Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Frankfurt am Main from October to December 2020 Reveals High Viral Diversity Including Spike Mutation N501Y in B.1.1.70 and B.1.1.7
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and RT-qPCR-Testing
2.2. Cell Culture and Viral Outgrowth Assay
2.3. RNA Isolation and Confirmatory RT-qPCR
2.4. NGS Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 Genomes
2.5. Bioinformatics
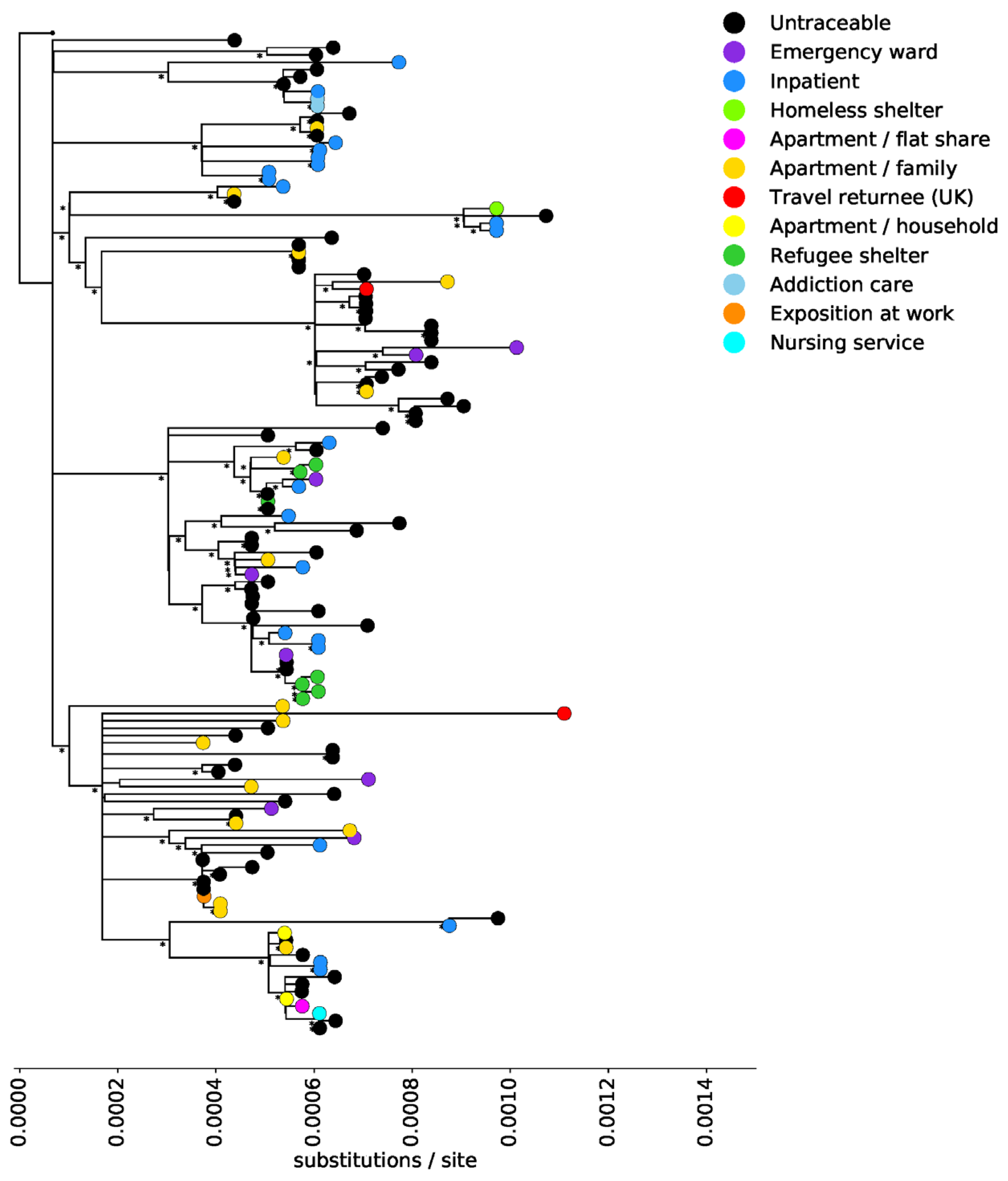
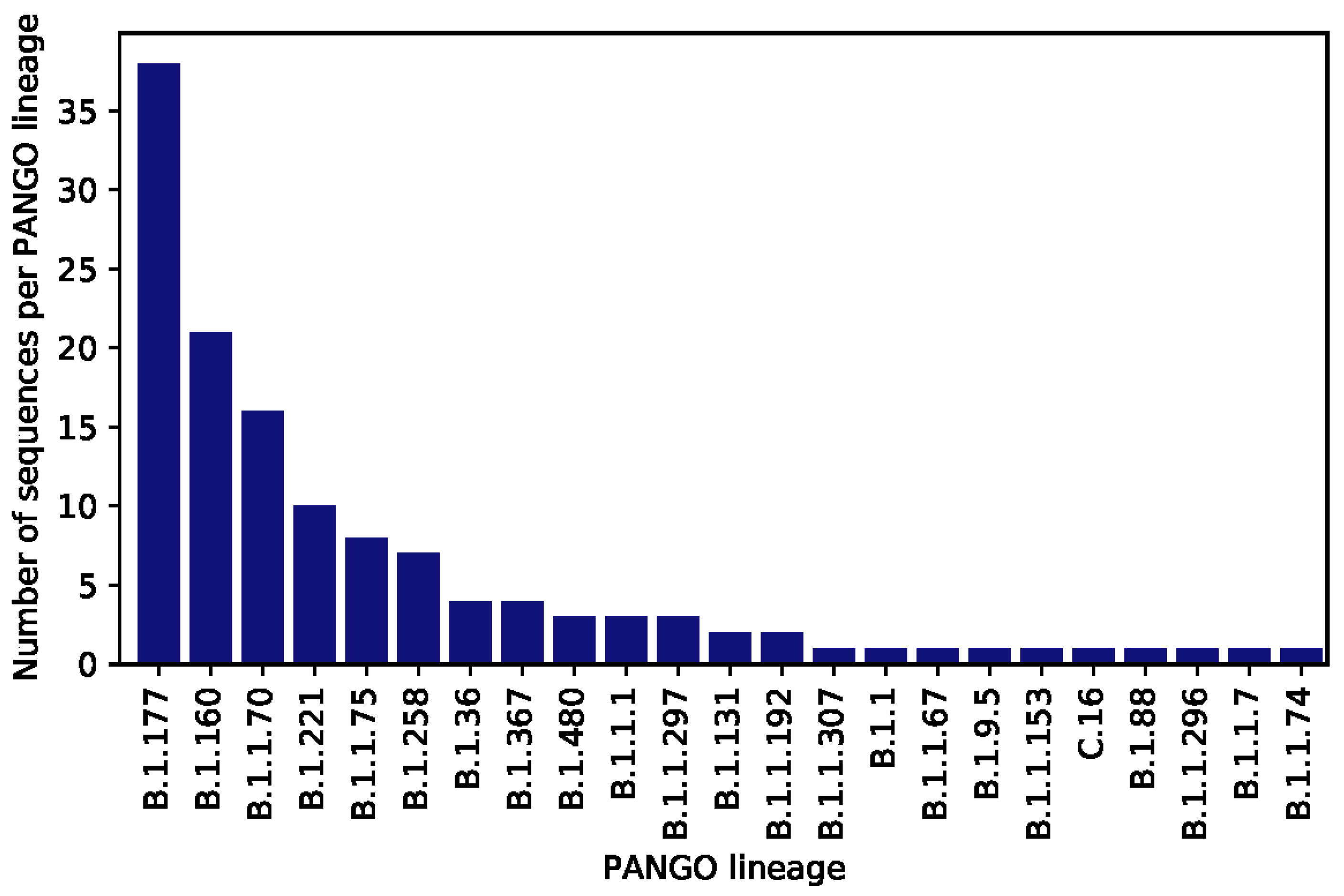
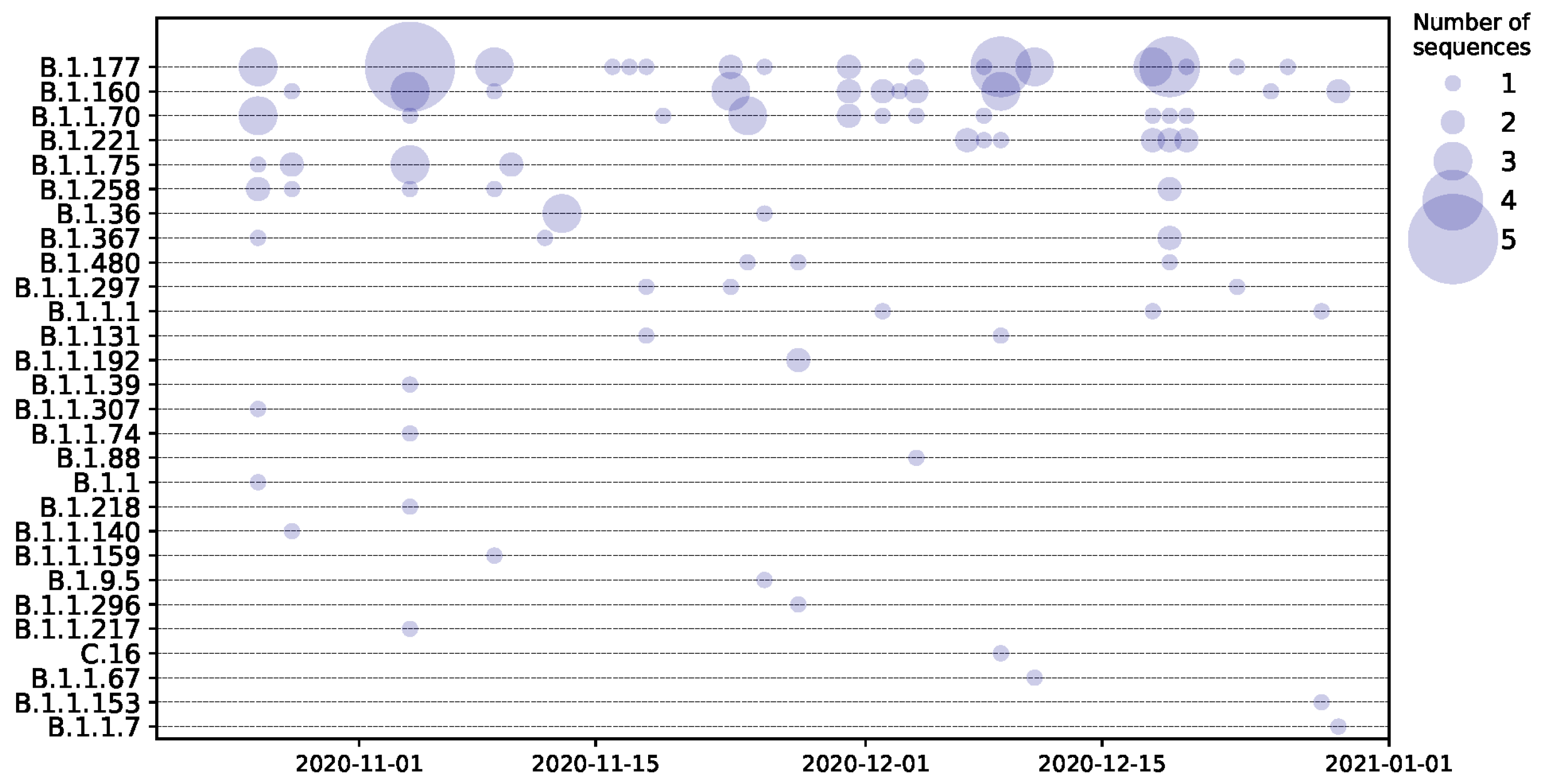
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Y.J.; Chiba, S.; Halfmann, P.; Ehre, C.; Kuroda, M.; Dinnon, K.H.; Leist, S.R.; Schäfer, A.; Nakajima, N.; Takahashi, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 D614G variant exhibits efficient replication ex vivo and transmission in vivo. Science 2020, 370, 1464–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaney, A.J.; Loes, A.N.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Starr, T.N.; Malone, K.D.; Chu, H.Y.; Bloom, J.D. Comprehensive mapping of mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain that affect recognition by polyclonal human serum antibodies. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, T.N.; Greaney, A.J.; Hilton, S.K.; Ellis, D.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Dingens, A.S.; Navarro, M.J.; Bowen, J.E.; Tortorici, M.A.; Walls, A.C.; et al. Deep Mutational Scanning of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Reveals Constraints on Folding and ACE2 Binding. Cell 2020, 182, 1295–1310.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahradník, J.; Marciano, S.; Shemesh, M.; Zoler, E.; Chiaravalli, J.; Meyer, B.; Dym, O.; Elad, N.; Schreiber, G. SARS-CoV-2 RBD in vitro evolution follows contagious mutation spread, yet generates an able infection inhibitor. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, E.; Mishra, S.; Chand, M.; Barrett, J.C.; Johnson, R.; Geidelberg, L.; Hinsley, W.R.; Laydon, D.J.; Dabrera, G.; O’Toole, Á.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Lineage B.1.1.7 in England: Insights from linking epidemiological and genetic data. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.G.; Abbott, S.; Barnard, R.C.; Jarvis, C.I.; Kucharski, A.J.; Munday, J.; Pearson, C.A.B.; Russell, T.W.; Tully, D.C.; Washburne, A.D.; et al. Estimated transmissibility and severity of novel SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern 202012/01 in England. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, S.; Harvey, W.; Lytras, S.; Carabelli, A.; Robertson, D.; Gupta, R. Recurrent emergence and transmission of a SARS-CoV-2 Spike deletion H69/V70. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Tang, H.; McDanal, C.; Wagh, K.; Fischer, W.; Theiler, J.; Yoon, H.; Li, D.; Haynes, B.F.; Sanders, K.O.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.7 is susceptible to neutralizing antibodies elicited by ancestral Spike vaccines. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muik, A.; Wallisch, A.-K.; Sänger, B.; Swanson, K.A.; Mühl, J.; Chen, W.; Cai, H.; Sarkar, R.; Türeci, Ö.; Dormitzer, P.R.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 pseudovirus by BNT162b2 vaccine-elicited human sera. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.; Fontes-Garfias, C.R.; Xia, H.; Swanson, K.A.; Cutler, M.; Cooper, D.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 spike 69/70 deletion, E484K and N501Y variants by BNT162b2 vaccine-elicited sera. Nat. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, L.; McCrone, J.T.; Zarebski, A.E.; Hill, V.; Ruis, C.; Gutierrez, B.; Raghwani, J.; Ashworth, J.; Colquhoun, R.; Connor, T.R.; et al. Establishment and lineage dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in the UK. Science 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westhaus, S.; Widera, M.; Rabenau, H.F.; Hoehl, S.; Bojkova, D.; Cinatl, J.; Ciesek, S. Evaluation of stability and inactivation methods of SARS-CoV-2 in context of laboratory settings. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.W.; Bleicker, T.; Brunink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. PCR Protocol—World Health Organization; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, N.; Kunze, M.; Steitz, F.; Saad, N.J.; Muhlemann, B.; Beheim-Schwarzbach, J.I.; Schneider, J.; Drosten, C.; Murajda, L.; Kochs, S.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Outbreak Related to a Nightclub, Germany, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 27, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, J.W.; Capoferri, A.A.; Katusiime, M.G.; Patro, S.C.; Kearney, M.F. Low genetic diversity may be an Achilles heel of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24614–24616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchene, S.; Featherstone, L.; Haritopoulou-Sinanidou, M.; Rambaut, A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G. Temporal signal and the phylodynamic threshold of SARS-CoV-2. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, S.; Isom, D.G. One Year of SARS-CoV-2: How Much Has the Virus Changed? Biology 2021, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.G.; Abbott, S.; Barnard, R.C.; Jarvis, C.I.; Kucharski, A.J.; Munday, J.D.; Pearson, C.A.B.; Russell, T.W.; Tully, D.C.; Washburne, A.D.; et al. Estimated transmissibility and impact of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England. Science 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.G.; Jarvis, C.I.; Edmunds, W.J.; Jewell, N.P.; Diaz-Ordaz, K.; Keogh, R.H. Increased mortality in community-tested cases of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmermann, N.; Lieb, B.; Laufs, T.; Renzaho, A.; Runkel, S.; Kohnen, W.; Linke, M.; Gerber, S.; Schweiger, S.; Michel, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 genome surveillance in Mainz, Germany, reveals convergent origin of the N501Y spike mutation in a hospital setting. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widera, M.; Wilhelm, A.; Hoehl, S.; Pallas, C.; Kohmer, N.; Wolf, T.; Rabenau, H.F.; Corman, V.; Drosten, C.; Vehreschild, M.J.; et al. Bamlanivimab does not neutralize two SARS-CoV-2 variants carrying E484K in vitro. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; Graham, B.S.; et al. Increased Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7 to Antibody Neutralization. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Arora, P.; Groß, R.; Seidel, A.; Hörnich, B.; Hahn, A.; Krüger, N.; Graichen, L.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Kempf, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.248: Escape from therapeutic antibodies and antibodies induced by infection and vaccination. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Arora, P.; Groß, R.; Seidel, A.; Hörnich, B.F.; Hahn, A.S.; Krüger, N.; Graichen, L.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Kempf, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and P.1 escape from neutralizing antibodies. Cell 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Deletion/Mutation | Number of Sequences | PANGO Lineage | Sequence ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 bp deletion in ORF1ab (amino acid position 141–143), 7 bp deletion in ORF7a which truncates ORF7a at amino acid position 108 | 1 | B.1.160 | ChVir21561 |
| Deletion of amino acid position 69/70 in S | 17 | B.1.1.70, B.1.258 | ChVir21551, ChVir21580, ChVir21582, ChVir21585, ChVir21586, ChVir21588, ChVir21589, ChVir21591, ChVir21596, ChVir21597, ChVir21598, ChVir21606, ChVir21609, ChVir21618, ChVir21619, ChVir21621, ChVir21626 |
| Deletion of amino acid positions 141-144 in S | 1 | B.1.1.153 | ChVir22027 |
| Deletion of amino acid position 210 in S | 4 | B.1.36 | ChVir21555, ChVir21563, ChVir21571, ChVir21603 |
| N501Y substitution in S | 1 | B.1.1.70 | ChVir21997 |
| 4 bp deletion in ORF3a, which truncates ORF3a at amino acid position 259 | 3 | B.1.160, B.1.1.67 | ChVir21565, ChVir21625, ChVir21632, ChVir22011 |
| 1 bp deletion in ORF3a, which truncates ORF3a at amino acid position 259 | 1 | B.1.160 | ChVir21550 |
| Deletion of amino acid position 58 in ORF8 | 1 | B.1.258 | ChVir21586 |
| 12 bp deletion in 3p UTR | 1 | B.1.258 | ChVir21502 |
| 41 bp deletion in the 3’ UTR | 4 | B.1.221 | ChVir21994, ChVir21995, ChVir21996, ChVir22006 |
| Substitutions typical of B.1.1.7, including a deletion of amino acid position 69/70 and N501Y in S | 1 | B.1.1.7 | ChVir22031 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Widera, M.; Mühlemann, B.; Corman, V.M.; Toptan, T.; Beheim-Schwarzbach, J.; Kohmer, N.; Schneider, J.; Berger, A.; Veith, T.; Pallas, C.; et al. Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Frankfurt am Main from October to December 2020 Reveals High Viral Diversity Including Spike Mutation N501Y in B.1.1.70 and B.1.1.7. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040748
Widera M, Mühlemann B, Corman VM, Toptan T, Beheim-Schwarzbach J, Kohmer N, Schneider J, Berger A, Veith T, Pallas C, et al. Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Frankfurt am Main from October to December 2020 Reveals High Viral Diversity Including Spike Mutation N501Y in B.1.1.70 and B.1.1.7. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(4):748. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040748
Chicago/Turabian StyleWidera, Marek, Barbara Mühlemann, Victor M. Corman, Tuna Toptan, Jörn Beheim-Schwarzbach, Niko Kohmer, Julia Schneider, Annemarie Berger, Talitha Veith, Christiane Pallas, and et al. 2021. "Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Frankfurt am Main from October to December 2020 Reveals High Viral Diversity Including Spike Mutation N501Y in B.1.1.70 and B.1.1.7" Microorganisms 9, no. 4: 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040748
APA StyleWidera, M., Mühlemann, B., Corman, V. M., Toptan, T., Beheim-Schwarzbach, J., Kohmer, N., Schneider, J., Berger, A., Veith, T., Pallas, C., Bleicker, T., Goetsch, U., Tesch, J., Gottschalk, R., Jones, T. C., Ciesek, S., & Drosten, C. (2021). Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Frankfurt am Main from October to December 2020 Reveals High Viral Diversity Including Spike Mutation N501Y in B.1.1.70 and B.1.1.7. Microorganisms, 9(4), 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040748






