Enhancing Drug Efficacy against Mastitis Pathogens—An In Vitro Pilot Study in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodology
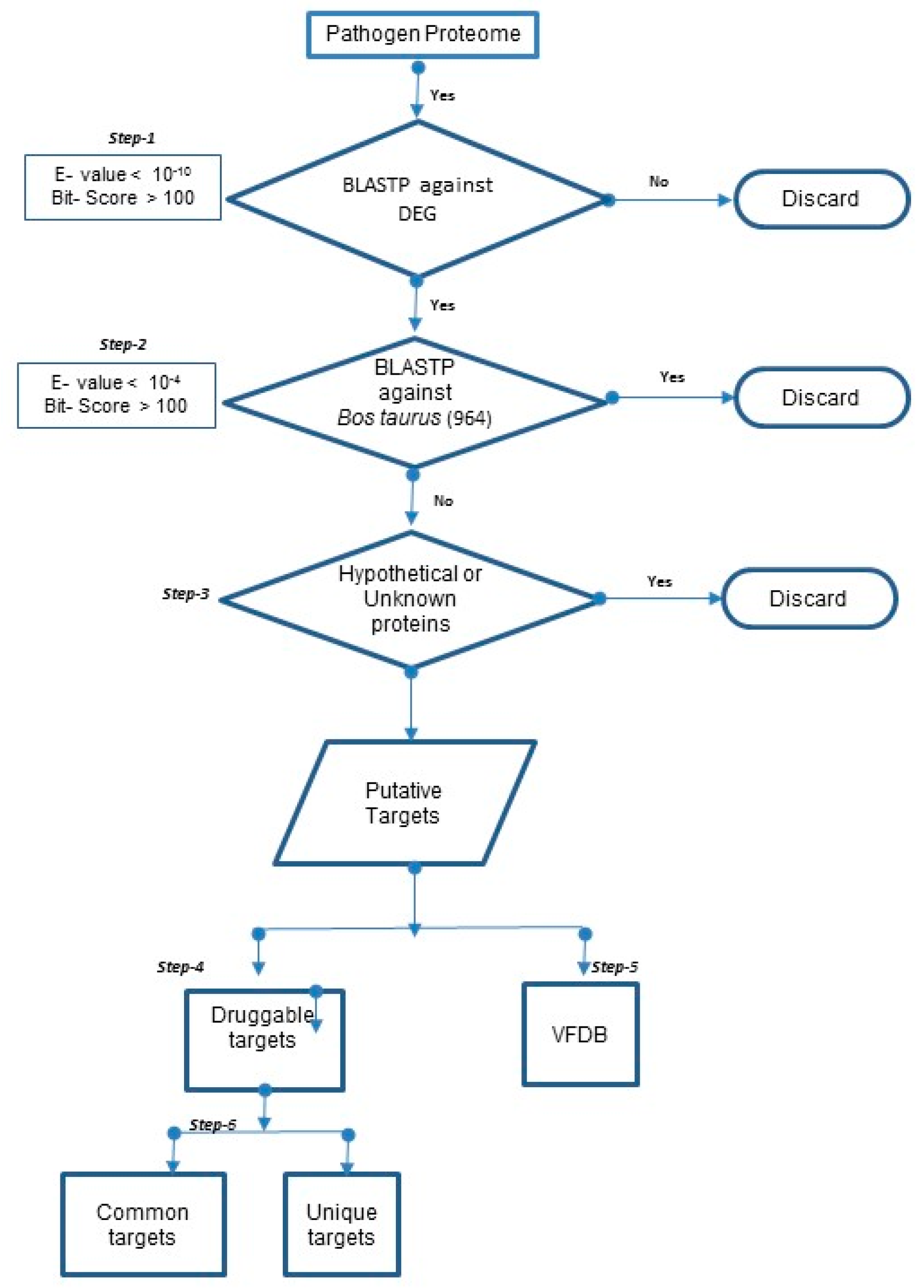
2.2.1. Prediction of “Essential” and “Specific” Targets in 20 Mastitis-Causing Bacteria
2.2.2. Prediction of Druggable Targets and Drugs in 20 Mastitis-Causing Bacteria
2.2.3. Prediction of Druggable Virulent Factors in 20 Mastitis-Causing Bacteria
2.2.4. Unique and Common Druggable Targets
2.2.5. Unique and Common Druggable Targets Staphylococcus Species
2.2.6. MIC for Phosphorylcholine and Ceftiofur and Their Combinations
3. Results
3.1. Prediction of Drug Targets in 20 Mastitis-Causing Bacteria
3.2. Prediction of Druggable Targets and Drugs in 20 Mastitis-Causing Bacteria
3.3. Unique and Common Druggable Targets
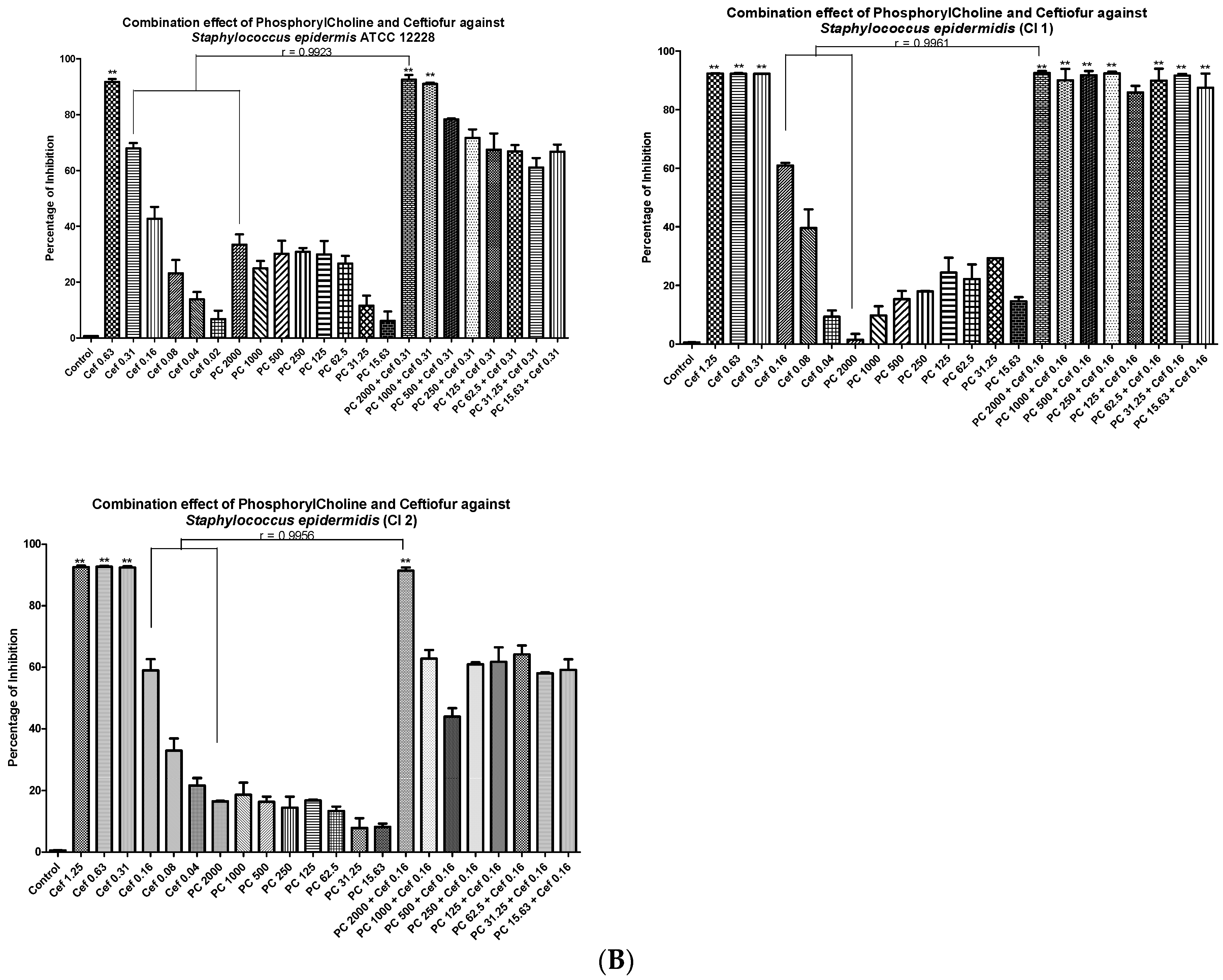
3.4. Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC) and Fractional Inhibitory Concentrations (FIC)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, G.M. Guidelines to Culling Cows with Mastitis; Virginia State University: Petersburg, VA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, C.; Pacheco, D.; Soares, L.; Romão, R.; Moitoso, M.; Maldonado, J.; Guix, R.; Simões, J. Prevalence of contagious and environmental mastitis-causing bacteria in bulk tank milk and its relationships with milking practices of dairy cattle herds in São Miguel Island (Azores). Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuzoğlu, B.; Baştan, A.; Salar, S. The effect of long term antibiotic treatment on bacteriological cure and somatic cell count at subclinical mastitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in lactating dairy cows. Ank. Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2015, 62, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Abebe, R.; Hatiya, H.; Abera, M.; Megersa, B.; Asmare, K. Bovine mastitis: Prevalence, risk factors and isolation of Staphylococcus aureus in dairy herds at Hawassa milk shed, South Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grispoldi, L.; Massetti, L.; Sechi, P.; Iulietto, M.F.; Ceccarelli, M.; Karama, M.; Popescu, P.A.; Pandolfi, F.; Cenci-Goga, B.T. Characterization of enterotoxin-producing Staphylococcus aureus isolated from mastitic cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, J.-P.; Keefe, G. Systematic review: What is the best antibiotic treatment for Staphylococcus aureus intramammary infection of lactating cows in North America? Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2012, 28, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durel, L.; Gallina, G.; Pellet, T. Assessment of ceftiofur residues in cow milk using commercial screening test kits. Vet. Rec. Open 2019, 6, e000329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganda, E.K.; Gaeta, N.; Sipka, A.; Pomeroy, B.; Oikonomou, G.; Schukken, Y.H.; Bicalho, R.C. Normal milk microbiome is reestablished following experimental infection with Escherichia coli independent of intramammary antibiotic treatment with a third-generation cephalosporin in bovines. Microbiome 2017, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.; Gillespie, B.; Headrick, S.; Moorehead, H.; Lunn, P.; Dowlen, H.; Johnson, D.; Lamar, K.; Chester, S.; Moseley, W. Efficacy of extended ceftiofur intramammary therapy for treatment of subclinical mastitis in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyne, K.; Honaker, R.W.; Hobbs, Z.; Richter, M.; Żaczek, M.; Spangler, T.; Steenbrugge, J.; Lu, R.; Kinkhabwala, A.; Marchon, B.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a bovine-associated Staphylococcus aureus phage cocktail in a murine model of mastitis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, S.; Ren, H.; Zhao, K.; Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, P.; Liu, Z. Cytotoxicity and degradation product identification of thermally treated ceftiofur. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 18407–18417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, D.; Lim, C.S.; Sakharkar, K.R.; Sakharkar, M.K. Differential genome analyses of metabolic enzymes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa for drug target identification. Silico Biol. 2007, 7, 453–465. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharkar, K.R.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Chow, V.T. A novel genomics approach for the identification of drug targets in pathogens, with special reference to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Silico Biol. 2004, 4, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Lin, Y.; Luo, H.; Gao, F. A comprehensive overview of online resources to identify and predict bacterial essential genes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanumolu, S.K.; Rout, C.; Chauhan, R.S. UniDrug-target: A computational tool to identify unique drug targets in pathogenic bacteria. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.J.; Lowy, F.D. Pathogenesis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, S350–S359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, T.L.; Carothers, K.E.; Lee, S.W. Virulence factor targeting of the bacterial pathogen Staphylococcus aureus for vaccine and therapeutics. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, D.; Lim, C.S.; Sakharkar, M.K. In silico identification of putative drug targets in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through metabolic pathway analysis. In Proceedings of the IAPR International Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Bioinformatics, Singapore, 1–2 October 2007; pp. 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Finan, C.; Gaulton, A.; Kruger, F.A.; Lumbers, R.T.; Shah, T.; Engmann, J.; Galver, L.; Kelley, R.; Karlsson, A.; Santos, R. The druggable genome and support for target identification and validation in drug development. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaag1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandoi, G.; Acencio, M.L.; Lemke, N. Prediction of druggable proteins using machine learning and systems biology: A mini-review. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, S.; Kumar, M.; Phougat, N.; Chaudhary, R.; Kumar Chhillar, A. Perspectives on phytochemicals as antibacterial agents: An outstanding contribution to modern therapeutics. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, P.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Lim, C.S.; Tang, T.H.; Sakharkar, K.R. Activity and interactions of antibiotic and phytochemical combinations against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 6, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asli, A.; Brouillette, E.; Ster, C.; Ghinet, M.G.; Brzezinski, R.; Lacasse, P.; Jacques, M.; Malouin, F. Antibiofilm and antibacterial effects of specific chitosan molecules on Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated with bovine mastitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kausche, F.M.; Robb, E.J. A comprehensive review of ceftiofur sodium and hydrochloride formulations for treatment of acute bovine foot rot. Vet. Ther. Res. Appl. Vet. Med. 2003, 4, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Pomorska-Mól, M.; Czyżewska-Dors, E.; Kwit, K.; Wierzchosławski, K.; Pejsak, Z. Ceftiofur hydrochloride affects the humoral and cellular immune response in pigs after vaccination against swine influenza and pseudorabies. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ster, C.; Lebeau, V.; Leclerc, J.; Fugère, A.; Veh, K.A.; Roy, J.-P.; Malouin, F. In vitro antibiotic susceptibility and biofilm production of Staphylococcus aureus isolates recovered from bovine intramammary infections that persisted or not following extended therapies with cephapirin, pirlimycin or ceftiofur. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wu, J.; Ali, T.; Li, J.; Lv, Y.; Han, B. Bovine mastitis Staphylococcus aureus: Antibiotic susceptibility profile, resistance genes and molecular typing of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive strains in China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 31, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyörälä, S.; Taponen, S. Coagulase-negative staphylococci—Emerging mastitis pathogens. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorberg, B.-M.; Danielsson-Tham, M.-L.; Emanuelson, U.; Waller, K.P. Bovine subclinical mastitis caused by different types of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4962–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ou, H.Y.; Zhang, C.T. DEG: A database of essential genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D271–D272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLea, K.S.; Trachtenberg, A.M. Complete genome sequence of Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228 chromosome and plasmids, generated by long-read sequencing. Genome Announc. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards; Barry, A.L. Methods for Determining Bactericidal Activity of Antimicrobial Agents: Approved Guideline; National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards: Wayne, PA, USA, 1999; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.L.; Caffrey, N.P.; Nóbrega, D.B.; Cork, S.C.; Ronksley, P.E.; Barkema, H.W.; Polachek, A.J.; Ganshorn, H.; Sharma, N.; Kellner, J.D. Restricting the use of antibiotics in food-producing animals and its associations with antibiotic resistance in food-producing animals and human beings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Planet. Health 2017, 1, e316–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Responsible Use of Medically Important Antimicrobials in Animals. Available online: http://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/antibiotic-antimicrobial-resistance/animals/actions/responsible-use-antimicrobials.html. (accessed on 6 February 2020).
- Lusk, J.L.; Norwood, F.B.; Pruitt, J.R. Consumer demand for a ban on antibiotic drug use in pork production. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2006, 88, 1015–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dötsch, A.; Klawonn, F.; Jarek, M.; Scharfe, M.; Blöcker, H.; Häussler, S. Evolutionary conservation of essential and highly expressed genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casjens, S. The diverse and dynamic structure of bacterial genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1998, 32, 339–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Z. Isolation and characterization of a virulent bacteriophage SPW specific for Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis of lactating dairy cattle. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 5829–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.M.; Nasrullah, I.; Tahir, S.; Tong, Y. Comparative genomics analysis of Mycobacterium ulcerans for the identification of putative essential genes and therapeutic candidates. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekerink, R.O.; Barkema, H.; Kelton, D.; Scholl, D. Incidence rate of clinical mastitis on Canadian dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 1366–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, C.J.; Portis, E.; Johansen, L.; Mullins, L.M.; Stoltman, G.A. Susceptibility to antimicrobial agents among bovine mastitis pathogens isolated from North American dairy cattle, 2002–2010. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottarel, G.; Wierzbowski, J. Combination drugs, an emerging option for antibacterial therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin, S.; Sakharkar, K.R.; Lim, C.S.; Sakharkar, M.K. Activity of Chitosans in combination with antibiotics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 5, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entenza, J.M.; Giddey, M.; Vouillamoz, J.; Moreillon, P. In vitro prevention of the emergence of daptomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and enterococci following combination with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid or ampicillin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobrega, D.B.; Naqvi, S.A.; Dufour, S.; Deardon, R.; Kastelic, J.P.; De Buck, J.; Barkema, H.W. Critically important antimicrobials are generally not needed to treat nonsevere clinical mastitis in lactating dairy cows: Results from a network meta-analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 10585–10603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| (A) Organism | (B) Genome ID | (C) # Proteins | (D) # Match DEG | (E) # Protein with No Match in B. taurus | (F) Proteins That Match in VFDB | (G) # of Putative Targets | (H) # of Putative Targets That Match in VFDB | (I) # of Druggable Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. melitensis | NC_003317 | 2972 | 1380 | 2458 | 266 | 889 | 123 | 229 |
| C. bovis | NZ_AENJ01000503 | 1829 | 850 | 1513 | 104 | 526 | 49 | 144 |
| E. faecalis | NZ_KE351595.1 | 2732 | 1025 | 2380 | 221 | 902 | 166 | 339 |
| E. faecium | NC_017960.1 | 3114 | 1076 | 2741 | 208 | 729 | 84 | 175 |
| E. coli | NC_018658 | 5138 | 2240 | 4644 | 530 | 1646 | 262 | 491 |
| K. oxytoca | NZ_CP011636 | 6816 | 2627 | 6293 | 589 | 2072 | 376 | 622 |
| K. pneumoniae | NC_016845 | 5779 | 2397 | 5257 | 476 | 1743 | 279 | 533 |
| M. bovis | NZ_CP007589 | 743 | 328 | 644 | 23 | 217 | 8 | 66 |
| N. abscessus | NZ_BAFP01000274.1 | 7296 | 2054 | 6782 | 394 | 1482 | 229 | 564 |
| P. bettyae | NZ_AJSX01000001 | 2059 | 1196 | 1756 | 160 | 852 | 90 | 226 |
| P. dagmatis | NZ_GG704823 | 1980 | 1239 | 1651 | 193 | 865 | 105 | 237 |
| P. multocida | NZ_CP008918 | 2013 | 1235 | 1700 | 192 | 885 | 107 | 236 |
| P. aeruginosa | NC_002516 | 5572 | 2476 | 5105 | 765 | 2476 | 407 | 649 |
| S. liquefaciens | NC_021741.1 | 4811 | 2246 | 4150 | 524 | 1722 | 142 | 521 |
| S. aureus | NC_007795 | 2767 | 1143 | 2392 | 234 | 534 | 67 | 161 |
| S. epidermidis | NC_004461 | 2482 | 1106 | 2114 | 164 | 636 | 73 | 173 |
| S. agalactiae | NC_004116 | 2127 | 941 | 1827 | 186 | 602 | 69 | 149 |
| S. dysgalactiae | NC_019042.1 | 1947 | 886 | 1641 | 157 | 586 | 53 | 145 |
| S. uberis | NC_012004.1 | 1762 | 883 | 1451 | 139 | 592 | 51 | 145 |
| T. pyogenes | NZ_JVLH01000002 | 1610 | 698 | 1328 | 92 | 455 | 38 | 119 |
| No | Strain Name | MIC of Phosphoryl Choline (µg/mL) | MIC of Ceftiofur (µg/mL) | Synergistic Action of Phosphoryl Choline + Ceftiofur (µg/mL) | FIC Index Value | FIC Value Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | >2000 | 1.25 | 2000 + 0.31 | 0.45 | Synergistic |
| 2 | Staphylococcus aureus (CI 1) | >2000 | 0.63 | 2000 + 0.31 | 0.75 | Strong additive or weak synergistic |
| 3 | Staphylococcus aureus (CI 2) | >2000 | 1.25 | 2000 + 0.31 | 0.75 | Strong additive or weak synergistic |
| 4 | Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228 | >2000 | 0.63 | 2000 + 0.31 | 0.75 | Strong additive or weak synergistic |
| 5 | Staphylococcus epidermidis (CI 1) | >2000 | 0.31 | 2000 + 0.16 | 0.75 | Strong additive or weak synergistic |
| 6 | Staphylococcus epidermidis (CI 2) | >2000 | 0.31 | 2000 + 0.16 | 0.75 | Strong additive or weak synergistic |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajamanickam, K.; Yang, J.; Chidambaram, S.B.; Sakharkar, M.K. Enhancing Drug Efficacy against Mastitis Pathogens—An In Vitro Pilot Study in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Animals 2020, 10, 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112117
Rajamanickam K, Yang J, Chidambaram SB, Sakharkar MK. Enhancing Drug Efficacy against Mastitis Pathogens—An In Vitro Pilot Study in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Animals. 2020; 10(11):2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112117
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajamanickam, Karthic, Jian Yang, Saravana Babu Chidambaram, and Meena Kishore Sakharkar. 2020. "Enhancing Drug Efficacy against Mastitis Pathogens—An In Vitro Pilot Study in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis" Animals 10, no. 11: 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112117
APA StyleRajamanickam, K., Yang, J., Chidambaram, S. B., & Sakharkar, M. K. (2020). Enhancing Drug Efficacy against Mastitis Pathogens—An In Vitro Pilot Study in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Animals, 10(11), 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112117






