The Effect of Recently Developed Synbiotic Preparations on Dominant Fecal Microbiota and Organic Acids Concentrations in Feces of Piglets from Nursing to Fattening
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feed Additives
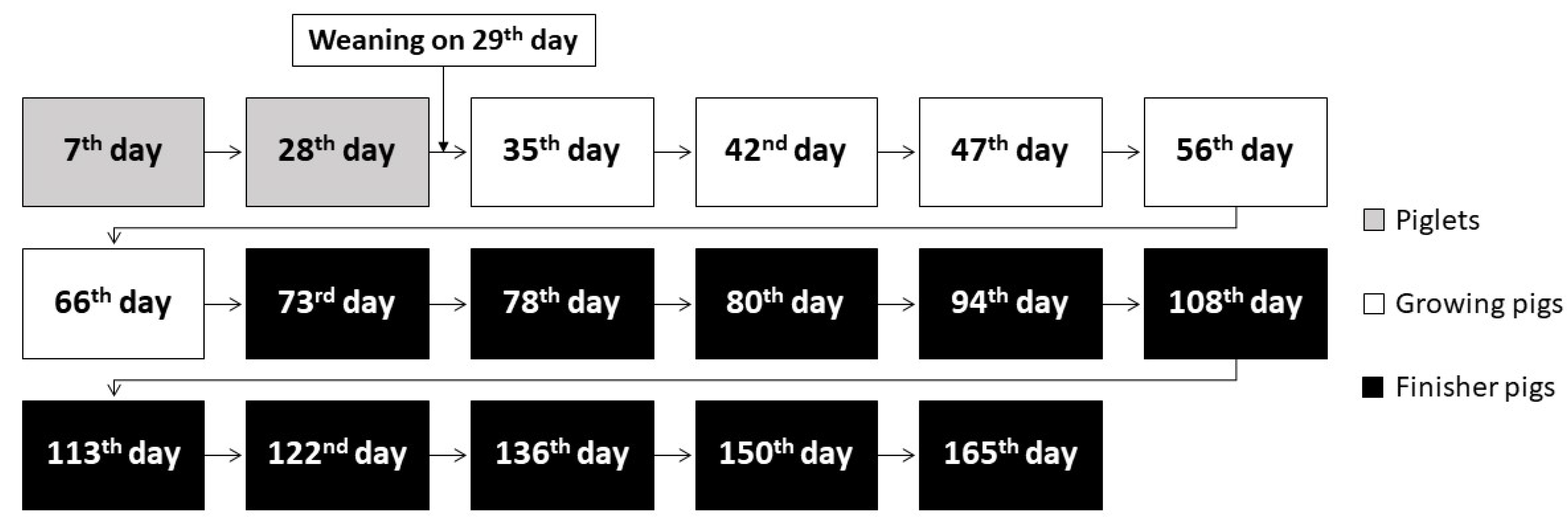
2.2. Animals Treatment
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Fecal Dominant Microorganisms Population Determination
2.3.2. Organic Acid Concentrations Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
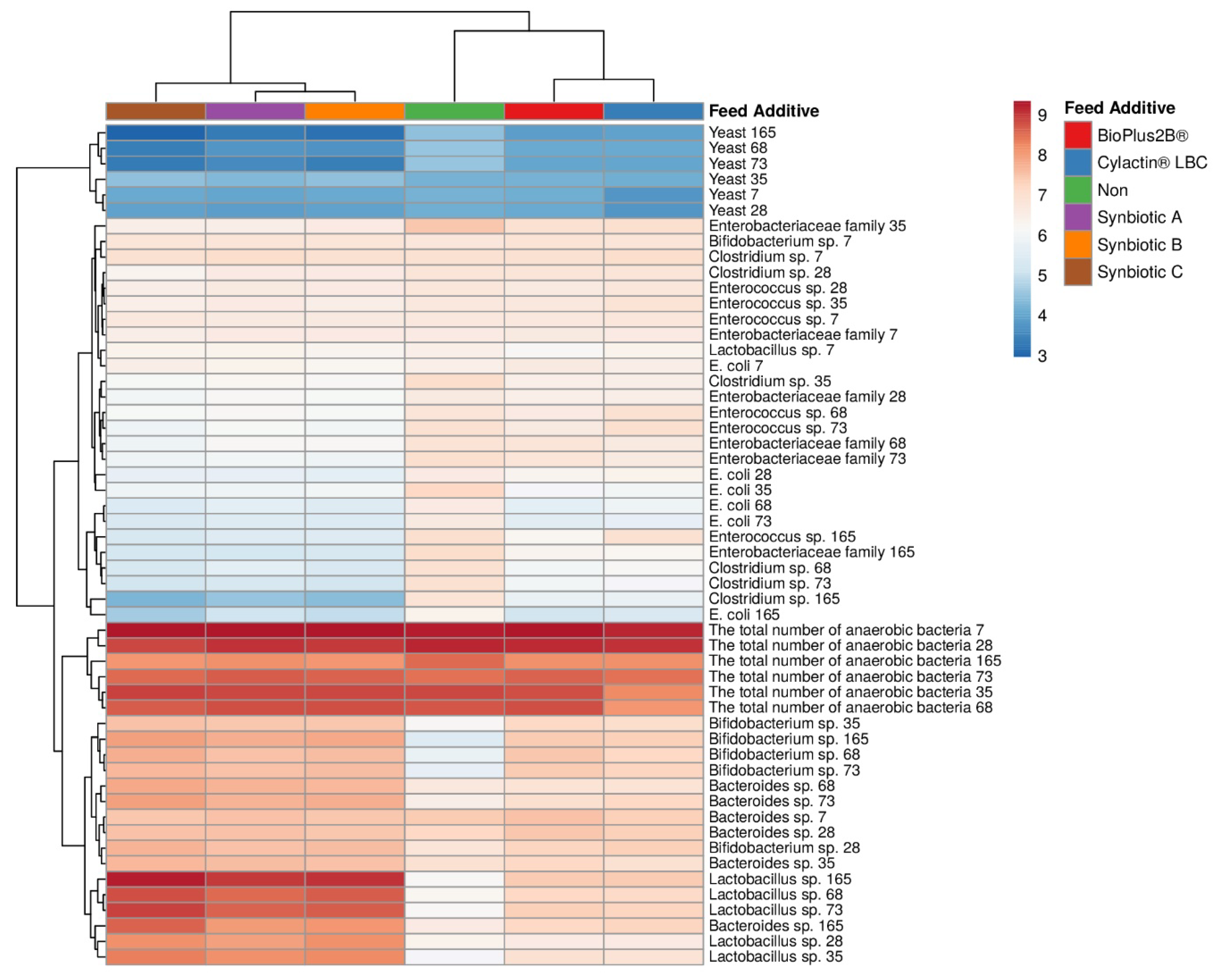
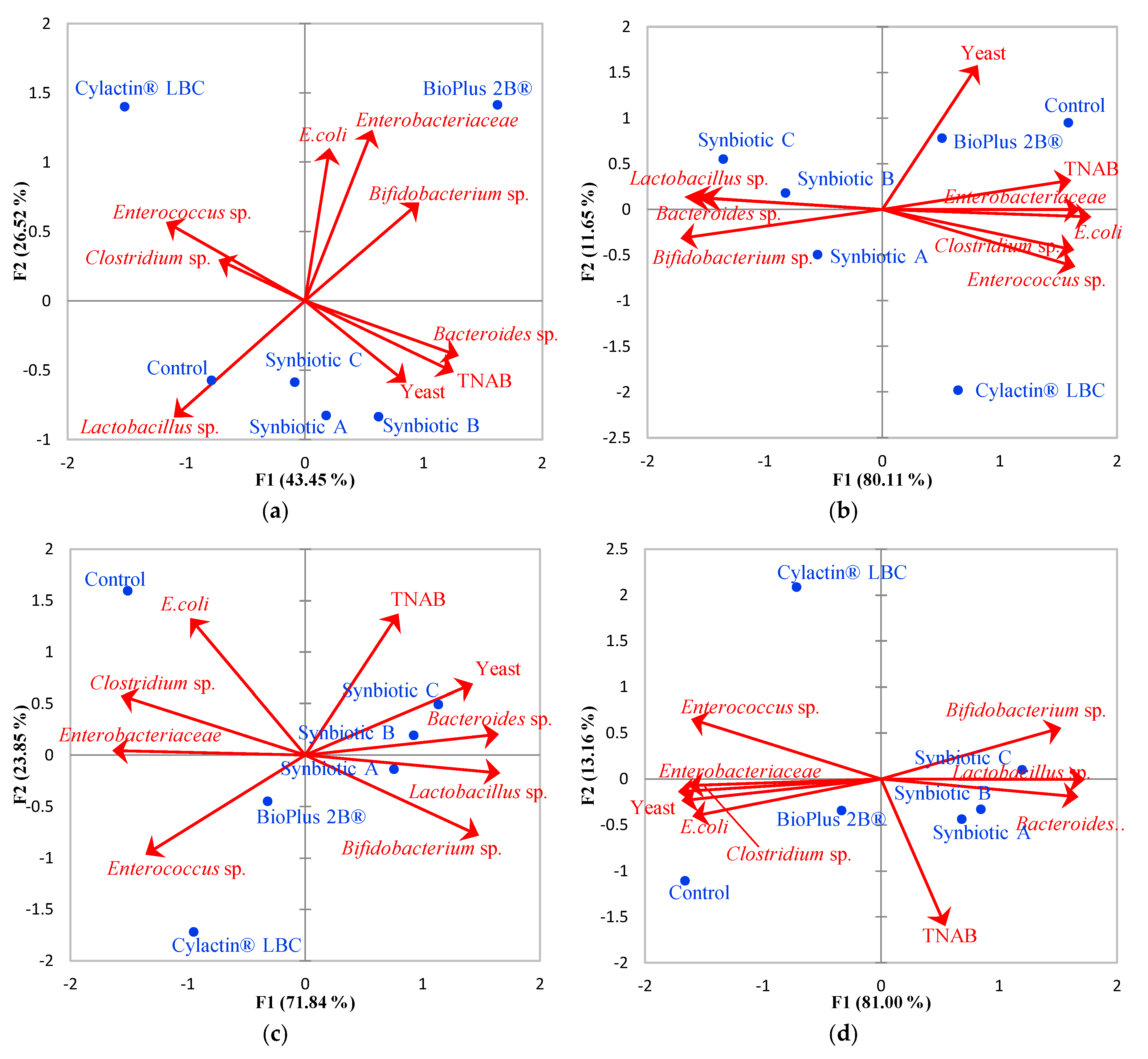
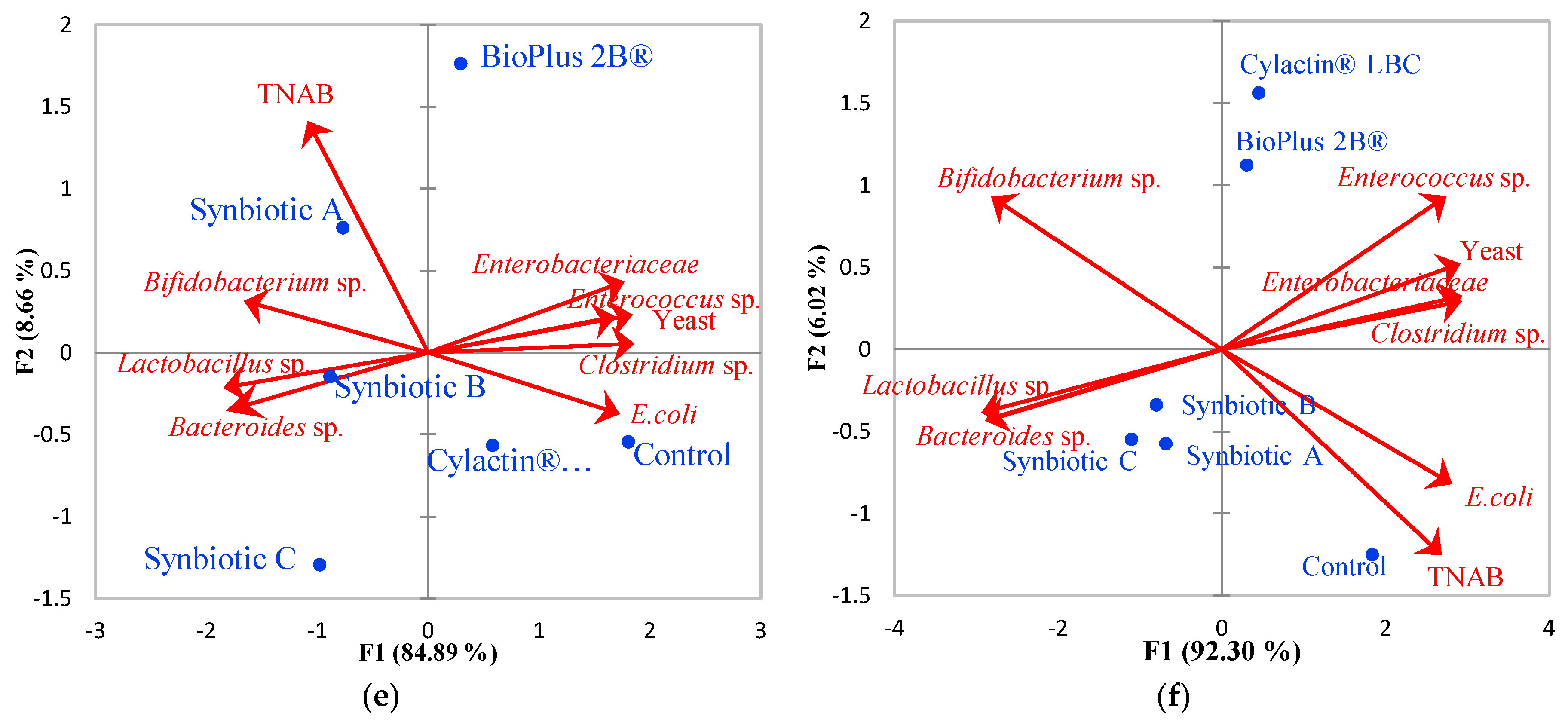
3.1. Faecal Microbiota
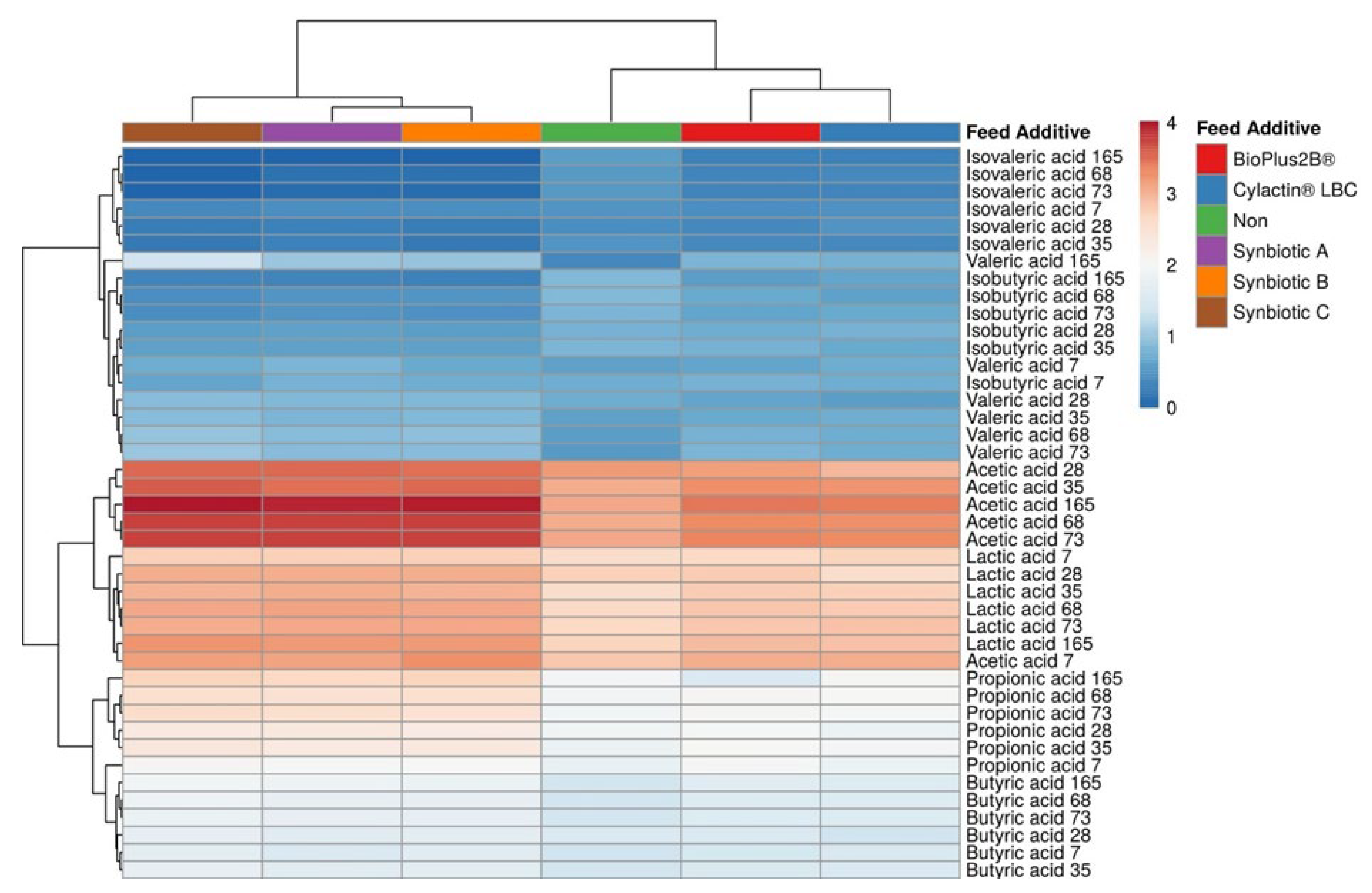
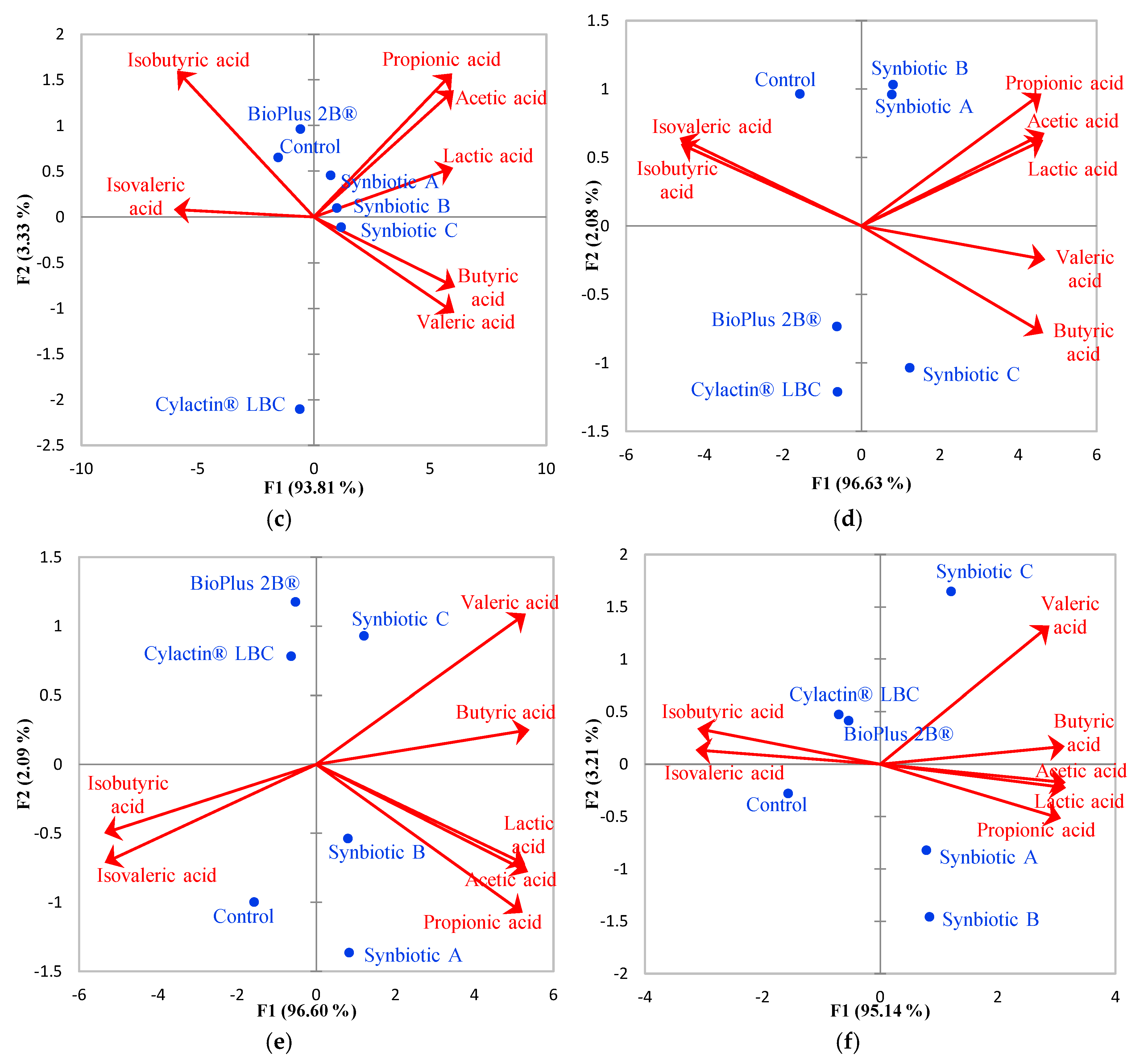
3.2. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Fecal Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Ji, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Changes in the diversity and composition of gut microbiota of weaned piglets after oral administration of Lactobacillus or an antibiotic. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 10081–10093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann-Bank, M.L.; Skovgaard, K.; Stockmarr, A.; Strube, M.L.; Larsen, N.; Kongsted, H.; Ingerslev, H.C.; Mølbak, L.; Boye, M. Characterization of the bacterial gut microbiota of piglets suffering from new neonatal porcine diarrhoea. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Ren, E.; Su, Y.; Zhu, W. Co-occurrence of early gut colonization in neonatal piglets with microbiota in the maternal and surrounding delivery environments. Anaerobe 2018, 49, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everaert, N.; Van Cruchten, S.; Weström, B.; Bailey, M.; Van Ginneken, C.; Thymann, T.; Pieper, R. A review on early gut maturation and colonization in pigs, including biological and dietary factors affecting gut homeostasis. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 233, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, B.; Talbot, G.; Beaulieu, C.; Lessard, M. Growth performance of piglets during the first two weeks of lactation affects the development of the intestinal microbiota. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradiaga, N.; Aldridge, B.; Zeineldin, M.; Lowe, J. Gastrointestinal microbiota and mucosal immune gene expression in neonatal pigs reared in a cross-fostering model. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 121, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Xu, Z.; Wan, J. Intestinal microbiota diversity and expression of pattern recognition receptors in newly weaned piglets. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevarra, R.B.; Hong, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, B.R.; Shin, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, B.N.; Kim, Y.H.; Wattanaphansak, S.; Isaacson, R.E.; et al. The dynamics of the piglet gut microbiome during the weaning transition in association with health and nutrition. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.R.; Dogi, C.A.; Ashworth, G.E.; Berardo, D.; Godoy, G.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; de Moreno de LeBlanc, A.; Greco, C.R. Effect of breast feeding time on physiological, immunological and microbial parameters of weaned piglets in an intensive breeding farm. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 176, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Fleury, M.A.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Postweaning Piglets: Understanding the Keys to Health. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Shi, B. Effects of chitosan as growth promoter on diarrhea, nutrient apparent digestibility, fecal microbiota and immune response in weaned piglets. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, T.; O’Doherty, J.V. Marine macroalgal extracts to maintain gut homeostasis in the weaning piglet. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Li, P.; Yi, D.; Wang, L.; Zhao, D.; Chen, H.; Gong, J.; Hou, Y. Beneficial impact and molecular mechanism of Bacillus coagulans on piglets’ intestine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.S.; Tang, C.H.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Zhan, T.F.; Zhang, K.; Han, Y.M.; Zhang, J.M. Effects of dietary supplementation with combinations of organic and medium chain fatty acids as replacements for chlortetracycline on growth performance, serum immunity, and fecal microbiota of weaned piglets. Livest. Sci. 2018, 216, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomba, L.; Minuti, A.; Moisá, S.J.; Trevisi, E.; Eufemi, E.; Lizier, M.; Chegdani, F.; Lucchini, F.; Rzepus, M.; Prandini, A.; et al. Gut response induced by weaning in piglet features marked changes in immune and inflammatory response. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2014, 14, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhouma, M.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Beaudry, F.; Letellier, A. Post weaning diarrhea in pigs: Risk factors and non-colistin-based control strategies. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.K.; Prakash, A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Gupta, R.C. Synbiotics in Animal Health and Production. In Nutraceuticals in Veterinary Medicine; Gupta, R.C., Srivastava, A., Rajiv, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 287–301. [Google Scholar]
- Śliżewska, K.; Motyl, I.; Libudzisz, Z.; Otlewska, A.; Burchardt, H.; Klecha, J.; Henzler, J. Lactobacillus plantarum Lactic Bacteria Strain. PL Patent 221959 B1, 30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Lactic Bacterial Strain of Lactobacillus reuteri. PL Patent 233263 B1, 30 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Lactic Bacterial Strain of Lactobacillus paracasei. PL Patent 233262 B1, 30 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Lactic Bacterial Strain of Lactobacillus pentosus. PL Patent 233261 B1, 30 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Lactic Bacterial Strain of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. PL Patent 233582 B1, 29 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Scion of Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PL Patent 233581, 29 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chlebicz, A.; Śliżewska, K. In Vitro Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1, Deoxynivalenol, Fumonisins, T-2 Toxin and Zearalenone by Probiotic Bacteria from Genus Lactobacillus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yeast. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 12, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz-Wójcik, A.; Nowak, A. Probiotic Properties of New Lactobacillus Strains Intended to Be Used as Feed Additives for Monogastric Animals. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebicz-Wójcik, A.; Śliżewska, K.; Nowak, A. Probiotic properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ŁOCK 0119 yeast. Żywność. Nauk. Technol. Jakość 2020, 3, 196–209. [Google Scholar]
- Czyżewska-Dors, E.; Kwit, K.; Stasiak, E.; Rachubik, J.; Śliżewska, K.; Pomorska-Mól, M. Effects of Newly Developed Synbiotic and Commercial Probiotic Products on The Haematological Indices, Serum Cytokines, Acute Phase Proteins Concentration, and Serum Immunoglobulins Amount in Sows and Growing Pigs—A Pilot Study. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliżewska, K.; Chlebicz, A. Synbiotics impact on dominant faecal microbiota and short-chain fatty acids production in sows. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldin, B.R. Health benefits of probiotics. Br. J. Nutr. 1998, 80, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluske, J.R.; Turpin, D.L.; Kim, J.C. Gastrointestinal tract (gut) health in the young pig. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarillo, E.A.B.; Chae, J.P.; Balolong, M.P.; Kim, H.B.; Kang, D.K. Assessment of fecal bacterial diversity among healthy piglets during the weaning transition. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Espinosa, C.D.; Abelilla, J.J.; Casas, G.A.; Lagos, L.V.; Lee, S.A.; Kwon, W.B.; Mathai, J.K.; Navarro, D.M.D.L.; Jaworski, N.W.; et al. Non-antibiotic feed additives in diets for pigs: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, C.; Plitzner, C.; Domig, K.J.; Schedle, K.; Windisch, W. Impact of inulin and a multispecies probiotic formulation on performance, microbial ecology and concomitant fermentation patterns in newly weaned piglets. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2010, 94, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Shinde, P.L.; Ingale, S.L.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, I.K.; Chae, B.J. Evaluation of multi-microbe probiotics prepared by submerged liquid or solid substrate fermentation and antibiotics in weaning pigs. Livest. Sci. 2011, 138, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.H.; Shinde, P.L.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Seo, D.K.; Pak, J.I.; Chae, B.J.; Kwon, I.K. Evaluation of multi-microbial probiotics produced by submerged liquid and solid substrate fermentation methods in broilers. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 23, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowarah, R.; Verma, A.K.; Agarwal, N.; Patel, B.H.M.; Singh, P. Effect of swine based probiotic on performance, diarrhoea scores, intestinal microbiota and gut health of grower-finisher crossbred pigs. Livest. Sci. 2017, 195, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.-L.; Chen, H.-C.; Chen, K.-N.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chen, M.-J. Optimizing Production of Two Potential Probiotic Lactobacilli Strains Isolated from Piglet Feces as Feed Additives for Weaned Piglets. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Vidal, E.; Martín-Orúe, S.M.; Castillejos, L. Practical aspects of the use of probiotics in pig production: A review. Livest. Sci. 2019, 223, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Trevisi, P.; Prates, J.A.M.; Tanghe, S.; Bosi, P.; Canibe, N.; Montagne, L.; Freire, J.; Zebeli, Q. Assessing the effect of dietary inulin supplementation on gastrointestinal fermentation, digestibility and growth in pigs: A meta-analysis. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 233, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.R.; Cho, K.J.; Kim, D.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, J.S.; Cho, W.T.; Wattanaphansak, S.; et al. Evaluation of synbiotics as gut health improvement agents against Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from the pig. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2019, 61, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Seok, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, B.N.; Johnson, T.J.; Isaacson, R.E.; Kim, H.B. Piglet gut microbial shifts early in life: Causes and effects. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, E.R.; Kowalczyk-Pecka, D.; Hanczakowska, E.; Matras, J. Effect of inulin and a probiotic supplement in the diet of pigs on selected traits of the gastrointestinal microbiome. Med. Weter. 2016, 72, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.P.; Pajarillo, E.A.B.; Oh, J.K.; Kim, H.; Kang, D.K. Revealing the combined effects of lactulose and probiotic enterococci on the swine faecal microbiota using 454 pyrosequencing. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.Y.; Kim, I.H. Effect of direct-fed microbial on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, fecal noxious gas emission, fecal microbial flora and diarrhea score in weanling pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 200, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Nyachoti, C.M.; Kim, I.H. Evaluation of effect of probiotics mixture supplementation on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, faecal bacterial enumeration, and noxious gas emission in weaning pigs. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsted, H.; Pedersen, K.; Hjulsager, C.K.; Larsen, L.E.; Pedersen, K.S.; Jorsal, S.E.; Bækbo, P. Diarrhoea in neonatal piglets: A case control study on microbiological findings. Porc. Health Manag. 2018, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Niu, Q.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Kim, S.W.; Lin, M.; Huang, R. Microbial shifts in the porcine distal gut in response to diets supplemented with Enterococcus faecalis as alternatives to antibiotics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.K.; Xue, H.X.; Zhou, Z.X.; Peng, J. A carvacrol-thymol blend decreased intestinal oxidative stress and influenced selected microbes without changing the messenger RNA levels of tight junction proteins in jejunal mucosa of weaning piglets. Animal 2017, 11, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.C.R.; Cardarelli, H.R.; Borst, W.; Albrecht, S.; Schols, H.; Gutiérrez, O.P.; Maathuis, A.J.H.; de Melo Franco, B.D.G.; De Martinis, E.C.P.; Zoetendal, E.G.; et al. Effect of galactooligosaccharides and Bifidobacterium animalis Bb-12 on growth of Lactobacillus amylovorus DSM 16698, microbial community structure, and metabolite production in an in vitro colonic model set up with human or pig microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 84, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, K.; Darby, A.C.; Hall, N.; Nau, A.; Bravo, D.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Dietary supplementation with lactose or artificial sweetener enhances swine gut Lactobacillus population abundance. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.J.; Budiño, F.E.L.; Prezzi, J.A.; Monferdini, R.P.; Otsuk, I.P.; de Moraes, J.E. Carcass traits and short-chain fatty acid profile in cecal digesta of piglets fed alfalfa hay and fructooligosaccharides. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2017, 46, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Cai, G.; Ye, J.; Yang, M.; Ding, R.; Wang, X.; Zheng, E.; Fu, D.; Li, S.; Zhou, S.; et al. A global comparison of the microbiome compositions of three gut locations in commercial pigs with extreme feed conversion ratios. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowarah, R.; Verma, A.K.; Agarwal, N. The use of Lactobacillus as an alternative of antibiotic growth promoters in pigs: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, Q.; Yin, Y. Effects of dietary nutrient levels on microbial community composition and diversity in the ileal contents of pregnant Huanjiang mini-pigs. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyasut, C.; Pattananandecha, T.; Sirilun, S.; Suwannalert, P.; Peerajan, S.; Sivamaruthi, B.S. Synbiotic preparation with lactic acid bacteria and inulin as a functional food: In vivo evaluation of microbial activities, and preneoplastic aberrant crypt foci. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 37, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zommiti, M.; Chikindas, M.L.; Ferchichi, M. Probiotics—Live Biotherapeutics: A Story of Success, Limitations, and Future Prospects—Not Only for Humans. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1266–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Feed Additive | Probiotic | Prebiotic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synbiotics | Synbiotic A | Lb. pentosus ŁOCK 1094 | Inulin |
| Lb. plantarum ŁOCK 0860 | |||
| Lb. reuteri ŁOCK 1092 | |||
| S. cerevisiae ŁOCK 0119 | |||
| Synbiotic B | Lb. pentosus ŁOCK 1094 | ||
| Lb. plantarum ŁOCK 0860 | |||
| Lb. reuteri ŁOCK 1092 | |||
| Lb. rhamnosus ŁOCK 1087 | |||
| S. cerevisiae ŁOCK 0119 | |||
| Synbiotic C | Lb. paracasei ŁOCK 1091 | ||
| Lb. pentosus ŁOCK 1094 | |||
| Lb. plantarum ŁOCK 0860 | |||
| Lb. reuteri ŁOCK 1092 | |||
| Lb. rhamnosus ŁOCK 1087 | |||
| S. cerevisiae ŁOCK 0119 | |||
| Probiotics | BioPlus 2B® | Bacillus subtilis CH201/DSM5749 | - 1 |
| Bacillus licheniformis CH200/DSM574 | |||
| Cylactin® LBC | Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 10415 | - | |
| Ingredient [g/kg] | Sow | Pre-Starter (2–8 Weeks) | Starter (8–12 Weeks) | Grower (12–18 Weeks) | Finisher (12–24 Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oats | 100 | - | - | - | 150 |
| Barley | 250 | 220 | 370 | 125 | 200 |
| Triticale | 110 | - | - | 544 | 361 |
| Wheat | 362 | 300 | 400 | 125 | 150 |
| Soybean meal | 90 | 50 | - | 100 | 110 |
| Soybean oil | 10 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 5 |
| Post-extraction soybean meal, heat-treated | 40 | 25 | 140 | - | - |
| Soybean, full-fat, heat-treated | - | 50 | - | - | - |
| Rapeseed meal | - | - | - | 60 | - |
| Whey permeate | - | 50 | - | - | - |
| LonoFish a | - | 50 | 25 | - | - |
| Specilac b | - | 40 | - | - | - |
| Lonacid Max c | - | 5 | 4 | 1 | - |
| LonoGrain d | - | 150 | - | - | - |
| Mycofix PLUS e | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| Vitamin-mineral-amino acid premix 1 | 36 | - | - | - | - |
| Vitamin-mineral-amino acid premix 2 | - | 40 | - | - | - |
| Vitamin-mineral-amino acid premix 3 | - | - | 40 | - | - |
| Vitamin-mineral-amino acid premix 4 | - | - | - | 30 | 25 |
| Chemical Composition | |||||
| Metabolizable energy (MJ/kg) | 13.1 | 13.8 | 13.8 | 13.6 | 13.5 |
| Crude protein (%) | 16.5 | 18.8 | 17.9 | 16.8 | 15.6 |
| Lysine (%) | 0.88 | 1.56 | 1.28 | 1.05 | 0.95 |
| Methionine + Cysteine (%) | 0.59 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.57 |
| Threonine (%) | 0.58 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.56 |
| Tryptophan (%) | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.18 |
| Valine (%) | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 0.75 | 0.71 |
| Calcium (%) | 1.03 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.68 | 0.67 |
| Phosphorus (%) | 0.47 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.38 |
| Vitamin A (IU/ kg) | 12,500 | 14,000 | 20,500 | 12,000 | 7700 |
| Vitamin D3 (IU/kg) | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 1540 |
| Vitamin E (mg/kg) | 80 | 84 | 100 | 63 | 100 |
| Microorganisms | Polish Standard | Cultivation Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Total no of anaerobic bacteria | PN-EN 4833-1:2013-12 | 37 °C, 48 h (anaerobically 1) |
| Bifidobacterium sp. | PN-EN 15785:2009E | |
| Clostridium sp. | PN-ISO 15213:2005 | |
| Bacteroides sp. | - 2 | 37 °C, 48 h |
| Lactobacillus sp. | PN-EN 15787:2009 | |
| Enterococcus sp. | PN-EN 15488:2009 | |
| Enterobacteriaceae family | PN-ISO 21528-2:2005 | |
| E. coli | PN-ISO 4832:2007 | 44 °C, 48 h |
| Yeast | PN-EN 15789:2009 (additional microscopic analysis) | 30 °C, 72 h |
| Parameter | Value/Type |
|---|---|
| Mobile Phase | 0.005M H2SO4 |
| Detector | refractive index (RI); ultraviolet (UV) |
| UV detector excitation wavelength (nm) | 210 |
| Autosampler | the loop dispensing valve with a syringe |
| Sample volume (μL) | 10 |
| Temperature (°C) | 60 |
| Flow rate (μL/min) | 0.6 |
| Duration (min) | 35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chlebicz-Wójcik, A.; Śliżewska, K. The Effect of Recently Developed Synbiotic Preparations on Dominant Fecal Microbiota and Organic Acids Concentrations in Feces of Piglets from Nursing to Fattening. Animals 2020, 10, 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10111999
Chlebicz-Wójcik A, Śliżewska K. The Effect of Recently Developed Synbiotic Preparations on Dominant Fecal Microbiota and Organic Acids Concentrations in Feces of Piglets from Nursing to Fattening. Animals. 2020; 10(11):1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10111999
Chicago/Turabian StyleChlebicz-Wójcik, Agnieszka, and Katarzyna Śliżewska. 2020. "The Effect of Recently Developed Synbiotic Preparations on Dominant Fecal Microbiota and Organic Acids Concentrations in Feces of Piglets from Nursing to Fattening" Animals 10, no. 11: 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10111999
APA StyleChlebicz-Wójcik, A., & Śliżewska, K. (2020). The Effect of Recently Developed Synbiotic Preparations on Dominant Fecal Microbiota and Organic Acids Concentrations in Feces of Piglets from Nursing to Fattening. Animals, 10(11), 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10111999






