Antibiofouling Activity of Graphene Materials and Graphene-Based Antimicrobial Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
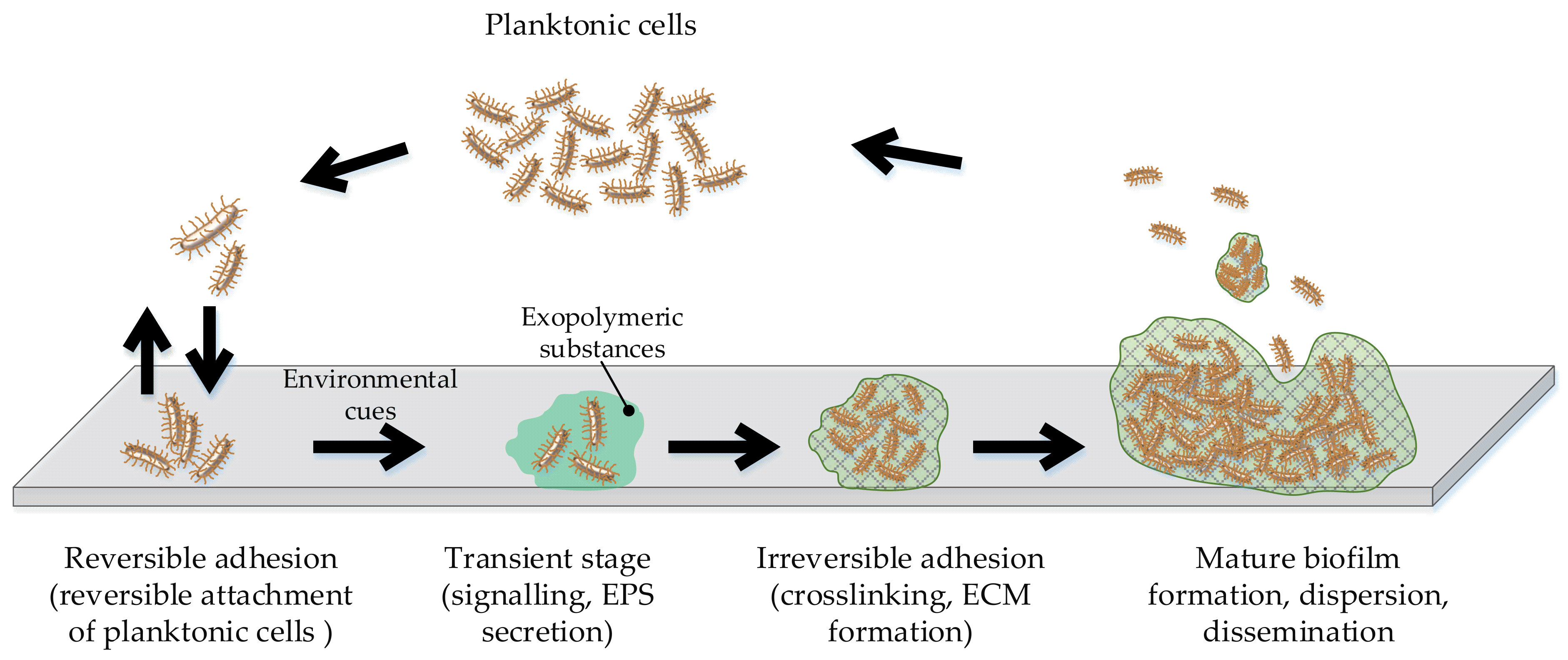
2. Microbial Biofilms
3. Antimicrobial Activity and Applications of Graphene Nanomaterials
3.1. Graphene and Its Derivatives
3.2. Graphene-Based Nanocomposites
3.3. Potential Applications of Graphene Nanomaterials
4. Antimicrobial Coatings Based on Graphene Materials
4.1. Coatings Based on Graphene and Graphene Derivatives (GO, RGO)
4.2. Graphene Nanocomposite Coatings
4.3. Wound Dressing and Healing
5. Proposed Mechanisms of Microbial Adhesion Inhibition by Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
6. Factors Influencing Antimicrobial Activity of Graphene Nanomaterials-Based Coatings
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ (accessed on 7 June 2021).
- Types of Healthcare-Associated Infections. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/hai/infectiontypes.html (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Jha, A.K.; Larizgoitia, I.; Audera-Lopez, C.; Prasopa-Plaizier, N.; Waters, H.; Bates, D.W. The Global Burden of Unsafe Medical Care: Analytic Modelling of Observational Studies. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2013, 22, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slawomirski, L.; Auraaen, A.; Klazinga, N.S. The Economics of Patient Safety: Strengthening a Value-Based Approach to Reducing Patient Harm at National Level; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). The Burden of Health Care-Associated Infection Worldwide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Antibiotic Resistance. Available online: https://arpsp.cdc.gov/profile/antibiotic-resistance?tab=antibiotic-resistance (accessed on 7 June 2021).
- Mahabubul Islam Majumder, M.; Ahmed, T.; Ahmed, S.; Rahman Khan, A. Microbiology of Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection. In Microbiology of Urinary Tract Infections-Microbial Agents and Predisposing Factors; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanwate, N.A.; Tiwari, A.A.; Thakare, P.V. Importance of Biofilm in Medical Sciences: With Special Reference to Uropathogens. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, S.L.; Suleman, L.; Vuotto, C.; Donelli, G. Healthcare-Associated Infections, Medical Devices and Biofilms: Risk, Tolerance and Control. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MarketsandMarkets. Antimicrobial Coatings Market. In Size Report, 2021–2028; MarketsandMarkets: Pune, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vladkova, T.; Staneva, A.; Gospodinova, D. Surface Engineered Biomaterials and Ureteral Stents Inhibiting Biofilm Formation and Encrustation. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2020, 404, 126424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deokar, A.R.; Sinha, M.; Gollavelli, G.; Ling, Y.C. Antimicrobial Perspectives for Graphene-Based Nanomaterials. In Graphene Science Handbook: Applications and Industrialization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Vladkova, T.; Akuzov, D. Current Approaches to Reduction Marine Biofilm Formation. In Biofilms Control: Biomedical and Industrial Environments; Raju, S., Thiyagarajan, V., Murthy, P.S., Eds.; Narosa Publishing House: New Delhi, India, 2019; p. 258. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, P.S.; Sekar, R.; Thiyagarajan, V. (Eds.) Biofilms in Environmental Biotechnology; Alpha Science: Temple City, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An Emergent Form of Bacterial Life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, T. Surface Engineering for Non-Toxic Biofouling Control (Review). J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2007, 42, 239–256. [Google Scholar]
- Vladkova, T.; Akuzov, D.; Klöppel, A.; Brümmer, F. Current Approaches to Reduction Marine Biofilm Formation. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2014, 49, 345–355. [Google Scholar]
- Vladkova, T.G. Surface Engineering of Polymeric Biomaterials; Smithers Rapra Technology: Shrewsbury, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vroman, L. Effect of Adsorbed Proteins on the Wettability of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Solids. Nature 1962, 196, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhalgh, R.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.C.; Whitehead, K.A. Antimicrobial Strategies to Reduce Polymer Biomaterial Infections and Their Economic Implications and Considerations. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 136, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, P.; Locklin, J.; Handa, H. A Review of the Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Coatings for Urinary Catheters. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran, P.L.; Hamood, A.N.; Reid, T.W. Antimicrobial Coatings to Prevent Biofilm Formation on Medical Devices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 175–204. [Google Scholar]
- Belanger, C.R.; Mansour, S.C.; Pletzer, D.; Hancock, R.E.W. Alternative Strategies for the Study and Treatment of Clinical Bacterial Biofilms. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2017, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gospodonova, D.; Ivanova, I.; Vladkova, T. Fabrication and Characterization of Antimicrobial Magnetron Cosputtered TiO2/Ag/Cu Composite Coatings. Coatings 2021, 11, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Huo, P.; Zhang, R.; Liu, B. Antibacterial Properties of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Ma, R.; Gao, M.; Tian, X.; Li, Y.Q.; Zeng, L.; Li, R. Antibacterial Applications of Graphene Oxides: Structure-Activity Relationships, Molecular Initiating Events and Biosafety. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tremblay, P.L. Graphene: An Antibacterial Agent or a Promoter of Bacterial Proliferation? iScience 2020, 23, 101787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Tan, S.; Xing, Y.; Pu, Q.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.X. Graphene Oxide as an Efficient Antimicrobial Nanomaterial for Eradicating Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria in Vitro and in Vivo. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 157, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, M.; Dadashpour, M.; Hejazi, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Behnam, B.; de la Guardia, M.; Shadjou, N.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Anti-Bacterial Activity of Graphene Oxide as a New Weapon Nanomaterial to Combat Multidrug-Resistance Bacteria. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bregnocchi, A.; Zanni, E.; Uccelletti, D.; Marra, F.; Cavallini, D.; De Angelis, F.; De Bellis, G.; Bossù, M.; Ierardo, G.; Polimeni, A.; et al. Graphene-Based Dental Adhesive with Anti-Biofilm Activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, D.S.; Ivanova, I.A.; Staneva, A.; Alby-Kaya, M.; Vladkova, T.G. Antifungal Potential of Some Collagen-Based Nanocomposites Against Candida Lusitaniae. Nanosci. Technol. Open Access 2016, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, T.G.; Ivanova, I.A.; Staneva, A.D.; Albu, M.G.; Shalaby, A.S.A.; Topousova, T.I.; Kostadinova, A.S. Preparation and Biological Activity of New Collagen Composites Part II: Collagen/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites. J. Arch. Mil. Med. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Giulio, M.; Zappacosta, R.; Di Lodovico, S.; Di Campli, E.; Siani, G.; Fontana, A.; Cellini, L. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Efficacy of Graphene Oxide against Chronic Wound Microorganisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, M.Y.; Xie, Y.; Yu, C.H.; Chen, G.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, T.; Peng, Q. Graphene-Based Nanomaterials: The Promising Active Agents for Antibiotics-Independent Antibacterial Applications. J. Control. Release 2019, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, F.; Calcaterra, A.; Ruggiero, V.; Pichichero, E.; Martino, A.; Iosi, F.; Bertuccini, L.; Antonaroli, S.; Mardente, S.; Zicari, A.; et al. Functionalized Graphene Derivatives: Antibacterial Properties and Cytotoxicity. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adlhart, C.; Verran, J.; Azevedo, N.F.; Olmez, H.; Keinänen-Toivola, M.M.; Gouveia, I.; Melo, L.F.; Crijns, F. Surface Modifications for Antimicrobial Effects in the Healthcare Setting: A Critical Overview. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 99, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, T.; Shi, X.; Cheng, L.; Luo, Y.; Dong, Z.; Gong, H.; Xu, L.; Zhong, Z.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Graphene-Based Nanocomposite as an Effective, Multifunctional, and Recyclable Antibacterial Agent. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 8542–8548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.H.; Gong, J.L.; Zeng, G.M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.Y.; Huan, S.Y. Graphene-CdS Nanocomposite Inactivation Performance toward Escherichia coli in the Presence of Humic Acid under Visible Light Irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Lekshmi, G.S.; Ostrikov, K.; Lussini, V.; Blinco, J.; Mohandas, M.; Vasilev, K.; Bottle, S.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Synergic Bactericidal Effects of Reduced Graphene Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ran, X.; Du, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Pu, F.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Hyaluronic Acid-Templated Ag Nanoparticles/Graphene Oxide Composites for Synergistic Therapy of Bacteria Infection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 19717–19724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dat, N.M.; Long, P.N.B.; Nhi, D.C.U.; Minh, N.N.; Duy, L.M.; Quan, L.N.; Nam, H.M.; Phong, M.T.; Hieu, N.H. Synthesis of Silver/Reduced Graphene Oxide for Antibacterial Activity and Catalytic Reduction of Organic Dyes. Synth. Met. 2020, 260, 116260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ameen, F.; Khan, F.; Al-Arfaj, A.; Ahmed, B. Fabrication and Antibacterial Activity of Nanoenhanced Conjugate of Silver (I) Oxide with Graphene Oxide. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.; Dat, N.M.; Thinh, D.B.; Minh Anh, T.N.; Nguyet, D.M.; Quan, T.H.; Bao Long, P.N.; Nam, H.M.; Phong, M.T.; Hieu, N.H. Optimization of the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles-Decorated Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. Synth. Met. 2020, 268, 116492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, F.; Li, K.; Wei, D.; Liu, Z. Efficient Loading of Silver Nanoparticles on Graphene Oxide and Its Antibacterial Properties. Nano Express 2020, 1, 010041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, C.; Longo, F.; Castagnola, R.; Marigo, L.; Grande, N.M.; Cordaro, M.; Cacaci, M.; Papi, M.; Palmieri, V.; Bugli, F.; et al. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Properties of Graphene Oxide on Enterococcus Faecalis. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Ni, H.; Hu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, J.; Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, H. Rapid Synthesis and Characterization of Silver-Loaded Graphene Oxide Nanomaterials and Their Antibacterial Applications. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Aslam, S.; Mustafa, F.; Arshad, U. Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Surfactant Free Ag–GO Nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh Dat, N.; Tan Tai, L.; Tan Khang, P.; Ngoc Minh Anh, T.; Minh Nguyet, D.; Hoang Quan, T.; Ba Thinh, D.; Thi Thien, D.; Minh Nam, H.; Thanh Phong, M.; et al. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity Investigation of Silver Nanoparticle-Decorated Graphene Oxide. Mater. Lett. 2021, 285, 128993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Li, P.; Sun, J.; Jiang, J.; Dai, F.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, G.; Tan, Y.; et al. Remarkable Antibacterial Activity of Reduced Graphene Oxide Functionalized by Copper Ions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staneva, A.; Kichukova, D. Kovacheva, D. Synthesis of Antibacterial Nanocomposites with Reduced Graphene Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2021, 56, 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Kichukova, D.; Kovacheva, D.; Staneva, A.; Spassova, I. Antimicrobial Impact of Nanocomposites of Reduced Graphene Oxide with Silver and Copper. Comptes Rendus L’Academie Bulg. Sci. 2021, 74, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, N.; Shalaby, A. Sol-Gel Synthesis of Materials in the System SiO2/ZnO/TiO2/RGO and Their Antimicrobial Efficiency against E.Coli K12. Comptes Rendus l’Académie Bulg. Sci. Sci. Mathématiques Nat. 2016, 69, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Yan, J.; Ning, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Bi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Guo, J. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Properties of Graphene and Its Derivatives. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syama, S.; Mohanan, P.V. Comprehensive Application of Graphene: Emphasis on Biomedical Concerns. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, H.; Sun, H.; Qu, X. Antibacterial Applications of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials: Recent Achievements and Challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Chen, J.; Teng, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, G.; Liu, S.; Luo, Z.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, L. The Antibacterial Applications of Graphene and Its Derivatives. Small 2016, 12, 4165–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, T.; Kamali, A.R. Anti-Pathogenic Activity of Graphene Nanomaterials: A Review. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 199, 111509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Li, N.; Pu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, T.; Tao, J. Advanced Review of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials in Drug Delivery Systems: Synthesis, Modification, Toxicity and Application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Graphene Family Nanomaterials (GFNs)-Promising Materials for Antimicrobial Coating and Film: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez de Saravia, S.G.; Rastelli, S.E.; Angulo-Pineda, C.; Palza, H.; Viera, M.R. Anti-Adhesion and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanoparticle Composites. Rev. Mater. 2020, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, S.; Jannesari, A.; Yousefzadi, M.; Ghaderi, A.; Shahdadi, A. Eco-Friendly Foul Release Coatings Based on a Novel Reduced Graphene Oxide/Ag Nanocomposite Prepared by a Green Synthesis Approach. Prog. Org. Coatings 2021, 151, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Lu, X.; Lei, P.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Cu-Decorated Graphene Oxide Coatings with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity for Surface Modification of Implant. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021, 141, 111345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchareb, S.; Doufnoune, R.; Riahi, F.; Cherif-Silini, H.; Belbahri, L. High Performance of Polysulfone/Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanocomposites with Excellent Antibacterial Capability for Medical Applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, S.; Gaska, K.; Kádár, R.; Mijakovic, I. Graphene-Based Antimicrobial Biomedical Surfaces. ChemPhysChem 2021, 22, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Guo, Z. Wettability of Graphene: From Influencing Factors and Reversible Conversions to Potential Applications. Nanoscale Horizons 2019, 4, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Zou, T.; Lee, A.H.C.; Zhang, C. The Potential Translational Applications of Nanoparticles in Endodontics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2087–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadnejad, J.; Yazdian, F.; Omidi, M.; Rostami, A.D.; Rasekh, B.; Fathinia, A. Graphene Oxide/Silver Nanohybrid: Optimization, Antibacterial Activity and Its Impregnation on Bacterial Cellulose as a Potential Wound Dressing Based on GO-Ag Nanocomposite-Coated BC. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, Q.; Gong, P.; Ma, L.; Yang, S. A Novel Wound Dressing Based on Ag/Graphene Polymer Hydrogel: Effectively Kill Bacteria and Accelerate Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3933–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Han, L.; Li, P.; Jia, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Tan, H.; Guo, T.; Lu, X. Mussel-Inspired Electroactive and Antioxidative Scaffolds with Incorporation of Polydopamine-Reduced Graphene Oxide for Enhancing Skin Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7703–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yan, Z.; Lian, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K. Graphene Oxide Coated Shell-Core Structured Chitosan/PLLA Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Wound Dressing. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 622–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielesz, A.; Fabia, J.; Biniaś, W.; Fryczkowski, R.; Fryczkowska, B.; Gawłowski, A.; Machnicka, A.; Bobiński, R.; Laane, H.M.; Waksmańska, W. Graphene Oxide and Stabilized Ortho-Silicic Acid as Modifiers of Amnion and Burn Affected Skin: A Comparative Study. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2021, 14, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, S.; Song, K.; Wang, Z.; Han, Z.; Zhao, K.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q. 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Hybrid Nano-Copper Scaffolds with a High Antibacterial Performance. Mater. Lett. 2020, 267, 127527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, C.D.; Mangadlao, J.; Fan, J.; De Leon, A.; Delgado-Ospina, J.; Rojas, J.G.; Rodrigues, D.F.; Advincula, R. Chitosan Cross-Linked Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Films with Antimicrobial Activity for Application in Food Industry. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 374, 1600114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Lu, X.; Kaneda, M.; Zhang, W.; Bernstein, R.; Ma, J.; Elimelech, M. Graphene Oxide-Functionalized Membranes: The Importance of Nanosheet Surface Exposure for Biofouling Resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slate, A.J.; Karaky, N.; Whitehead, K.A. Antimicrobial Properties of Modified Graphene and Other Advanced 2D Material Coated Surfaces. In 2D Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 86–104. [Google Scholar]
- Spikes of Graphene Can Kill Bacteria on Implants. Available online: https://www.chalmers.se/en/departments/bio/news/Pages/Spikes-of-graphene-can-kill-bacteria-on-implants.aspx (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Pandit, S.; Cao, Z.; Mokkapati, V.R.S.S.; Celauro, E.; Yurgens, A.; Lovmar, M.; Westerlund, F.; Sun, J.; Mijakovic, I. Vertically Aligned Graphene Coating Is Bactericidal and Prevents the Formation of Bacterial Biofilms. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1701331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.N.; Borges, I.; Pereira, A.T.; Maia, A.F.; Pestana, M.; Magalhães, F.D.; Pinto, A.M.; Gonçalves, I.C. Antimicrobial Graphene Nanoplatelets Coatings for Silicone Catheters. Carbon N. Y. 2018, 139, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, N.; Ellepola, K.; Decroix, F.E.D.; Morin, J.L.P.; Castro Neto, A.H.; Seneviratne, C.J.; Rosa, V. Graphene onto Medical Grade Titanium: An Atom-Thick Multimodal Coating That Promotes Osteoblast Maturation and Inhibits Biofilm Formation from Distinct Species. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu, M.; Gopal, J.; Chun, S.; Lee, S.K. Hydrophobic Bacteria-Repellant Graphene Coatings from Recycled Pencil Stubs. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yang, C.M.; Sun, X.F.; Xia, P.F.; Qin, J.; Guo, B.B.; Wang, S.G. Influences of Graphene Oxide on Biofilm Formation of Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2853–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wei, S.; Ge, C.; Zhao, C.; Guo, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J. Ultrafast Growth of Uniform Multi-Layer Graphene Films Directly on Silicon Dioxide Substrates. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, P.; Das, S.K. Bio-Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Nanoscale Antimicrobial Coating for Medical Devices. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, I.; Henriques, P.C.; Gomes, R.N.; Pinto, A.M.; Pestana, M.; Magalhães, F.D.; Gonçalves, I.C. Exposure of Smaller and Oxidized Graphene on Polyurethane Surface Improves Its Antimicrobial Performance. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Chen, D.; Gu, P.; Wang, G.; Fan, X. Distinct Antibacterial Activity of a Vertically Aligned Graphene Coating against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 6069–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankus, D. Antimicrobial Properties of Graphite and Coal-Derived Graphene Oxides as an Advanced Coating for Titanium Implants; Virginia Tech: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Major, R.; Sanak, M.; Mzyk, A.; Lipinska, L.; Kot, M.; Lacki, P.; Bruckert, F.; Major, B. Graphene Based Porous Coatings with Antibacterial and Antithrombogenous Function-Materials and Design. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2014, 14, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janković, A.; Eraković, S.; Vukašinović-Sekulić, M.; Mišković-Stanković, V.; Park, S.J.; Rhee, K.Y. Graphene-Based Antibacterial Composite Coatings Electrodeposited on Titanium for Biomedical Applications. Prog. Org. Coatings 2015, 83, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybowska-Sarapuk, Ł.; Kotela, A.; Krzemiński, J.; Wróblewska, M.; Marchel, H.; Romaniec, M.; Łȩgosz, P.; Jakubowska, M. Graphene Nanolayers as a New Method for Bacterial Biofilm Prevention: Preliminary Results. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.S.; El-Safty, S.A.; Fatthallah, N.A.; Shenashen, M.A. Silicone/Graphene Oxide Sheet-Alumina Nanorod Ternary Composite for Superhydrophobic Antifouling Coating. Prog. Org. Coatings 2018, 121, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, S.; Wierzbicki, M.; Sawosz, E.; Jung, A.; Gielerak, G.; Biernat, J.; Jaremek, H.; Łojkowski, W.; Woźniak, B.; Wojnarowicz, J.; et al. Graphene Oxide-Based Nanocomposites Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles as an Antibacterial Agent. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stan, M.S.; Nica, I.C.; Popa, M.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Iordache, O.; Dumitrescu, I.; Diamandescu, L.; Dinischiotu, A. Reduced Graphene Oxide/TiO2 Nanocomposites Coating of Cotton Fabrics with Antibacterial and Self-Cleaning Properties. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 49, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhang, T.; Bing, W.; Dong, S.; Tian, L. Antifouling Performance and Mechanism of Elastic Graphene-Silicone Rubber Composite Membranes. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Pan, Q.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zan, X.; Guan, Y. Graphene Oxide and Lysozyme Ultrathin Films with Strong Antibacterial and Enhanced Osteogenesis. Langmuir 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, A.; Naeimi, F.; Fakhrizadeh, A.A. Electrodeposited Hydroxyapatite/Graphene Oxide/Zirconia Oxide Composite Coatings: Characterization and Antibacterial Activity. Adv. Ceram. Prog. 2020, 6, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, A.; Jena, G.; Pongachira George, R.; Philip, J. Polydimethylsiloxane–Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Coatings with Improved Anti-Corrosion and Anti-Biofouling Properties. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 7404–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wen, S.F.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yue, Z.F. Hybrid Siloxane-Epoxy Coating Reinforced by Worm-like Graphene Oxide with Improved Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance. Mater. Des. 2021, 207, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, N.A.; Ehsani, M.; Zaarei, D.; Kalaee, M.R.; Khajavi, R. Nanocomposite Coatings Based on Modified Graphene Oxide and Polydimethylsiloxane: Characterization and Thermal Properties. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2020, 93, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtari, M.; Dehghani-Firouzabadi, M.; Aliabadi, M.; Arefkhani, M. Effect of Graphene Oxide Nanoparticle Coatings on the Strength of Packaging Paper and Its Barrier and Antibacterial Properties. Bois Forets des Trop. 2019, 342, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacaci, M.; Martini, C.; Guarino, C.; Torelli, R.; Bugli, F.; Sanguinetti, M. Graphene Oxide Coatings as Tools to Prevent Microbial Biofilm Formation on Medical Device. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, M.; Pan, N.; Huang, T.S.; Kim, I.S.; Ren, X. Antibacterial Chitosan Hybrid Films with N-Halamine-Functionalized Graphene Oxide. Nano 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CVD Graphene on Silicon Substrate (Si). Available online: https://www.acsmaterial.com/graphene-on-silicon-substrate.html (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Graphene Coatings. Available online: https://microspray.com/graphene-coatings (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Vladkova, T.G.; Ivanova, I.A.; Staneva, A.D.; Albu-Kaya, M.G.; Shalaby, A.S.A.; Moskova-Doumanova, V.; Kostadinova, A.S. Preparation and Biological Activity of New Collagen Composites, Part III. Collagen/(Ag/RGO) and Collagen/(Ag/RGO/SiO2) Composites. J. Arch. Mil. Med. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staneva, A.; Albu-Kaya, M.; Martinov, B.; Ivanova, I.; Vladkova, T. Antimicrobial Activity of Collagen/(RGO/ZnO/TiO2 /SiO2) Composites. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2020, 55, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giulio, M.; Di Lodovico, S.; Fontana, A.; Traini, T.; Di Campli, E.; Pilato, S.; D’Ercole, S.; Cellini, L. Graphene Oxide Affects Staphylococcus Aureus and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Dual Species Biofilm in Lubbock Chronic Wound Biofilm Model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; Zhu, S.; Yin, W.; Chen, C.; Nie, G.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials beyond Graphene for Antibacterial Applications: Current Progress and Future Perspectives. Theranostics 2020, 10, 757–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial Activity of Graphite, Graphite Oxide, Graphene Oxide, and Reduced Graphene Oxide: Membrane and Oxidative Stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Veerapandian, M.; Zhang, L.H.; Yun, K.; Kim, S.J. Antibacterial Efficiency of Graphene Nanosheets against Pathogenic Bacteria via Lipid Peroxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 17280–17287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, F.; De Faria, A.F.; Nejati, S.; Elimelech, M. Antimicrobial Properties of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets: Why Size Matters. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7226–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of the Antimicrobial Activities of Graphene Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Antibacterial Activity of Graphene-Based Materials. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6892–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rojas-Andrade, M.D.; Chata, G.; Rouholiman, D.; Liu, J.; Saltikov, C.; Chen, S. Antibacterial Mechanisms of Graphene-Based Composite Nanomaterials. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, V.; Bugli, F.; Lauriola, M.C.; Cacaci, M.; Torelli, R.; Ciasca, G.; Conti, C.; Sanguinetti, M.; Papi, M.; De Spirito, M. Bacteria Meet Graphene: Modulation of Graphene Oxide Nanosheet Interaction with Human Pathogens for Effective Antimicrobial Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi-Lalabadi, M.; Hashemi, H.; Feng, J.; Jafari, S.M. Carbon Nanomaterials against Pathogens; the Antimicrobial Activity of Carbon Nanotubes, Graphene/Graphene Oxide, Fullerenes, and Their Nanocomposites. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Kumar, A.; Bekyarova, E.; Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Ansari, M.S.; Cochis, A.; Rimondini, L. Antimicrobial Mechanisms and Effectiveness of Graphene and Graphene-Functionalized Biomaterials. A Scope Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Luo, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z. Underlying Mechanisms of Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress Photoinduced by Graphene and Its Surface-Functionalized Derivatives. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, H.; Qiu, C.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Coy, E.; Moya, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, G. Electron Transfer Correlated Antibacterial Activity of Biocompatible Graphene Nanosheets-TiO2 Coatings. Carbon N. Y. 2020, 166, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Liu, L.; Qian, S.; Qian, W.; Liu, X. Why Does Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Lose the Antibacterial Activity? J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Graphene Nanocomposite | Preparation Mode | In Vitro Antibacterial Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gr/Ag NPs/iron NPs | Growth of Ag and iron NPs on the surface | E. coli; S. aureus | [37] |
| Gr/cadmium sulfide | Decoration | E. coli in presence of humic acid, under visible light | [38] |
| RGO/Ag NPs | Using hyaluronic acid template | E. coli in presence of humic acid, under visible light | [39] |
| GO/Hyaluronic acid/Ag NPs | Co-precipitation | Human pathogenic S. aureus; E. coli; P. mirabilis, S. aureus in vitro and wound disinfection model in vivo | [40] |
| RGO/Ag NPs (diam.16 ± 3.7 nm) | Sonication decoration | S. aureus; E. coli, P. aeruginosa | [41] |
| GO/Ag2O | In situ method; glucose as reducing agent | Multidrug resistant E. coli, P. aeruginosa; K. pneumonia; S. aureus | [42] |
| GO/Ag NPs | Without dispersing agent | S. aureus; S. enterica | [43] |
| RGO/Ag NPs | Film on dentin | S. aureus; E. coli E. faecalis | [44] |
| GO | Ultrasound assisted conditions | S. aureus | [45] |
| GO/Ag, water soluble | One step procedure, without surfactants and reductant | E. coli | [46] |
| GO/Ag | Exfoliation | E. coli | [47] |
| GO/Ag NPs | Co-precipitation; green reducing agent | E. coli | [48] |
| RGO/copper | Decoration | Algicidal activity without toxicity to mammalian cells | [49] |
| RGO/Ag | Modified method of Hummer | E. coli | [50] |
| RGO/Ag/Cu | Modified method of Hummer | E. coli | [51] |
| RGO/ZnO/TiO2/SiO2 | Modified method of Hammer | E. coli | [52] |
| Coating | Deposition Mode | Potential Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gr, GO and RGO coatings | |||
| Graphene coating, horizontally grown | Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) | A variety of applications | [76] |
| Graphene coating, vertically grown | Plasma-enhanced CVD | A variety of applications | [77] |
| Gr NPs coating | Dip and spray coating | Silicone rubber catheters | [78] |
| Atom thick GR coating | Hot pressing, dry transfer | Medical grade titanium | [79] |
| Gr coating from recycled pencil tubes | Sonication exfoliation | Protection against pathogenic bacteria | [80] |
| GO coating | Spraying | Antibiofilm protection | [81] |
| Uniform Gr film | Ultrafast CVD | A variety of applications | [82] |
| Bio-RGO coating | Spaying | Medical devices | [83] |
| Gr coatings with tunable wettability | Surface immobilization | Smart material surfaces | [65] |
| Surfaces functionalized by 2D GO | Poly(dopamine) chemistry | Water purification membranes | [74] |
| Small, oxidized GR nanoplatelets on polyurethane (PU) | Meld blending and dip coating | Antimicrobial protection of PU | [84] |
| Vertically and horizontally aligned Gr on semiconductor silicone (Si) and insulator silicon dioxide (SiO2) | CVD | Antibiofouling protection | [85] |
| Coal derived GO coatings | One pot process | Titanium implants | [86] |
| Gr nanocomposite coatings | |||
| Porous polyelectrolyte coating with RGO flakes | Layer-by-layer deposition | Cardiovascular devices | [87] |
| Porous silver/hydroxyapatite/graphene coating | Electrophoretical deposition | Medical grade titanium | [88] |
| Gr- and Ag-NPs decorated GR nanolayers | Spray coating | A variety of applications | [89] |
| Chitosan cross-linked GO nanocomposite coating | Spraying | A variety of applications | [73] |
| A ternary Si/GO/Al2O3 hybrid nanorods coatings | Solution casting | Superhydrophobic antifouling coatings | [90] |
| GO based nanocomposites, decorated with Ag NPs | Ultrasonic deposition | Multifunctional antibacterial and antifungal protection of SiO2/Si substrates | [91] |
| RGO/TiO2 nanocomposite coating | Deeping | Cotton fabrics | [92] |
| Gr/silicon rubber | Spray coating | Biofouling prevention | [93] |
| GO and lysozyme ultrathin films | Surface immobilization | Antibacterial protection and improved ontogenesis (orthopedic) | [94] |
| Chitozan hybrid films/N-halamin-functionalized GO | Surface immobilization | Medical devices | [95] |
| Hydroxyapatite/GO/ZrO composite coating | Electrophoretic deposition | Titanium substrates | [95] |
| GO/Si/PDMS coating | Spraying, brushing | Carbon steel anticorrosion and antimicrobial protection | [96] |
| Hybrid PDMS/Epoxy/Worm-like GO nanoscrolls | Multistep procedure | AA24 alloy anticorrosion and antimicrobial protection | [97] |
| Modified GO/PDMS | Multistep procedure | Hydrophobic antifouling surfaces | [98] |
| Hybrid GO/Ag NPs nanocomposite coatings | Multistep procedure | Antibiofilm applications | [60] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Staneva, A.D.; Dimitrov, D.K.; Gospodinova, D.N.; Vladkova, T.G. Antibiofouling Activity of Graphene Materials and Graphene-Based Antimicrobial Coatings. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091839
Staneva AD, Dimitrov DK, Gospodinova DN, Vladkova TG. Antibiofouling Activity of Graphene Materials and Graphene-Based Antimicrobial Coatings. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(9):1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091839
Chicago/Turabian StyleStaneva, Anna D., Dimitar K. Dimitrov, Dilyana N. Gospodinova, and Todorka G. Vladkova. 2021. "Antibiofouling Activity of Graphene Materials and Graphene-Based Antimicrobial Coatings" Microorganisms 9, no. 9: 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091839
APA StyleStaneva, A. D., Dimitrov, D. K., Gospodinova, D. N., & Vladkova, T. G. (2021). Antibiofouling Activity of Graphene Materials and Graphene-Based Antimicrobial Coatings. Microorganisms, 9(9), 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091839






