.4. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
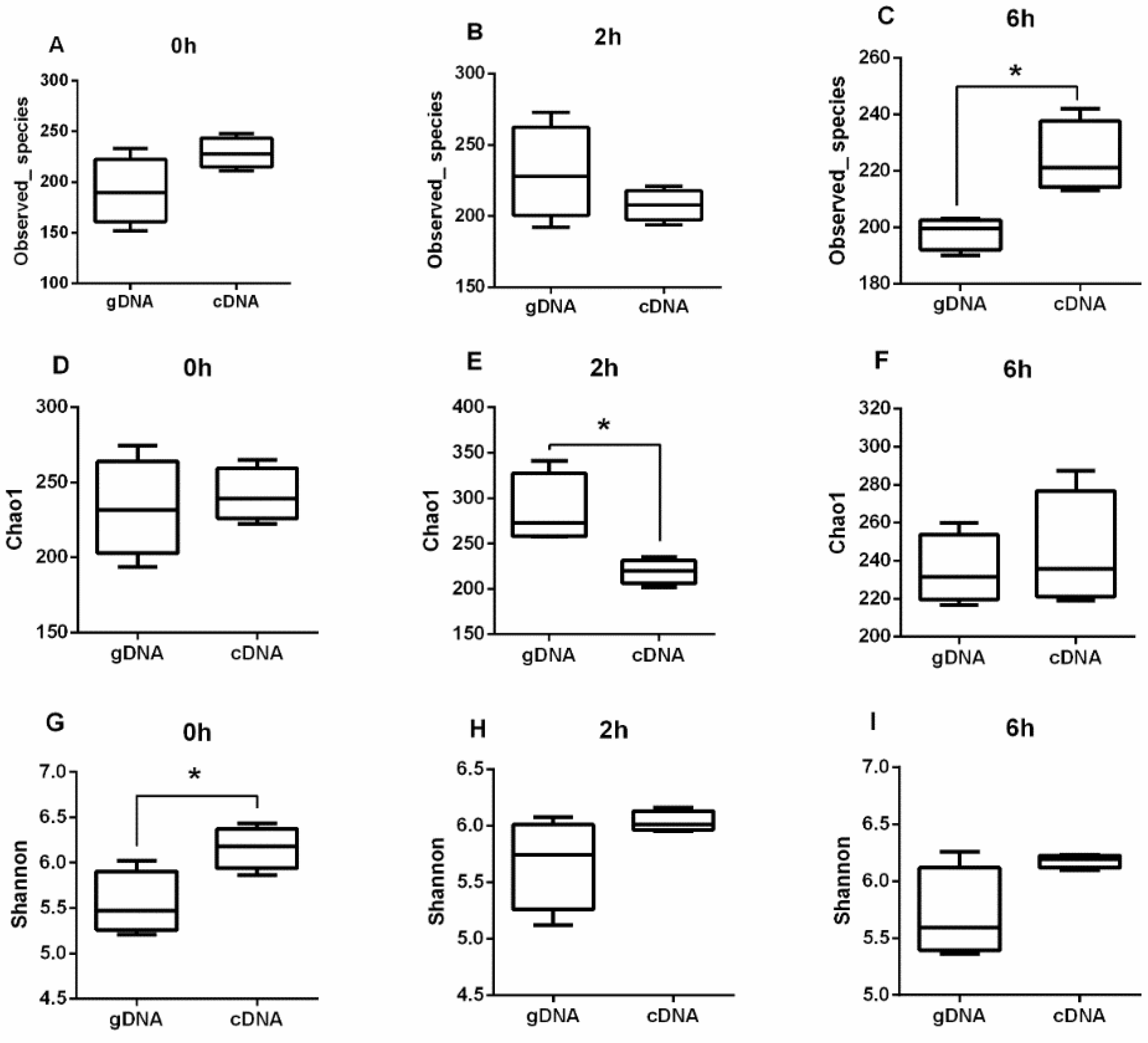
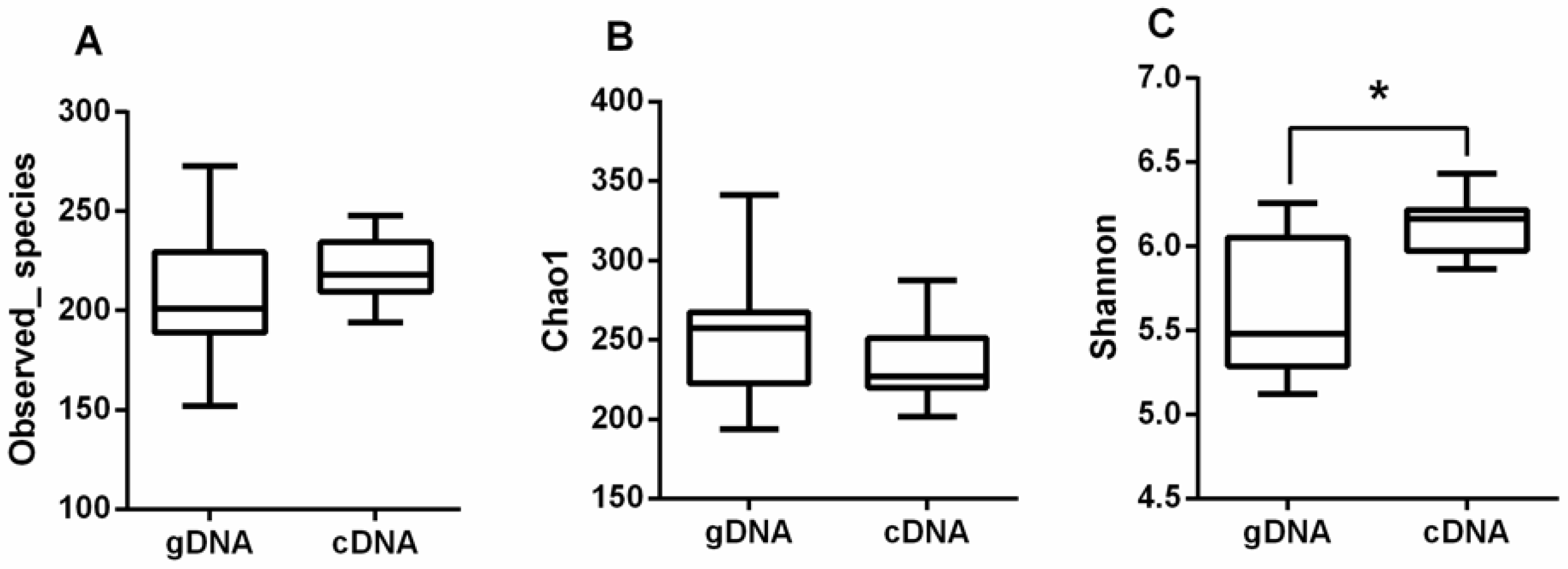
3.1. Alpha Diversity of UreC Genes
3.2. Beta Diversity of UreC Genes
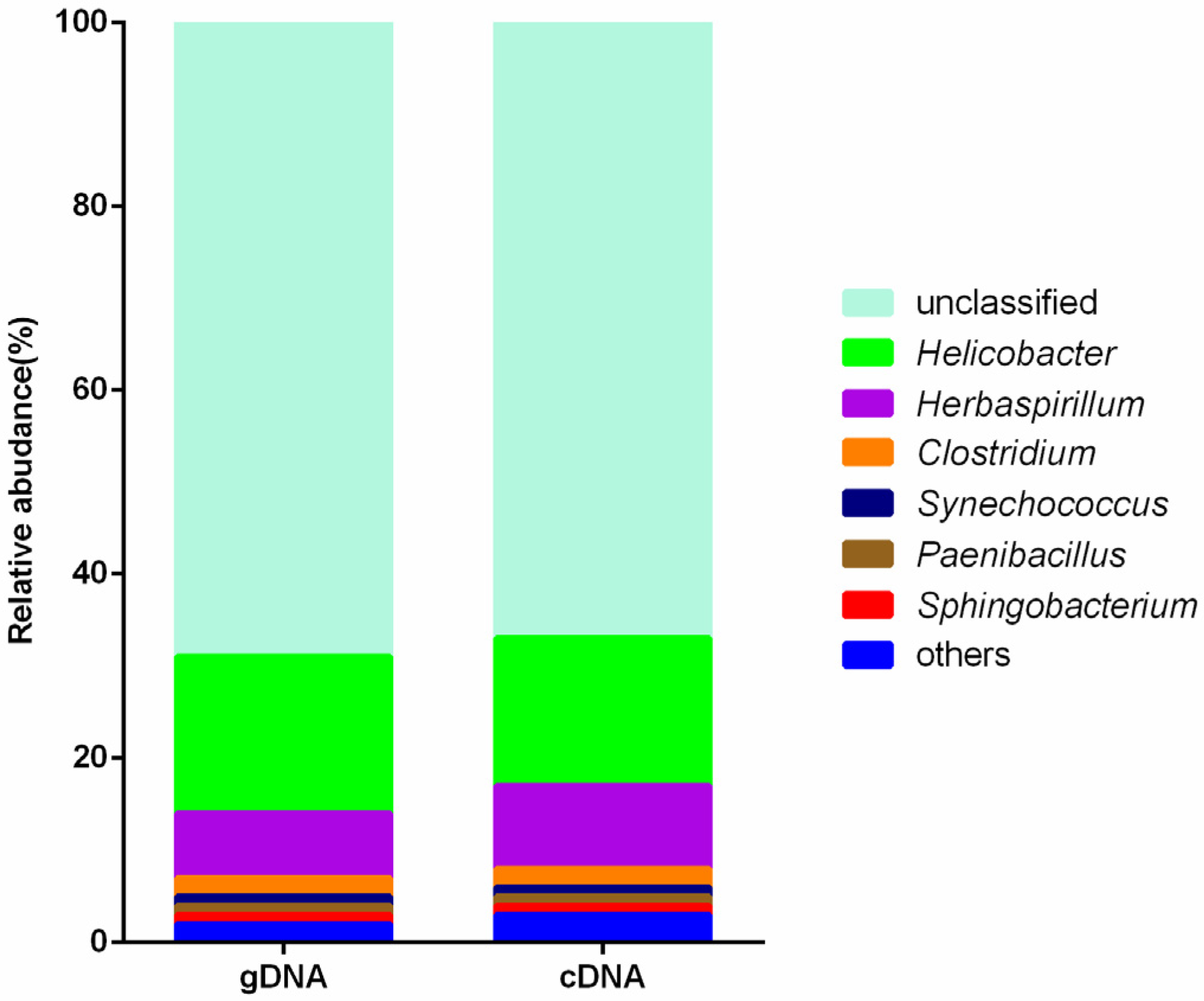
3.3. Composition of Ureolytic Bacteria
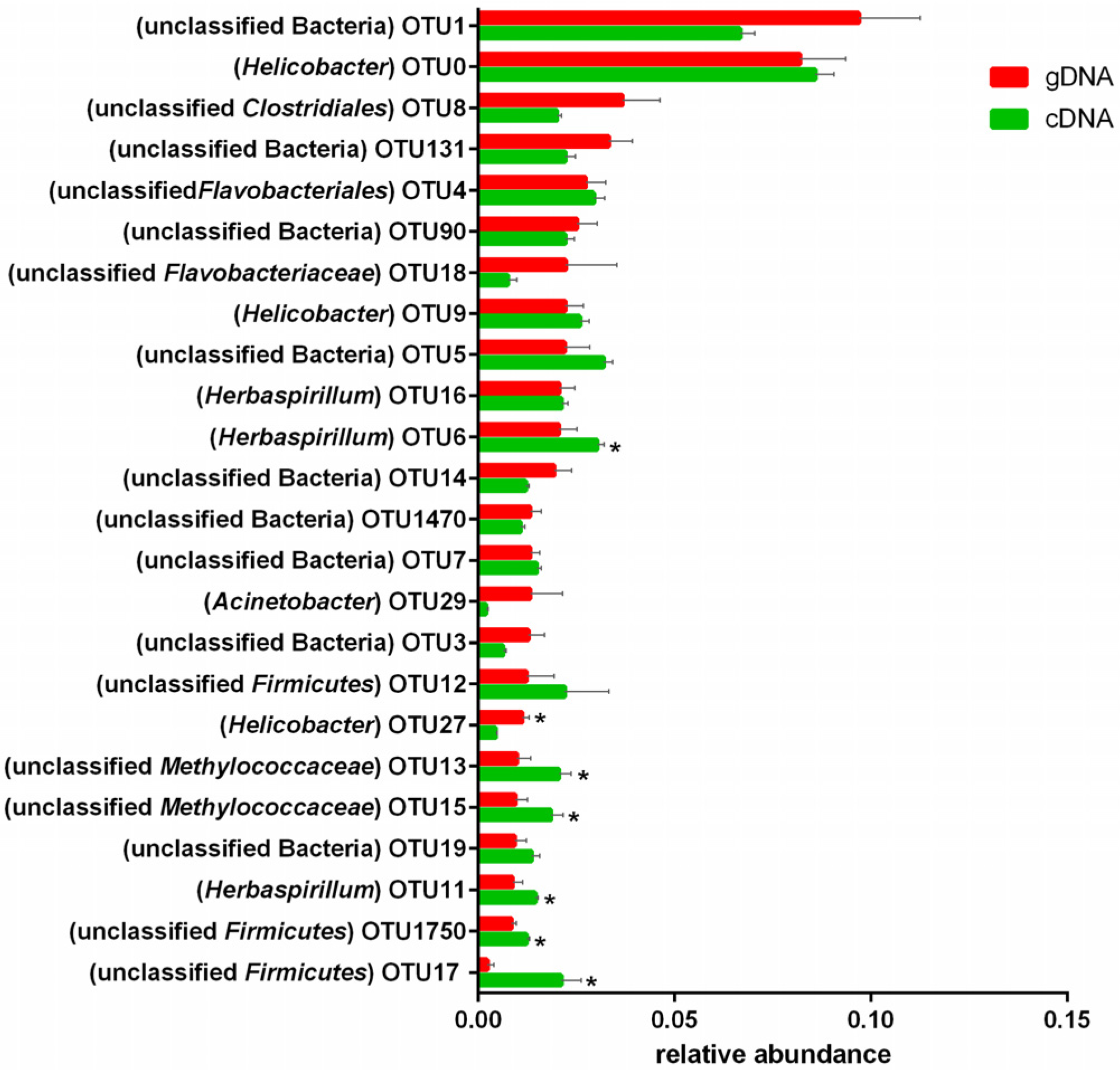
3.4. Changes in the Abundances of OTUs of the UreC Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kertz, A. Review: Urea Feeding to Dairy Cattle: A Historical Perspective and Review. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2010, 26, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, F.N.; Lusby, K.S.; Mizwicki, K.; Forero, O. Slow Ammonia Release from Urea: Rumen and Metabolism Studies. J. Anim. Sci. 1980, 50, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, N.; Bu, D.; Beckers, Y.; Wang, J. Urea nitrogen induces changes in rumen microbial and host metabolic profiles in dairy cows. Livest. Sci. 2018, 210, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Jin, S.Z.; Nan, Z.; Wang, J. Urea metabolism and regulation by rumen bacterial urease in ruminants—A review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2017, 18, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemneh, T. Urea Metabolism and Recycling in Ruminants. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019, 20, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, N.; Bu, D.; Beckers, Y.; Denman, S.E.; McSweeney, C.S.; Wang, J. Differences in Ureolytic Bacterial Composition between the Rumen Digesta and Rumen Wall Based on ureC Gene Classification. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, J.; Pinto, A.J.; Sloan, W.T.; Ijaz, U.Z. The active microbial community more accurately reflects the anaerobic digestion process: 16S rRNA (gene) sequencing as a predictive tool. Microbiome 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, J.V.; Jungfer, C.; Obst, U.; Schwartz, T. DNase I and Proteinase K eliminate DNA from injured or dead bacteria but not from living bacteria in microbial reference systems and natural drinking water biofilms for subsequent molecular biology analyses. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 94, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazewicz, S.J.; Barnard, R.L.; A Daly, R.; Firestone, M.K. Evaluating rRNA as an indicator of microbial activity in environmental communities: Limitations and uses. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.L.; Ordal, Z.J. Thermal injury and recovery of Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Microbiol. 1972, 24, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, L.J.; Iandolo, J.J. Thermally Induced Intracellular Alteration of Ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid. J. Bacteriol. 1970, 103, 833–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.; Wang, P.; O’Toole, N.; Barboza, P.S.; Ungerfeld, E.M.; Leigh, M.B.; Selinger, L.B.; Butler, G.; Tsang, A.; McAllister, T.A.; et al. Snapshot of the Eukaryotic Gene Expression in Muskoxen Rumen—A Metatranscriptomic Approach. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzén, A.; Jørgensen, S.L.; Bengtsson, M.M.; Jonassen, I.; Øvreås, L.; Urich, T. Exploring the composition and diversity of microbial communities at the Jan Mayen hydrothermal vent field using RNA and DNA. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 77, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MaiväLi, Ü.; Paier, A.; Tenson, T. When stable RNA becomes unstable: The degradation of ribosomes in bacteria and beyond. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.M.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Jaffe, D.A.; Levin, D.A.; Green, J.L. Molecular Evidence for Metabolically Active Bacteria in the Atmosphere. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugoni, M.; Agogué, H.; Taib, N.; Domaizon, I.; Moné, A.; Galand, P.E.; Mary, I. Temporal Dynamics of Active Prokaryotic Nitrifiers and Archaeal Communities from River to Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minas, K.; McEwan, N.R.; Newbold, C.J.; Scott, K.P. Optimization of a high-throughput CTAB-based protocol for the extraction of qPCR-grade DNA from rumen fluid, plant and bacterial pure cultures. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 325, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.T.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, P.P.; Bremer, H. Modulation of Chemical Composition and Other Parameters of the Cell at Different Exponential Growth Rates. Ecosal. Plus. 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Henderson, G.; Sun, X.; Cox, F.; Janssen, P.H.; Guan le, L. Taxonomic Assessment of Rumen Microbiota Using Total RNA and Targeted Amplicon Sequencing Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agle, M.; Hristov, A.N.; Zaman, S.; Schneider, C.; Ndegwa, P.; Vaddella, V.K. The effects of ruminally degraded protein on rumen fermentation and ammonia losses from manure in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recktenwald, E.B.; Ross, D.A.; Fessenden, S.W.; Wall, C.J.; Amburgh, M.E.V. Urea-N recycling in lactating dairy cows fed diets with 2 different levels of dietary crude protein and starch with or without monensin. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, A.N.; Pfeffer, E. Nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition of cattle. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2005, 128, 342–343. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar, G.; Paoli, L.; Alberti, A.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Ruscheweyh, H.-J.; Cuenca, M.; Field, C.M.; Coelho, L.P.; Cruaud, C.; Engelen, S.; et al. Gene Expression Changes and Community Turnover Differentially Shape the Global Ocean Metatranscriptome. Cell 2019, 179, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.S.; Lee, A.; McGuire, K.L. Phylogenetic and Functional Diversity of Total (DNA) and Expressed (RNA) Bacterial Communities in Urban Green Infrastructure Bioswale Soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00287-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, I.; Snell, H.; Bardgett, R.D. High throughput method for measuring urease activity in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashok, A.; Doriya, K.; Rao, J.V.; Qureshi, A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Kumar, D.S. Microbes Producing L-Asparaginase free of Glutaminase and Urease isolated from Extreme Locations of Antarctic Soil and Moss. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbank, M.B.; Weaver, T.J.; Williams, B.C.; Crawford, R.L. Urease Activity of Ureolytic Bacteria Isolated from Six Soils in which Calcite was Precipitated by Indigenous Bacteria. Geomicrobiol. J. 2012, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Sáez, L.; Waller, A.S.; Mende, D.R.; Bakker, K.; Farnelid, H.; Yager, P.L.; Lovejoy, C.; Tremblay, J.É.; Potvin, M.; Heinrich, F.; et al. Role for urea in nitrification by polar marine Archaea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17989–17994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, J.L.; Baker, K.M.; Bell, S.L. Diversity of urea-degrading microorganisms in open-ocean and estuarine planktonic communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 3118–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Jin, L.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z. Phylogenetically Diverse ureC Genes and Their Expression Suggest the Urea Utilization by Bacterial Symbionts in Marine Sponge Xestospongia testudinaria. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N.; Bu, D.; Sun, P.; Yu, Z. Reducing microbial ureolytic activity in the rumen by immunization against urease therein. BMC Veter. Res. 2015, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coldham, T.; Rose, K.; O’Rourke, J.; Neilan, B.A.; Dalton, H.; Lee, A. Detection, Isolation, and Characterization of Helicobacter Species from the Gastrointestinal Tract of the Brushtail Possum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marques, A.C.Q.; Paludo, K.S.; Dallagassa, C.B.; Surek, M.; Pedrosa, F.O.; Souza, E.M.; Cruz, L.M.; Lipuma, J.J.; Zanata, S.M.; Rego, F.G.M.; et al. Biochemical Characteristics, Adhesion, and Cytotoxicity of Environmental and Clinical Isolates of Herbaspirillum spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 53, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotný, P. Composition of Cell Walls of Clostridium Sordellii and Clostridium BiferMentans and Its Relation to Taxonomy. J. Med. Microbiol. 1969, 2, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crociani, F.; Matteuzzi, D.; Minardi, A.; Brigidi, P.; Gioffre, F. Urease activity in gastrointestinal tract of rabbit and electrophoretic behaviour of urease. Ann. Institut. Pasteur. Microbiol. 1986, 137, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Du, N.; Shu, S.; Sun, J.; Li, S.; Guo, S. Paenibacillus polymyxa NSY50 suppresses Fusarium wilt in cucumbers by regulating the rhizospheric microbial community. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep41234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, J.L.; Brahamsha, B.; Palenik, B. The marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. WH7805 requires urease (urea amiohydrolase, EC 3.5.1.5) to utilize urea as a nitrogen source: Molecular-genetic and biochemical analysis of the enzyme. Microbiology 1999, 145, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, H.; Sharma, S.; Mishra, S.; Tanuku, N.R.S.; Pinnaka, A.K. Sphingobacterium bovisgrunnientis sp. nov., isolated from yak milk. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zheng, N.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. Exploring the Diversity of Active Ureolytic Bacteria in the Rumen by Comparison of cDNA and gDNA. Animals 2020, 10, 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112162
Liu S, Zheng N, Zhao S, Wang J. Exploring the Diversity of Active Ureolytic Bacteria in the Rumen by Comparison of cDNA and gDNA. Animals. 2020; 10(11):2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112162
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Sijia, Nan Zheng, Shengguo Zhao, and Jiaqi Wang. 2020. "Exploring the Diversity of Active Ureolytic Bacteria in the Rumen by Comparison of cDNA and gDNA" Animals 10, no. 11: 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112162
APA StyleLiu, S., Zheng, N., Zhao, S., & Wang, J. (2020). Exploring the Diversity of Active Ureolytic Bacteria in the Rumen by Comparison of cDNA and gDNA. Animals, 10(11), 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112162






